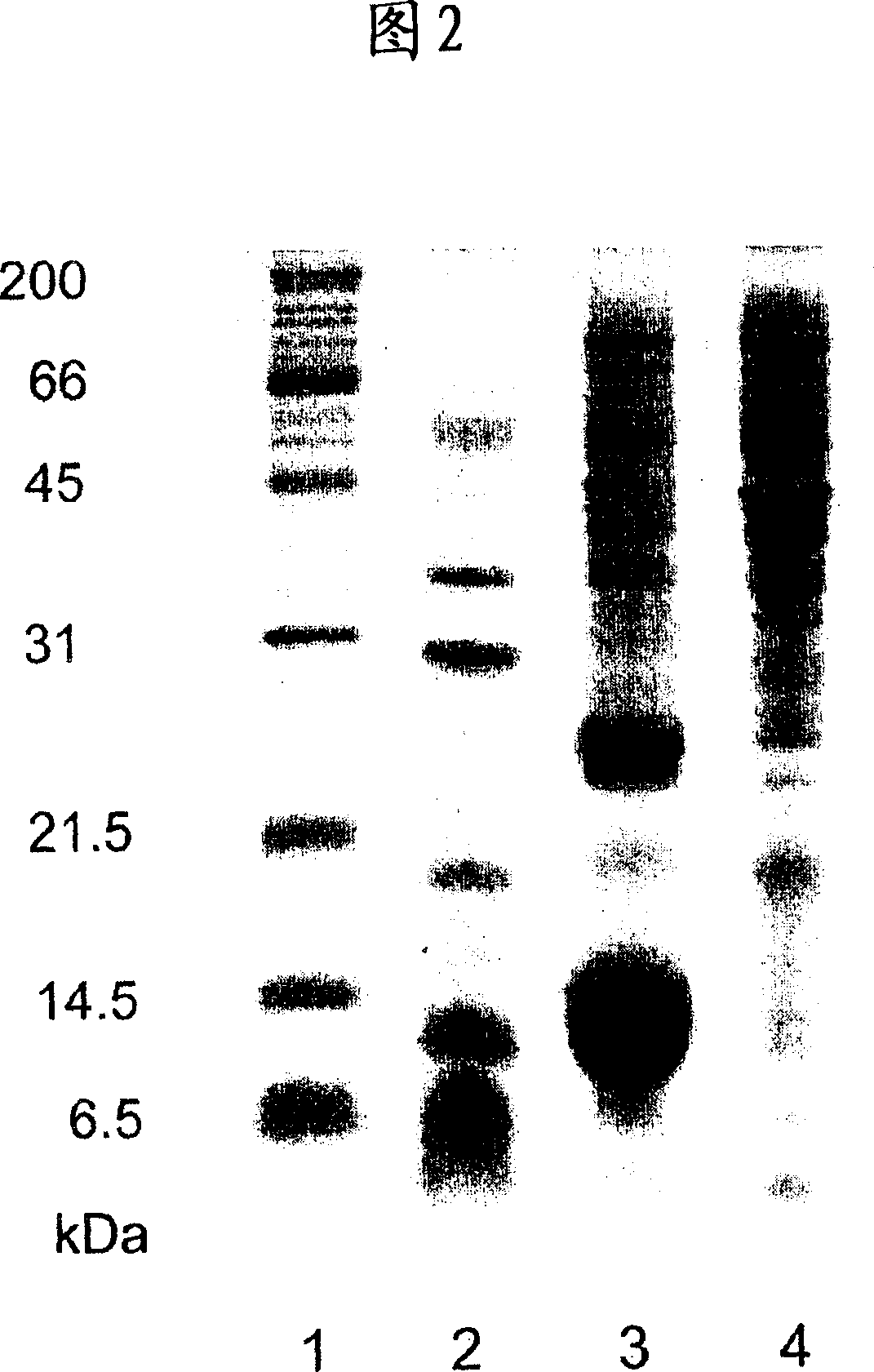Protein-free natural rubber latex, process for producing the same and use thereof
A technology of natural rubber latex, manufacturing method, applied in applications, male contraceptives, catheters, etc., can solve problems such as incomplete protein removal
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] In 1.9L of fresh latex (abbreviated as FL latex) adjusted to 30% DRC (dry rubber content), add 100 mL aqueous solution containing 30 g of sodium hydroxide and Emulgen-70 (polyoxyethylene nonyl) as a nonionic surfactant Phenyl ether) 4g, carry out saponification reaction at 70 ℃ for 3 hours. The latex solution was centrifuged at 13000 rpm for 8 minutes to separate the cream phase, and water was added to the cream phase to adjust to 60% DRC. Then 0.5 g of ammonium laurate was added.
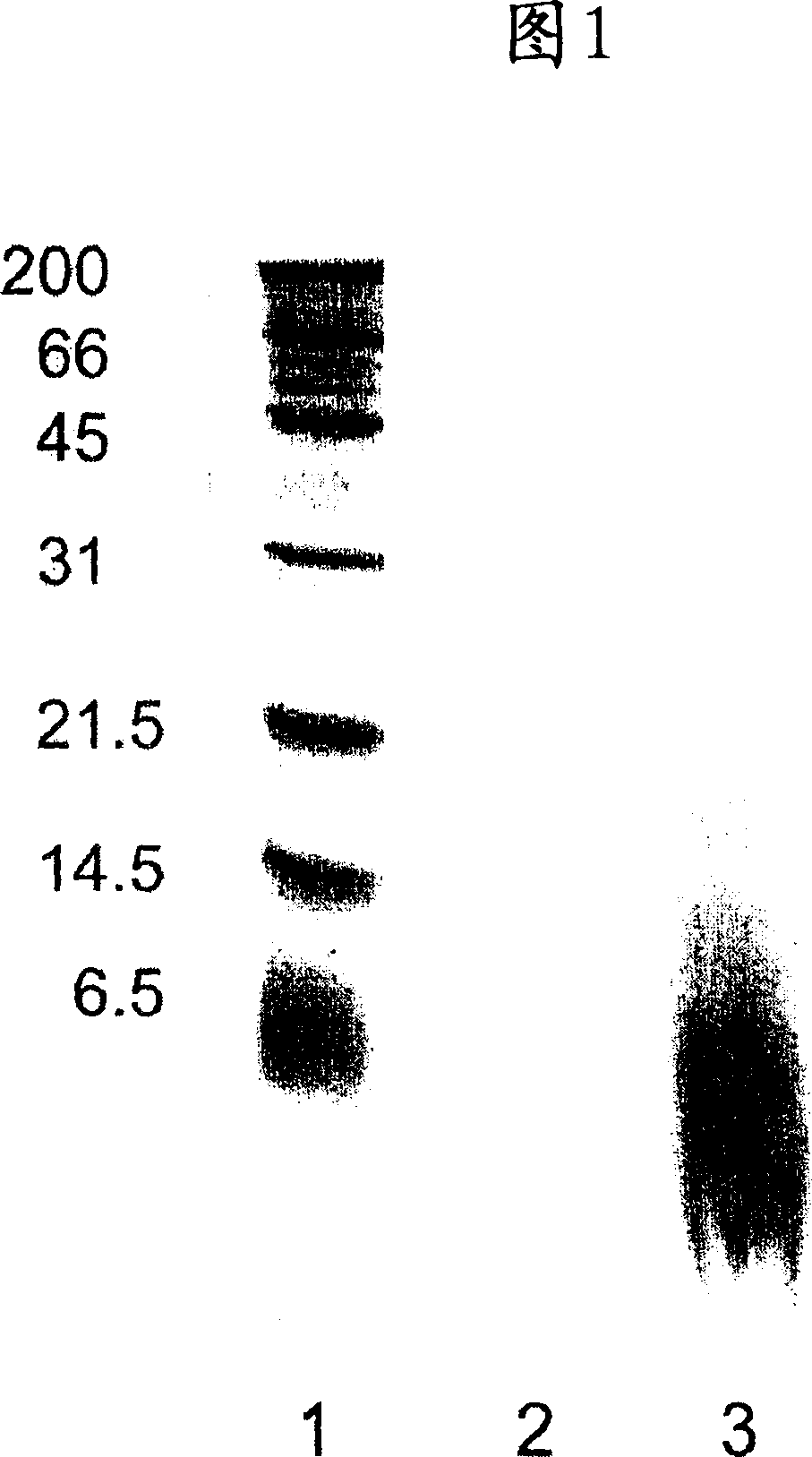
[0055] Proteins present in the cream phase and the serum phase of the saponified natural rubber latex thus obtained were determined by the SDS-PAGE method.
[0056] The protein contained in the cream phase was determined as follows.
[0057] 17 g of the cream phase was extracted with 17 mL of 2% SDS at room temperature for 24 hours. Using a dialysis membrane with a molecular weight cut-off of 3.5 kDa, the extract was dialyzed at room temperature for 24 hours while stirring in cold water. ...
Embodiment 2~4
[0061] Example showing changes in saponification conditions of natural rubber latex
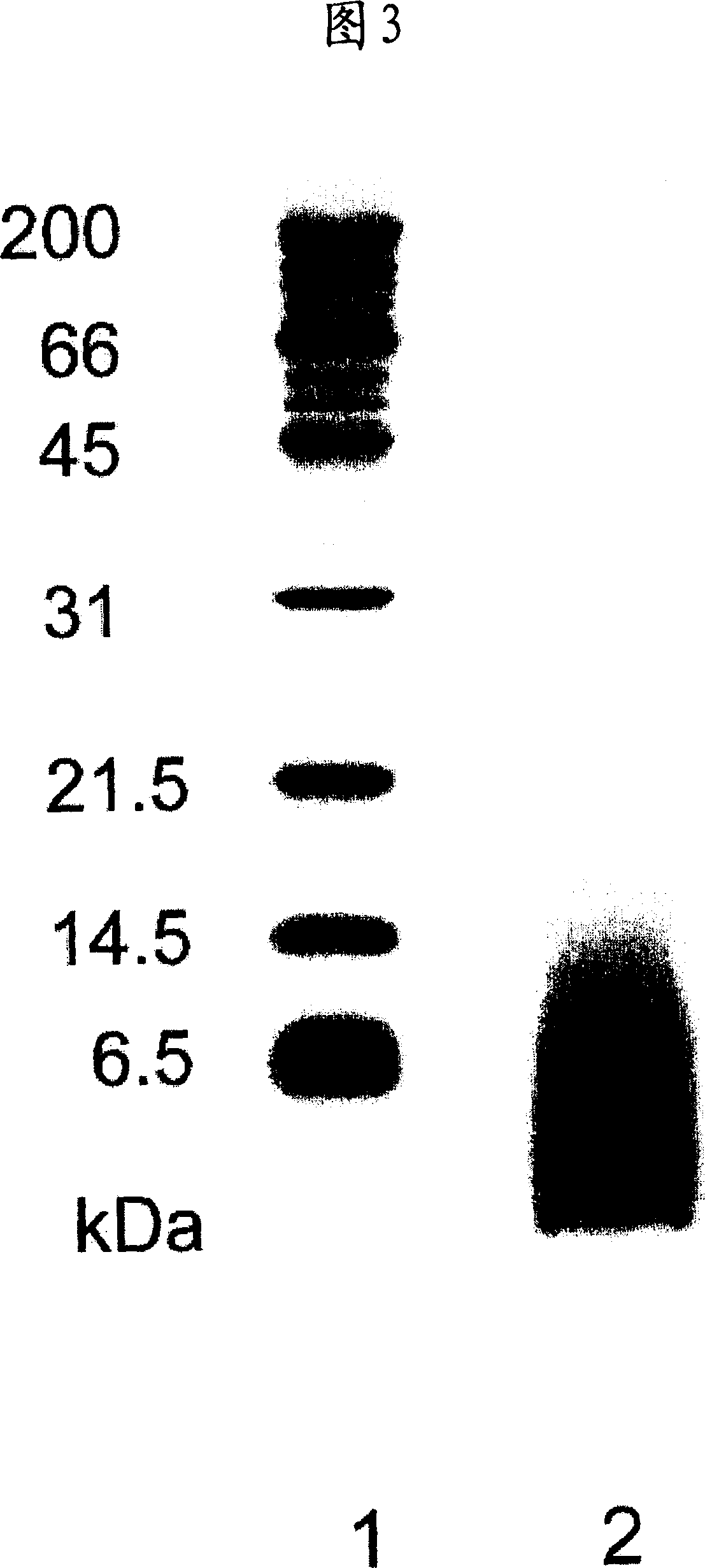
[0062] Saponification conditions are shown in Table 1. The experiment was carried out under the same conditions as in Example 1 except for the saponification conditions. In the cream phase of these saponified natural rubber latexes, no bands of 14, 31 and 45 kDa appeared in the results of SDS-PAGE measurement.
[0063] saponification condition
Example 2
NaOH 1%-70℃-1 hour
Example 3
NaOH 2% - room temperature - 5 hours
Example 4
NaOH 3% - room temperature - 2.5 hours
[0064] In the table, saponification conditions represent the concentration (w / v%) of NaOH, reaction temperature, and reaction time.
[0065] The results of SDS-PAGE measurement of the cream phase of the obtained latex under the same conditions as in Example 1 are shown in FIG. 4 . Under the conditions of Examples 2-4, no bands of 14, 31, and 45 kDa appeared at all. It was fo...
Embodiment 5~6
[0068] It carried out similarly to Example 1. However, the compounds of Table 2 were used instead of Emulgen-70 as the surfactant. As a result, it can be seen that none of the latexes of the examples contained the proteins of the bands of 14, 31 and 45 kDa as measured by SDS-PAGE.
[0069] Example
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com