Cooling technique
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[First Embodiment]
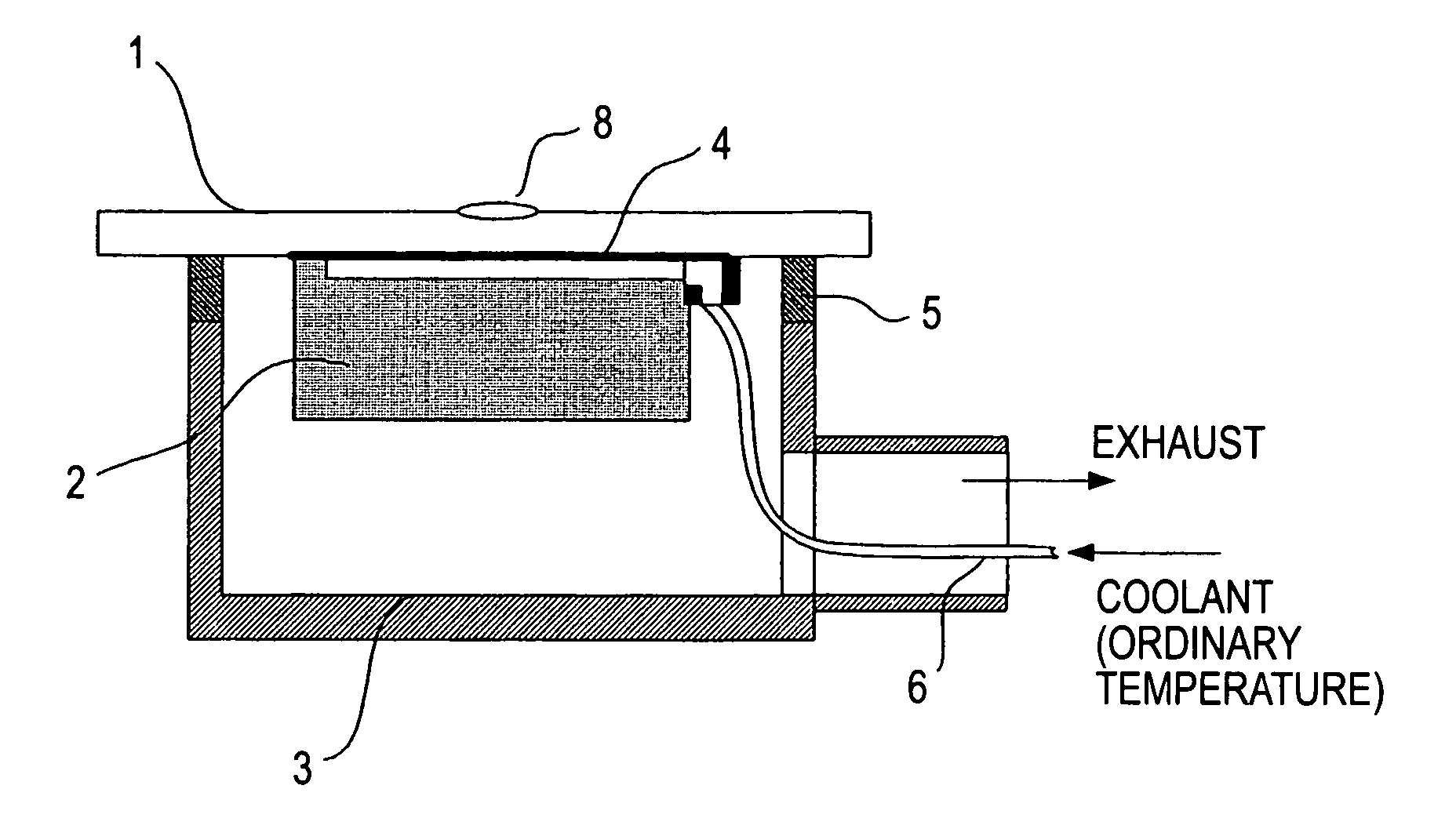
[0026]FIG. 1 shows a cooling mechanism according to a first embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 1 illustrates the structure for controlling a radiation plate temperature on the basis of heat of vaporization of water. Water which is temperature controlled to about the same temperature of the structure 110 and 211 (FIG. 5) which constitutes a positioning device, that is, usually about 23° C., is supplied to a porous material member 2 through a flowpassage 6. The porous material member 2 is disposed inside a container 3 which is vacuum exhausted by means of a vacuum pump, for example. The water supplied therein is dispersed within the porous material member 2 and, when a vapor pressure (or steam pressure) or lower pressure is reached, vaporization occurs. For example, the vapor pressure of water at 0° C. is 610 Pa and, therefore, by keeping the inside pressure of the container 3 at about 100 Pa, the water can be well vaporized even if the temperature of the poro...
second embodiment
[Second Embodiment]
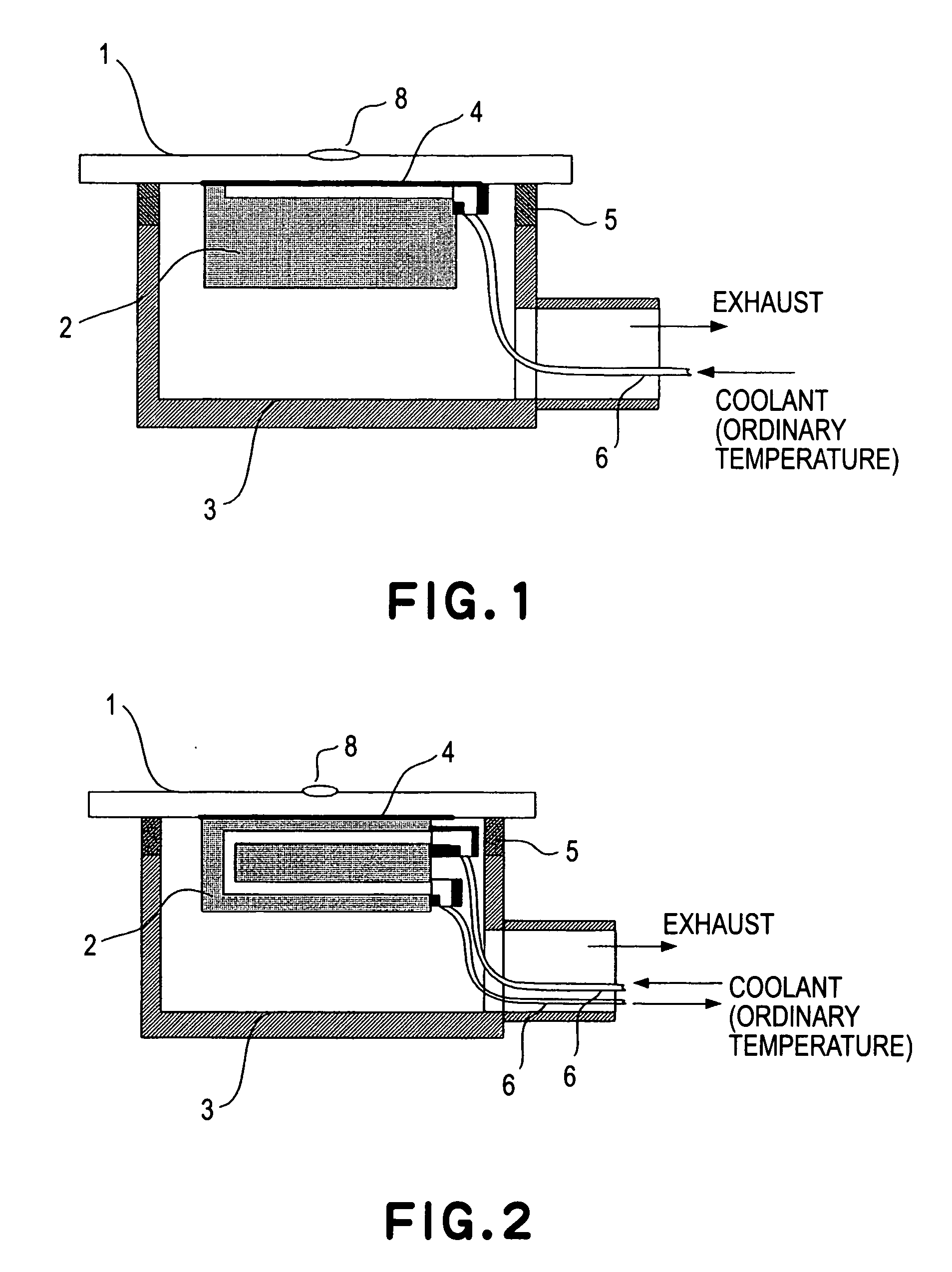
[0033]FIG. 2 shows a second embodiment of the present invention. This embodiment differs from the first embodiment in that water (coolant) is circulated through a porous material member 2 and that a portion of the circulated water is vaporized through the porous material member 2. Usually, a positioning device may be equipped with circulation of water for cooling. Thus, a portion of such circulation water may be bypassed toward the porous material member 2. In that occasion, there are advantages that the liquid pressure control is easy, and that the liquid is not easily solidified within the flowpassage 6 even if the set radiation plate temperature is low.
third embodiment
[Third Embodiment]
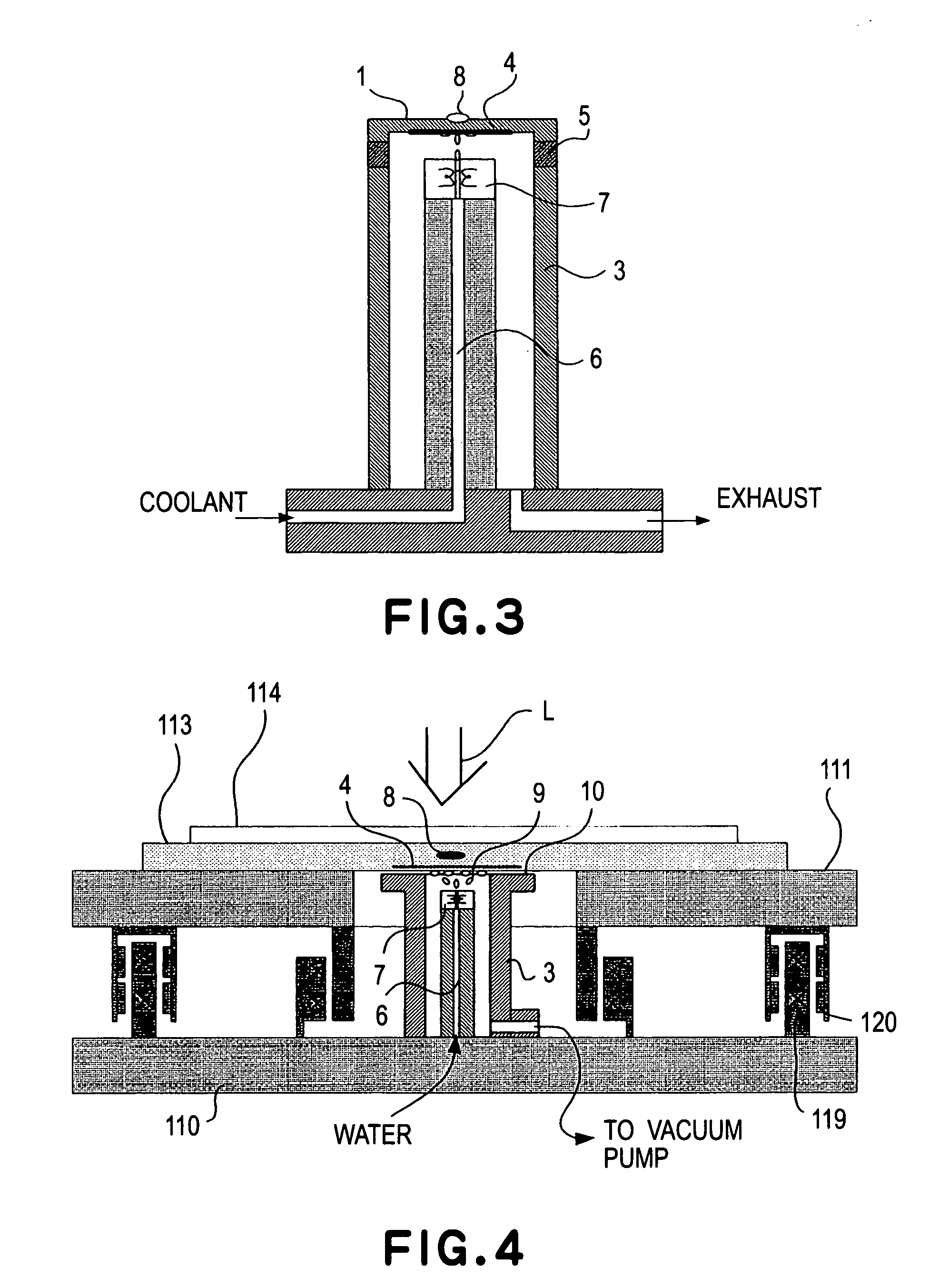
[0034]FIG. 3 shows a third embodiment of the present invention. In the cooling mechanism of FIG. 3, a liquid is directly applied against the back of a radiation plate. More specifically, water being supplied through a flowpassage 6 is applied (or discharged) from a nozzle 7 directly against the back of a radiation plate 1. Since the inside pressure of a vacuum container 3 is held by means of a vacuum pump (not shown), for example, at a pressure sufficiently smaller than the steam pressure of the water, the discharged water is vaporized while depriving, from the radiation plate, a heat quantity corresponding to the vaporization heat. With this arrangement, the radiation plate 1 can be cooled, and the temperature thereof can be reduced to about 0° C. As described with reference to the first embodiment, the temperature control for the radiation plate may be carried out by controlling energization of a heater 4 provided adjacent the radiation plate (at the back of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com