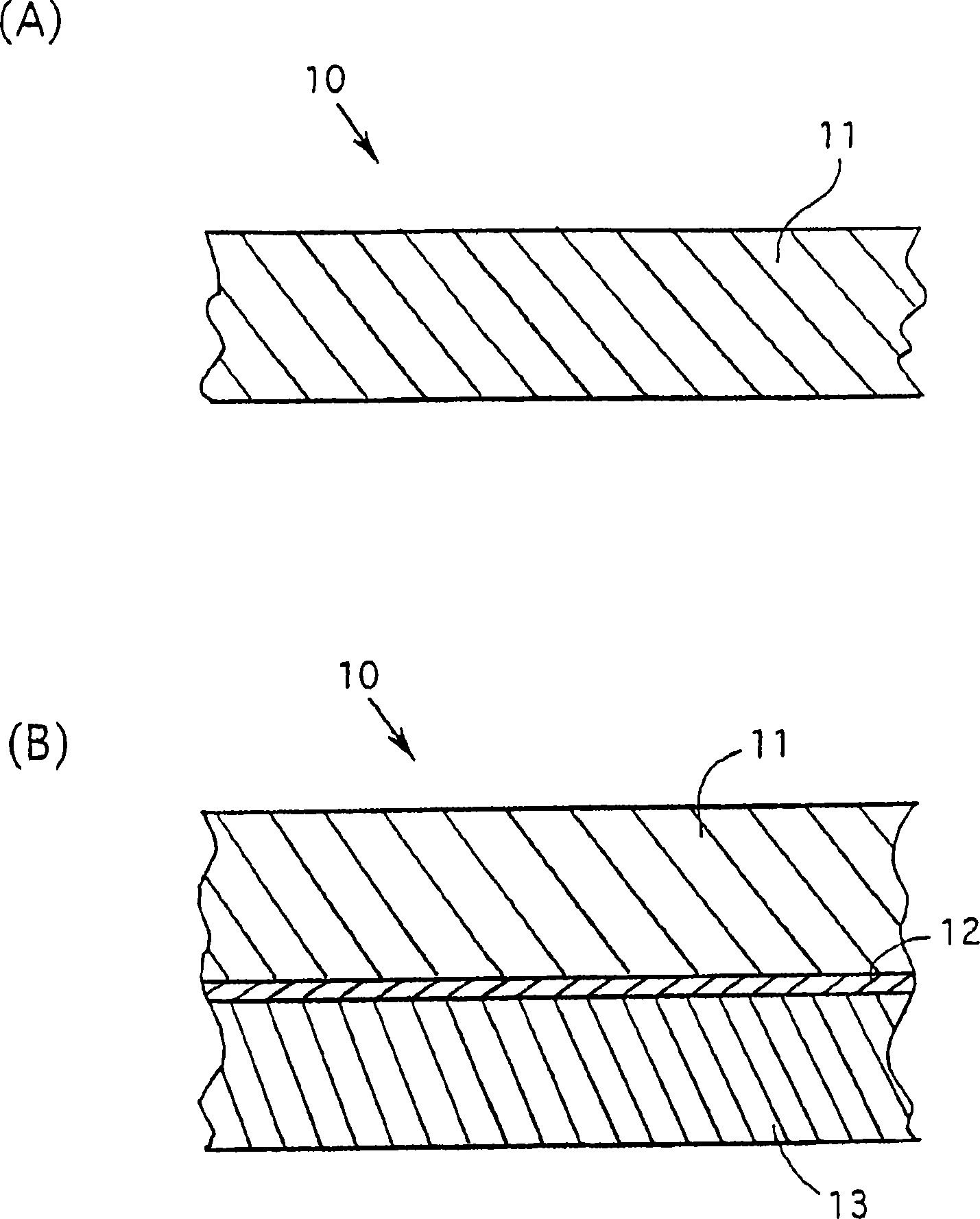
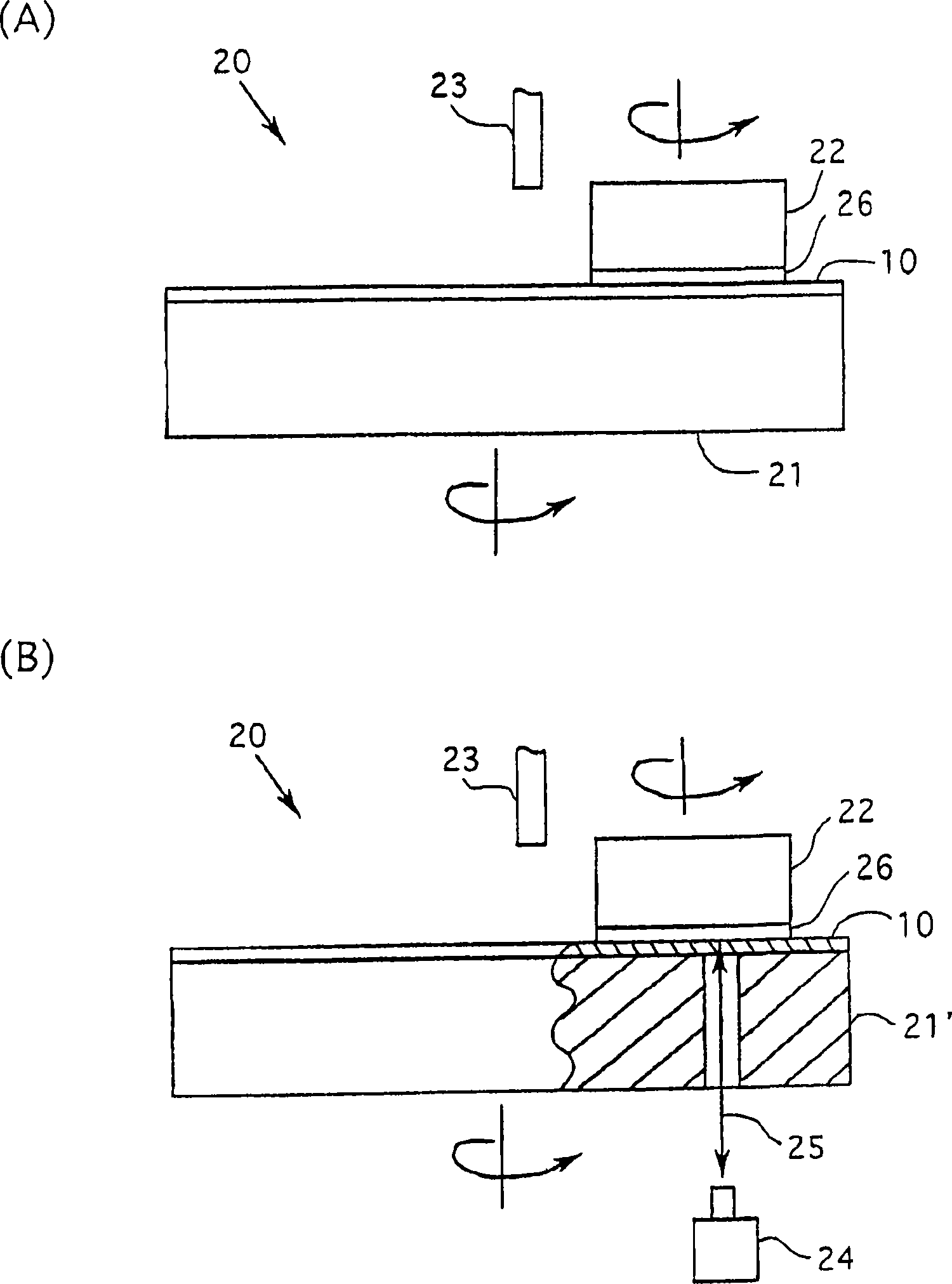
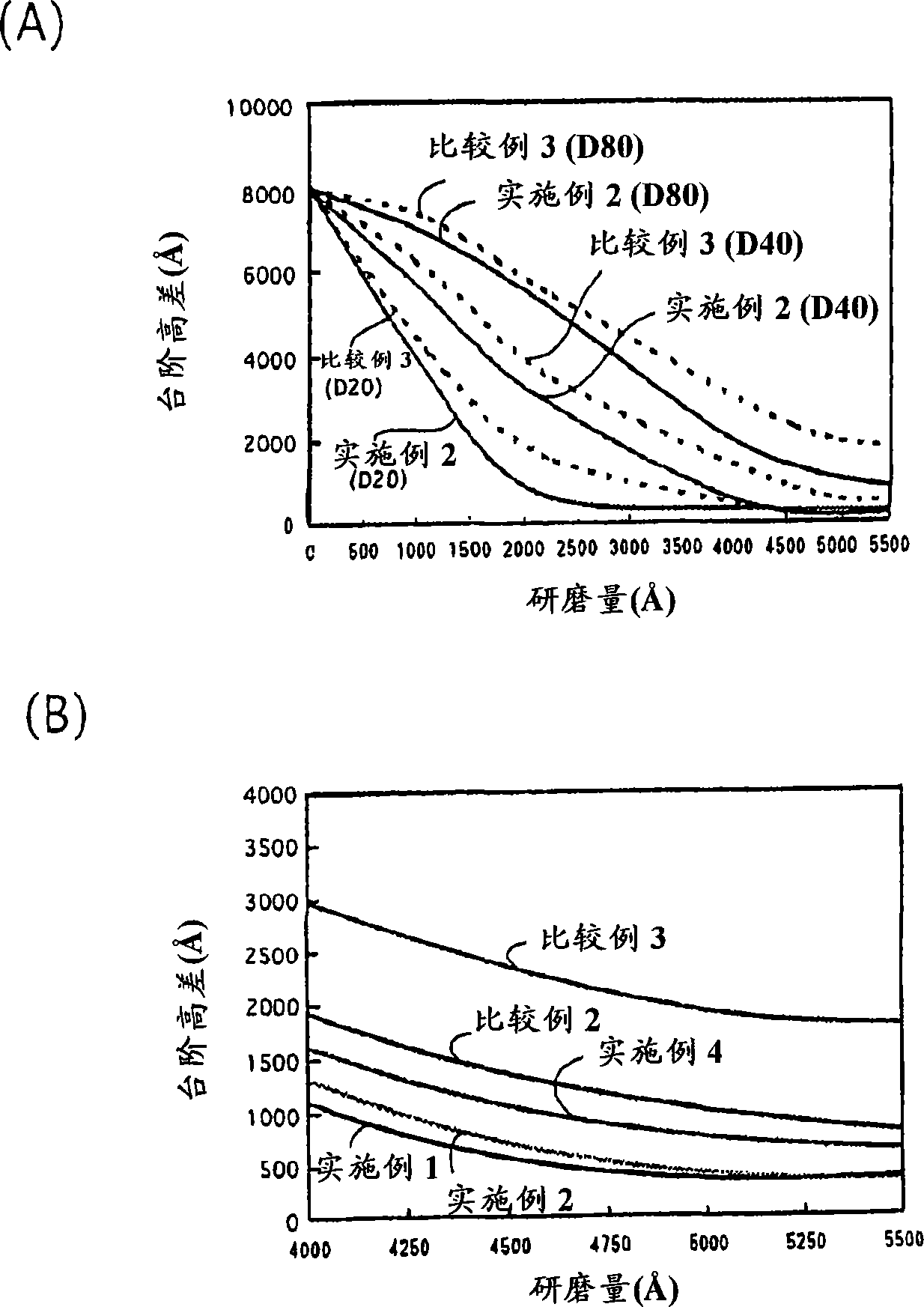
Polishing pad
A polishing pad and range technology, applied in the field of polishing pads, can solve the problems of uneven grinding pressure and repulsion, deviation of grinding amount, easy compression of foam pads, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing residual step height difference and high grinding speed.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0079] Using 3,3'-dichloro-4,4'diamino-diphenylmethane (26.5 parts) as a curing agent, add TDI (toluene diisocyanate)-based polyurethane preprepared with an average molecular weight of about 750. polymer (100 parts) to prepare a resin solution. This resin solution was poured into a metal mold, hardened in the mold, molded into a non-foam block, sliced at a thickness of 1.5 mm, and made into a pad body having a Shore D hardness of 78.0 (measurement temperature: 23.0° C.), and then Use a lathe to do groove processing (groove shape: spiral, groove size: boss width 0.6mm / groove width 0.3mm, groove occupancy rate 33.3%) to the surface of the pad main body, use it as the grinding of embodiment 1 pad.
[0080] 0039
Embodiment 2
[0081] Using 3,3'-dichloro-4,4'diamino-diphenylmethane (26.5 parts) as a curing agent, add TDI-based polyurethane prepolymer (100 parts) with an average molecular weight of about 900 ) to prepare a resin solution. This resin solution was poured into a metal mold, hardened in the mold, molded into a non-foam block, sliced at a thickness of 1.5 mm, and made into a pad body having a Shore D hardness of 75.0 (measurement temperature 23.0° C.), and then Use a lathe to groove the surface of the pad main body (groove shape: spiral, groove size: boss 0.6mm / groove 0.3mm, groove occupancy 33.3%), and use it as the polishing pad of Example 2.
[0082] 0040
Embodiment 3
[0083] Using 3,3'-dichloro-4,4'diamino-diphenylmethane (26.3 parts) as a hardening agent, add TDI-based polyurethane prepolymer (100 parts) with an average molecular weight of about 960 ) to prepare a resin solution. This resin solution was poured into a metal mold, hardened in the mold, molded into a non-foam block, and sliced at a thickness of 1.5 mm to produce a pad main body with a Shore D hardness of 72.0 (measurement temperature 23.0° C.), followed by Use a lathe to groove the surface of the pad main body (groove shape: spiral, groove size: boss 0.6 mm / groove 0.3 mm, groove occupancy 33.3%), and use it as the polishing pad of Example 3.
[0084] 0041
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com