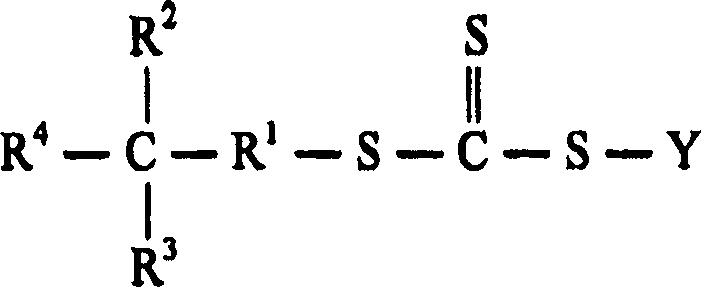Water-based process for the preparation of polymer-clay nanocomposites
A technology of nanocomposite materials and copolymers, applied in the direction of nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanotechnology for materials and surface science, etc., can solve the problem of not reaching the limit state of the dispersed phase
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0021] It will be appreciated that the preparation of elastomer / clay nanocomposites has been disclosed in WO 2004 / 078785 and WO 2004 / 078839. There is no disclosure or suggestion that cationically charged water-soluble polyelectrolytes prepared from CFRP / RAFT can be used as macroinitiators for the synthesis of amphiphilic block copolymer latexes containing one or more cationic charged block and at least one non-polar block. Furthermore, neither patent suggests or demonstrates that such "surfactant-free" core-shell amphiphilic elastomer latexes can be used directly with dispersed ion-exchangeable clays for the rapid and efficient preparation of Polymer-clay nanocomposites.
[0022] It is important to understand that an important aspect of the present invention is the channeling between the layers of an amphiphilic block copolymer latex containing one or more cationically charged blocks and at least one nonpolar block. Multilayer water-swellable clays (such as smectite-type cla...
Embodiment 1
[0146] Preparation of poly(4-vinylpyridine) with diphenylmethyltrithiocarbonate (DBTTC) RAFT reagent via an "in situ" emulsification method
[0147] 1.33 g (~0.00459 moles) of benzhydryl trithiocarbonate, 60.0 g (~0.57 moles) of distilled 4-vinylpyridine and 3.6 g (~0.0127 moles) of oleic acid were added to a machine equipped with a mechanical paddle Stirrer, nitrogen inlet, enclosed thermometer, heating mantle and condenser in a 500ml three necked round bottom flask. The stirred reactor was then purged with a slow stream of nitrogen before adding 0.36 g (~0.00133 moles) of potassium persulfate, 0.88 g (~0.0083 moles) of sodium carbonate, 0.88 g of (-0.010 mol) sodium bicarbonate and 0.82 g (-0.0126 mol) potassium hydroxide in water. A yellow emulsion formed immediately. The emulsion was then rapidly heated to 65°C and maintained at this temperature with the aid of a heat gauge controller. The progress of the polymerization was then gravimetrically analyzed. After one hour...
Embodiment 2
[0149] Preparation of poly(4-vinylpyridine) with S-benzyl-S'-(2-hydroxydecyl)trithiocarbonate (BHDTTC) RAFT reagent by an "in situ" emulsification method
[0150] Procedure: Same as Example 1 except 1.80 g (-0.00464 moles) of BHDTTCRAFT reagent was used instead of DBTTC. After a reaction time of 4 hours at 65° C., the reaction was worked up in the same manner as in Example 1. A solution of 19.66% solids in 289 g of methanol represented 56.8 g of poly(4-vinylpyridine) or 92% conversion.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com