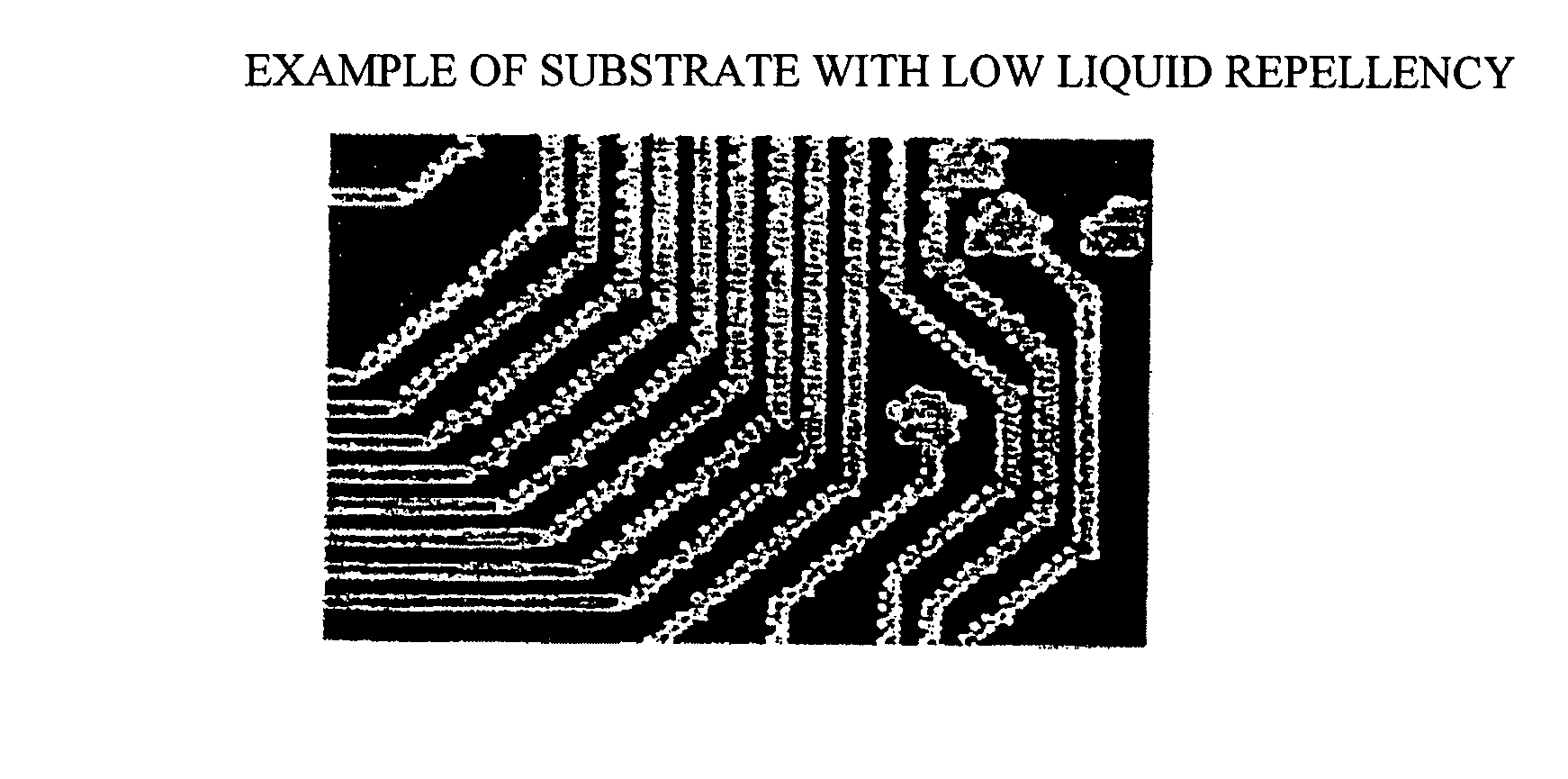
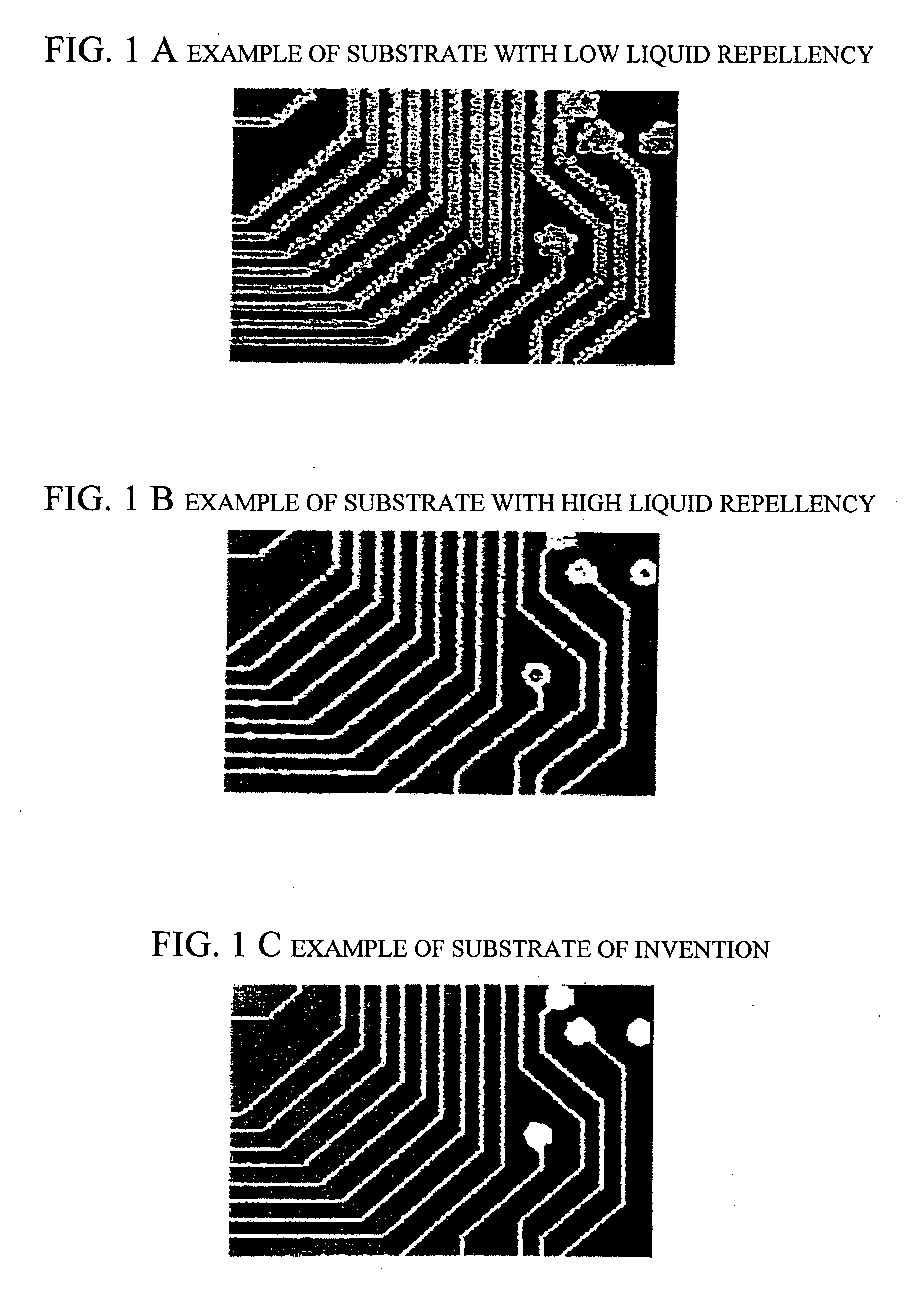
Wiring substrate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0122] This example relates to the method of preparing a substrate using a general-purpose substrate (see FIG. 2(1-1)).
1. Preparation of a Substrate for Wiring
[0123] The surface of a glass substrate measuring 100×50 mm and having a thickness of 1 mm was coarsened using a sandblasting apparatus (Pneuma-Blaster SFK 2 from Fuji Manufacturing Co., Ltd.). The polishing material used was a Fuji Random A ceramic polishing material from Fuji Manufacturing Co., Ltd. (where a particle range of 53 to 75 μm was used for Ra<1 μm and a range of 180 to 212 μm was used for Ra≧1 μm). A surface with varying Ra was formed by varying the blast time.
[0124] To impart liquid repellency to the substrate, the thus coarsened glass substrate was then dipped in a 0.5% by weight solution of Compound 17 (with a Frorinart PF-5080 solvent from 3M Company). The substrate was then raised and heated at 130° C. for 15 minutes to obtain a substrate for wiring.
[0125] Table 1 shows the Ra values of the substrate and...
example 2
[0139] After the coarsening of the surface, substrates for wiring were prepared by the same procedure as in Example 1 except that a 0.5% by weight solution of Compounds 18 to 28 (with Frorinart PF-5080 solvent from 3M Company) was used instead of the 0.5% by weight solution of Compound 17 (with Frorinart PF-5080 solvent from 3M Company).
[0140] The substrates were provided with wiring by the same method as in Example 1. In the present example, since the objective was to examine the difference in the condition of the wires formed due to different liquid repellent agents, the width of wires was limited to 60 μm. The results of the examination are shown in Table 4.
TABLE 4Condition of wires formed on substrates with different deviation of profile when different liquid repellent agents were usedRaLiquid repellent agent used (Compound)(μm)1718192021222324252627280.011C(112)C(112)C(115)C(115)S(88)S(88)S(92)S(92)C(111)C(113)C(111)C(113)0.036C(126)C(126)C(128)C(128)S(92)S(92)S(96)S(96)C(12...
example 3
[0143] The present example relates to the method of preparing a substrate using a highly liquid-repellent substrate (see FIG. 2 [1-1]).
1. Preparation of a Substrate for Wiring
[0144] The surface of a substrate made of polytetrafluoroethylene-ethylene copolymer and measuring 100×50 mm and having a thickness of 1 mm was coarsened using a sandblasting apparatus (an integral sandblasting apparatus SFK-2 from Fuji Manufacturing Co., Ltd.). The polishing material used was of ceramic type (zirconia beads from Fuji Manufacturing Co., Ltd., with a particle size ranging from 75 to 106 μm). Surfaces with various Ra were formed by varying the time of blast, thereby producing the substrates for wiring.
[0145] Table 5 shows the Ra and contact angle of the substrate thus prepared.
TABLE 5Condition of wires formed on substrates with different deviation of profileContact angleWidth ofwithwire drawn (μm)Ra (μm)water (°)1001500.041123CC0.057133CC0.063134XX0.078141XX0.57>150XX0.62>150XX1.17>150XX3.1...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Nanoscale particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com