Patents
Literature
82 results about "Phonon scattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Phonons can scatter through several mechanisms as they travel through the material. These scattering mechanisms are: Umklapp phonon-phonon scattering, phonon-impurity scattering, phonon-electron scattering, and phonon-boundary scattering. Each scattering mechanism can be characterised by a relaxation rate 1/τ which is the inverse of the corresponding relaxation time. All scattering processes can be taken into account using Matthiessen's rule.
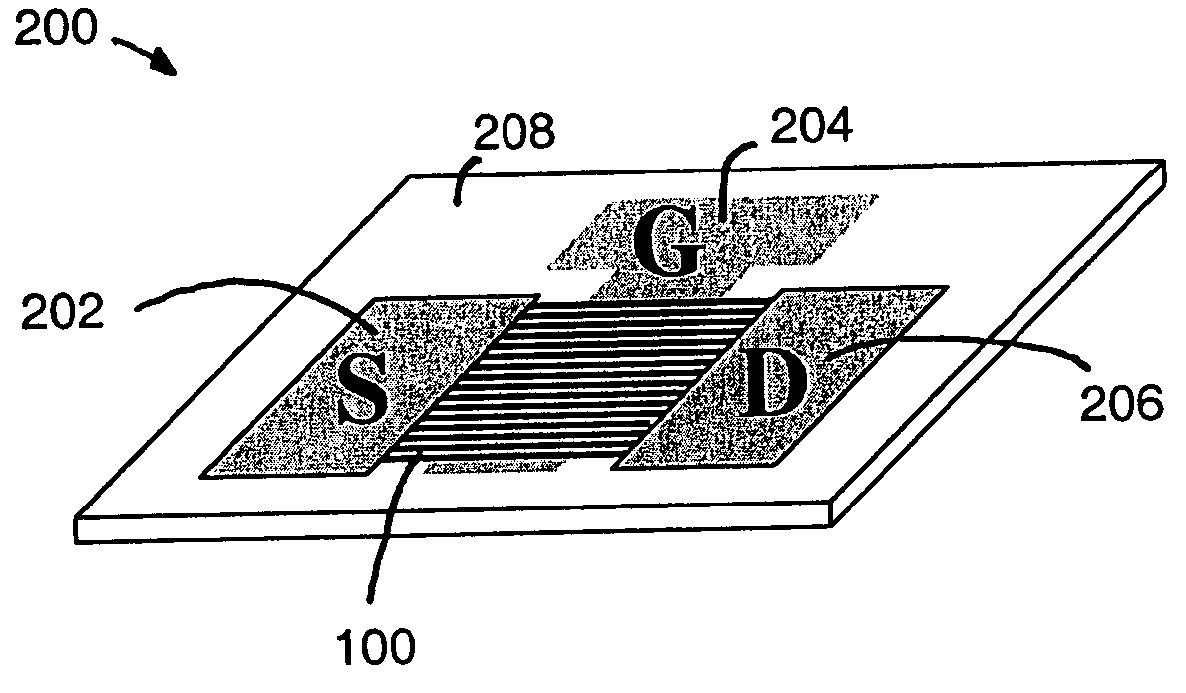
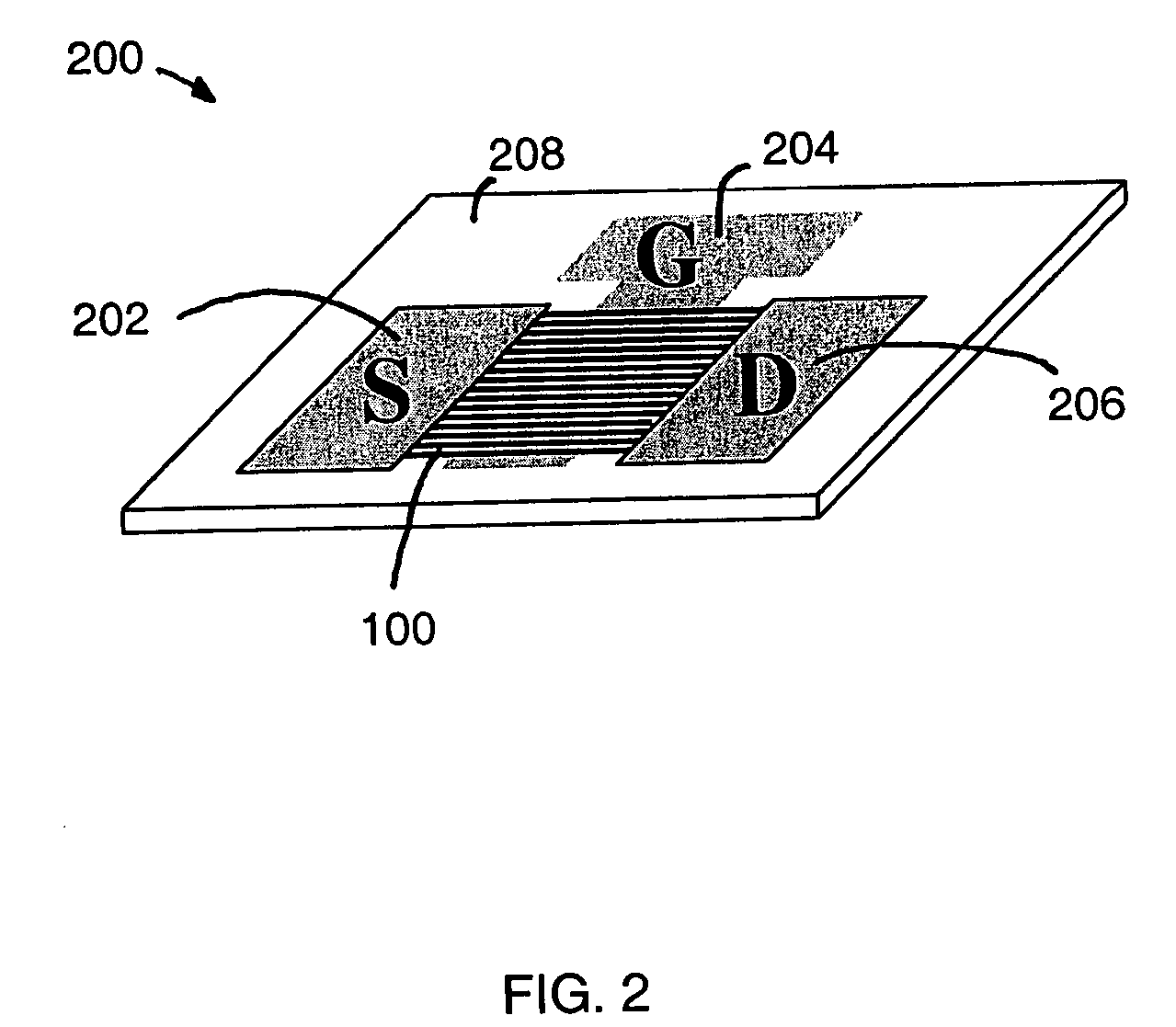
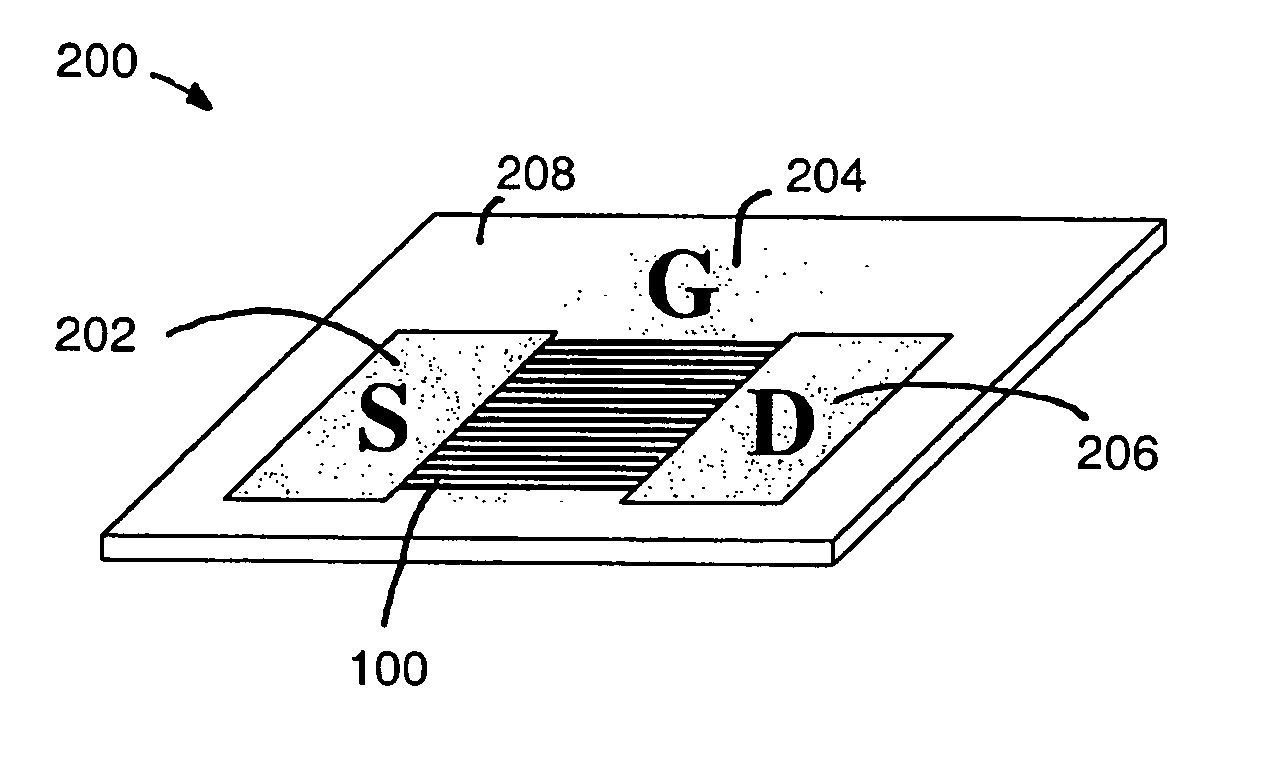
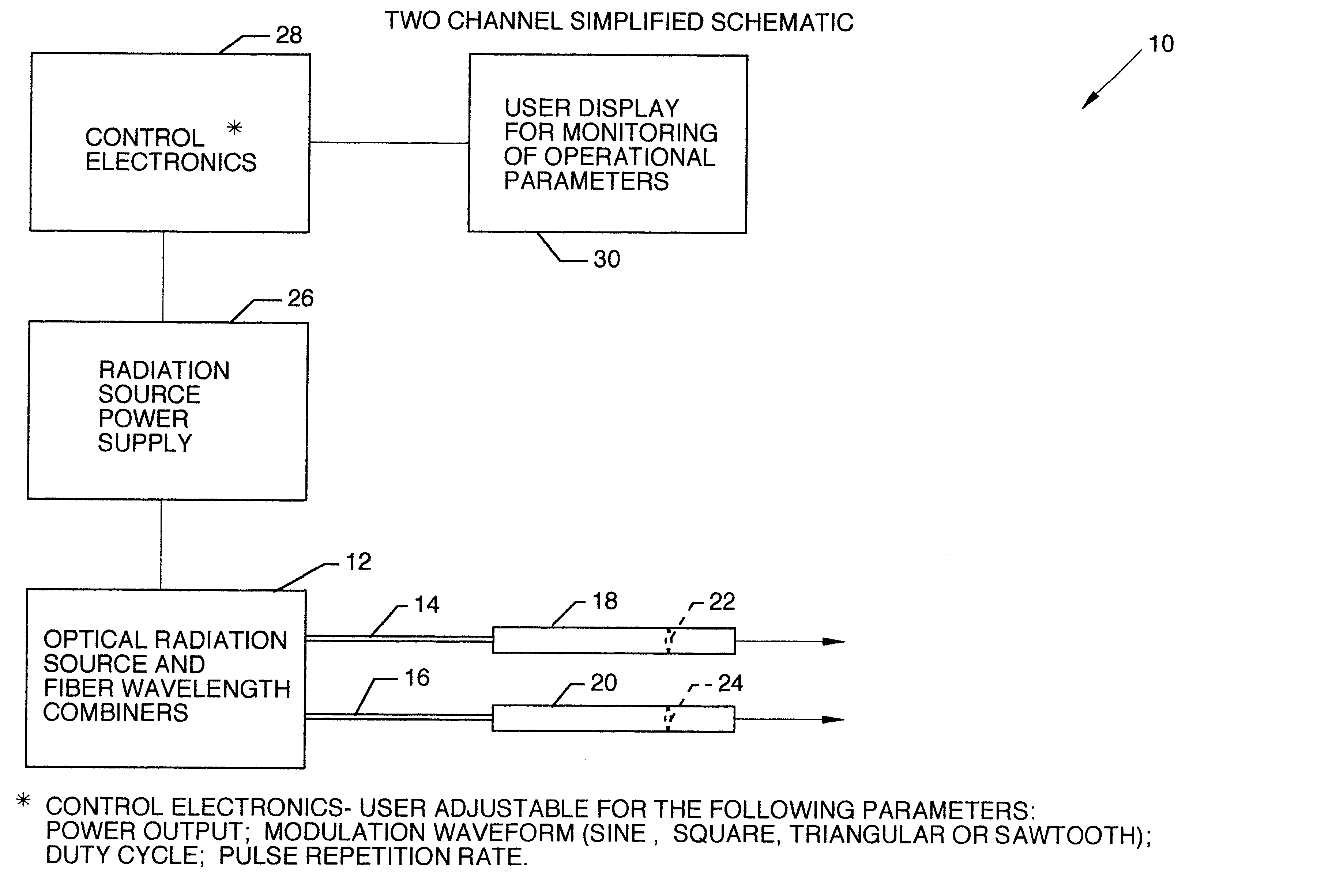
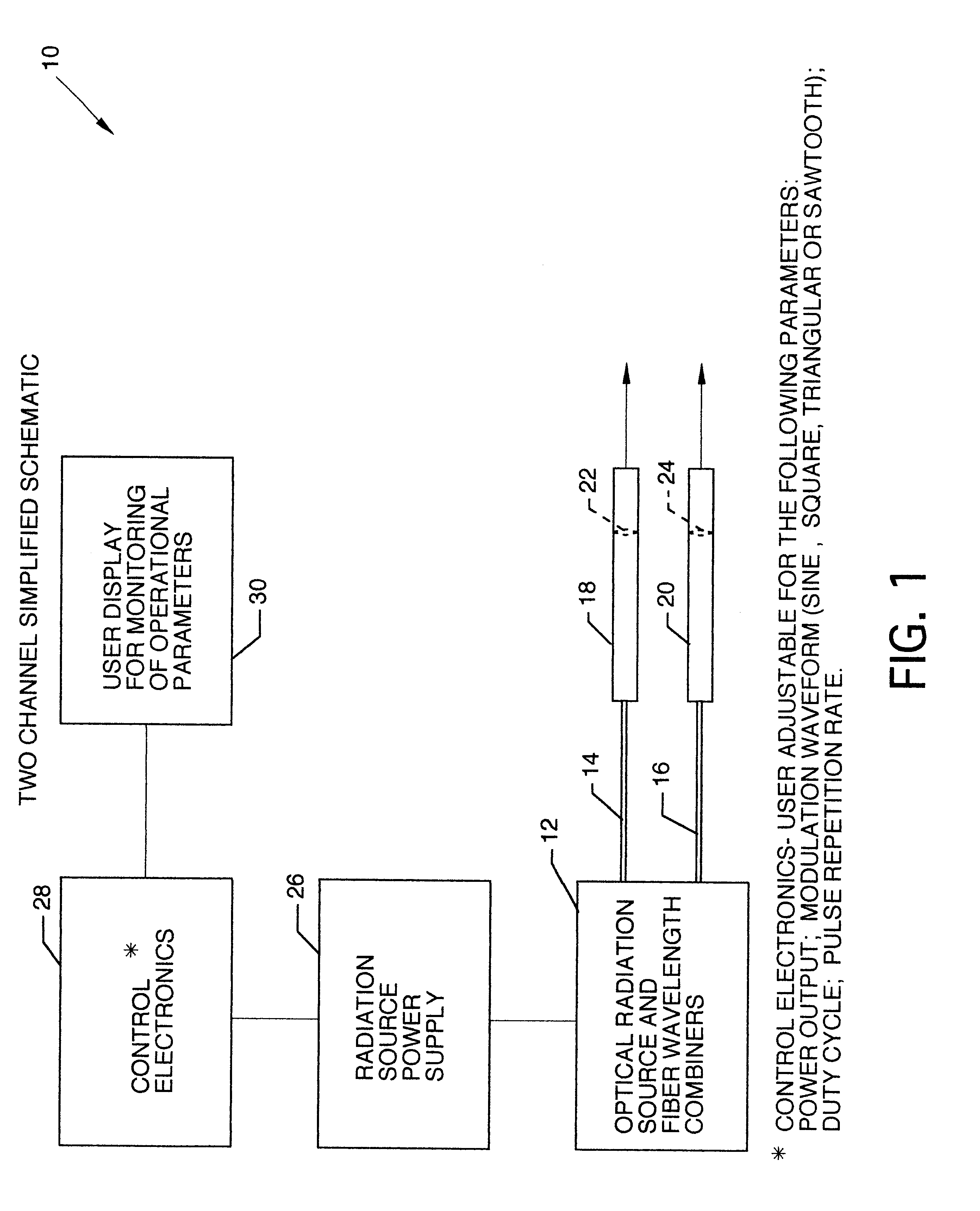
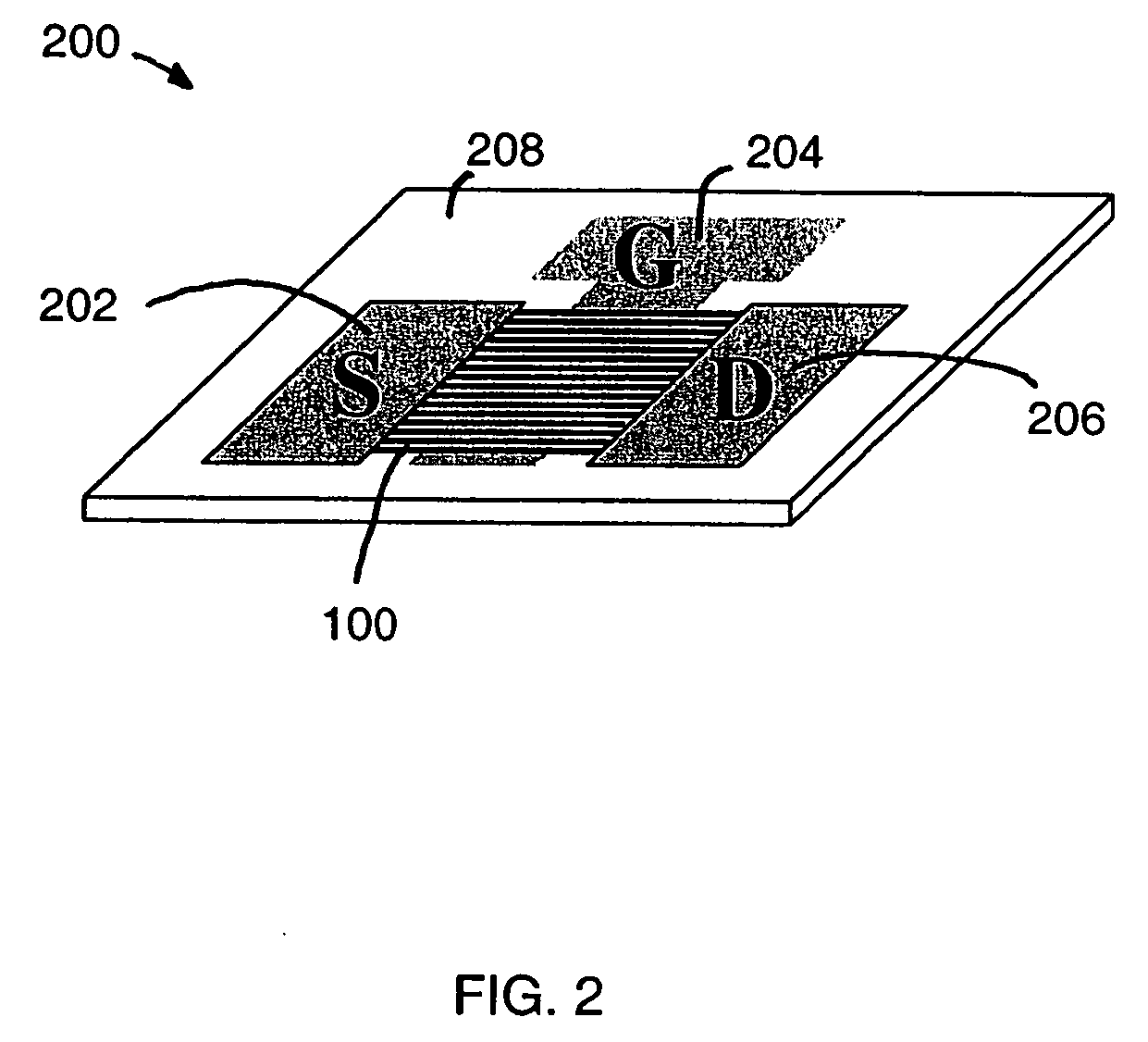
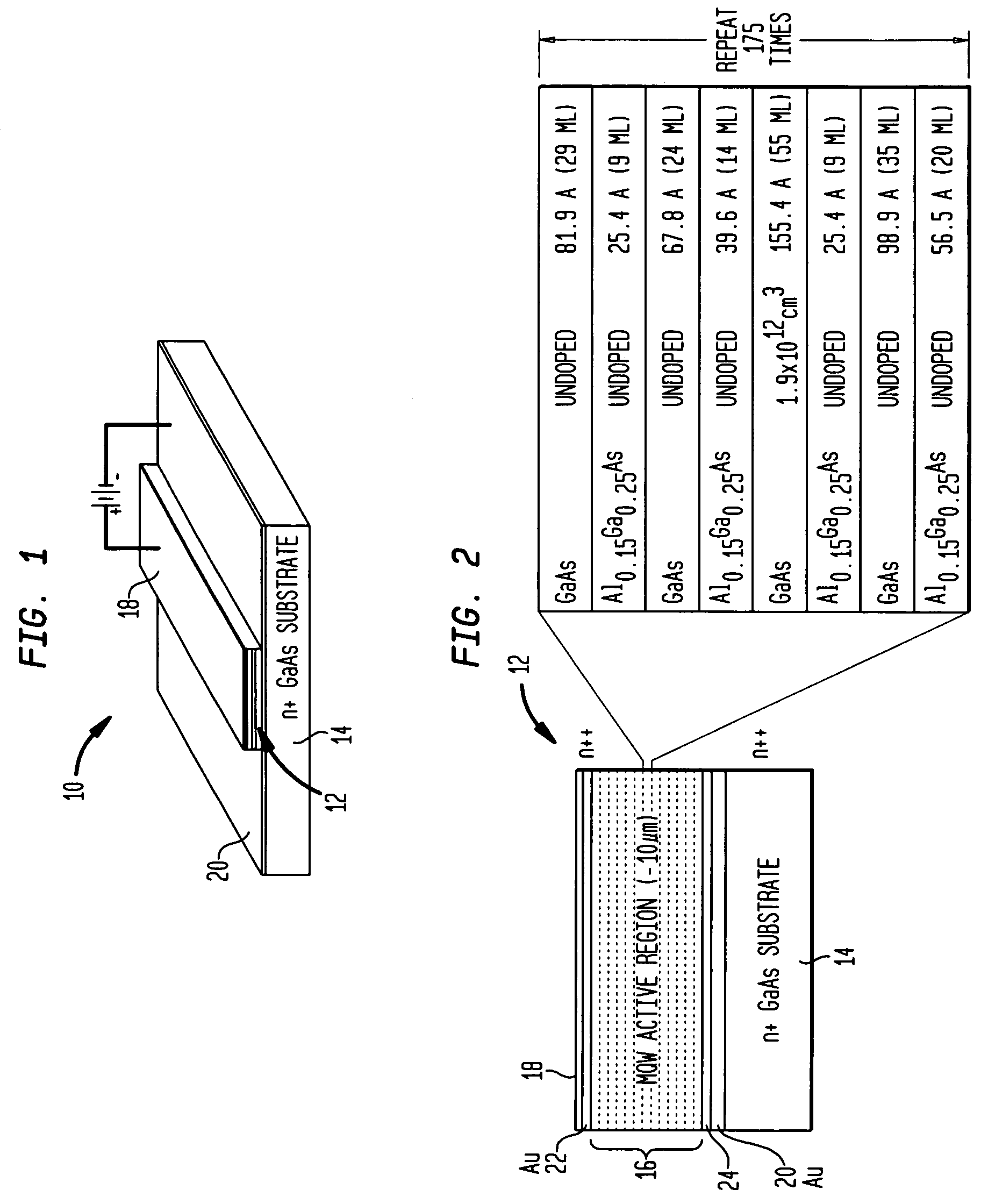
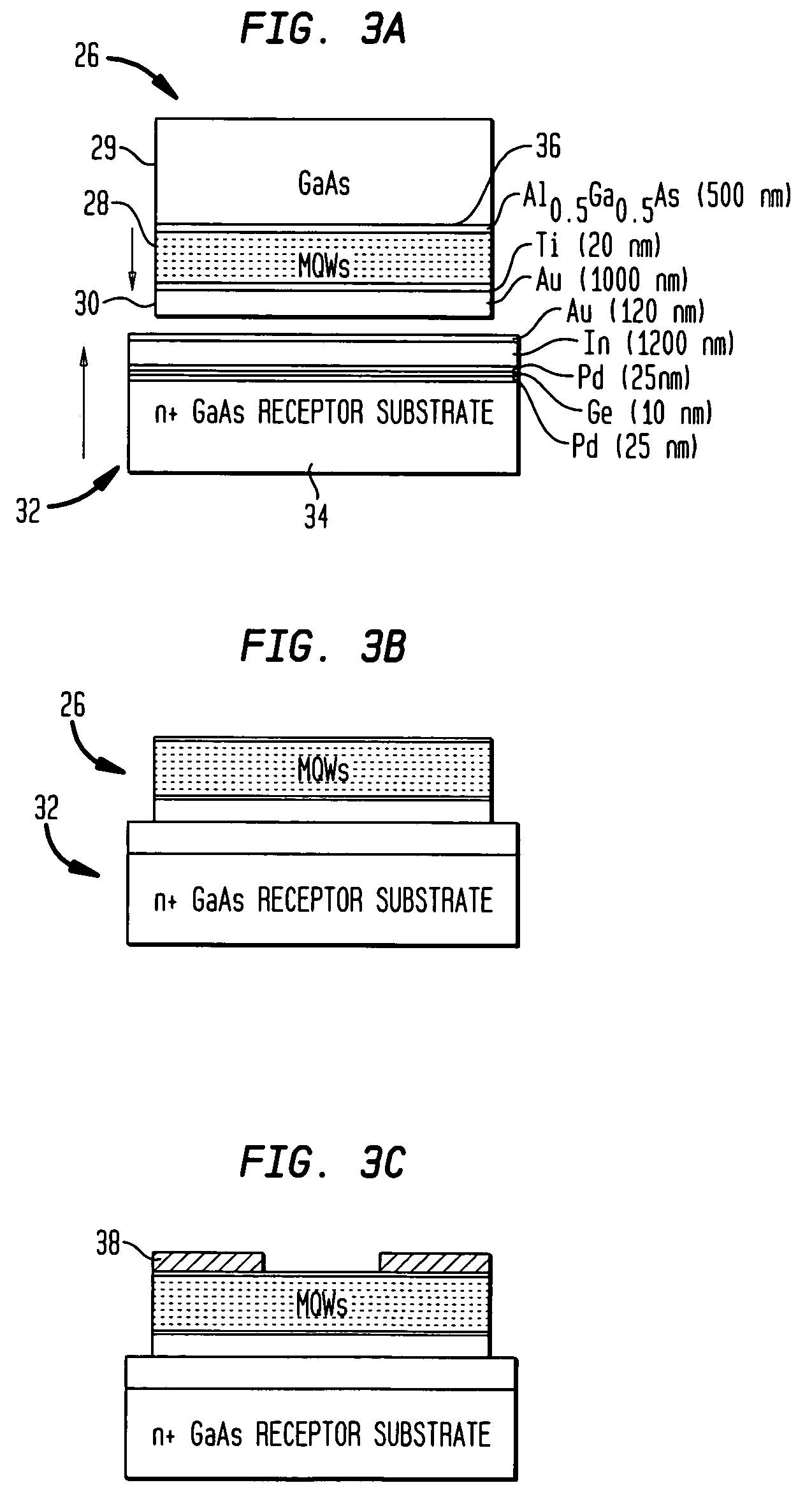
Large-area nanoenabled macroelectronic substrates and uses therefor
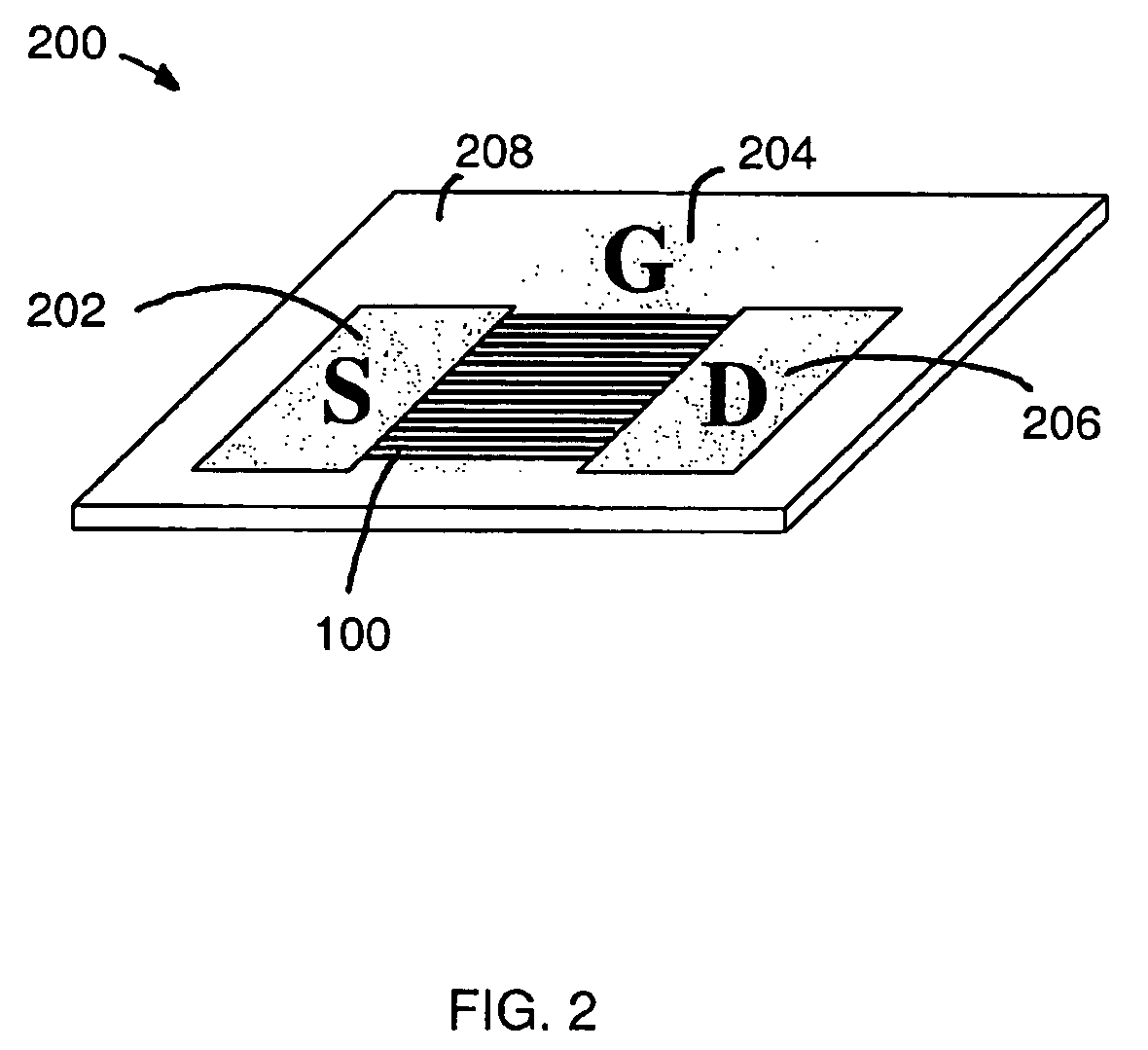
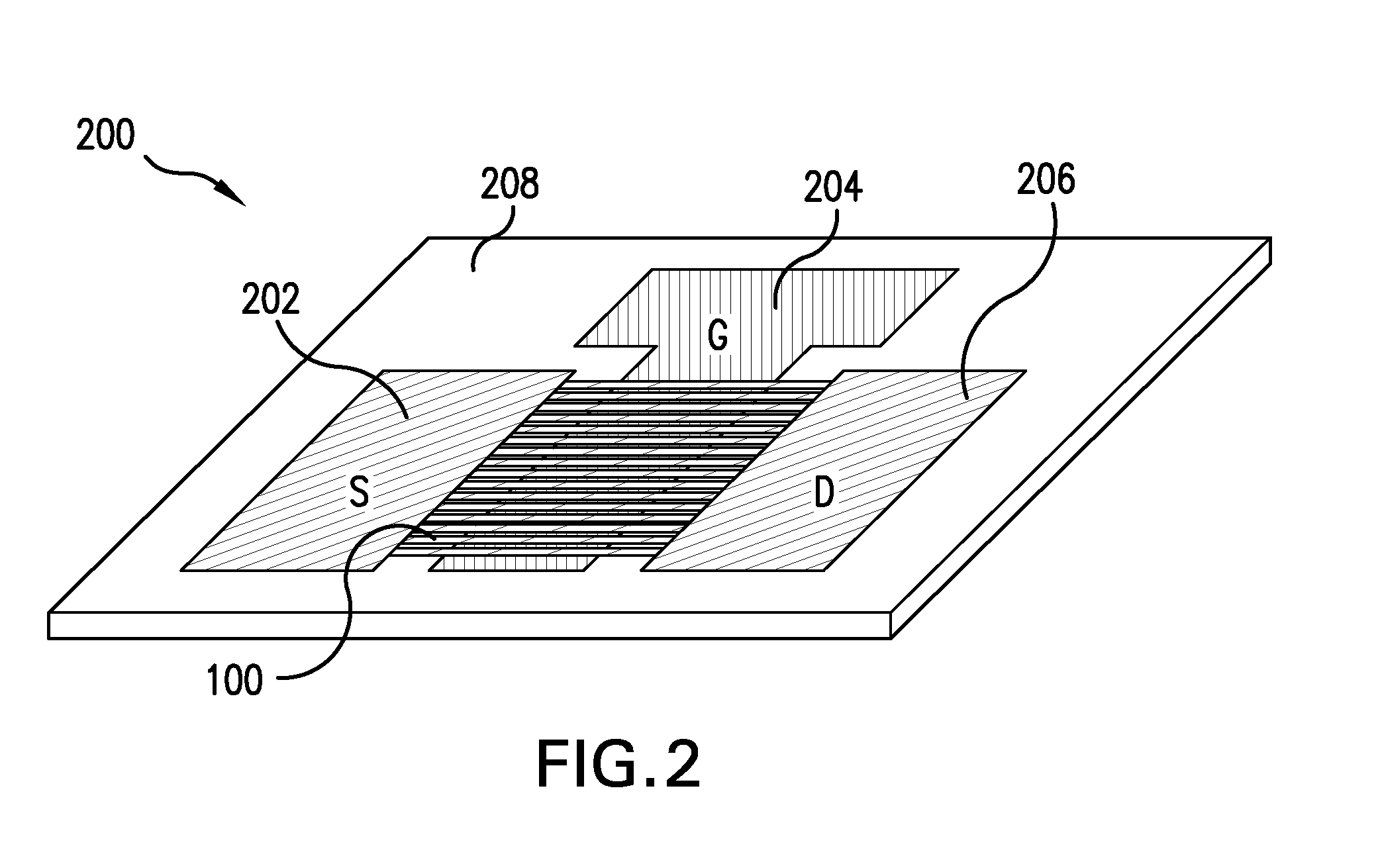
ActiveUS20050079659A1Reduce and entirely eliminate scatteringHigh carrier mobilityTransistorNanoinformaticsNanowireDevice material
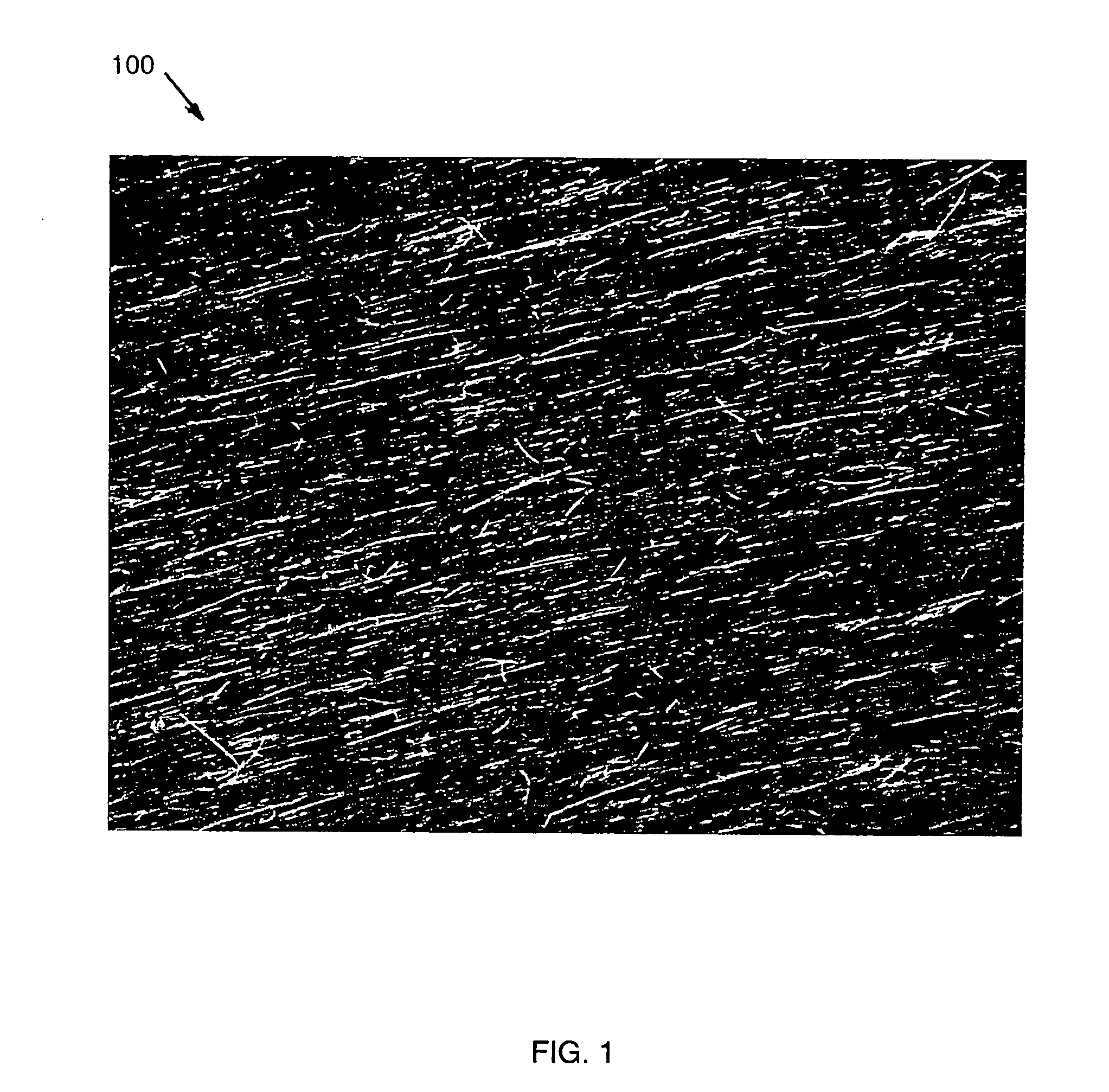
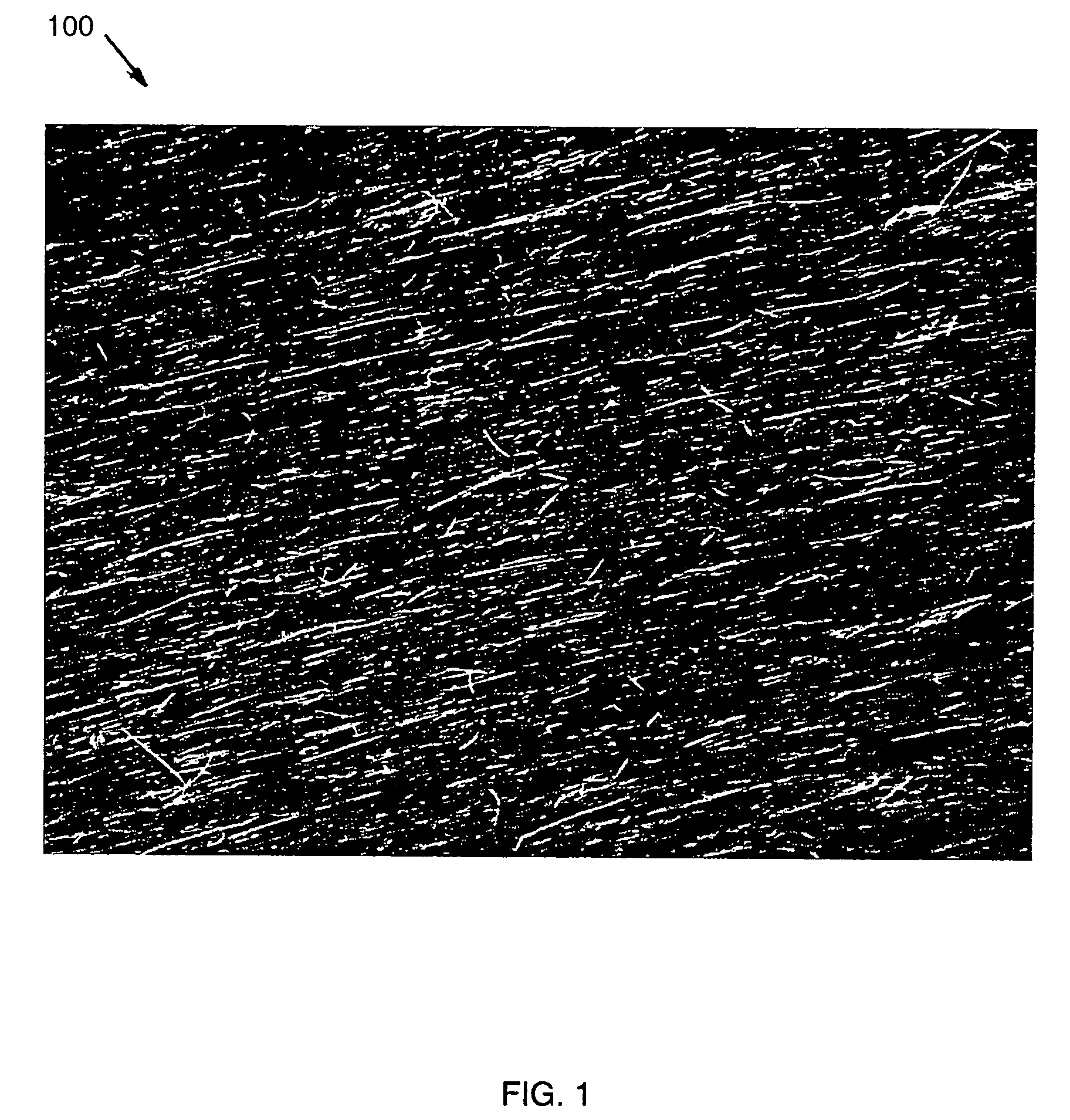
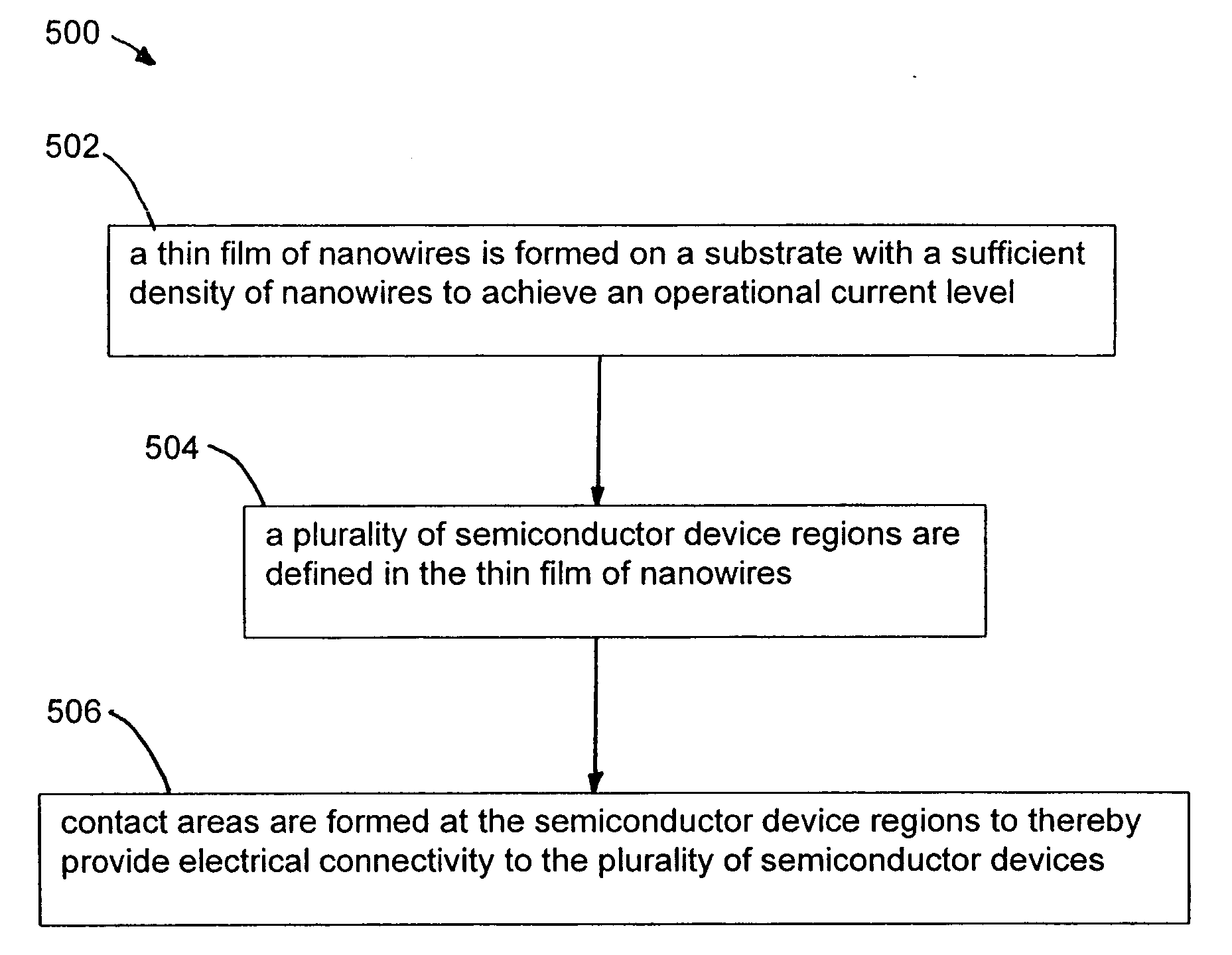
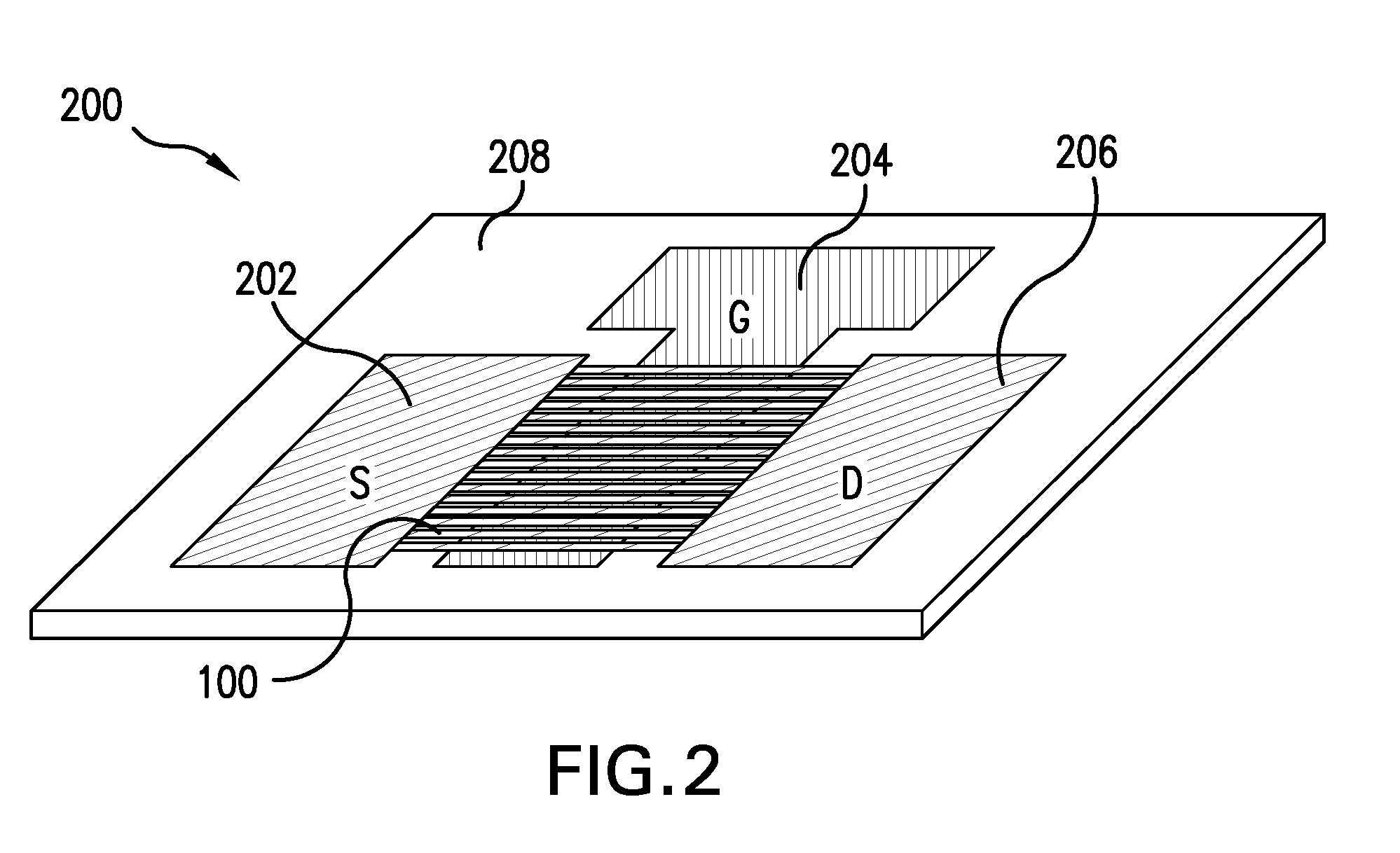
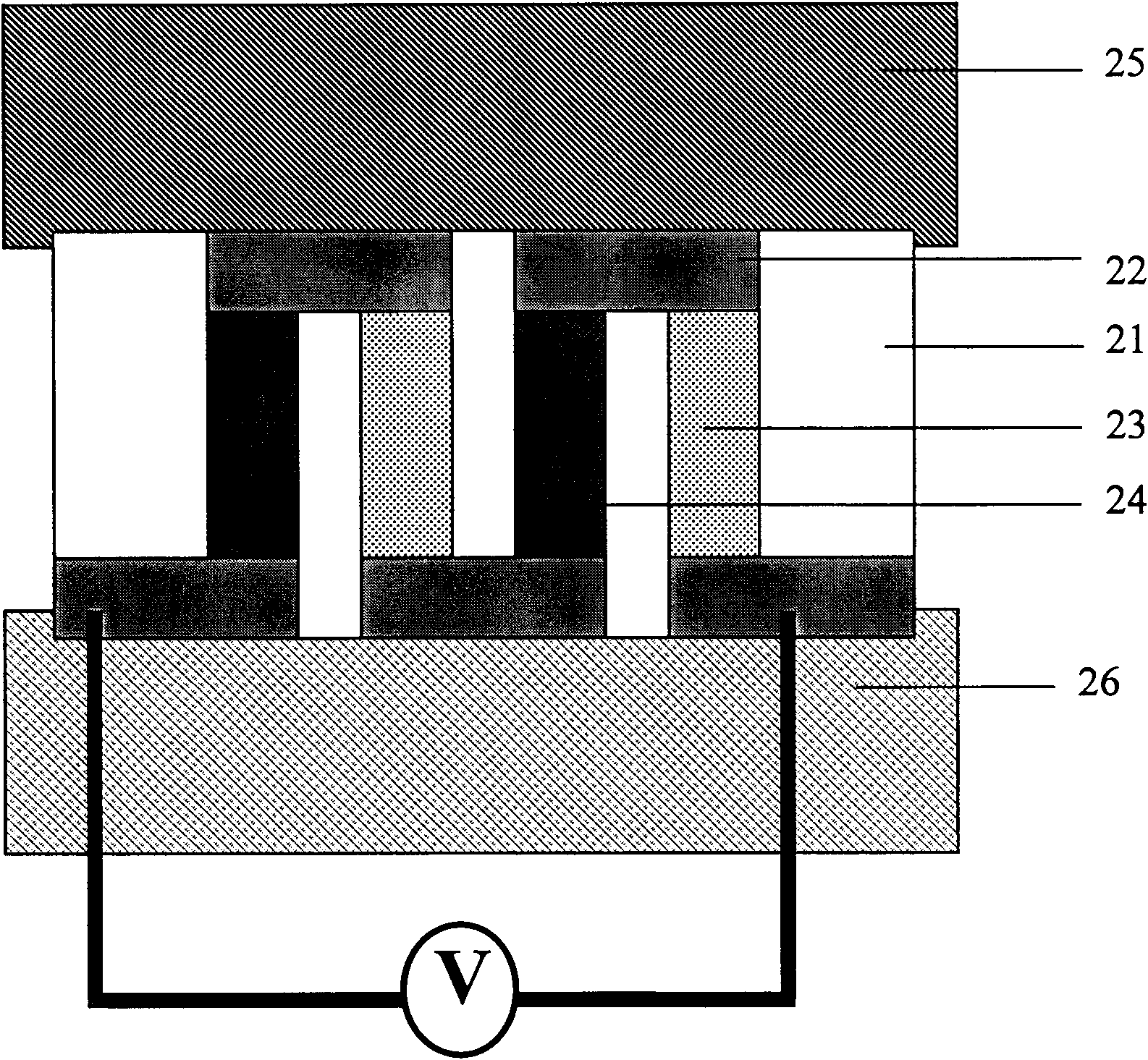
A method and apparatus for an electronic substrate having a plurality of semiconductor devices is described. A thin film of nanowires is formed on a substrate. The thin film of nanowires is formed to have a sufficient density of nanowires to achieve an operational current level. A plurality of semiconductor regions are defined in the thin film of nanowires. Contacts are formed at the semiconductor device regions to thereby provide electrical connectivity to the plurality of semiconductor devices. Furthermore, various materials for fabricating nanowires, thin films including p-doped nanowires and n-doped nanowires, nanowire heterostructures, light emitting nanowire heterostructures, flow masks for positioning nanowires on substrates, nanowire spraying techniques for depositing nanowires, techniques for reducing or eliminating phonon scattering of electrons in nanowires, and techniques for reducing surface states in nanowires are described.
Owner:ONED MATERIAL INC
Large-area nanoenabled macroelectronic substrates and uses therefor
ActiveUS20050181587A1Improve performanceHigh carrier mobilityTransistorNanoinformaticsNanowireElectron scattering
A method and apparatus for an electronic substrate having a plurality of semiconductor devices is described. A thin film of nanowires is formed on a substrate. The thin film of nanowires is formed to have a sufficient density of nanowires to achieve an operational current level. A plurality of semiconductor regions are defined in the thin film of nanowires. Contacts are formed at the semiconductor device regions to thereby provide electrical connectivity to the plurality of semiconductor devices. Furthermore, various materials for fabricating nanowires, thin films including p-doped nanowires and n-doped nanowires, nanowire heterostructures, light emitting nanowire heterostructures, flow masks for positioning nanowires on substrates, nanowire spraying techniques for depositing nanowires, techniques for reducing or eliminating phonon scattering of electrons in nanowires, and techniques for reducing surface states in nanowires are described.
Owner:ONED MATERIAL INC
Large-area nanoenabled macroelectronic substrates and uses therefor
InactiveUS7135728B2Reduce and entirely eliminate scatteringHigh carrier mobilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanowireElectron scattering
A method and apparatus for an electronic substrate having a plurality of semiconductor devices is described. A thin film of nanowires is formed on a substrate. The thin film of nanowires is formed to have a sufficient density of nanowires to achieve an operational current level. A plurality of semiconductor regions are defined in the thin film of nanowires. Contacts are formed at the semiconductor device regions to thereby provide electrical connectivity to the plurality of semiconductor devices. Furthermore, various materials for fabricating nanowires, thin films including p-doped nanowires and n-doped nanowires, nanowire heterostructures, light emitting nanowire heterostructures, flow masks for positioning nanowires on substrates, nanowire spraying techniques for depositing nanowires, techniques for reducing or eliminating phonon scattering of electrons in nanowires, and techniques for reducing surface states in nanowires are described.
Owner:ONED MATERIAL INC
Large-area nanoenabled macroelectronic substrates and uses therefor
InactiveUS20050110064A1Reduce and entirely eliminate scatteringHigh carrier mobilityTransistorNanoinformaticsNanowirePhonon scattering
A method and apparatus for an electronic substrate having a plurality of semiconductor devices is described. A thin film of nanowires is formed on a substrate. The thin film of nanowires is formed to have a sufficient density of nanowires to achieve an operational current level. A plurality of semiconductor regions are defined in the thin film of nanowires. Contacts are formed at the semiconductor device regions to thereby provide electrical connectivity to the plurality of semiconductor devices. Furthermore, various materials for fabricating nanowires, thin films including p-doped nanowires and n-doped nanowires, nanowire heterostructures, light emitting nanowire heterostructures, flow masks for positioning nanowires on substrates, nanowire spraying techniques for depositing nanowires, techniques for reducing or eliminating phonon scattering of electrons in nanowires, and techniques for reducing surface states in nanowires are described.
Owner:ONED MATERIAL INC
Large-area nanoenabled macroelectronic substrates and uses therefor
InactiveUS7064372B2Reduce and entirely eliminate scatteringHigh carrier mobilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanowirePhonon scattering
A method and apparatus for an electronic substrate having a plurality of semiconductor devices is described. A thin film of nanowires is formed on a substrate. The thin film of nanowires is formed to have a sufficient density of nanowires to achieve an operational current level. A plurality of semiconductor regions are defined in the thin film of nanowires. Contacts are formed at the semiconductor device regions to thereby provide electrical connectivity to the plurality of semiconductor devices. Furthermore, various materials for fabricating nanowires, thin films including p-doped nanowires and n-doped nanowires, nanowire heterostructures, light emitting nanowire heterostructures, flow masks for positioning nanowires on substrates, nanowire spraying techniques for depositing nanowires, techniques for reducing or eliminating phonon scattering of electrons in nanowires, and techniques for reducing surface states in nanowires are described.
Owner:ONED MATERIAL INC
Multifunctionally graded environmental barrier coatings for silicon-base ceramic components
InactiveUS7740960B1Low thermal conductivityIncrease flow ratePropellersReaction enginesCombustionWater vapor
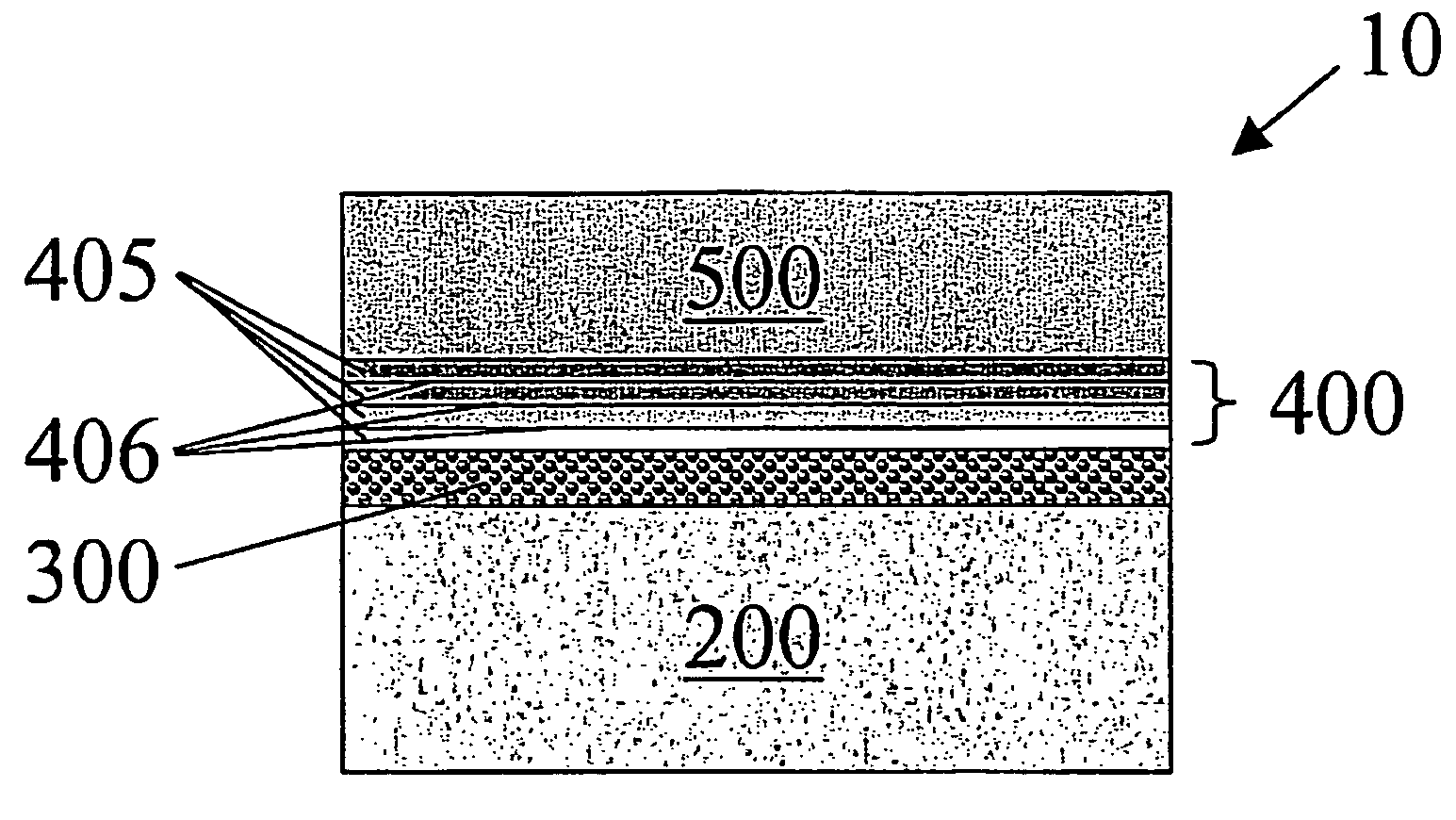
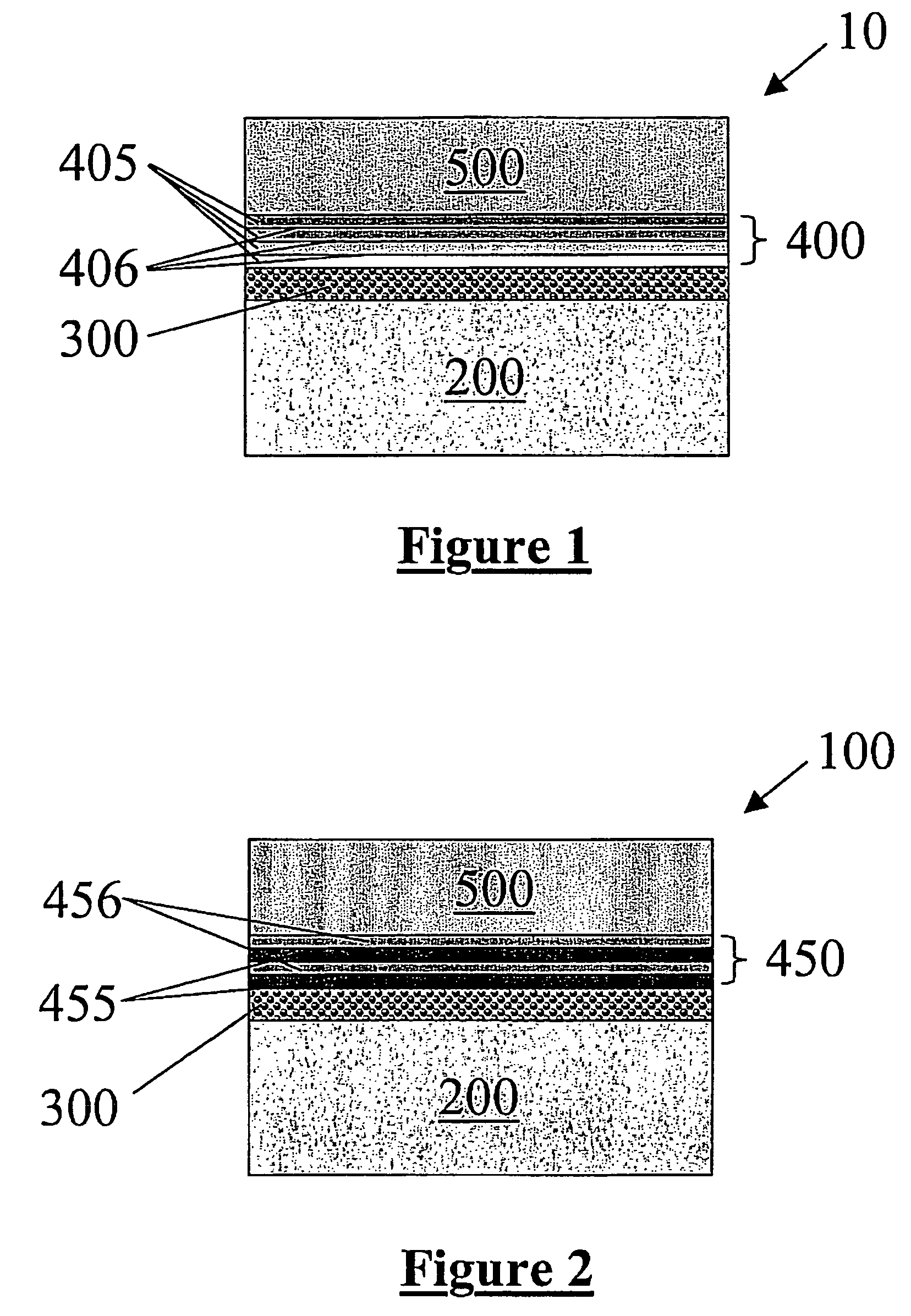
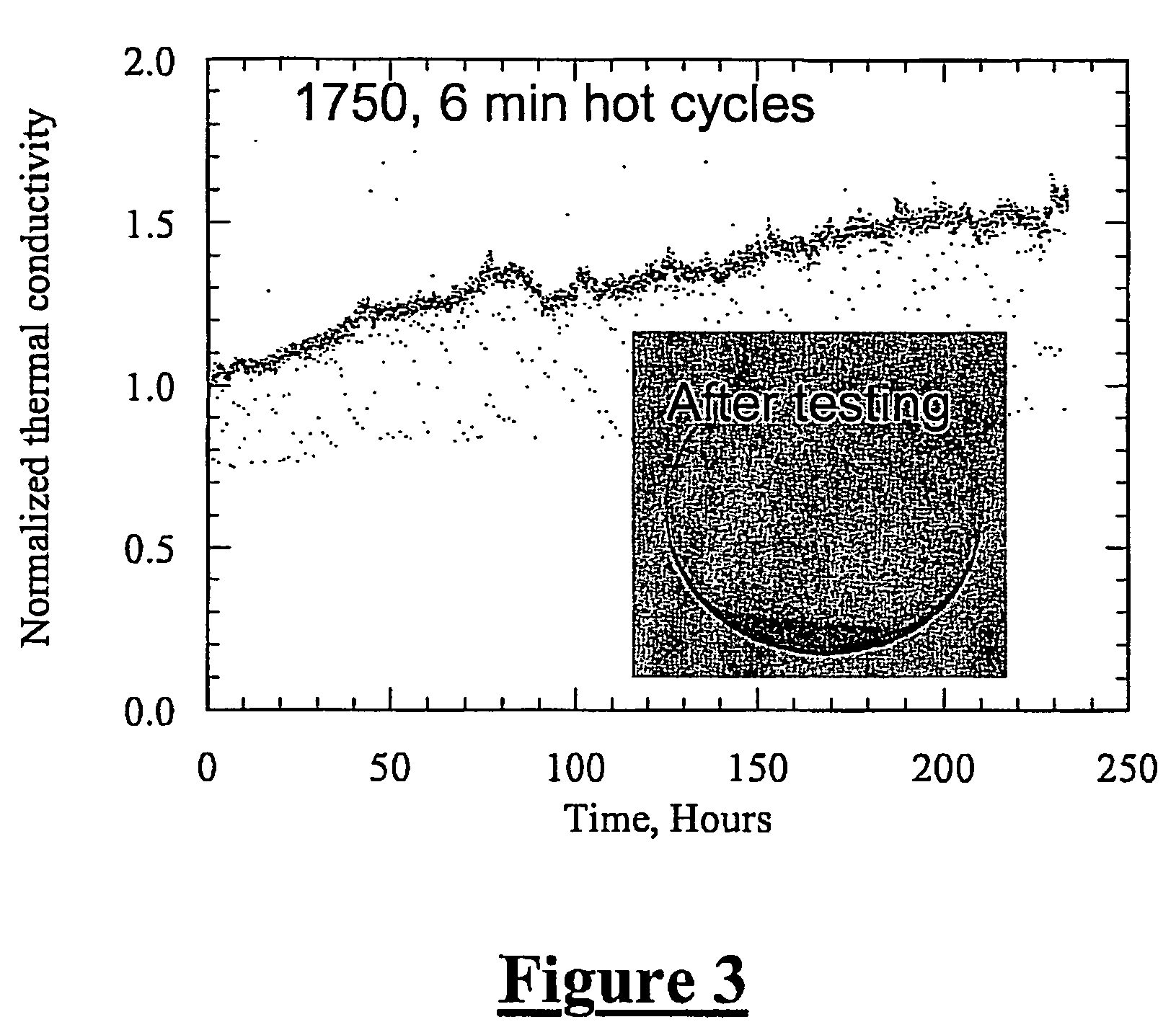
A multilayered coating system consisting of a multicomponent zirconia-base or hafnia-base oxide top layer, an interlayer comprised of a plurality of sublayers and a bond coat layer is provided. The multilayered coating system of the present invention, with an interlayer comprised of a plurality of sublayers, provides a protective coating solution for silicon-base ceramic components exposed to very high temperatures and / or high gas flow velocity water vapor combustion environments. The plurality of sublayers affords for a multitude of interfaces that aid in phonon scattering within the coating system and thereby reduces its thermal conductivity. Furthermore, the plurality of interlayer sublayers afford a strain tolerant buffer between the top layer and substrate and thereby accommodate the thermal expansion mismatch between the oxide top layer (coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) up to ˜8-10×10−6 m / m-C) and the silicon-base ceramic substrate (CTE≈4-5×10−6 m / m-C).
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE
Violation of time reversal invariance in living tissue
InactiveUS6592611B1Eliminate needSynergistic effectivenessSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyDiseaseWavenumber
The present invention provides for a device, a method, and a treatment system for chronic disease conditions. The present invention was designed using the theoretical concepts of Quantum Biology. The principles of operation are based on the device's ability to stimulate a Bose-Einstein condensate and excitation of Frolich resonance in living tissue The wavenumbers necessary for this excitation are derived from the solution to the equations for optical phonon scattering in living tissue generated by optical photon excitation. The establishment of this degeneracy condition induces a super conducting state in the tissue. This super conducting state facilitates DNA replication, transcription and translation, thereby allowing the proper formation or regeneration of healthy tissue. This superconducting state provides the conditions necessary for establishing the violation of time reversal invariance in living tissue.
Owner:HOBSON MICHAEL A
Large-area nanoenabled macroelectronic substrates and uses therefor
InactiveUS20060151820A1Reduce and entirely eliminate scatteringHigh carrier mobilityTransistorNanoinformaticsNanowireElectron scattering
Owner:NANOSYS INC
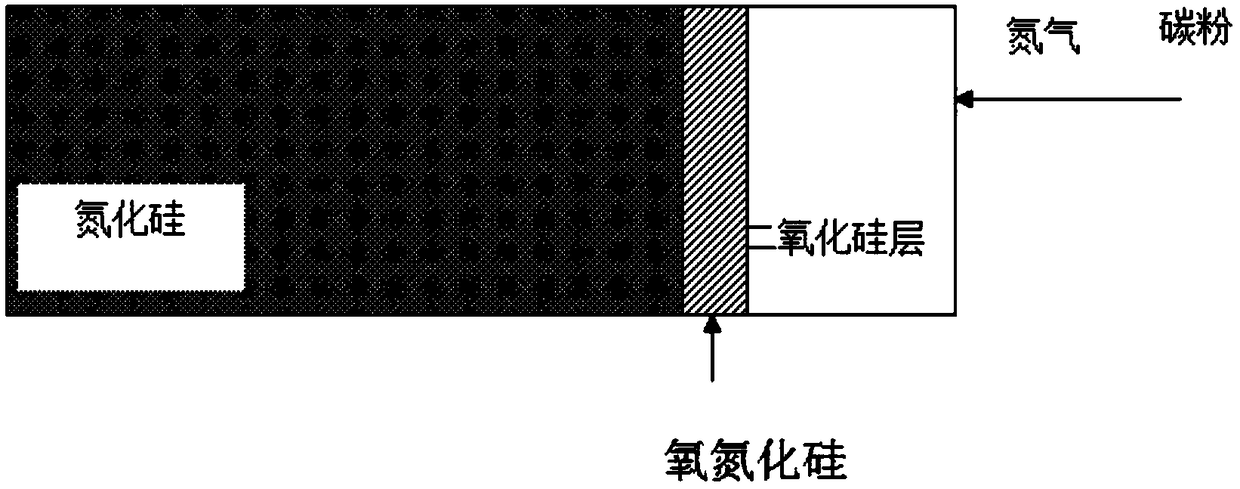
High-heat-conductivity silicon nitride ceramic and preparation method thereof
The invention provides high-heat-conductivity silicon nitride ceramic and a preparation method thereof, which are used for solving the technical problem that the existing heat conductivity is low. Thepreparation method comprises the following steps: performing deoxygenation treatment on silicon nitride powder, naturally cooling the silicon nitride powder, and grinding and sieving the obtained silicon nitride powder; mixing the powder and a sintering aid under the action of a mixed medium, and drying and sieving after mixing to obtain powder; performing pressing formation to obtain a silicon nitride ceramic green body; and performing gas pressure sintering to obtain the silicon nitride ceramic material. Compared with the prior art, the high-heat-conductivity silicon nitride ceramic and thepreparation method thereof have the following advantages: the silicon nitride powder is subjected to deoxygenation treatment, the oxygen content of the original powder is low, the degree of reducingthe lattice oxygen content in the sintering process is higher, and phonon scattering is avoided, so that the heat conductivity of the silicon nitride ceramic is improved; and the prepared silicon nitride ceramic has high heat conductivity, high thermal shock resistance and high-temperature resistance, is safe to use and is a silicon nitride ceramic substrate material with excellent mechanical, thermal and electric comprehensive performance.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Large-Area Nanoenabled Macroelectronic Substrates and Uses Therefor
InactiveUS20110045660A1Reduce and entirely eliminate scatteringHigh carrier mobilityNanostructure manufactureNanomagnetismNanowirePhonon scattering
A method and apparatus for an electronic substrate having a plurality of semiconductor devices is described. A thin film of nanowires is formed on a substrate. The thin film of nanowires is formed to have a sufficient density of nanowires to achieve an operational current level. A plurality of semiconductor regions are defined in the thin film of nanowires. Contacts are formed at the semiconductor device regions to thereby provide electrical connectivity to the plurality of semiconductor devices. Furthermore, various materials for fabricating nanowires, thin films including p-doped nanowires and n-doped nanowires, nanowire heterostructures, light emitting nanowire heterostructures, flow masks for positioning nanowires on substrates, nanowire spraying techniques for depositing nanowires, techniques for reducing or eliminating phonon scattering of electrons in nanowires, and techniques for reducing surface states in nanowires are described.
Owner:ONED MATERIAL INC
Quasi one-dimensional nano structural thermoelectric material, device and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101969095AOptimal Control StructureFast preparationThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric device detailsThermoelectric materialsNanowire
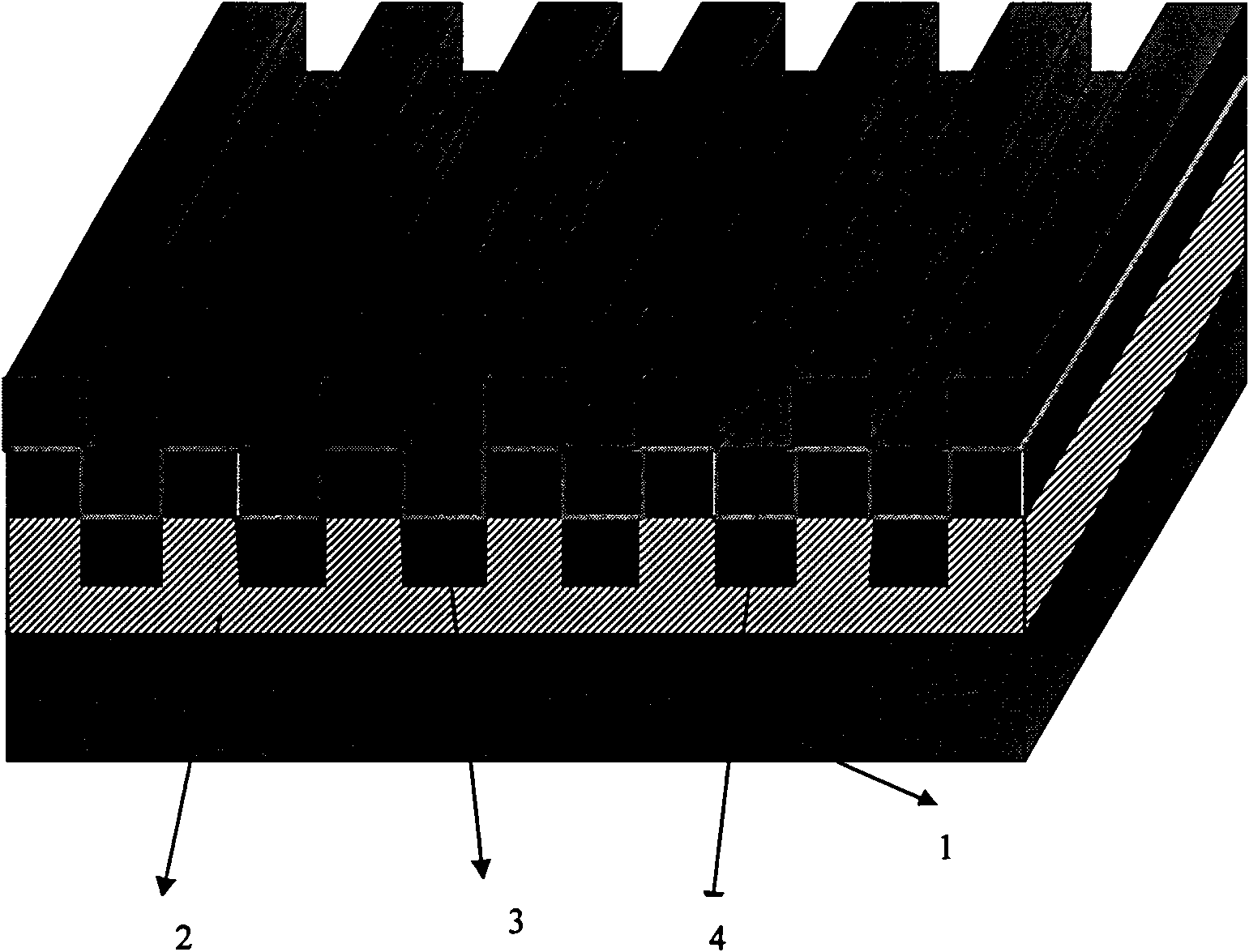
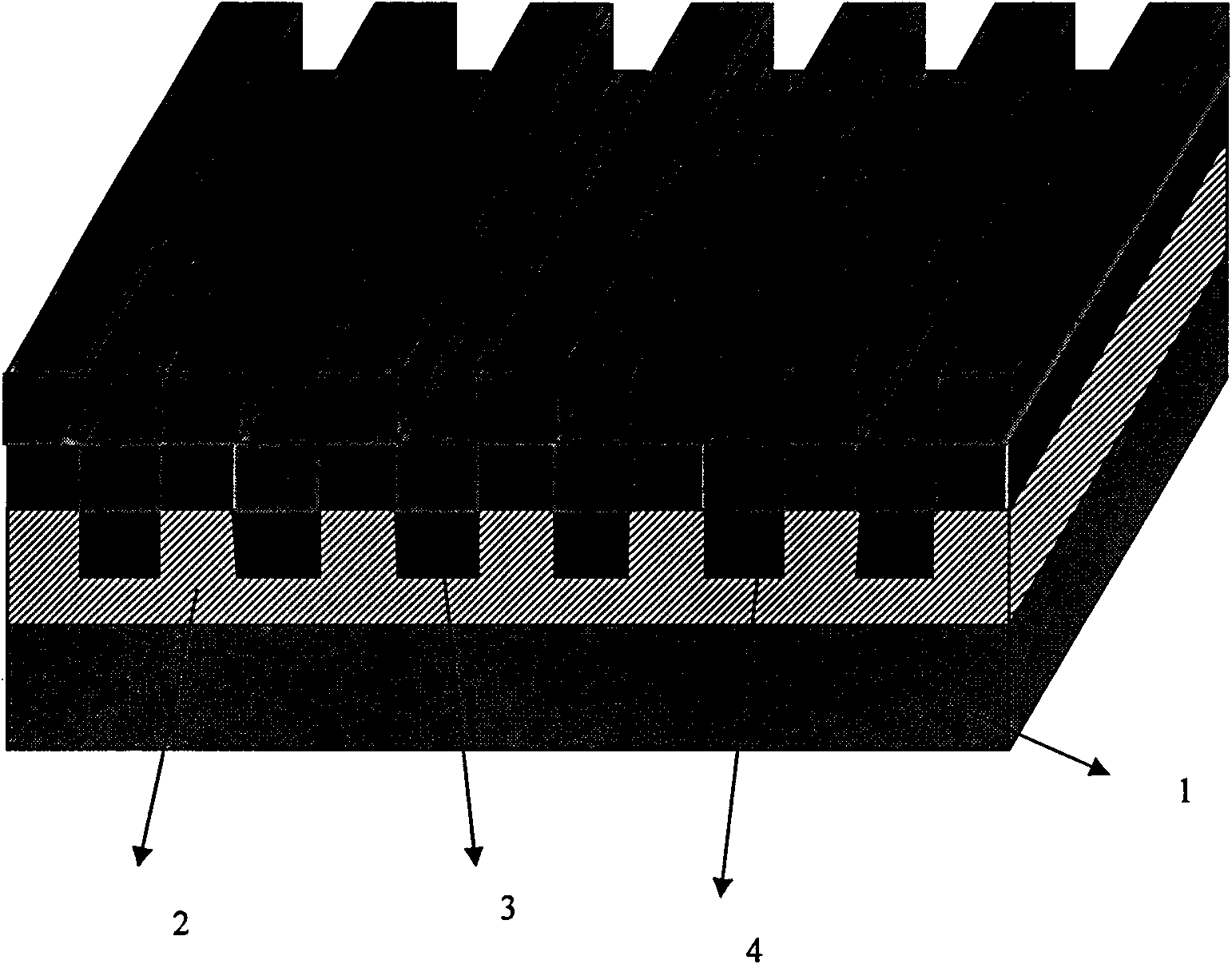
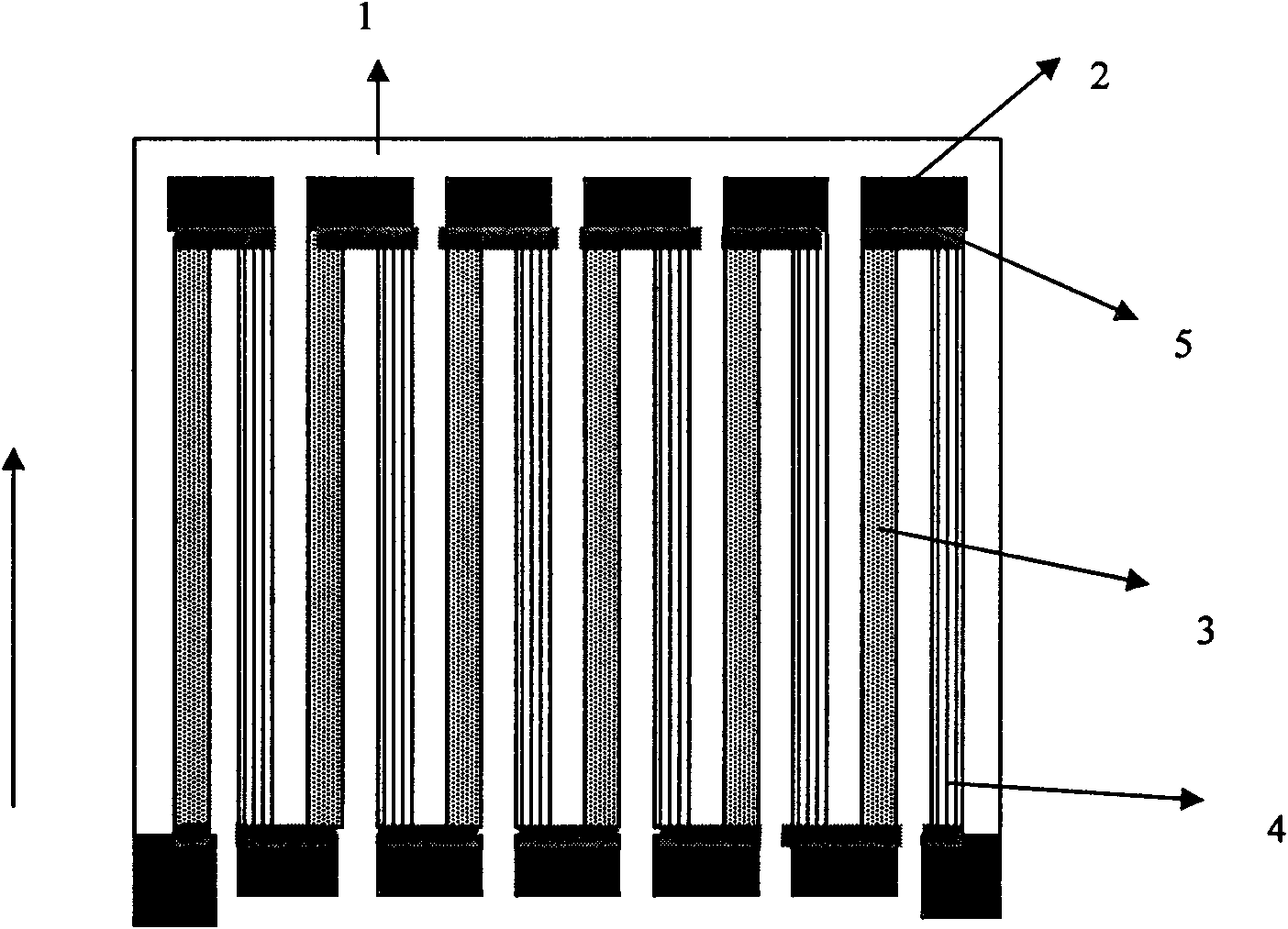
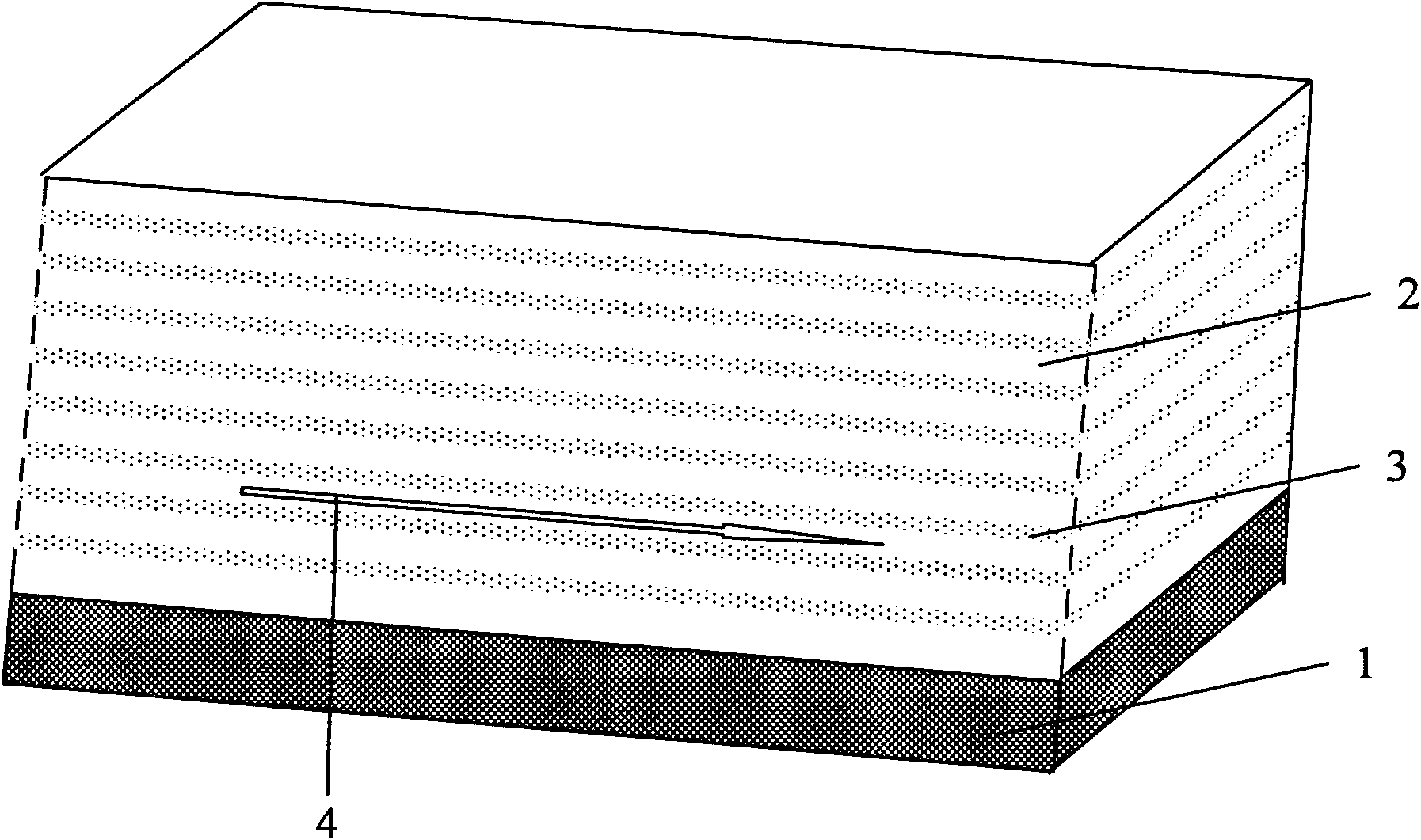
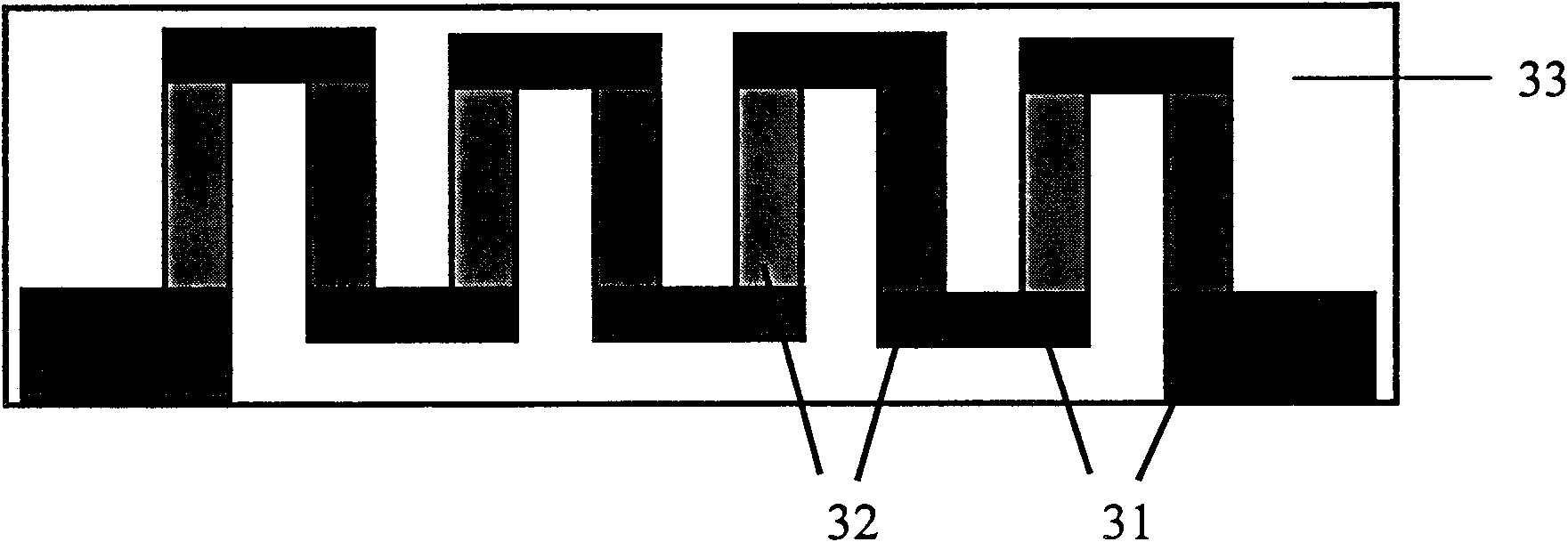
The invention discloses a quasi one-dimensional nano structural thermoelectric material, a device and a preparation method thereof. The thermoelectric material comprises an insulating substrate, at least two thermoelectric material layers ant at least two phonon scattering layers; parallel nano grooves arranged periodically are distributed on the surface of the insulating substrate, and the cross sections of the grooves have rectangular fluctuated structures; the thermoelectric material layers are covered on the surface of the substrate, and the cross sections of the thermoelectric material layers have rectangular fluctuated periodical structures; and the thermoelectric material layers and the phonon scattering layers are alternately covered in rectangular fluctuated periodical structures. The size of the nano wire cross section can be controlled by changing the size of the substrate grooves and the deposition time, the scattering of phonons transmitted along the nano wire direction can be increased by changing the nano wire cross section area and the interface between the nano wires, the thermal conductivity of the material can be reduced, and the thermoelectric conversion efficiency of the material can be improved; and the prepared device has high thermoelectric conversion efficiency and good thermal stability.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
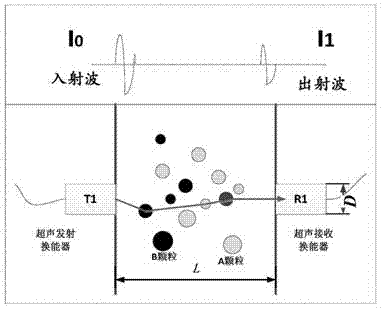
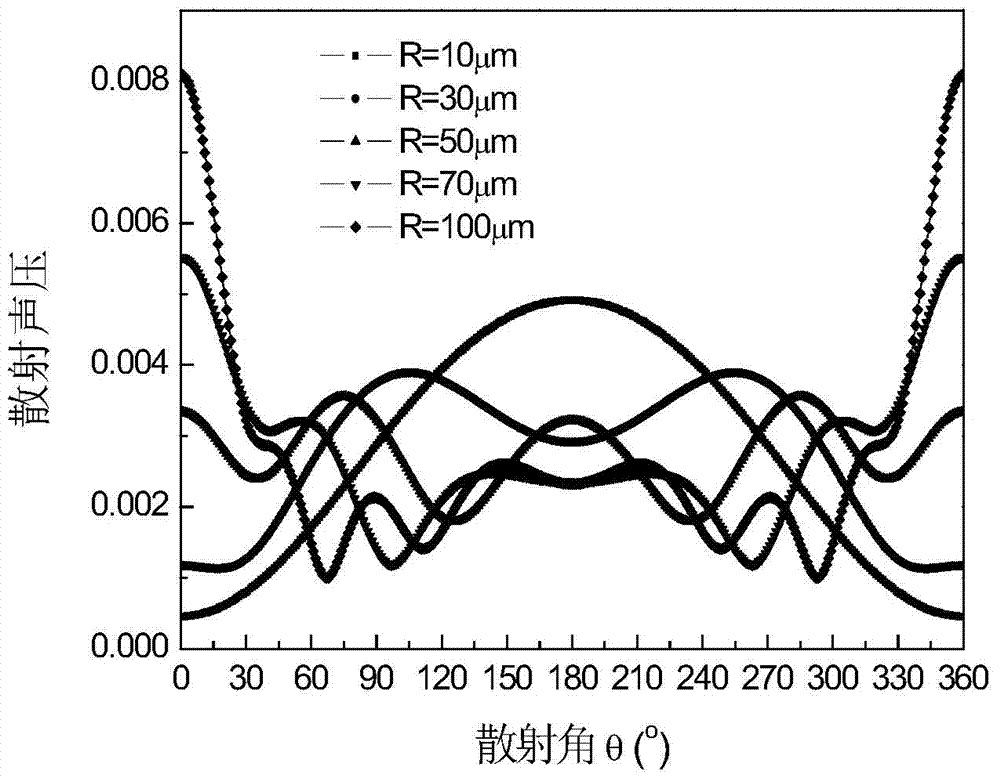
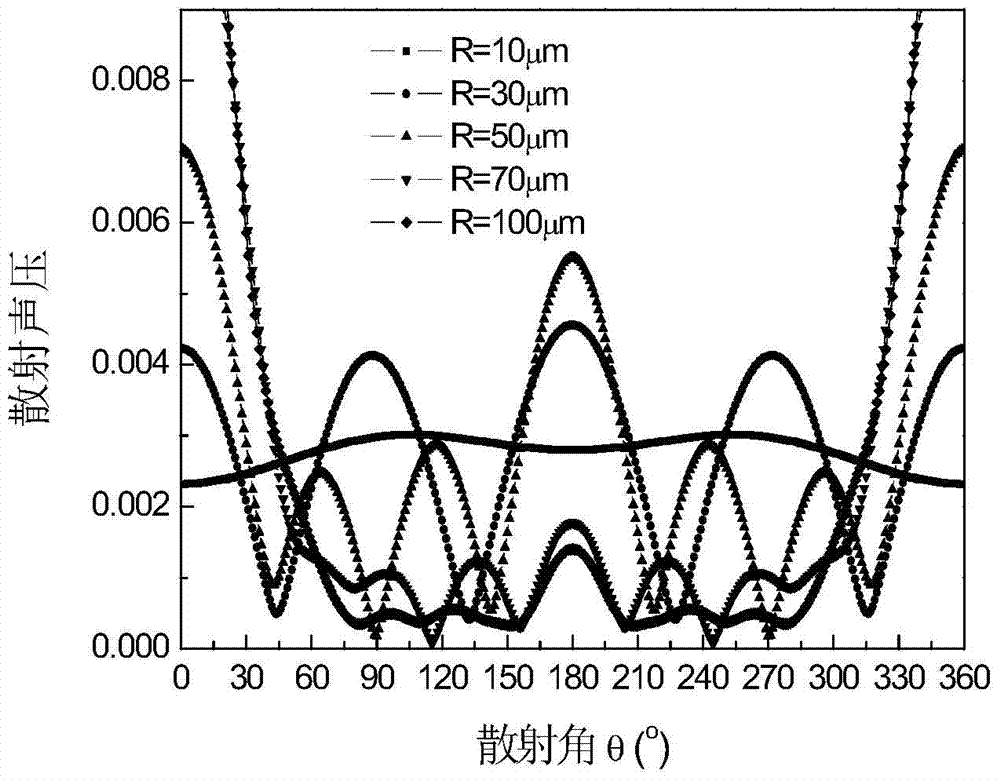
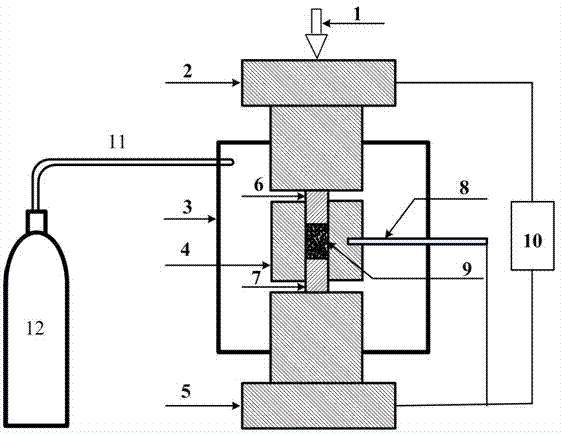
Ultrasonic attenuation spectrum based mixed solid particle size and concentration measurement method
InactiveCN104849183ASimple structureSmall structureParticle size analysisParticle suspension analysisSolid massUltrasonic attenuation
The invention relates to an ultrasonic attenuation spectrum principle based method for measuring the average particle size and concentration of two types of mixed solid particles in a liquid or gas medium. The ultrasonic attenuation spectrum principle based method comprises the following steps of step 1, measuring an experimental measurement ultrasonic attenuation spectrum alpha (f) under the condition that the two types of solid particles A and B are located in a measurement area, wherein f is the ultrasonic frequency; step 2, calculating an acoustic attenuation coefficient Kext of the particle and acoustic wave effect; step 3, determining whether the particles are A particles or B particles and determining whether phonons are absorbed or scattered through the acoustic attenuation coefficient; step 4, calculating a scattering emergence angle theta M1 of the scattered phonons; step 5, continuing to calculate a theoretical ultrasonic attenuation spectrum through a result of the step 4; step 6, establishing an objective function according to the theoretical ultrasonic attenuation spectrum and the experimental measurement ultrasonic attenuation spectrum to solve the particle size and volume concentration. The ultrasonic attenuation spectrum based mixed solid particle size and concentration measurement method can be applied to the two types of mixed solid particles and laboratory scientific research and the online measurement and the application of the industrial field can be implemented.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Large-area nanoenabled macroelectronic substrates and uses therefor
InactiveUS8030186B2Reduce and entirely eliminate scatteringHigh carrier mobilityNanomagnetismNanostructure manufactureNanowirePower flow
A method and apparatus for an electronic substrate having a plurality of semiconductor devices is described. A thin film of nanowires is formed on a substrate. The thin film of nanowires is formed to have a sufficient density of nanowires to achieve an operational current level. A plurality of semiconductor regions are defined in the thin film of nanowires. Contacts are formed at the semiconductor device regions to thereby provide electrical connectivity to the plurality of semiconductor devices. Furthermore, various materials for fabricating nanowires, thin films including p-doped nanowires and n-doped nanowires, nanowire heterostructures, light emitting nanowire heterostructures, flow masks for positioning nanowires on substrates, nanowire spraying techniques for depositing nanowires, techniques for reducing or eliminating phonon scattering of electrons in nanowires, and techniques for reducing surface states in nanowires are described.
Owner:ONED MATERIAL INC
High-thermal-conductivity pressurelessly-sintered silicon carbide ceramic material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a high-thermal-conductivity pressurelessly-sintered silicon carbide ceramic material and a preparation method thereof. The high-thermal-conductivity pressurelessly-sintered silicon carbide ceramic material comprises 75-95wt.% of silicon carbide, 0.5-10wt.% of graphene, 1-3wt.% of surfactants, 0.5-2.5wt.% of dispersing agents, 2-10wt.% of binders and 0.5-3.5wt.% of boron carbide. The high-thermal-conductivity pressurelessly-sintered silicon carbide ceramic material and the preparation method thereof have the advantages that by a specific ratio among the silicon carbide, the graphene and the boron carbide, a green body is formed by means of pressing and then is subjected to pressureless sintering under a vacuum condition to obtain the SiC (silicon carbide) ceramic material; the graphene is distributed in an SiC matrix material uniformly and is closely combined with SiC, and the problems that decreasing and counteracting of thermal conductivity result from phonon scattering of internal pores of the material and exceed the increasing effect of the introduced graphene on the thermal conductivity are avoided, so that densification and uniformity of the ceramic material are guaranteed, and the high thermal conductivity is achieved.
Owner:LAIWU ADVANCED CERAMIC TECH
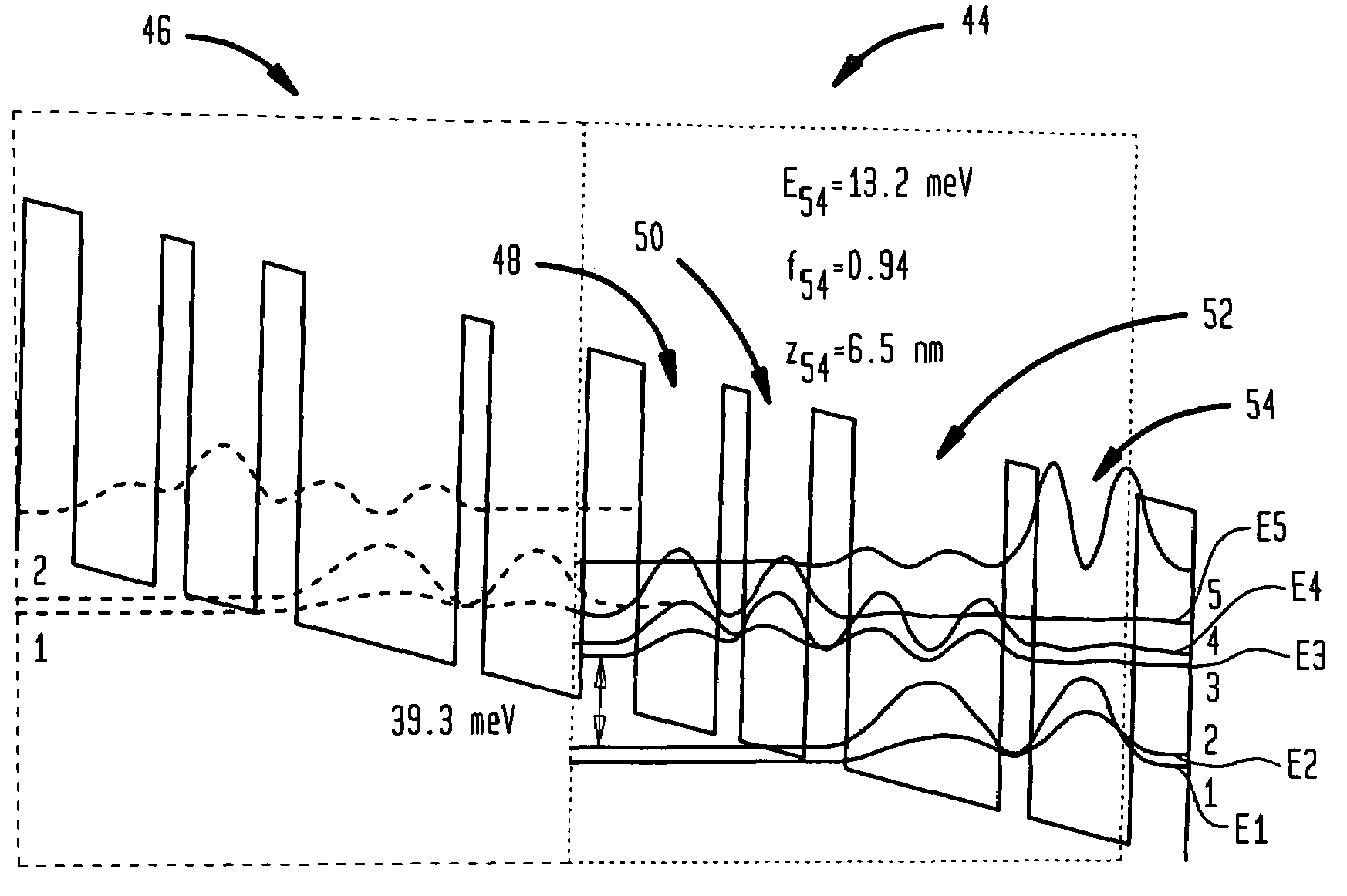
Terahertz lasers and amplifiers based on resonant optical phonon scattering to achieve population inversion
ActiveUS20050058168A1Highly selective and very fast depopulationPromote generationOptical wave guidanceLaser using scattering effectsAudio power amplifierQuantum well
The present invention provides quantum cascade lasers and amplifier that operate in a frequency range of about 1 Terahertz to about 10 Terahertz. In one aspect, a quantum cascade laser of the invention includes a semiconductor heterostructure that provides a plurality of lasing modules connected in series. Each lasing module includes a plurality of quantum well structure that collectively generate at least an upper lasing state, a lower lasing state, and a relaxation state such that the upper and the lower lasing states are separated by an energy corresponding to an optical frequency in a range of about 1 to about 10 Terahertz. The lower lasing state is selectively depopulated via resonant LO-phonon scattering of electrons into the relaxation state.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
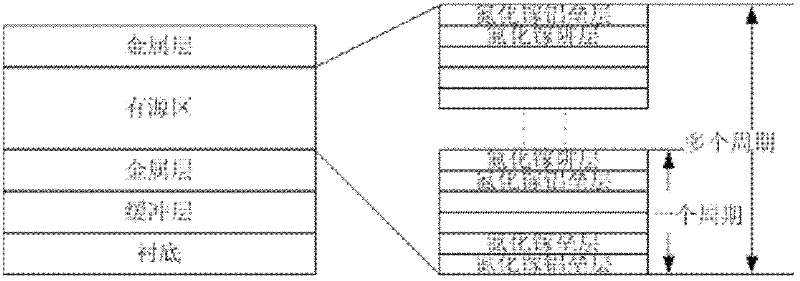
High-performance thermoelectric device and ultrafast fabrication method thereof
ActiveCN107946452AImprove electrical output performanceImprove job stabilityThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric materialsEnergy conversion efficiency
The invention discloses a high-performance thermoelectric device and an ultrafast fabrication method thereof. In the high-performance thermoelectric device, a segmented structure is employed to perform optimal matching of a thermoelectric material and a temperature difference environment, a blocking layer and a buffer stress layer are employed to reduce interface element migration and longitudinalcontact thermal expansion stress and improve bonding strength, a phonon scattering layer and a negative thermal expansion buffer layer are embedded to fix a thermoelectric leg so as to improve internal thermal resistance and horizontal thermal matching performance of the high-performance thermoelectric device, internal package and external package are employed to prevent the thermoelectric material from being oxidized and sublimed and improve external collision-resistant capability, the technical bottlenecks of low energy conversion efficiency, small specific power, poor thermal stability, poor collision performance, complicated fabrication process and the like of a traditional thermoelectric device are effectively broken through, meanwhile, the thermal stability and the mechanical structural performance of the high-performance thermoelectric device are improved to a great extent, long-term and excellent electrical output performance is guaranteed, and the working environment is expanded.
Owner:深圳热电新能源科技有限公司
Terahertz lasers and amplifiers based on resonant optical phonon scattering to achieve population inversion
ActiveUS7158545B2Promote generationHigh selectivityOptical wave guidanceLaser using scattering effectsAudio power amplifierOptical frequencies
The present invention provides quantum cascade lasers and amplifier that operate in a frequency range of about 1 Terahertz to about 10 Terahertz. In one aspect, a quantum cascade laser of the invention includes a semiconductor heterostructure that provides a plurality of lasing modules connected in series. Each lasing module includes a plurality of quantum well structure that collectively generate at least an upper lasing state, a lower lasing state, and a relaxation state such that the upper and the lower lasing states are separated by an energy corresponding to an optical frequency in a range of about 1 to about 10 Terahertz. The lower lasing state is selectively depopulated via resonant LO-phonon scattering of electrons into the relaxation state.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method for preparing porous nano magnesium silicon based block body thermoelectric material by hot press method in electric field reaction
The invention relates to a method for preparing a porous nano magnesium silicon based block body thermoelectric material by a hot press method in an electric field reaction, and belongs to the technical field of thermoelectric materials and preparation methods. The method is characterized in that the method for preparing the porous nano Mg2Si-based block body thermoelectric material by the hot press method in the electric field reaction realizes reactive synthesis and compact sintering of Mg2Si in one step, so that the method is simple in step, low in cost, and high in purity of products. Various doping substances are convenient to add, and the products have porous nano-structures. Sustained pollution to the products in a multi-step preparation method can be effectively avoided. Meanwhile, reaction and compact sintering are performed at the same time, so that the temperature and time required by the preparation of products are reduced, and grain coarsening is effectively inhibited. Under the effect of protective gases, reaction byproducts are gathered in grain boundary in the form of nanoholes, so that grain growth is further inhibited and phonon scattering is enhanced. The generated products are completely reacted, the grain size is less than 70nm, the sectional hole ratio is about 5-15%, and holes and the nanocrystals coexist to the benefit of reducing the heat conductivity of the products.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Boron nitride nanotube-nano-cellulose fiber composite material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106977773AImprove thermal conductivityGood mechanical propertiesHeat-exchange elementsHeat conductingCellulose fiber
The invention relates to a boron nitride nanotube-nano-cellulose fiber composite material. The composite material is prepared from the following materials in percentage by mass: 5 to 40 percent of boron nitride nanotube, and 60 to 95 percent of nano-cellulose fiber. The invention further relates to a preparation method of the boron nitride nanotube-nano-cellulose fiber composite material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing the boron nitride nanotube with a nano-cellulose fiber aqueous solution; performing ultrasonic treatment; performing solid-liquid separation to obtain the boron nitride nanotube-nano-cellulose fiber composite material. By adopting the composite material, the interface thermal resistance and phonon scattering action are reduced effectively, the heat-conducting property of the composite material is improved, and high dimension stability is achieved; the composite material is biodegradable. The preparation method is simple and mild, and can be applied to industrial production.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Method for preparing thermoelectric material with P-type nano-structure and bismuth telluride matrix
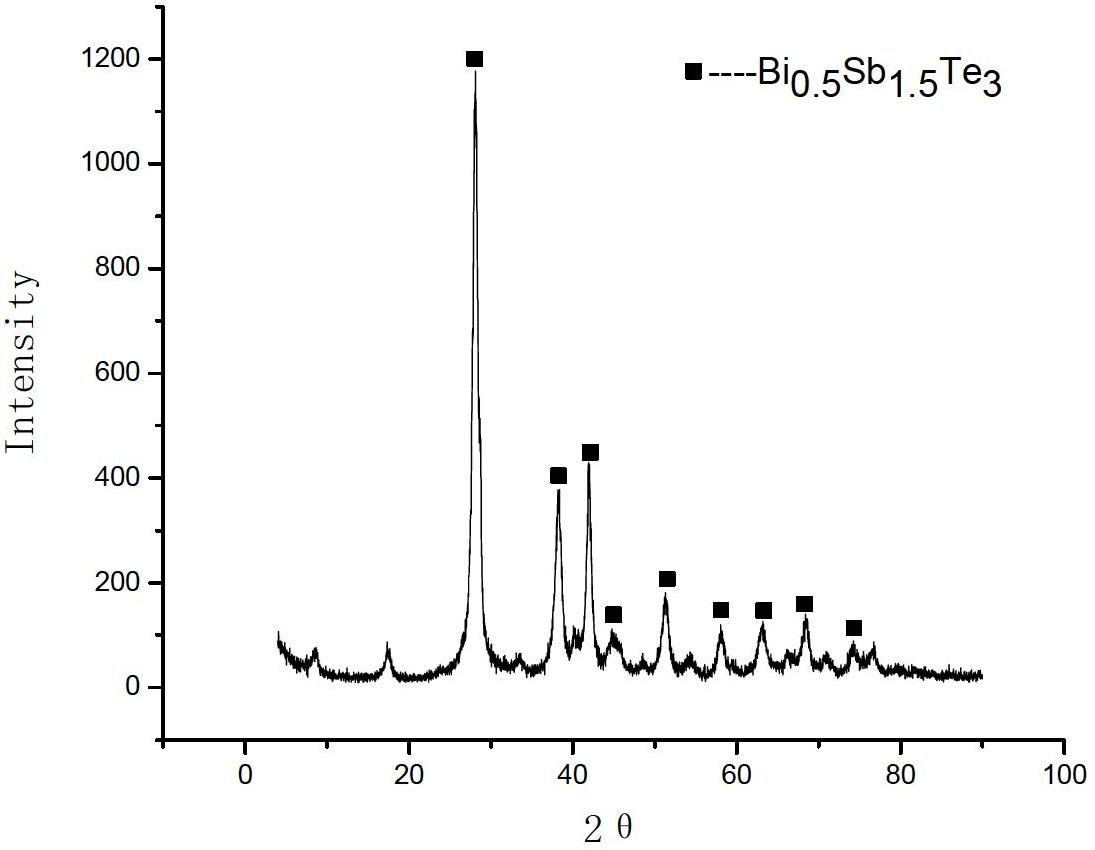
InactiveCN102694116AUniform compositionSmall tissueThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentMolten stateBismuth telluride
The invention discloses a method for preparing a thermoelectric material with a P-type nano-structure and a Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 matrix. The method includes synthesizing P-type Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 compound nanometer powder from high-purity Bi powder (with purity of 99.99%), Sb powder and Te powder in a mechanical alloying (MA) manner; and sintering the Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 precursor nanometer powder into the dense fine crystal thermoelectric material by a vacuum hot-pressing sintering (HP) method. The problem of volatility of elements such as Bi, Sb and Te in a melting state is avoided, and the material with uniform components and fine texture can be prepared. The granularity of the powder reaches a nanometer grade, phonon scattering is increased effectively, thermal conductivity is lowered, and the thermoelectric performance is enhanced.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same
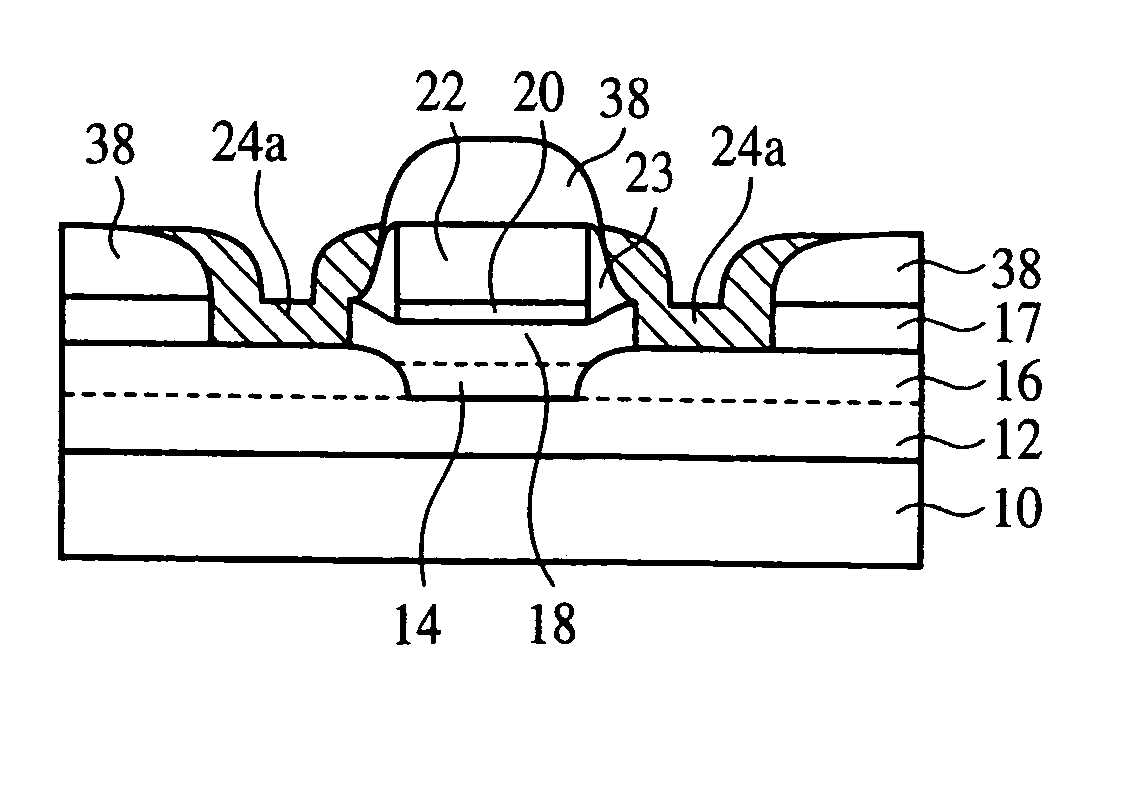
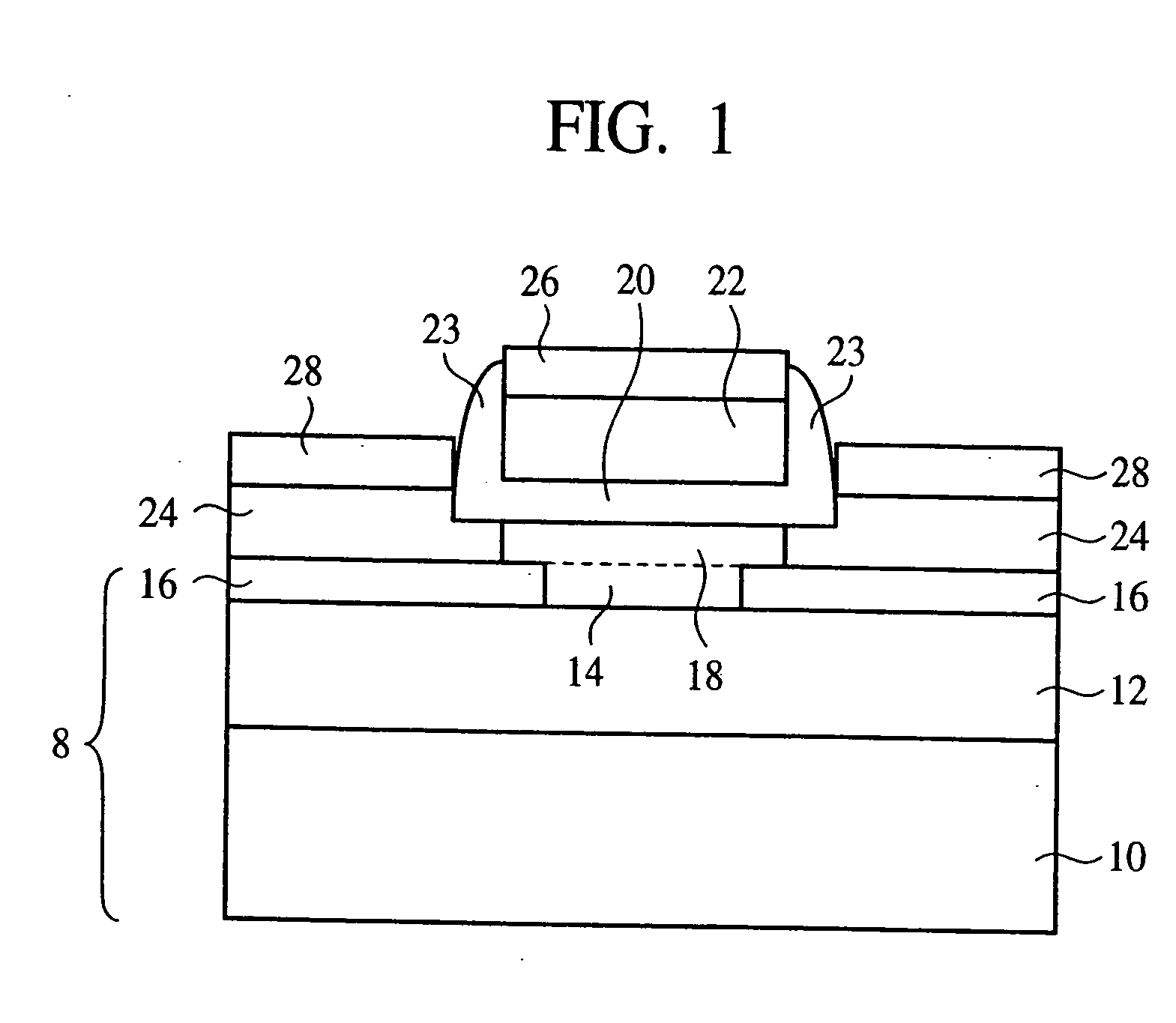
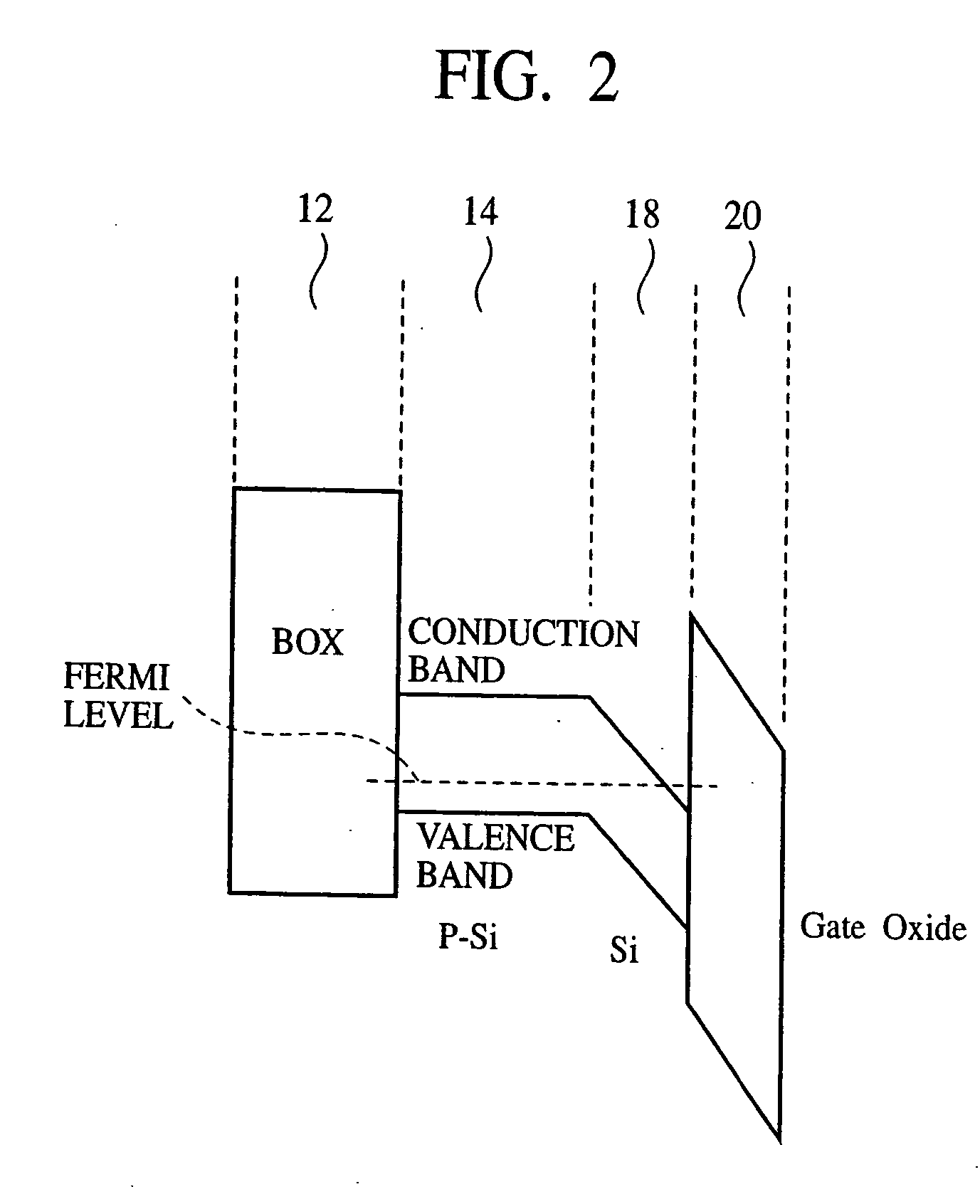
InactiveUS20050085027A1High carrier mobilityPrevent surfaceTransistorThyristorInsulation layerDevice material
The semiconductor device comprises a semiconductor layer 18 formed on an insulation layer 16, a gate electrode 22 formed on the semiconductor layer with a gate insulation film 20 formed therebetween, a source / drain region 24 formed on the semiconductor layer on both sides of the gate electrode, and a semiconductor region 14 buried in the insulation layer 16 in a region below the gate electrode. The surface scattering of the carriers and phonon scattering can be prevented while suppressing the short channel effect. Resultantly the semiconductor device can have high mobility and high speed.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
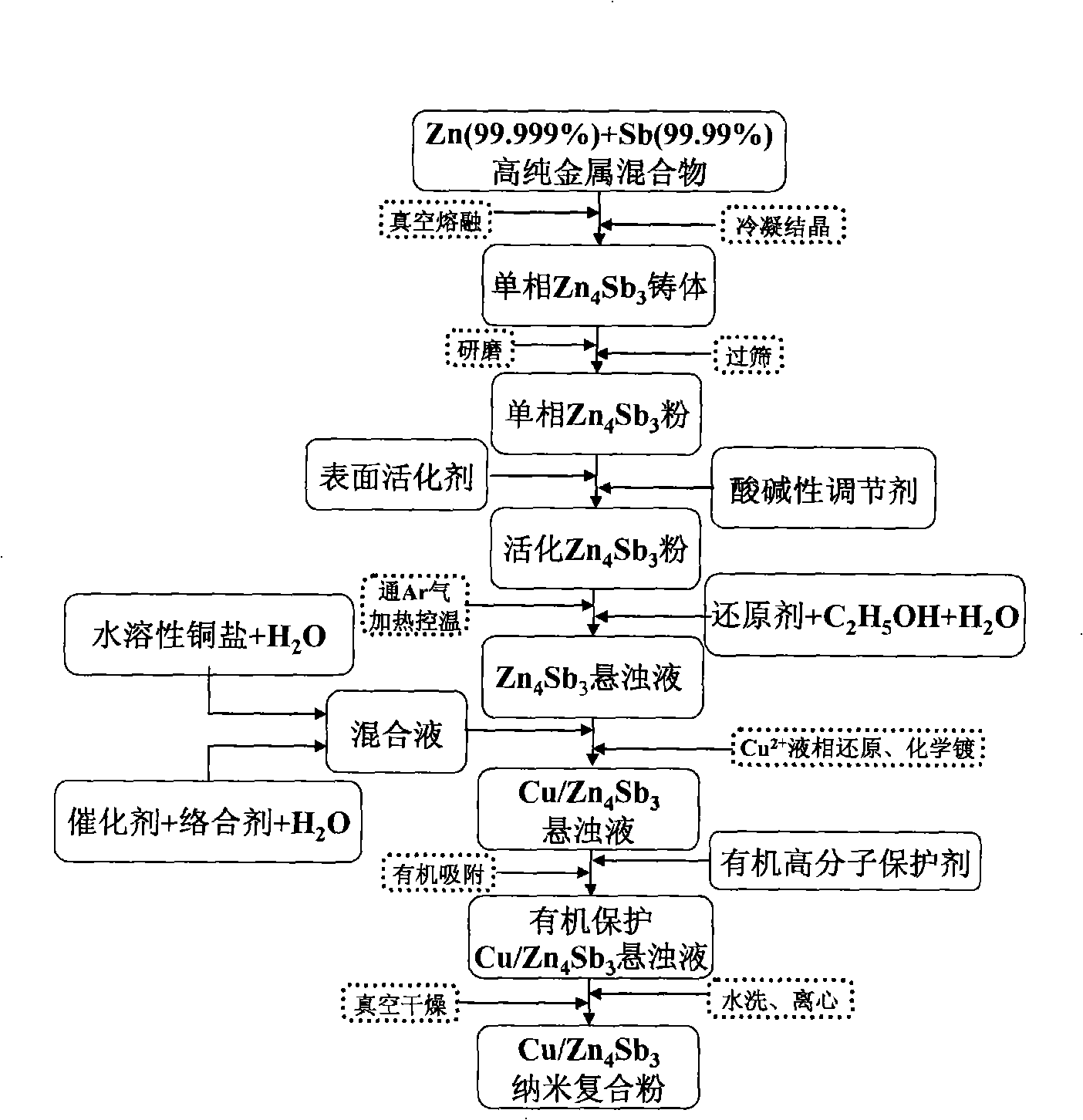
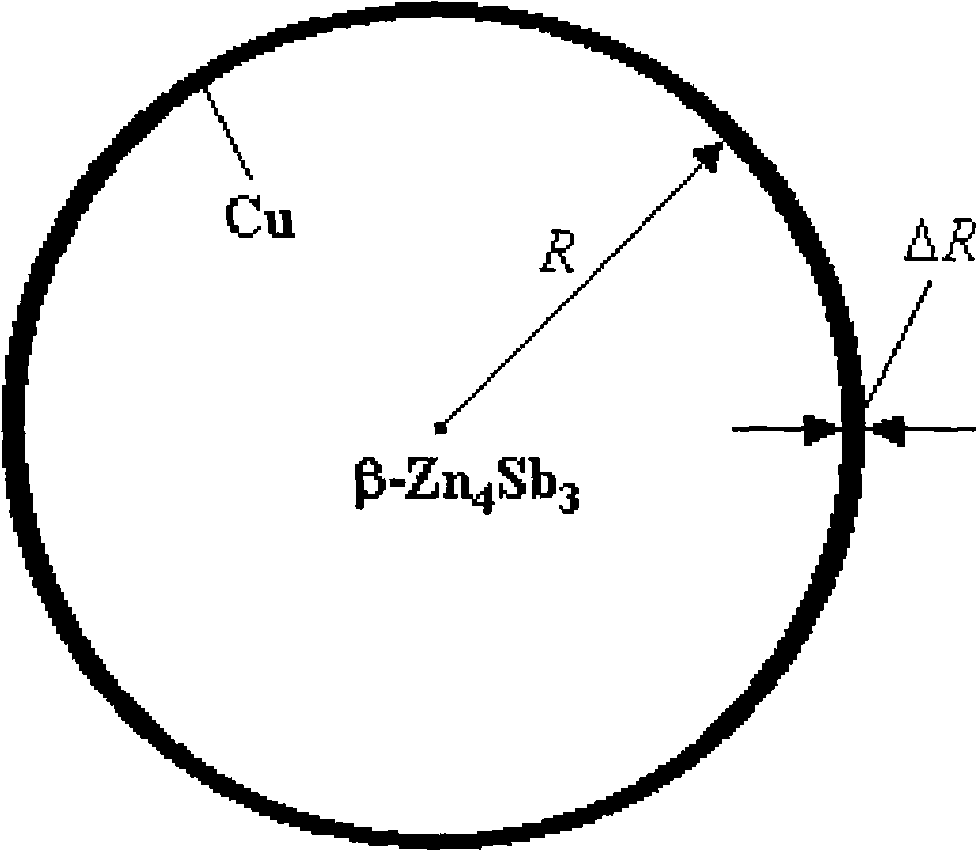
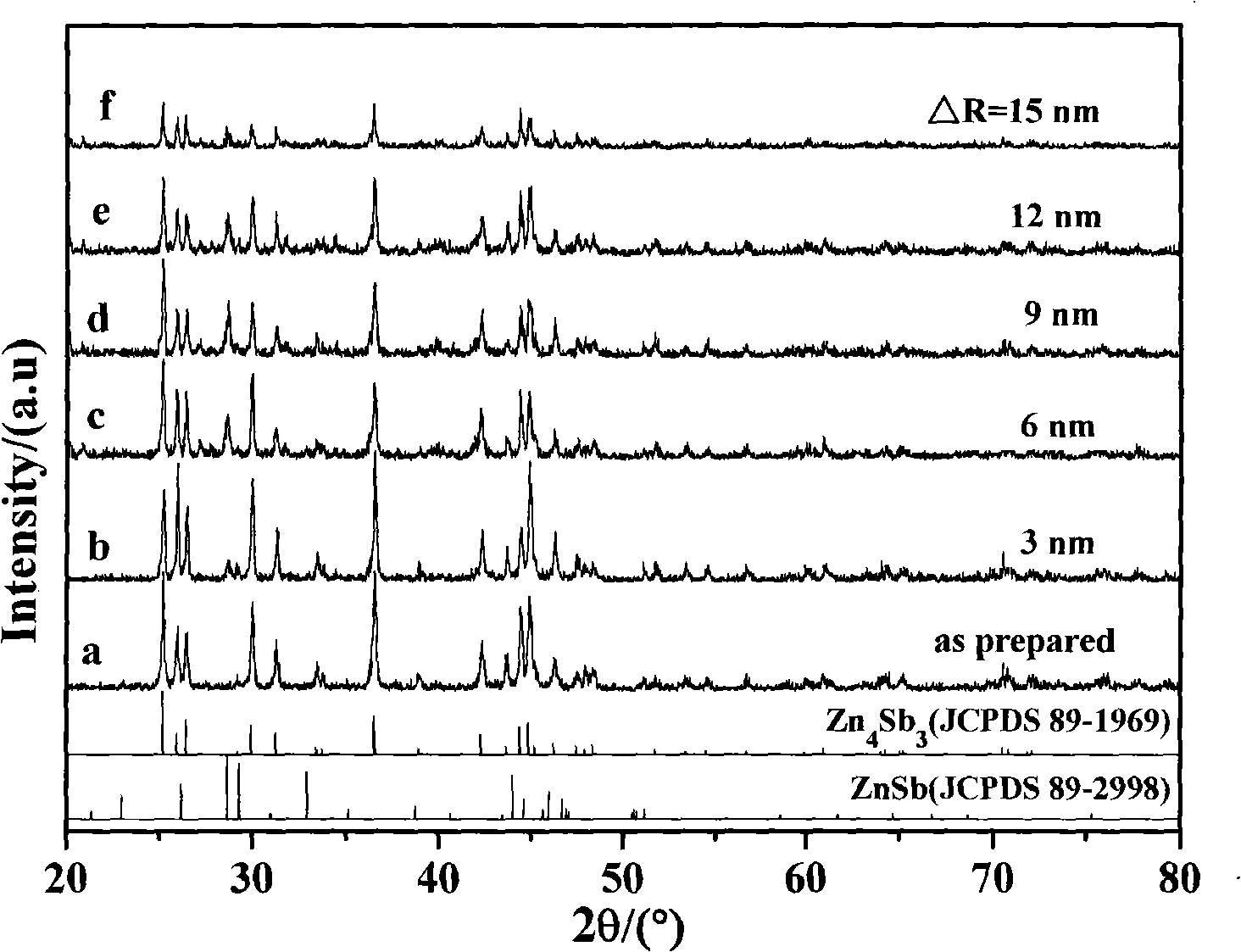
Method for preparing nano-Cu uniformly coated Zn4Sb3 powder
InactiveCN101274368AMaintain thermoelectric transfer propertiesEffective control of thermoelectric transfer characteristicsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingScattering effectFilter effect
The invention relates to a preparation method of Zn4Sb3 powder that is evenly coated with nano Cu. The method is characterized in that: the mixture of highly pure metal Zn powder and Sb powder is firstly smelted under vacuum, condensed and crystallized to obtain the casting body of a single-phase beta-Zn4Sb3 compound, the casting body is ground and sieved to obtain beta-Zn4Sb3 powder, to which surface processing is carried out; then an acid and alkali regulator is used for regulating pH value to obtain activating beta-Zn4Sb3 powder; then the activating beta-Zn4Sb3 powder is used as a parent stock and water soluble cupric salt is used as a Cu source to form the Zn4Sb3 powder that is evenly coated with the nano Cu by liquid phase reduction reaction, electroless plating process and organic protection treatment. The preparation method is characterized by low cost, simple operation, even coating of the nano Cu and environmental protection, etc. The powder not only can keep the thermoelectric transmission properties of the beta-Zn4Sb3 compound, but also has improved phonon scattering effect and electron energy filtering effect electron energy for being evenly coated by nano second phase.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for analog designing of active area of AlGaN/GaN terahertz quantum cascade laser
InactiveCN102508940AOptimum Active Region StructureLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersPotential wellSchrödinger equation
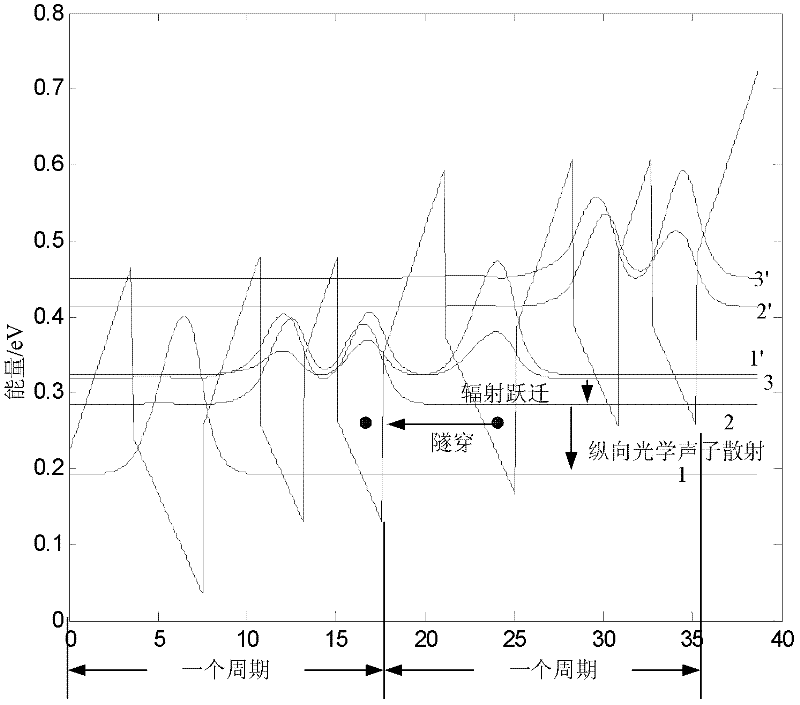
A method for analog designing of an active area of an AlGaN / GaN terahertz quantum cascade laser relates to methods for analog designing of active areas of terahertz quantum cascade lasers. The method includes: firstly, determining parameters required in one-dimensional effective mass Schrodinger equation; secondly, solving the Schrodinger equation; thirdly, calculating delta E21, delta E32 and delta E1'3; fourthly, judging; fifthly, searching the optimum structure; and sixthly, outputting the structure. The active area consists of n periods, and each period consists of three barrier layers and three potential well layers. The method can be applied to designing of active areas of terahertz quantum cascade lasers, and has the advantages that the longitudinal optical phonon scattering principle and the tunneling principle are fully used while the optimum active area structure can be searched out.
Owner:HARBIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of Bi2Te3/graphene composite thermoelectric material
InactiveCN109309156AAvoid damageEasy to removeThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric device junction materialsThermoelectric materialsReducing agent
The invention provides a preparation method of a Bi2Te3 / graphene composite thermoelectric material. The preparation method includes adding nano graphene powder and sodium chlorate into concentrated sulfuric acid, performing stirring under an ice-bath state, and modifying trace hydroxy and epoxy groups on the surface of the nano graphene; and adding a Te source, alkali and a reducing agent after aBi source and the nano graphene are uniformly stirred and mixed, and preparing a Bi2Te3 / graphene composite thermoelectric material by adopting a low temperature wet chemical method. Through the disclosed method, the nano graphene can prevent Bi2Te3 nucleation from growing into particles with larger sizes, so that phonon scattering interfaces can be increased, and the thermal conductivity of the material can be reduced; the high conductivity of the nano graphene can provide higher mobility ratio for the composite material; and the method is mild in reaction condition, simple in preparation, lowin cost and easy to perform industrial batch production.
Owner:YANCHENG TEACHERS UNIV
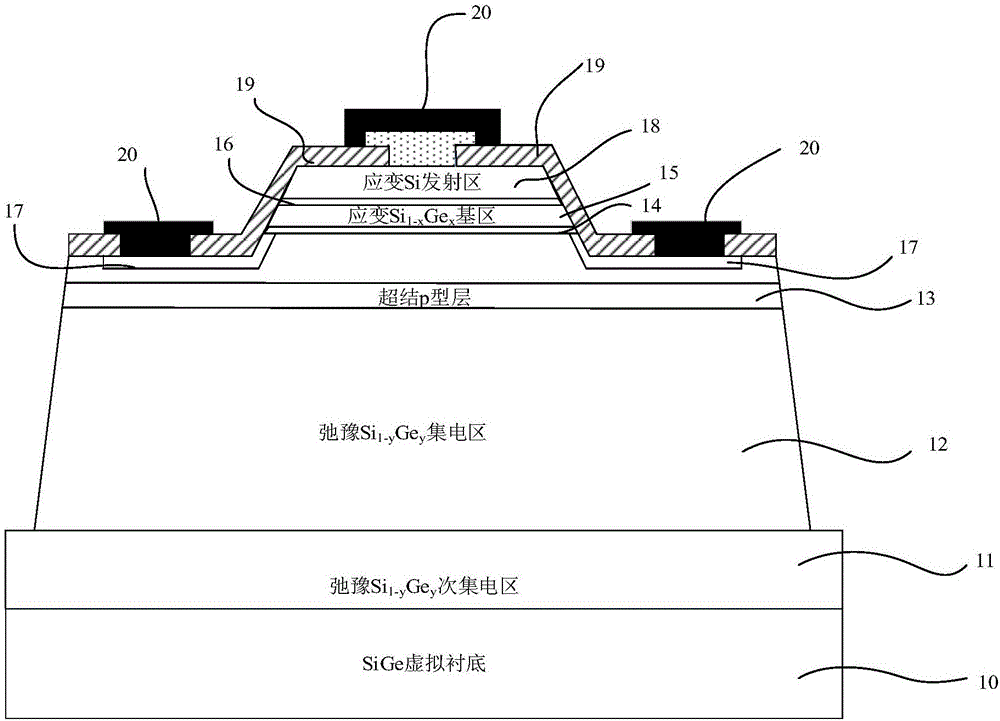
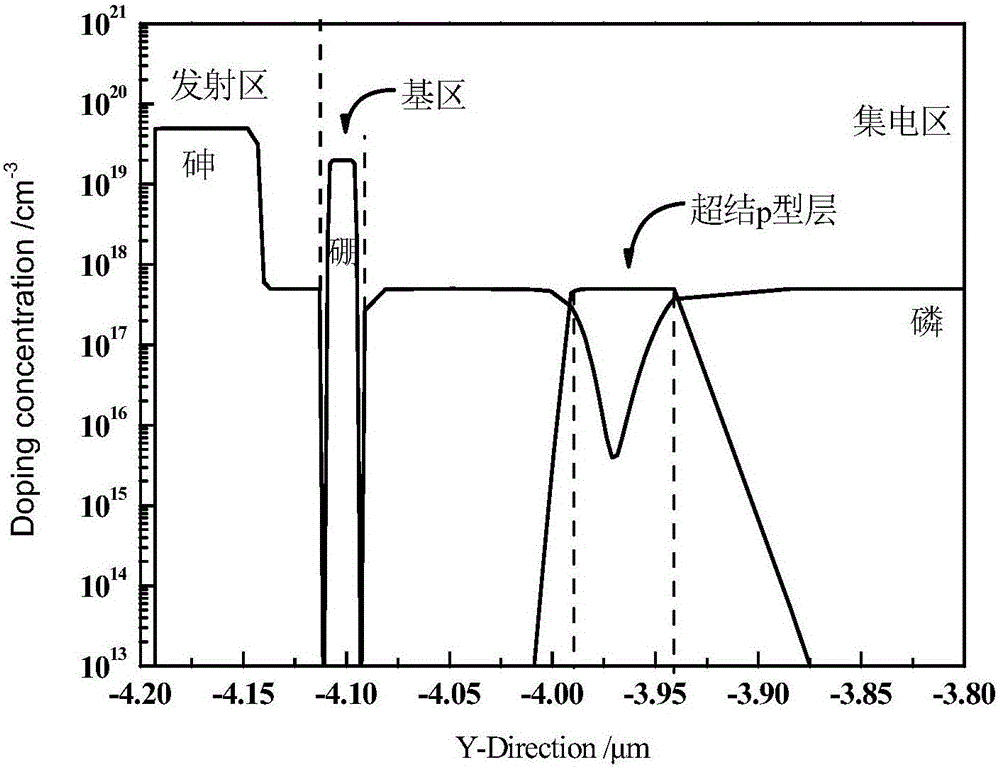
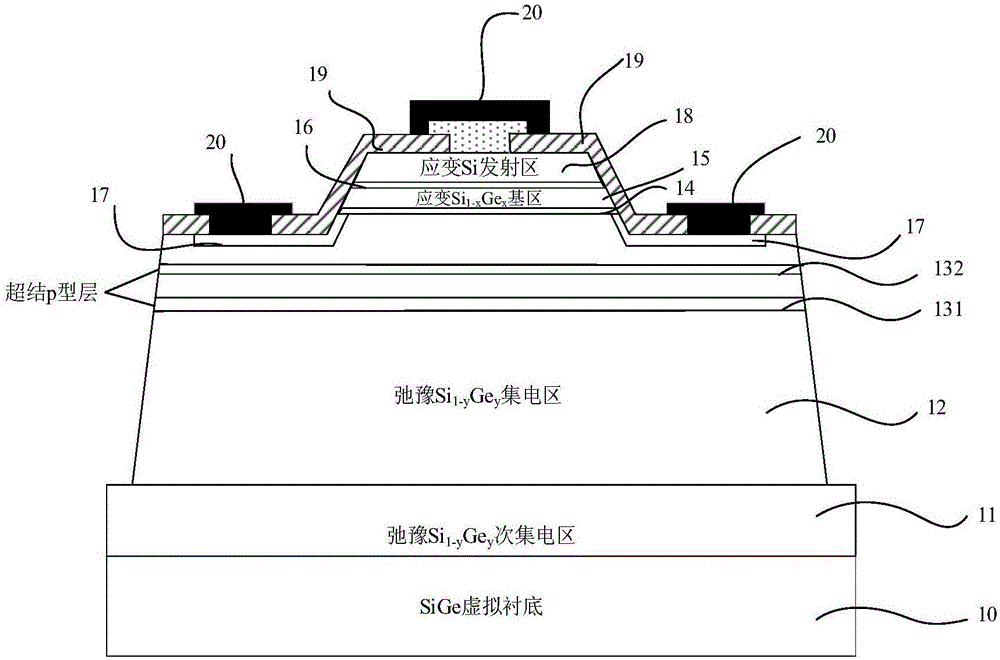
High-thermostability super-junction stress Si/SiGe heterojunction bipolar transistor
ActiveCN106169498AImprove thermal stabilityIncreased sensitivitySemiconductor devicesElectronic temperatureWorking temperature
The invention discloses a super-junction stress Si / SiGe heterojunction bipolar transistor with a high thermostability. A SiGe virtual substrate structure is adopted by the transistor; and a Si<1-y>Ge<y> secondary collector region, a relaxation Si<1-y>Ge<y> collector region, a stress Si<1-x>Ge<x> base region and a stress Si emitter region are respectively and epitaxially grown on the SiGe virtual substrate structure. According to the transistor, by introducing a super-junction p-type layer parallel to the stress Si<1-x>Ge<x> base region to the relaxation Si<1-y>Ge<y> collector region, the purposes of improving the electric field distribution in a collector junction space-charge region, reducing the peak electronic temperature, inhibiting the impact ionization and improving a device breakdown voltage are achieved; and meanwhile, with the introduction of the super-junction p-type layer, the doping concentration and the phonon scattering rate of the relaxation Si<1-y>Ge<y> collector region are effectively reduced, and the thermal conductivity of the relaxation Si<1-y>Ge<y> collector region is improved; the transistor has the characteristics of large current gain and high breakdown voltage; the internal temperature distribution is significantly reduced, the characteristic frequency and the temperature sensibility are improved, and the high-thermostability work can be realized in a relatively wide working temperature range.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Nanocomposite thermoelectric conversion material and method of producing the same
ActiveUS20120085977A1High phonon-scattering effectLow thermal conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentOxidation-Reduction AgentRedox
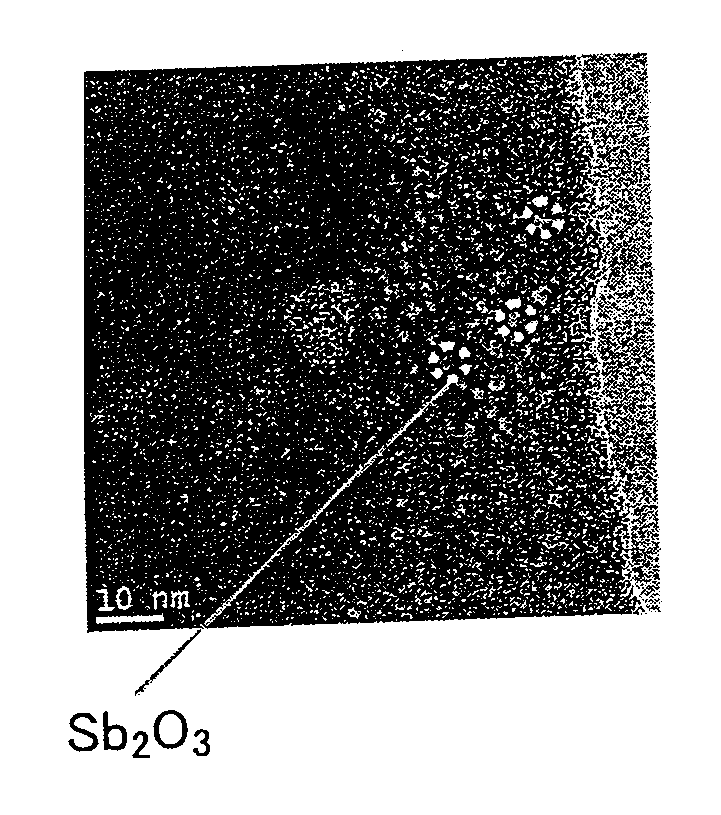
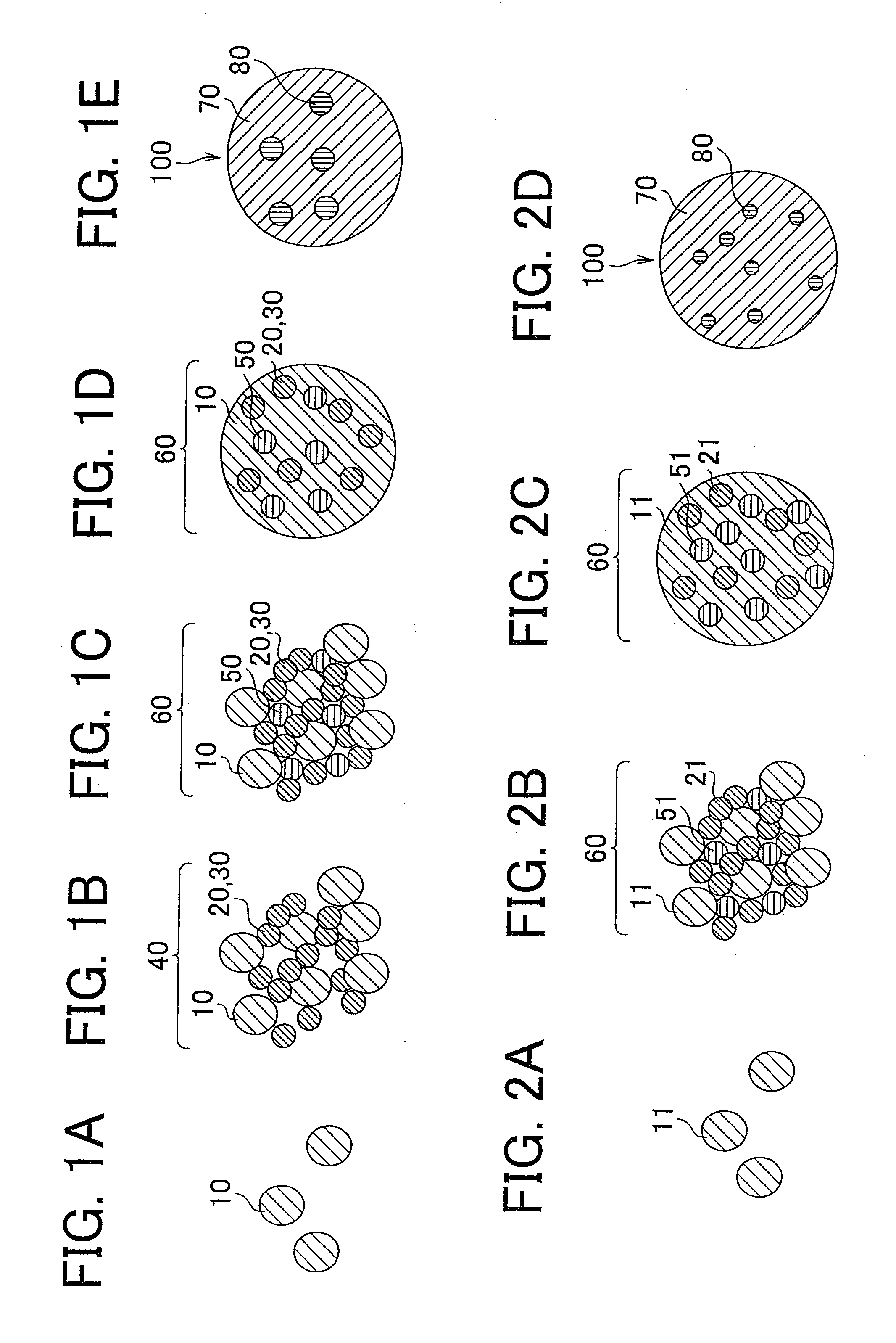
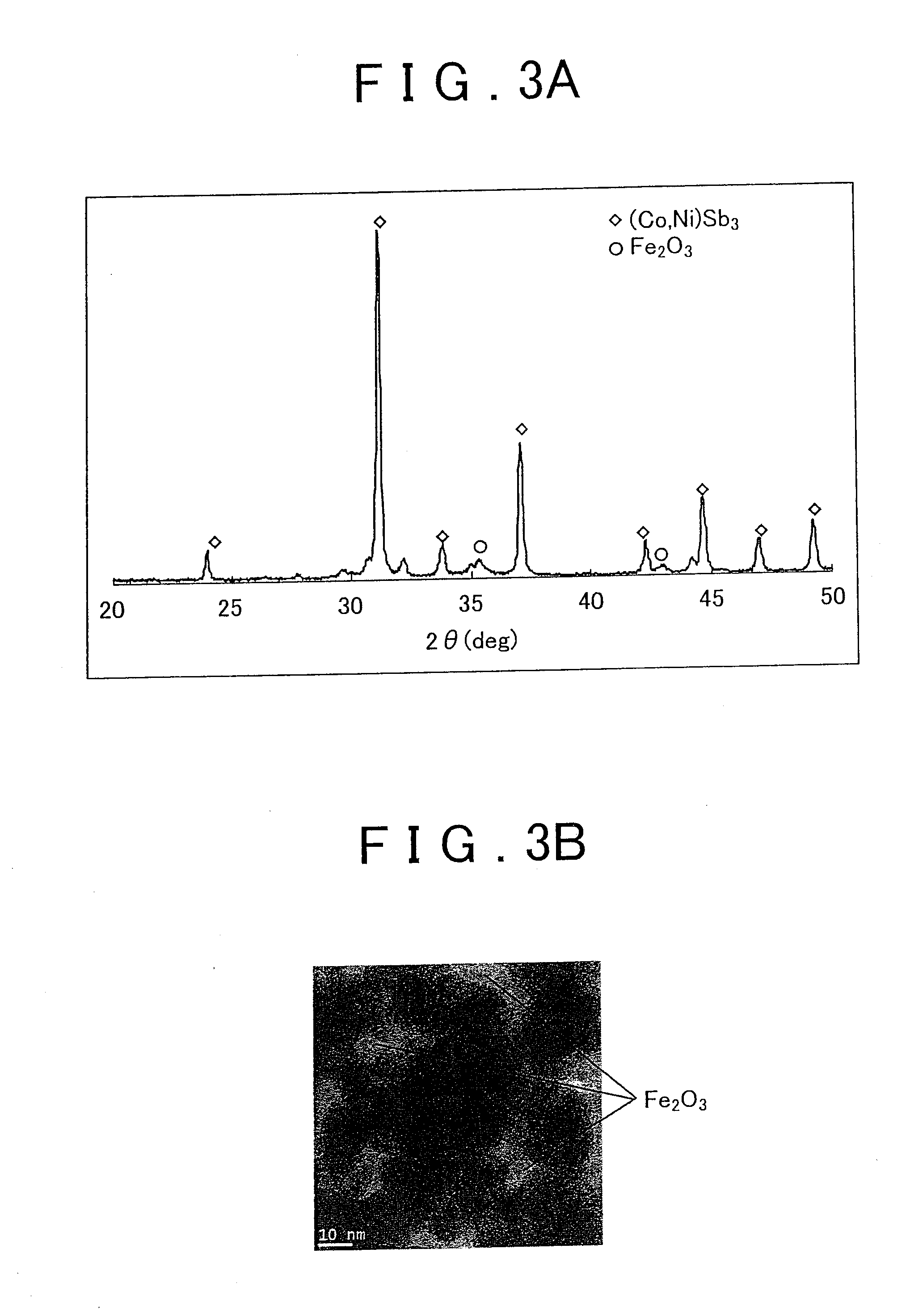
A method of producing a nanocomposite thermoelectric conversion material includes preparing a solution that contains salts of a plurality of first elements constituting a thermoelectric conversion material, and a salt of a second element that has a redox potential lower than redox potentials of the first elements; precipitating the first elements, thereby producing a matrix-precursor that is a precursor of a matrix made of the thermoelectric conversion material, by adding a reducing agent to the solution; precipitating the second element in the matrix-precursor, thereby producing slurry containing the first elements and the second element, by further adding the reducing agent to the solution; and alloying the plurality of the first elements, thereby producing the matrix (70) made of the thermoelectric conversion material, and producing nano-sized phonon-scattering particles (80) including the second element, which are dispersed in the matrix (70), by filtering and washing the slurry, and then, heat-treating the slurry.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
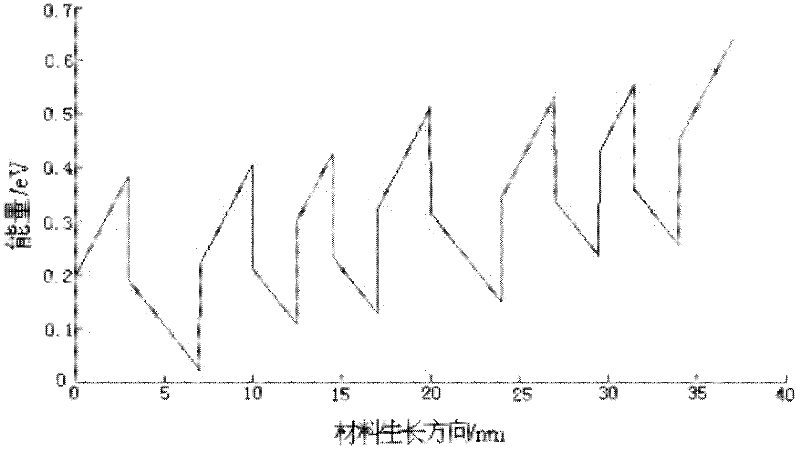
Nanostructured thermoelectric material and device and production method thereof
InactiveCN101969096AHigh crystallinityOvercoming the reduced case of quantum confinement effectsThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric device detailsThermoelectric materialsNano structuring
The invention discloses a nanostructured thermoelectric material, a nanostructured thermoelectric device and a production method thereof. The thermoelectric material comprises an insulating substrate and a nanostructured thermoelectric membrane, wherein the nanostructured thermoelectric membrane is composed of at least two nano-thickness thermoelectric material layers and at least two phonon scattering layers, and the thermoelectric material layers and the phonon scattering layers are overlapped alternately. The thermoelectric material can be a p-type thermoelectric material or an n-type thermoelectric material, which depends on the type of charge carrier of the thermoelectric material layers. Connecting electrodes are plated between the thermoelectric membranes of a p-type nanostructured thermoelectric material and a n-type nanostructured thermoelectric material so as to form a thermoelectric pair; and then a plurality of thermoelectric pairs are connected in parallel or in series so as to form the thermoelectric device. The nanostructured thermoelectric material of the invention has the advantages of good thermal stability, high nanostructured membrane deposition efficiency, high thermoelectric conversion efficiency, and lower cost; and the nanostructured thermoelectric device has the advantages of simple structure, easy preparation, low internal resistance, and great practical value in the fields such as refrigeration / calorification or temperature differential power generation, and the like.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Nano-particle electromagnetic interference prevention thermal barrier coating and manufacture method thereof
InactiveCN105063544AImprove insulation performanceWith anti-electromagnetic interferenceMolten spray coatingPlasma jetPorosity
The invention discloses a nano-particle electromagnetic interference prevention thermal barrier coating. Compared with a traditional thermal barrier coating, carbon dust is added; the porosity of a ceramic phase can be improved after high-temperature calcination modification; in a spraying process, part of particles are not melted fully in a plasma jet, so that the deformation degree of the particles is lower during impact on a base, and porous structures in lap joint with one another can be easily formed; and therefore the heat-insulating property of the coating can be obviously improved. Furthermore, according to the nano-particle electromagnetic interference prevention thermal barrier coating disclosed by the invention, by adopting the modification method, Zr<4+> in a zirconium dioxide crystal lattice is replaced by Y<3+> and Ce<4+>, so that oxygen vacancies and a partial stress field are formed; phonon scattering in the crystal lattice is increased; the heat conductivity is obviously lowered; besides, the atomic weight of the solid solution atom Ce is much greater than that of Y, so that the scattering intensity of phonons in the product can be obviously improved, and accordingly the heat conductivity is reduced. The manufacture process disclosed by the invention is simple, and the manufactured coating has an electromagnetic interference prevention property, a fused salt corrosion prevention property and a good thermal shock property.
Owner:MAANSHAN LANKE REMFG TECH
Thermal barrier coating with abrasion resisting function and manufacturing method of thermal barrier coating
InactiveCN105063542AHigh porosityImprove insulation performanceMolten spray coatingPlasma jetPorosity
The invention discloses a thermal barrier coating with the abrasion resisting function. Compared with a traditional thermal barrier coating, carbon powder is added, and is sintered and modified at the high temperature, and the porosity of a ceramic phase can be increased. In the spraying process, part of particles are not smelted sufficiently in plasma jet flow, when a base body is subjected to the impact, the deformation degree is slightly weak, porous structures in lap joint together are easily formed, and the thermal insulation performance of the coating is obviously improved. In addition, by means of the modification method, Zr4+ is replaced by Y3+ and Ce4+ in a zirconium dioxide crystal lattice and the oxygen vacancy and the local stress field are generated. The phonon scattering in the crystal lattice is increased, and the thermal conductivity is obviously reduced. The atomic weight of the solid solution atom Ce is far larger than that of Y, the scattering strength of phonons in the coating can be obviously improved, and therefore the thermal conductivity is reduced. The thermal barrier coating is simple in preparing technology. The prepared coating has the beneficial effects of being high in porosity, resistant to abrasion, low in water absorbing rate, good in tenacity, not prone to cracking or layering and the like.
Owner:MAANSHAN LANKE REMFG TECH
Nanocomposite thermoelectric conversion material and method of producing the same
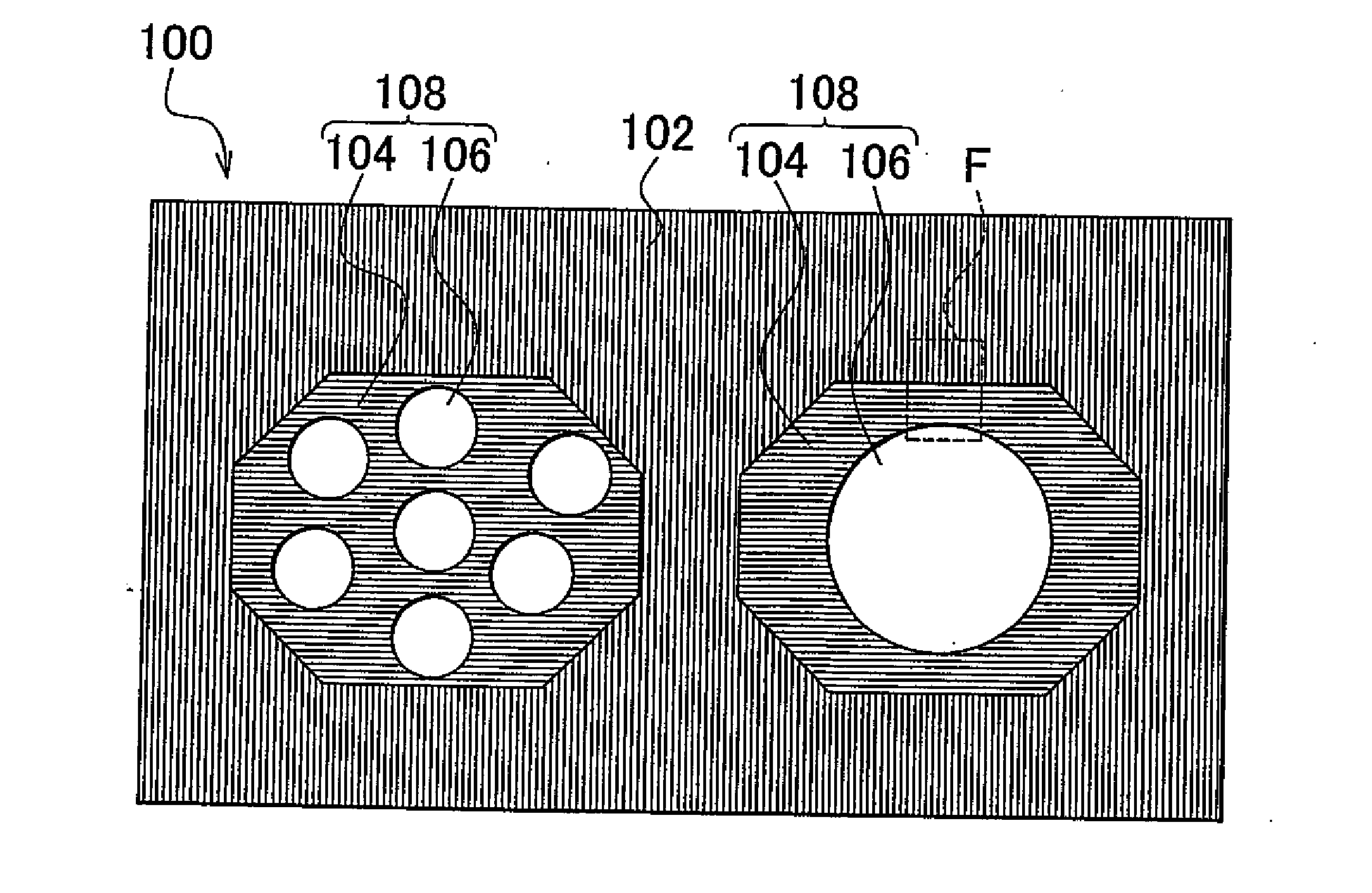
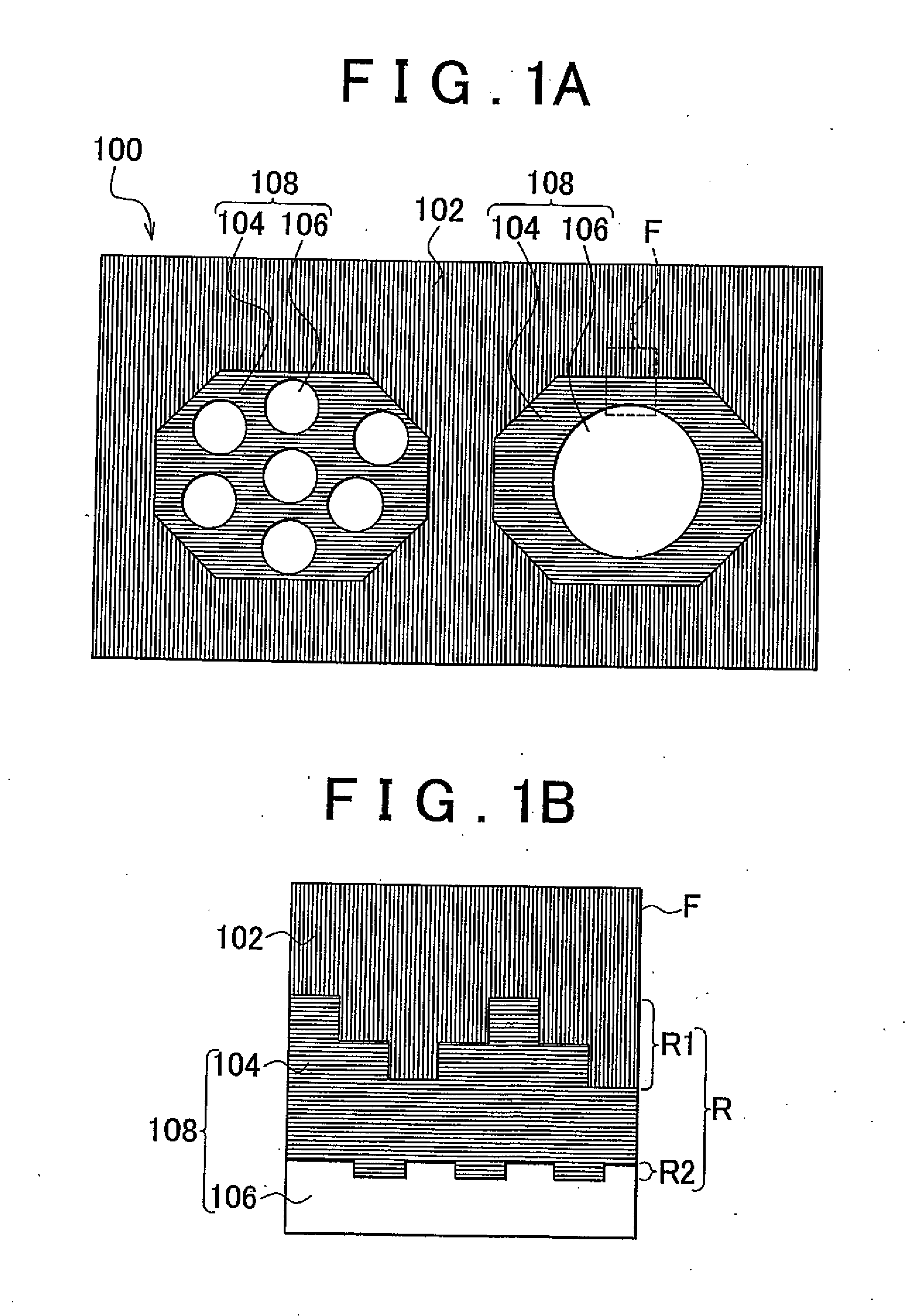
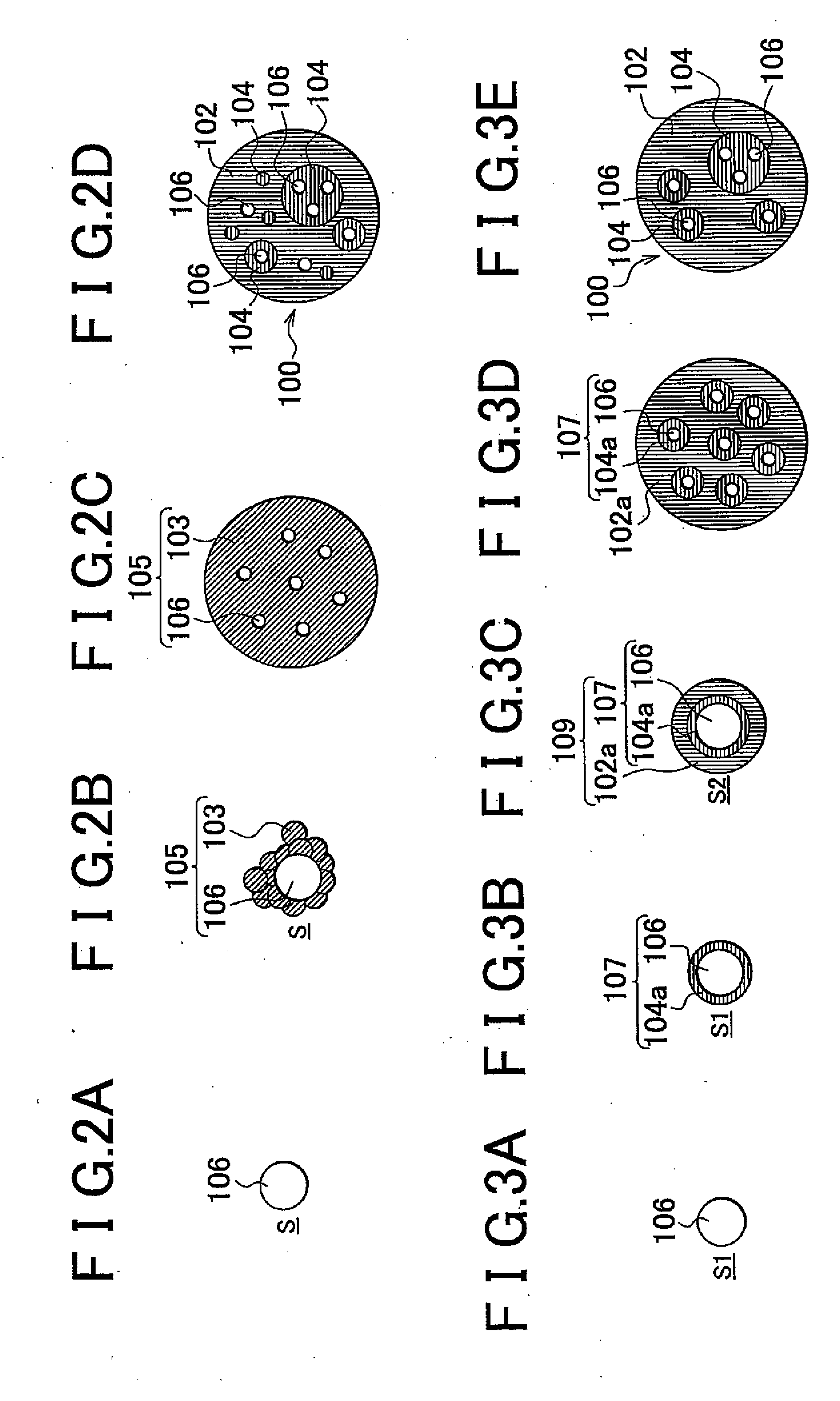
InactiveUS20120217447A1Novel structureLow thermal conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyConductive materialNanoparticleCrystal structure
A nanocomposite thermoelectric conversion material (100) includes a crystalline matrix (102) made of a thermoelectric conversion material; and phonon-scattering particles (108) dispersed in the crystalline matrix (102). Each phonon-scattering particle (108) includes at least one amorphous nanoparticle (106) coated with a crystalline film (104) having a nano-order thickness, and the crystalline structure of the crystalline film (104) is different from the crystalline structure of the thermoelectric conversion material. The nanocomposite thermoelectric conversion material (100) is produced by i) precipitating a matrix-precursor oversaturated with one element of the thermoelectric conversion material, around the amorphous nanoparticles, thereby producing nanocomposite particles, and heat-treating the nanocomposite particles, or ii) by precipitating only one element of the thermoelectric conversion material around the amorphous nanoparticles, thereby producing first nanocomposite particles, and then, precipitating the matrix-precursor made of the thermoelectric conversion material, around the first nanocomposite particles, thereby producing second nano composite particles, and heat-treating the second nanocomposite particles.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com