Patents
Literature
1061 results about "Surface states" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Surface states are electronic states found at the surface of materials. They are formed due to the sharp transition from solid material that ends with a surface and are found only at the atom layers closest to the surface. The termination of a material with a surface leads to a change of the electronic band structure from the bulk material to the vacuum. In the weakened potential at the surface, new electronic states can be formed, so called surface states.
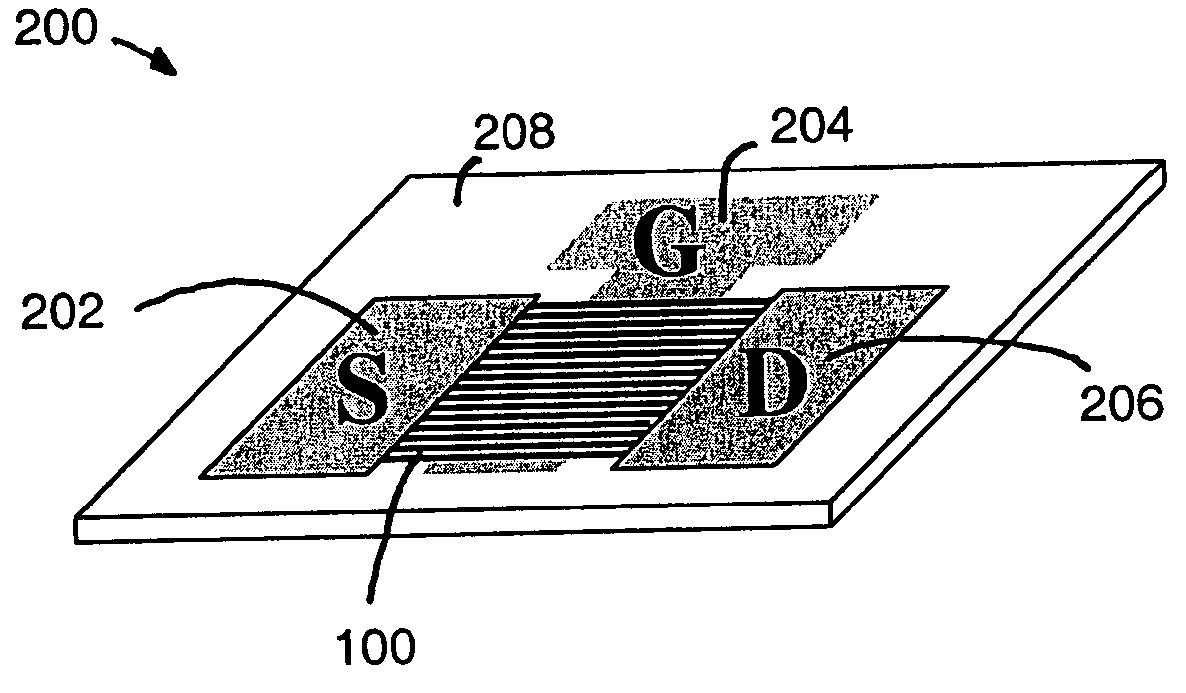
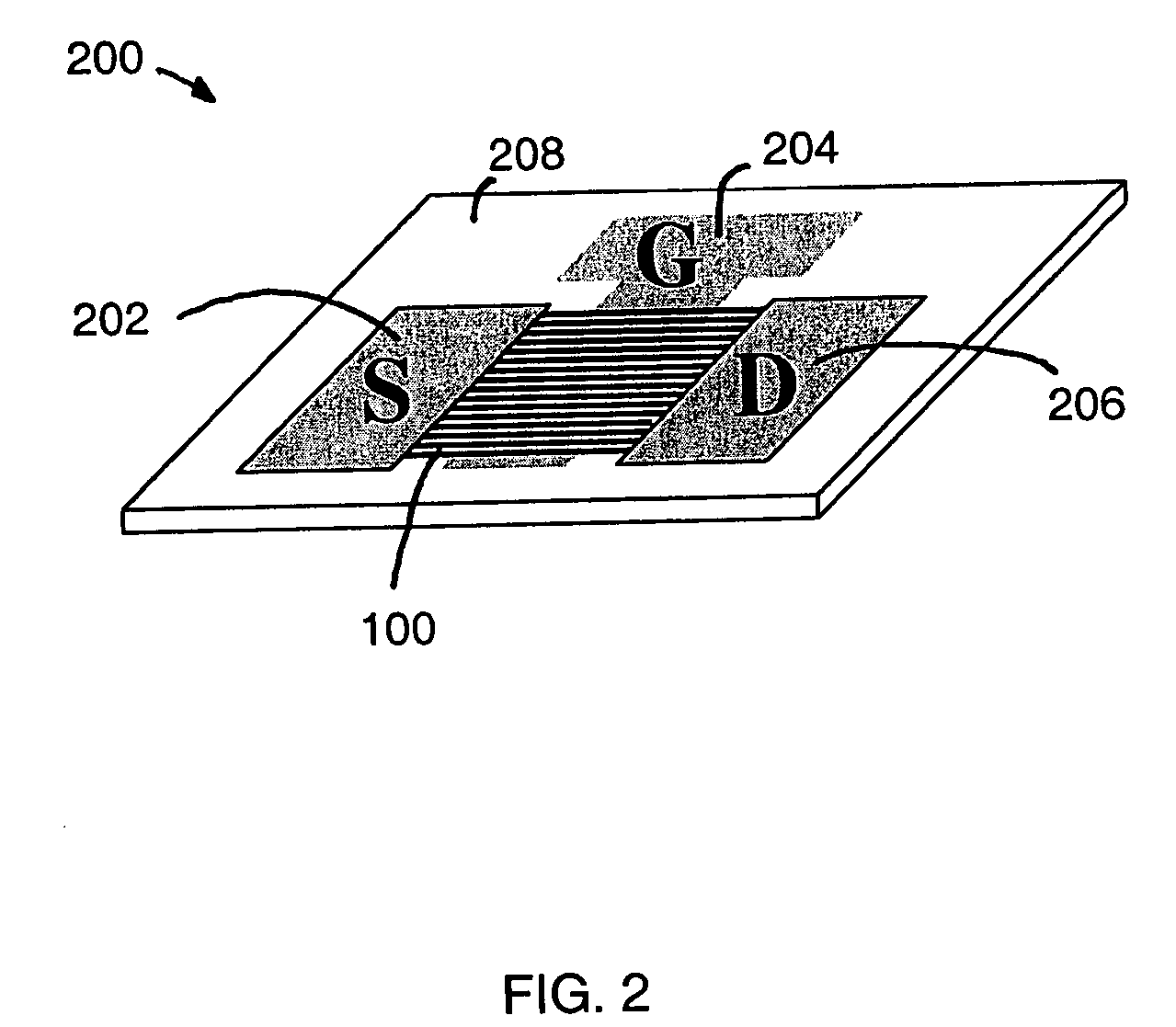
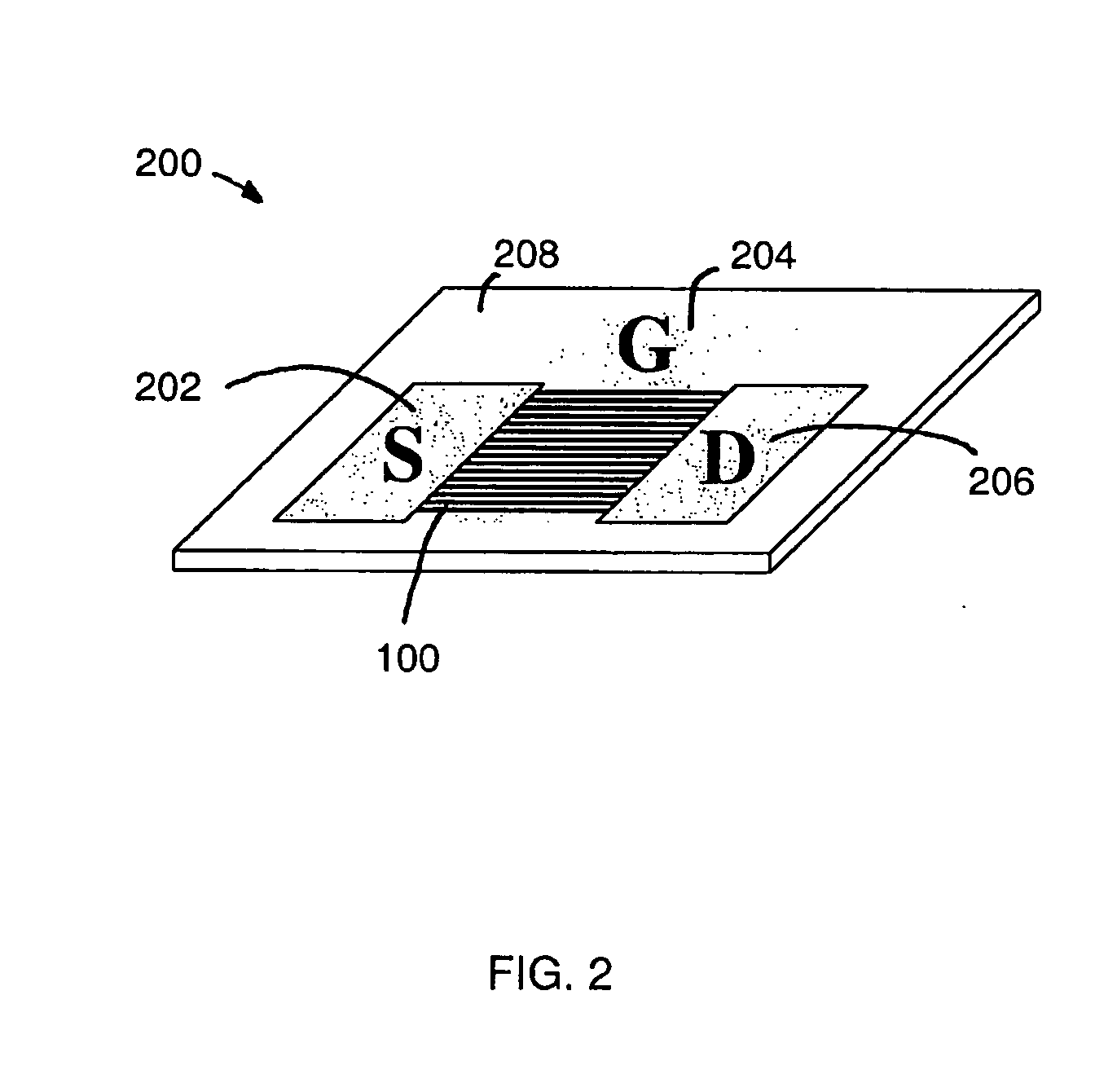
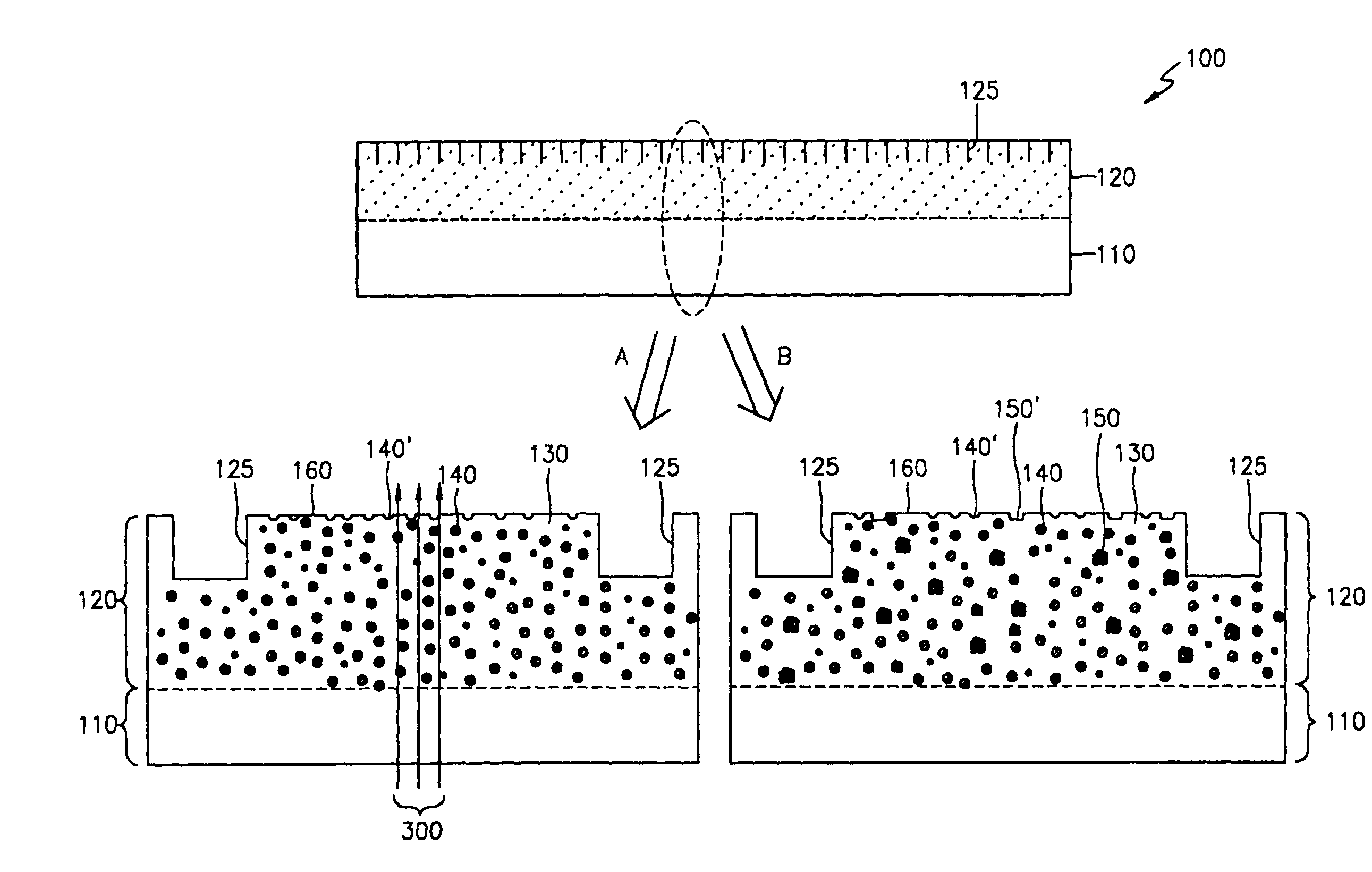
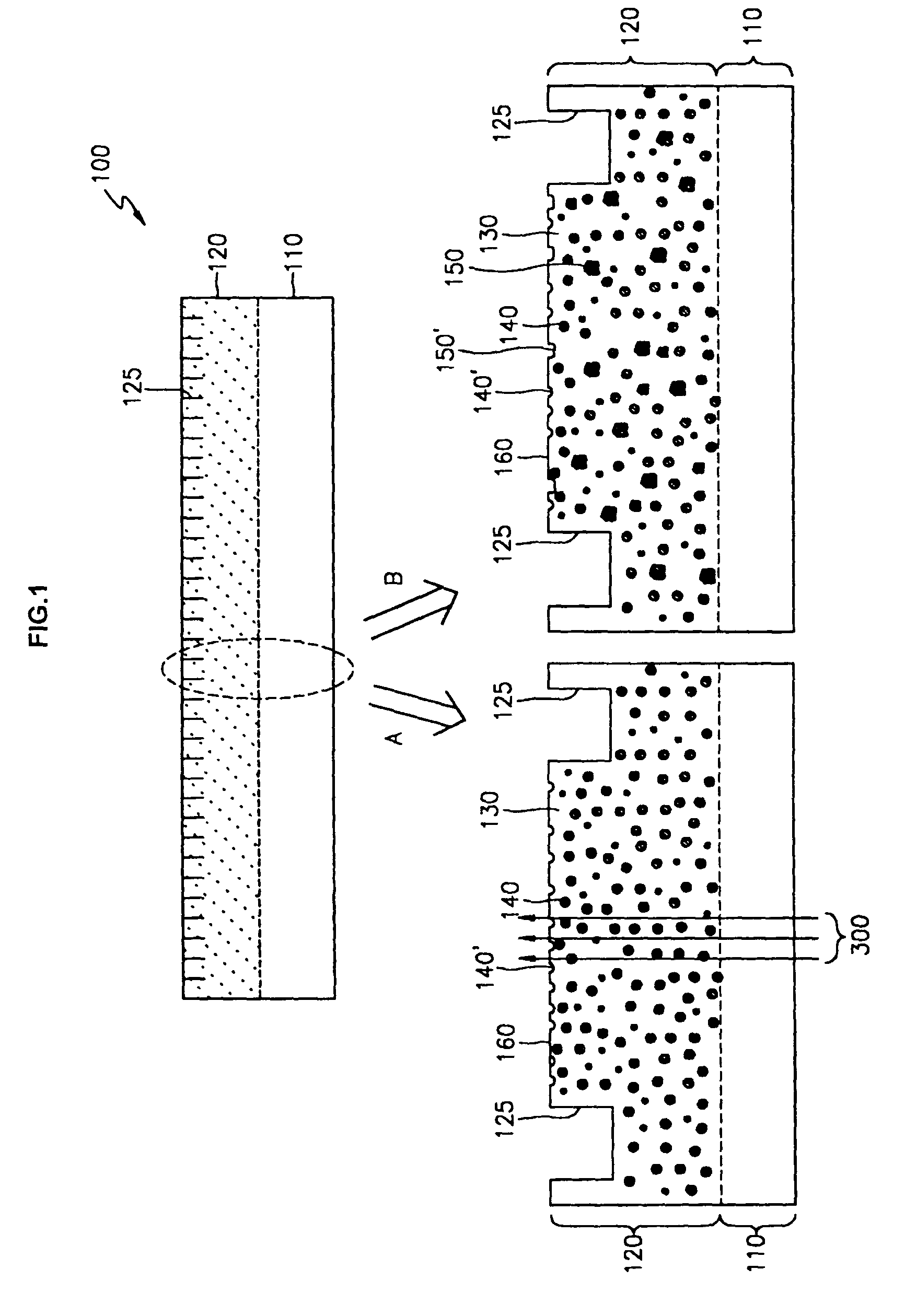
Large-area nanoenabled macroelectronic substrates and uses therefor
ActiveUS20050079659A1Reduce and entirely eliminate scatteringHigh carrier mobilityTransistorNanoinformaticsNanowireDevice material
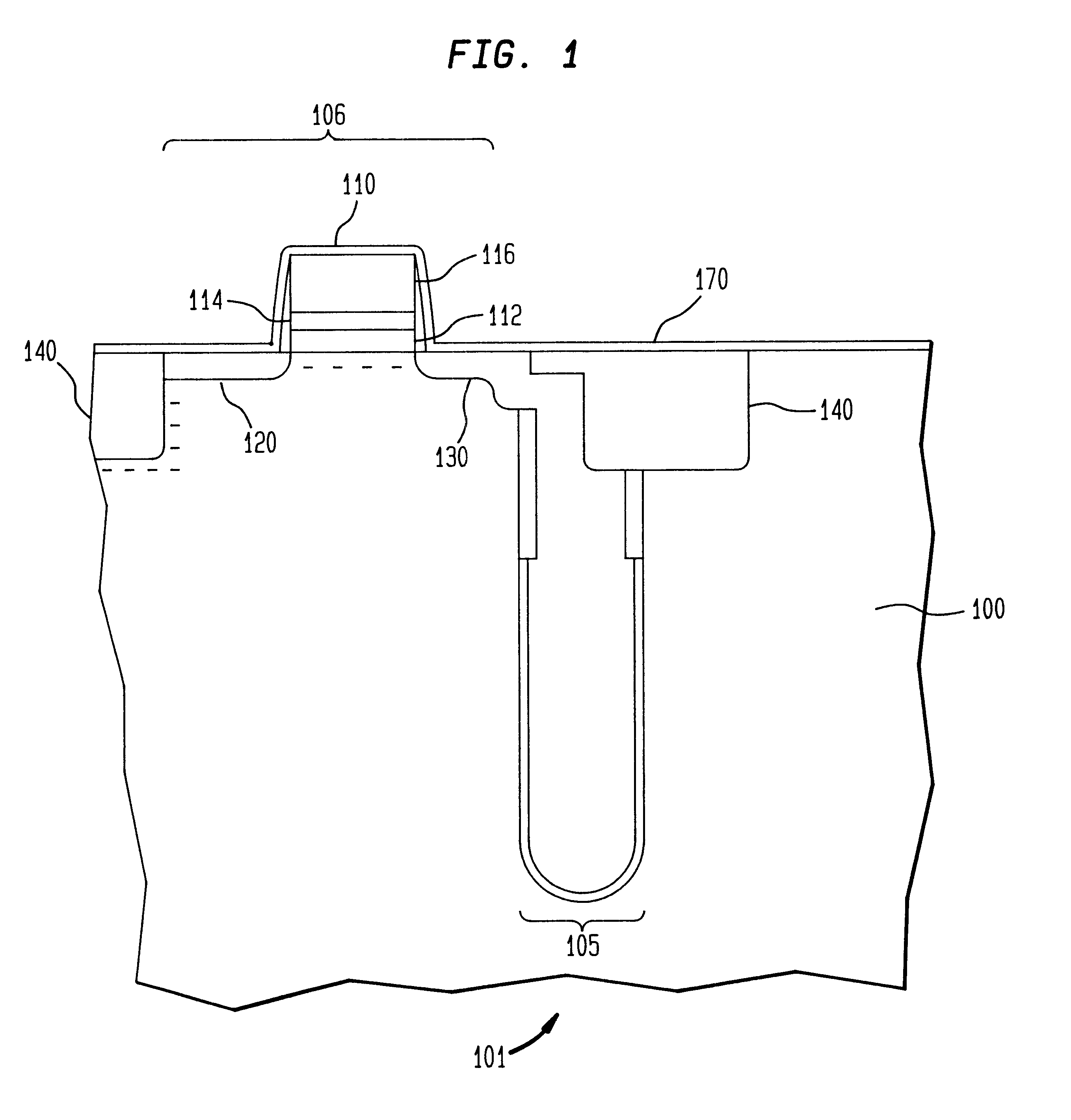
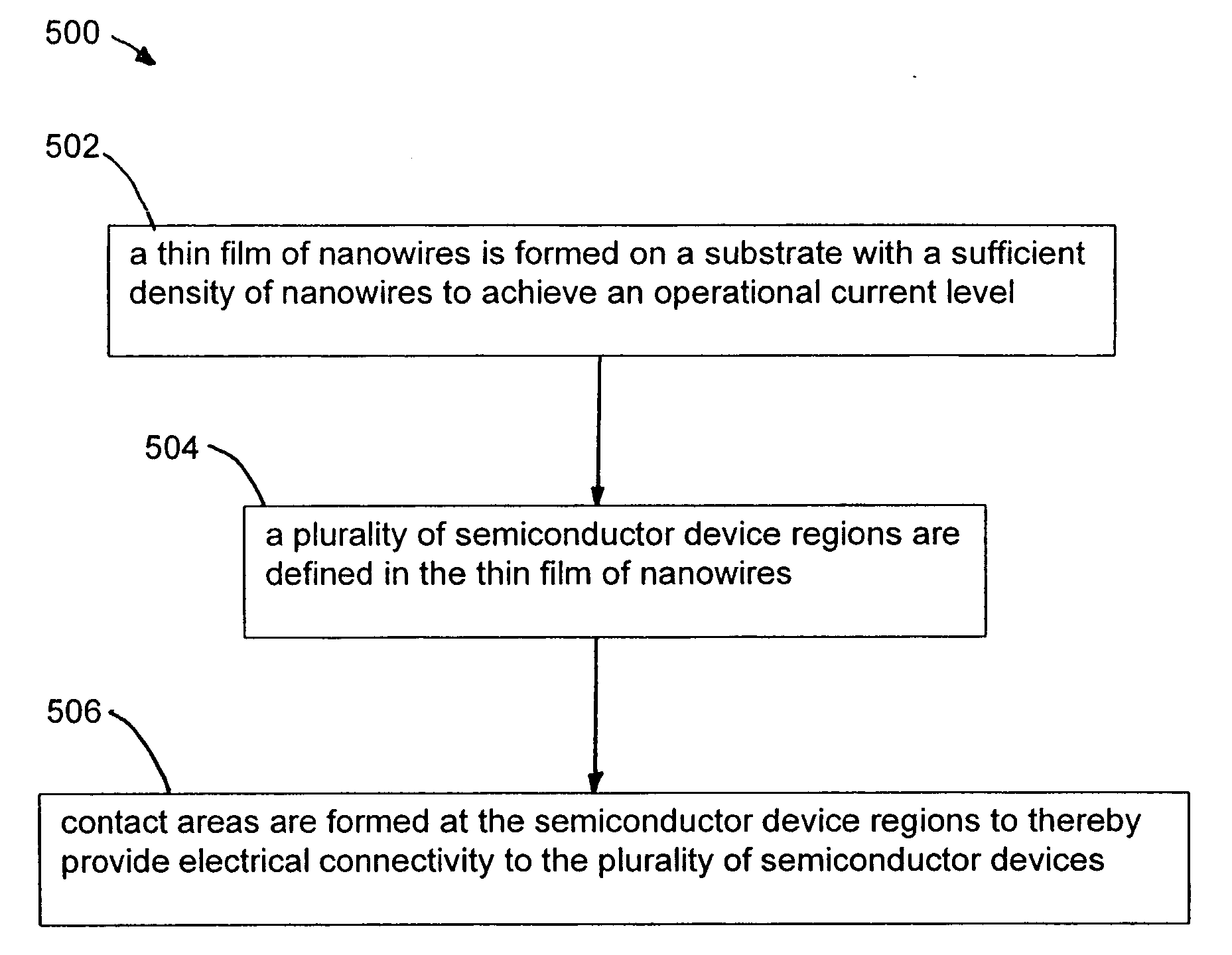
A method and apparatus for an electronic substrate having a plurality of semiconductor devices is described. A thin film of nanowires is formed on a substrate. The thin film of nanowires is formed to have a sufficient density of nanowires to achieve an operational current level. A plurality of semiconductor regions are defined in the thin film of nanowires. Contacts are formed at the semiconductor device regions to thereby provide electrical connectivity to the plurality of semiconductor devices. Furthermore, various materials for fabricating nanowires, thin films including p-doped nanowires and n-doped nanowires, nanowire heterostructures, light emitting nanowire heterostructures, flow masks for positioning nanowires on substrates, nanowire spraying techniques for depositing nanowires, techniques for reducing or eliminating phonon scattering of electrons in nanowires, and techniques for reducing surface states in nanowires are described.
Owner:ONED MATERIAL INC
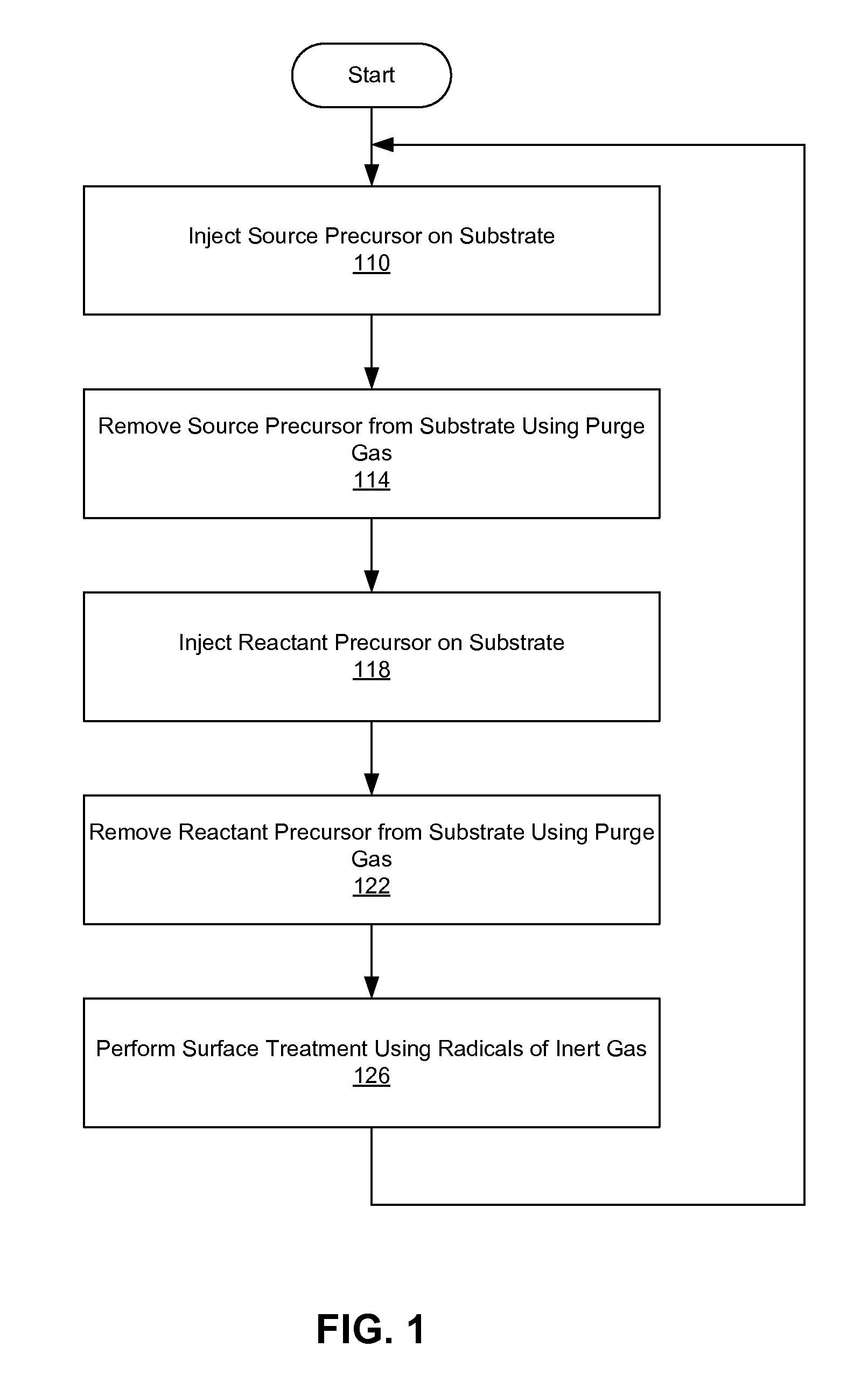
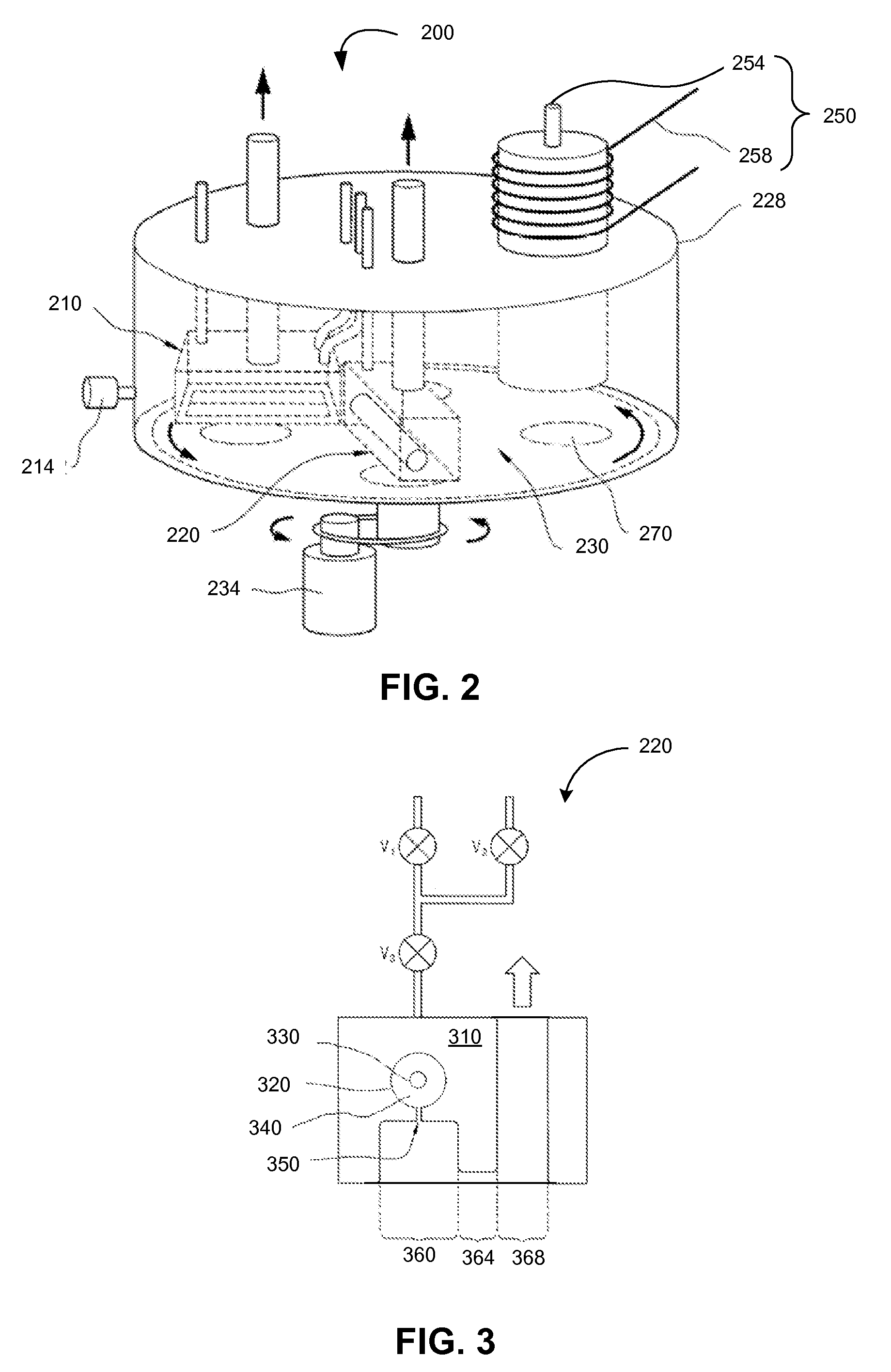
Treating Surface of Substrate Using Inert Gas Plasma in Atomic Layer Deposition
InactiveUS20120021252A1Increase deposition rateElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDangling bondGas plasma
Depositing one or more layers of material on a substrate using atomic layer deposition (ALD) followed by surface treating the substrate with radicals of inert gas before subjecting the substrate to further deposition of layers. The radicals of the inert gas appear to change the surface state of the deposited layer to a state more amenable to absorb subsequent source precursor molecules. The radicals of the inert gas disconnect bonding of molecules on the surface of the substrate, and render the molecules on the surface to have dangling bonds. The dangling bonds facilitate absorption of subsequently injected source precursor molecules into the surface. Exposure to the radicals of the inert gas thereby increases the deposition rate and improves the properties of the deposited layer.
Owner:VEECO ALD
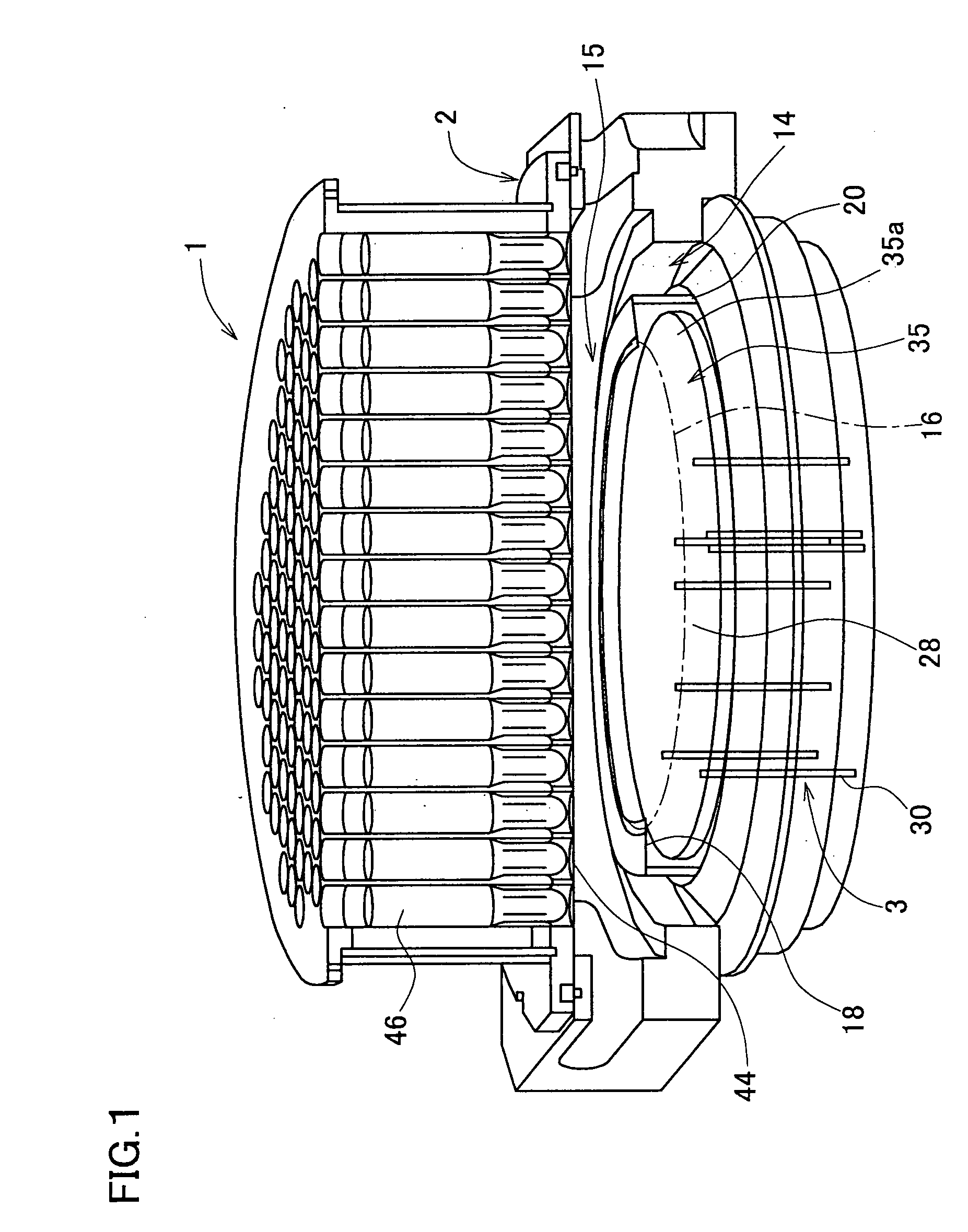
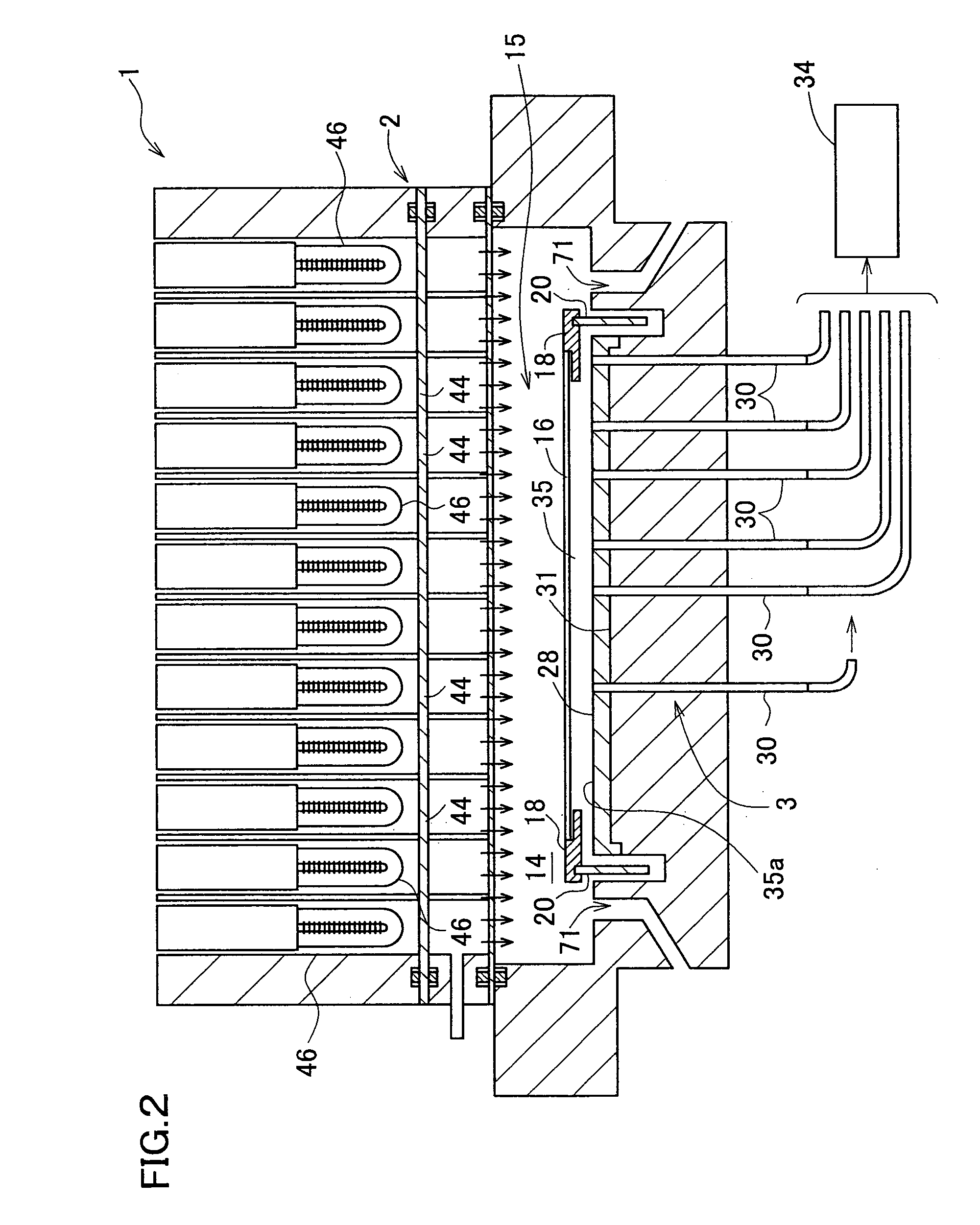
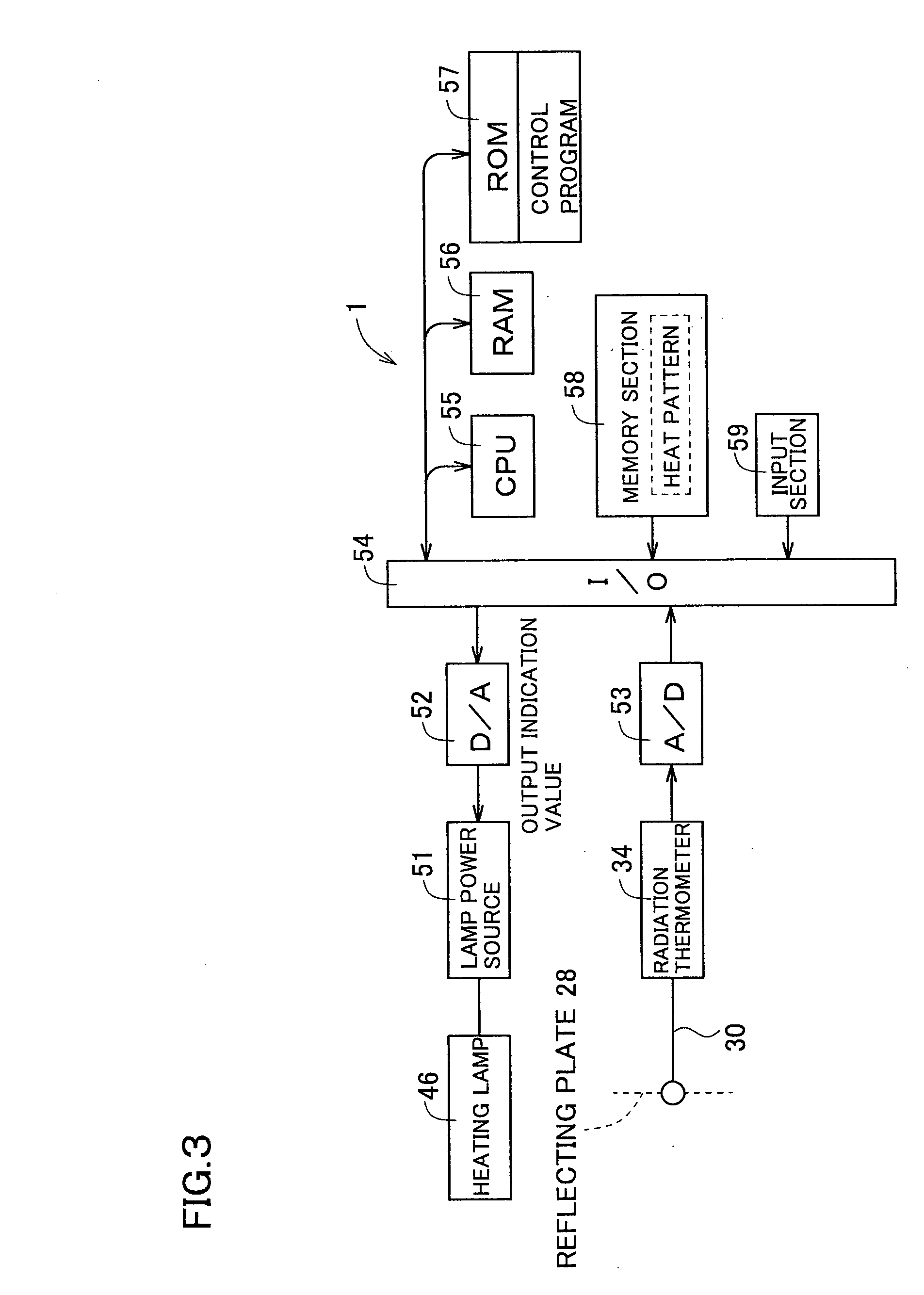
Temperature measuring system, heating device using it and production method for semiconductor wafer, heat ray insulating translucent member, visible light reflection membner, exposure system-use reflection mirror and exposure system, and semiconductor device produced by using them and vetical heat treating device
InactiveUS20050063451A1Necessary numberGood choiceRadiation pyrometryDoor/window protective devicesDevice materialRadiation thermometer
Oppositely of a temperature measuring surface of an object-to-be-measured 16, a reflecting member 28 is disposed while being spaced by a reflection gap 35 from the temperature measuring surface. The reflecting member 28 is composed of a heat ray reflecting material capable of reflecting heat ray in a specific wavelength band, in a portion including a reflection surface 35a. A heat ray extraction pathway section 30 is disposed through the reflecting member 28 so that one end thereof faces the temperature measuring surface. Heat ray extracted through the heat ray extraction pathway section from the reflection gap is detected by a temperature detection section 34. The heat ray reflecting material is configured in a form of a stack comprising a plurality of element reflecting layers composed of a material having transparent properties to the heat ray, in which every adjacent two element reflecting layers are composed of a combination of materials having refractive indices which differ from each other by 1.1 or more. This makes the measurement be hardly affected by radiation ratio of the object-to-be-measured when temperature of the object-to-be-measured is measured by a radiation thermometer, enables to measure its temperature more correctly irrespective of the surface state thereof, and can simplify configuration of a measurement system.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Large-area nanoenabled macroelectronic substrates and uses therefor
ActiveUS20050181587A1Improve performanceHigh carrier mobilityTransistorNanoinformaticsNanowireElectron scattering
A method and apparatus for an electronic substrate having a plurality of semiconductor devices is described. A thin film of nanowires is formed on a substrate. The thin film of nanowires is formed to have a sufficient density of nanowires to achieve an operational current level. A plurality of semiconductor regions are defined in the thin film of nanowires. Contacts are formed at the semiconductor device regions to thereby provide electrical connectivity to the plurality of semiconductor devices. Furthermore, various materials for fabricating nanowires, thin films including p-doped nanowires and n-doped nanowires, nanowire heterostructures, light emitting nanowire heterostructures, flow masks for positioning nanowires on substrates, nanowire spraying techniques for depositing nanowires, techniques for reducing or eliminating phonon scattering of electrons in nanowires, and techniques for reducing surface states in nanowires are described.
Owner:ONED MATERIAL INC
Large-area nanoenabled macroelectronic substrates and uses therefor
InactiveUS7135728B2Reduce and entirely eliminate scatteringHigh carrier mobilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanowireElectron scattering
A method and apparatus for an electronic substrate having a plurality of semiconductor devices is described. A thin film of nanowires is formed on a substrate. The thin film of nanowires is formed to have a sufficient density of nanowires to achieve an operational current level. A plurality of semiconductor regions are defined in the thin film of nanowires. Contacts are formed at the semiconductor device regions to thereby provide electrical connectivity to the plurality of semiconductor devices. Furthermore, various materials for fabricating nanowires, thin films including p-doped nanowires and n-doped nanowires, nanowire heterostructures, light emitting nanowire heterostructures, flow masks for positioning nanowires on substrates, nanowire spraying techniques for depositing nanowires, techniques for reducing or eliminating phonon scattering of electrons in nanowires, and techniques for reducing surface states in nanowires are described.
Owner:ONED MATERIAL INC
Large-area nanoenabled macroelectronic substrates and uses therefor
InactiveUS20050110064A1Reduce and entirely eliminate scatteringHigh carrier mobilityTransistorNanoinformaticsNanowirePhonon scattering
A method and apparatus for an electronic substrate having a plurality of semiconductor devices is described. A thin film of nanowires is formed on a substrate. The thin film of nanowires is formed to have a sufficient density of nanowires to achieve an operational current level. A plurality of semiconductor regions are defined in the thin film of nanowires. Contacts are formed at the semiconductor device regions to thereby provide electrical connectivity to the plurality of semiconductor devices. Furthermore, various materials for fabricating nanowires, thin films including p-doped nanowires and n-doped nanowires, nanowire heterostructures, light emitting nanowire heterostructures, flow masks for positioning nanowires on substrates, nanowire spraying techniques for depositing nanowires, techniques for reducing or eliminating phonon scattering of electrons in nanowires, and techniques for reducing surface states in nanowires are described.
Owner:ONED MATERIAL INC
Enhanced electroless deposition of dielectric precursor materials for use in in-laid gate MOS transistors
InactiveUS6465334B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectroless depositionOxygen
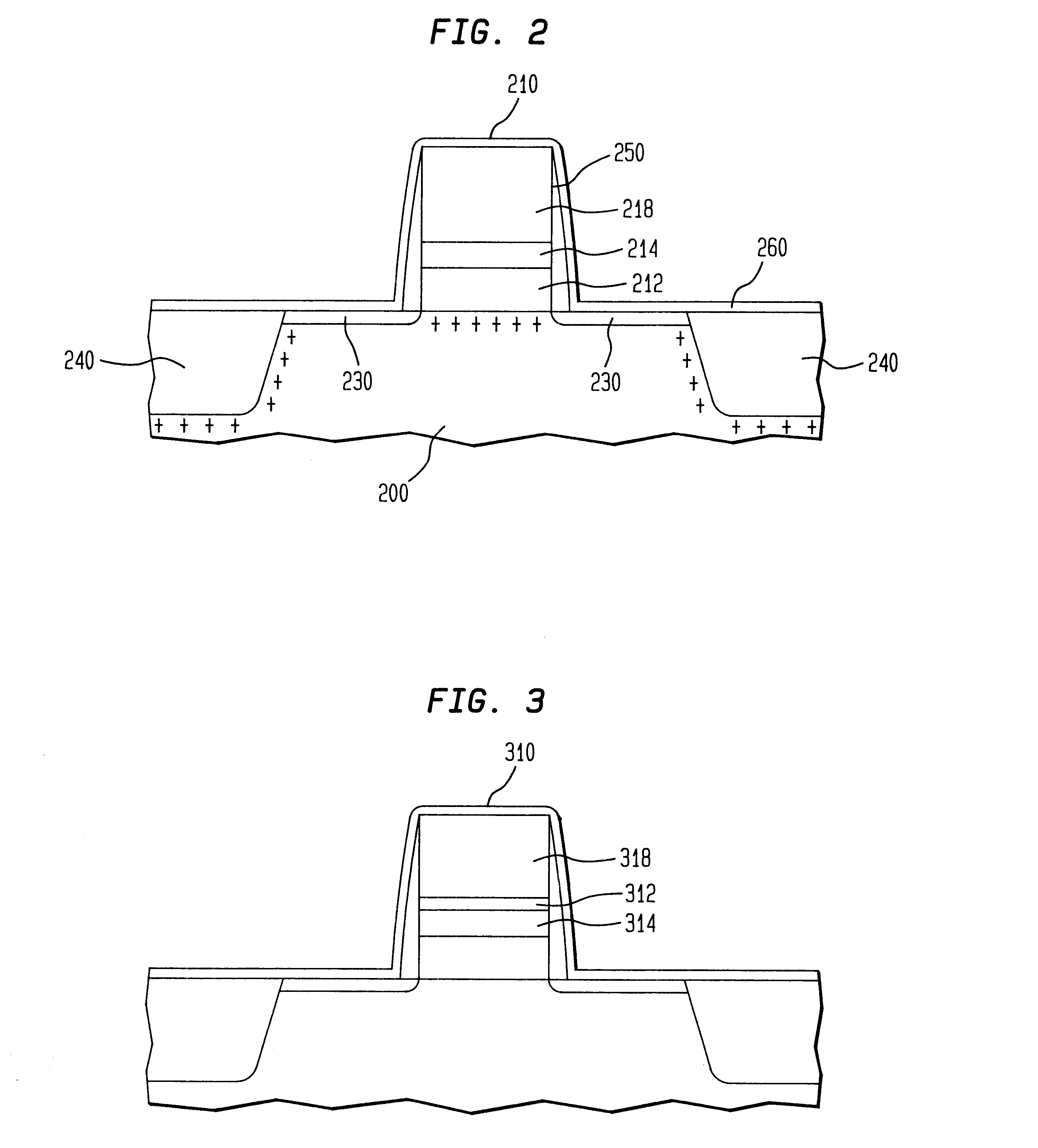
High quality dielectric layers, e.g., high-k dielectric layers comprised of at least one refractory or lanthanum series transition metal oxide or silicate, for use as gate insulator layers in in-laid metal gate MOS transistors and CMOS devices, are fabricated by forming an ultra-thin catalytic metal layer, e.g., a monolayer thick layer of Pd or Pd, on a Si-based semiconductor substrate, electrolessly plating on the catalytic layer comprising at least one refractory or lanthanum series transition metal or metal-based dielectric precursor layer, such as of Zr and / or Hf, and then reacting the precursor layer with oxygen or with oxygen and the semiconductor substrate to form the at least one high-k metal oxide or silicate. The inventive methodology prevents, or at least substantially reduces, oxygen access to the substrate surface during at least the initial stage(s) of formation of the gate insulator layer, thereby minimizing deleterious formation of oxygen-induced surface states at the semiconductor substrate / gate insulator interface.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Large-area nanoenabled macroelectronic substrates and uses therefor
InactiveUS7064372B2Reduce and entirely eliminate scatteringHigh carrier mobilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanowirePhonon scattering
A method and apparatus for an electronic substrate having a plurality of semiconductor devices is described. A thin film of nanowires is formed on a substrate. The thin film of nanowires is formed to have a sufficient density of nanowires to achieve an operational current level. A plurality of semiconductor regions are defined in the thin film of nanowires. Contacts are formed at the semiconductor device regions to thereby provide electrical connectivity to the plurality of semiconductor devices. Furthermore, various materials for fabricating nanowires, thin films including p-doped nanowires and n-doped nanowires, nanowire heterostructures, light emitting nanowire heterostructures, flow masks for positioning nanowires on substrates, nanowire spraying techniques for depositing nanowires, techniques for reducing or eliminating phonon scattering of electrons in nanowires, and techniques for reducing surface states in nanowires are described.
Owner:ONED MATERIAL INC
Method of manufacturing nitride semiconductor and nitride semiconductor element
ActiveUS8709843B2Improve surface morphologyReduce layeringPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSource materialCrystallinity
The present invention provides a method of manufacturing a nitride semiconductor capable of improving the crystallinity and the surface state of the nitride semiconductor crystal formed on top of a high-temperature AlN buffer layer. An AlN buffer layer is formed on top of a growth substrate, and then nitride semiconductor crystals are grown on top of the AlN buffer layer. In a stage of manufacturing the nitride semiconductor, the crystal of the AlN buffer layer is grown at a high temperature of 900° C. or higher. In addition, an Al-source material of the AlN buffer layer is started to be supplied first to a reaction chamber and continues to be supplied without interruption, and then a N-source material is supplied intermittently.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Method and apparatus for scanning corrosion and surface defects
InactiveUS20060288756A1Readily usable outputAccurately determineAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWave based measurement systemsSurface conditionsPrediction system
The present invention relates to a method and an apparatus for determining the life span for secure use of a pipeline comprising the steps of a) defining an area for surface corrosion analysis on the pipeline, b) providing a corrosion scanning system for scanning the defined area on the pipeline, c) localizing and measuring the corrosion on the surface of the defined area by means of the corrosion scanning system, d) determining the remaining wall-thickness of the pipeline at the defined area by means of the corrosion scanning system, and e) processing the surface condition data related to corrosion at the defined area obtained in steps c) and d) to determine the life span for secure use of the pipeline. In another aspect the present invention relates to a corrosion scanning system for performing for performing the method according to the invention. In another aspect the invention relates to a prediction system for predicting the secure life span of a pipeline.
Owner:DE MEURECHY GUIDO D K
Electrolytic deposition of dielectric precursor materials for use in in-laid gate MOS transistors
InactiveUS6300203B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectrolysisOxygen
High quality dielectric layers, e.g., high-k dielectric layers comprised of at least one refractory or lanthanum series transition metal oxide or silicate, for use as gate insulator layers in in-laid metal gate MOS transistors and CMOS devices, are formed by electrolytically plating a metal or metal-based dielectric precursor layer comprising at least one refractory or lanthanum series transition metal, on a semiconductor substrate, typically a silicon-based substrate, and then reacting the precursor layer with oxygen or with oxygen and the semiconductor substrate to form the at least one refractory or lanthanum series transition metal oxide or silicate. The inventive methodology prevents, or at least substantially reduces, oxygen access to the substrate surface during at least the initial stage(s) of formation of the gate insulator layer, thereby minimizing deleterious formation of oxygen-induced surface states at the semiconductor substrate / gate insulator interface.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
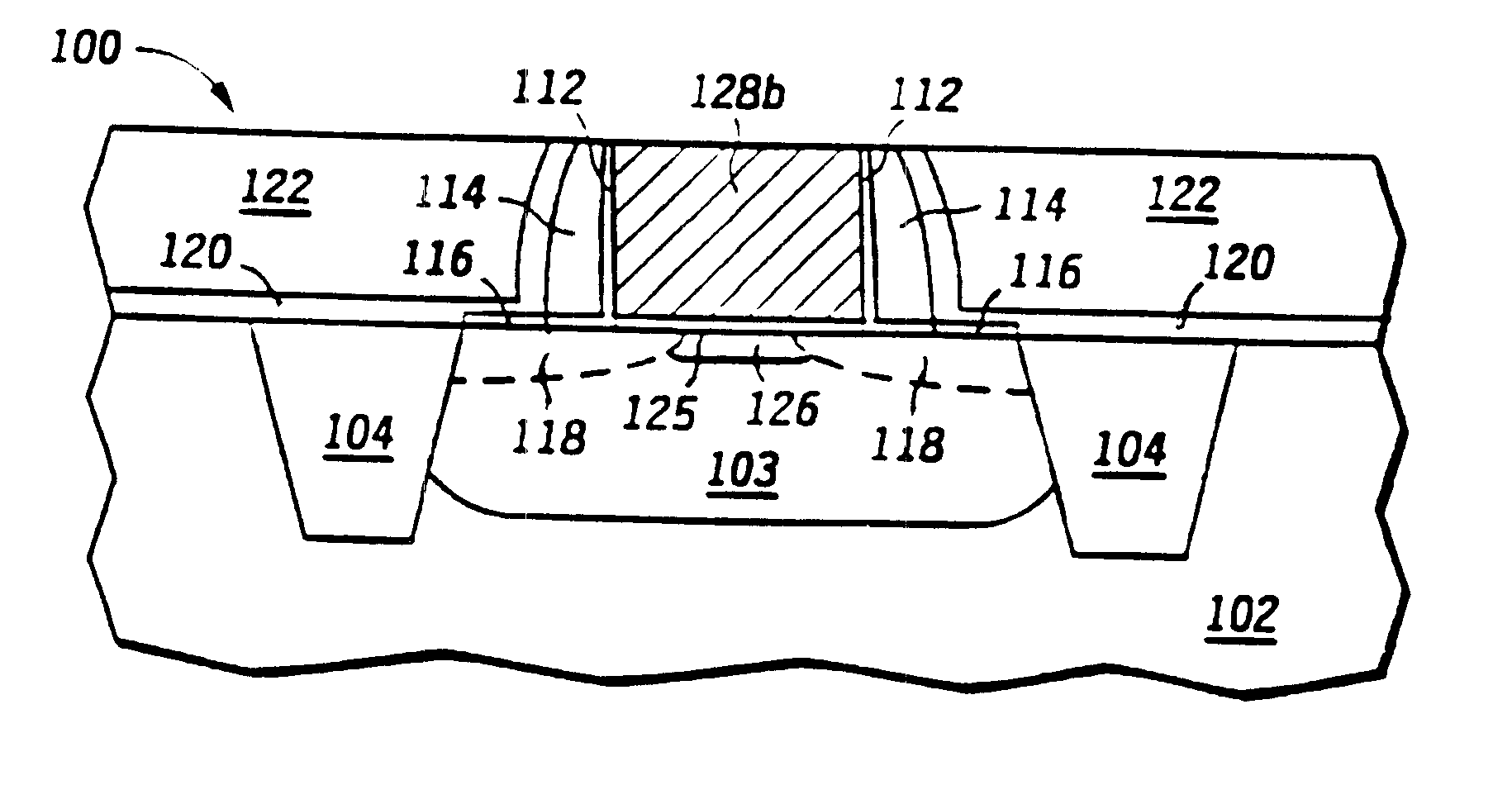
Semiconductor device structure with hydrogen-rich layer for facilitating passivation of surface states
A process for fabricating a device including the step of forming a structure for facilitating the passivation of surface states is disclosed. The structure comprises an oxynitride layer formed as part of the device structure. The oxynitride facilitates the passivation of surface states when heated.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
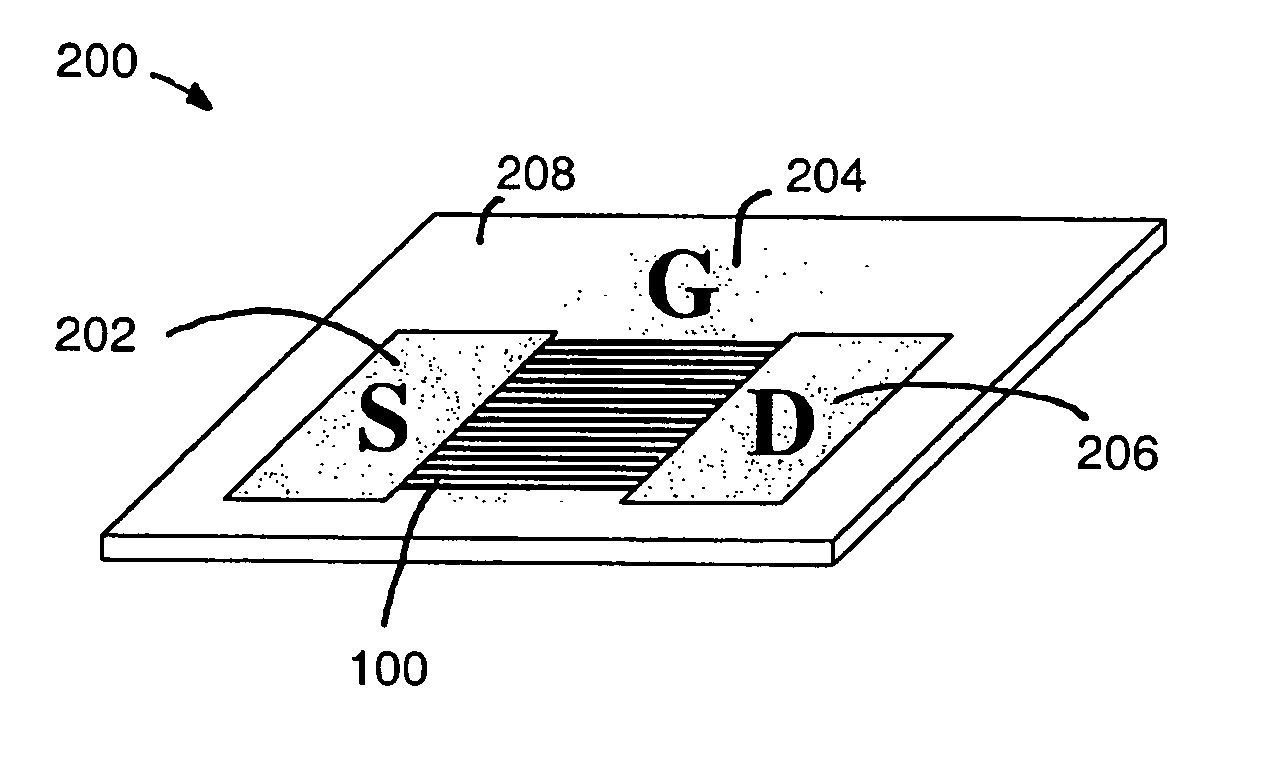
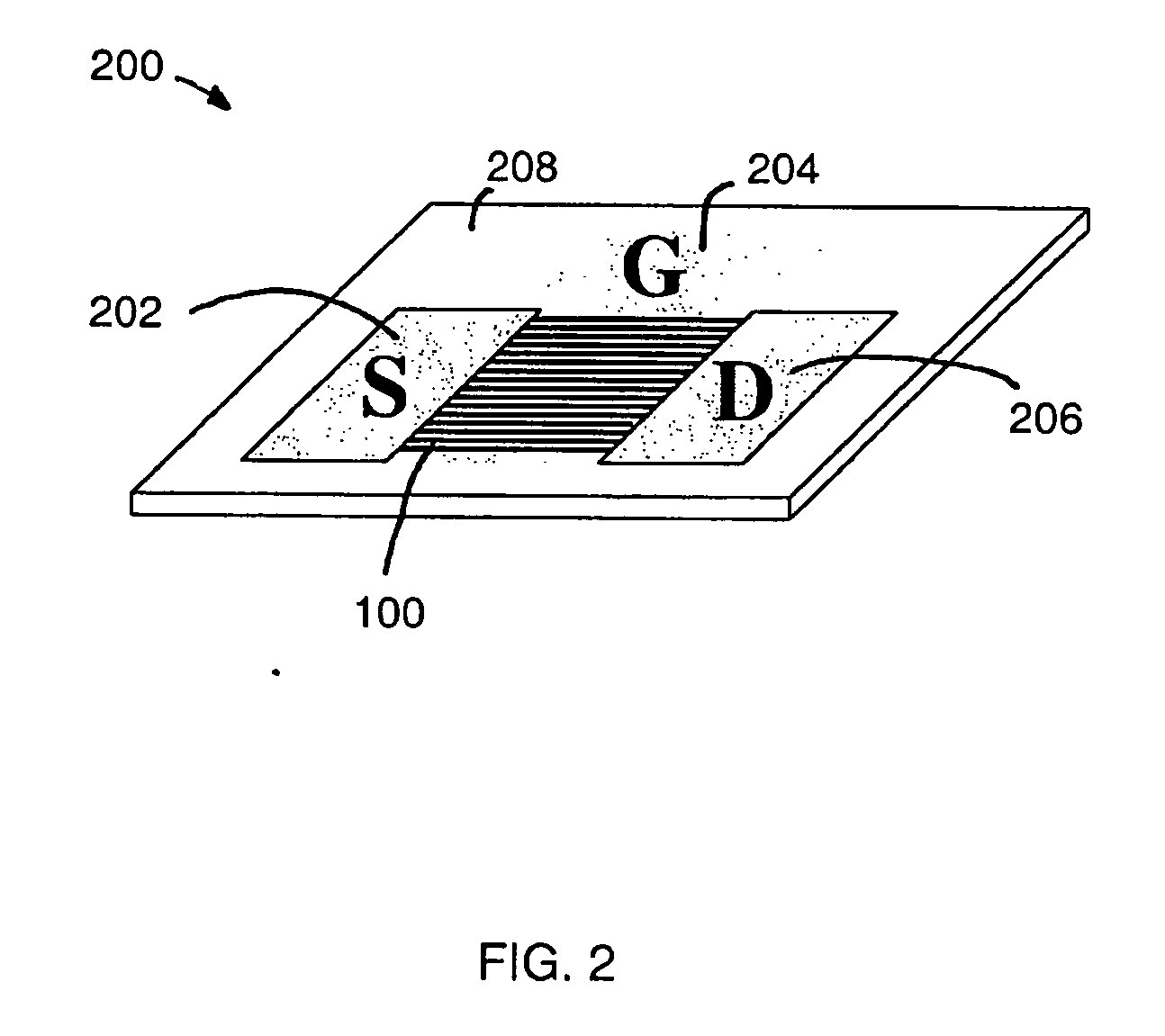
Semiconductor device, its manufacturing method, and electronic device
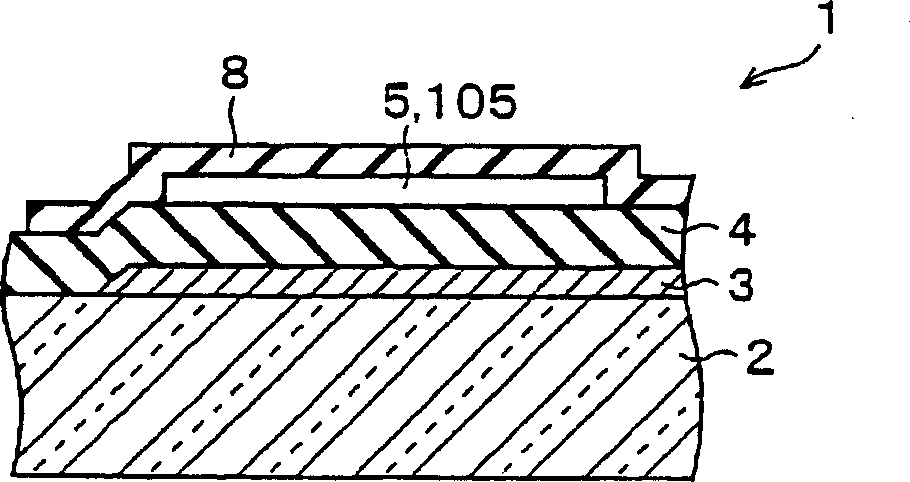
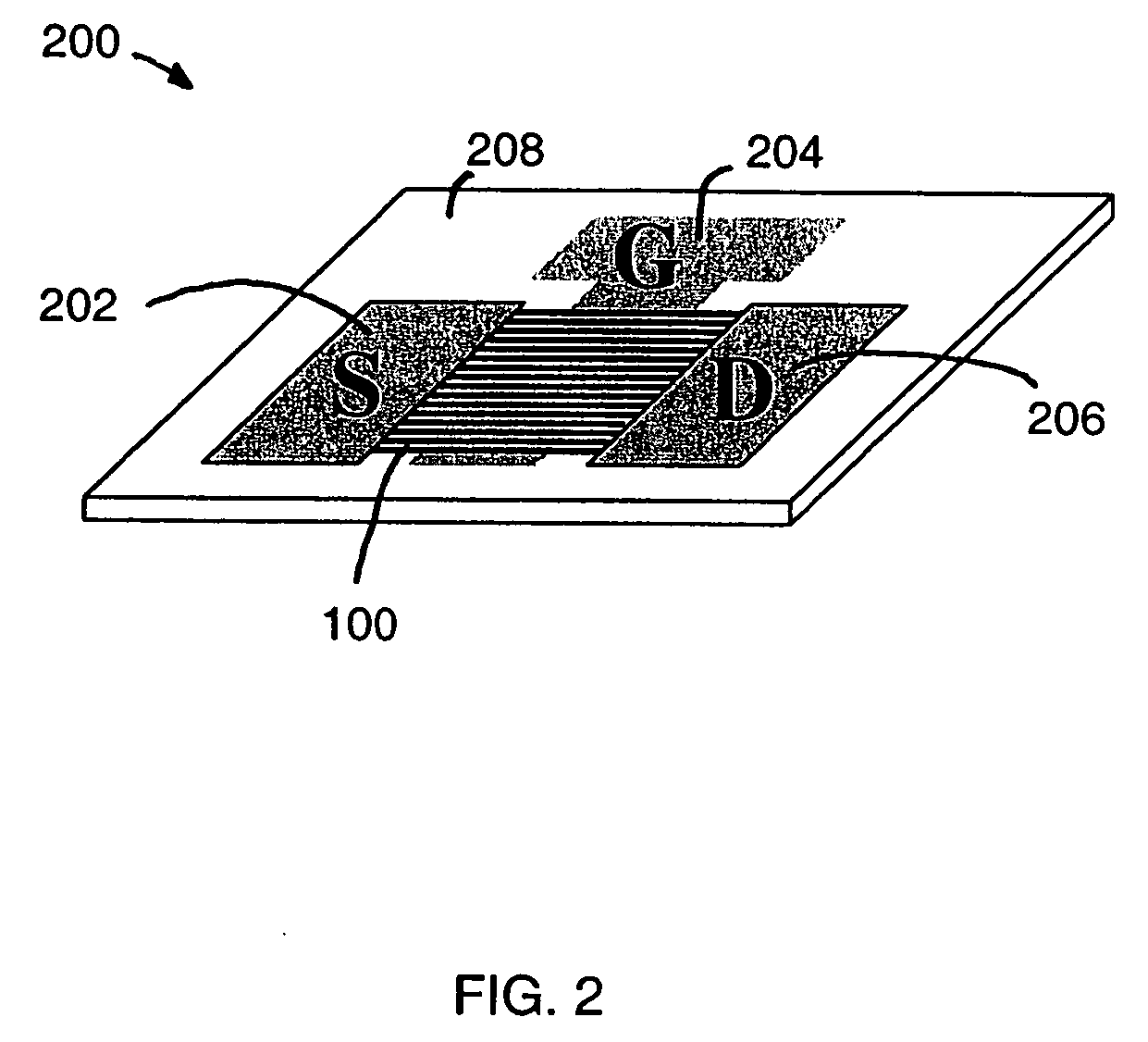
InactiveCN1806322ATransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIntrinsic resistanceGate voltage
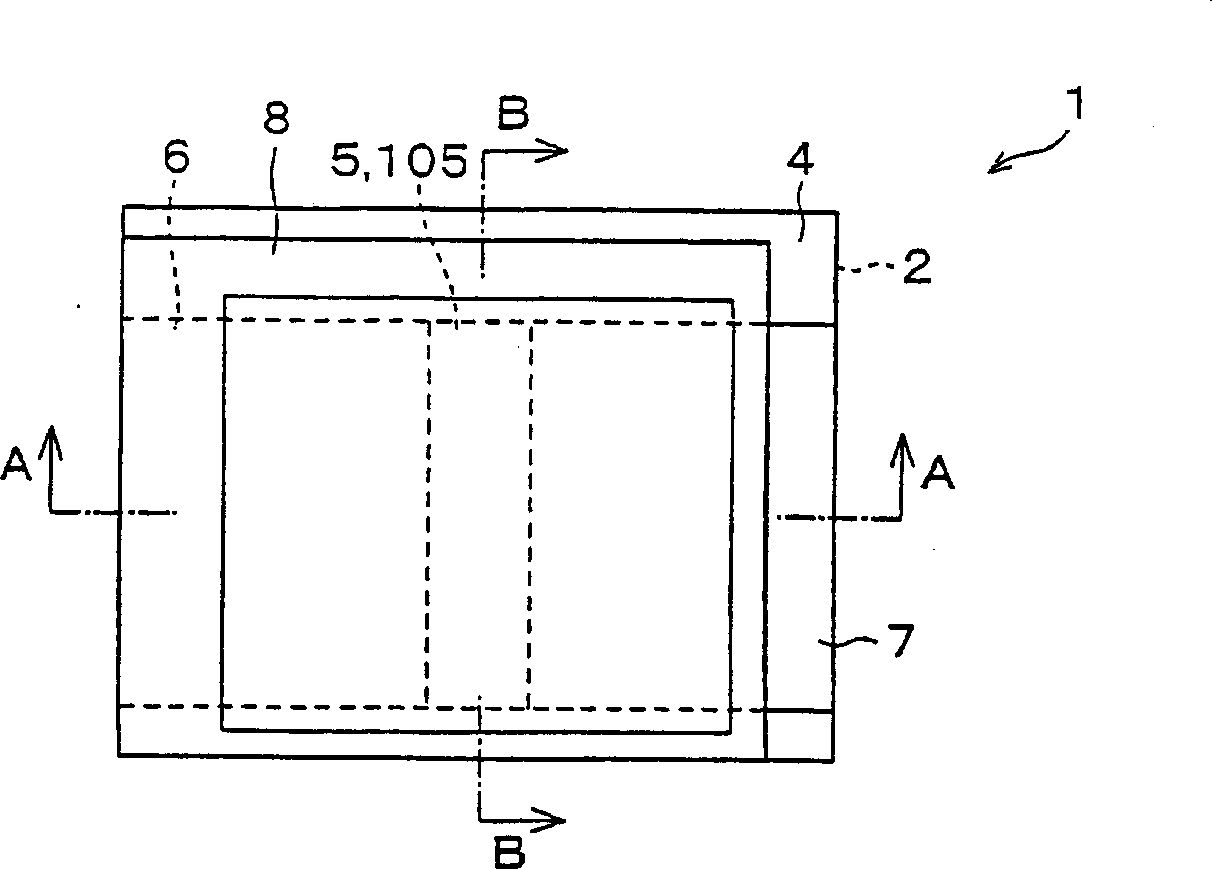
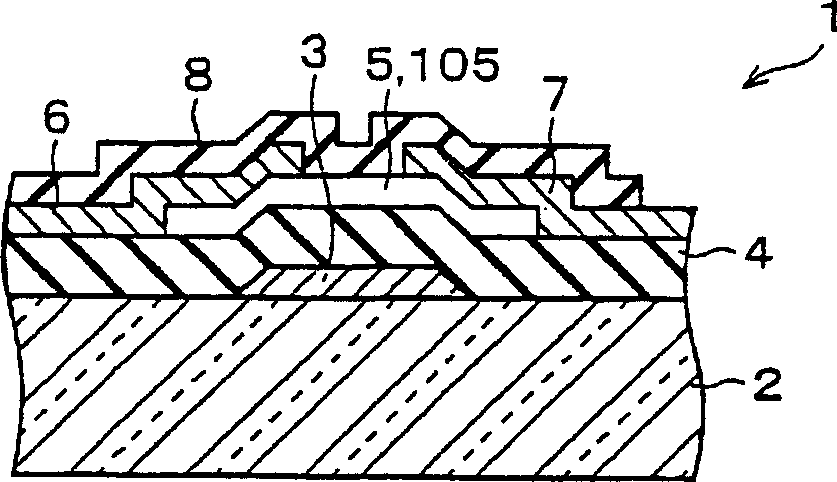
A thin film transistor (1) wherein a gate electrode (3) is formed on an insulative substrate (2), a gate insulating layer (4) is formed on the gate electrode (3), a semiconductor layer (5) is formed on the gate insulating layer (4), a source electrode (6) and a drain electrode (7) are formed on the semiconductor layer (5), and a protective layer (8) covering them are formed. The semiconductor layer (5) is isolated from the atmosphere. The semiconductor layer (5) (active layer) is formed of a ZnO polycrystalline semiconductor doped with, for example, a group V element. Since the surface state of the ZnO semiconductor is reduced thanks to the protective layer (8) and inward expansion of the depletion layer is prevented, the ZnO semiconductor is of an n-type showing its intrinsic resistance value and contains excessive free electrons. The added element acts as acceptor impurities in the ZnO semiconductor, decreasing the excessive electrons. Thus the gate voltage to eliminate the excessive free electrons lowers, thereby making the threshold voltage around 0 V. A semiconductor device using a zinc oxide for an active layer and having a protective layer for isolating the active layer from the atmosphere can be actually used.
Owner:SHARP KK +2
Fabrication method of a semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050074963A1Favorable contact holeSimple processTransistorSolid-state devicesResistOrganic film
In the case where a contact hole is formed by a conventional process of the semiconductor device fabrication, a resist is required to be formed almost entirely over a substrate in order to form the resist over the film where the contact hole is not formed. Accordingly, the throughput is considerably low. Further, when the resist spreads to the area of the contact hole when the amount of the resist to be applied and the surface state of the base are not fully controlled, contact defect would occur. Thus, improvements are required. According to the invention, in forming a semiconductor device, a part to be a contact hole of the semiconductor device may be covered with a first organic film that is liquid repellent. Subsequently, a second organic film serving as an insulating film is formed on the area where the first organic film is not formed, and the first organic film is removed thereafter to form a contact hole.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Information output apparatus
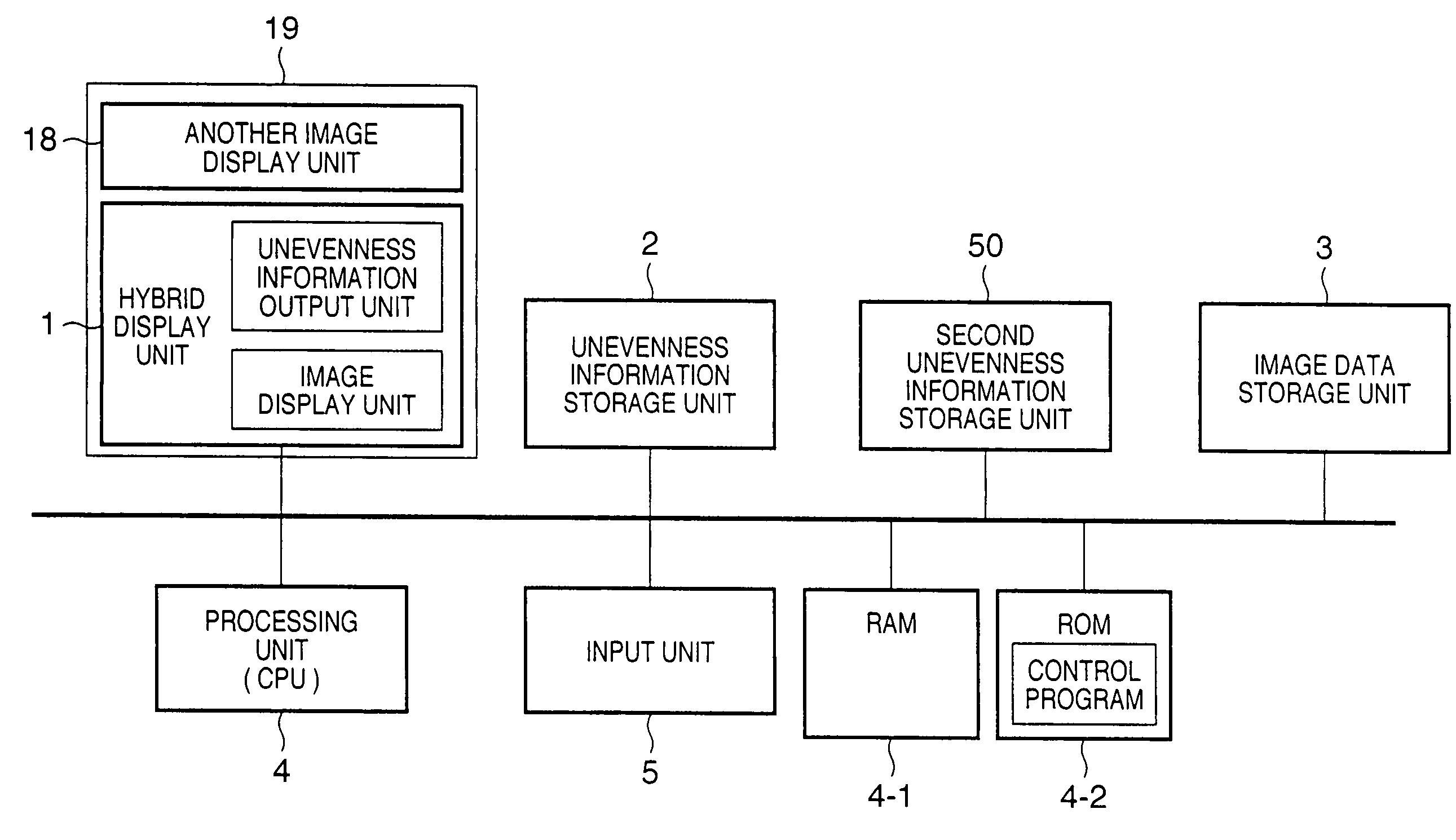
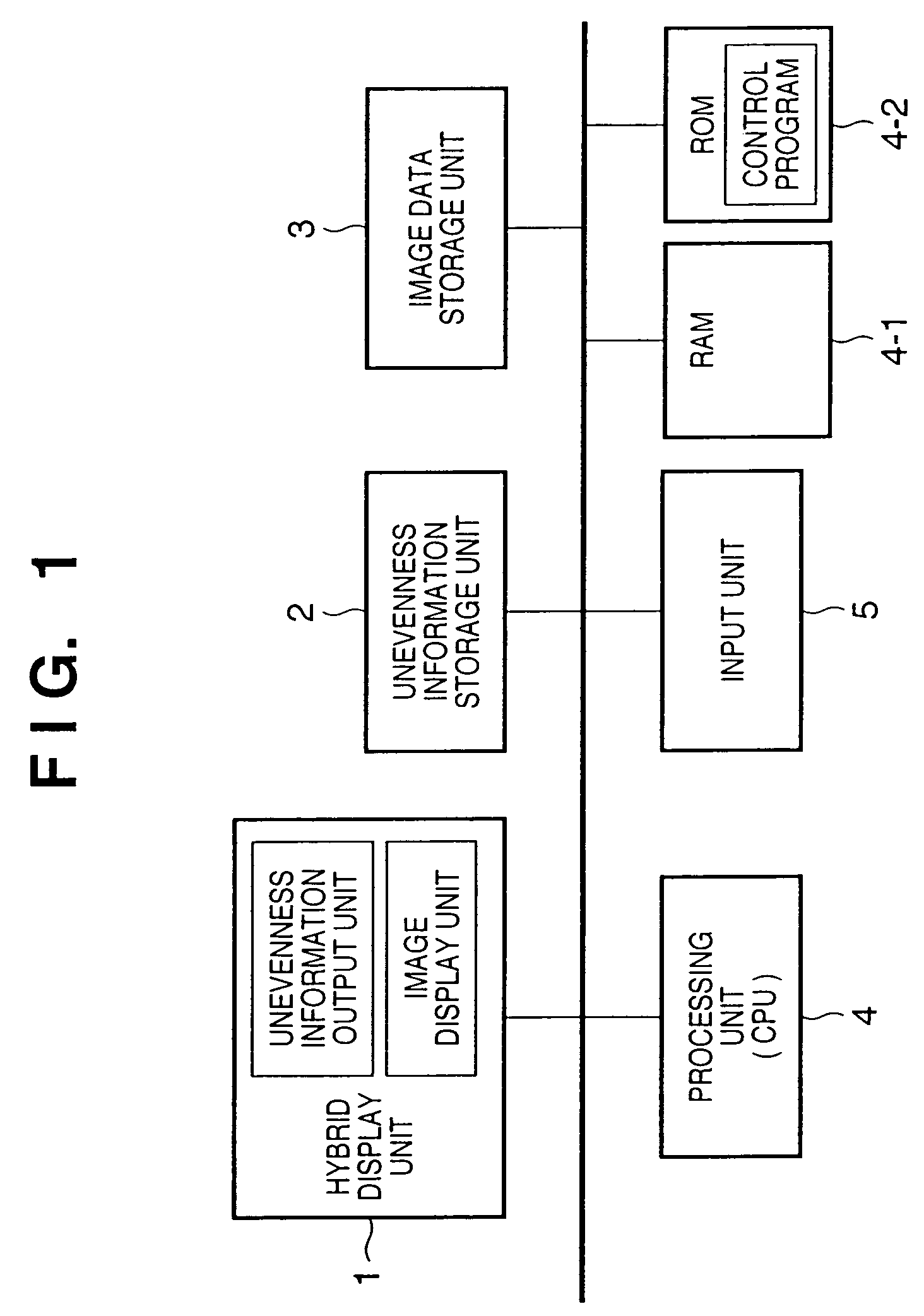
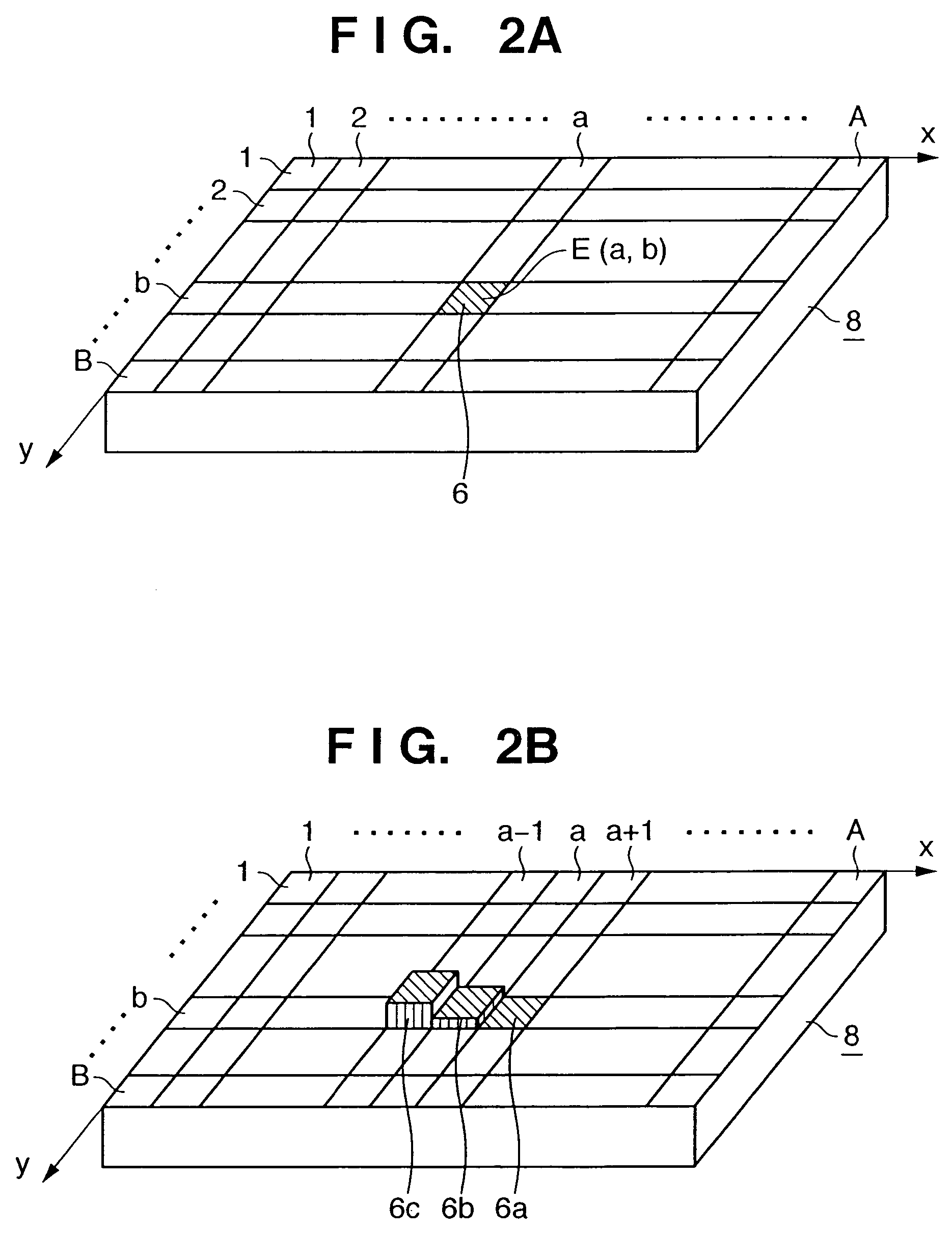
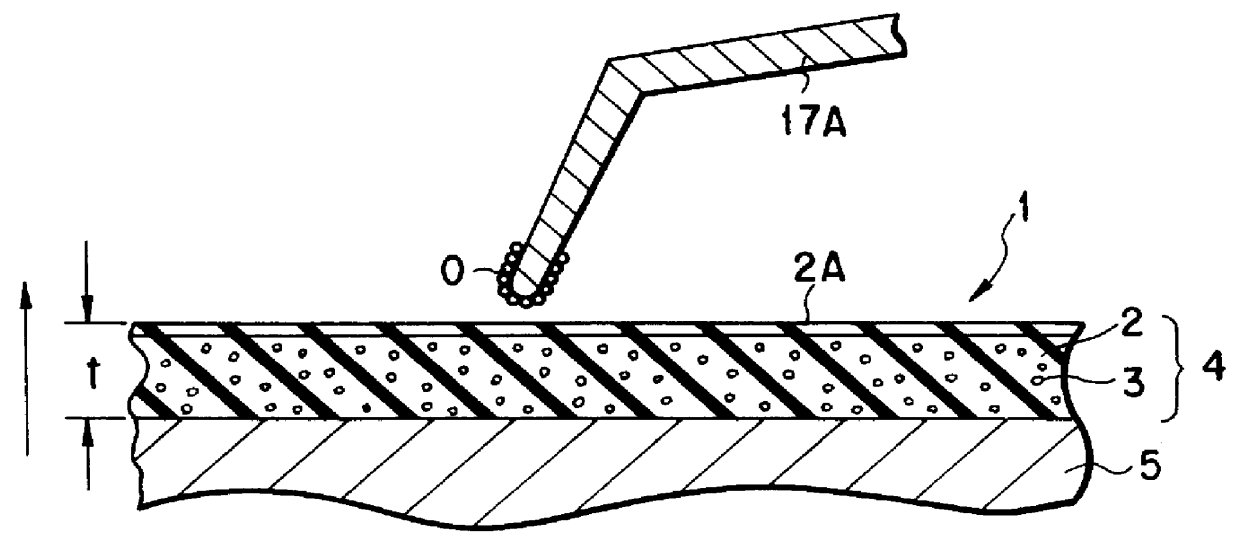
InactiveUS7202837B2Easily discriminatedInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsOutput deviceSurface states
This invention provides an information output apparatus which outputs tactile information or the like corresponding to the surface state of an object as three-dimensional information together with image information, and allows the user to easily discriminate the surface material or the like of an image object in the image information.A hybrid display unit of the information display apparatus of this invention has a structure formed by overlaying, e.g., a display panel used to display an image, and an unevenness output element group used to output the unevenness level of that image, and voltage values to be applied to respective unevenness output elements of the unevenness output element group are determined on the basis of, e.g., unevenness information stored in a memory. Therefore, material differences (smooth or rough touch) of images displayed on the display panel can be felt by touching unevenness output by the unevenness output elements.
Owner:CANON KK
Cellulose acylate, cellulose acylate film, and method for production and use thereof
InactiveUS20060222786A1Good optical performanceImprove thermal stability performanceLiquid crystal compositionsThin material handlingCelluloseSulfur
A cellulose acylate solution containing a cellulose acylate which satisfies 2.5≦A+B≦3, 0≦A≦2.5, 0.3≦B≦3 (wherein A is the substitution degree of an acetyl group, and B is the sum of the substitution degrees of an acyl group having 3 to 7 carbon atoms) and whose content of sulfur atoms of residual sulfate moiety S is such that 50 ppm<S<500 ppm. When solution casting is carried out using this solution, a cellulose acylate film having good surface state and low peel-off load can be produced.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Cleaner for inspecting projections, and inspection apparatus and method for integrated circuits
InactiveUS6130104AImprove surface conditionAnalog circuit testingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementWaddingBiomedical engineering
A cleaner of this invention is a cleaner for inspecting projections and removes any substance, e.g., aluminum oxide, which attaches to needle points of probe needles, when the probe needles pierce into the cleaner. The cleaner has a cleaner layer and a substrate. The cleaner layer is constituted by an elastic material layer, and a filler having a surface state improving function of the inspecting projections and dispersed in the elastic material layer. As the filler having a surface state improving function, a powder including at least one of ceramic materials, e.g., sand, glass, alumina, Carborundum (trade name), and the like, or a fiber layer made of an inorganic fiber or organic fiber can be employed.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
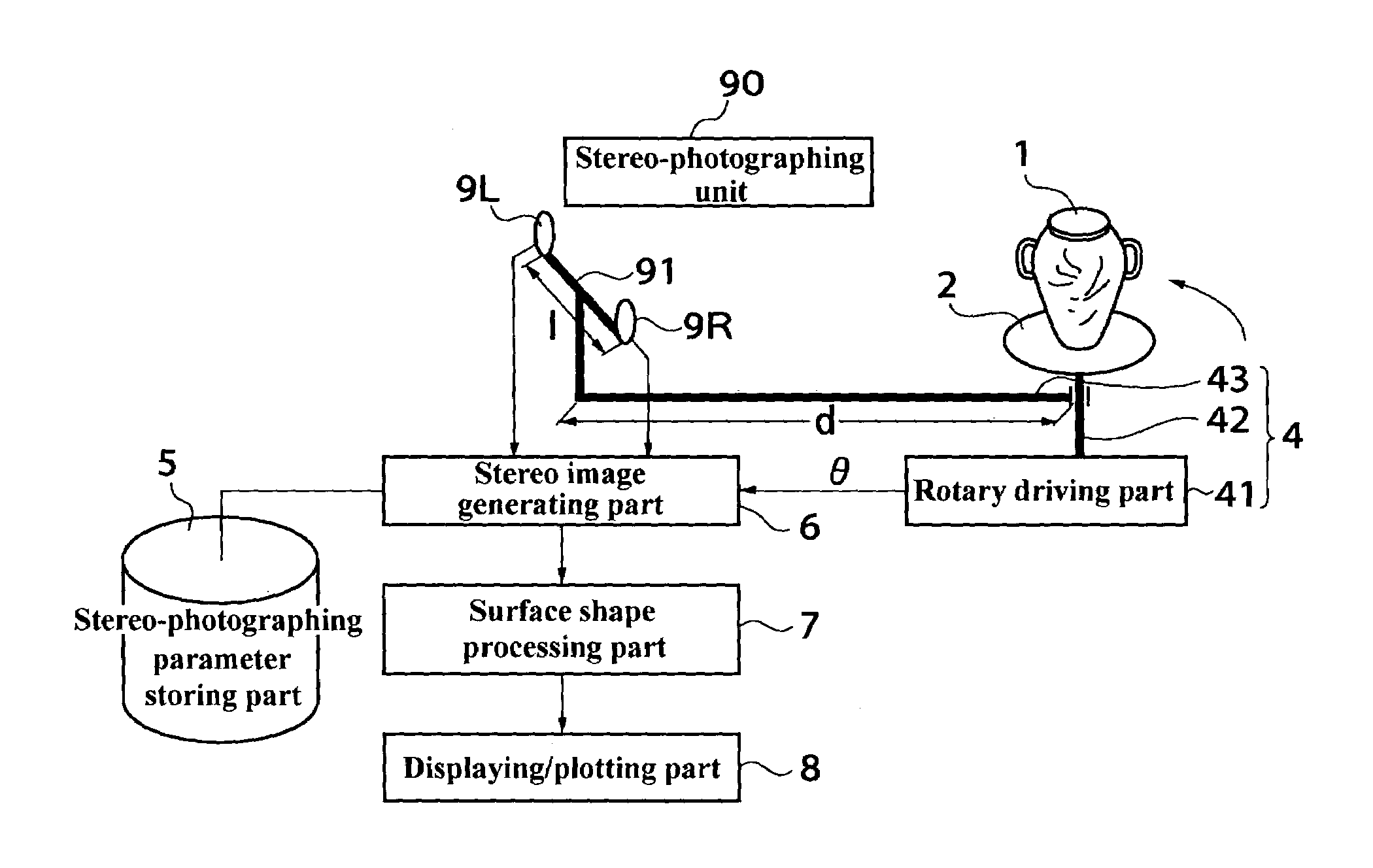
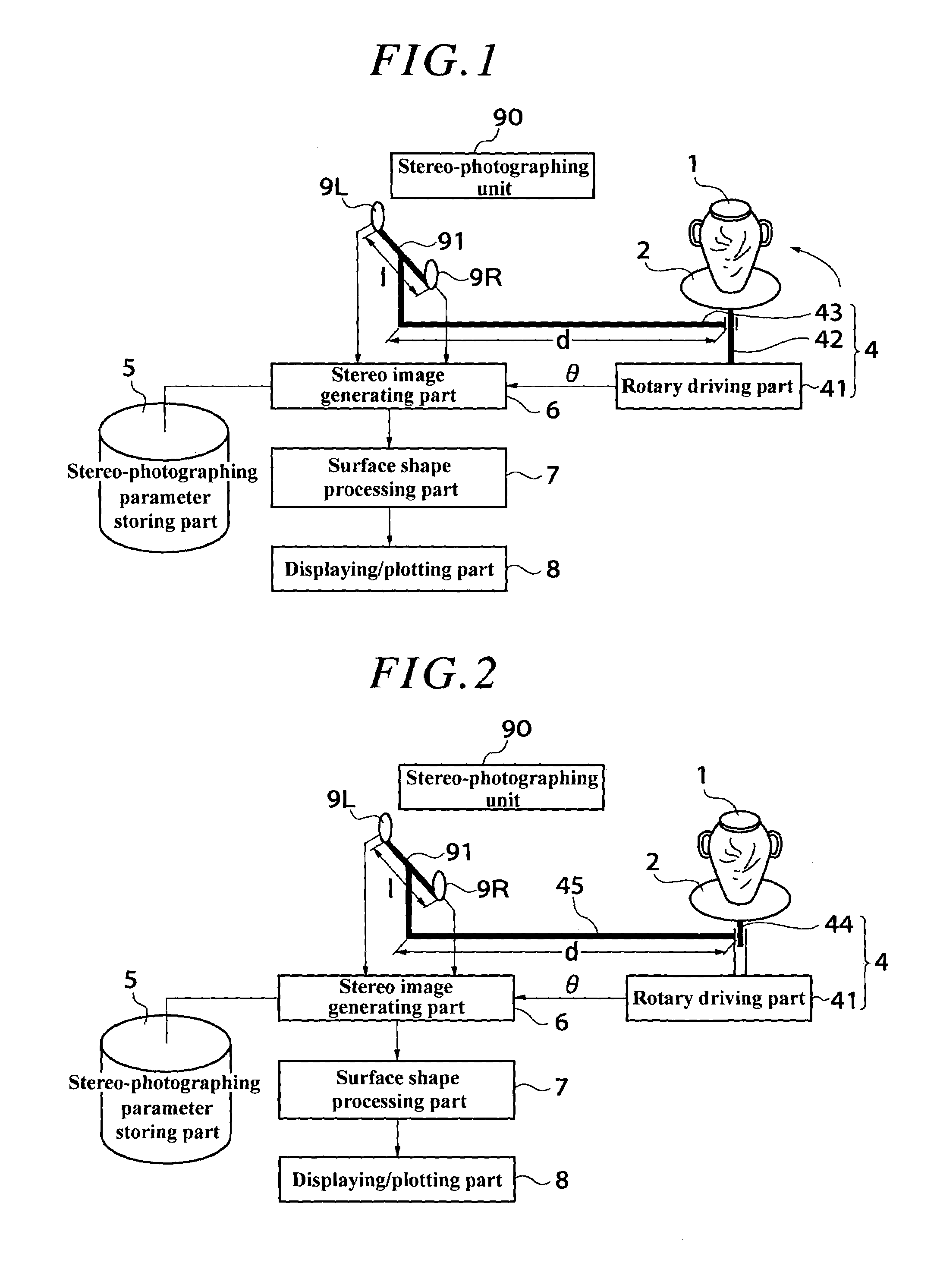
Surface shape measurement apparatus, surface shape measurement method, surface state graphic apparatus
InactiveUS7206080B2Wide rangeAccurate measurementImage enhancementImage analysisStereo imageSurface states
A surface shape measuring apparatus, comprising: a stereo-photographing part 3 for photographing an object 1 in stereo; a relative position changing part 4 for changing the positional relation between the stereo-photographing part 3 and the object 1; means 5 for storing stereo-photographing parameters in a plurality of directions from which the stereo-photographing part 3 photographs the object 1; a stereo-image generating means 6 for controlling the stereo-photographing part 3 to photograph the object 1 from the plurality of directions with the stored stereo-photographing parameters and generating stereo images of the object 1; and a surface shape processing means 7 for measuring the surface shape of the object 1 based on the stereo images of the object 1.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Detection device, movable body apparatus, pattern formation apparatus and pattern formation method, exposure apparatus and exposure method, and device manufacturing method
ActiveUS20090004580A1Improve accuracyHigh-precision exposurePhotomechanical apparatusUsing optical meansForeign matterLight beam
By irradiating a detection beam from an irradiation system of a detection device to a scale used for measuring the position of a wafer stage, and detecting the detection beam via the scale by a photodetection system, a surface state (an existence state of foreign substance) of the scale is detected. With this operation, detection of the surface state can be performed contactlessly with respect to the scale. Moreover, movement control of the wafer stage can be performed with high precision by taking the surface state into consideration.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Integral polishing pad and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7029747B2Improve planarization efficiencyEasy to manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTraffic signalsAdhesiveHardness
Owner:KPX CHEM
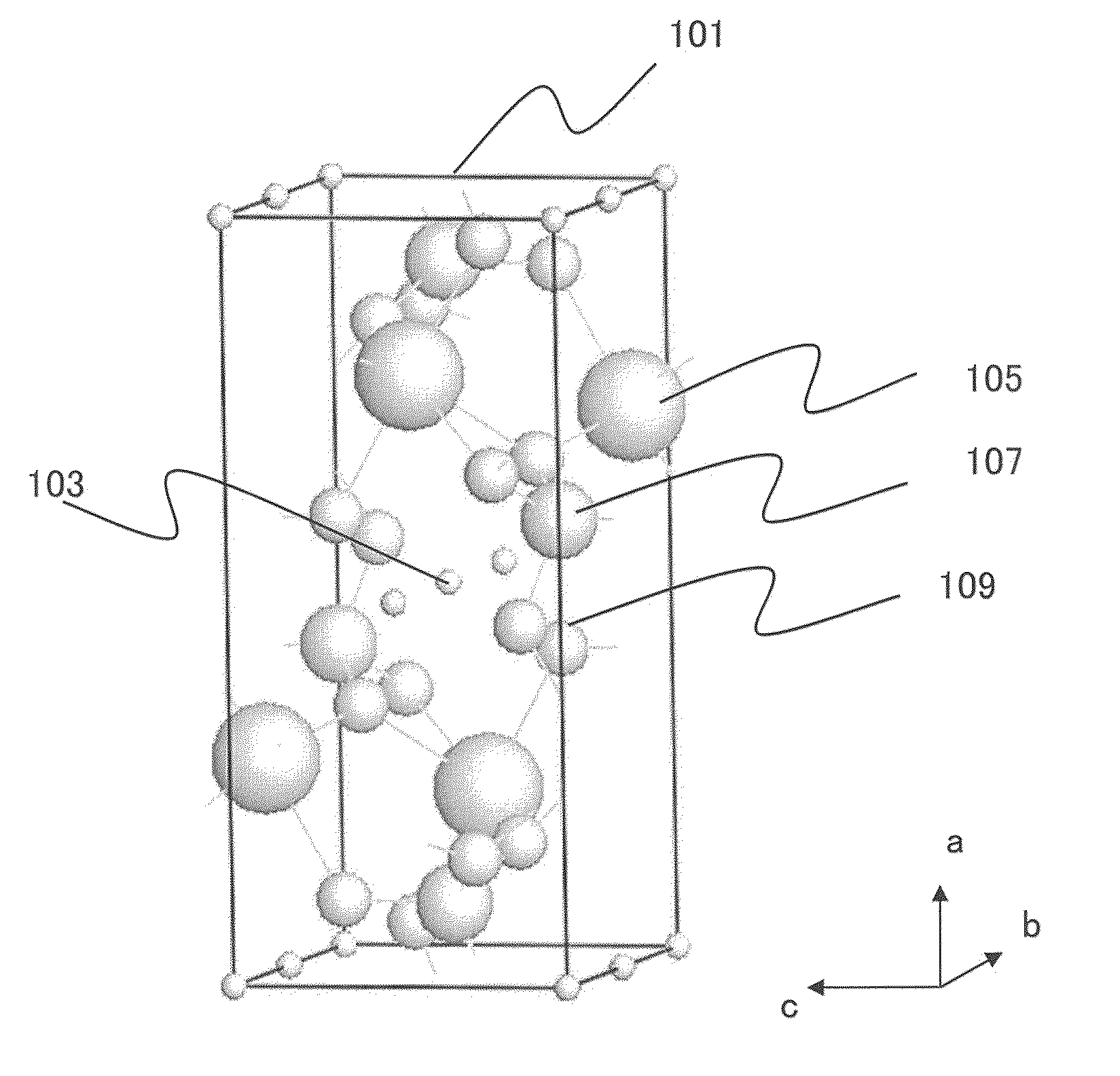
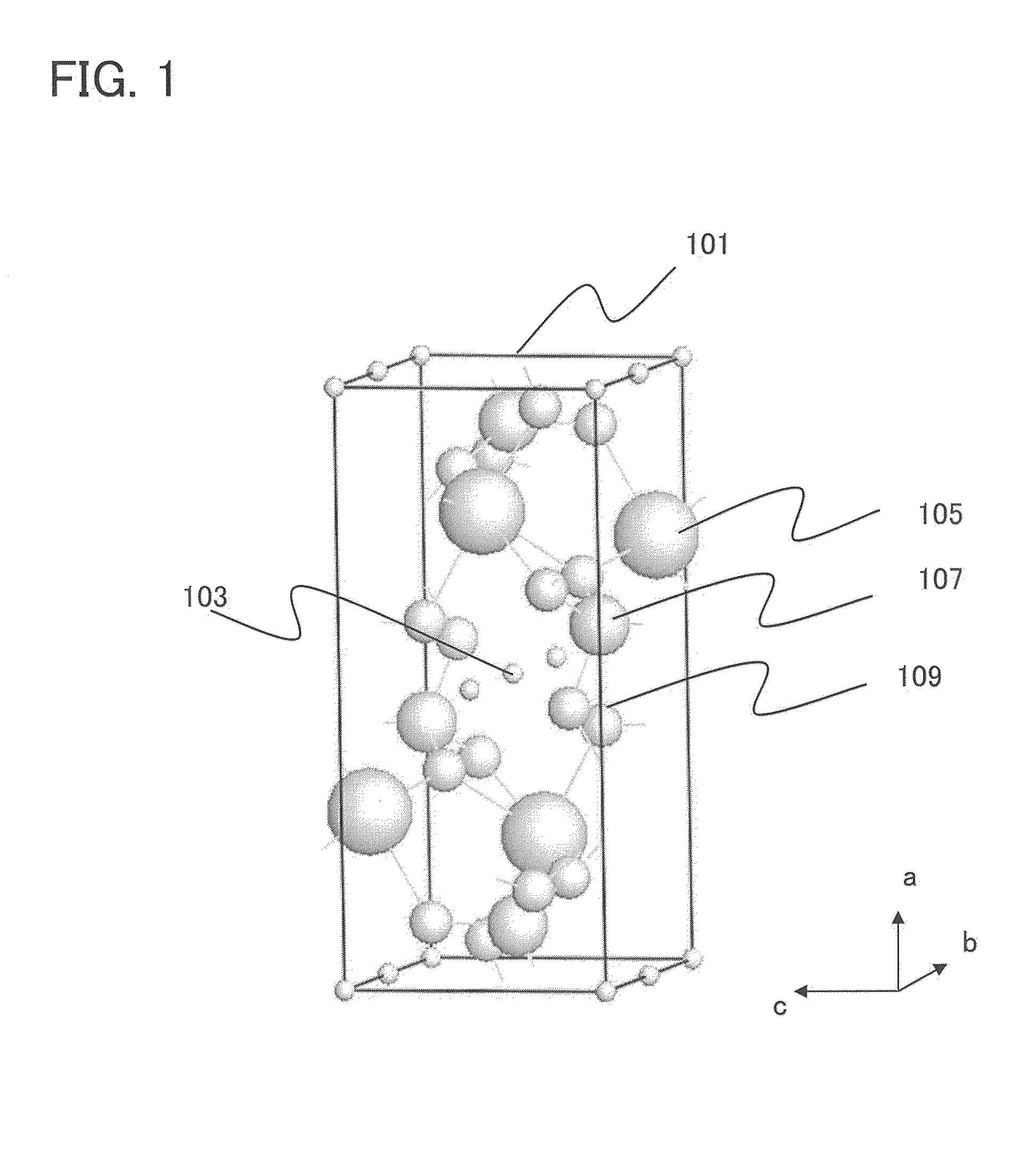
Method for forming nitrogen and sulfur co-doped graphene quantum dots
ActiveCN104812697AHigh fluorescence quantum yieldExcitation-independentMaterial nanotechnologyGrapheneHigh densityDoped graphene
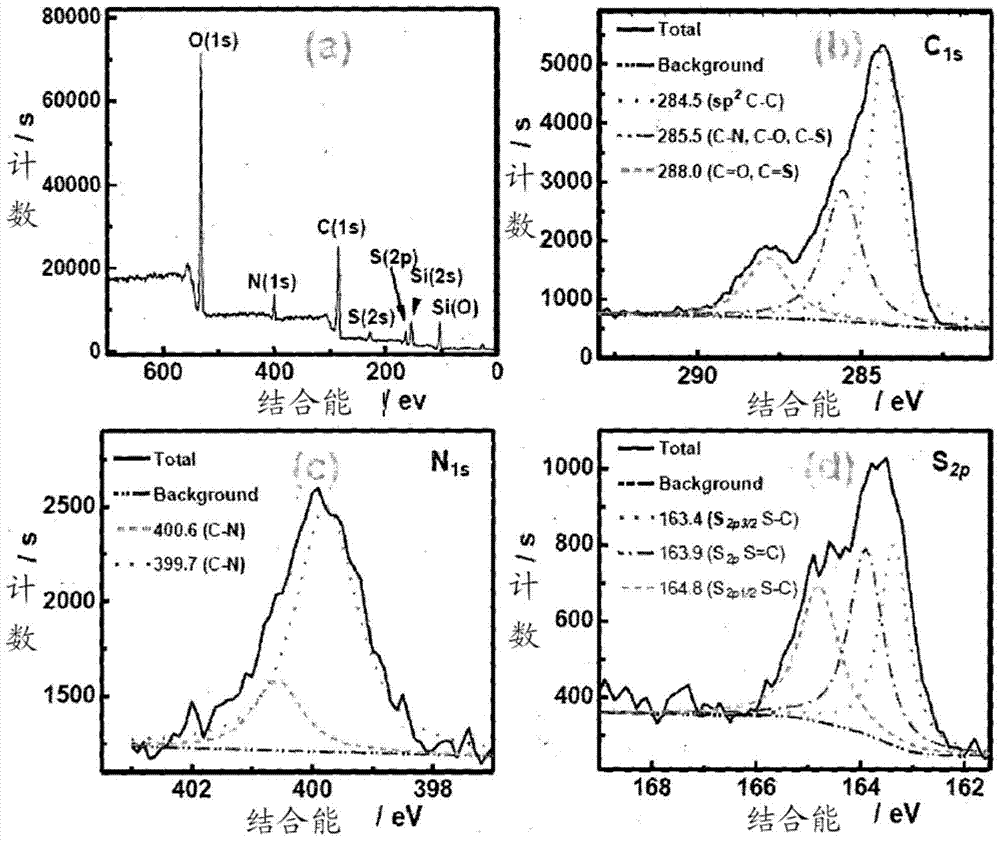
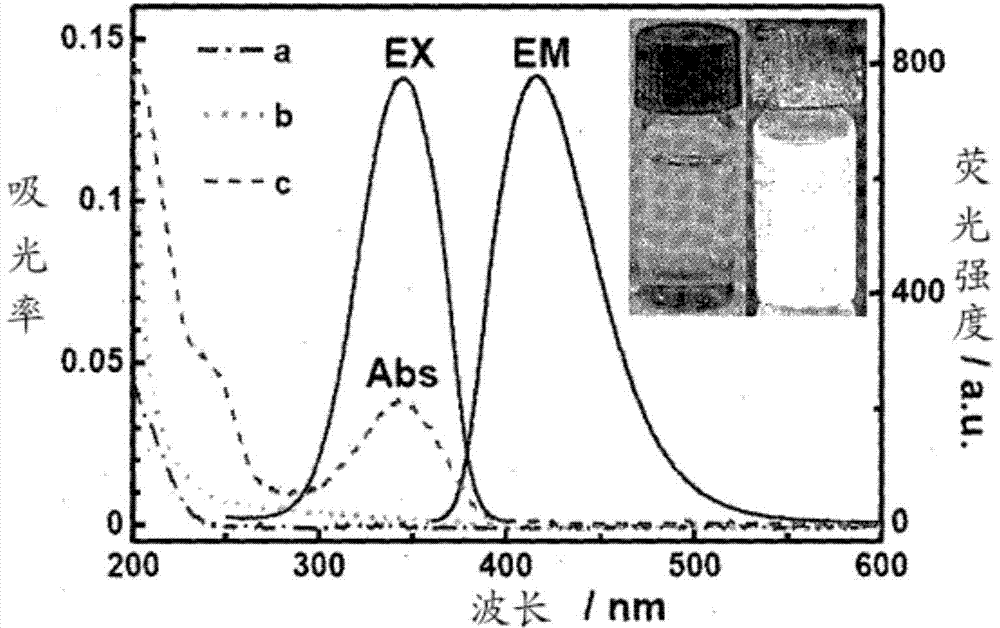
The invention relates to a method for forming graphene quantum dots, and in particular, to doped graphene quantum dots. The graphene quantum dots are co-doped with nitrogen and sulfur. The co-doped elements introduce a new type and high density of surface state of graphene quantum dots, leading to high yield and excitation-independent emission.
Owner:BEIJING XINNA INT NEW MATERIALS TECH CO LTD
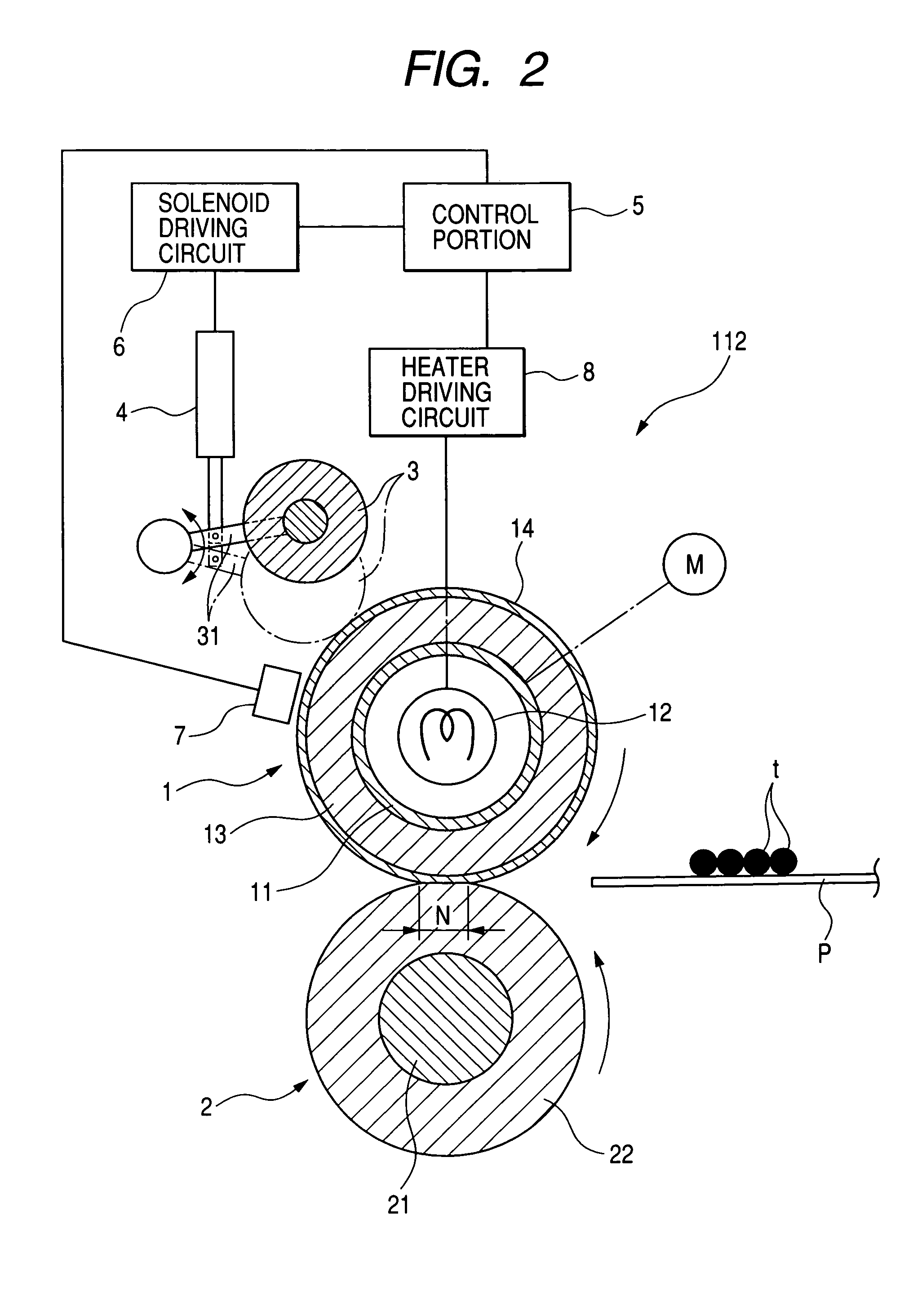
Image fixing apparatus capable of changing surface condition of fixing rotary member and fixing rotary member for use therein
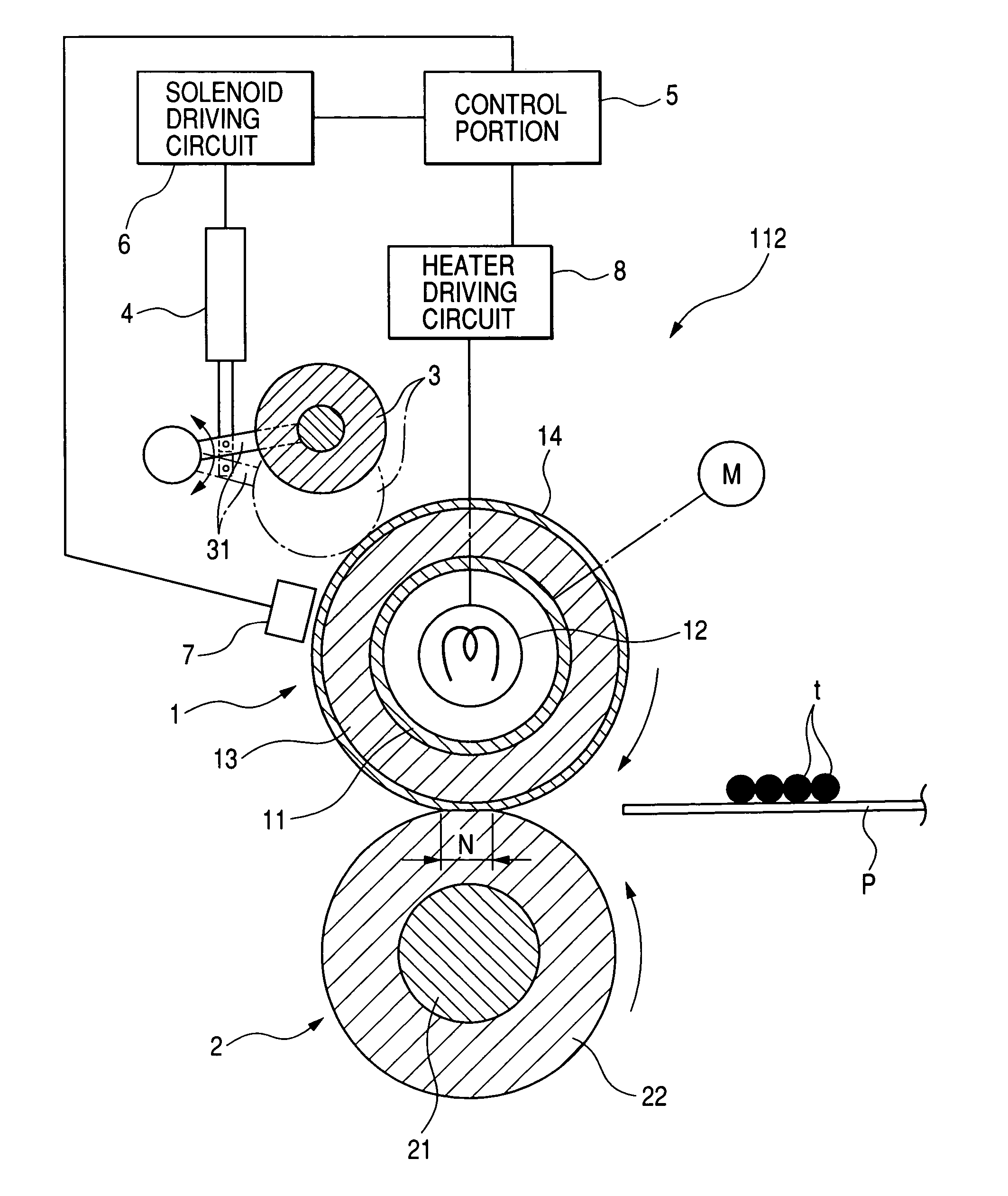
The present invention provides a fixing apparatus including a rotatable member, a heater for heating the rotatable member, and control means which controls a heat generation of the heater, wherein a toner image on a recording material is heated by the rotatable member, the apparatus has a surface condition changing mode for changing a surface condition of the rotatable member, and, when the surface condition changing mode is selected, the control means controls the heat generation of the heater in such a manner that a surface temperature of the rotatable member becomes equal to or higher than a melting temperature of a surface layer of the rotatable member.
Owner:CANON KK
Large-area nanoenabled macroelectronic substrates and uses therefor
InactiveUS20060151820A1Reduce and entirely eliminate scatteringHigh carrier mobilityTransistorNanoinformaticsNanowireElectron scattering
Owner:NANOSYS INC
Process and equipment for bonding by molecular adhesion
ActiveUS20070119812A1Rectify disadvantageImprove bindingDecorative surface effectsSolid-state devicesSurface statesClose contact
The invention relates to a process for bonding by molecular adhesion of two substrates to one another during which the surfaces of the substrates are placed in close contact and bonding occurs by propagation of a bonding front between the substrates. The invention includes, prior to bonding, a step of modifying the surface state of one or both of the surfaces of the substrates so as to regulate the propagation speed of the bonding front. The surface can be modified by locally or uniformly heating or roughening the surface(s) of the substrate(s).
Owner:S O I TEC SILICON ON INSULATOR THECHNOLOGIES
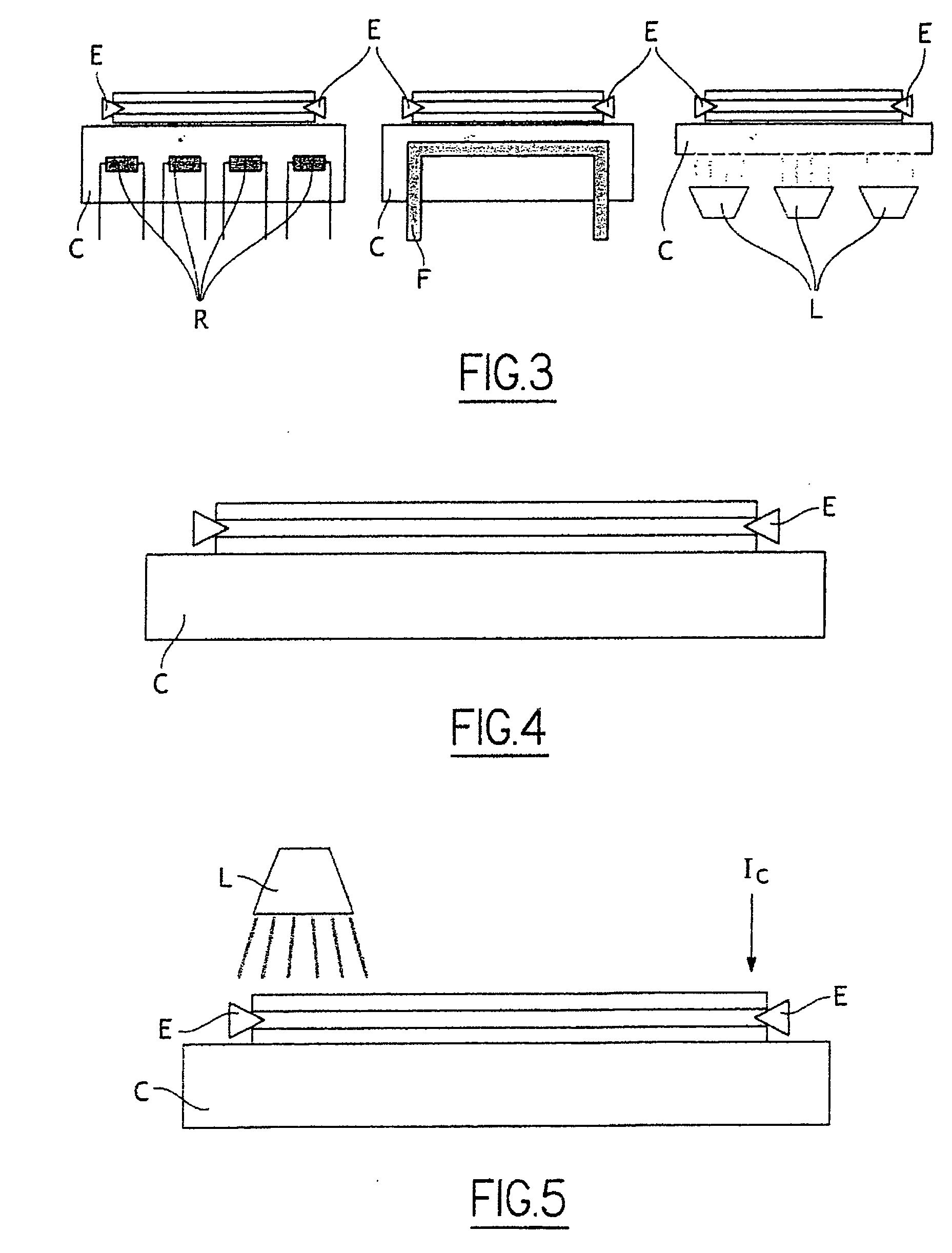
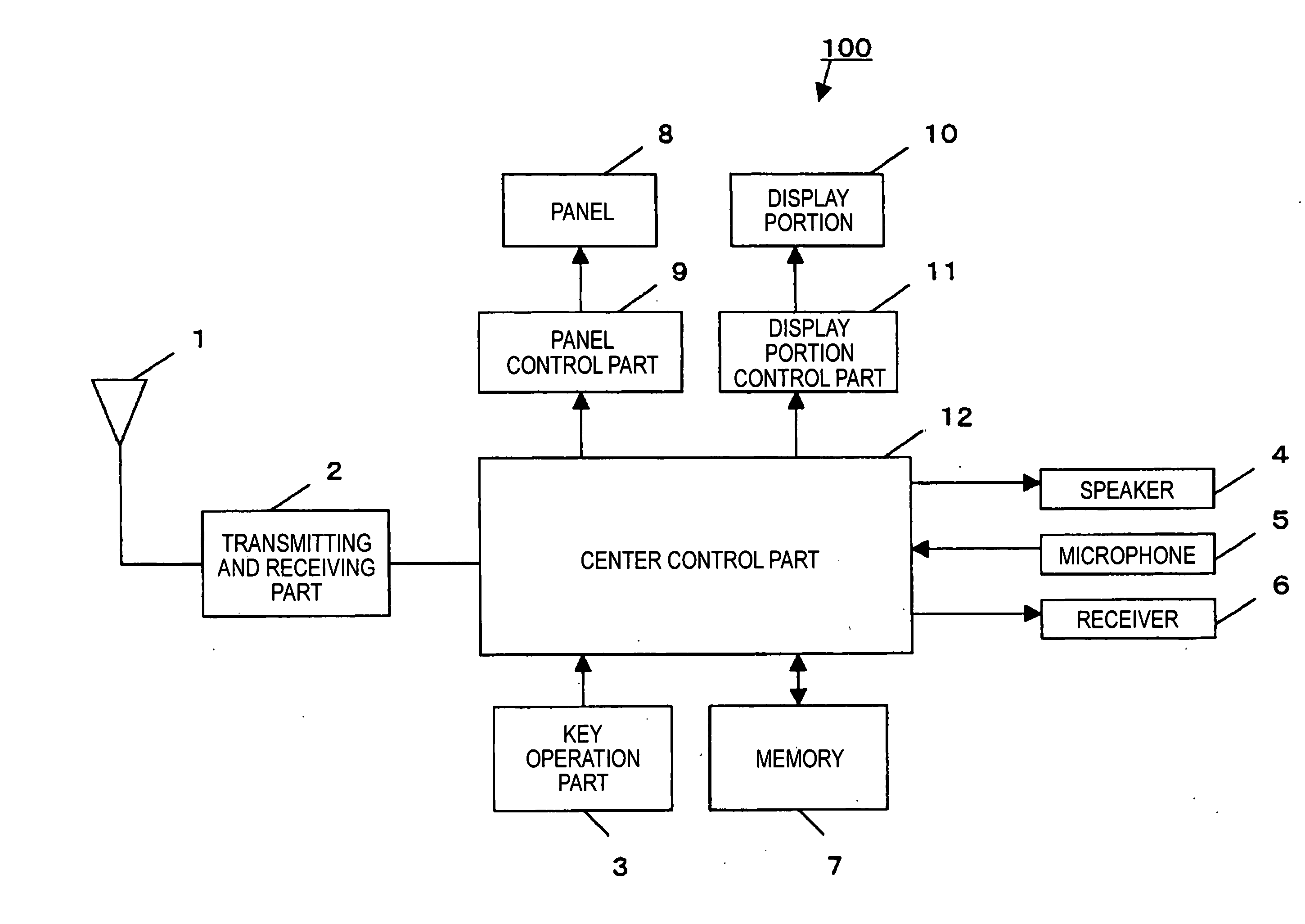
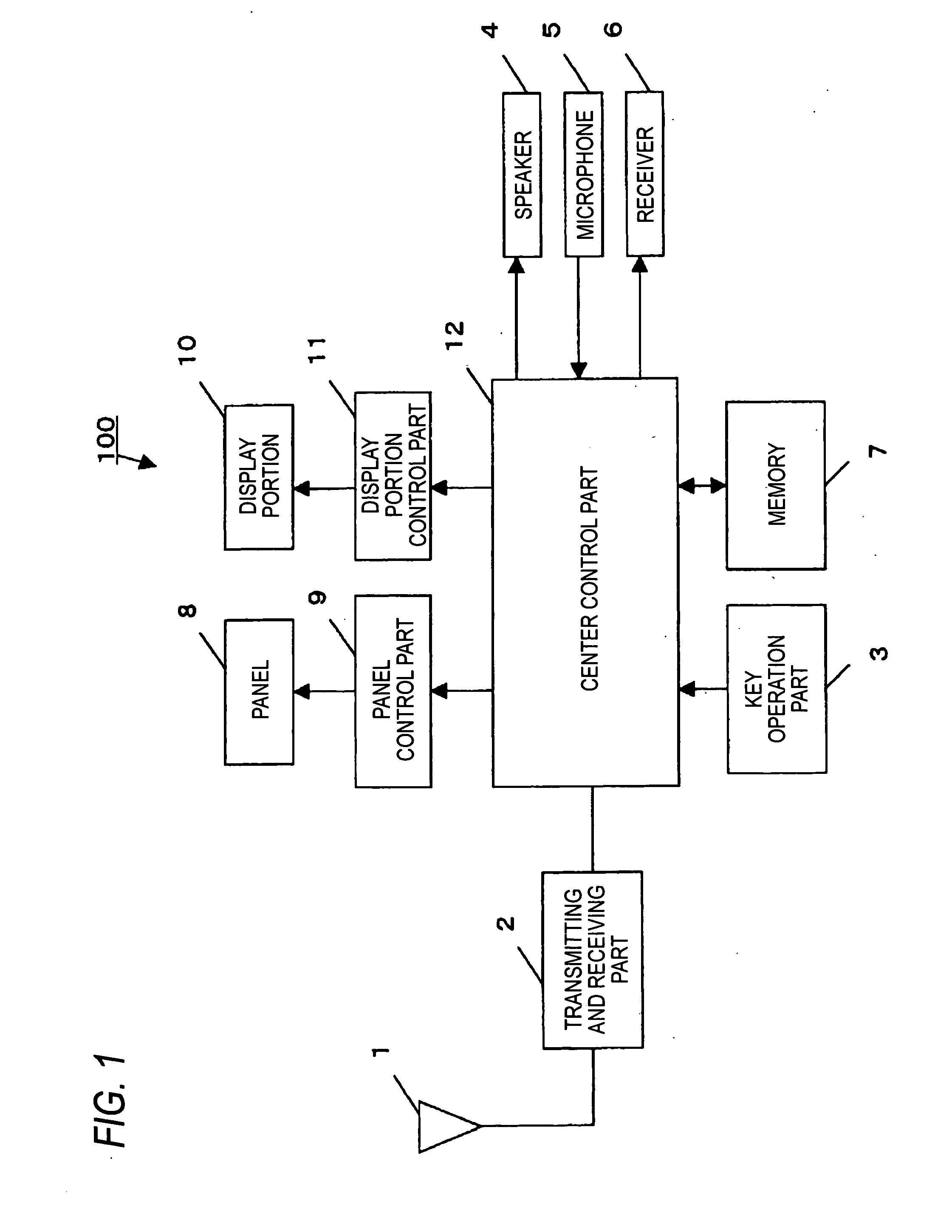
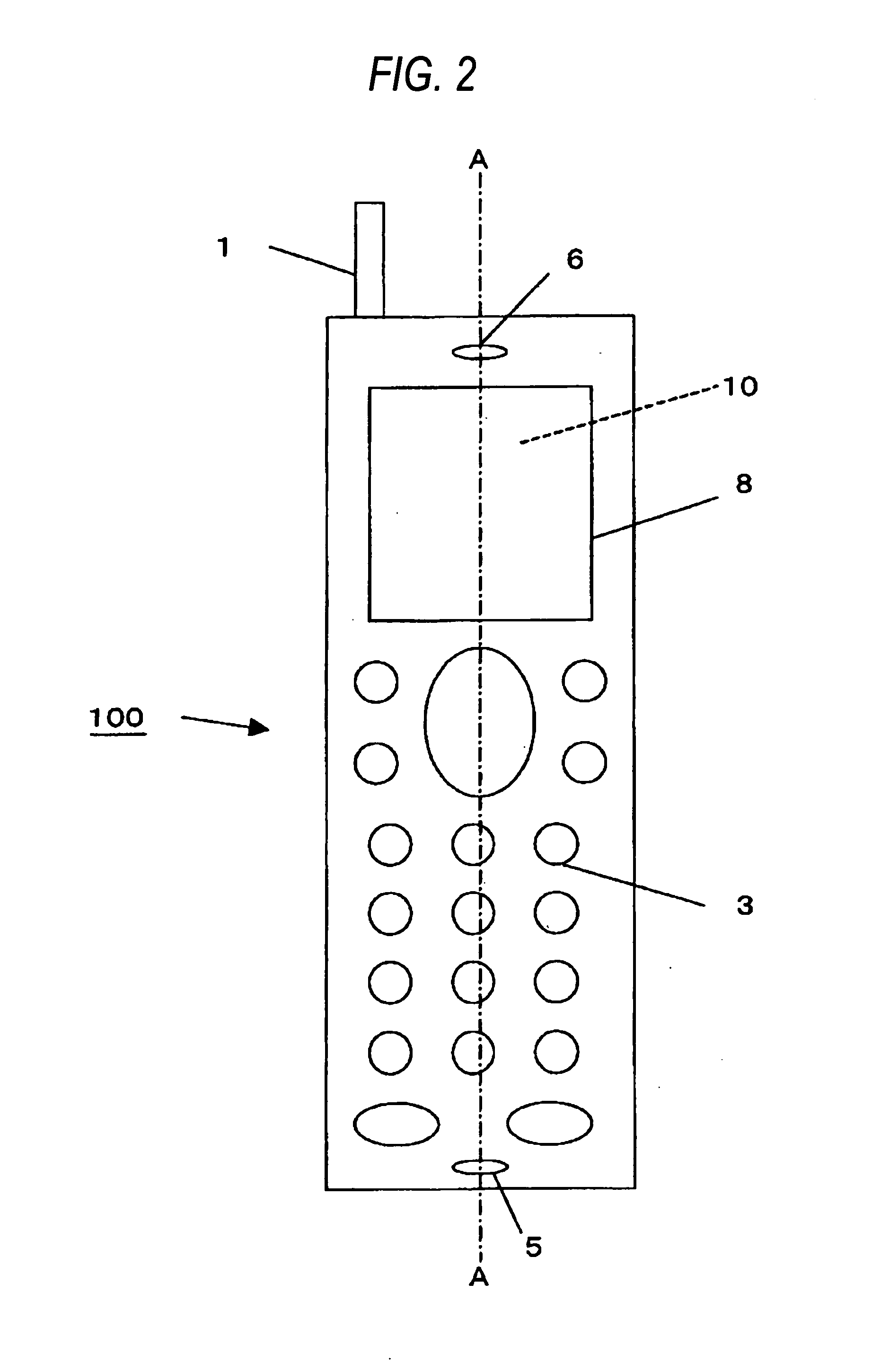
Telephone apparatus
InactiveUS20060105814A1Reduce power consumptionReduce consumptionPower managementEnergy efficient ICTEngineeringElectric power
It is an object of the present invention to provide a portable telephone in which a display portion can be used as a mirror and electric power can be saved under a key locked state. In the telephone according to the present invention, in a front surface of a display portion (10), a panel (8) that is brought into a transparent state when voltage is not applied thereto, and is brought into a mirror surface state when voltage is applied is arranged. When the telephone is set to a key locked state, the panel (8) is brought to the mirror surface state and the display of the display portion (10) is turned off. Under a specific condition that, for instance, a call is received in the key locked state, the panel (8) can be suitably brought to the transparent state and the display of the display portion (10) can be turned on. Under a key unlocked state, while any key is operated, at least the panel (8) is brought to the transparent state and the display of the display portion (10) is turned on. When the key is not operated for a prescribed time, the panel (8) is brought to the mirror surface state and the display of the display portion (10) is turned off.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Manufacturing method for positive electrode active material
ActiveUS20110031105A1Highly uniform surface conditionImprove performanceCell electrodesFinal product manufactureMicrowaveSource material
It is an object to provide a manufacturing method for a large amount of positive electrode active material with few variations, having a highly uniform surface condition, micro-size, and high performance. An aqueous solution of a compound, which becomes the source material for the positive electrode active material, is put in an airtight container and irradiated with microwaves, thus heating while water in the airtight container is evaporated and a high pressure is formed in the air tight container. A large amount of micro-sized positive electrode active material having a highly uniform surface condition can be formed. A compound, which becomes the source material for the positive electrode active material, is put in an airtight container and irradiated with microwaves, thus heating while water in the airtight container is evaporated and a high pressure is formed in the air tight container.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Graded composition gate insulators to reduce tunneling barriers in flash memory devices
InactiveUS6955968B2Reduce device erase timeLarge problemsTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricComposite insulators
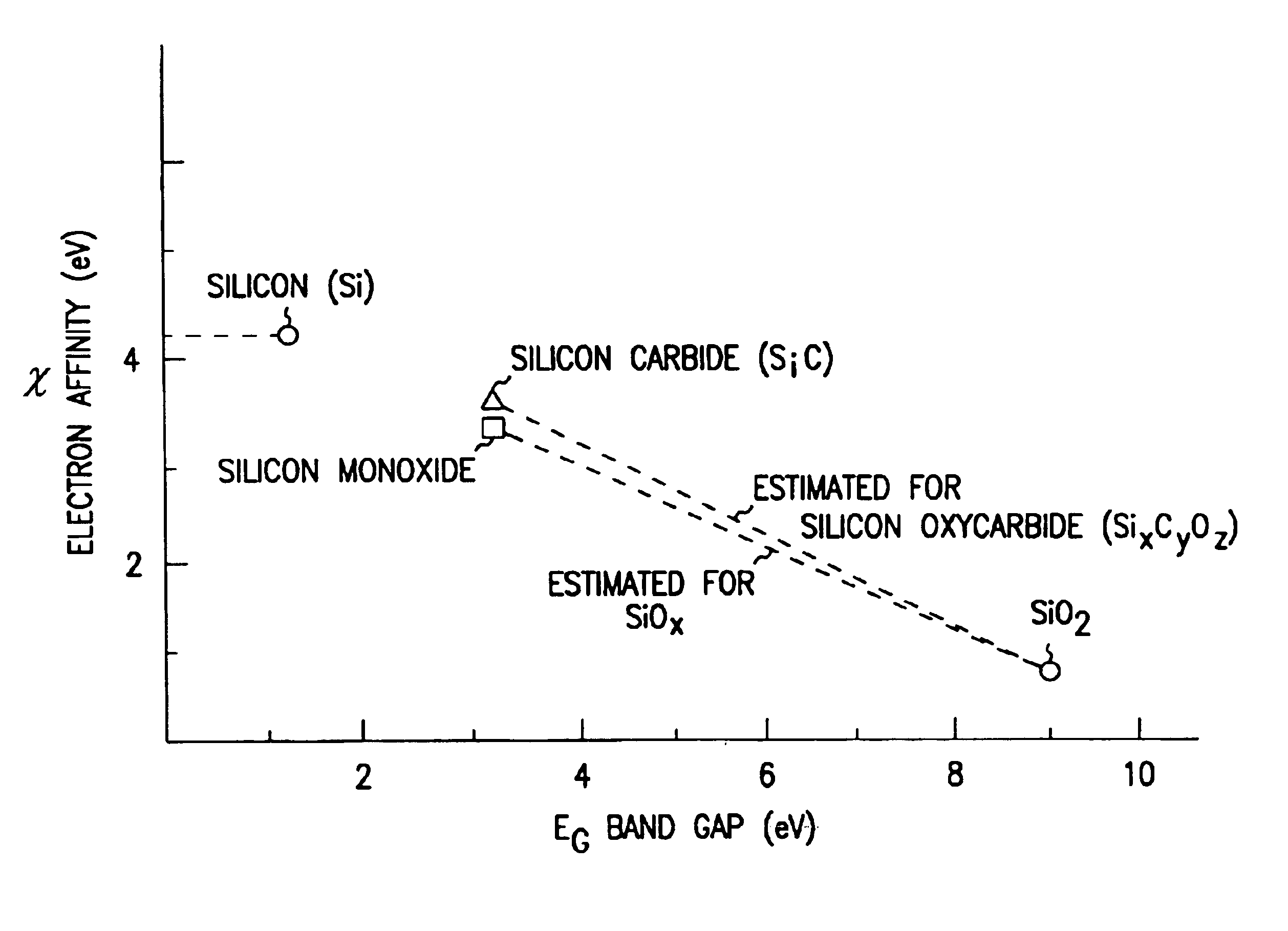
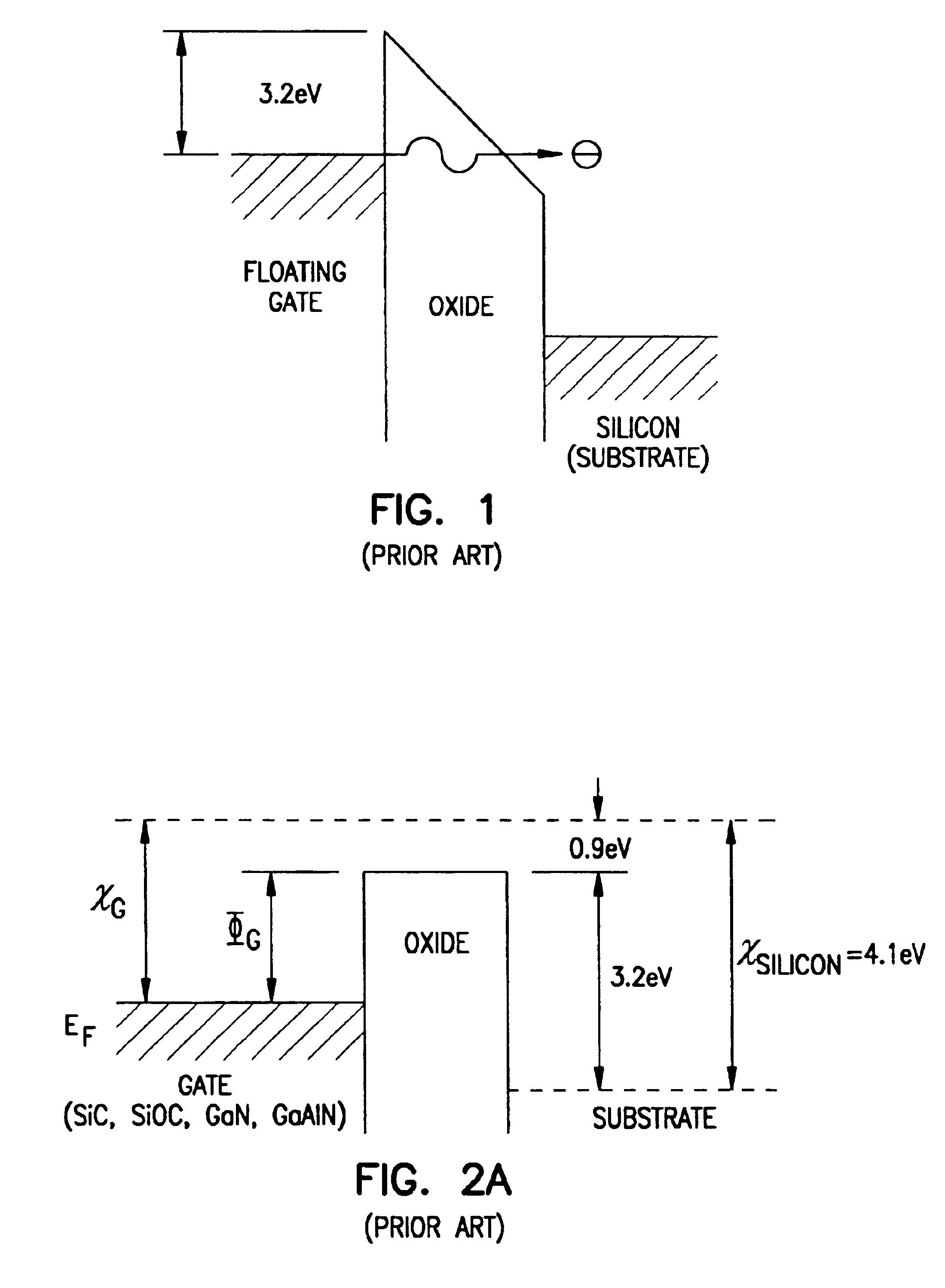
Flash memory cells are provided that include a first source / drain region and a second source / drain region separated by a channel region. A first gate opposes. A first gate insulator separates the first gate from the channel. The first gate insulator includes a graded composition gate insulator. A second gate is separated from the first gate insulator by a second gate insulator. The above memory cells produce gate insulators with less charging at the interface between composite insulator layers and provide gate insulators with low surface state densities. The memory cells substantially reduce large barrier heights or energy problems by using dielectrics having suitably, adjustably lower barrier heights in contact with the polysilicon floating gate. Such adjustable barrier heights of controlled thicknesses can be formed using a silicon suboxide and a silicon oxycarbide dielectrics prepared according to the process as described herein.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Image forming apparatus
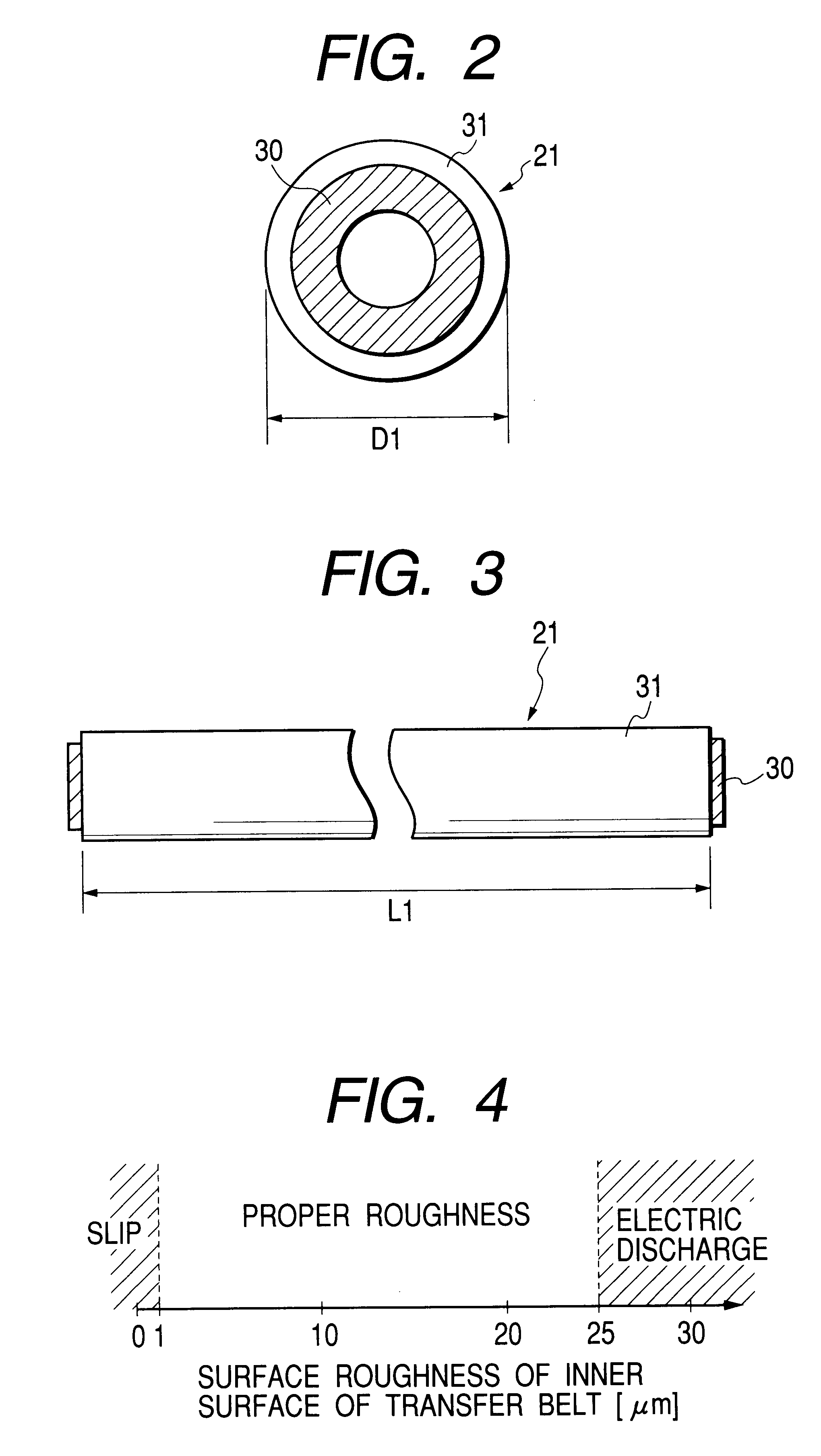
In an image forming apparatus wherein the slip of a transporting belt relative to a driving device due to a change in the surface state the inner surface of the transporting belt and a bad image can be reliably prevented, and having a photosensitive drum on the surface of which a toner image is formed, a transfer belt and a driving roller for driving the transfer belt, wherein the toner image formed on the surface of the photosensitive drum is transferred onto the transfer belt or a recording material borne on the transfer belt, an abrasive roller is provided at a position, in contact with a surface on which the driving roller abuts against the transfer belt.
Owner:CANON KK
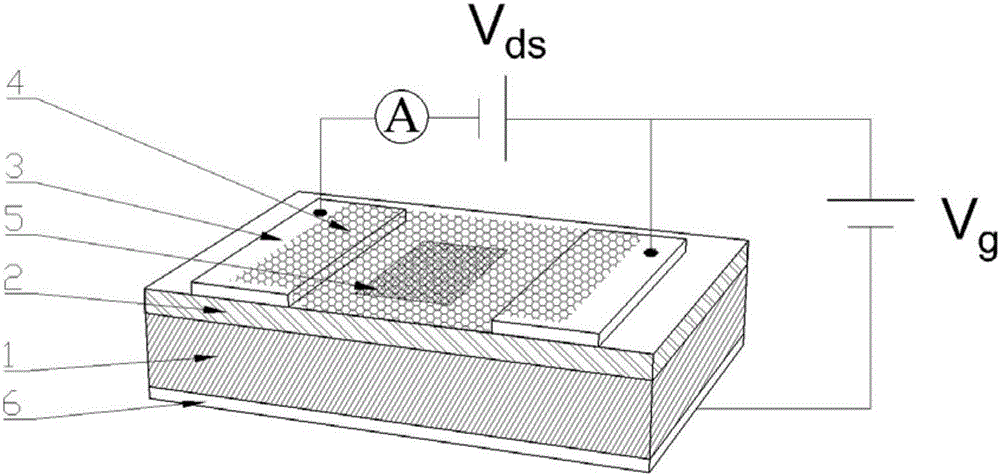
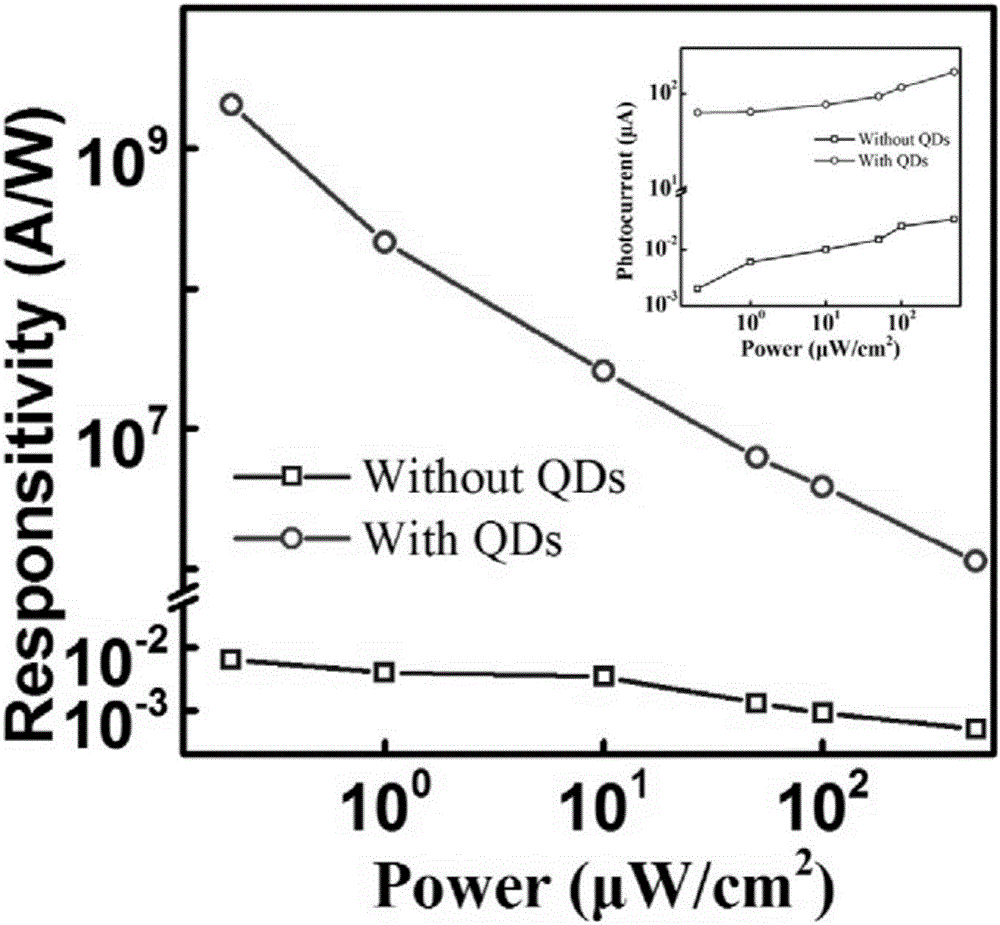
Photoconductive detector based on boron-doped silicon quantum dot/graphene/silicon dioxide and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106601857ALarge light signal currentHigh gainFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesPhotoconductive detectorP type silicon
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
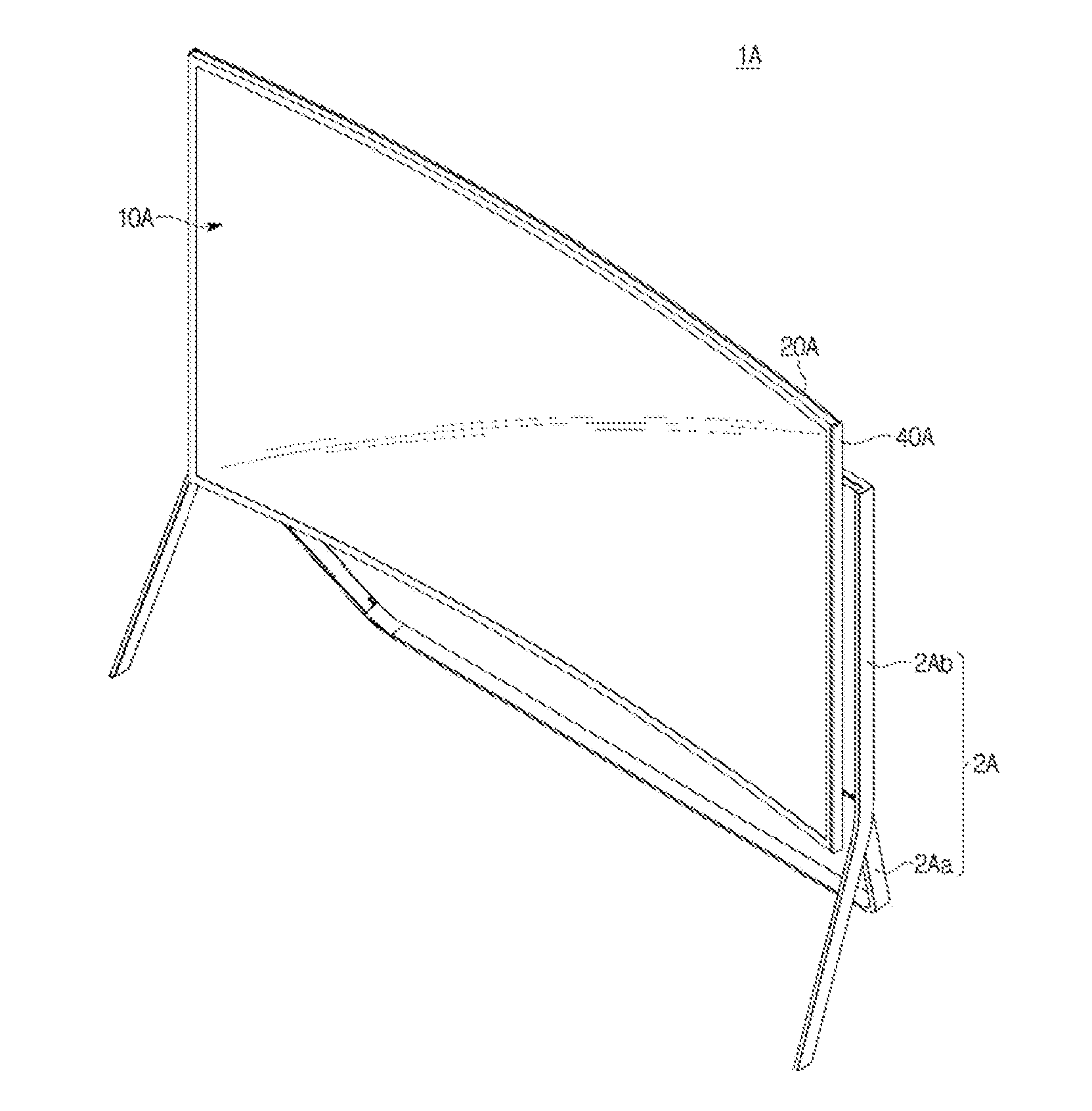
Display apparatus
ActiveUS20150192952A1Digital data processing detailsCasings with display/control unitsEngineeringSurface states
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com