Apparatus and method for automatic power control
a technology of automatic power control and apparatus, applied in the field of automatic power control apparatus, can solve the problems of medium-speed sampling device not being able to correctly sample the desired fpdo value, fpdo being likely to be slower, and only having a short steady-state time period, etc., to achieve stable power control, low response speed, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
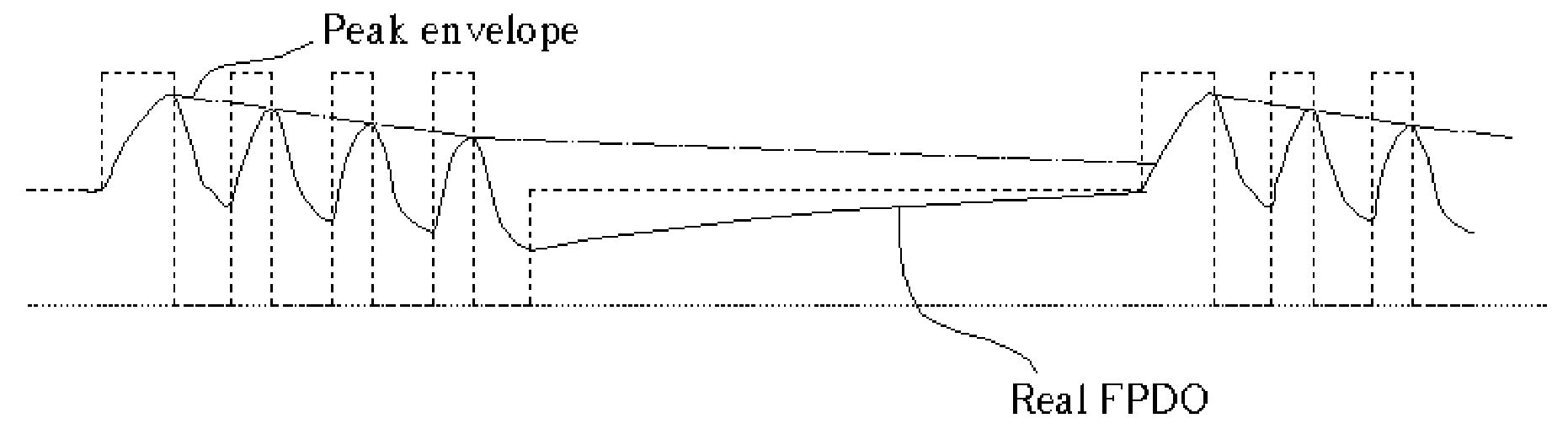
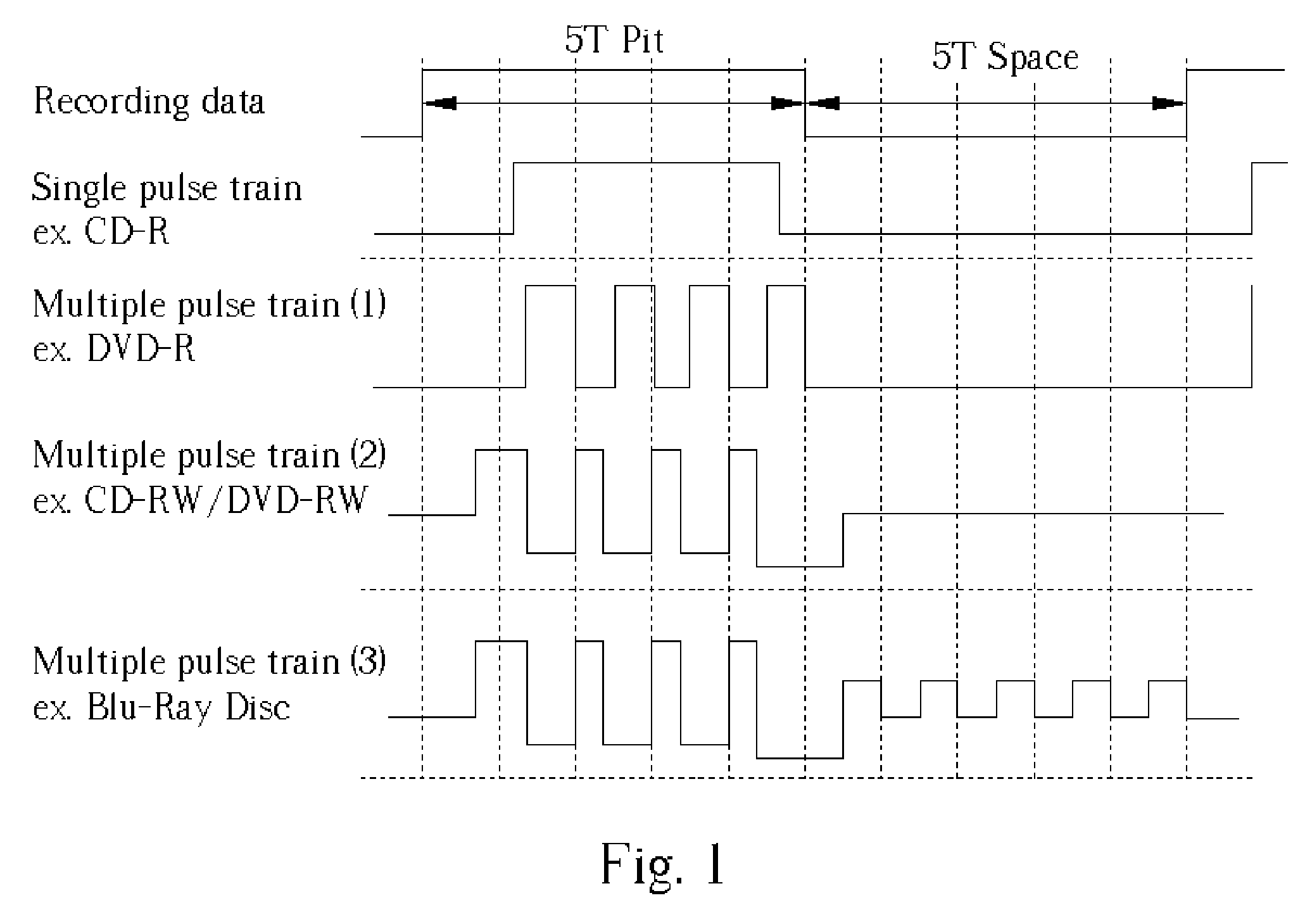
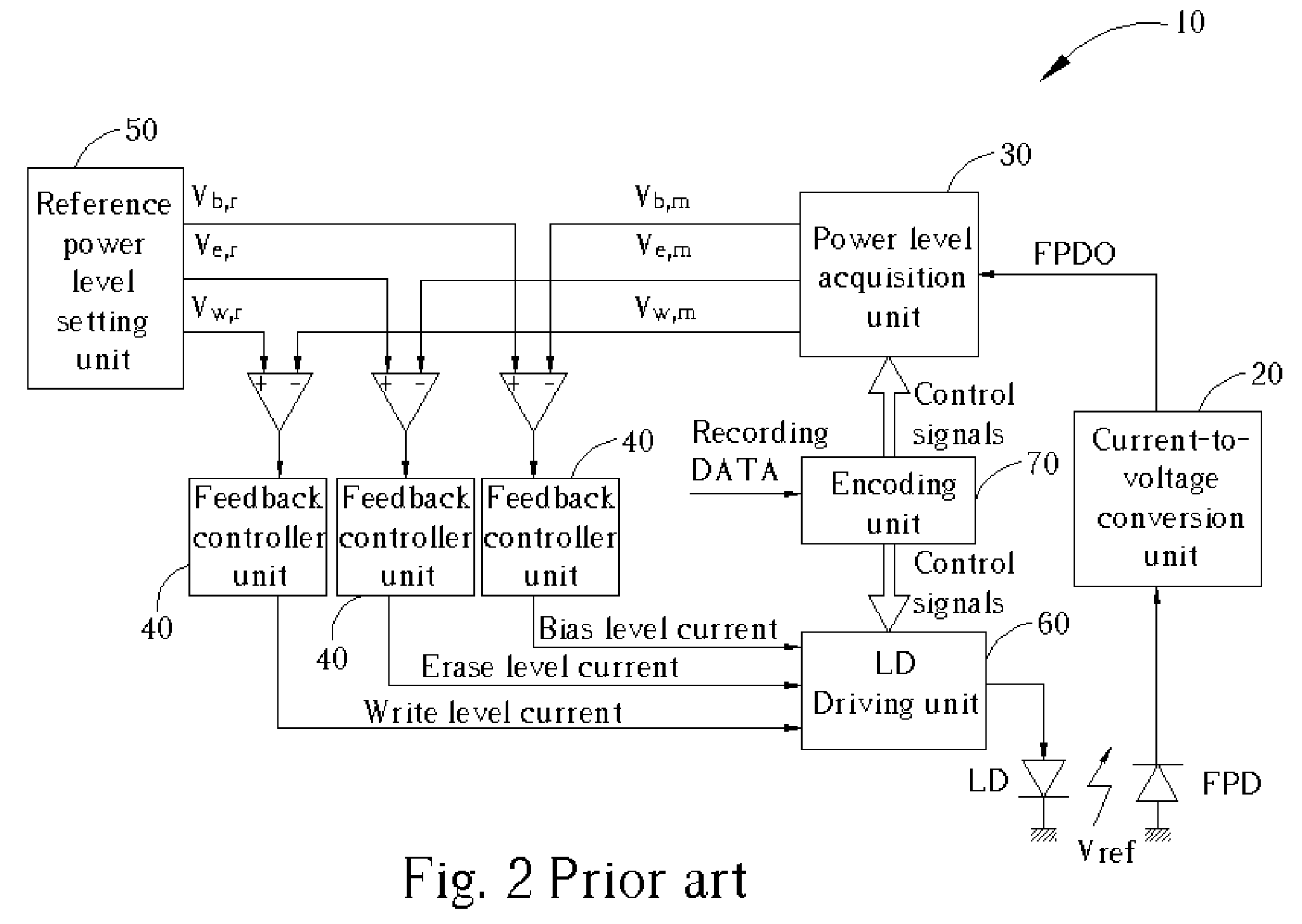
[0035] The present invention proposes a multi-pulse peak-hold device in a power level acquisition unit, instead of using a high-speed sample and hold circuit such as those frequently adopted in a conventional optical recording apparatus. FIG. 8 is a block diagram of the present invention if three power level controls are configured in an Automatic Power Control (APC) structure 110. Similar reference numerals are used for those components of the APC 110 that serve the same function as the corresponding components of the prior art APC 10. These functions have been previously described in this paper and will not be again elaborated on here. The obvious differencesin the present invention APC 110 from the prior art are the multi-pulse peak-hold (or bottom-hold) device 130 and the calibration gain 140 located in the output of the multi-pulse peak-hold (or bottom-hold) device 130thatis manifested in high-speed and / or high-density optical storage applications when a relatively low speed fr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| optical output power level | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| optical output power | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com