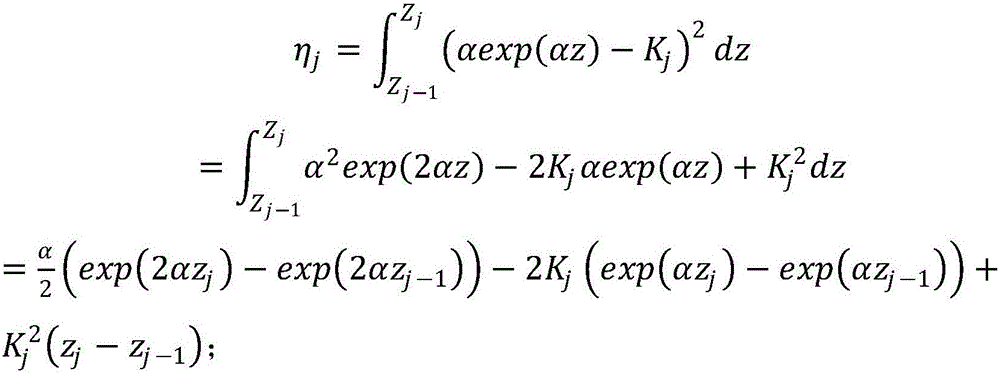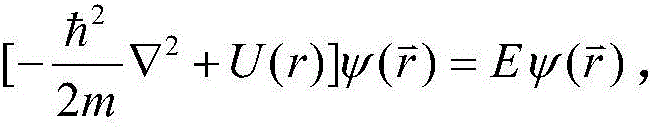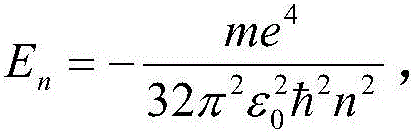Patents
Literature
40 results about "Schrödinger equation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Schrödinger equation is a linear partial differential equation that describes the wave function or state function of a quantum-mechanical system. It is a key result in quantum mechanics, and its discovery was a significant landmark in the development of the subject. The equation is named after Erwin Schrödinger, who postulated the equation in 1925, and published it in 1926, forming the basis for the work that resulted in his Nobel Prize in Physics in 1933.
Idea model device, spontaneous feeling model device, method thereof, and program
ActiveUS20060167694A1Increase probabilityReduce probabilitySpeech analysisUnstructured textual data retrievalPattern recognitionSchrödinger equation
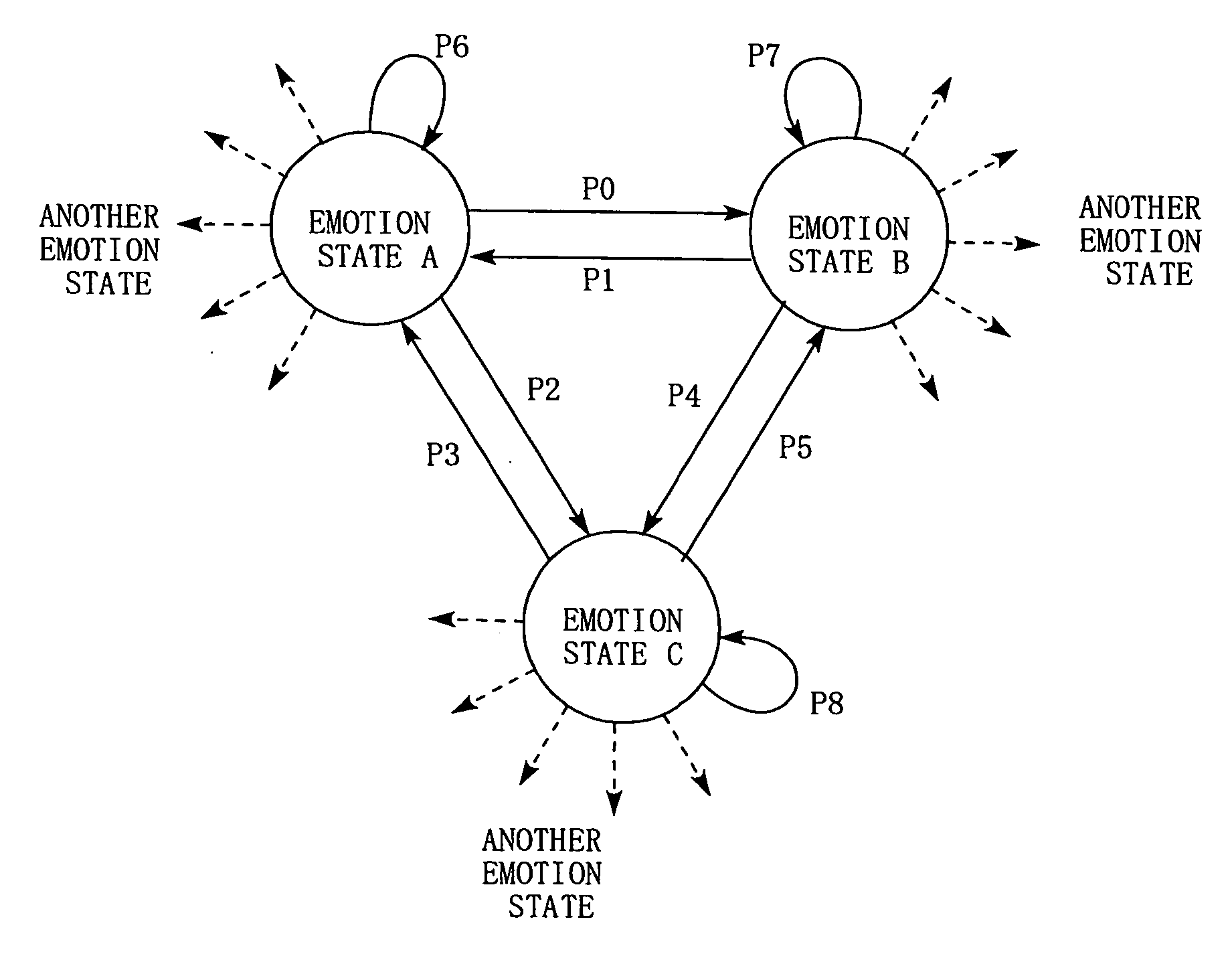
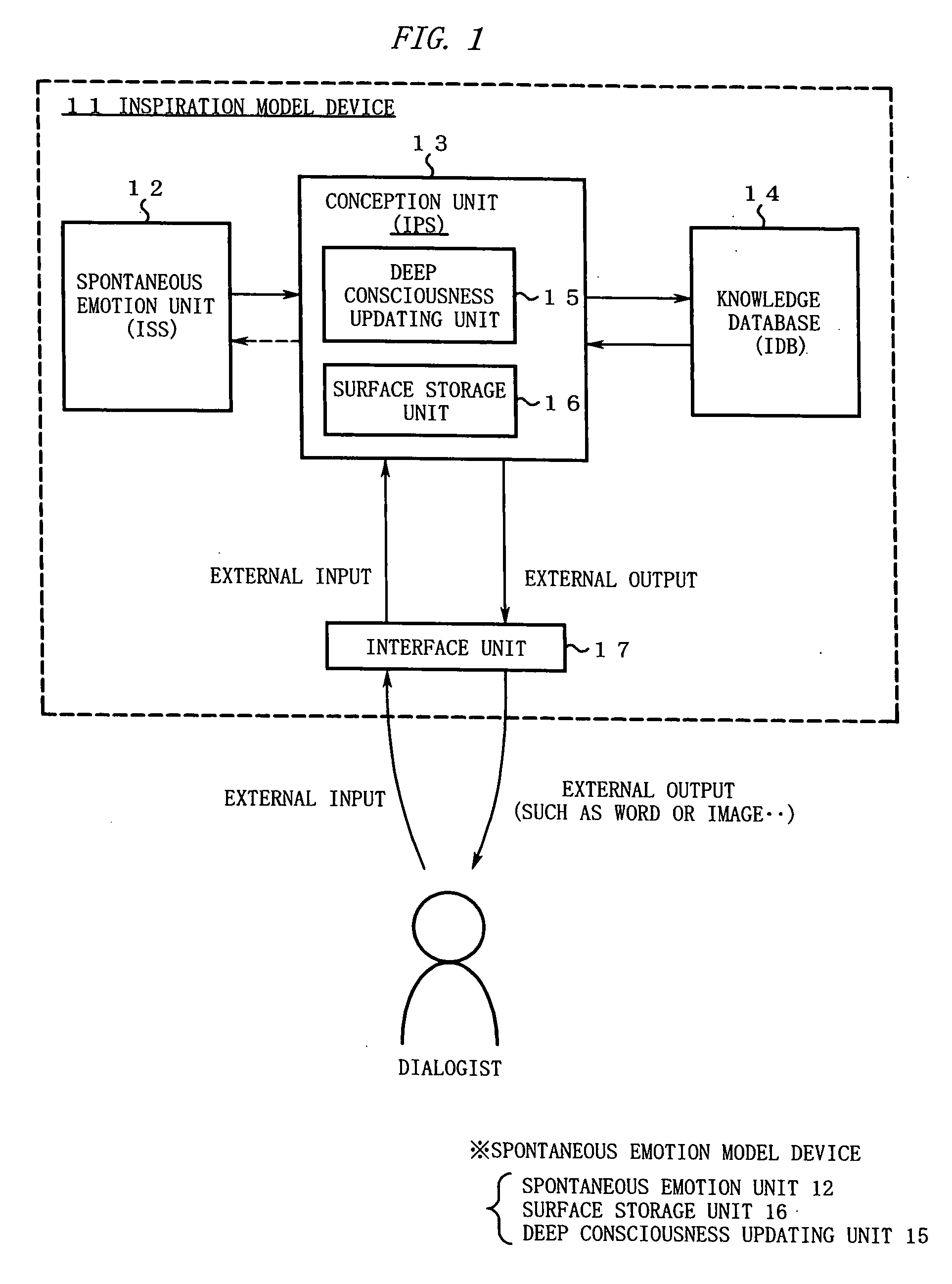
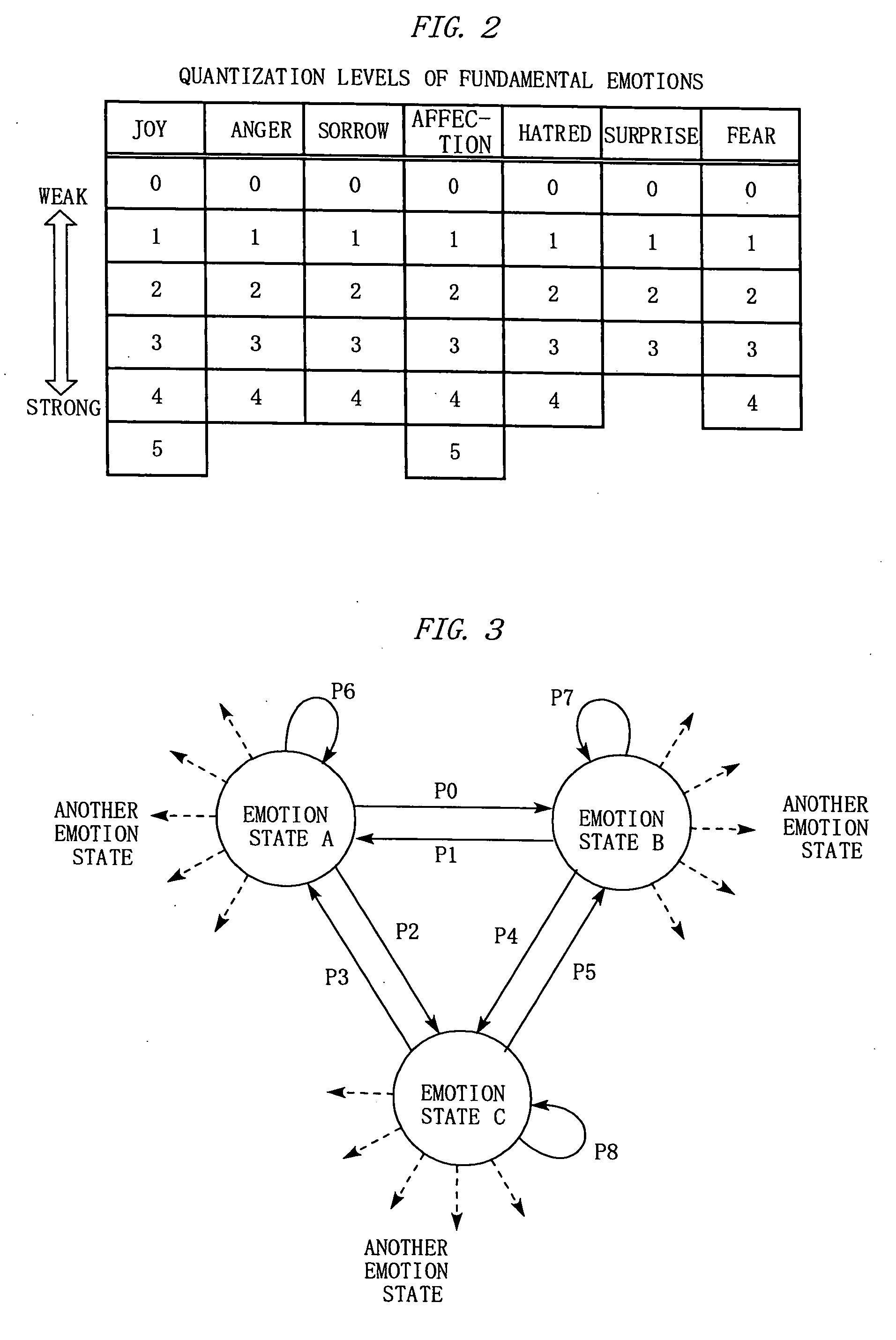
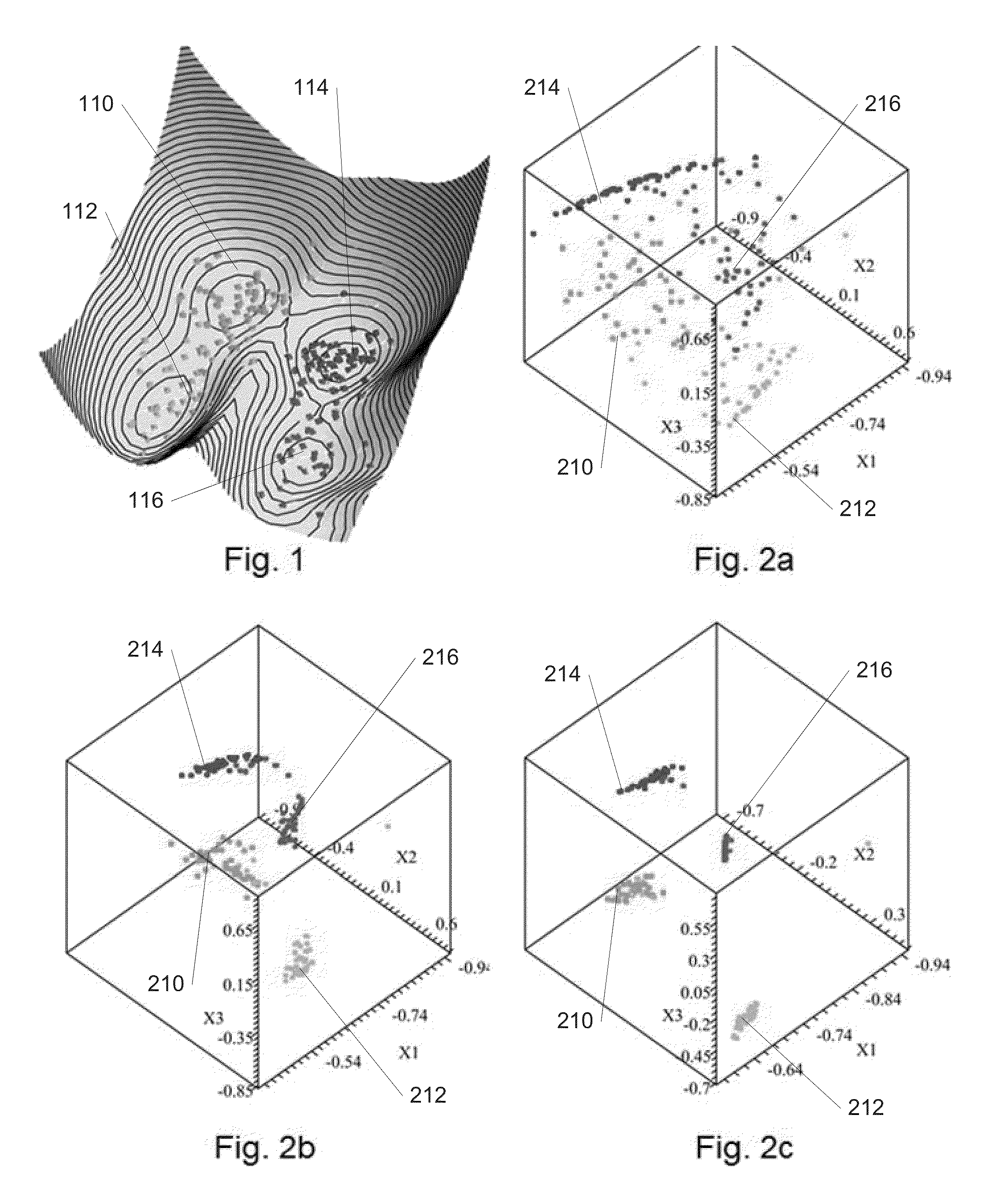
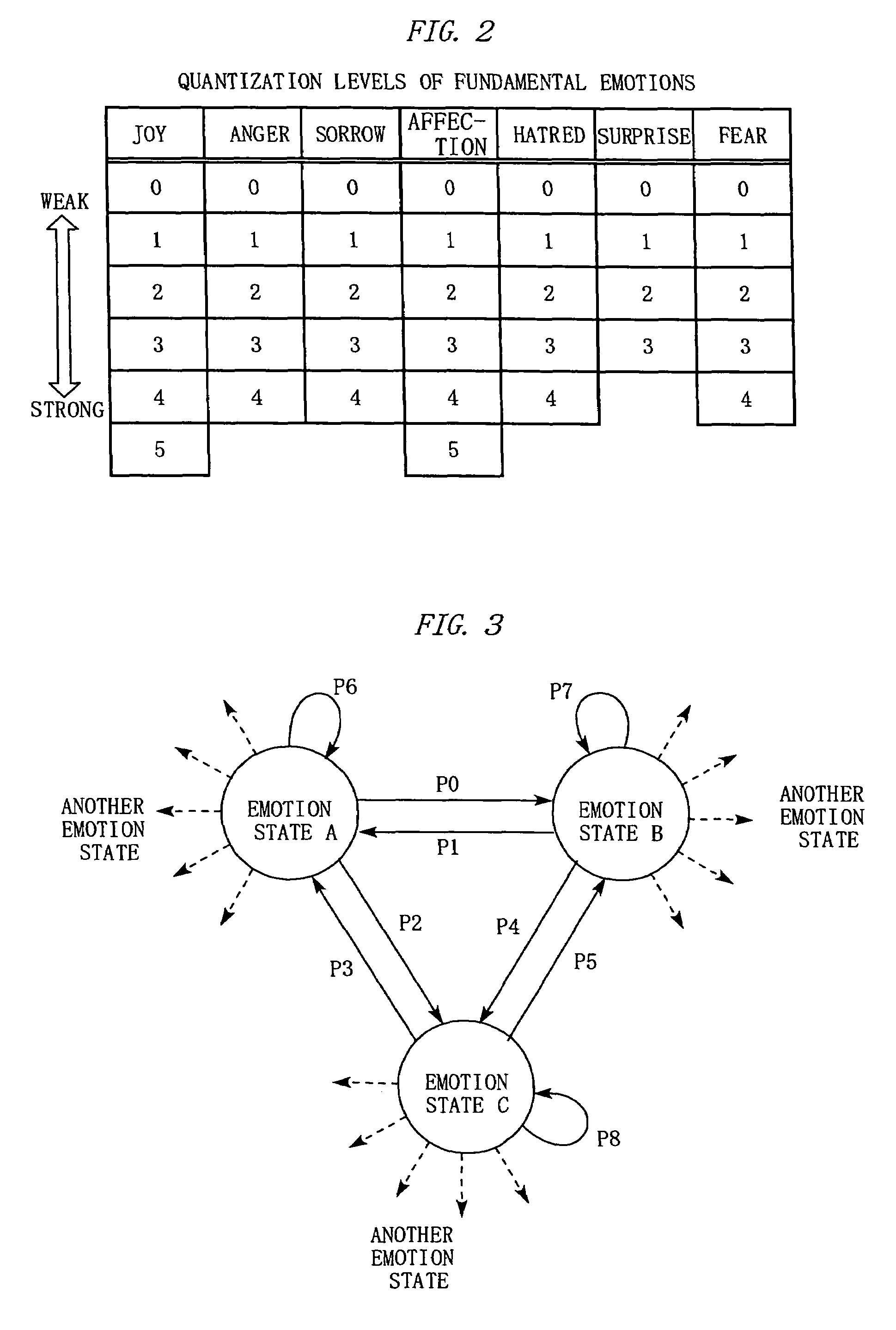
An inspiration model device according to the invention is provided with a spontaneous emotion unit, a knowledge database, and a conception unit. The spontaneous emotion unit prepares, as data, plural emotion states in advance, which are obtained by modeling human emotions, and causes state transitions to occur repeatedly between the emotion states according a stochastic model of the Schrödinger equation. The knowledge database simulates a human inspiration source that is influenced by sensibility by classifying externally collected knowledge data depending on the degrees of correlation with the emotion states, and accumulates the knowledge data. When receiving an external input, the conception unit simulates human conception by combining the external input with an emotion state of the spontaneous emotion unit and searching the knowledge database for related knowledge data using, as a search key, the combination or the like.
Owner:AGI INC
Systems and methods for determining optimal parameters for dynamic quantum clustering analyses
ActiveUS20150046457A1Reduce dimensionalityDigital data processing detailsRelational databasesSingular value decompositionCoherent states
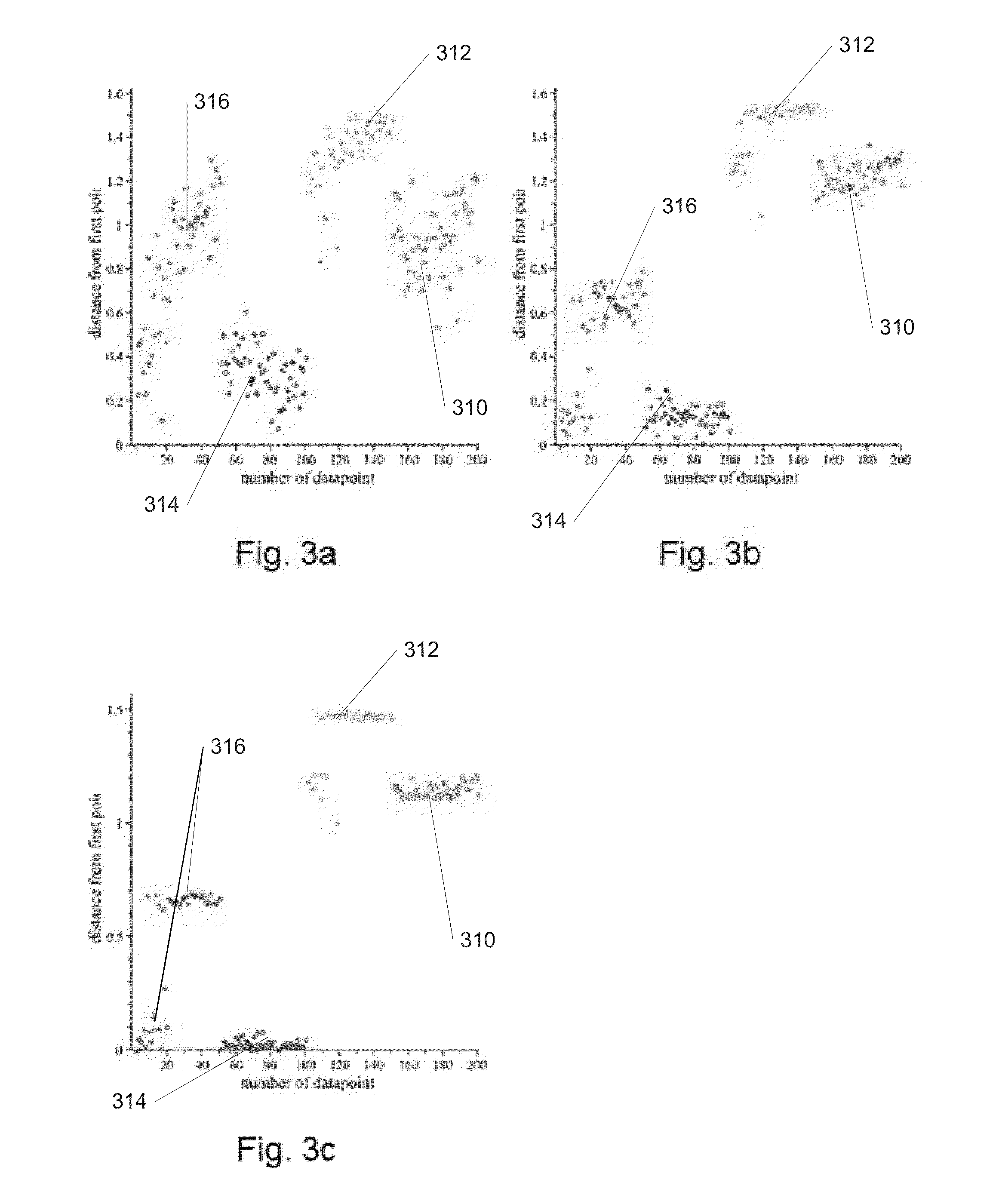
In the present work, quantum clustering is extended to provide a dynamical approach for data clustering using a time-dependent Schrödinger equation. To expedite computations, we can approximate the time-dependent Hamiltonian formalism by a truncated calculation within a set of Gaussian wave-functions (coherent states) centered around the original points. This allows for analytic evaluation of the time evolution of all such states, opening up the possibility of exploration of relationships among data points through observation of varying dynamical-distances among points and convergence of points into clusters. This formalism may be further supplemented by preprocessing, such as dimensional reduction through singular value decomposition and / or feature filtering. Additionally, the parameters of the analysis can be modified in order to improve the efficiency of the dynamic quantum clustering processes.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Inspiration model device, spontaneous emotion model device, and related methods and programs
ActiveUS7664627B2Speech analysisUnstructured textual data retrievalPattern recognitionSchrödinger equation
An inspiration model device according to the invention is provided with a spontaneous emotion unit, a knowledge database, and a conception unit. The spontaneous emotion unit prepares, as data, plural emotion states in advance, which are obtained by modeling human emotions, and causes state transitions to occur repeatedly between the emotion states according a stochastic model of the Schrödinger equation. The knowledge database simulates a human inspiration source that is influenced by sensibility by classifying externally collected knowledge data depending on the degrees of correlation with the emotion states, and accumulates the knowledge data. When receiving an external input, the conception unit simulates human conception by combining the external input with an emotion state of the spontaneous emotion unit and searching the knowledge database for related knowledge data using, as a search key, the combination or the like.
Owner:AGI INC
Stock price trend prediction method based on quantum mechanics and social network
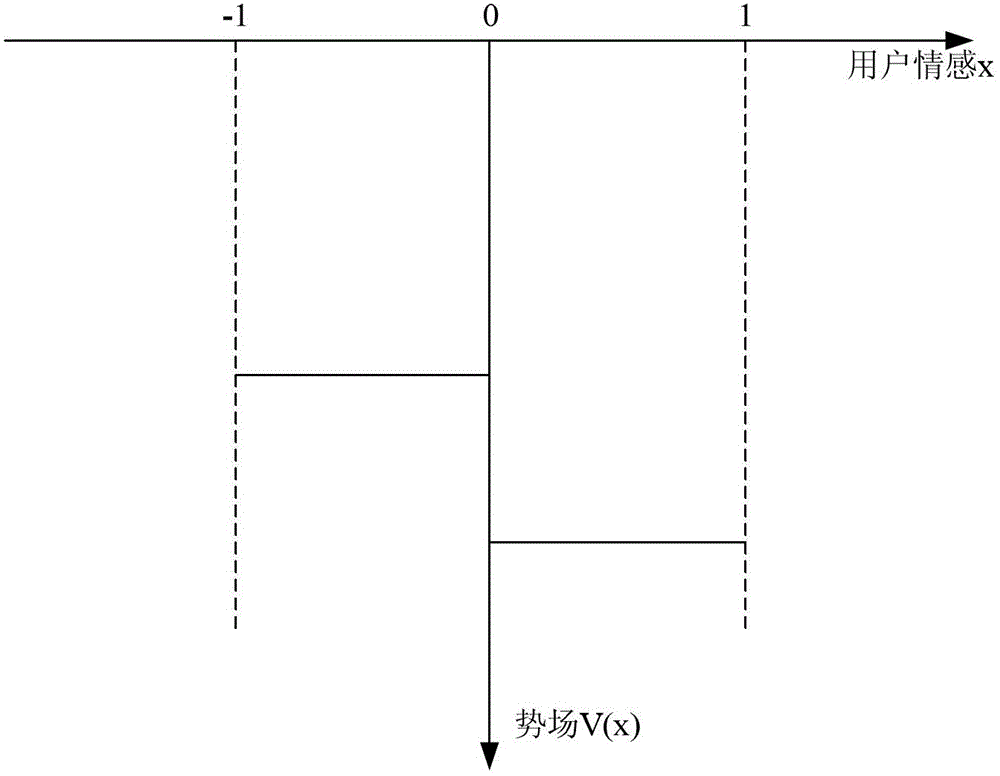
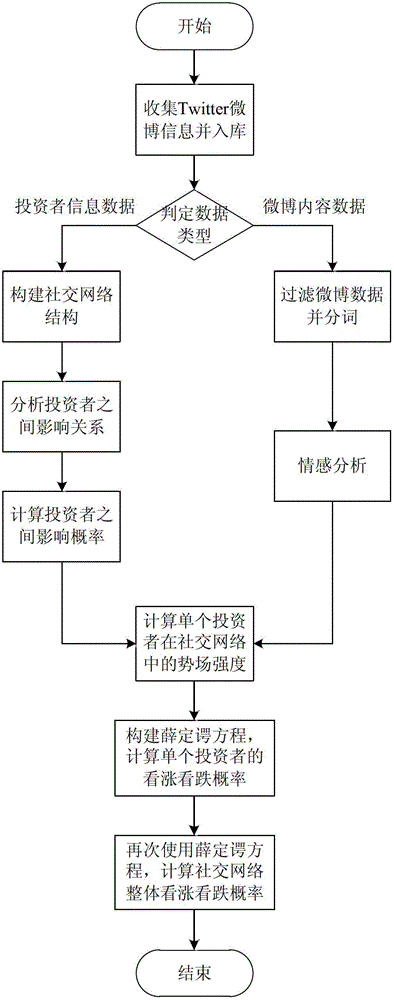
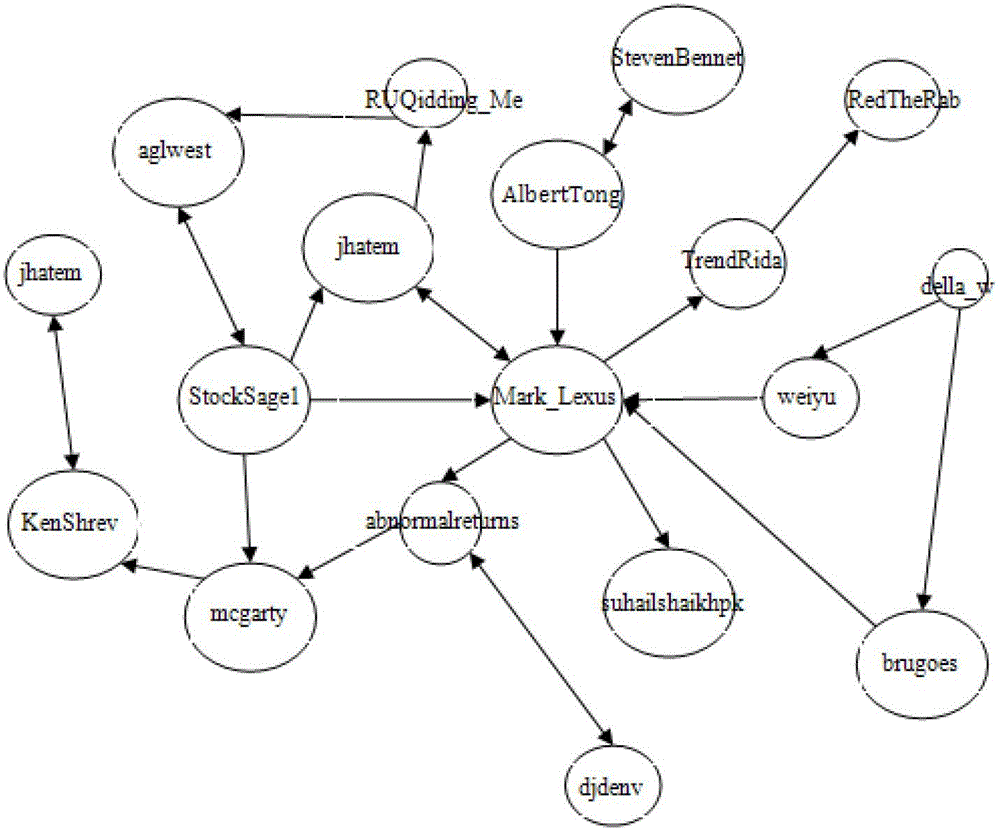
ActiveCN103049804APredicting Sentiment ProbabilityPredict the trend of ups and downsFinanceForecastingPotential wellSchrödinger equation
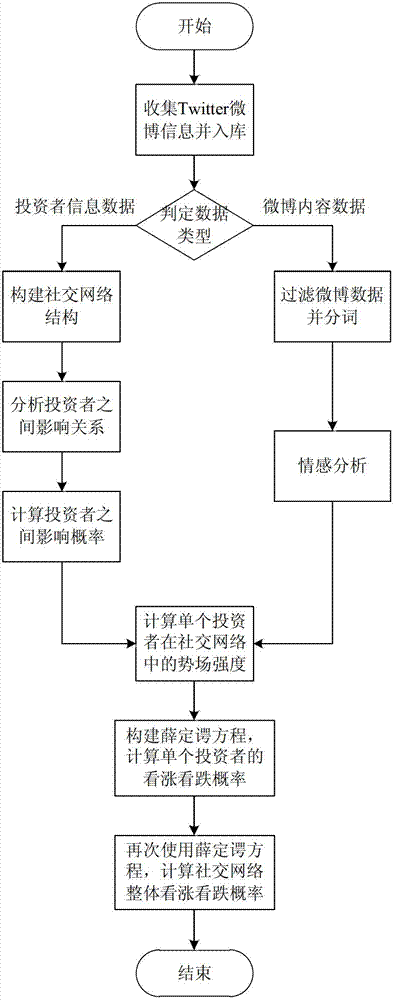
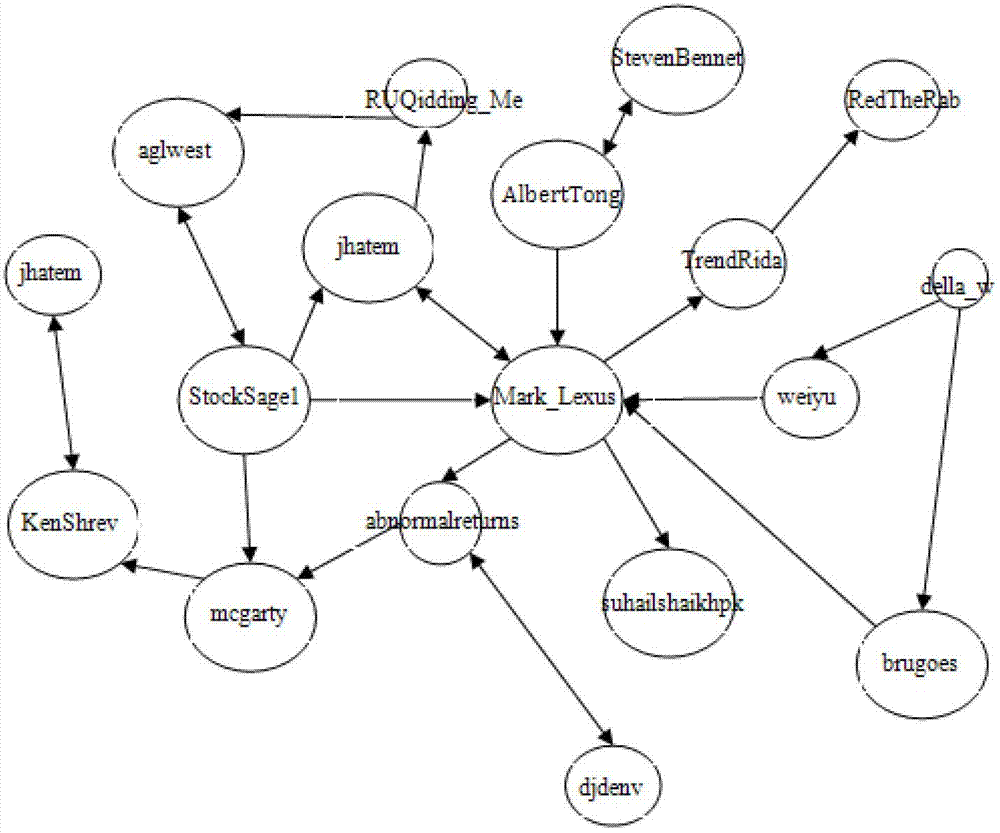
The invention discloses a stock price trend prediction method based on the quantum mechanics and the social network. The micro particle characteristics of an individual investor affective decision in the social network are fully considered, the wave function and the operator of the individual decision in the network are defined, the influence relation between individuals in the social network is simulated by a segmented infinite potential well, the emotion of a single investor is predicted by a schrodinger equation and is overlaid by the emotion in the social network, the stock price variation trend is described, and the quantum mechanics model of the social network can be used for effectively improving the stock price trend prediction accuracy. The stock price trend prediction method based on the quantum mechanics and the social network has an important theoretical significance and economic value.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Optical pulse generating method capable of creating three-energy-level system quantum bit random superposition state
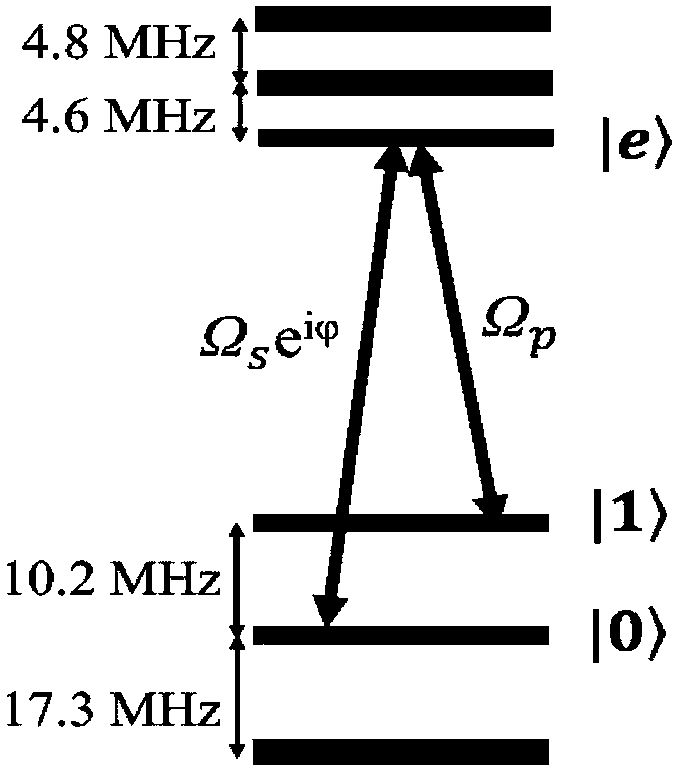
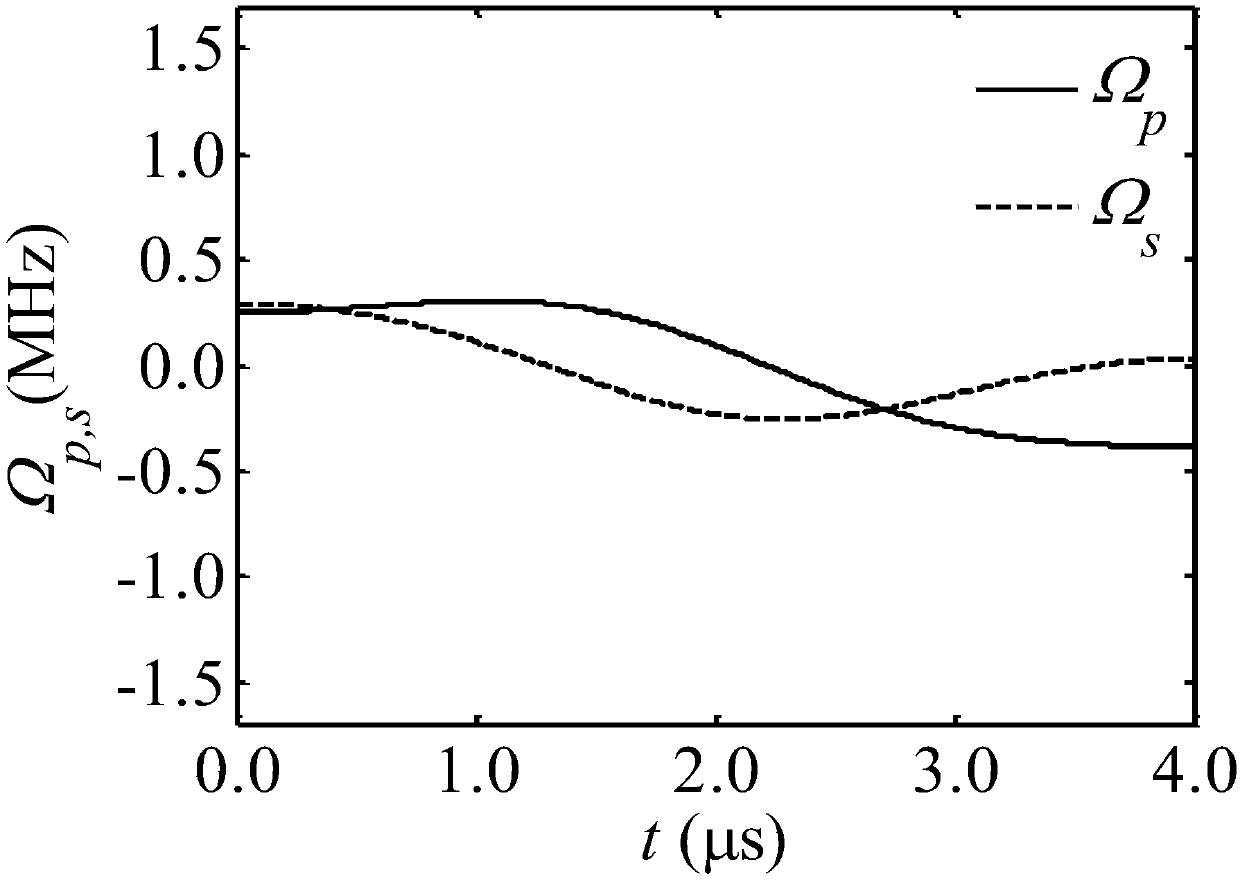
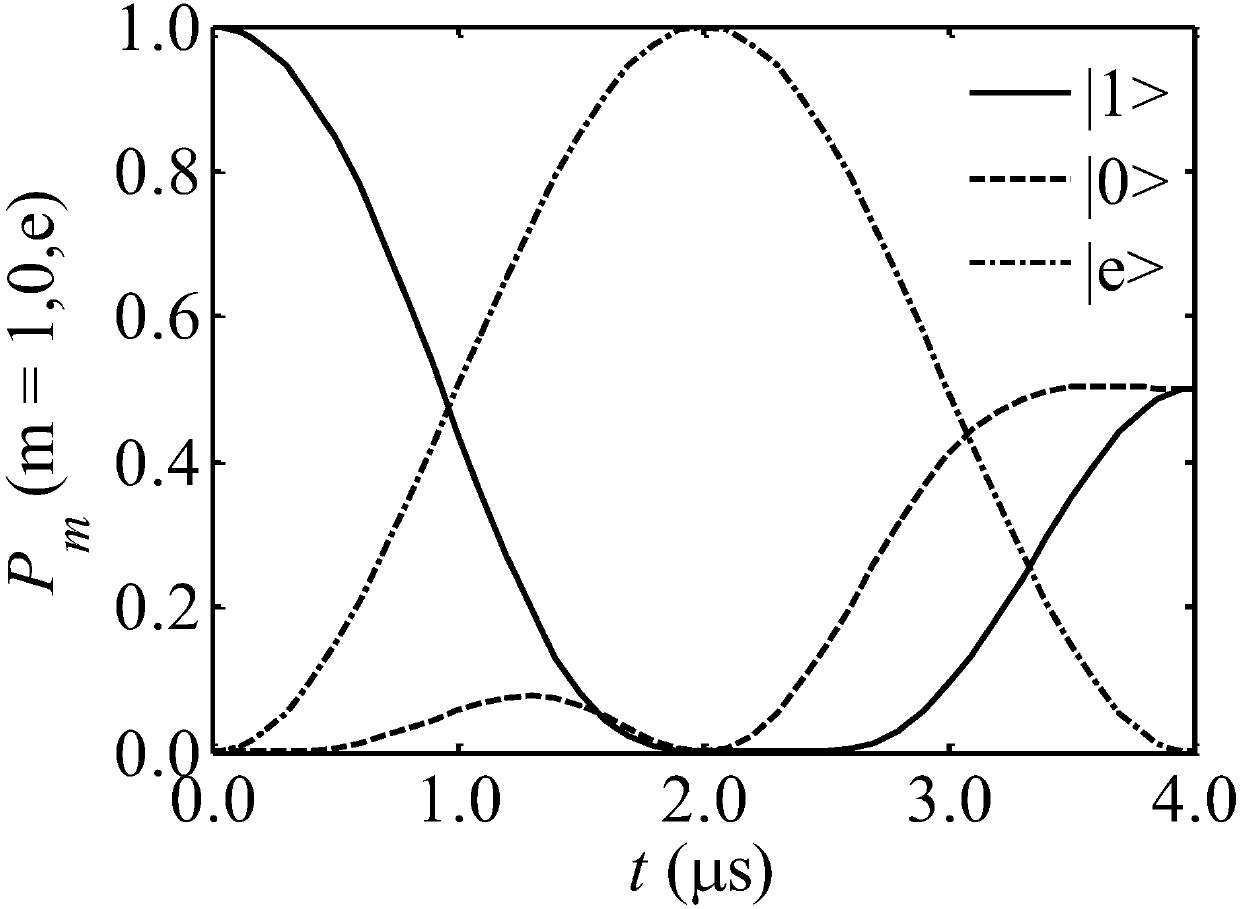
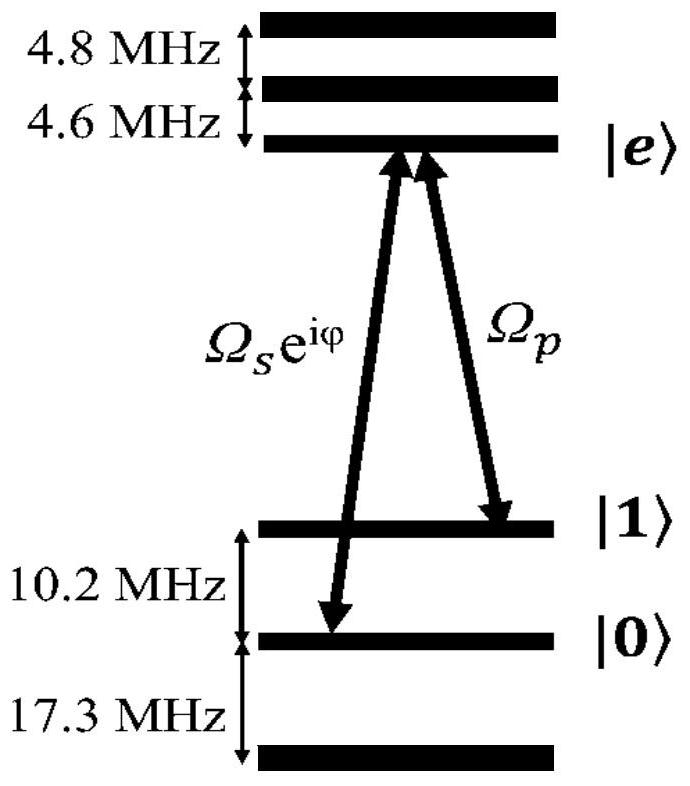
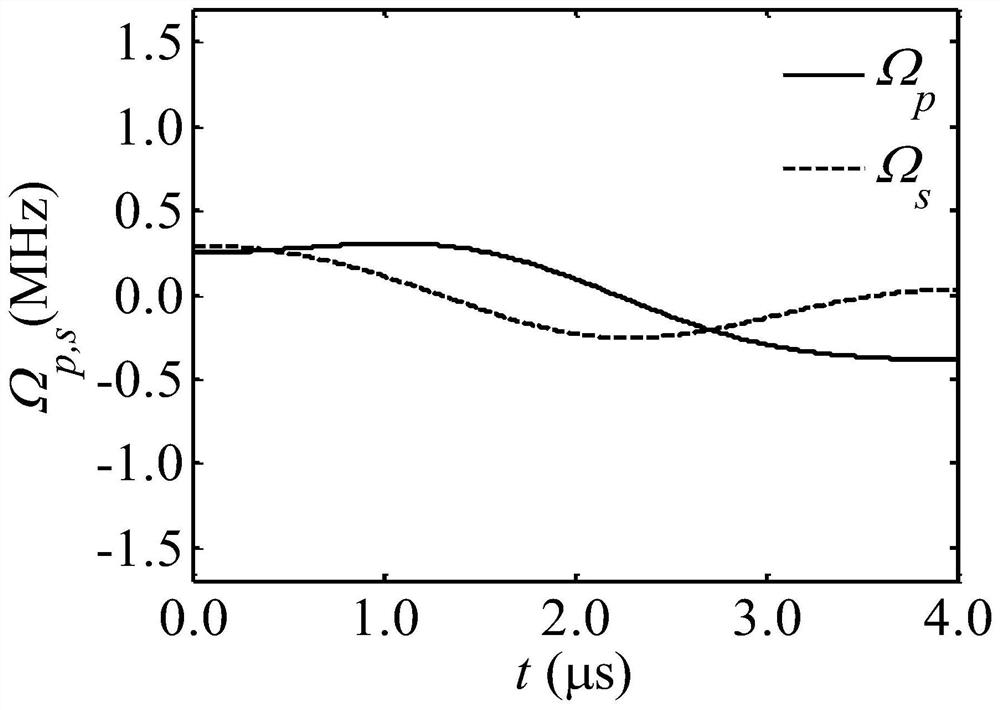
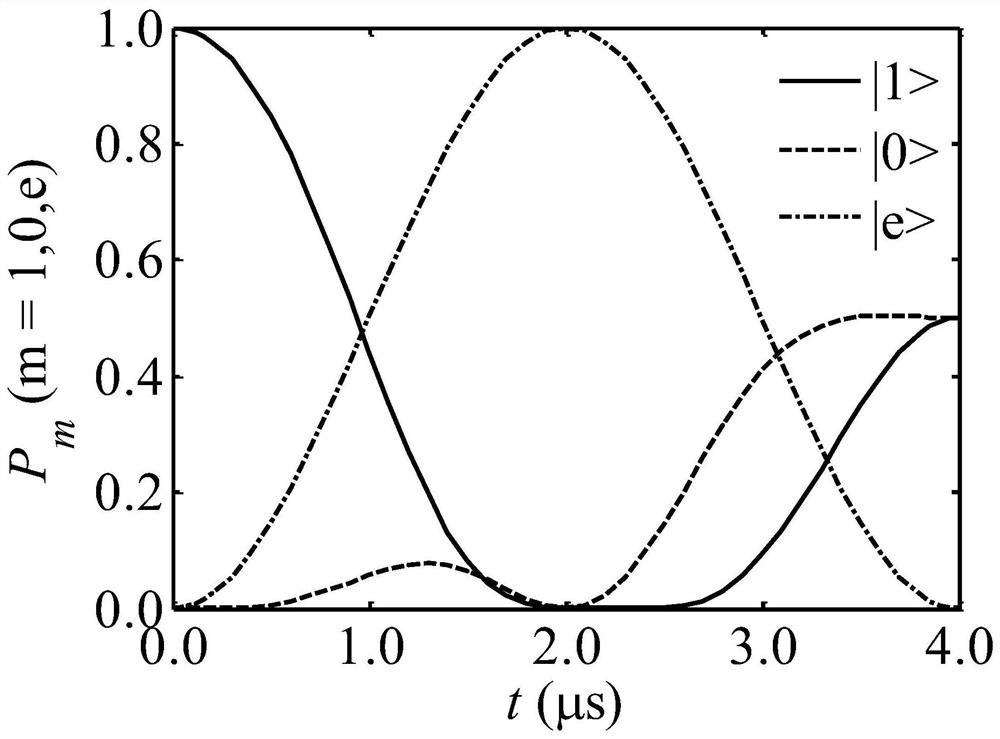
The invention discloses an optical pulse generating method capable of creating the three-energy-level system quantum bit random superposition state. An invariant theory is adopted to reversely solve atime-dependent Schrodinger equation of a three-energy-level system, field intensity information of a group of polychromatic optical pulses capable of generating the quantum bit random superposition state is constructed, an arbitrary wave generator and an acoustic and optical modulator are utilized to generate the polychromatic optical pulses, the extra degree of freedom in the polychromatic optical pulse field intensity is utilized to optimize the shape of the pulses, so that the pulses show robustness to the frequency detuning amount existing in the system, and have small-enough non-resonance excitation of background ions existing in the system, and thus the quantum bit random superposition state is created with the fidelity within a short acting time. By means of the optical pulse generating method, the optical pulses can generate the quantum bit random superposition state within the acting time of 4 microseconds, the fidelity within the frequency detuning amount range of + / -340 kHzis not lower than 99.5%, and the non-resonance excitation of the background ions does not exceed 2%.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV +1
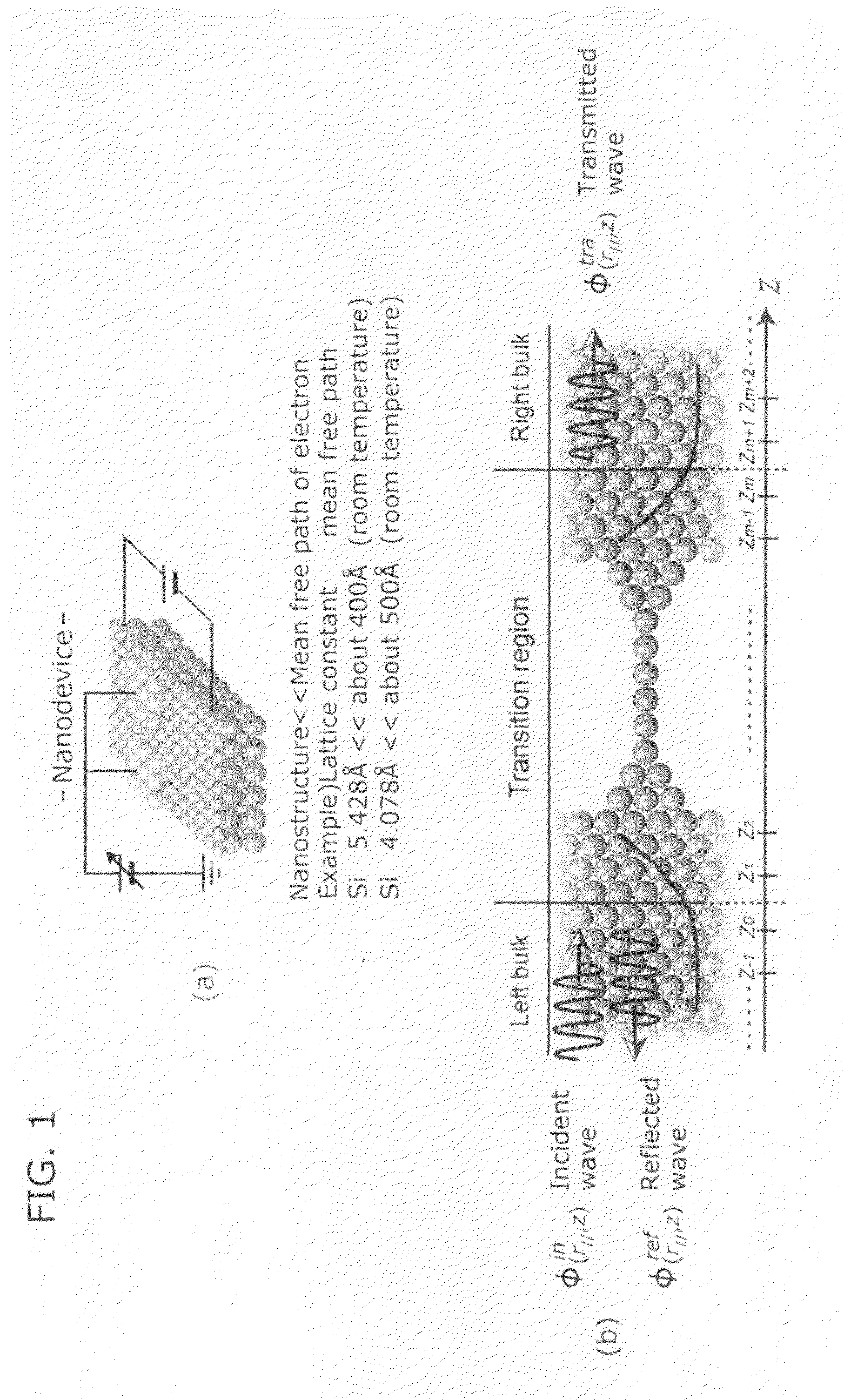
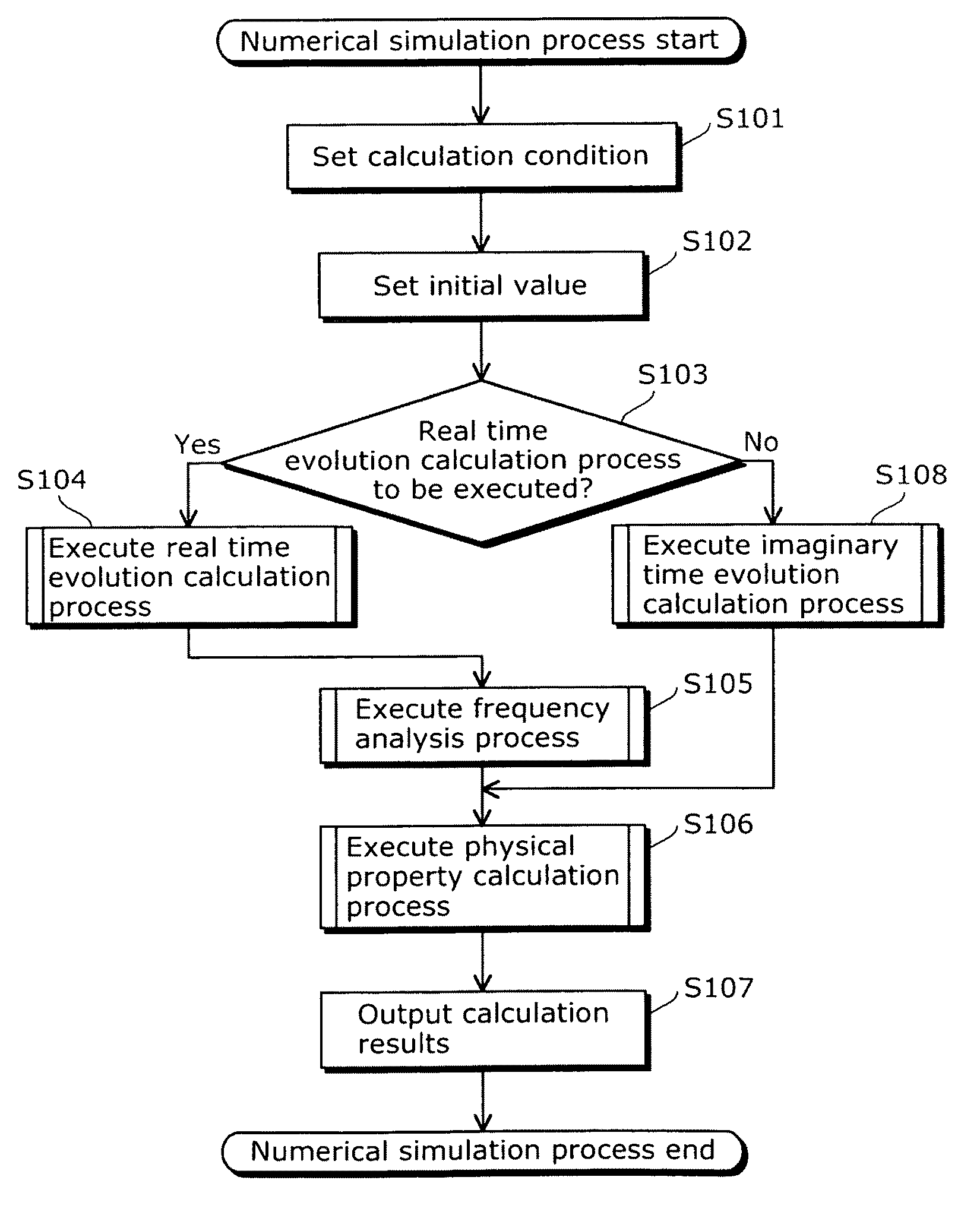
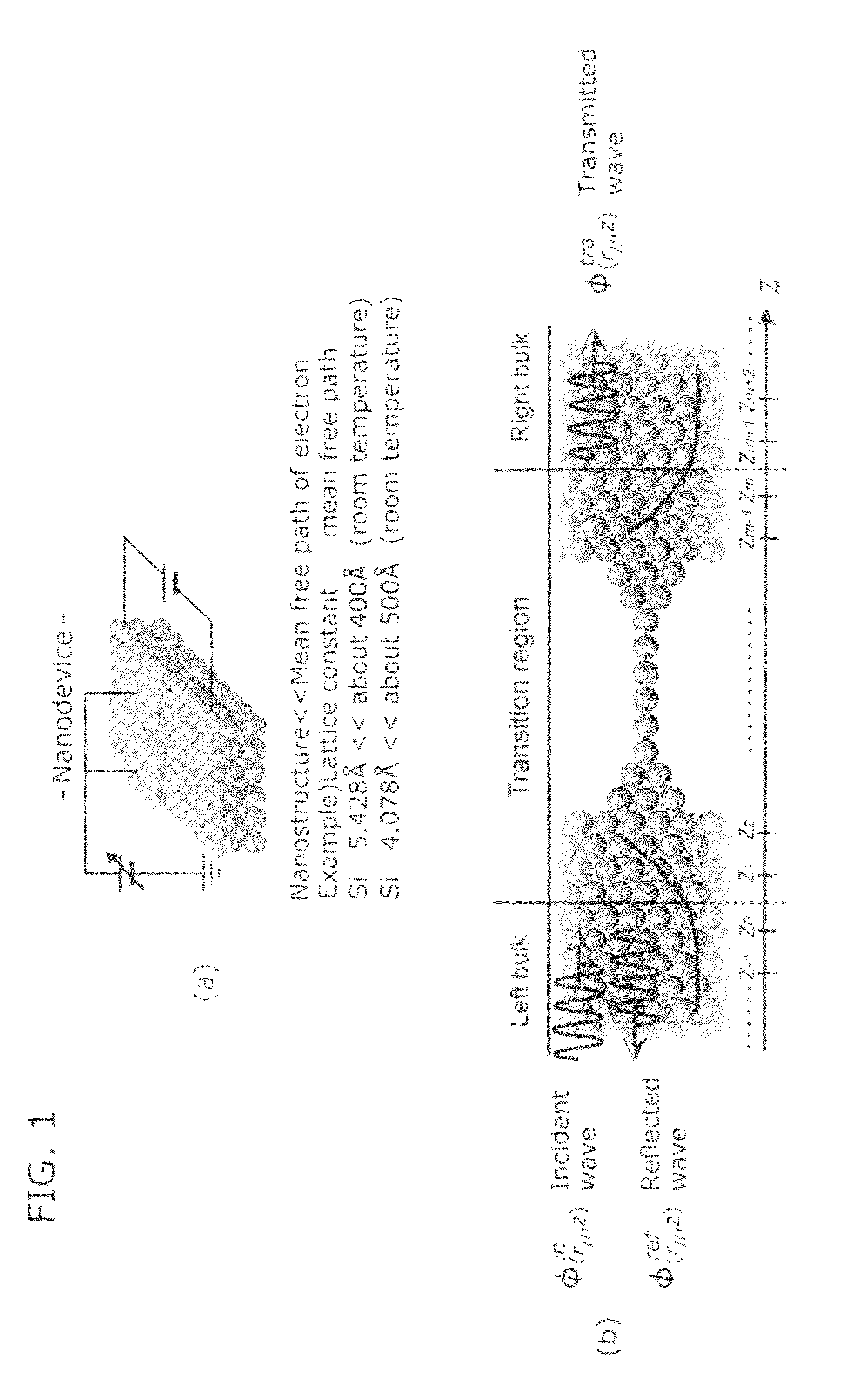
Numerical simulation apparatus for time dependent schrodinger equation
InactiveUS20090204375A1Increase speedHigh precisionComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationComputation complexitySchrödinger equation
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
Quantum mechanical model-based system and method for global optimization
InactiveUS7398162B2Minimizes energy expectationQuantum computersNanoinformaticsNormal densityMechanical models
A model-based system and method for global optimization that utilizes quantum mechanics in order to approximate the global minimum of a given problem (e.g., mathematical function). A quantum mechanical particle with a sufficiently large mass has a ground state solution to the Schrödinger Equation which is localized to the global minimum of the energy field, or potential, it experiences. A given function is modeled as a potential, and a quantum mechanical particle with a sufficiently large mass is placed in the potential. The ground state of the particle is determined, and the probability density function of the ground state of the particle is calculated. The peak of the probability density function is localized to the global minimum of the potential.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Systems and methods for determining optimal parameters for dynamic quantum clustering analyses
ActiveUS10169445B2Reduce dimensionalityRelational databasesCharacter and pattern recognitionSingular value decompositionCoherent states
In the present work, quantum clustering is extended to provide a dynamical approach for data clustering using a time-dependent Schrödinger equation. To expedite computations, we can approximate the time-dependent Hamiltonian formalism by a truncated calculation within a set of Gaussian wave-functions (coherent states) centered around the original points. This allows for analytic evaluation of the time evolution of all such states, opening up the possibility of exploration of relationships among data points through observation of varying dynamical-distances among points and convergence of points into clusters. This formalism may be further supplemented by preprocessing, such as dimensional reduction through singular value decomposition and / or feature filtering. Additionally, the parameters of the analysis can be modified in order to improve the efficiency of the dynamic quantum clustering processes.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
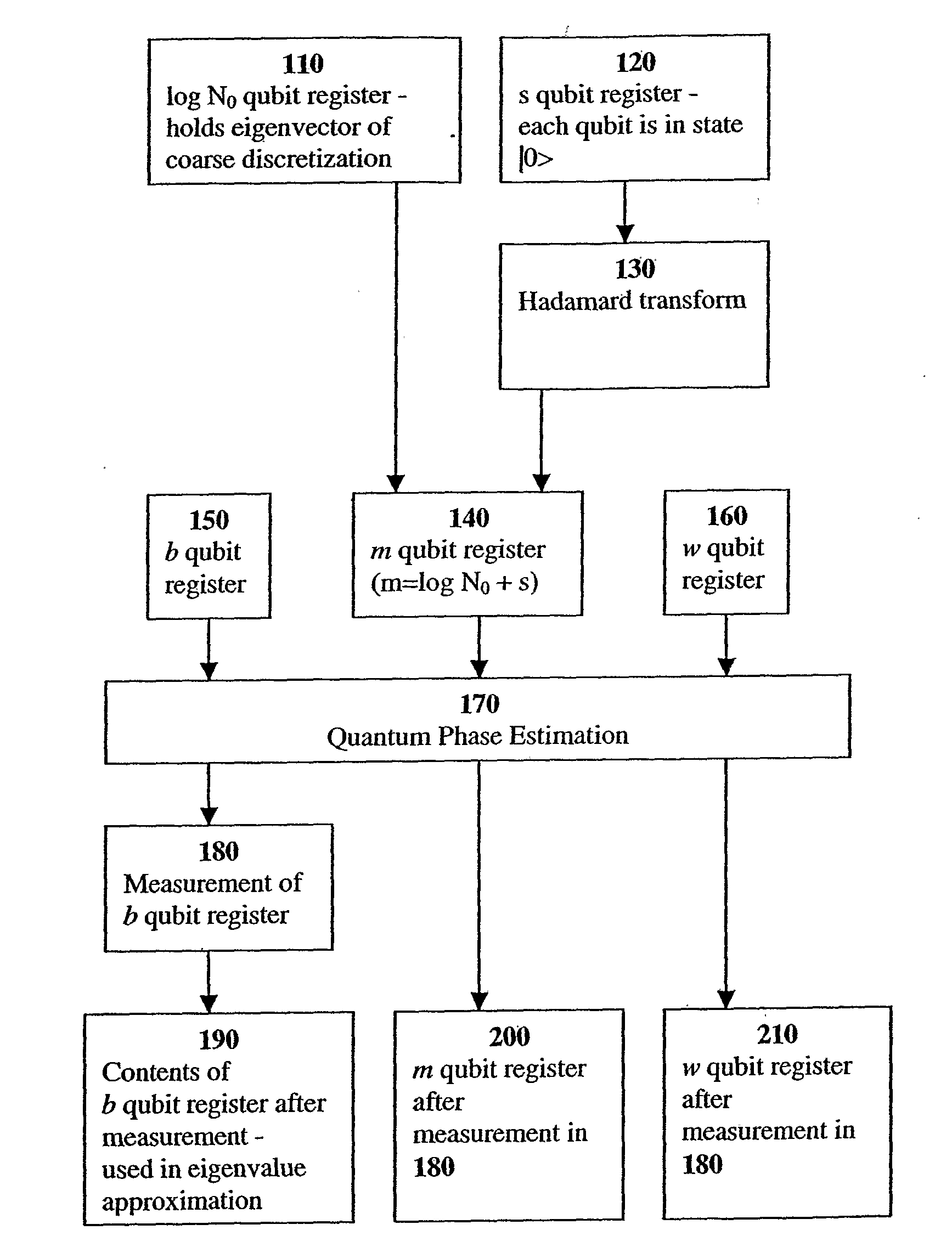
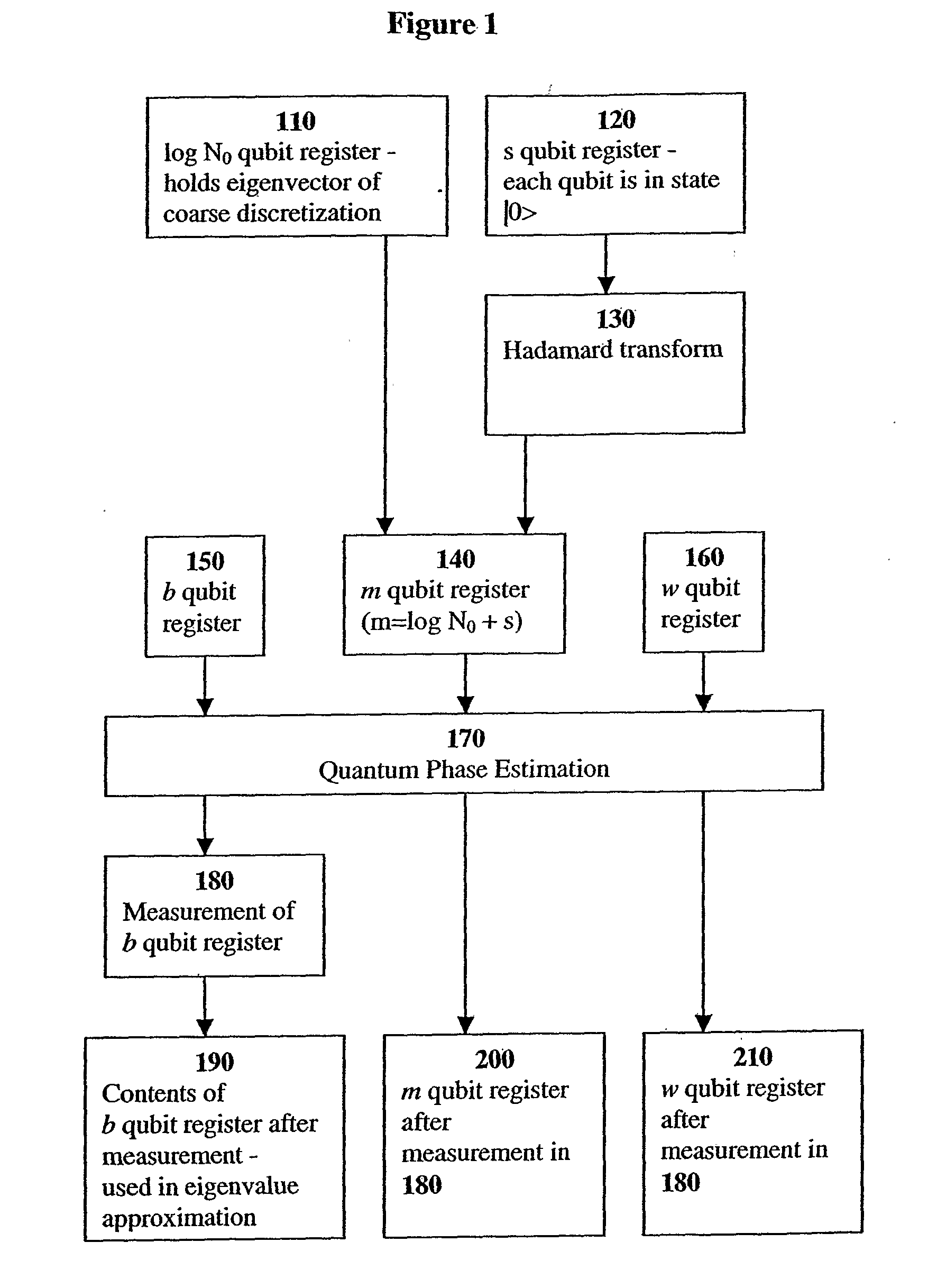
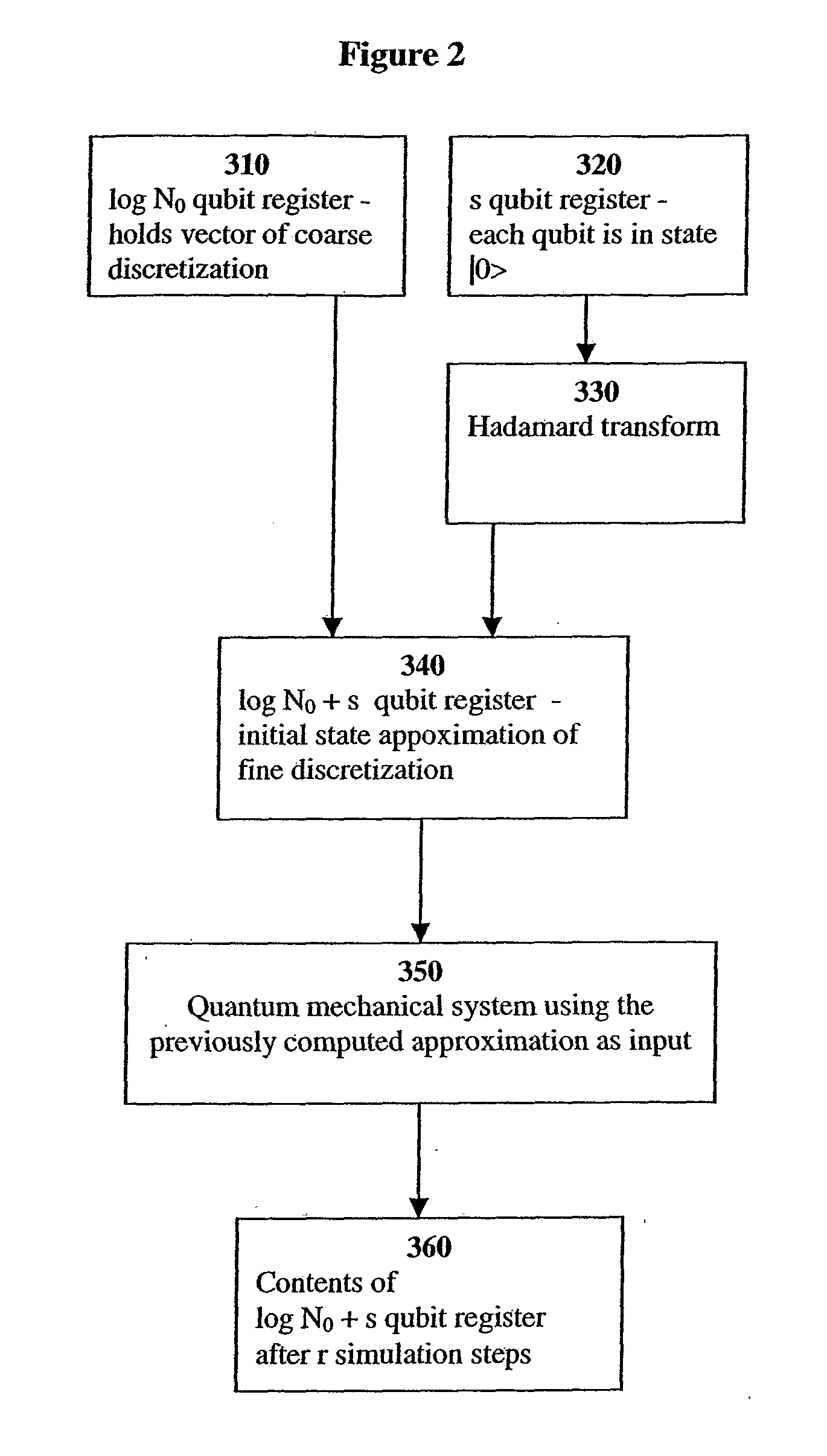
Fast Quantum Mechanical Initial State Approximation
InactiveUS20080140746A1Efficient preparationEfficient constructionQuantum computersNanoinformaticsFeature vectorQuantum algorithm
A system and method efficiently prepare the initial state of q quantum computer required by the eigenvalue approximation method of Abrams and Lloyd. The system and method can be applied when solving continuous Hermitian eigenproblems, e.g. the Schrodinger equation, on a discrete gird, and allows for efficient calculation of their eigenvalues with quantum computers. A system and method efficiently prepare an approximate initial state (not limited to eigenvectors) of a quantum computer required by a quantum algorithm as input.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
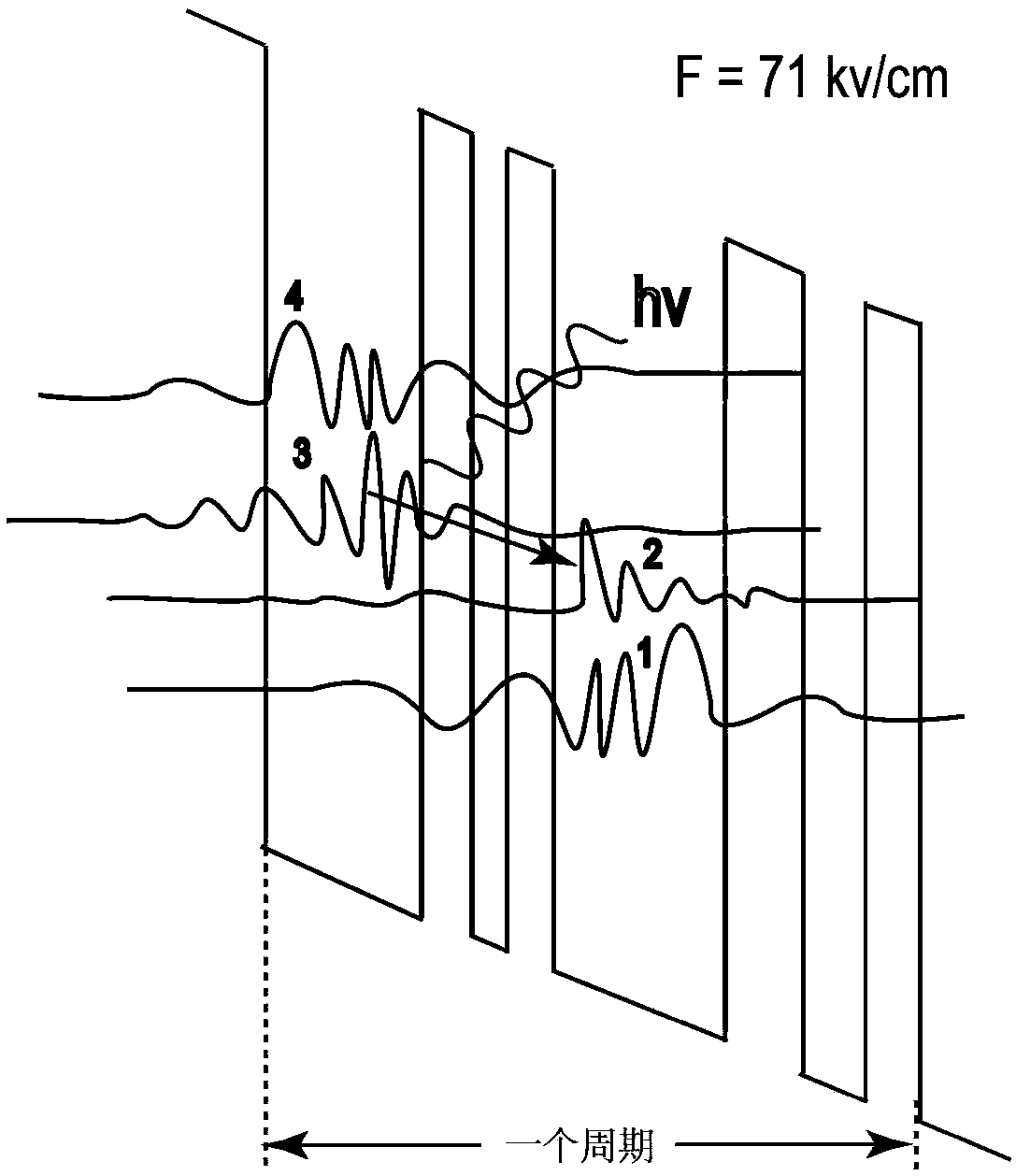
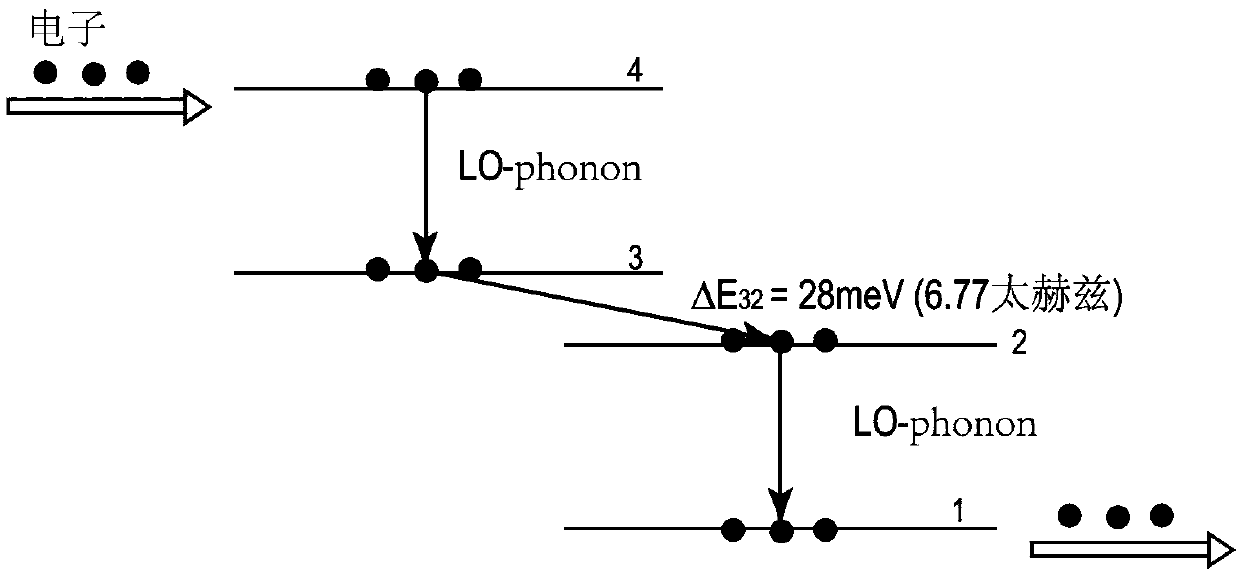
Method for analog designing of active area of AlGaN/GaN terahertz quantum cascade laser
InactiveCN102508940AOptimum Active Region StructureLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersPotential wellSchrödinger equation
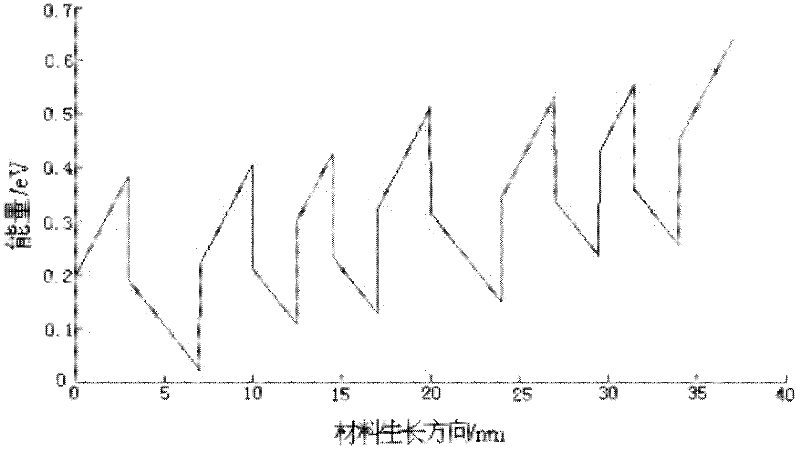
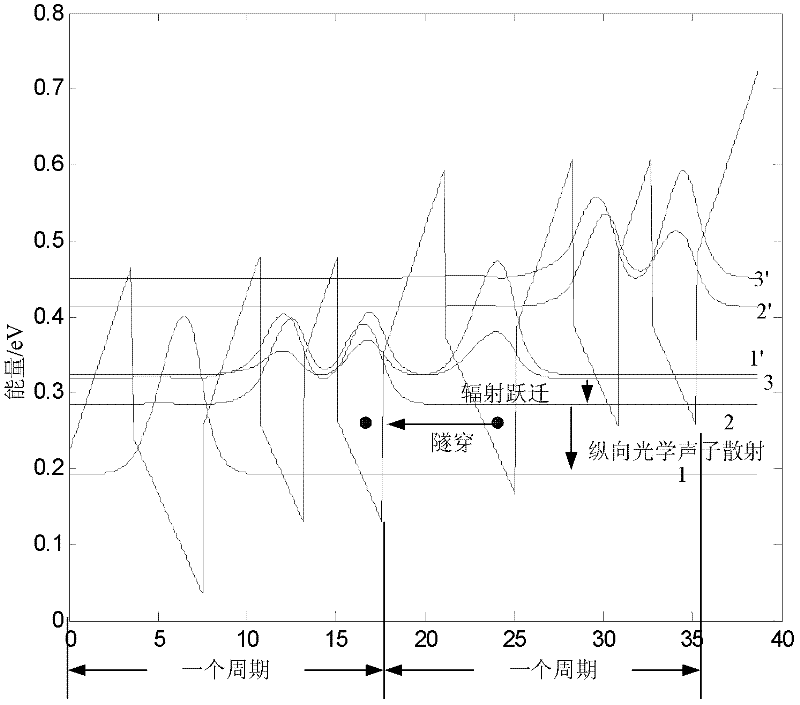
A method for analog designing of an active area of an AlGaN / GaN terahertz quantum cascade laser relates to methods for analog designing of active areas of terahertz quantum cascade lasers. The method includes: firstly, determining parameters required in one-dimensional effective mass Schrodinger equation; secondly, solving the Schrodinger equation; thirdly, calculating delta E21, delta E32 and delta E1'3; fourthly, judging; fifthly, searching the optimum structure; and sixthly, outputting the structure. The active area consists of n periods, and each period consists of three barrier layers and three potential well layers. The method can be applied to designing of active areas of terahertz quantum cascade lasers, and has the advantages that the longitudinal optical phonon scattering principle and the tunneling principle are fully used while the optimum active area structure can be searched out.
Owner:HARBIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method of displaying electromagnetic field in hydrogen atom
InactiveUS20140220533A1Easy to analyze and useSimple internal structureEducational modelsHydrogen atomClassical mechanics
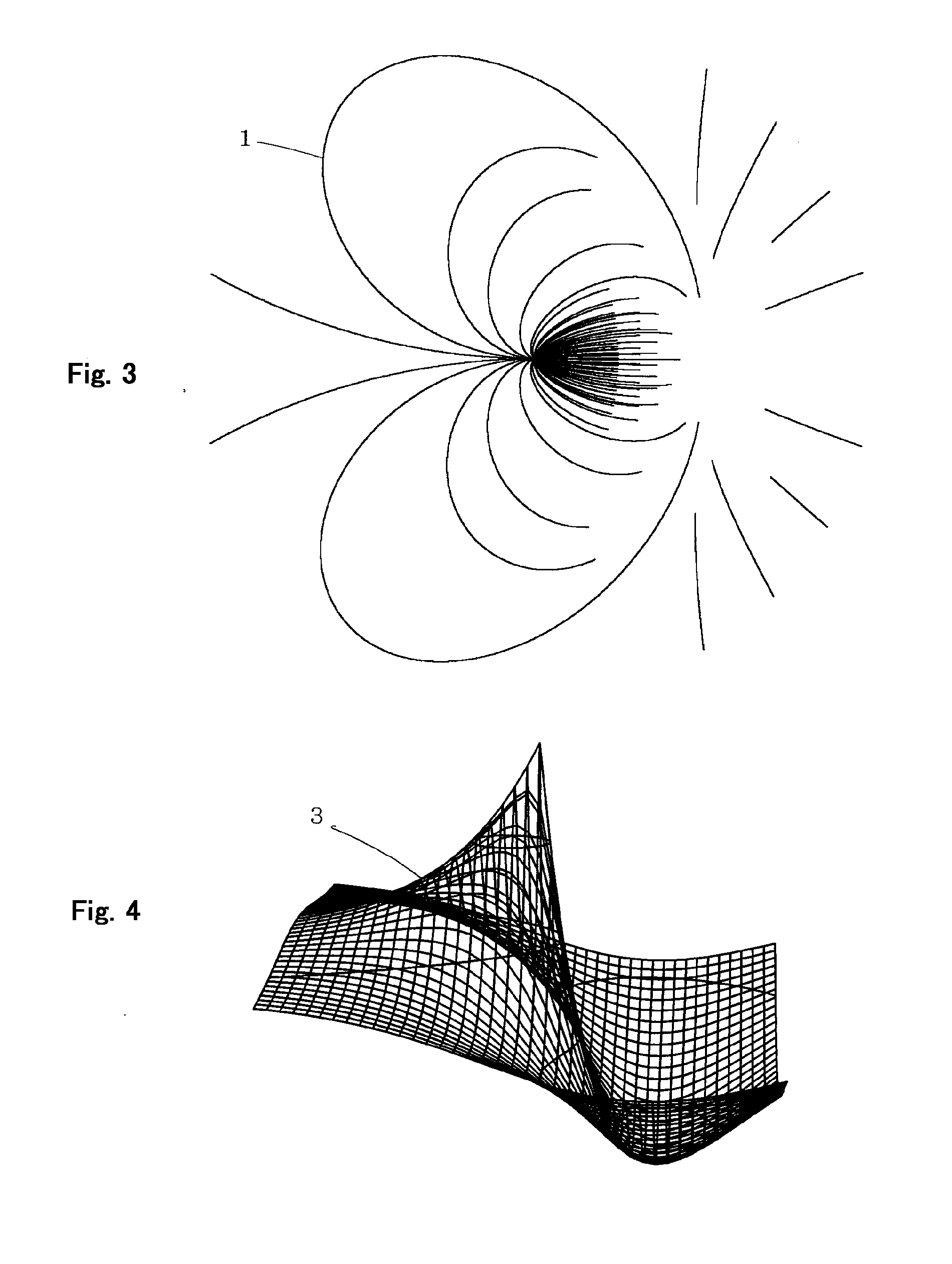
The method assumes that a single solution or addition or subtraction of solutions of Schrodinger equation represented by polar or parabolic coordinates having its maximum value at the origin gives a wave function and an electric potential of a hydrogen atom. The method further: (1) regards the result of applying a gradient vector operation and thereafter a sign inversion to the wave function as an electric field; regards segments connected successively along the direction of the electric field as electric lines of force; and draws the electric lines of force so as to be approximately proportional in number to the percentage of the wave function with a difference between the maximum and minimum values of the wave function regarded as 100; and (2) displaying the wave function as an electric potential in a contour drawing.
Owner:MATSUSHIMA HARUO
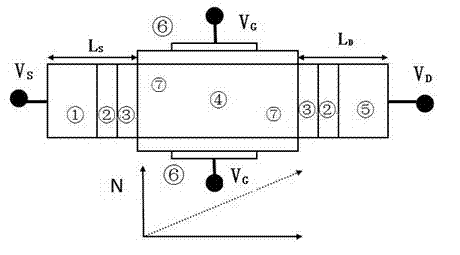
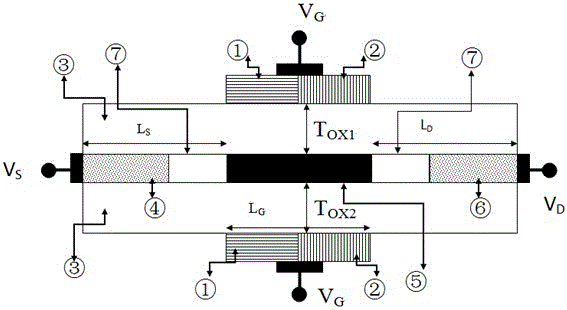
Linear doped spin field-effect tube (Spin-FET)
InactiveCN103094327AReduce off-state currentRaise the threshold voltageSemiconductor devicesSwitched currentSchrödinger equation
The invention discloses a spin field-effect tube (Spin-FET) with a linear light dope structure. A transport model which is suitable for the linear doped Spin-FET is constructed based on the quantum mechanics nonequilibrium green function theoretical framework and through the self-consistent solving Poisson and the Schrodinger equation, and the influence of a linear doping strategy and a common doping strategy on the electrical properties of the Spin-FET is calculated by using the model. Compared with the electrical properties of other doping strategies such as output characteristics, transfer characteristics, switch current ratio and magnetism current rate, the linear doped Spin-FET has larger switch current ratio, higher magnetism current rate, and smaller sub-threshold swing and threshold voltage drift. Not only can show that linear doping has better grid control capability, but also short-channel effect and hot carrier effect can be effectively restrained.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
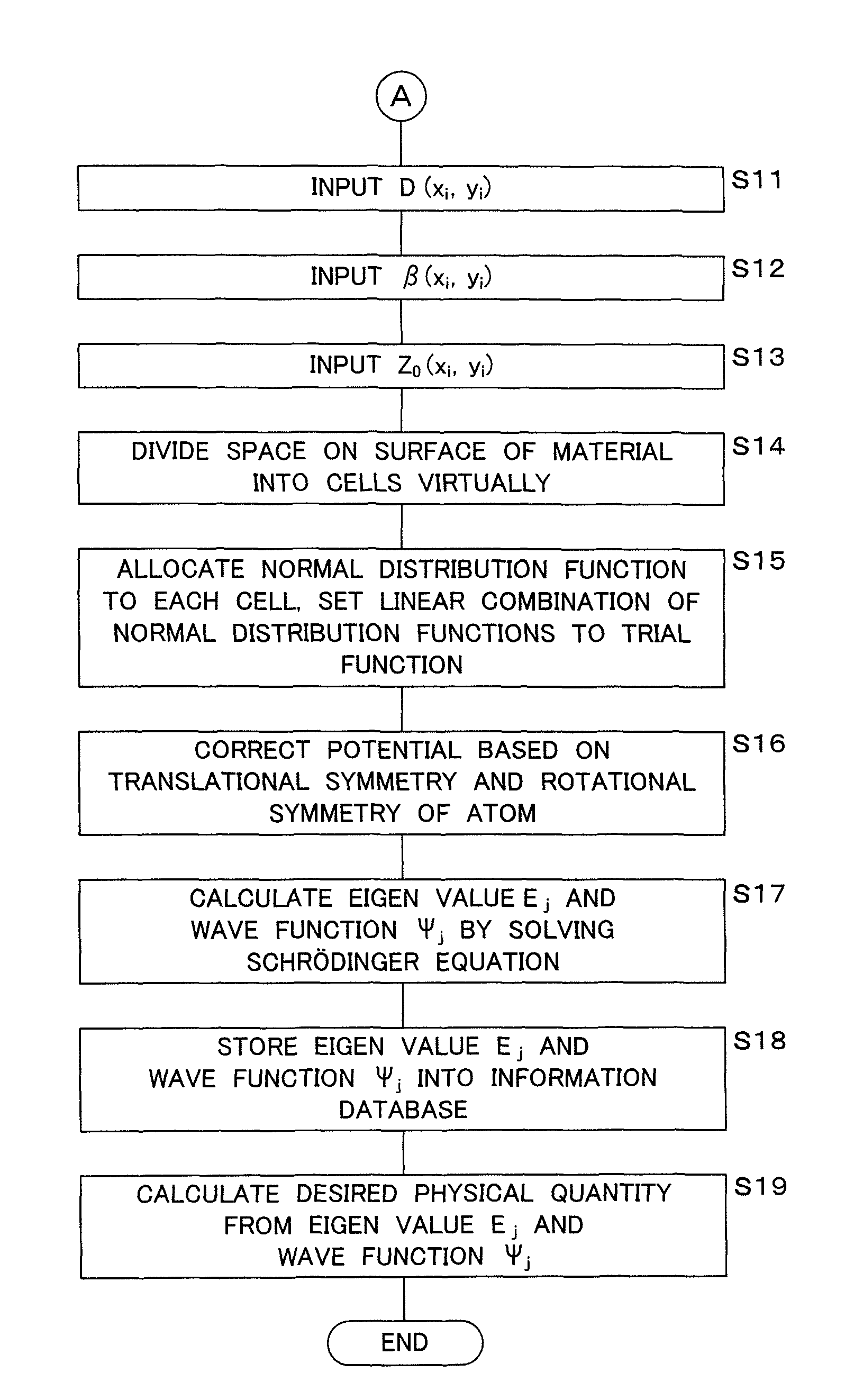
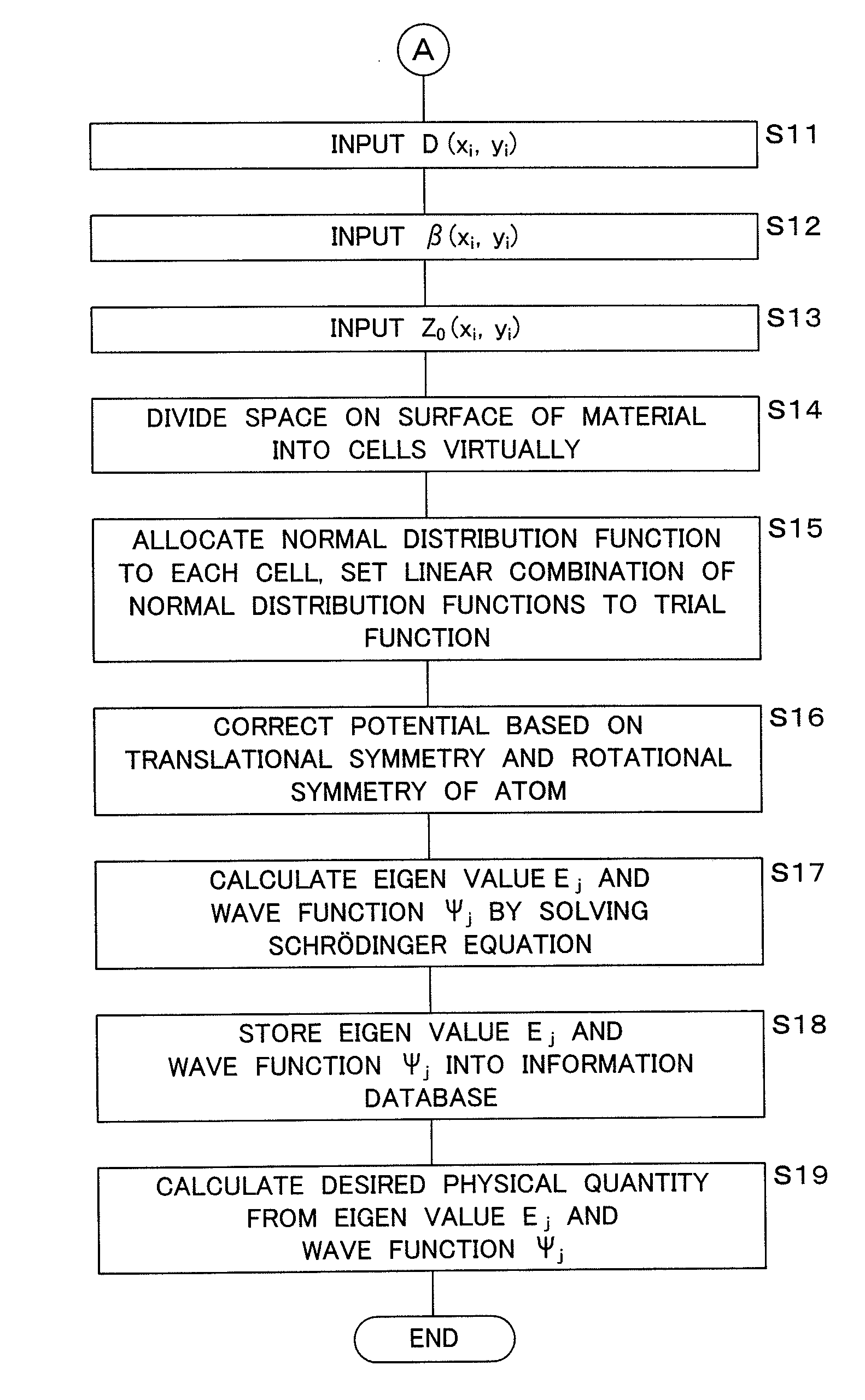
Quantum state estimation method, quantum state estimation device and computer program
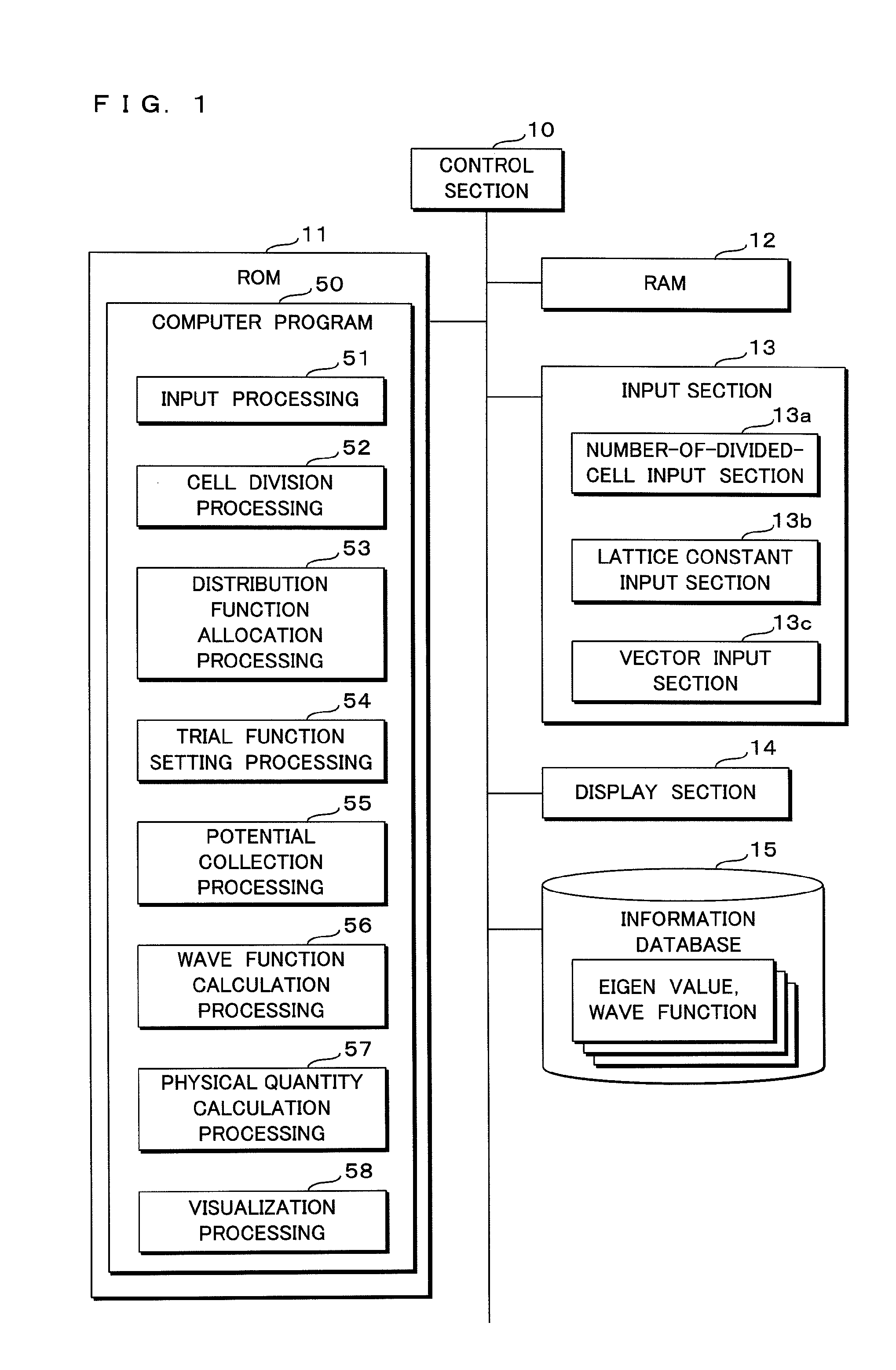
ActiveUS8140467B2Improve estimation accuracyTechnique is effectiveQuantum computersNanoinformaticsEstimation methodsDividing cell
A control section virtually divides a surface of an adsorbing material into a plurality of regions (cells) in accordance with a computer program. Further, the control section-allocates a normal distribution function to each of the divided cells, and sets a linear combination of the normal distribution functions allocated to all cells to a trial function. Moreover, the control section solves a Schrödinger equation based upon a potential on the surface of the adsorbing material by a numerical variational method, to calculate a wave function. Then, based upon the calculated wave function, the quantum state of the atom or the molecule adsorbed on the surface of the adsorbing material is estimated.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
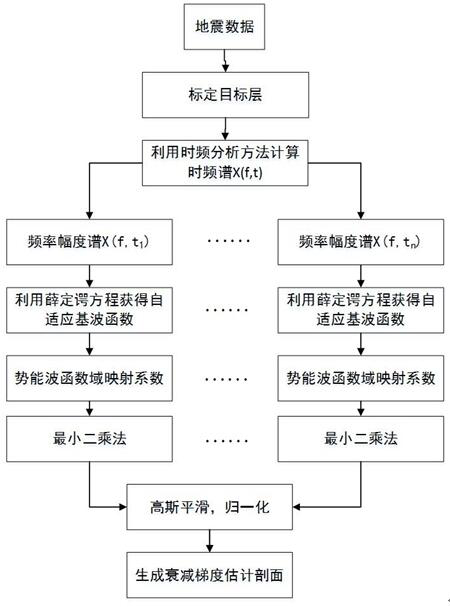
Method for estimating seismic wave attenuation gradient by using Schrodinger equation
ActiveCN114089416AImprove accuracyImprove effectivenessSeismic signal processingGradient estimationSchrödinger equation
The invention belongs to the field of geophysical processing methods for oil-gas exploration. The invention discloses a method for estimating seismic wave attenuation gradient by using a quantum mechanics Schrodinger equation (Figure 1). According to the method, seismic data is converted into a time-frequency domain by using a time-frequency analysis method, a quantum mechanics Schrodinger equation is adopted for the seismic data in the time-frequency domain to solve an adaptive fundamental wave function, and on the basis of obtaining a mapping coefficient sequence of the adaptive fundamental wave function, a least square method is combined to realize high-resolution estimation of the attenuation gradient. According to the method for estimating the seismic wave attenuation gradient by using the quantum mechanics Schrodinger equation, the Schrodinger equation is used for performing quantum feature representation on seismic data, the intrinsic change relation of multi-frequency-component seismic signals can be deeply excavated, a traditional attenuation gradient estimation algorithm is expanded to a potential energy-wave function domain, the Schrodinger equation is used for estimating the energy attenuation in the potential energy-wave function domain, and compared with a traditional method for estimating the attenuation gradient through energy high-frequency attenuation in the frequency domain, the method has higher identifiability and accuracy and can improve the accuracy and effectiveness of oil and gas indication.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Multi-soliton implement method based on simultaneous schrodinger equation
InactiveCN103199932AMore difficult to avoidThe method is concise and easy to understandFibre transmissionRiccati equationSchrödinger equation
The invention relates to a multi-soliton implement method based on a simultaneous schrodinger equation, and belongs to the technical field of optical fiber communication. According to the multi-soliton implement method, through introduction of topologies and nonlinear transformation and by utilization of a Riccati equation mapping method, the simultaneous schrodinger equation is researched to construct a precise solution of a system. Through proper setting for an arbitrary function in an equation analytical solution, a novel oscillating soliton structure is obtained, and eventually multi-solitons of different numbers can be obtained by utilization of a Weierstrassp function. The problem that the multi-solitons are difficult to generate in the optical fiber communication technology is solved. The multi-soliton implement method based on the simultaneous schrodinger equation is simple, easy to understand, convenient to implement, strong in practicability, and capable of being adjustable in relevant parameters according to actual situations, providing powerful support for in-depth study of the filed of optical fiber communication systems and promoting the development of the subject.
Owner:王少夫
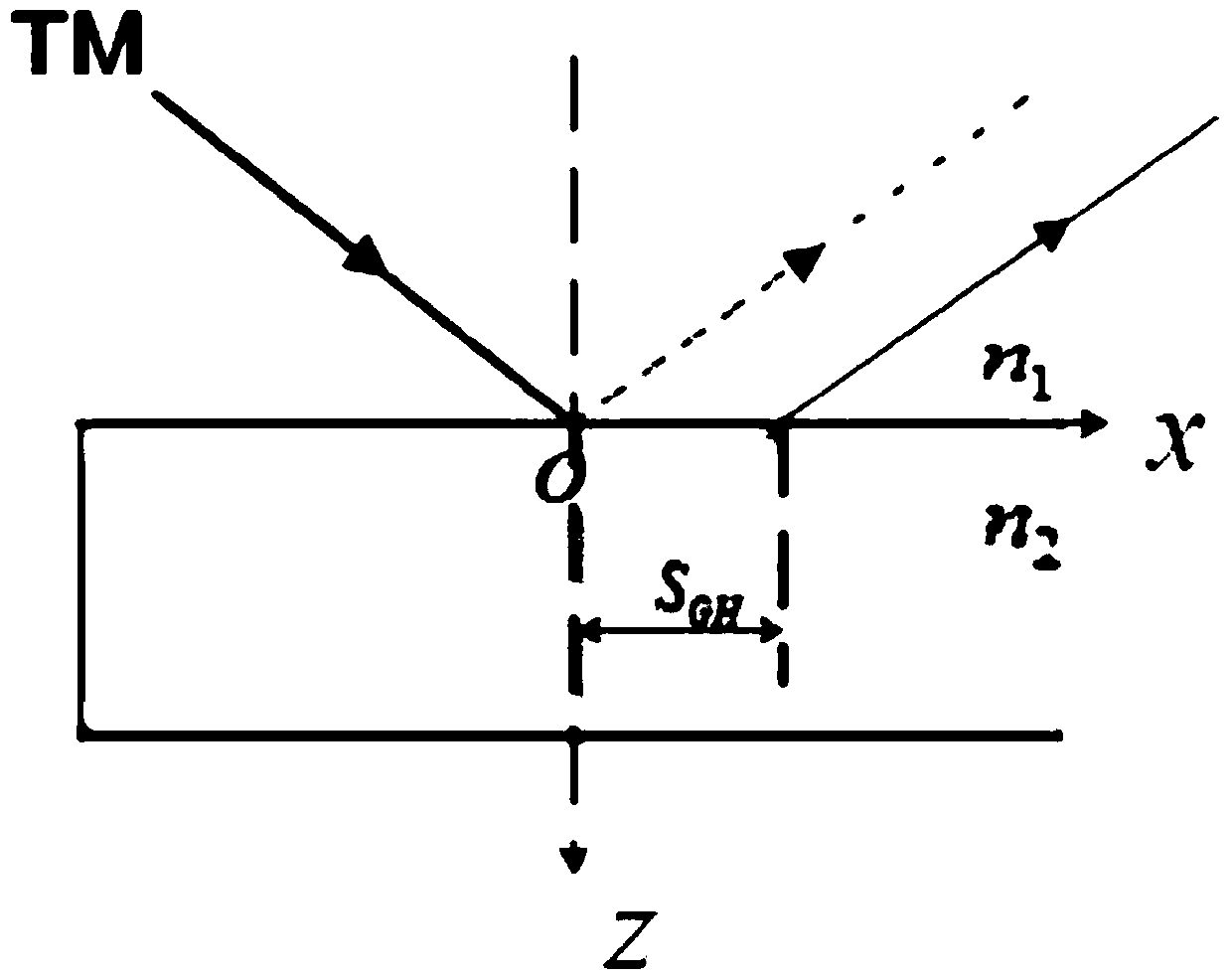
Method and apparatus for detecting relation between evanescent field and Goos-Hanchen displacement, and optical device
ActiveCN105606032AEasy to controlMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansMomentumPotential field
The invention is applied to the technical field of optics, and provides a method and apparatus for detecting a relation between an evanescent field and Goos-Hanchen displacement, and an optical device. The method comprises the following steps: according to physical meanings of a stress function and a potential field function of light in the evanescent field, obtaining a potential field function of the evanescent field for total-reflection light; through combination with the potential field function of the evanescent field for the total-reflection light, obtaining a wave function of the total-reflection light after perturbation through a Schrodinger equation; and comparing the wave function of the total-reflection light after the perturbation with a wave function of free total-reflection light without an evanescent field effect, and the total-reflection light obtaining momentum having the same momentum property as the evanescent field under the effect of the evanescent field. According to the invention, better regulation and control of the Goos-Hanchen displacement can be realized, and the Goos-Hanchen displacement can be better applied to such fields as optical sensors, all-optical switches, light beam displacement modulators and the like.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Adiabatic shortcut method for high-fidelity population inversion in two-energy-level system
PendingCN110120799AImprove robustnessShort evolution timeQuantum computersMultiple input and output pulse circuitsPhase noiseQuantum invariant
The invention discloses a heat insulation shortcut method for high-fidelity population inversion in a two-energy-level system. A time-containing schrodinger equation of a two-energy-level system by adopting an inverse control method based on Lewis-Riesenfield quantum invariants; a group of pulse signals capable of achieving population inversion of the two-energy-level system are constructed, an arbitrary wave generator is used for generating the pulse signals, and therefore the population inversion is achieved in a high-fidelity mode within a short action time. On the premise that the Ratio frequency of a generated pulse signal does not exceed 15GHz, inversion of the population number of a two-level system can be achieved within the action time of 1ns, the fidelity is not lower than 92% under the influence of phase noise and decorrelation, and the fidelity is not lower than 99.85% within the frequency detuning amount range.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
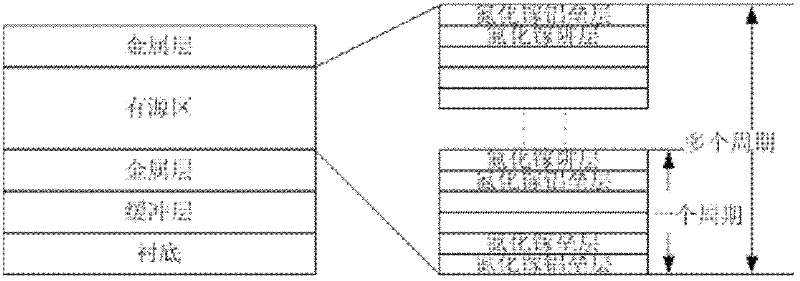
Design method of trap type dual-phonon active region energy level structure in terahertz quantum cascade laser
ActiveCN108923258AGood reversalGood temperature characteristicsLaser active region structureRate equationQuantum well
The invention discloses a design method of a trap type dual-phonon active region energy level structure in a terahertz quantum cascade laser. The design method comprises the following steps of (1) designing a well width barrier width of one period of an active region of the terahertz quantum cascade laser; (2) solving the energy level of the active region through a schrodinger equation, and determining whether the energy level distributions satisfies the design requirements or not; and (3) solving an active region rate equation, and obtaining the output characteristic of the active region of the laser, and therefore, the design feasibility is verified. According to the method, the quantum well energy level theory is calculated by using schrodinger, so that the accuracy of the energy levelposition is determined, so that the problems of thermal excitation and thermal leakage caused by too high temperature of electrons in the terahertz quantum cascade laser can be solved, and higher operation temperature and the output characteristic of the laser can be obtained.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Quantum state estimation method, quantum state estimation device and computer program
ActiveUS20090254508A1Improve accuracyHigh precision estimationNanoinformaticsFuzzy logic based systemsEstimation methodsDividing cell
A control section virtually divides a surface of an adsorbing material into a plurality of regions (cells) in accordance with a computer program. Further, the control section-allocates a normal distribution function to each of the divided cells, and sets a linear combination of the normal distribution functions allocated to all cells to a trial function. Moreover, the control section solves a Schrödinger equation based upon a potential on the surface of the adsorbing material by a numerical variational method, to calculate a wave function. Then, based upon the calculated wave function, the quantum state of the atom or the molecule adsorbed on the surface of the adsorbing material is estimated.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
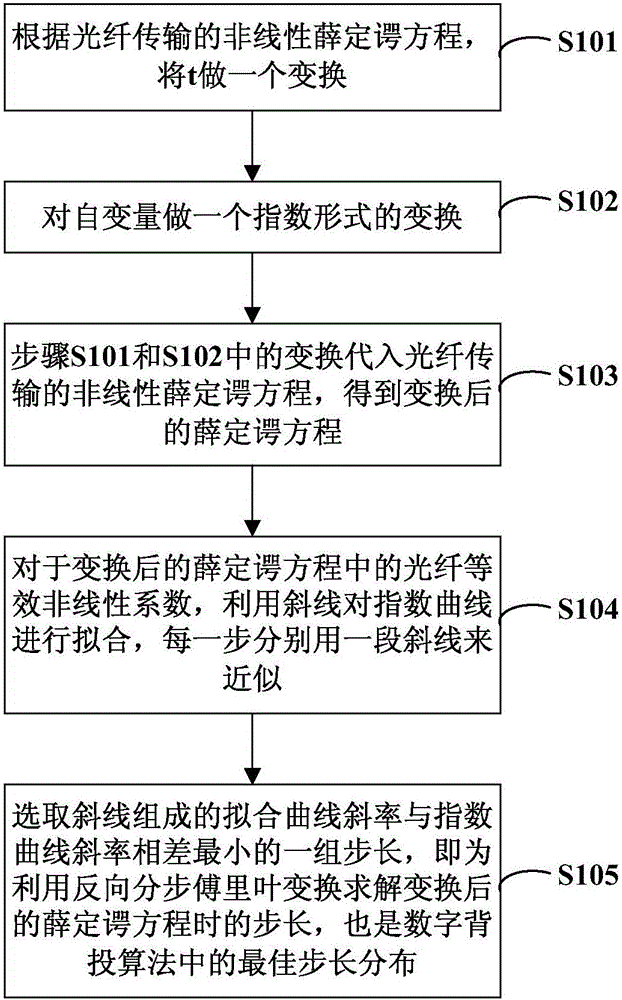
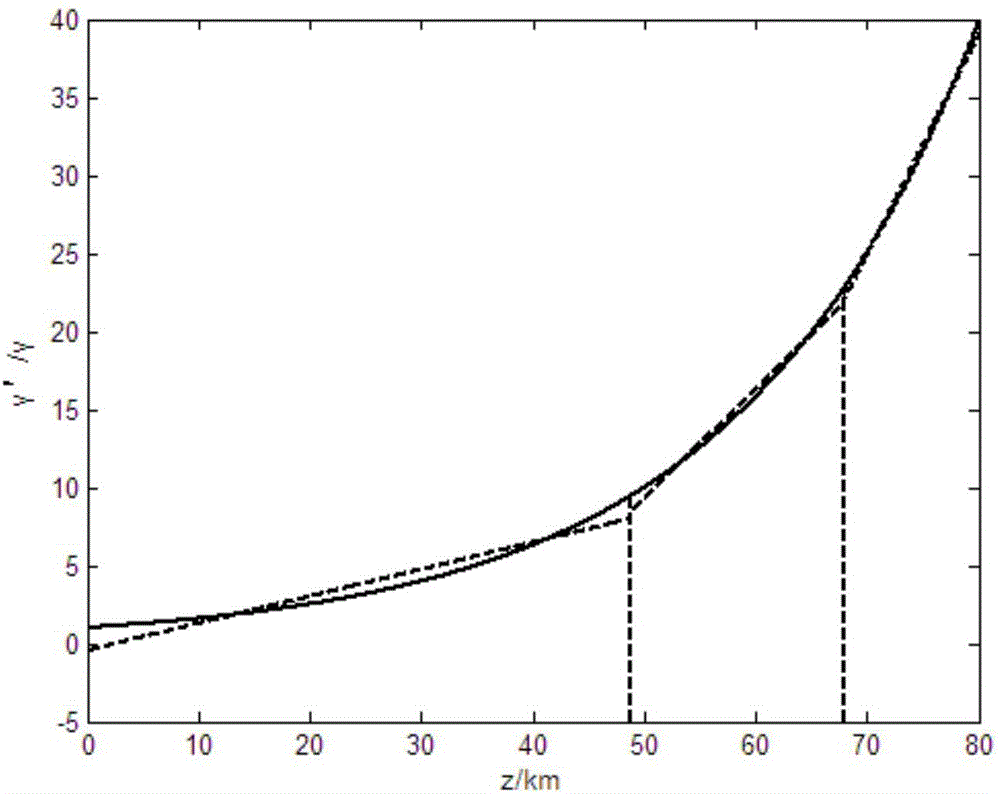
Determination method of optimum step in digital rear projection algorithm of optical fiber transmission loss compensation
ActiveCN105915289ABest damageGood compensationDistortion/dispersion eliminationCompensation effectFourier transform on finite groups
A determination method of an optimum step in a digital rear projection algorithm of optical fiber transmission loss compensation relates to the optical fiber communication field. A change amount whose group speed moves a position along with a pulse is introduced into a time variable of an optical fiber transmission nonlinearity Schrodinger equation NLSE. Variable substitution is performed on the Schrodinger equation. And then, for the converted Schrodinger equation, a split-step Fourier transform is used to realize a digital rear projection DBP algorithm. In the digital rear projection DBP algorithm, an envelope index curve of oblique line pair optical pulse transmission is used to carry out fitting, one segment of oblique line is used to approximate each step, and a group with the smallest difference of a fitting curve slope formed by the oblique lines and an index curve slope is selected to be served as the step of the algorithm, which is optimum step distribution. In the invention, different optical power positions correspond to different steps so as to acquire an optimum transmission loss compensation effect.
Owner:WUHAN POST & TELECOMM RES INST CO LTD
Method for measuring semiconductor quantum point dimension distribution using fluorescence spectrum
InactiveCN101251485AEasy to classifyEasy to operateUsing optical meansFluorescence/phosphorescenceEffective mass approximationLuminescence
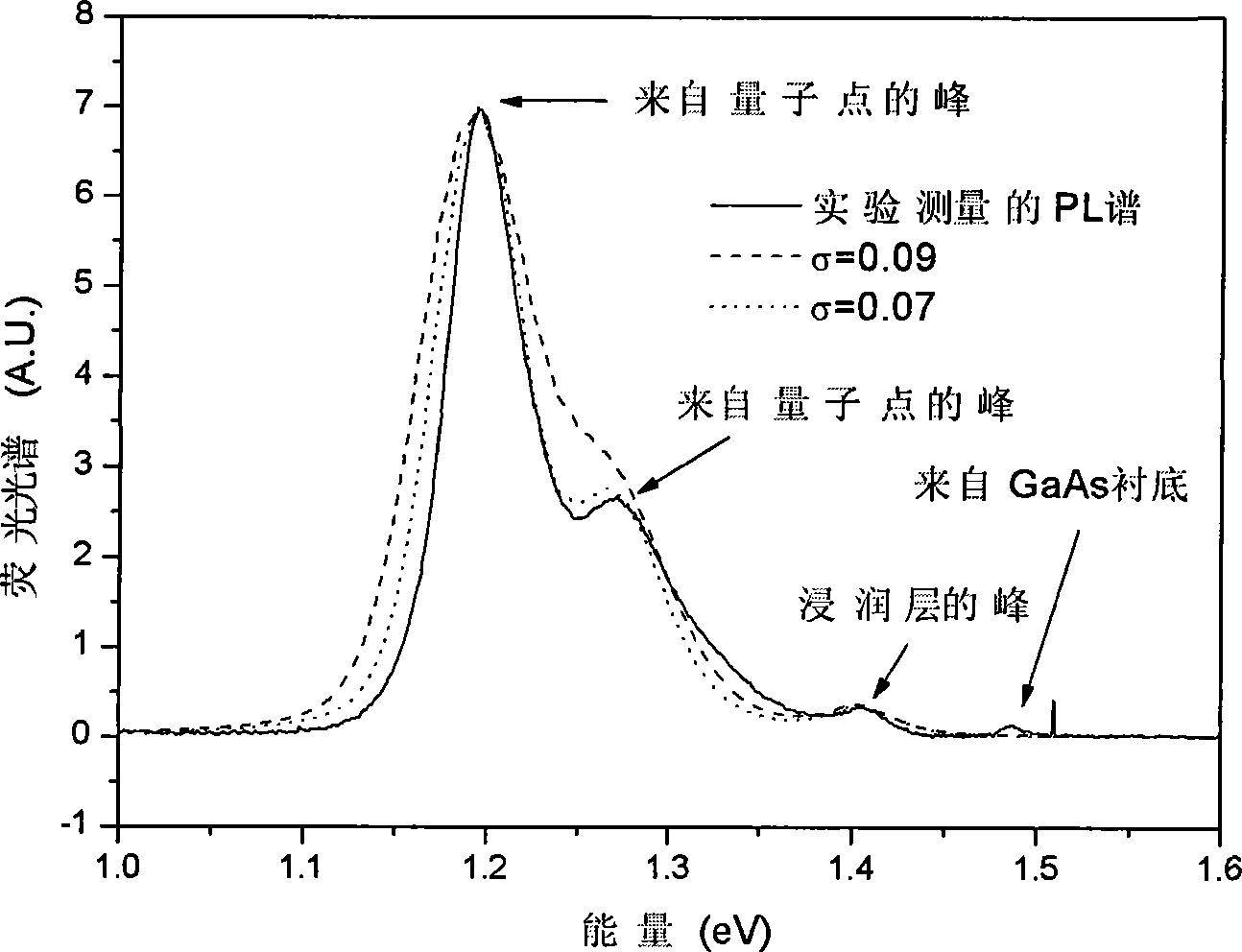
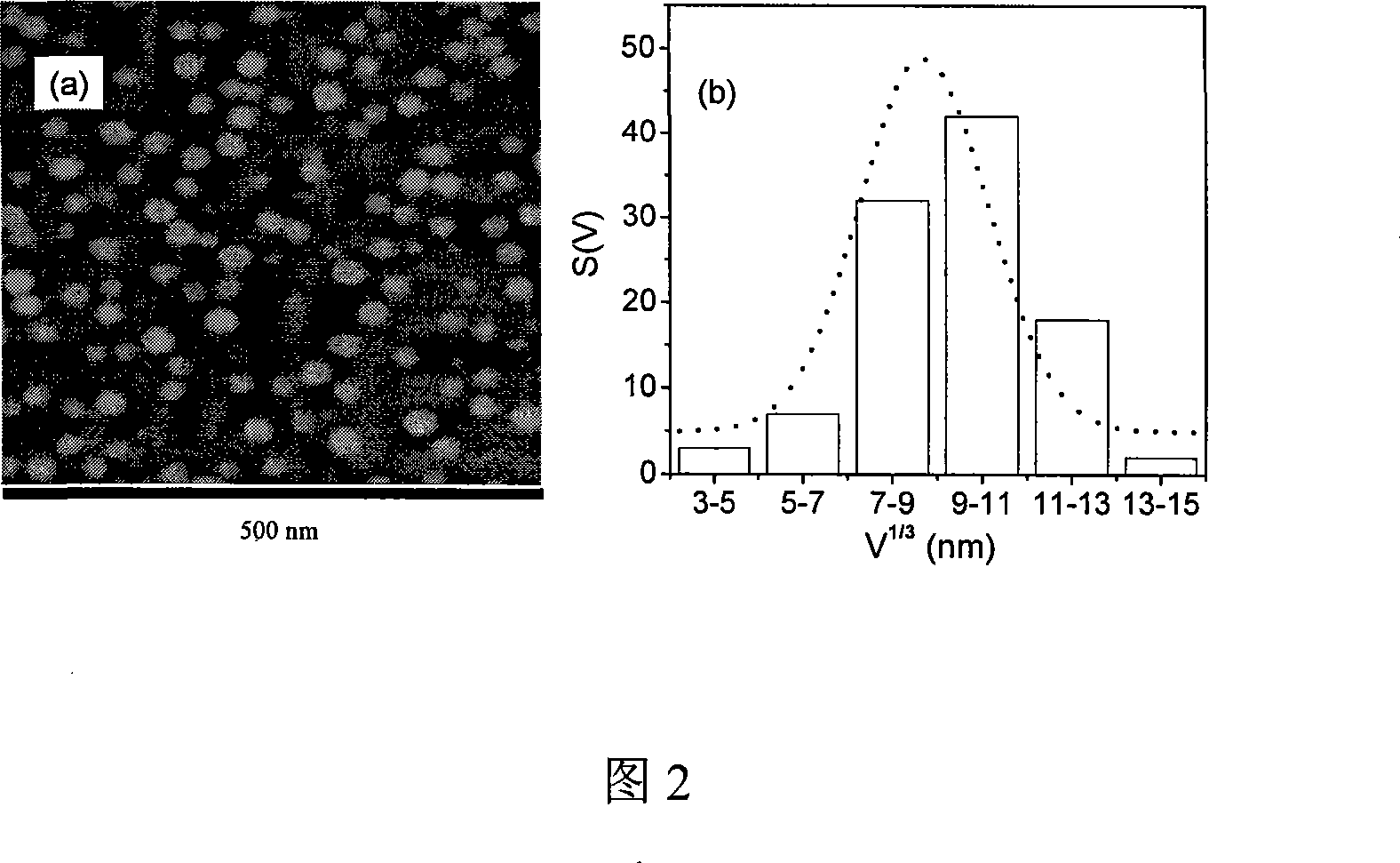
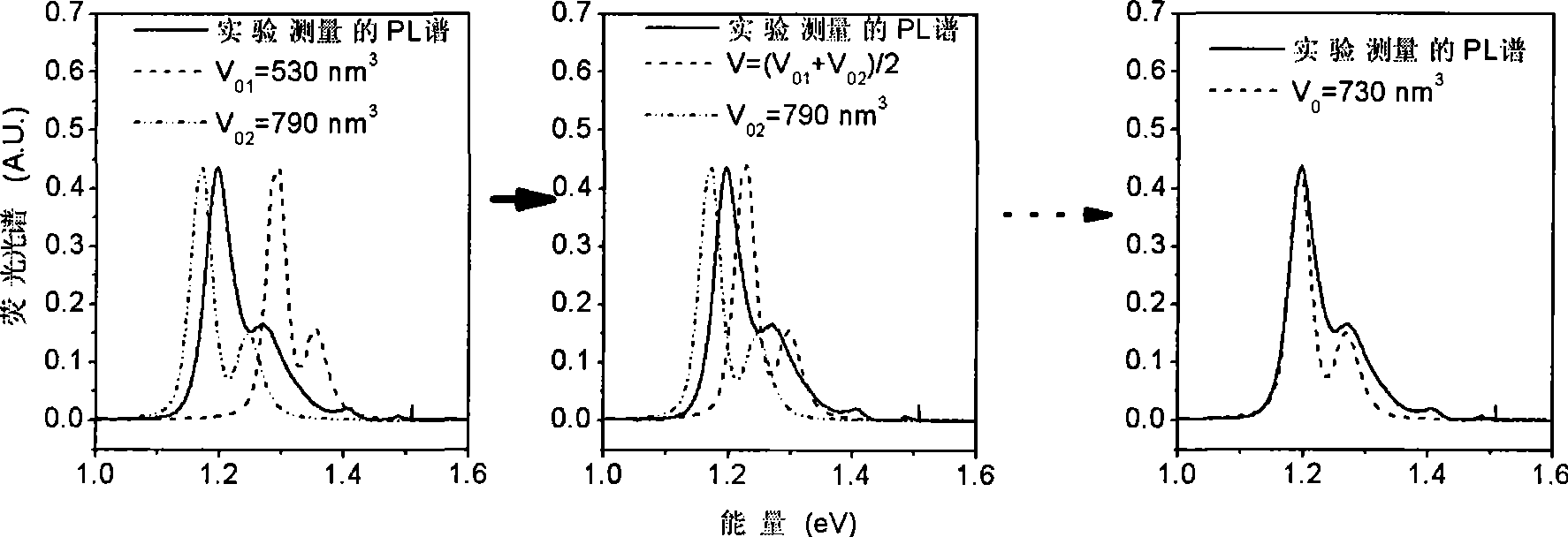
The invention discloses a method for utilizing fluorescence spectrums to measure size distribution of quantum dots of a semiconductor. The method obtains the size distribution of the quantum dots through field measurement of PL spectrums of a multiple quantum dot system of the semiconductor, calculation of the PL spectrums of the quantum dots of the semiconductor beginning from a time-dependent perturbation Schrodinger equation with approximate active mass, and then through theoretical and experimental PL spectrum contrast, wherein, the central wavelength of the PL spectrums corresponds to composite luminescence of a quantum dot with the largest ratio, and the shape of the PL spectrums corresponds to size distribution rules. The method for utilizing the fluorescence spectrums to measure the size distribution of the quantum dots of the semiconductor is simple and convenient in operation and short in time consumption, and can clearly and definitely obtain the size distribution of the multiple quantum dot system of the semiconductor.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A Stock Price Trend Prediction Method Based on Quantum Mechanics and Social Networks
ActiveCN103049804BPredicting Sentiment ProbabilityPredict the trend of ups and downsFinanceForecastingPotential wellPredictive methods
The invention discloses a stock price trend prediction method based on the quantum mechanics and the social network. The micro particle characteristics of an individual investor affective decision in the social network are fully considered, the wave function and the operator of the individual decision in the network are defined, the influence relation between individuals in the social network is simulated by a segmented infinite potential well, the emotion of a single investor is predicted by a schrodinger equation and is overlaid by the emotion in the social network, the stock price variation trend is described, and the quantum mechanics model of the social network can be used for effectively improving the stock price trend prediction accuracy. The stock price trend prediction method based on the quantum mechanics and the social network has an important theoretical significance and economic value.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
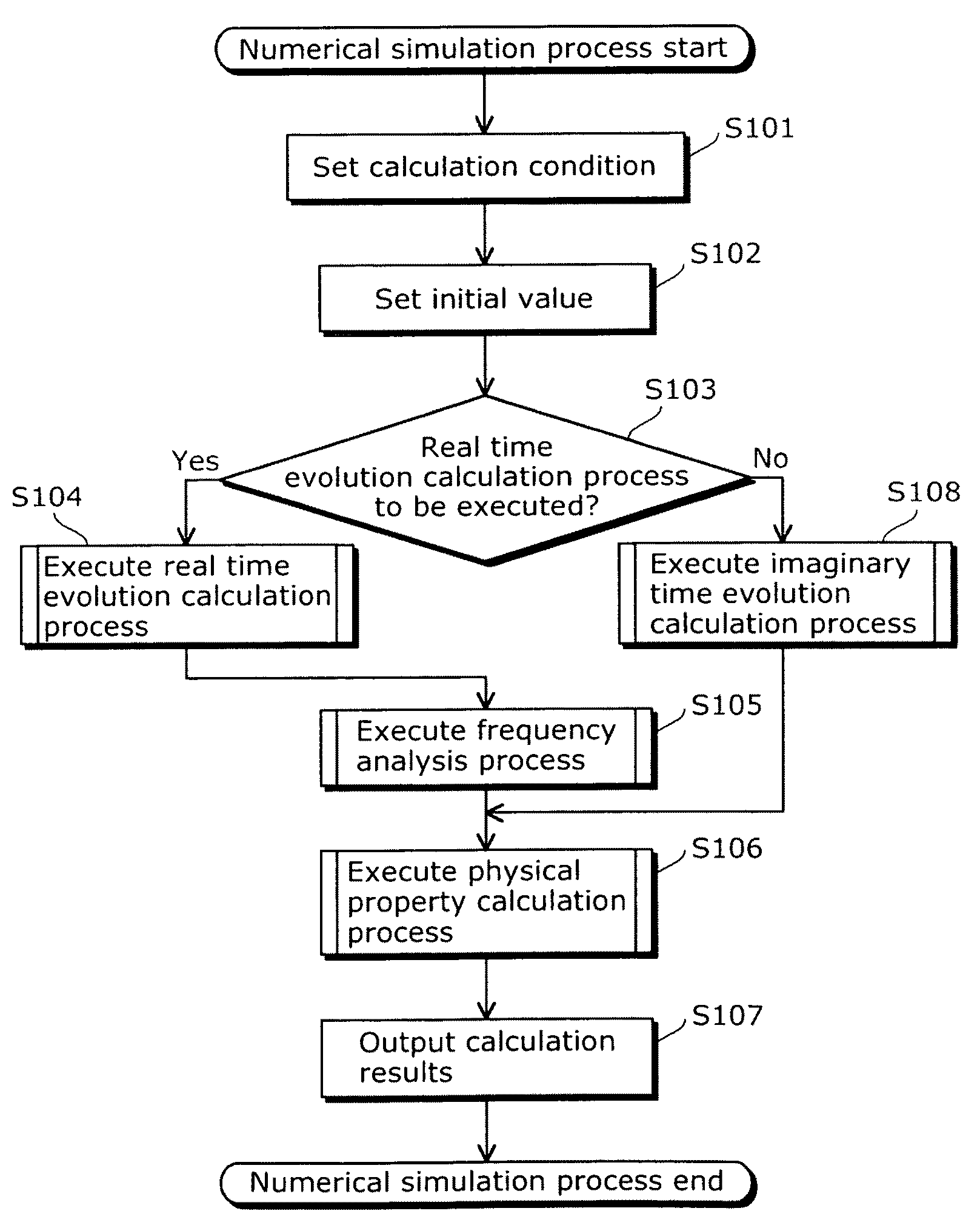
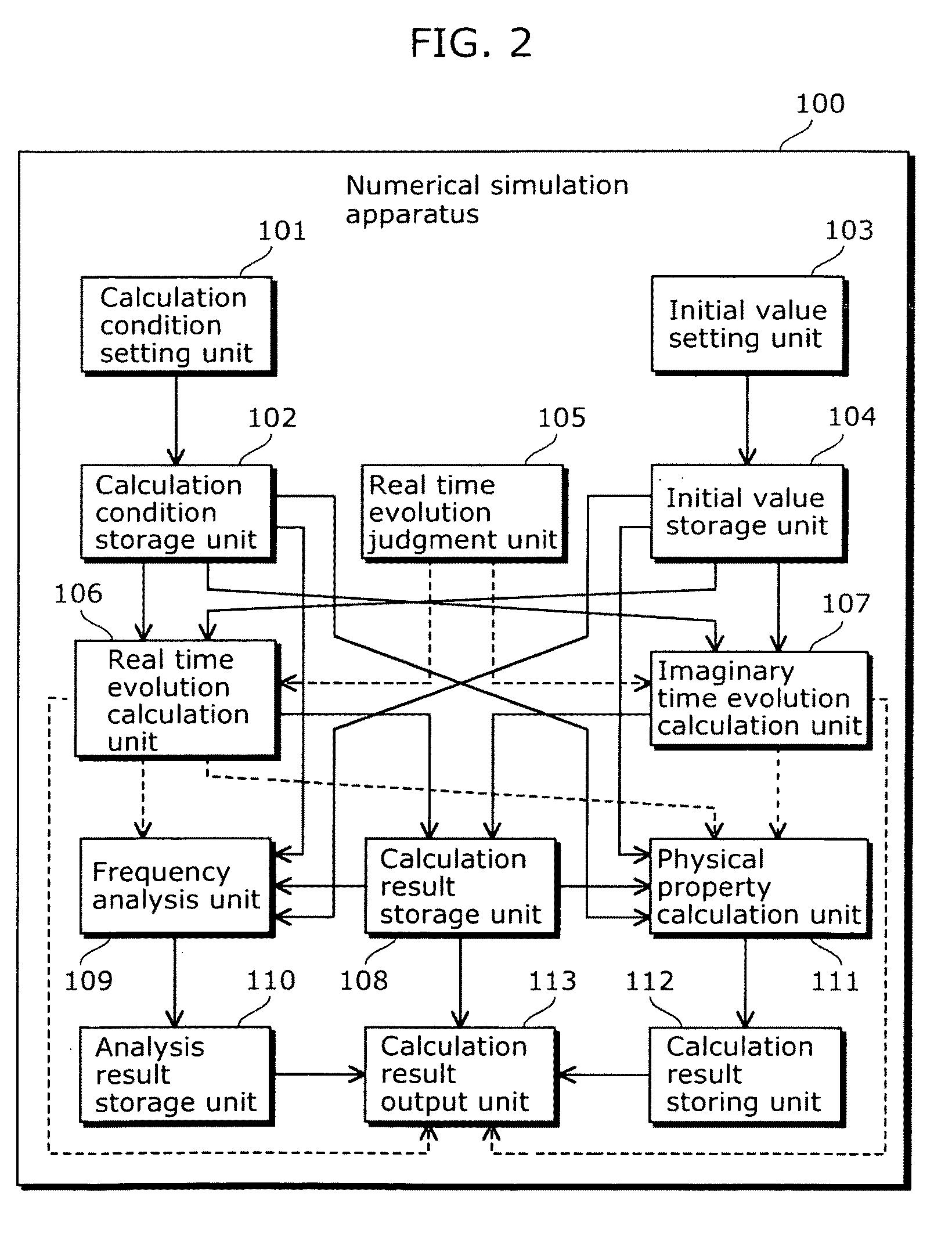
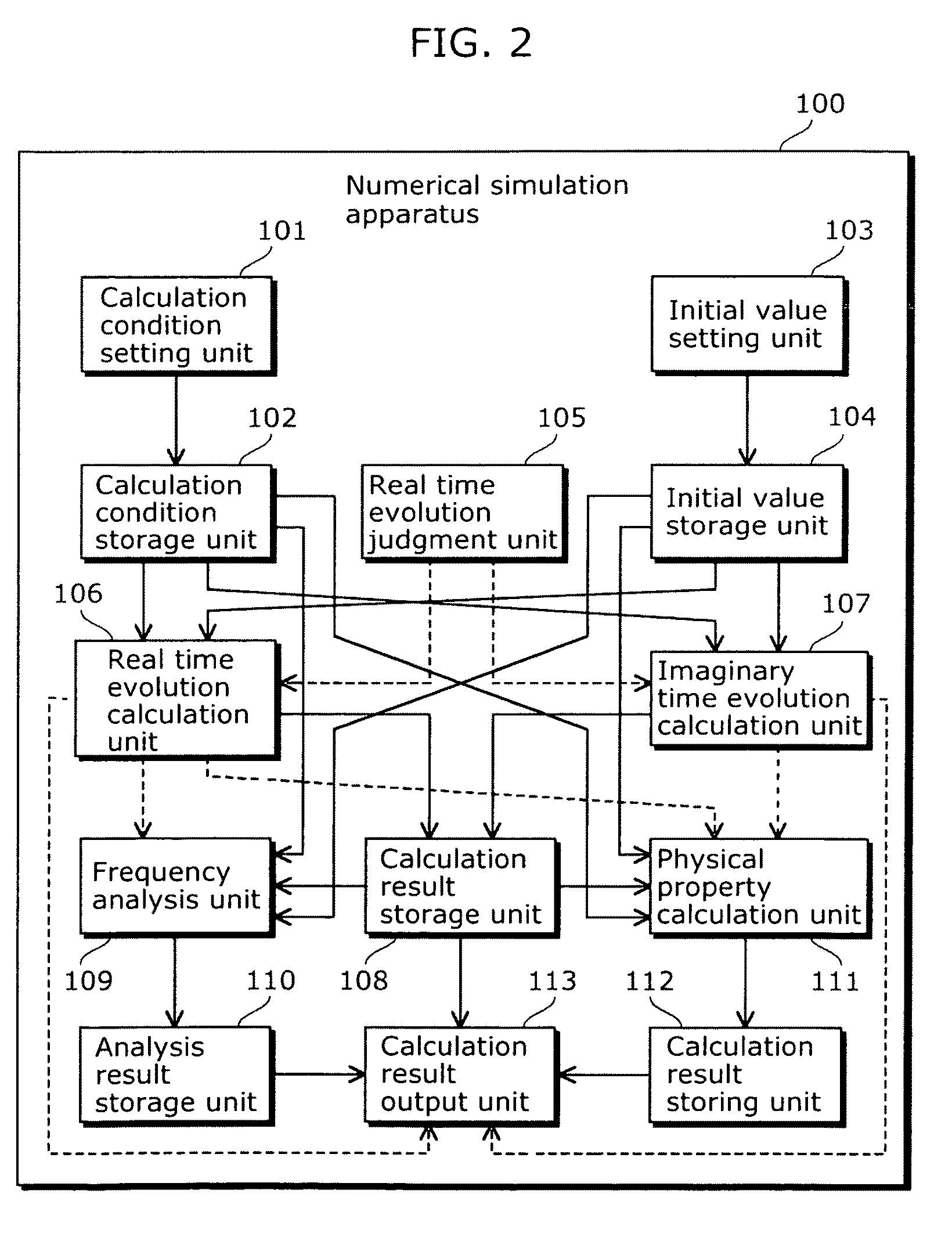
Numerical simulation apparatus for time dependent schrödinger equation
InactiveUS8374827B2High precisionIncrease speedComputation using non-contact making devicesComputation using non-denominational number representationComputation complexityTime segment
To provide a numerical simulation apparatus capable of executing a numerical simulation with high speed and precision by reducing computational complexity. A numerical simulation apparatus that executes a numerical simulation using a wave function which is a solution of a time dependent Schrödinger equation includes: a real time evolution calculation unit that calculates a second wave function while evolving the second wave function from an initial time in increments of a predetermined time period, the second wave function being obtained by applying a central difference approximation in a real-space finite-difference method to a first wave function expressed using a propagator, and being expressed using a Bessel function; and a calculation result storage unit that stores a calculation result of the second wave function obtained at each time by the time evolution calculation unit while evolving the second wave function in increments of the predetermined time period.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
Method for realizing multiple optical solitons in any space based on Schrodinger equation
InactiveCN103117806AMore difficult to avoidThe method is concise and easy to understandFibre transmissionNonlinear Schrödinger equationSchrödinger equation
The invention relates to a method for realizing multiple optical solitons in any space based on a Schrodinger equation, belonging to the technical field of optical fiber communication. The method provided by the invention comprises the steps of: researching the variable-coefficient nonlinear Schrodinger equation through the introduction of topologic and nonlinear transformation and by the utilization of a variable separation method so as to structure a plurality of exact solutions in the variable separation form of the system; and obtaining a new oscillation soliton structure by setting any function in the solutions properly so as to obtain multiple optical solitons of any space. The method for realizing multiple optical solitons in any space based on the Schrodinger equation solves the problem that multiple solitions are difficult to realize in the optical fiber communication technology, is simple and easy to know, convenient to realize and strong in practicability, provides powerful support for deep research in the field of the optical fiber communication system through the adjustment of relevant parameters based on the practical condition, and promotes the development of the subject.
Owner:王少夫
Potential energy wave function domain seismic data quality factor estimation method
ActiveCN114152981AThe calculation result is accurateHigh precisionQuantum computersSeismic signal processingSchrödinger equationSelf adaptive
The invention belongs to the field of geophysical processing methods for oil-gas exploration. The invention discloses a potential energy wave function domain seismic data quality factor estimation method. The method comprises the following steps: decomposing seismic data of a target area in a potential energy-wave function domain by using a Schrodinger equation of non-relativistic quantum mechanics, constructing an adaptive basis function through a Hamiltonian matrix, and calculating a mapping coefficient sequence of the seismic data in a potential energy-wave function space channel by channel; and calculating the Q estimation result of the adjacent horizon by using the mapping coefficient sequence of the potential energy-wave function space in combination with a least square method. The invention provides a seismic signal self-adaptive decomposition algorithm based on a quantum mechanics Schrodinger equation, derives a potential energy-wave function domain Q estimation algorithm, develops a high-precision potential energy-wave function domain seismic data Q estimation method, improves the accuracy of Q estimation, and provides a seismic signal self-adaptive decomposition algorithm based on a quantum mechanics Schrodinger equation. The problems that a traditional Q estimation method needs to select a frequency band and various assumption preconditions exist are solved.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH
Manufacturing method of muon hydrogen atom type high-frequency laser
InactiveCN106207740AImproved energy level structureHigh energyWave amplification devicesWavelengthQuantum number
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of a muon hydrogen atom type high-frequency laser. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps of: colliding hydrogen atoms by using a muon beams to ensure that electronic around the hydrogen atoms are ionized by the muons and captured by the hydrogen atoms so as to generate muon hydrogen atoms; obtaining an energy level structure of the muon hydrogen atoms through a Schrodinger equation for solving the muon hydrogen atoms; taking a carbon monoxide laser with a wave length of 5.8 microns as a pump laser to realize the overturning of amount of the muons on a 2p excited state; and enabling the muons located at a 2p energy level to jump to a 1s energy level (muons at the 2p energy level jumps to the 1s energy level to carry out spontaneous radiation jump), so as to generate 1.9 Kev of high-frequency X waveband laser. According to the manufacturing method disclosed by the invention, a working substance which is likely to generate X waveband lasers is disclosed through theoretical analysis, and a feasible working principle is disclosed; under the condition that the main quantum number is smaller than 30, the energy level life of the muon hydrogen atoms is much shorter than the life of the muons; and a proper energy level structure is searched in the part with an energy level smaller than 30, so that X waveband light is generated.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Optical pulse generation method for creating arbitrary superposition states of qubits in three-level systems
The invention discloses a light pulse generation method capable of creating an arbitrary superposition state of qubits in a three-level system. The invariant theory is used to reversely solve the time-dependent Schrodinger equation of the three-level system to construct a set of two-color light capable of generating an arbitrary superposition state of qubits. Field-strength information of the pulse, using an arbitrary wave generator and an acousto-optic modulator, to generate a two-color light pulse, the additional degrees of freedom in the field strength of the two-color light pulse are used to optimize the shape of the pulse for the frequency disturbances present in the system. Harmonic quantities exhibit robustness, and the off-resonance excitation of background ions present in the system is small enough to create arbitrary superposition states of qubits with fidelity in short action times; An arbitrary superposition state of a qubit is generated within the action time, the fidelity is not less than 99.5% in the range of frequency detuning of ±340kHz, and the non-resonant excitation of background ions is not more than 2%.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV +1
Time sequence signal prediction method based on quantum filtering model
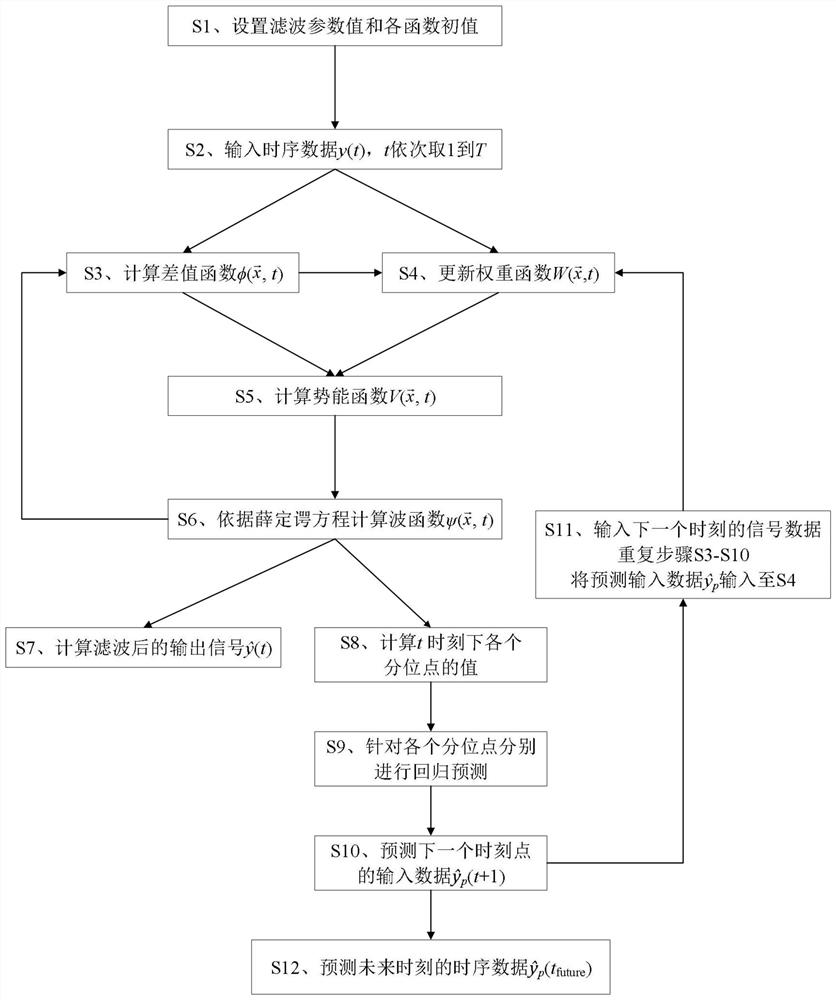
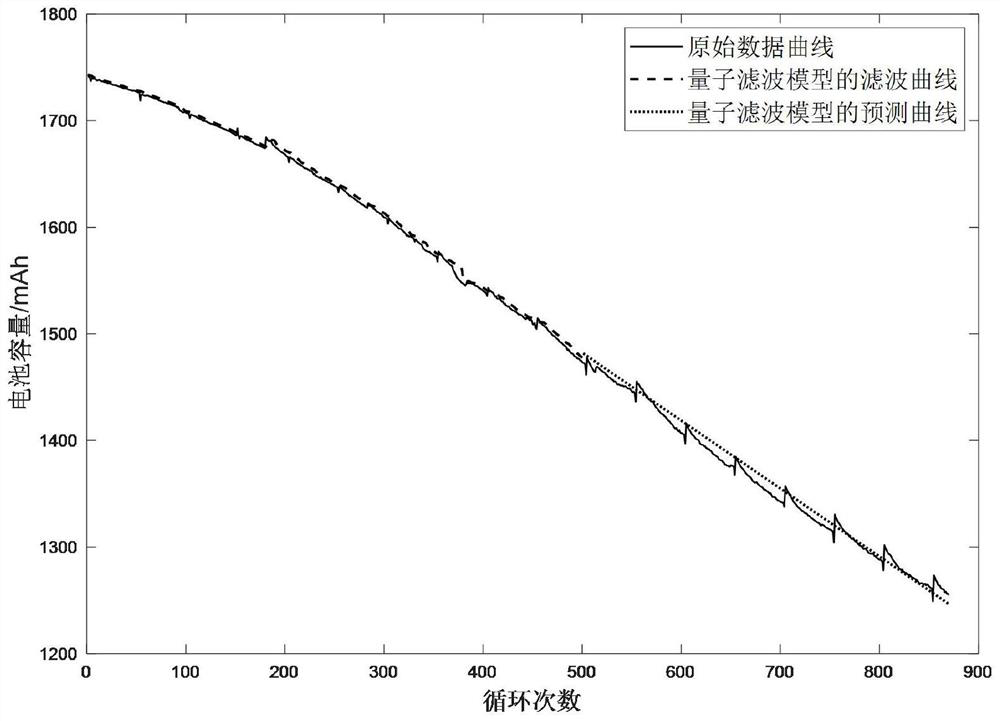
PendingCN114528878APractical and simple and convenientRealize the predictive functionQuantum computersCharacter and pattern recognitionPredictive functionSchrödinger equation
The invention provides a time sequence signal prediction method based on a quantum filtering model, and the method comprises the steps: setting a filtering parameter value and an initial value of each function, obtaining all time sequence signal data, sequentially calculating a difference function at each moment, updating a weight function, and calculating a potential energy function. Calculating a wave function and filtered time sequence signal data according to a Schrodinger equation in a difference form, calculating the value of each quantile of the density matrix, carrying out regression on each quantile, predicting the quantile value of each moment, and sequentially predicting the time sequence signal data value of the next moment; and the time sequence signal data with the time greater than the last moment in the time sequence signal data is predicted. According to the method, on the basis of a basic quantum filtering model, filtering processing can be achieved without making any assumption processing on the distribution form of noise signals, and the prediction function of quantum filtering is achieved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
A linearly doped graphene field effect transistor with a dual-material gate
ActiveCN103247688BReduce doping concentrationGood gating abilitySemiconductor devicesPower flowSwitched current
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM INST AT NANJING CO LTD
A method of manufacturing electron gas back barrier gallium nitride heterojunction field effect transistor
ActiveCN104576371BImprove efficiencyIncrease output powerSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionGallium nitride
Owner:NO 55 INST CHINA ELECTRONIC SCI & TECHNOLOGYGROUP CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com