Differential driving circuit and electronic equipment including the same
A differential drive and circuit technology, applied in differential amplifiers, logic circuit connections/interface layouts, amplifiers with semiconductor devices/discharge tubes, etc., to achieve high drive capabilities, reduce EMI problems, and solve oscillation problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
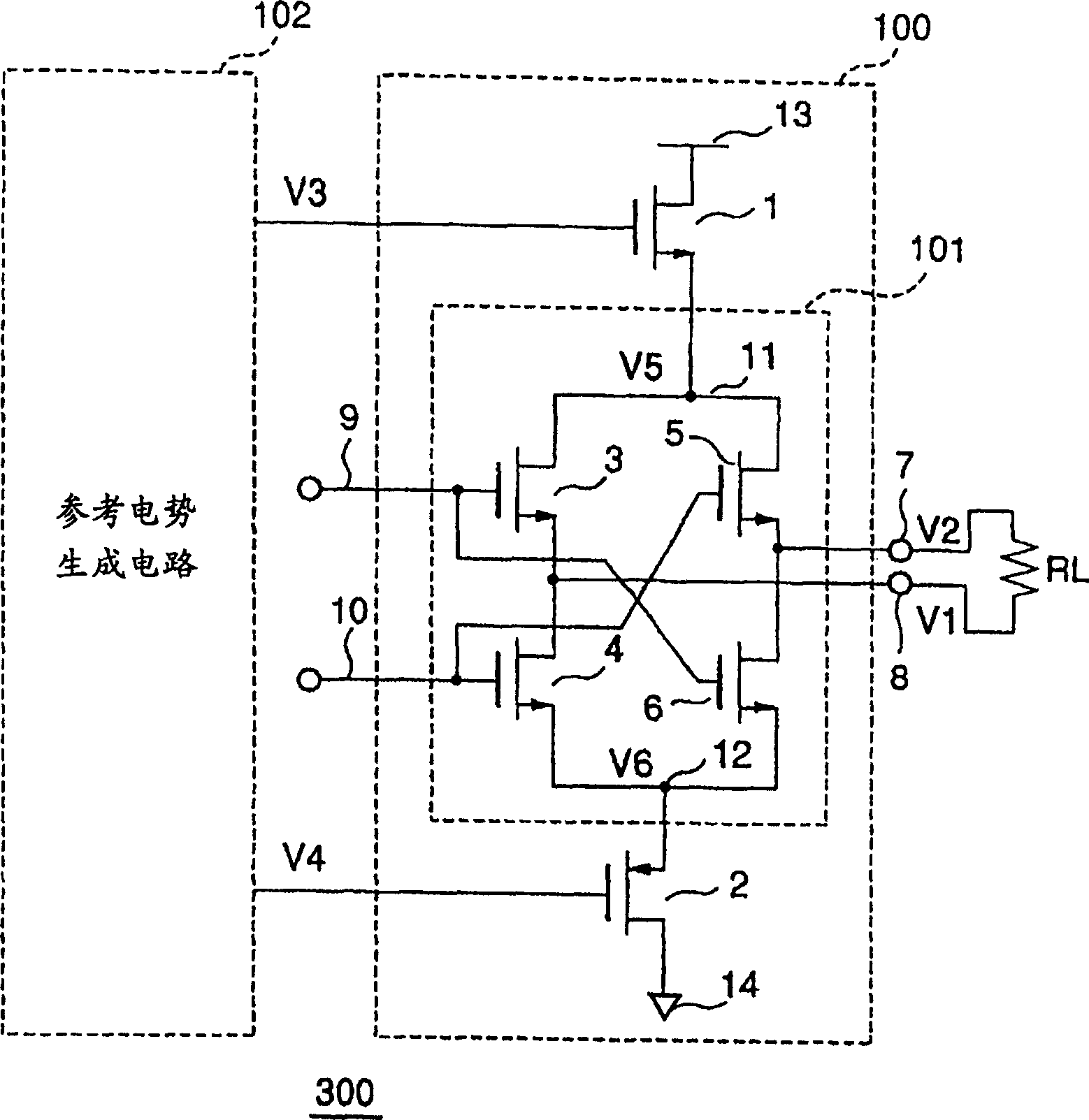
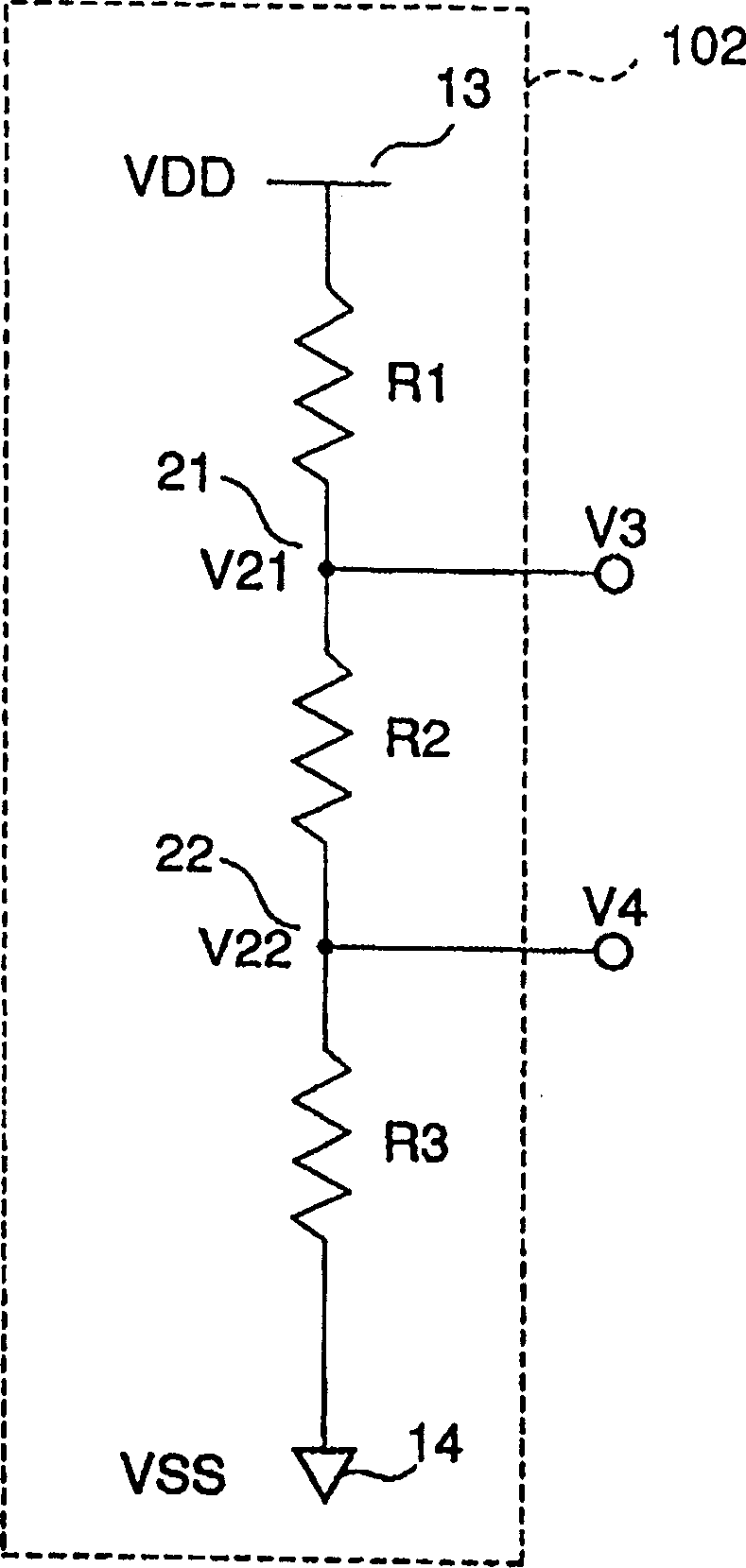
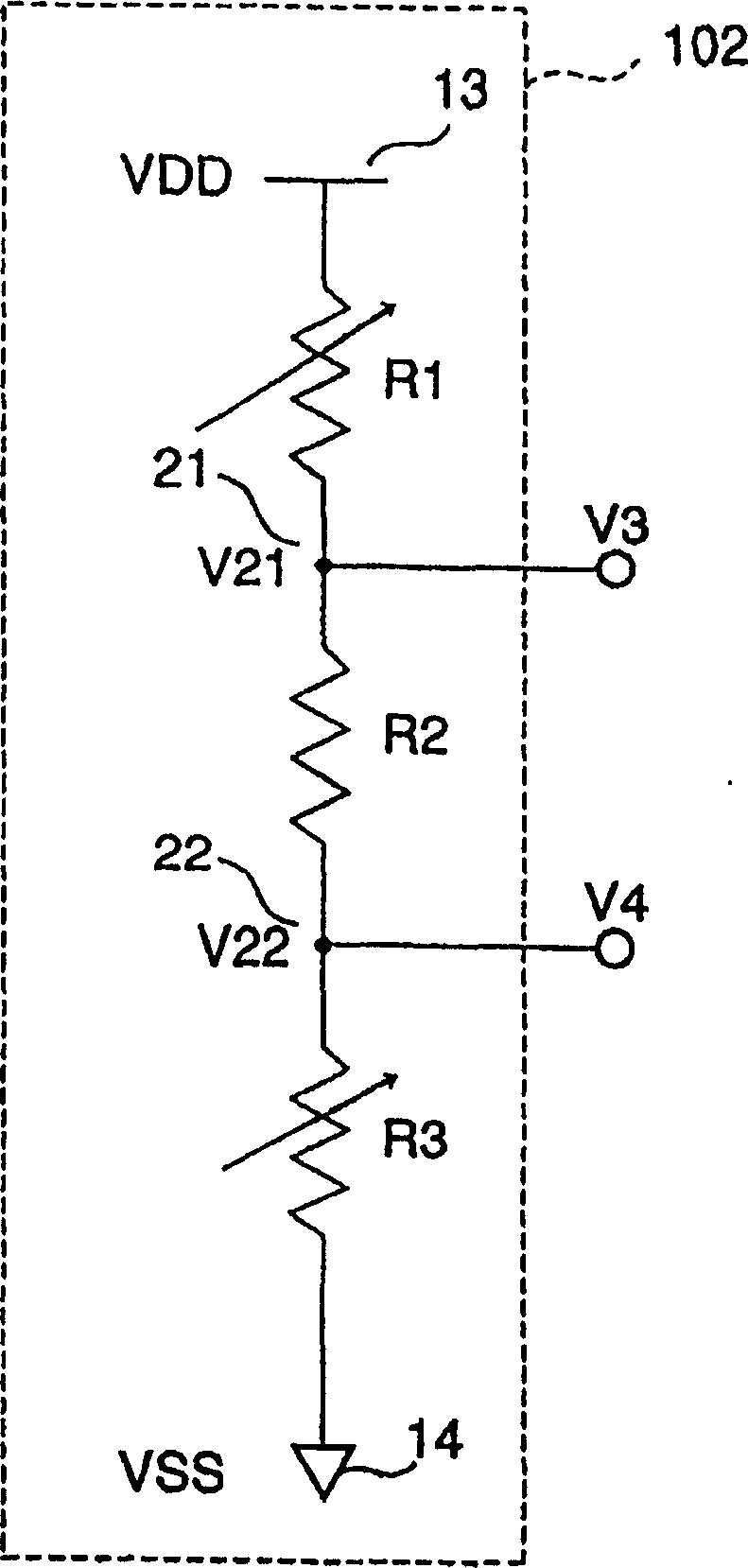
[0099] The following will use figure 1 A first embodiment of a differential drive circuit for low-voltage differential signals according to the present invention will be described. figure 1 is a circuit block diagram illustrating the configuration of the differential drive circuit for low voltage differential signals of the present invention. The differential drive circuit 300 for low-voltage differential signals of the present invention includes an output circuit 100 and a reference voltage generation circuit 102 complying with the LVDS interface standard (IEEE P1596, 3).
[0100] The output circuit 100 includes: a switch circuit 101 that receives a differential signal input to a terminating resistor RL and outputs a current signal to the terminating resistor RL; a PMOS (P-channel metal oxide semiconductor) transistor 2 that has one end connected to a low A power supply potential 14 on the potential side and the other end is connected to the node 12 in the switch circuit 101...
no. 2 example
[0110] The following will be done by using Image 6 A second embodiment of the differential drive circuit for low-voltage differential signals according to the present invention will be described. Image 6 is a circuit block diagram describing the configuration of the high output differential drive circuit of the present invention. The differential drive circuit 300 for low-voltage differential signals of the present invention includes an output circuit 100 , a strengthening circuit 300 and a bias circuit (not shown) for these circuits, such as a reference potential generating circuit 102 .
[0111] The output circuit 100 is figure 1 circuit described in . In the booster circuit 400, the drain of the PMOS transistor 61 is connected to a node 71 in a switch circuit for a booster circuit including a MOS transistor to which a differential signal different from the signal input to the drive circuit 100 is input. , and the switching circuit outputs a current signal. The source ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com