Patents
Literature
96 results about "Electron scattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors.
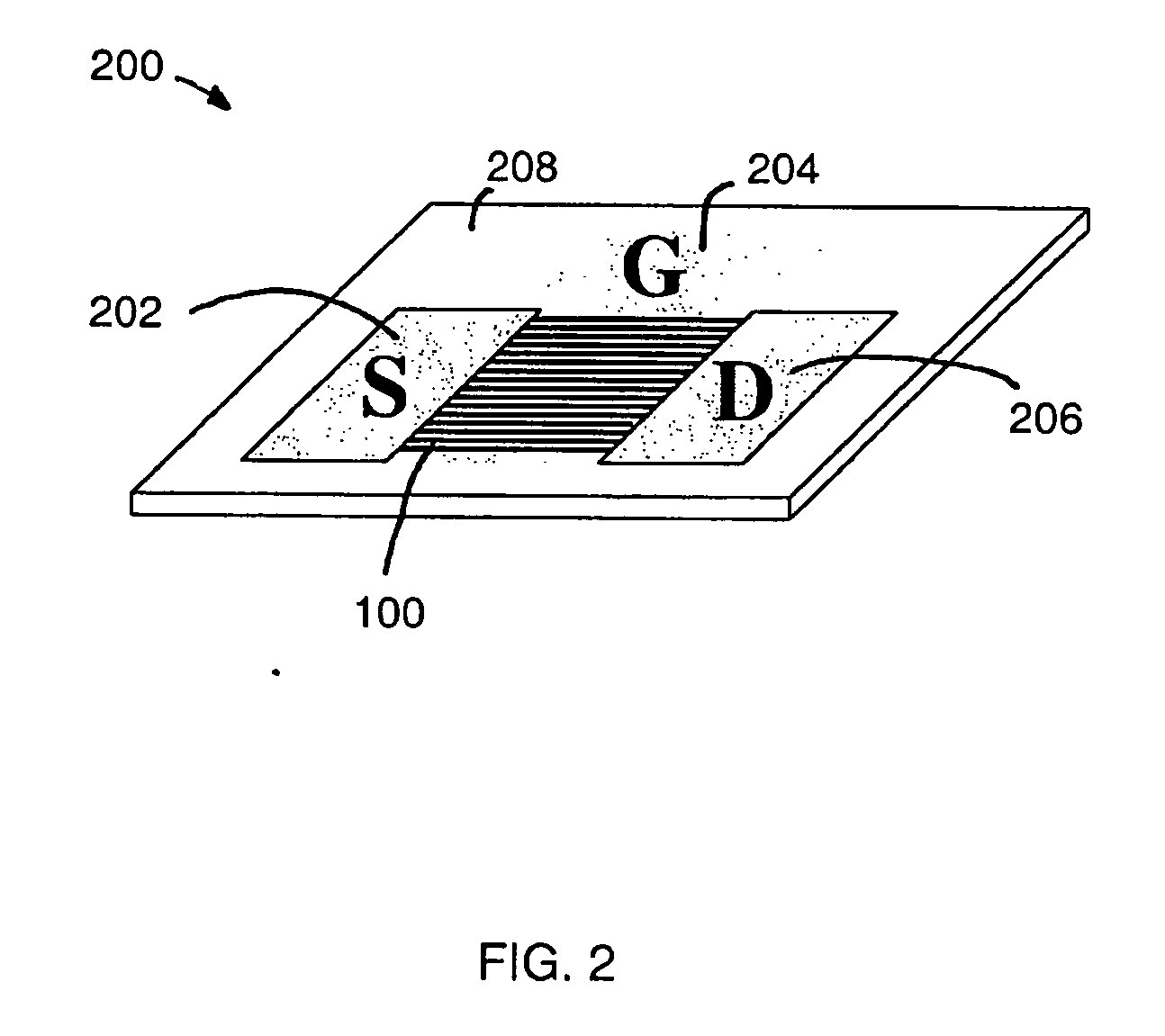
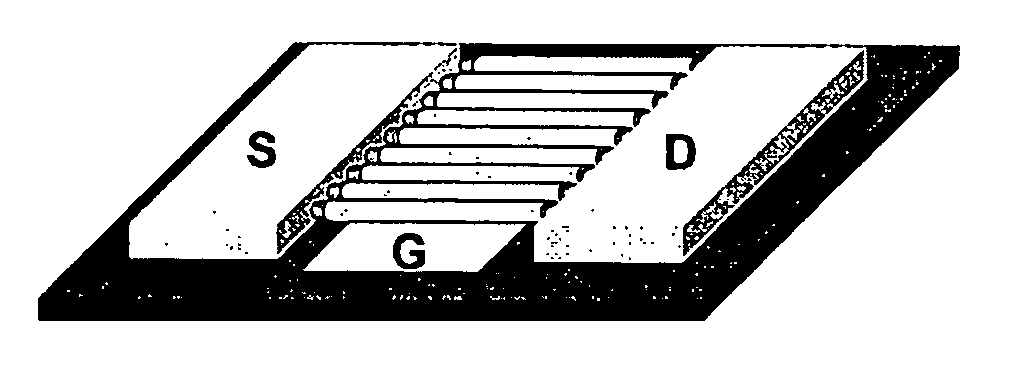
Large-area nanoenabled macroelectronic substrates and uses therefor
ActiveUS20050181587A1Improve performanceHigh carrier mobilityTransistorNanoinformaticsNanowireElectron scattering
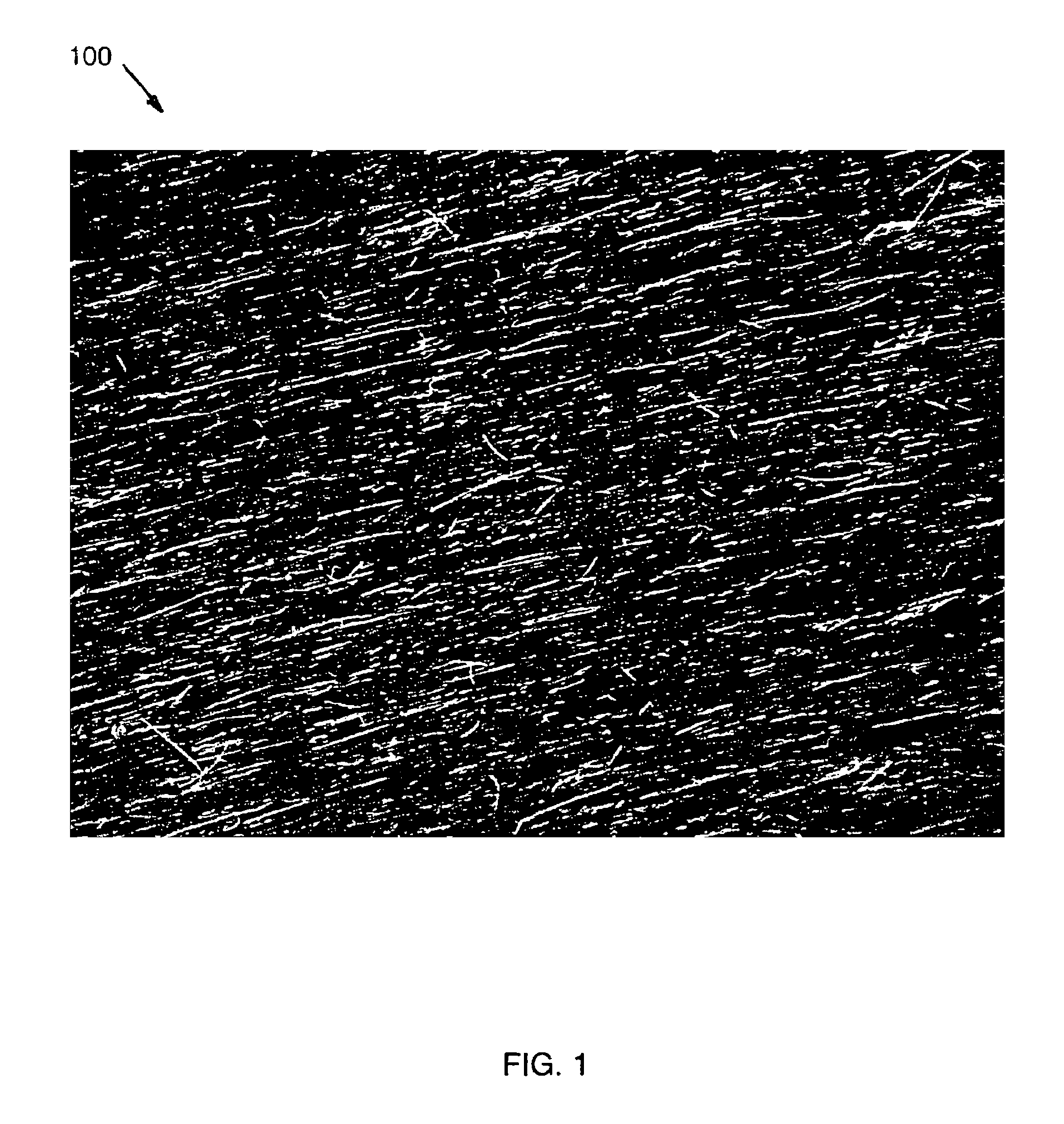
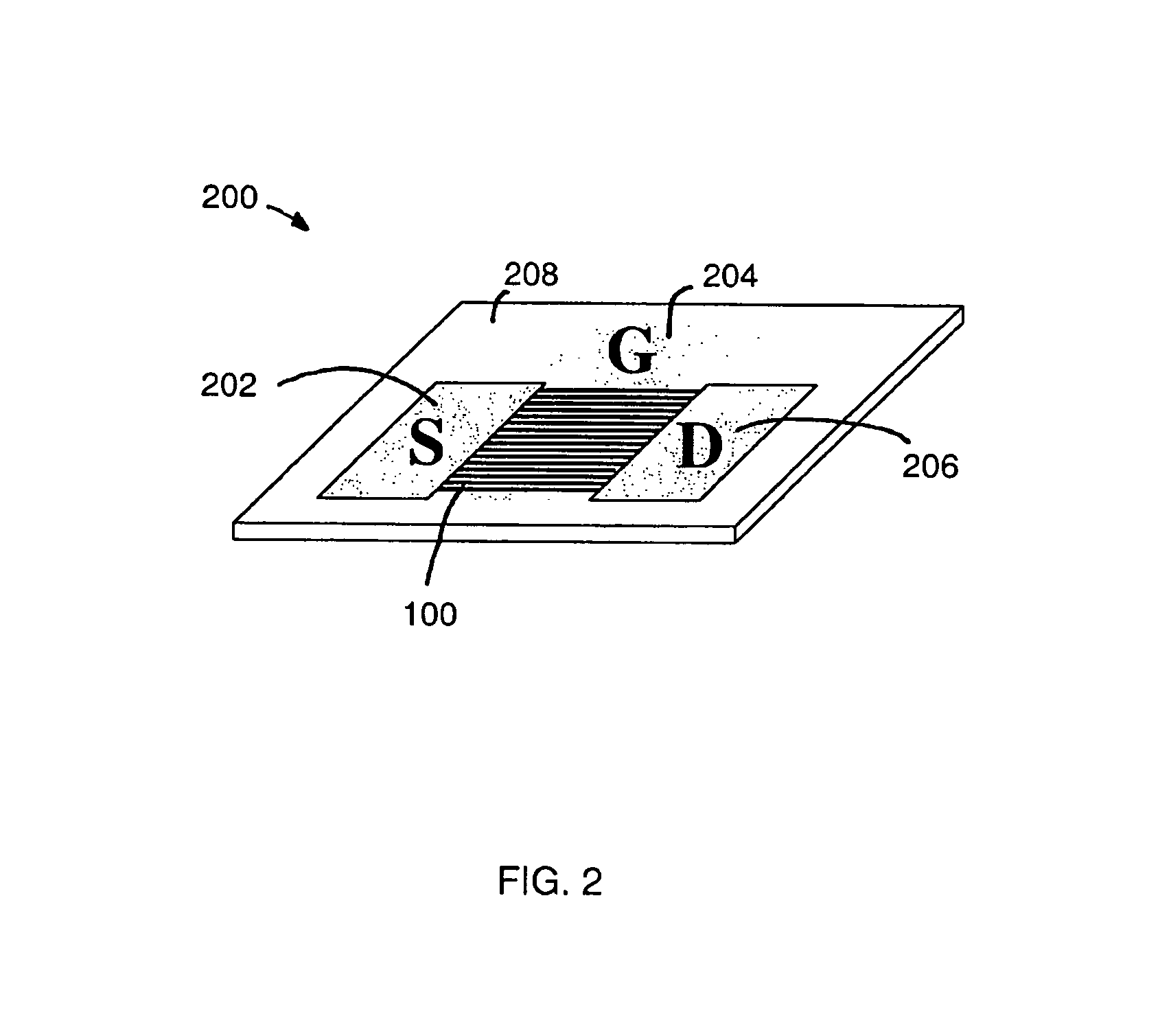
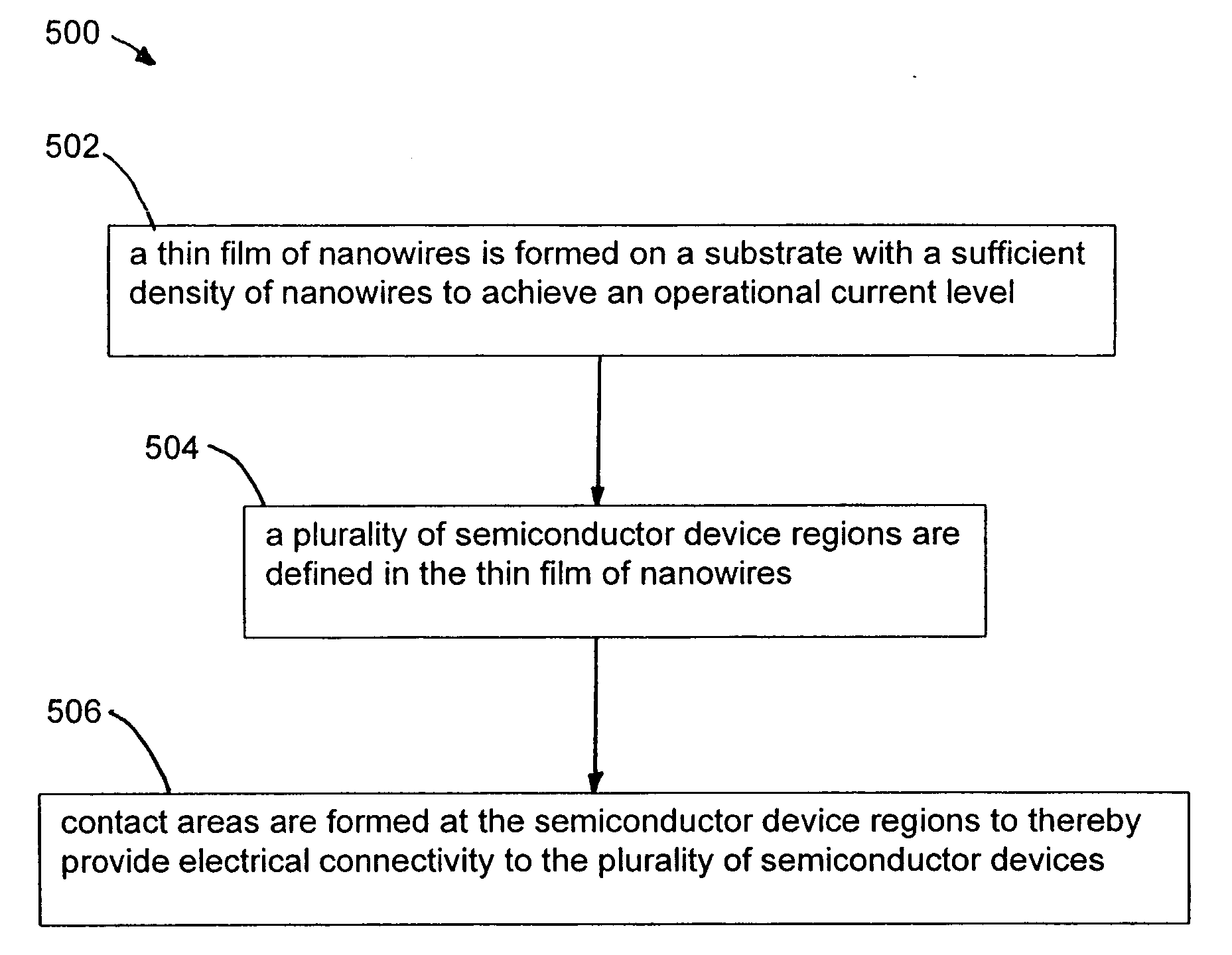
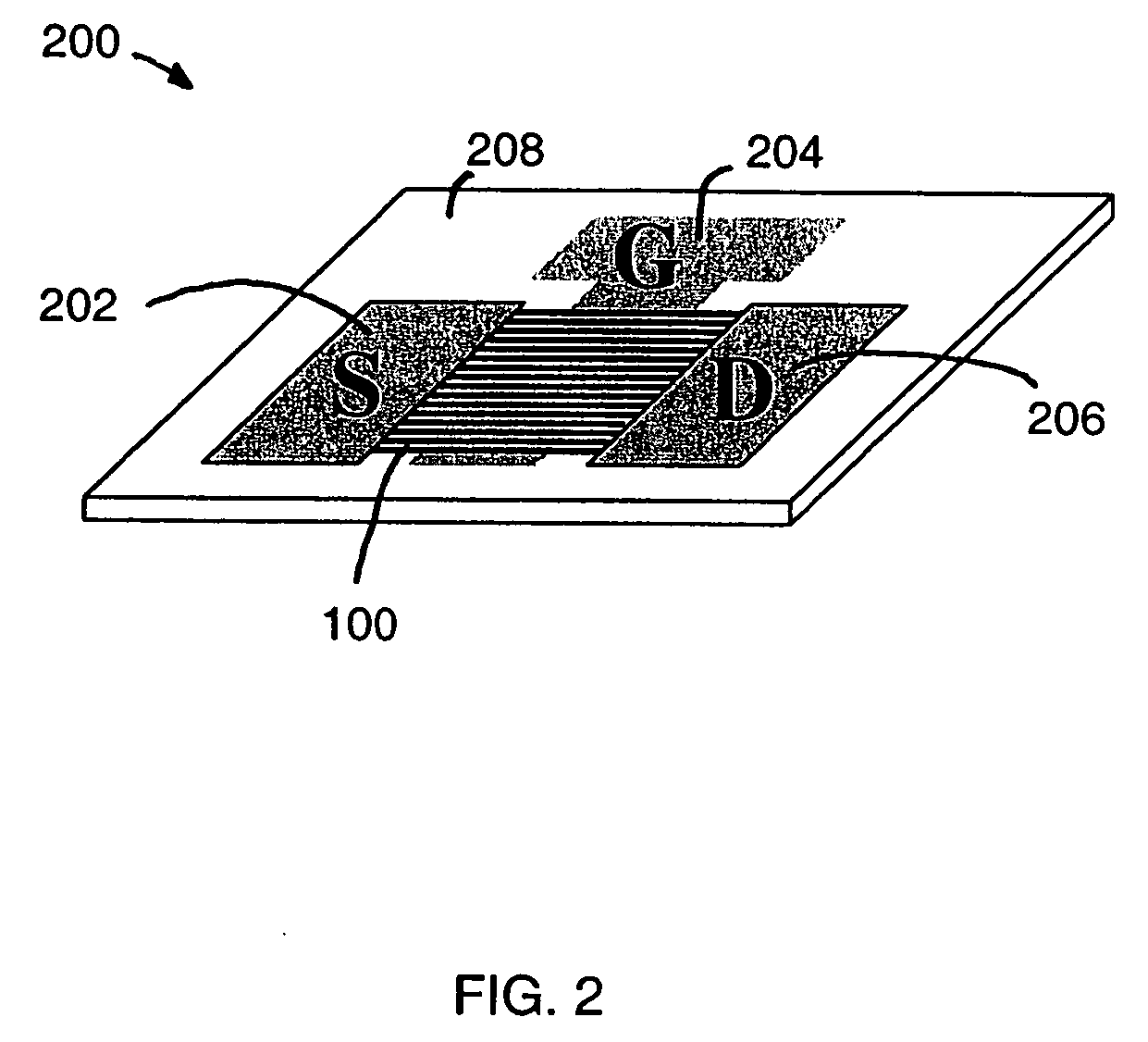
A method and apparatus for an electronic substrate having a plurality of semiconductor devices is described. A thin film of nanowires is formed on a substrate. The thin film of nanowires is formed to have a sufficient density of nanowires to achieve an operational current level. A plurality of semiconductor regions are defined in the thin film of nanowires. Contacts are formed at the semiconductor device regions to thereby provide electrical connectivity to the plurality of semiconductor devices. Furthermore, various materials for fabricating nanowires, thin films including p-doped nanowires and n-doped nanowires, nanowire heterostructures, light emitting nanowire heterostructures, flow masks for positioning nanowires on substrates, nanowire spraying techniques for depositing nanowires, techniques for reducing or eliminating phonon scattering of electrons in nanowires, and techniques for reducing surface states in nanowires are described.
Owner:ONED MATERIAL INC
Large-area nanoenabled macroelectronic substrates and uses therefor
InactiveUS7135728B2Reduce and entirely eliminate scatteringHigh carrier mobilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanowireElectron scattering
A method and apparatus for an electronic substrate having a plurality of semiconductor devices is described. A thin film of nanowires is formed on a substrate. The thin film of nanowires is formed to have a sufficient density of nanowires to achieve an operational current level. A plurality of semiconductor regions are defined in the thin film of nanowires. Contacts are formed at the semiconductor device regions to thereby provide electrical connectivity to the plurality of semiconductor devices. Furthermore, various materials for fabricating nanowires, thin films including p-doped nanowires and n-doped nanowires, nanowire heterostructures, light emitting nanowire heterostructures, flow masks for positioning nanowires on substrates, nanowire spraying techniques for depositing nanowires, techniques for reducing or eliminating phonon scattering of electrons in nanowires, and techniques for reducing surface states in nanowires are described.
Owner:ONED MATERIAL INC
Large-area nanoenabled macroelectronic substrates and uses therefor
InactiveUS20060151820A1Reduce and entirely eliminate scatteringHigh carrier mobilityTransistorNanoinformaticsNanowireElectron scattering
Owner:NANOSYS INC
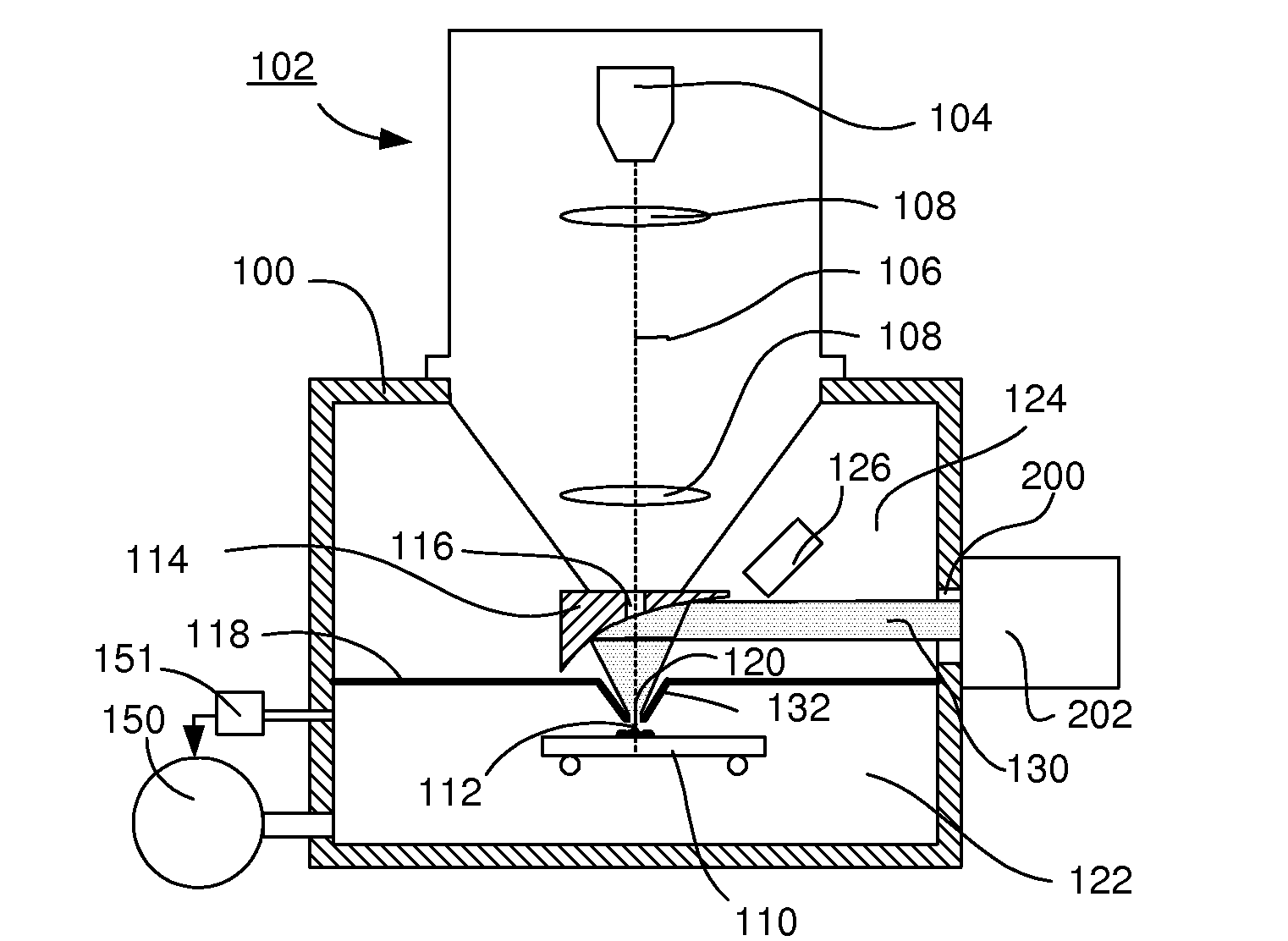
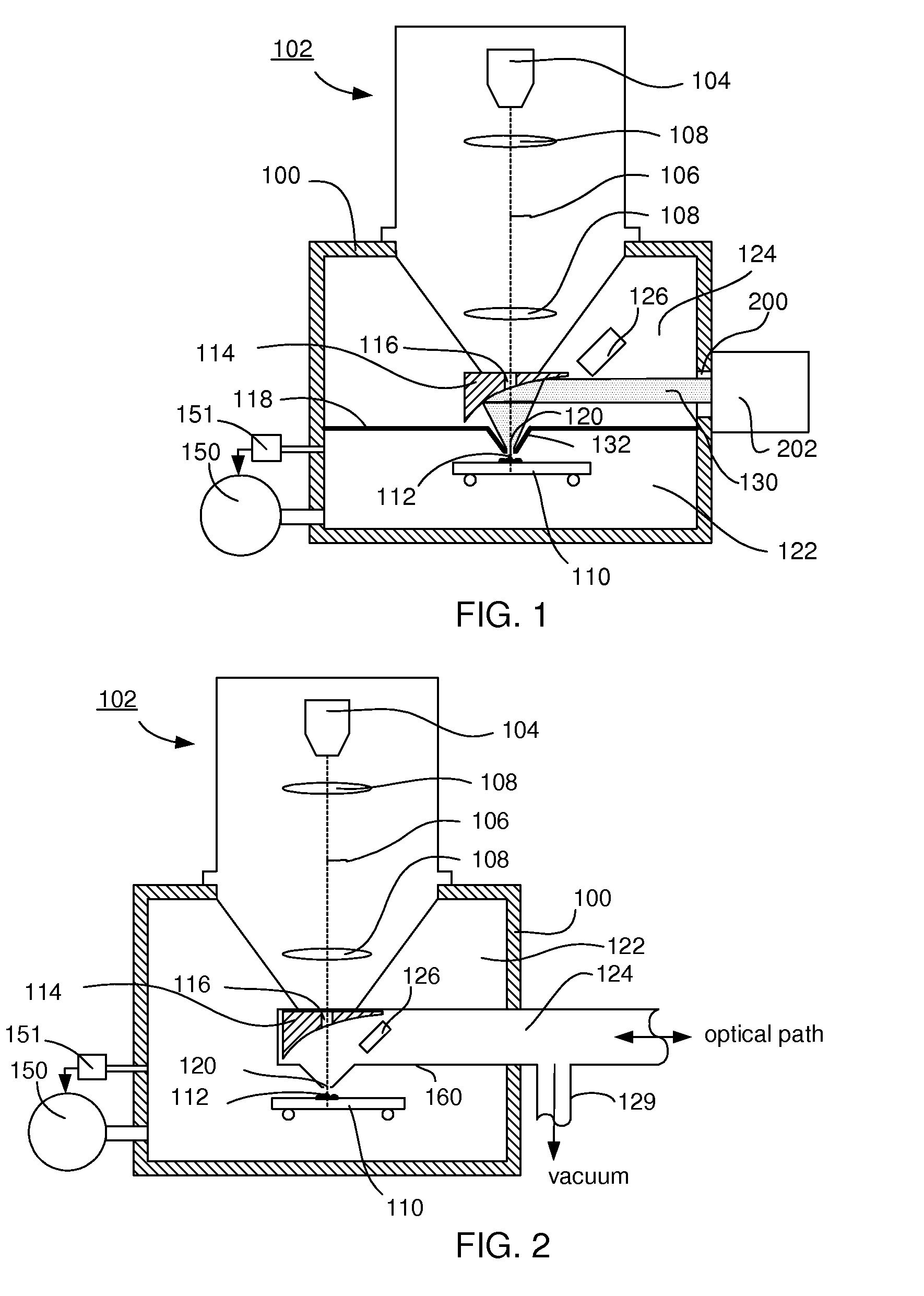
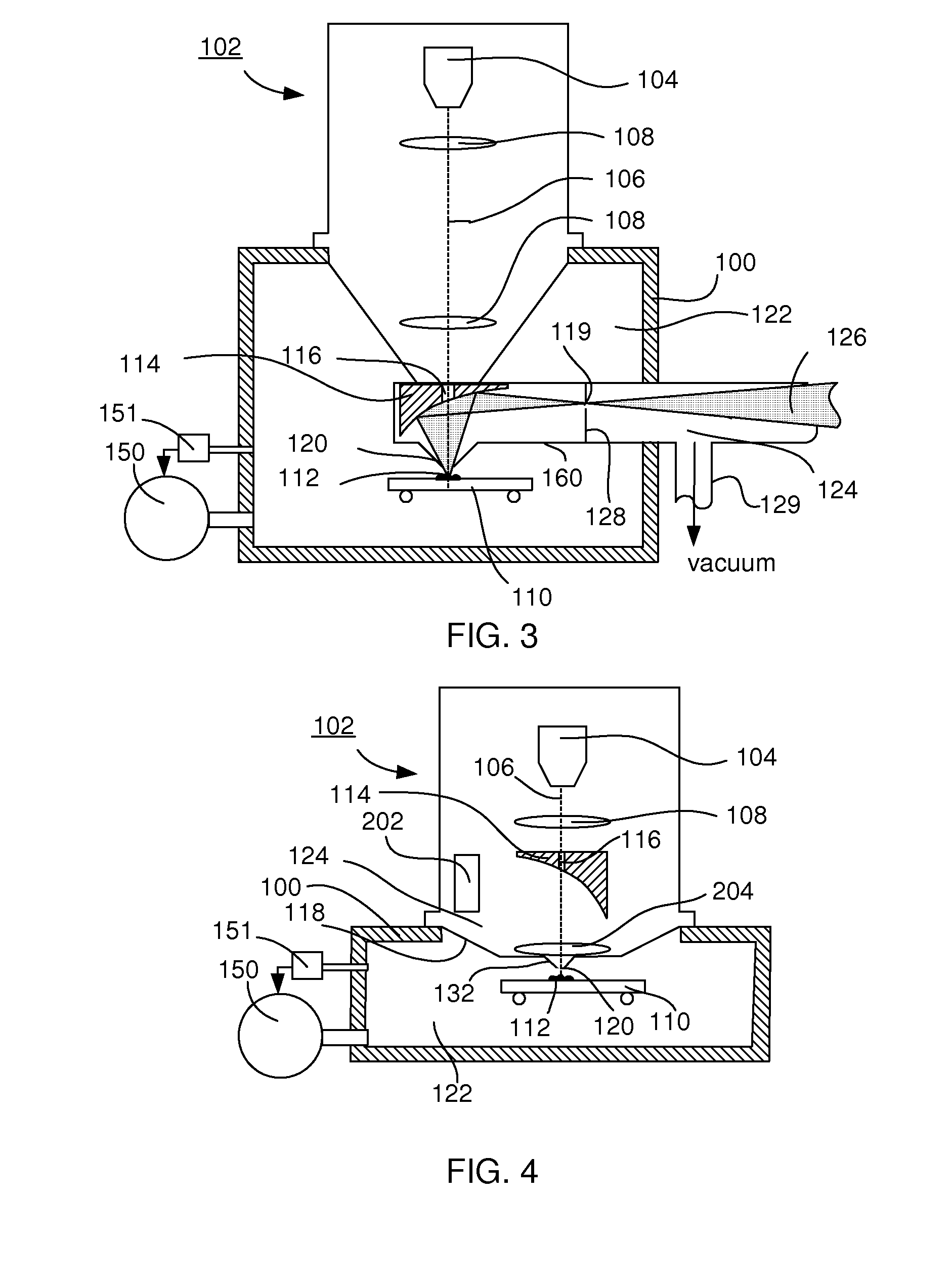
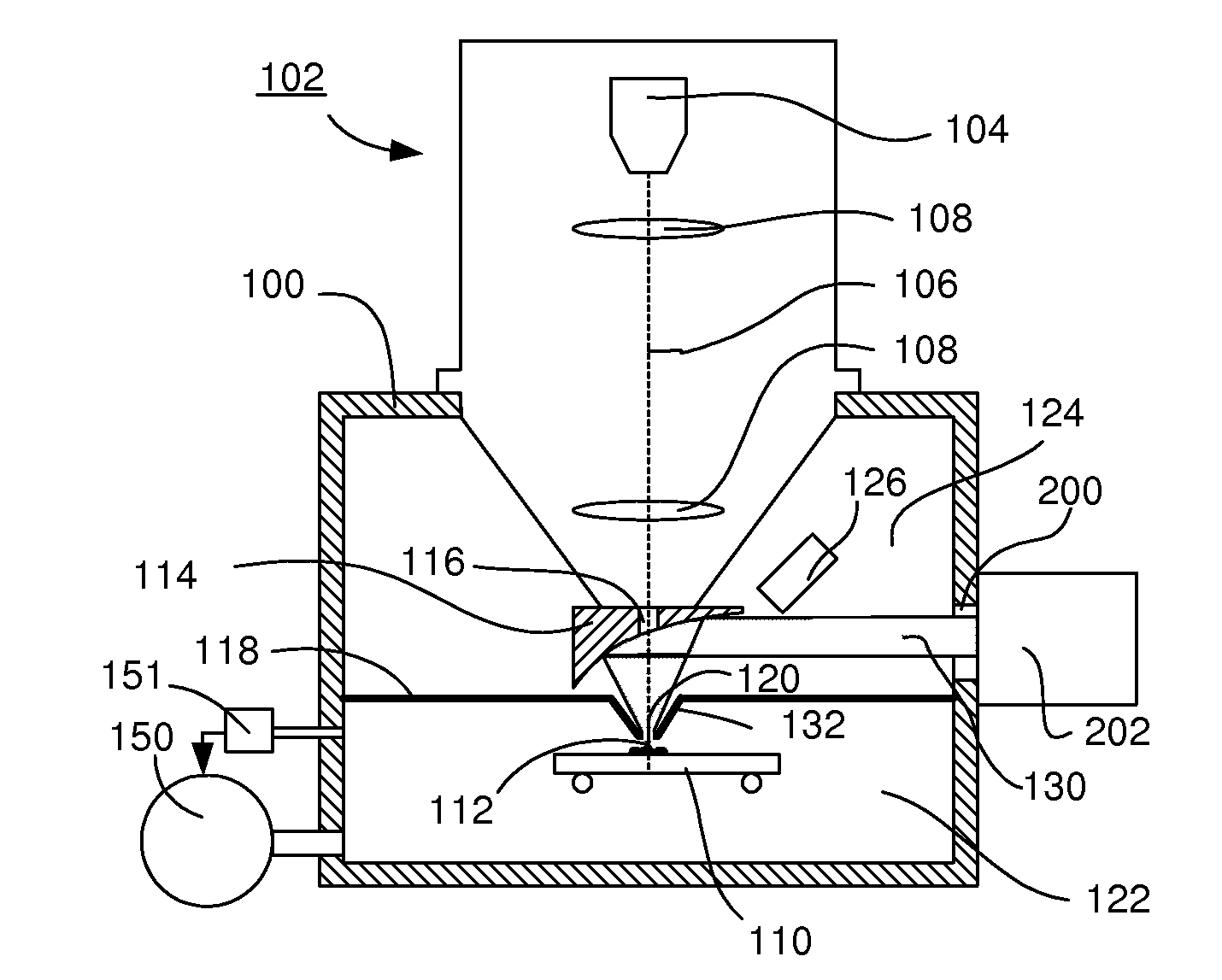
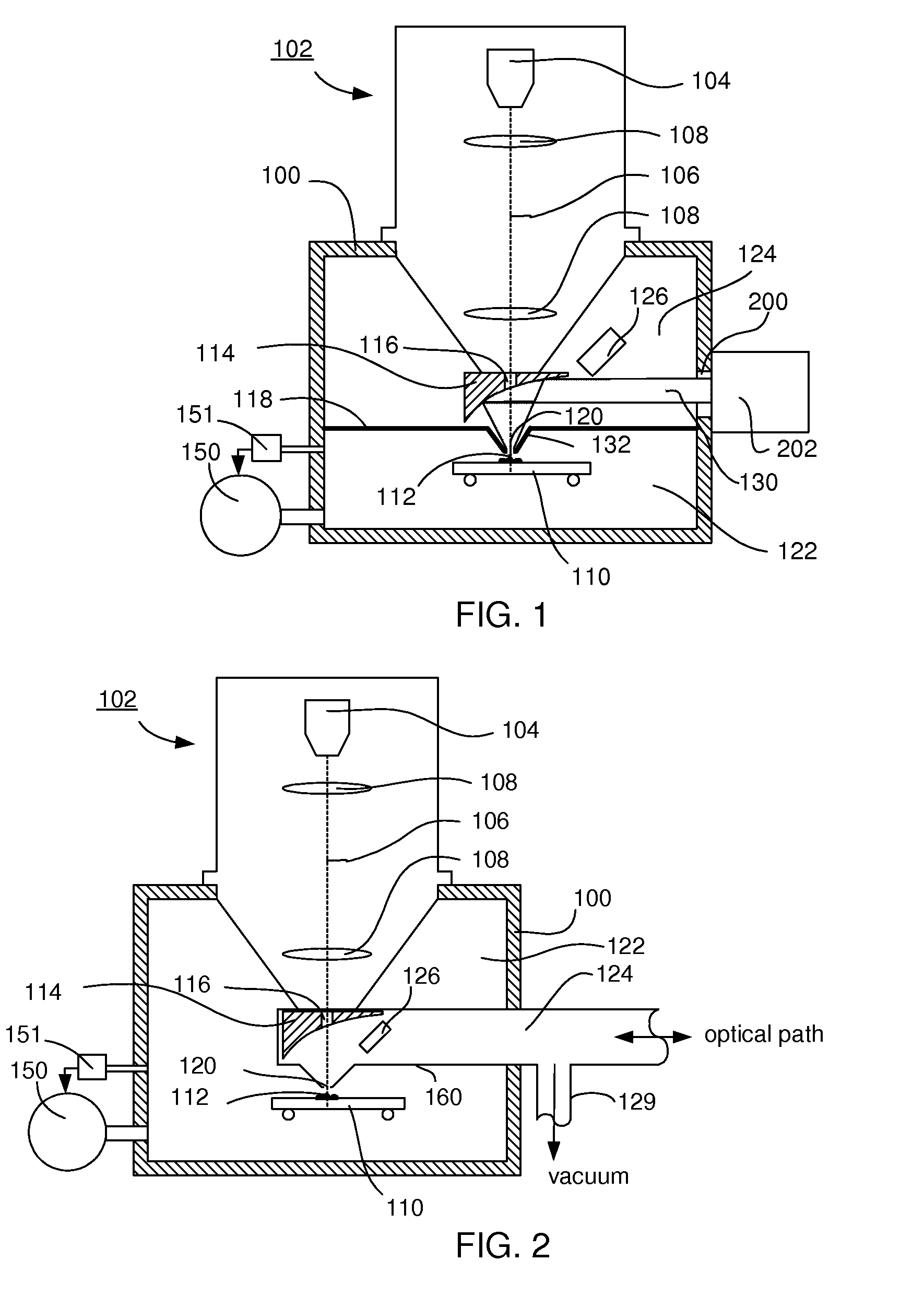
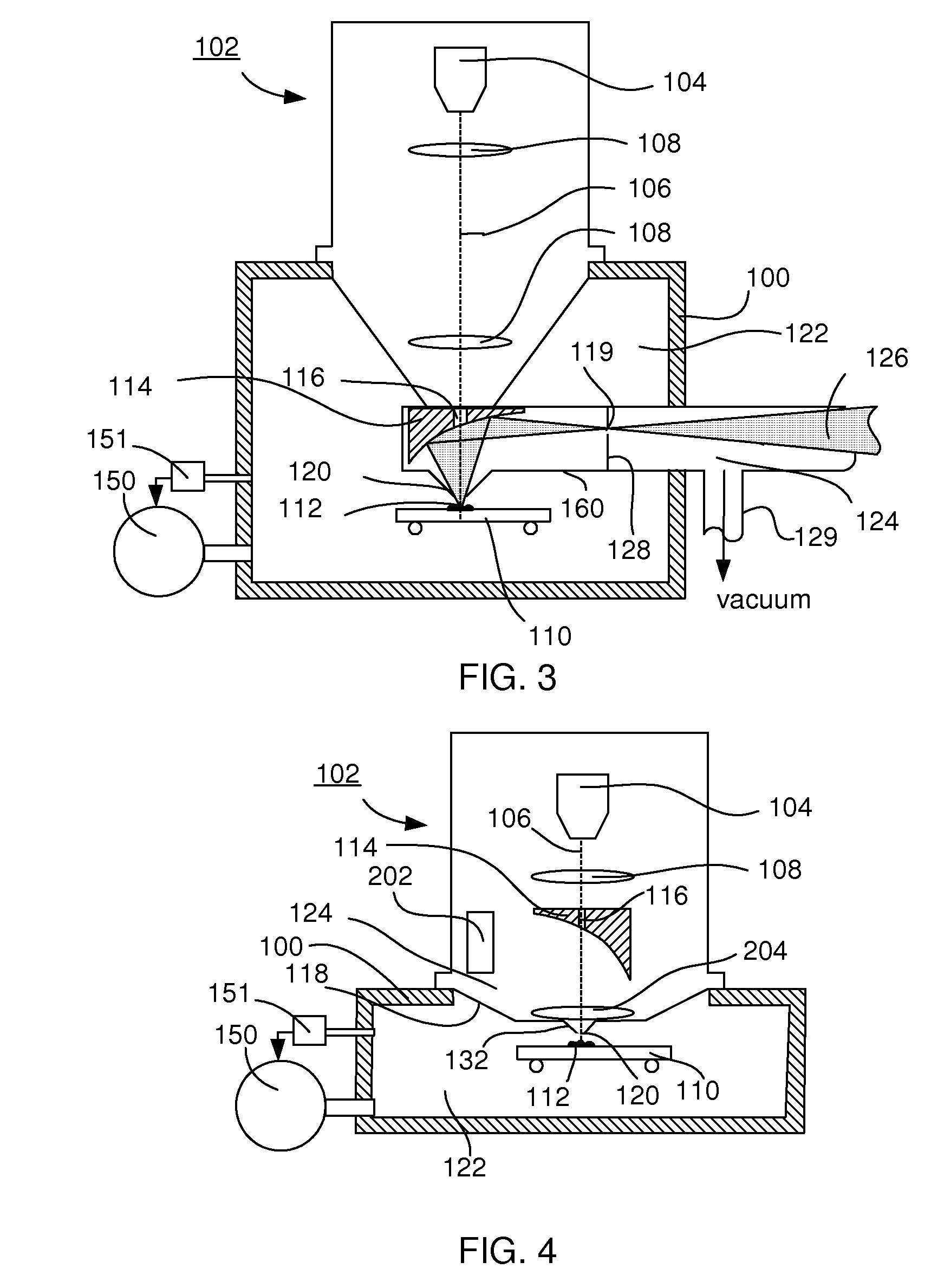
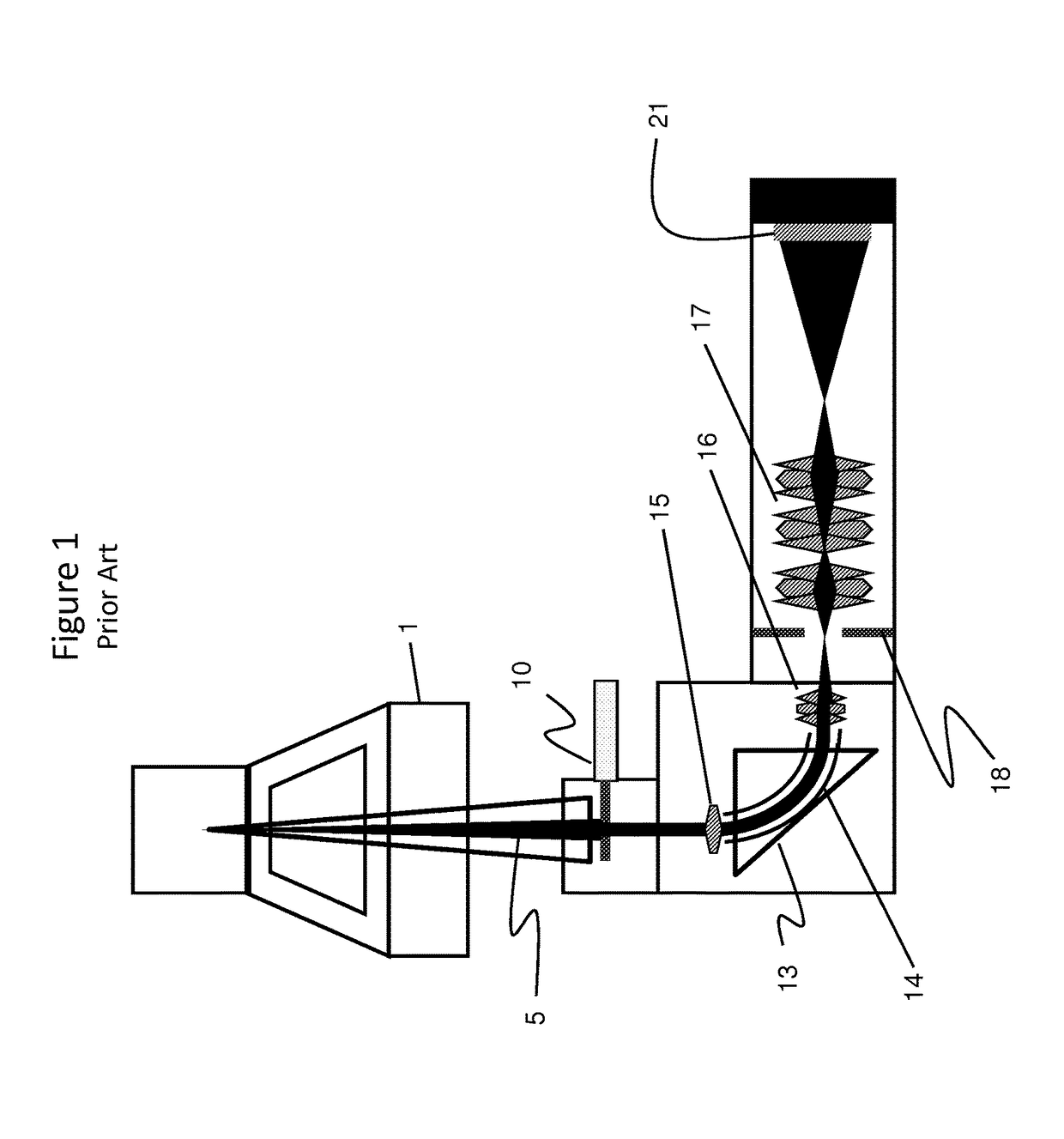
Particle-optical apparatus for simultaneous observing a sample with particles and photons
ActiveUS20080185509A1Less scatteringLarge numerical apertureLaser detailsElectric discharge tubesHigh-pressure areaElectron scattering
A particle-optical apparatus, such as an ESEM®, for simultaneous observing a sample with particles and photons. A pressure limiting aperture (PLA) is placed in a diaphragm between the objective lens of the ESEM® and the sample position. The distance between the sample position and the aperture is sufficiently small to allow a large collection angle of the photons through this aperture. A mirror is placed between the diaphragm and the objective lens. Due to the large collection angle for photons a large NA is achieved. The small distance between sample position and aperture also result in less scattering of electrons than occurs in ESEM's where a mirror is placed between aperture and sample position, as the electrons have to travel through only a limited length in a high pressure area. Embodiments describe combinations where e.g. an immersion lens is used.
Owner:FEI CO
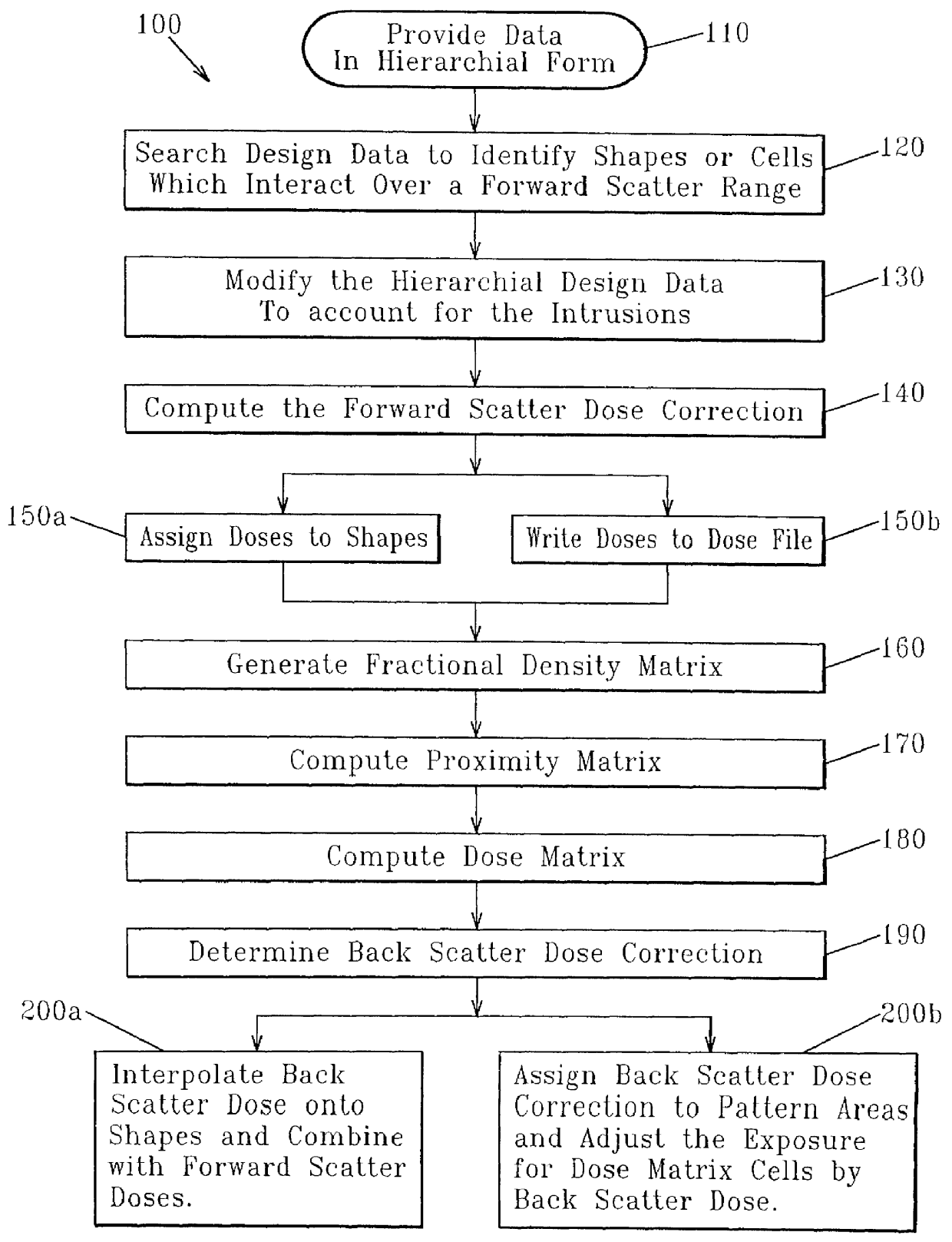
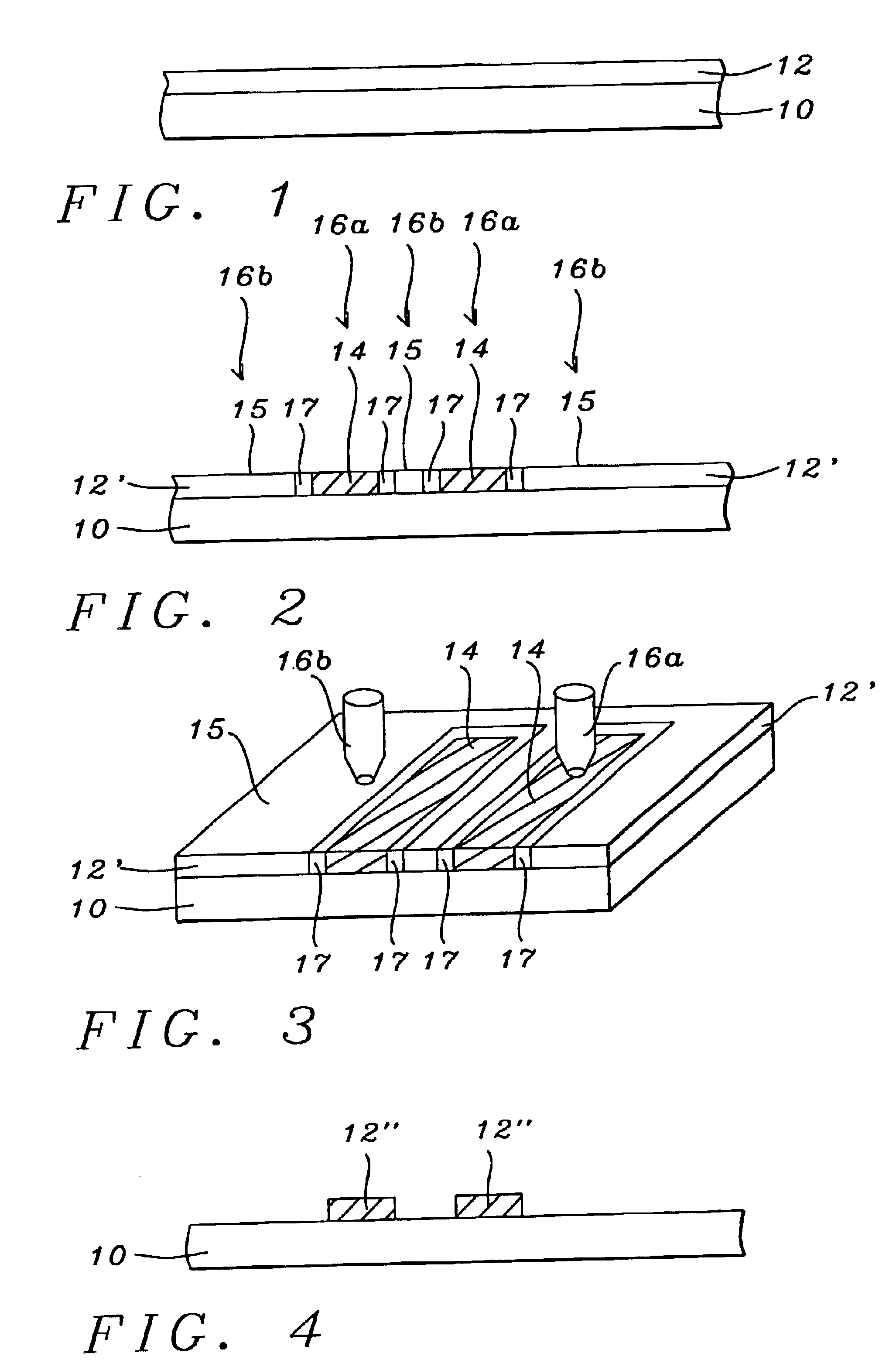
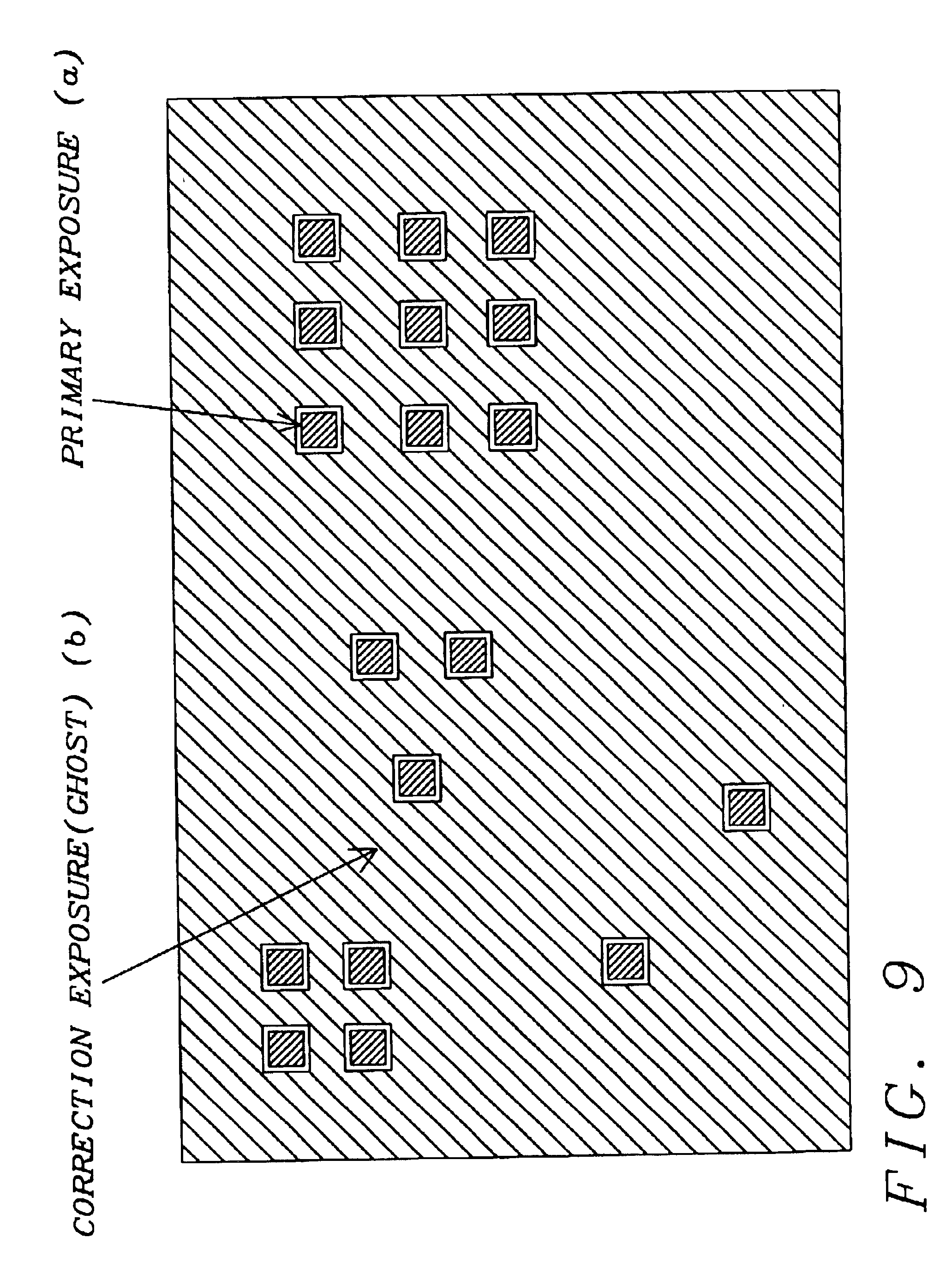
Electron beam proximity correction method for hierarchical design data
InactiveUS6035113AReduce proximity effectImprove computing efficiencyElectric discharge tubesSpecial data processing applicationsForward scatterResist
A method for formulating an exposure dose for an electron beam on a resist film for a pattern of geometric shapes which compensates for electron scattering effects utilizing hierarchial design data which is preserved to as great as an extent as possible in the computation of the exposure dose. The exposure dose is corrected for both the forward scatter and backscatter effects of the electron beam in which the design data is modified for interactions of shapes which are affected only over the forward scatter range. In another version of the method, a multiple Gaussian approximation is used where the short term Gaussian terms are treated as the forward scatter terms and the long term Gaussian terms are treated as the back scatter terms.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
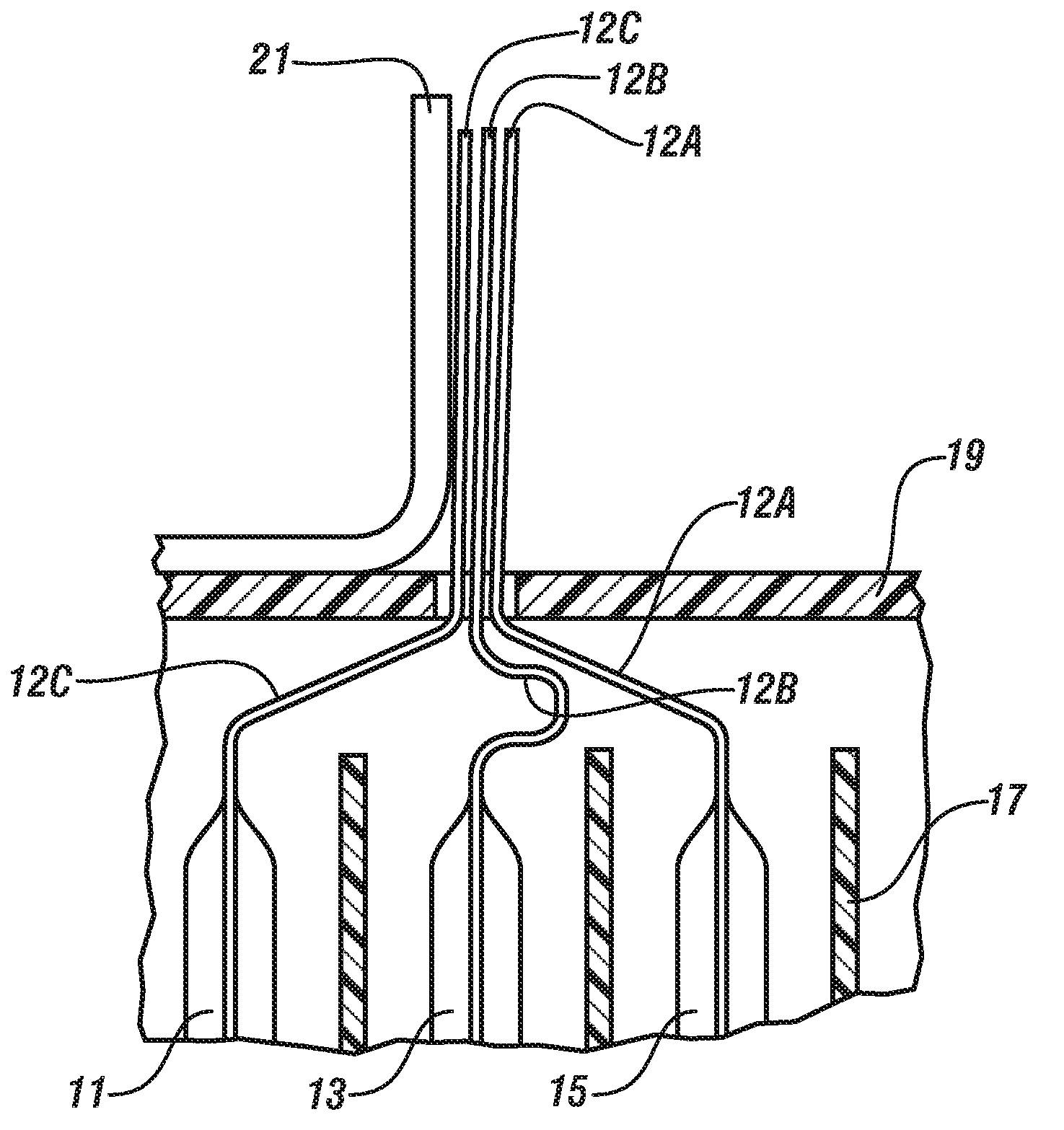
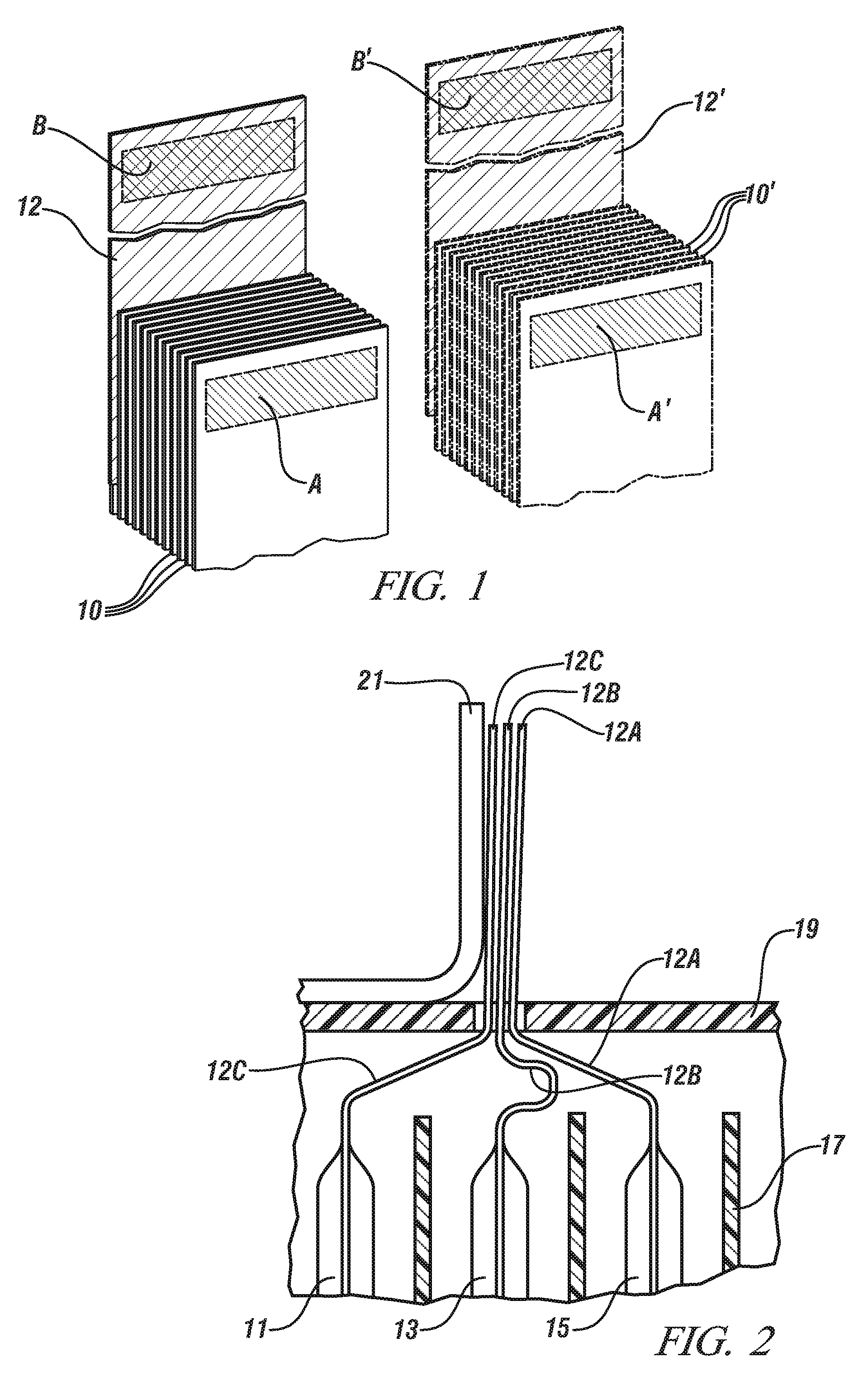
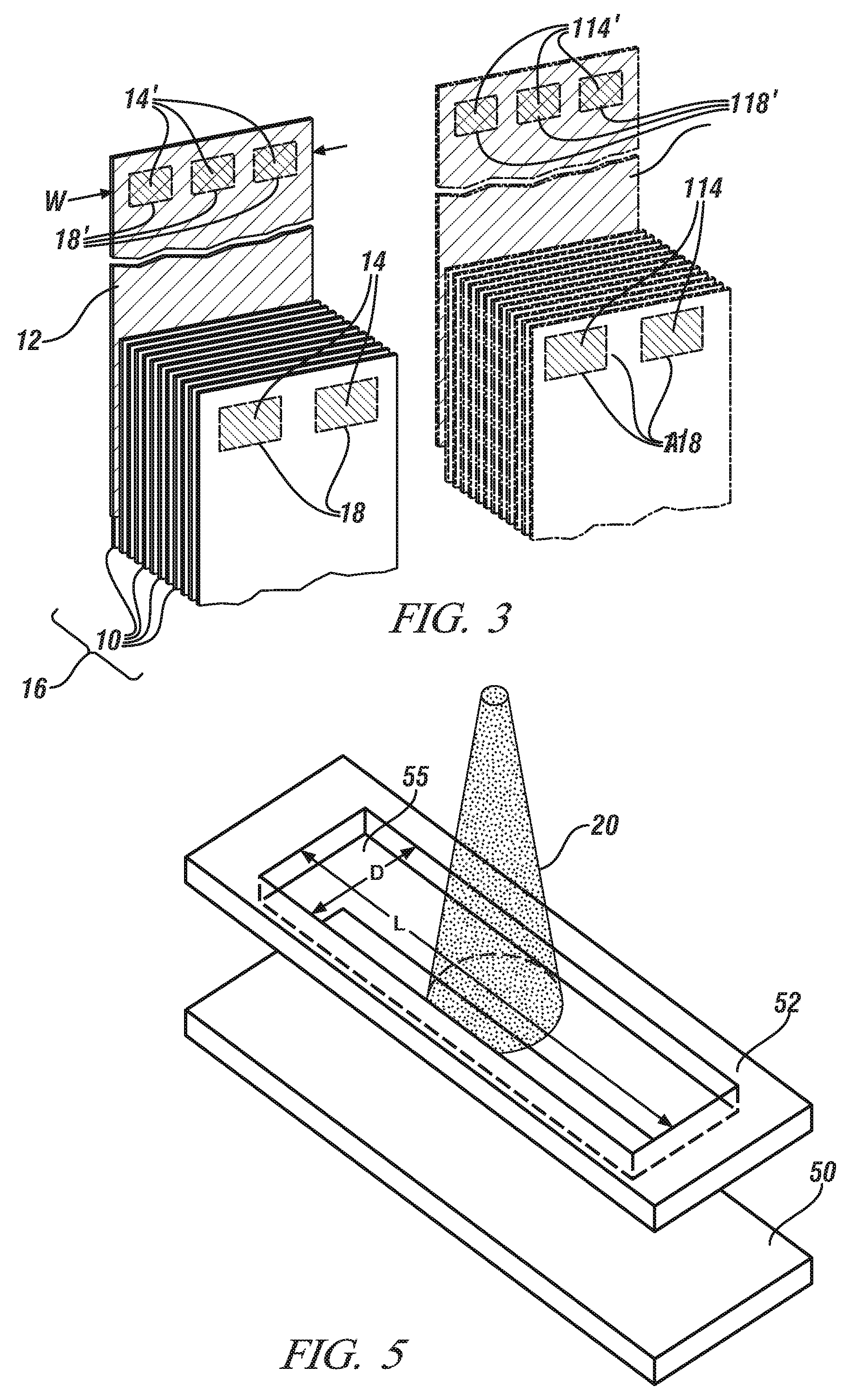
Low pressure electron beam welding of li-ion battery connections
ActiveUS20130029206A1Lower resistanceReduce sensitivityFinal product manufacturePrimary cellsLithiumElectrical battery
A method for connecting individual lithium ion cells into a battery suited for powering an electric or hybrid vehicle is disclosed. The cell current collectors are electron beam welded to one another and to a connector tab in an substantially oxygen-free atmosphere. The cell current collectors and the connector tab are temporarily secured with a clamp, one portion of which has an opening. The electron beam size may be controlled, by magnetic coils and by the extent of electron scattering by the gas atmosphere, to minimally fill the clamp opening to minimize any irradiation of the clamp. The beam or the workpieces may be displaced, if required, fuse the entire opening area. A similar procedure may be followed to weld a plurality of connector tabs to a busbar.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Nano copper-tin alloy conductive ink and preparation method and usage of nano copper-tin alloy conductive ink
ActiveCN102675960ALower sintering temperatureImprove antioxidant capacityInksMetallic pattern materialsRare earthElectron scattering
The invention belongs to the technical field of material chemistry, relates to conductive ink, and particularly relates to nano copper-tin alloy conductive ink and a preparation method and usage of the nano copper-tin alloy conductive ink. Nano copper-silver alloy is replaced by nano copper-tin alloy to be used as conductive filler in the conductive ink, sintering temperature of the conductive ink is lowered, and when the nano copper-tin alloy conductive ink is compared with nano copper-silver alloy conductive ink, antioxidant capacity of the conductive ink during sintering is improved, mechanical property and solderability of a conductive circuit formed after sintering of the conductive ink are improved, and the problem of silver ion migration is avoided. Further, since rare earth metal elements are doped in the nano copper-tin alloy, grain boundary of the nano copper-tin alloy is increased, electron scattering power is increased, and conductivity is improved as compared with that of nano copper alloy. On the other hand, tin is much cheaper than silver, so that raw material cost of the nano copper-tin alloy conductive ink is reduced.
Owner:深圳市尊业纳米材料有限公司
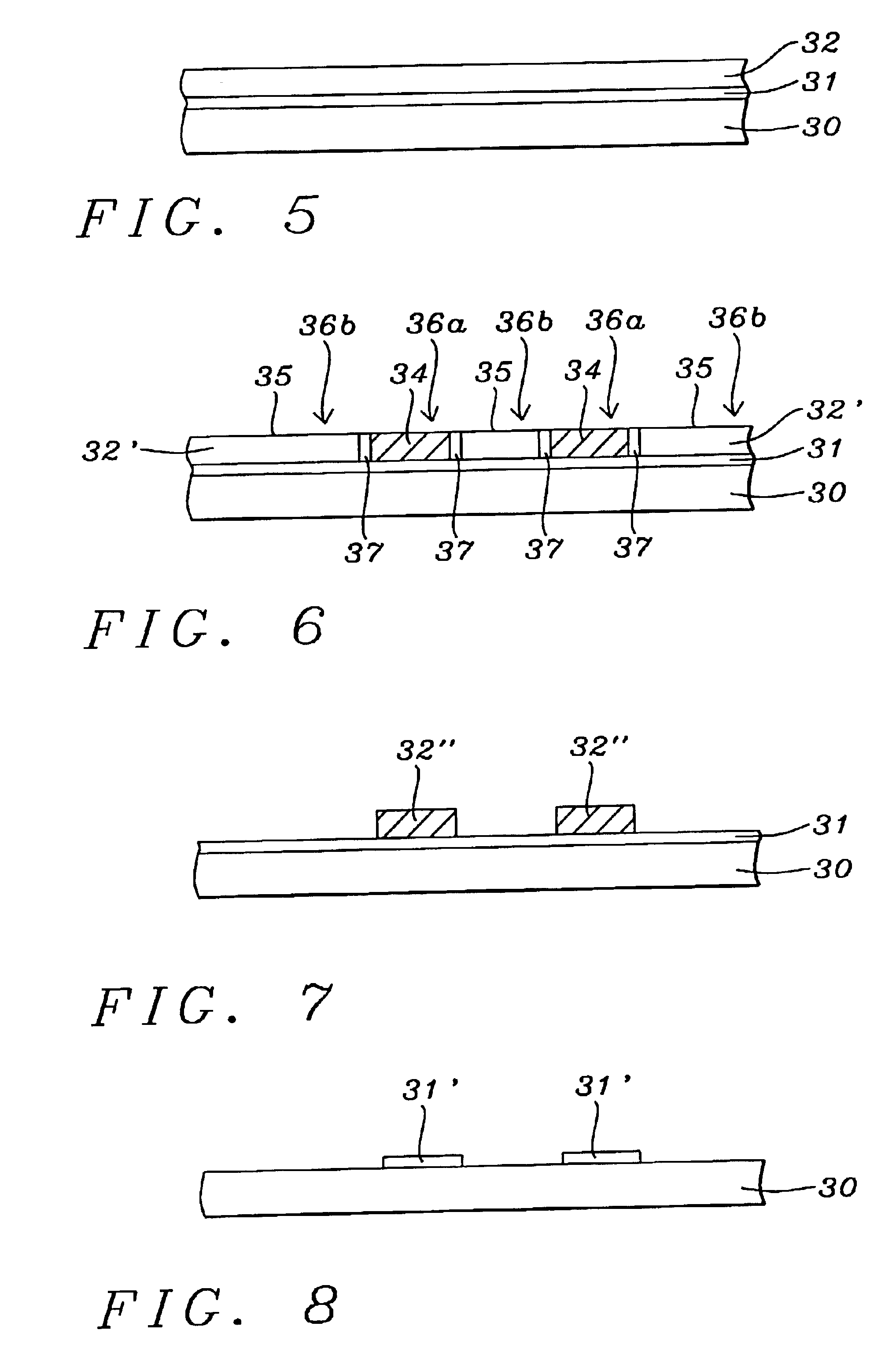
Radiation correction method for electron beam lithography
InactiveUS6872507B2Readily commercially implementedOptimal correction for proximity effectsElectric discharge tubesRadiation applicationsResistLight beam
A method for forming a patterned microelectronics layer employing electron beam lithography in a sensitive material upon a substrate with optimal correction for proximity effects resulting from electron back scattering into the resist material. There is provided a substrate having formed thereon a layer of resist material sensitive to electron beam exposure. There is then exposed the sensitive layer to a vector scan shaped electron beam to write a primary pattern with dose correction of the beam dose for proximity effects due to electron scattering at each point in the primary pattern. There is then written a secondary pattern which is a negative reversed image of the primary pattern in a secondary exposure employing a vector scan shaped focused electron beam at an exposure dose substantially below the primary beam dose, there being provided a gap between the primary pattern and the secondary pattern. There is then developed the primary pattern in the sensitive resist layer to form the final corrected pattern on the substrate. The patterned layer of resist material may be employed directly on the substrate on which it is formed, or alternatively the patterned resist layer may be employed formed over an opaque layer upon the transparent substrate and subsequently the pattern etched into the opaque layer to form a photomask.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
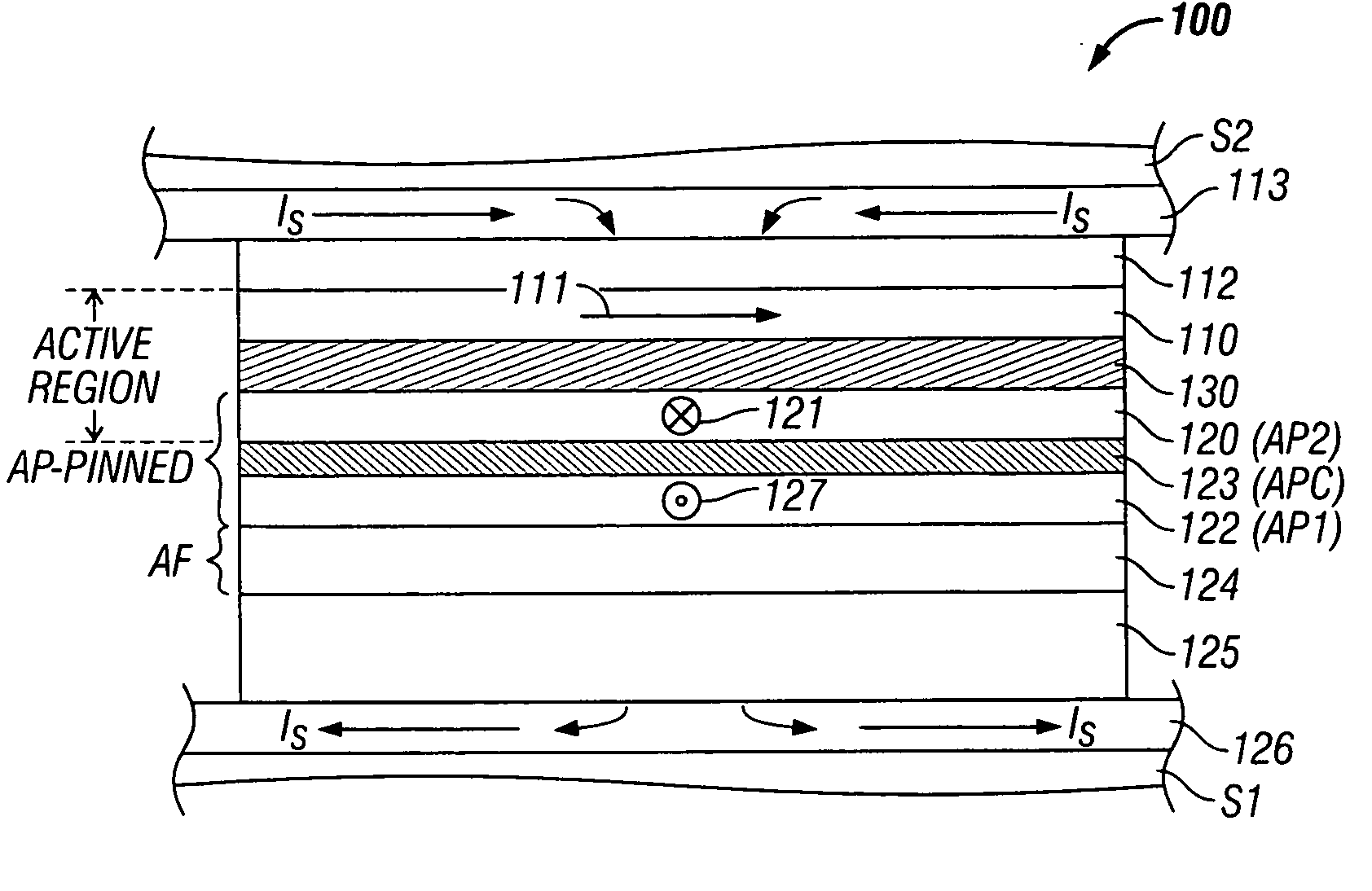
Current-perpendicular-to-the-plane (CPP) magnetoresistive sensor with high-resistivity amorphous ferromagnetic layers
InactiveUS20070188937A1Simple fixed structureIncreased electrical resistivityNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsElectron scatteringHigh resistivity
A current-perpendicular-to-the-plane spin-valve (CPP-SV) magnetoresistive sensor has a high-resistivity amorphous ferromagnetic alloy in the free layer and / or the pinned layer. The sensor may have an antiparallel (AP)-pinned structure, in which case the AP2 layer may be formed of the high-resistivity amorphous ferromagnetic alloy. The amorphous alloy is an alloy of one or more elements selected from Co, Fe and Ni, and at least one nonmagnetic element X. The additive element or elements is present in an amount that renders the otherwise crystalline alloy amorphous and thus substantially increases the electrical resistivity of the layer. As a result the resistance of the active region of the sensor is increased. The amount of additive element or elements is chosen to be sufficient to render the alloy amorphous but not high enough to substantially reduce the magnetic moment M or bulk electron scattering parameter β.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
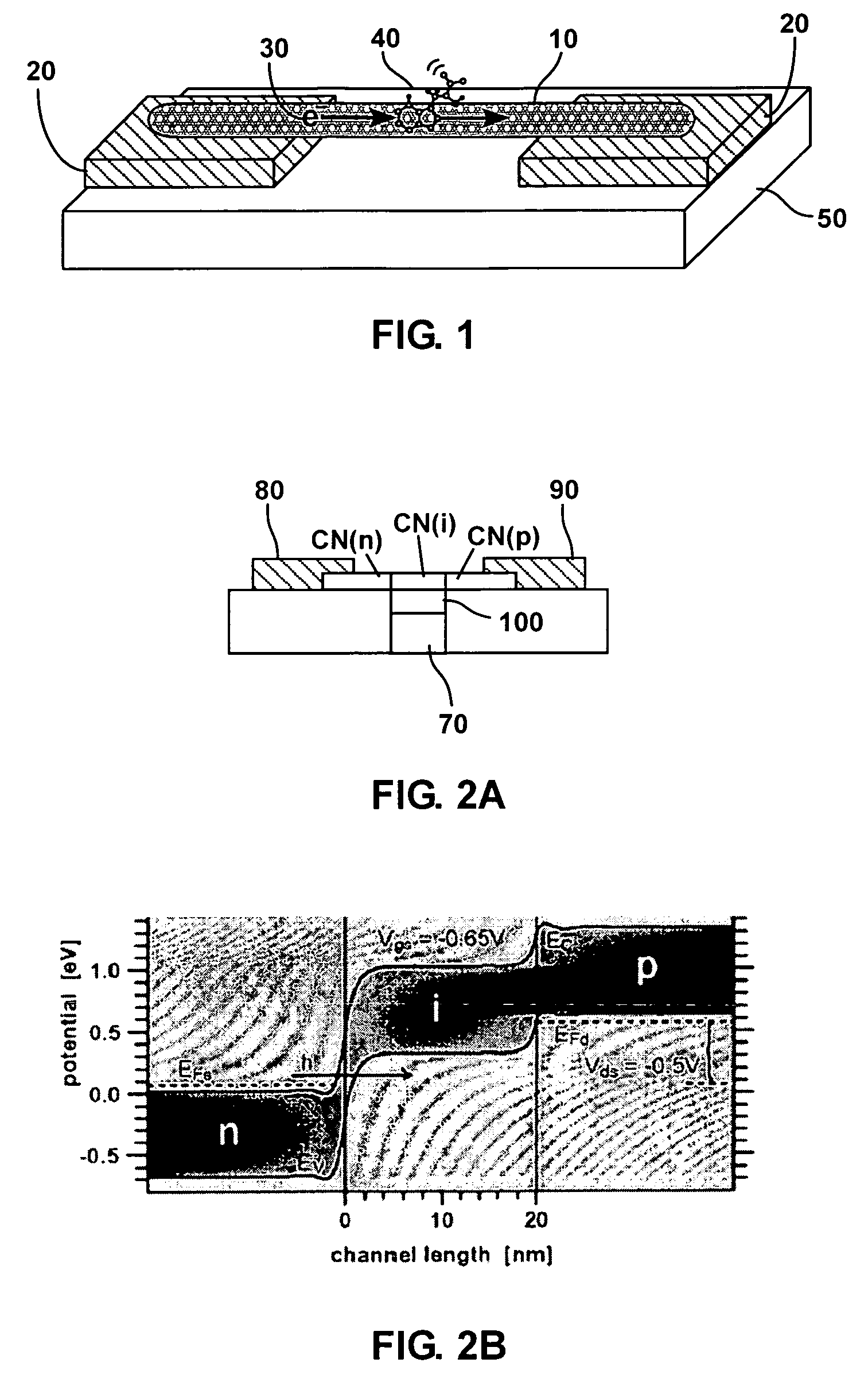
Nanowire electron scattering spectroscopy
InactiveUS20090072137A1Simple and direct electrical readoutFully integratedRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationNanowireSpectroscopy methods
Methods and devices for spectroscopic identification of molecules using nanoscale wires are disclosed. According to one of the methods, nanoscale wires are provided, electrons are injected into the nanoscale wire; and inelastic electron scattering is measured via excitation of low-lying vibrational energy levels of molecules bound to the nanoscale wire.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
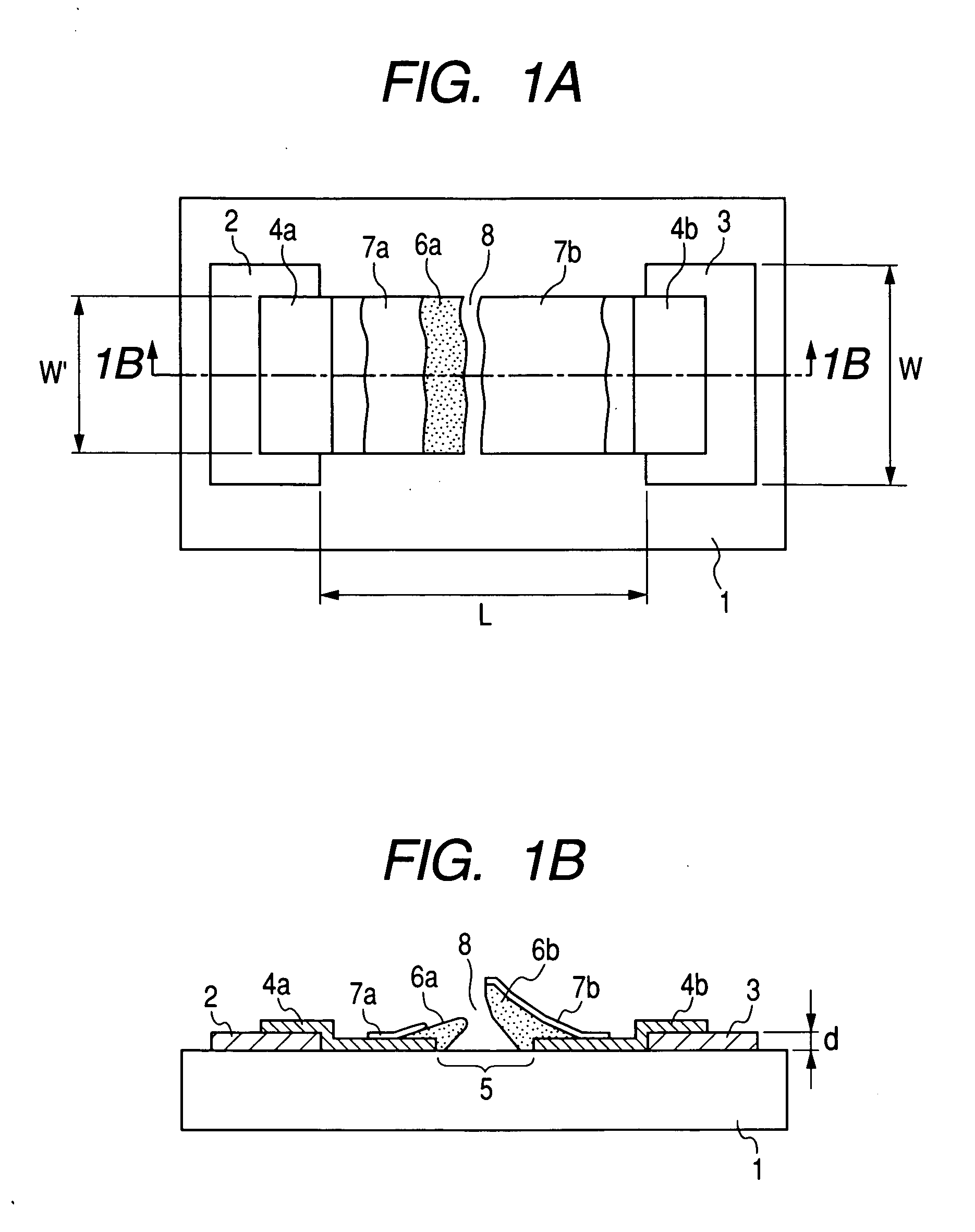
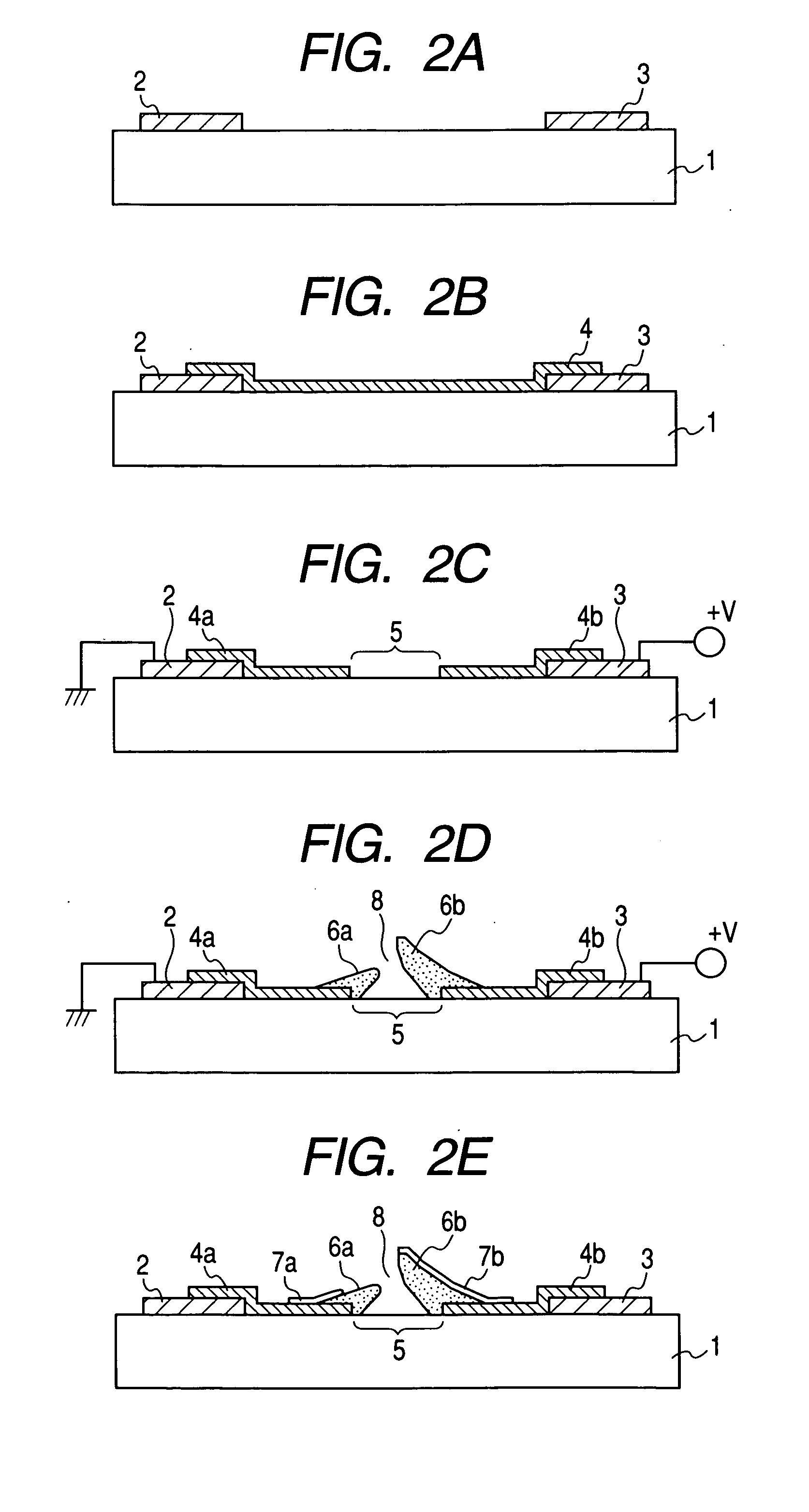
Electron-emitting device, electron source, and method for manufacturing image displaying apparatus
InactiveUS7312561B2Good electron emission characteristicExtend your lifeDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsElectron sourceElectron scattering
An electron-emitting device is equipped with a pair of first electroconductive members arranged on a substrate with an interval between them, wherein the interval becomes narrower at an upper position distant from a surface of the substrate than at a position on the surface, and a peak of one of the pair of the first electroconductive members is higher than a peak of the other of the pair of the first electroconductive members, and further an electron scattering surface forming film including an element having an atomic number larger than those of elements constituting the first electroconductive members as a principal component is provided on a surface of the one of the first electroconductive members.
Owner:CANON KK
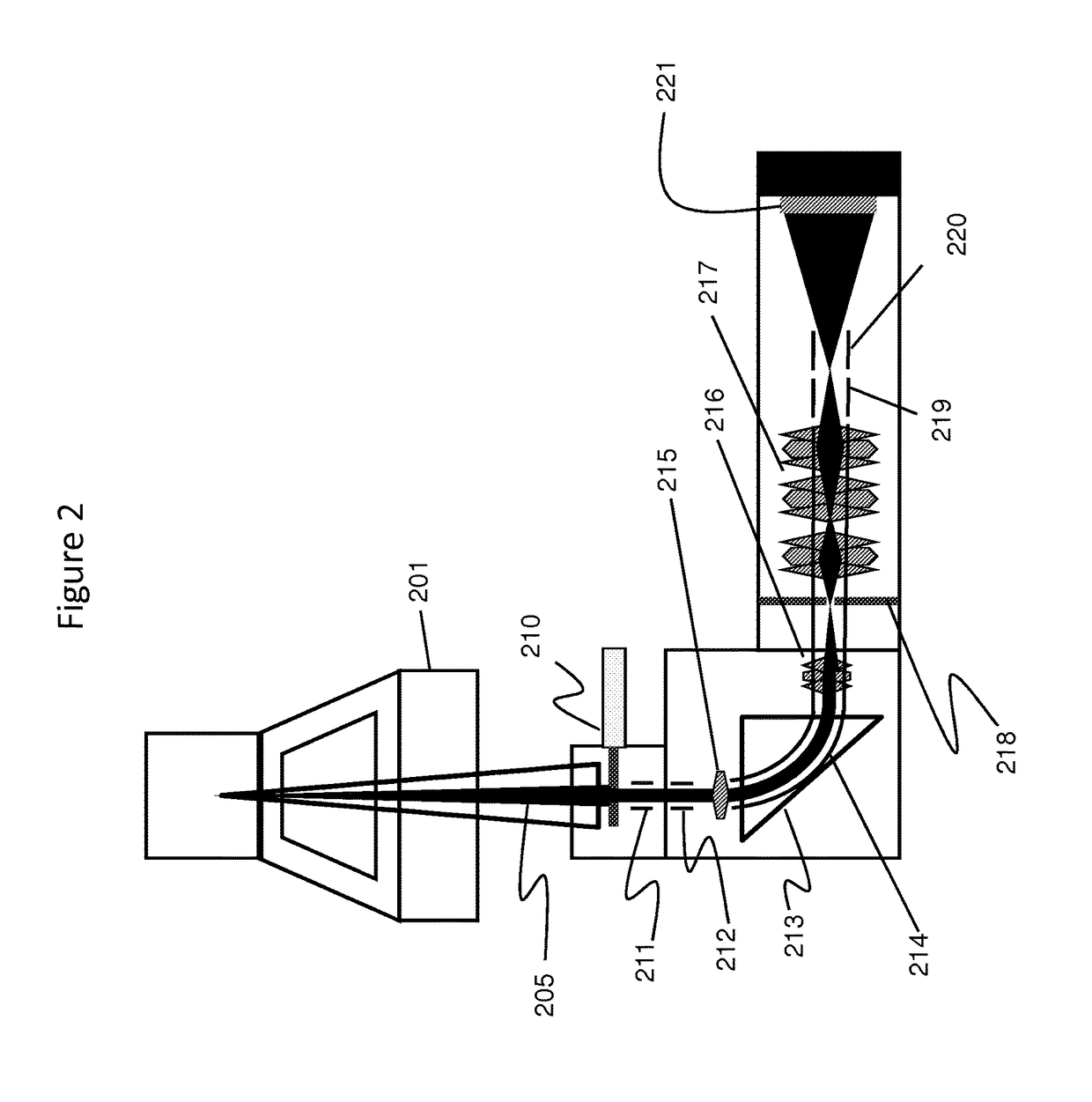
Particle-optical apparatus for simultaneous observing a sample with particles and photons
A particle-optical apparatus, such as an ESEM®, for simultaneous observing a sample with particles and photons. A pressure limiting aperture (PLA) is placed in a diaphragm between the objective lens of the ESEM® and the sample position. The distance between the sample position and the aperture is sufficiently small to allow a large collection angle of the photons through this aperture. A mirror is placed between the diaphragm and the objective lens. Due to the large collection angle for photons a large NA is achieved. The small distance between sample position and aperture also result in less scattering of electrons than occurs in ESEM's where a mirror is placed between aperture and sample position, as the electrons have to travel through only a limited length in a high pressure area. Embodiments describe combinations where e.g. an immersion lens is used.
Owner:FEI CO
Electron-emitting device, electron source, and method for manufacturing image displaying apparatus
InactiveUS20050236952A1Good electron emission characteristicExtend your lifeDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsElectron sourceElectron scattering
Owner:CANON KK
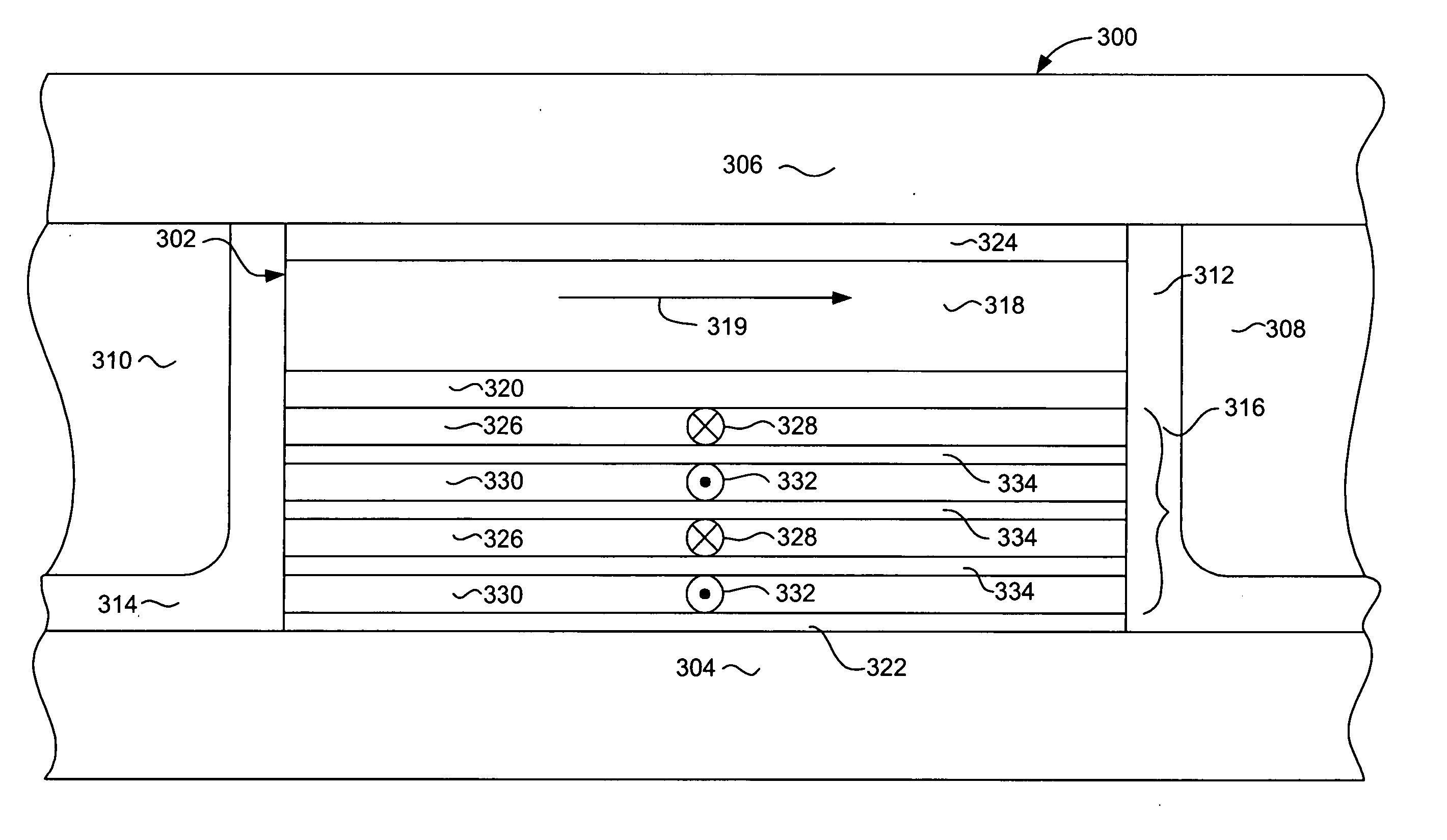
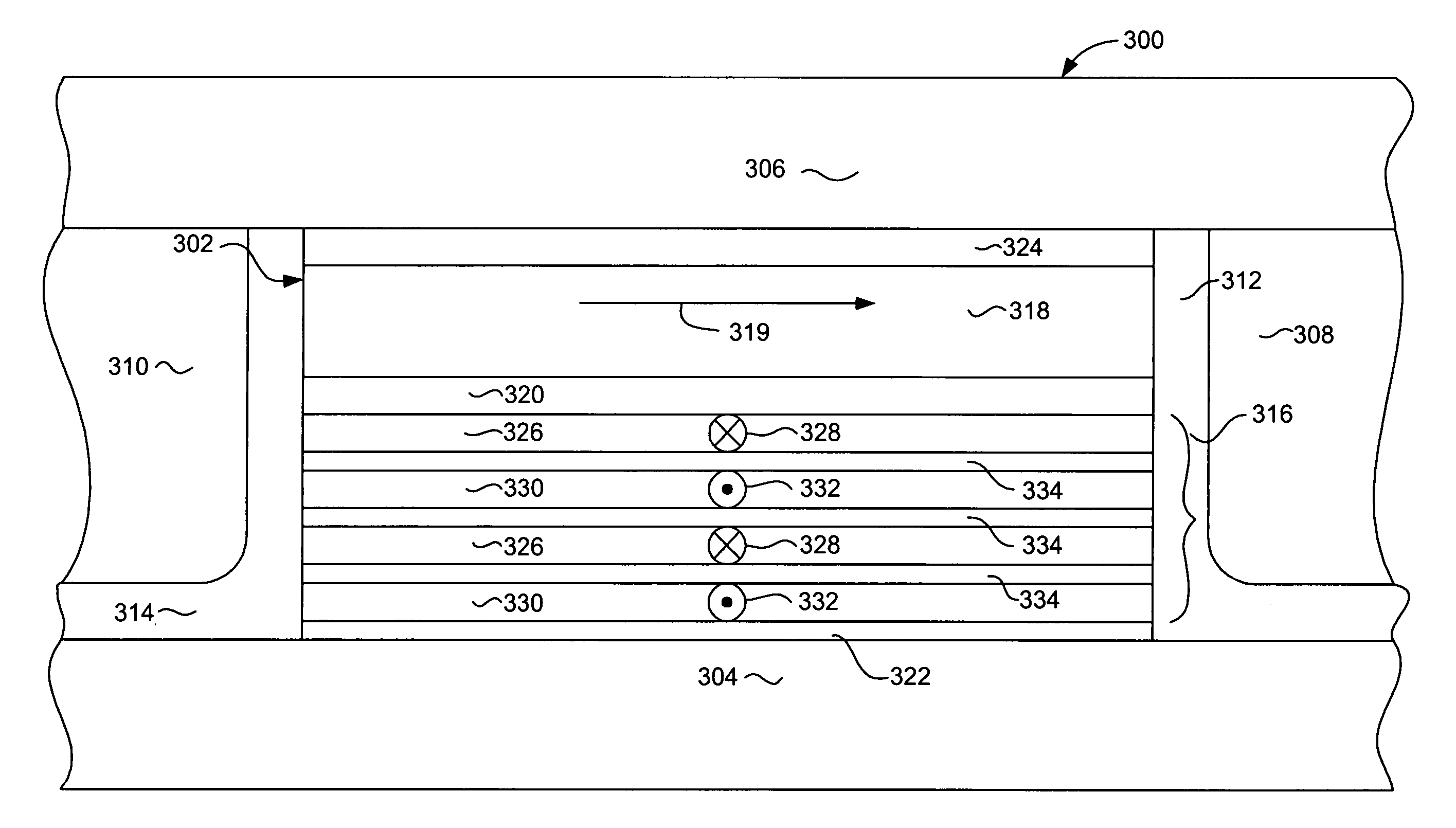
Current perpendicular to plane (CPP) GMR structure having vanadium doped, AP coupled, multi-layered pinned structure
InactiveUS20060087771A1Reduces spin dependent scatteringMinimizing negative dRRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsVanadium dopingSpins
A current perpendicular to plane (CPP) giant magnetoresistive (GMR) sensor having an antiparallel coupled (AP coupled) pinned layer structure wherein the pinning layer have a greatly reduced negative contribution to dR. The pinned layer structure includes a first a first set of magnetic layers such as CoFe and a second set of magnetic layer comprising CoFeV that are antiparallel coupled with the first set of magnetic layers. The magnetic layers of the pinned layer structure alternate between a one of the first set of magnetic layers (eg. CoFe) and one of the second set of magnetic layers (CoFeV). The magnetic layers of the first set contribute to the GMR of the sensor and provide a positive magnetostriction that assists with the pinning of the pinned layer structure. The magnetic layers of the second set contribute pinning, but do not contribute to GMR. The presence of V in the second set of greatly reduces the negative contribution to dR that would otherwise be provided by these pinning layers of the second set by reducing the spin dependent electron scattering through these layers.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Spin polarization enhancement artificial magnet
InactiveUS7099122B2Increased polarizationImprove stabilityNanoinformaticsRecord information storageSpinsElectron scattering
A spin polarization enhancement artificial (SPEA) magnet comprises combinations of positive spin asymmetry interfaces and inverse spin asymmetry interfaces arranged antiferromagnetically such that current passed through the SPEA magnet has enhanced spin polarization. The SPEA magnet additionally may combine bulk material properties of electron scattering to either supplement or replace the interfacial spin differentiation. A basic functional unit of the SPEA magnet includes two ferromagnetic layers separated by two spacer layers. Each spacer forms an interface such that adjacent ferromagnetic layers produce different spin symmetry. Antiferromagnetic arrangement of adjacent ferromagnetic layers coordinates the different spin symmetries such that a single spin state is selected and also provides additional stabilization to the SPEA magnet.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Cu-Ni-Nb ternary alloy film with low resistivity and high chemical inertia and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN102808150AEliminate scattering effectsReduce scatterVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingChemical reactionBlock effect
The invention provides a Cu-Ni-Nb ternary alloy film with low resistivity and high chemical inertia and a preparation process thereof, and belongs to the field of materials. Under the guidance of a cluster model of a stable solid solution, the selection and the addition quantity of alloying elements in the Cu film are determined, and factors such as the enthalpy of mixing, a cluster structure and atomic radius dimension are comprehensively considered, so that the solid solution alloy film with relatively high thermal stability and relatively low chemical reaction activity is formed. By adopting a solid solution structure, resistivity rising caused by mass precipitation of solute elements is avoided; due to the introduction of an element Nb with a large atomic radius, interdiffusion between Cu and surrounding media can be effectively blocked; and due to the proportional addition of the second group of elements Ni, the addition quantity of Nb can be greatly reduced, thereby reducing an electron scattering effect caused by large atom selves to a large extent, facilitating the stabilization of the Cu film and guaranteeing that the resistivity of the Cu film is minimally influenced. The Cu-Ni-Nb ternary alloy film can be expected to simultaneously have a diffusion blocking effect as well as high temperature stability.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for measuring pore distribution of porous structure body
The invention discloses a method for measuring the pore distribution of a porous structure body. The method comprises the following steps: filling products obtained through hydrolyzing an organic matter containing a characteristic element in an acidic / alkaline environment to the porous structure body, carrying out brittle failure and section exposing, acquiring the characteristic element distribution on the section through adopting an electron scattering spectrometer, and computing through using a computer image analyzing and processing method to obtain the area occupied by the characteristic element, and the ratio of the area to the total area to obtain the pore distribution at a specific position, and the porosity amount distribution. The method of the invention can be widely applied to the characterization of the pore distribution in the porous structure body, can be used for detecting influences of a technological process and an electrochemical process to porous structures in lithium ion battery electrode slices, and is important for the optimization of technological parameters and electrochemical process parameters.
Owner:NINGDE AMPEREX TECH
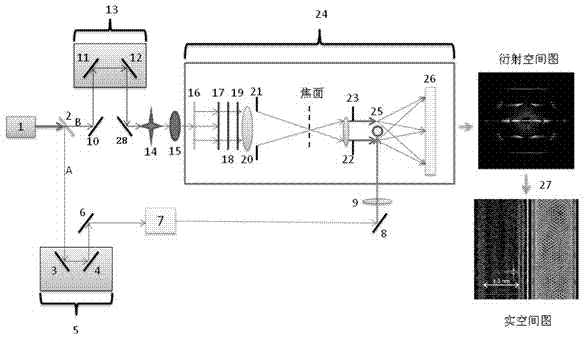
Ultrafast lens-free coherent electron diffraction imaging method and device
InactiveCN102903591AImprove time resolutionLow costElectric discharge tubesImage resolutionBack calculation
The invention discloses an ultrafast lens-free coherent electron diffraction imaging method and device. The method is combined with the electronic pulse which is in precise synchronization with process exciting sources (such as femtosecond laser pulses) and a lens-free coherent electron diffraction imaging technology, and comprises the steps of analyzing the strength distribution of the diffracted coherent electronic pulses, and carrying out back calculation to determine the electronic scattering phase, so as to achieve the reconstruction of the structure and the appearance of three-dimensional transient atomic scale. By adopting the method and device disclosed by the invention, the technical problem that the conventional electronic microimaging method has no high time resolution or the existing ultrafast electronic imaging time and space resolution are limited can be solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Spin polarization enhancement artificial magnet
InactiveUS20050128651A1Enhanced spin polarizationImprove stabilityNanoinformaticsRecord information storageSpinsElectron scattering
A spin polarization enhancement artificial (SPEA) magnet comprises combinations of positive spin asymmetry interfaces and inverse spin asymmetry interfaces arranged antiferromagnetically such that current passed through the SPEA magnet has enhanced spin polarization. The SPEA magnet additionally may combine bulk material properties of electron scattering to either supplement or replace the interfacial spin differentiation. A basic functional unit of the SPEA magnet includes two ferromagnetic layers separated by two spacer layers. Each spacer forms an interface such that adjacent ferromagnetic layers produce different spin symmetry. Antiferromagnetic arrangement of adjacent ferromagnetic layers coordinates the different spin symmetries such that a single spin state is selected and also provides additional stabilization to the SPEA magnet.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Current perpendicular to plane (CPP) GMR structure having vanadium doped, AP coupled, multi-layered pinned structure
InactiveUS7268982B2Reduces spin dependent scatteringMinimizing negative dRRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsVanadium dopingSpins
A current perpendicular to plane (CPP) giant magnetoresistive (GMR) sensor having an antiparallel coupled (AP coupled) pinned layer structure wherein the pinning layer have a greatly reduced negative contribution to dR. The pinned layer structure includes a first a first set of magnetic layers such as CoFe and a second set of magnetic layer comprising CoFeV that are antiparallel coupled with the first set of magnetic layers. The magnetic layers of the pinned layer structure alternate between a one of the first set of magnetic layers (eg. CoFe) and one of the second set of magnetic layers (CoFeV). The magnetic layers of the first set contribute to the GMR of the sensor and provide a positive magnetostriction that assists with the pinning of the pinned layer structure. The magnetic layers of the second set contribute pinning, but do not contribute to GMR. The presence of V in the second set of greatly reduces the negative contribution to dR that would otherwise be provided by these pinning layers of the second set by reducing the spin dependent electron scattering through these layers.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Electron energy loss spectrometer
An electron energy loss spectrometer for electron microscopy is disclosed having an electrically isolated drift tube extending through the bending magnet and through subsequent optics that focus and magnify the spectrum. An electrostatic or magnetic lens is located either before or after or both before and after the drift tube and the lens or lenses are adjusted as a function of the bending magnet drift tube voltage to maintain a constant net focal length and to avoid defocusing. An energy selecting slit is included in certain embodiments to cleanly cut off electrons dispersed outside the energy range incident on the detector, thereby eliminating artifacts caused by unwanted electrons scattering back into the spectrum.
Owner:GATAN INC
Cu-containing high-conductivity and high-electromagnetic-shielding-property wrought magnesium alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a Cu-containing high-conductivity and high-electromagnetic-shielding-property wrought magnesium alloy which comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 4.90-5.20% of Zn, 0.50-0.80% of Zr, 0.37-2.32% of Cu and the balance of Mg and unavoidable impurities. The preparation method comprises the steps of ingot smelting, homogenization, hot extrusion and the like, because the alloy contains Cu, and Cu, Mg and Zn are combined so as to generate a MgZnCu ternary phase, Zn solute atoms in a matrix are greatly reduced, the lattice distortion of the matrix decreases, and electron scattering is inhibited. Therefore, the alloy subjected to homogenization and extrusion has good conductivity, the electromagnetic shielding property of the alloy is markedly improved, and compared with alloys without containing Cu, the alloy has the advantages that the electromagnetic shielding effectiveness is increased by over 17db. The application scope of high-conductivity, high-electromagnetic-shielding-property and light-weight alloy materials in the fields of aerospace, military industry, microelectronics, and the like is effectively broadened.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Conductive Mg-P co-doped Cu2V2O7-graphene negative thermal expansion material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111170295AImprove conductivityImprove mechanical propertiesGraphenePhosphorus compoundsThermal dilatationElectron scattering
The invention relates to the technical field of negative thermal expansion materials, and discloses a conductive Mg-P co-doped Cu2V2O7-graphene negative thermal expansion material and a preparation method thereof. The conductive Mg-P co-doped Cu2V2O7-graphene negative thermal expansion material comprises the following formula raw materials: graphene oxide, CuO, MgO, V2O5 and NH4H2PO4. According tothe conductive Mg-P co-doped Cu2V2O7-graphene negative thermal expansion material and the preparation method thereof, Cu2V2O7 has a stable linear negative thermal expansion coefficient, a centrosymmetric monoclinic phase structure is formed by doping Cu2V2O7 with Mg, under temperature variation, the Mg-O bond generates a vibration effect, the internal coupling effect of the Cu2V2O7 crystal is improved, a linear chain-shaped monoclinic phase in the crystal is destroyed, oxygen atoms form a new arrangement in the crystal lattice, local collapse occurs, the Cu2V2O7 is enabled to show a negativethermal expansion phenomenon, P atoms replace part of V atoms, the grain size of Cu2V2O7 is reduced, the bond energy of P-O bonds is larger than that of V-O bonds, stress in Cu2V2O7 lattices is reduced, lattice distortion is reduced, the electron scattering probability and the high-frequency dielectric constant are reduced, and therefore the conductivity of Cu2V2O7 is enhanced.
Owner:管玲飞
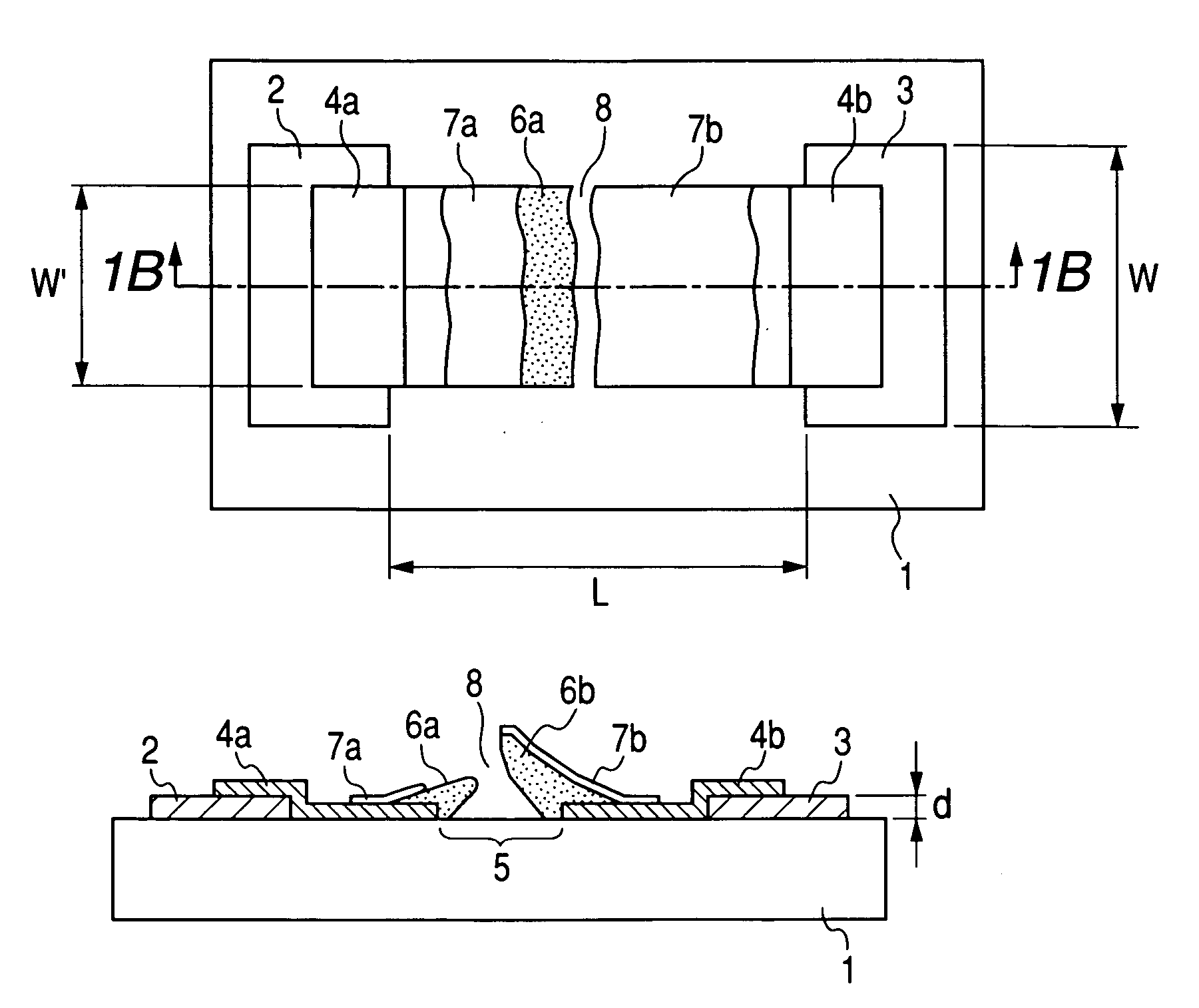
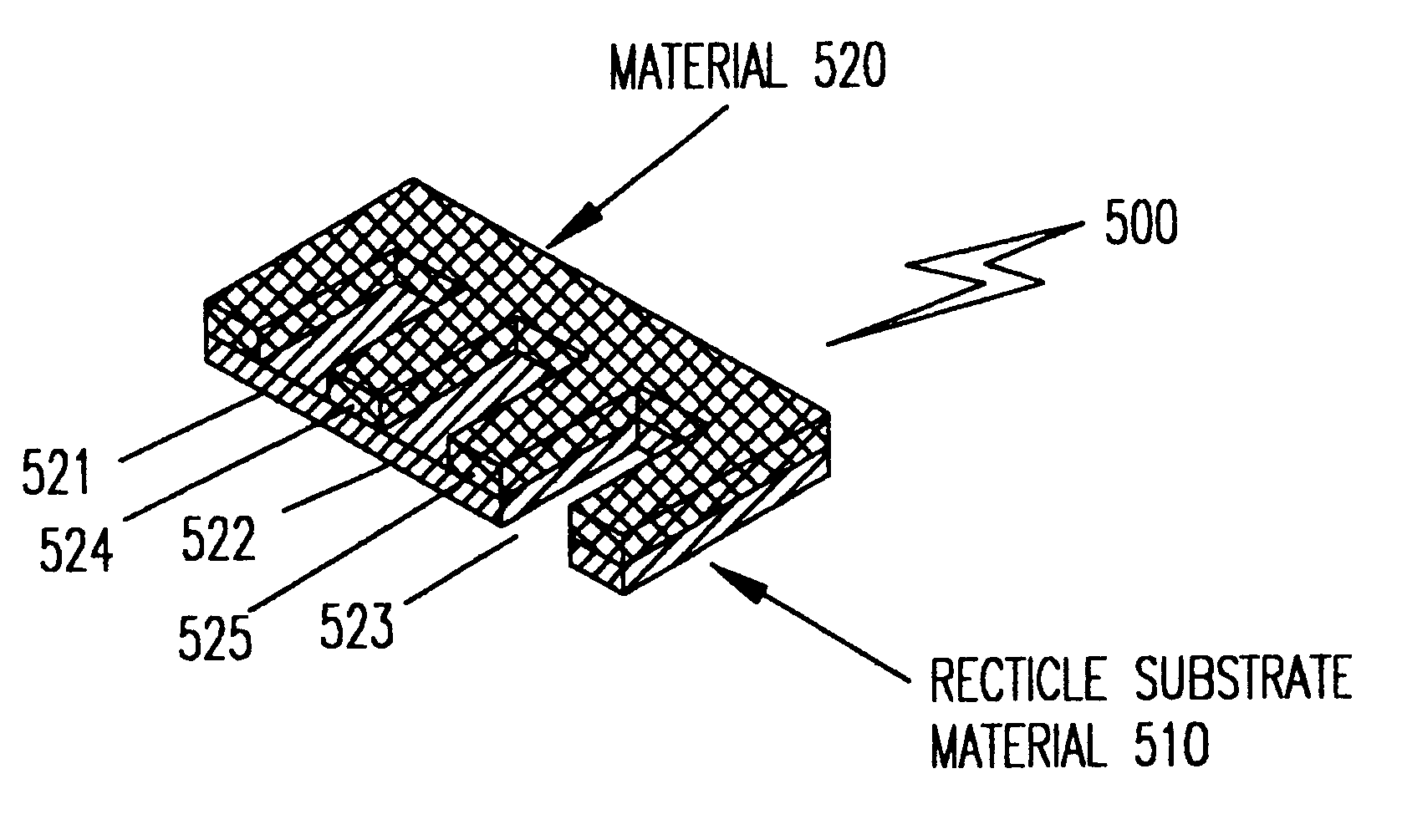
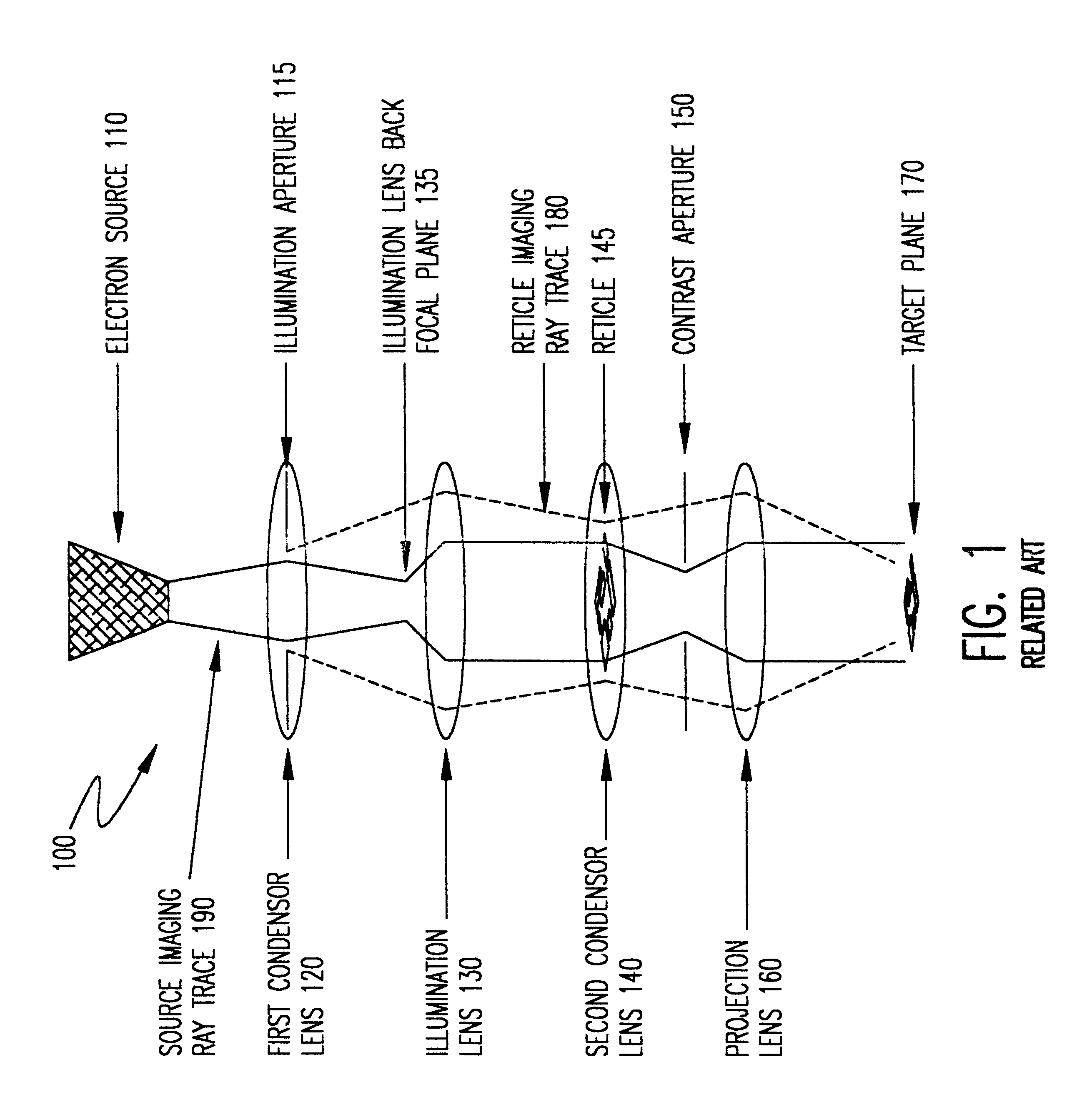
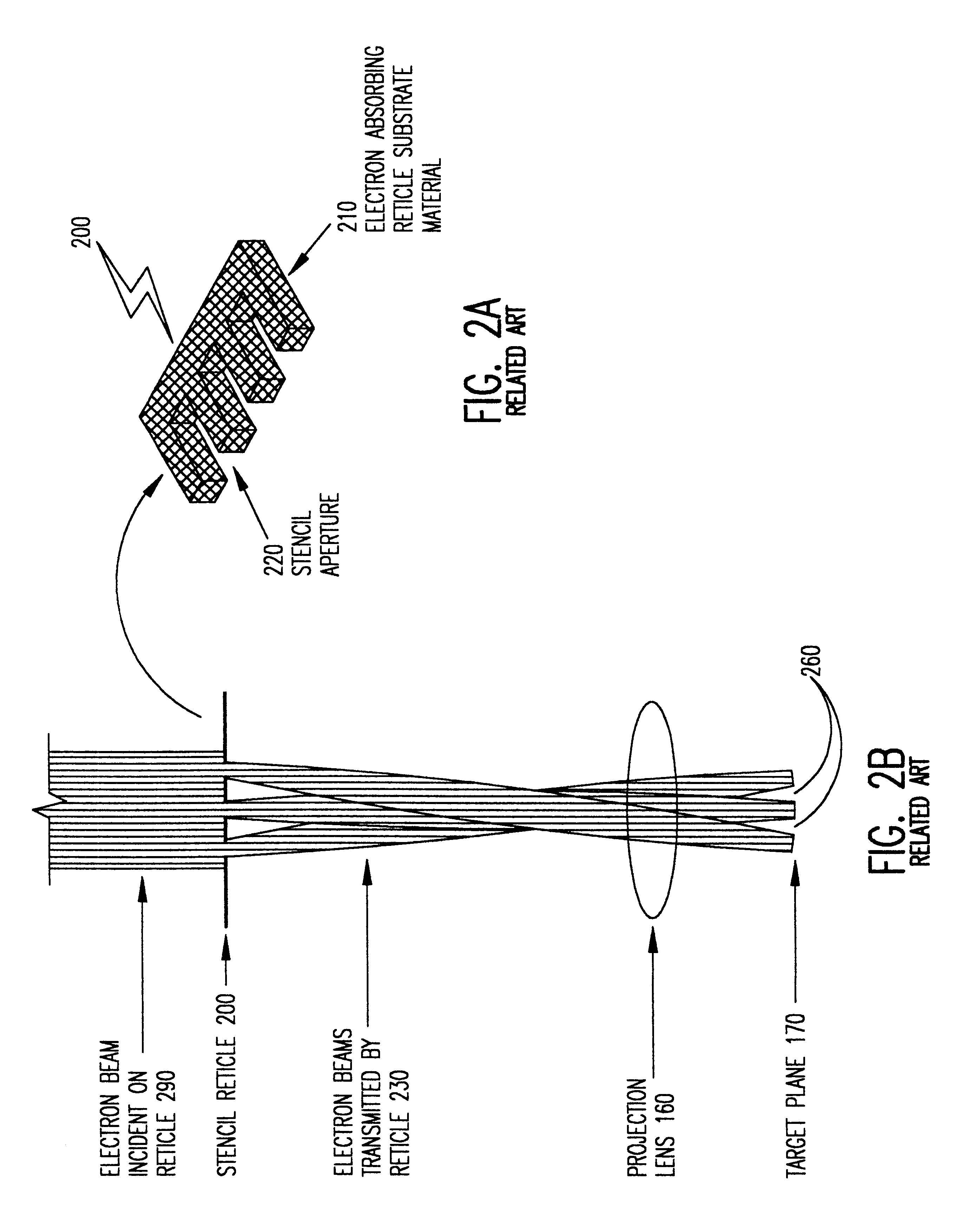
Stencil reticle incorporating scattering features for electron beam projection lithography
InactiveUS6541783B1Improve performanceImprove fidelityRadiation/particle handlingNanoinformaticsResistElectron scattering
Proximity (exposure dose) effects and / or local Coulomb (space charge defocussing) effects, both dependent on local pattern density of exposed areas, are simultaneously compensated in a charged particle beam projection device or tool by a projection reticle having an apertured weakly scattering membrane with selective strongly scattering regions between the apertures in the membrane. A reticle so constructed provides at least three independent exposure dosage levels that can be mixed to provide a wide range of exposure levels with high contrast. The more weakly the electrons are scattered (in the extreme, the electrons are not scattered at all through apertures), the greater the number that pass through a given beam contrast aperture, the higher the corresponding dose received at the target plane and the more space charge is contained in the beam bundle. Therefore, to compensate for the proximity effect (i.e. provide dose boost) and the local Coulomb effect (i.e. provide additional space charge) regions with reduced scattering characteristics are employed. Use of a hybrid doped resist allows exposure corresponding to an intermediate exposure dose in a preferred variant implementation exploiting the three dosage levels developed.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Topological insulator/graphene compound flexible transparent conductive thin film and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104979038ALow conductivityImprove conductivityConductive layers on insulating-supportsCarbon-silicon compound conductorsElectron scatteringMechanical property
The invention discloses a topological insulator / graphene compound flexible transparent conductive thin film and a preparation method and application thereof. The topological insulator / graphene compound flexible transparent conductive thin film is combined by a nanosheet formed by a topological insulator and a graphene thin film by virtue of Van der Waals' force. The preparation method comprises the step: by taking inertial gas as carrier gas, putting the topological insulator in the upstream of a gas flow direction and putting the graphene thin film in the downstream of the gas flow direction for chemical vapor deposition to obtain the topological insulator / graphene compound flexible transparent conductive thin film. According to the topological insulator / graphene compound flexible transparent conductive thin film disclosed by the invention, a stable conductive channel can be provided by virtue of a special metal surface state of the topological insulator, the crystal boundary of the domain is sewed, and reduction of conductivity caused by electron scattering at the crystal boundary is improved, so that the topological insulator / graphene compound flexible transparent conductive thin film is obtained. The thin film has high transmission of light in a wide wavelength coverage, high conductivity, outstanding chemical stability and mechanical property, and can be used for the field of photoelectrons, nano-electrons and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
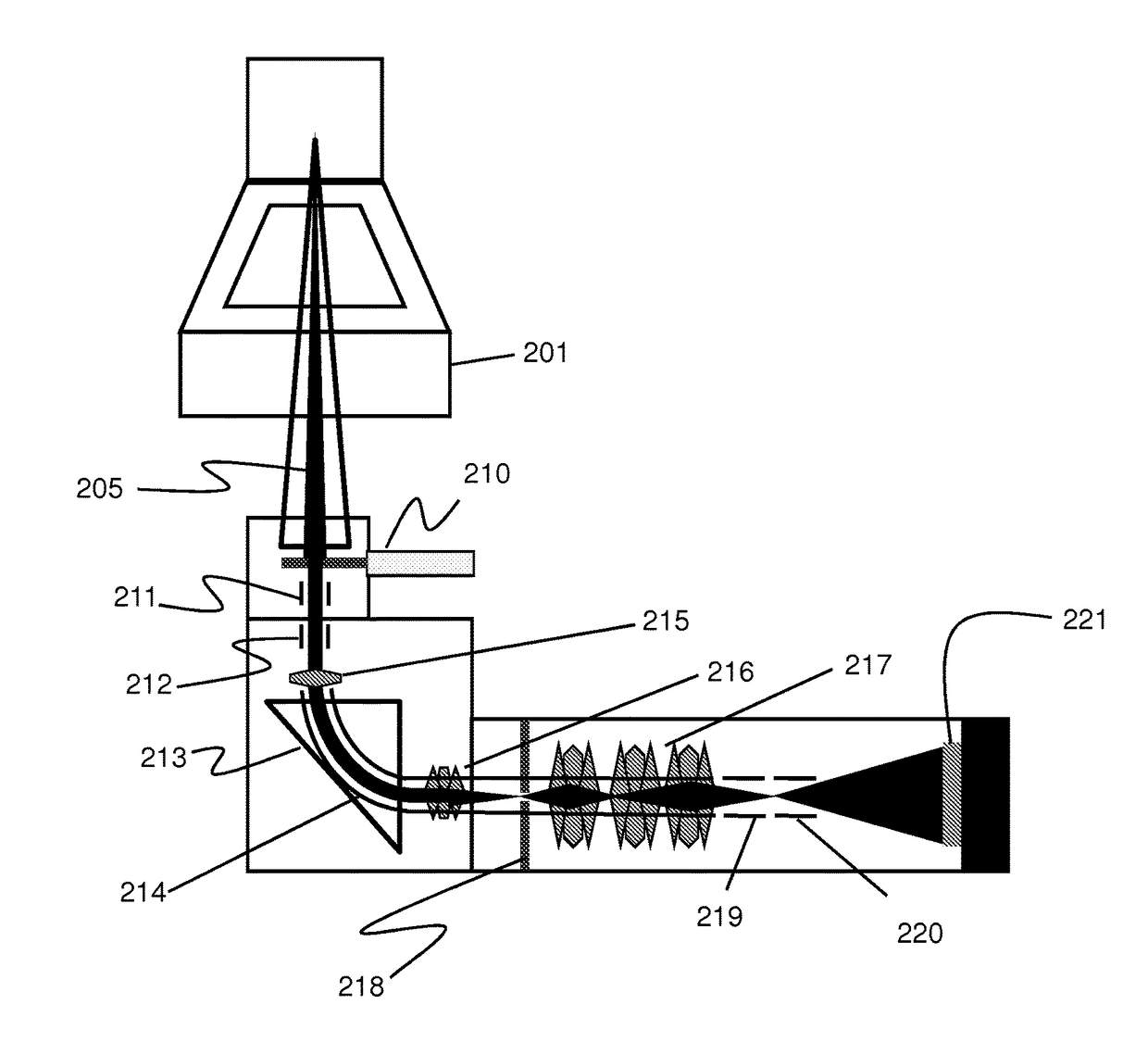
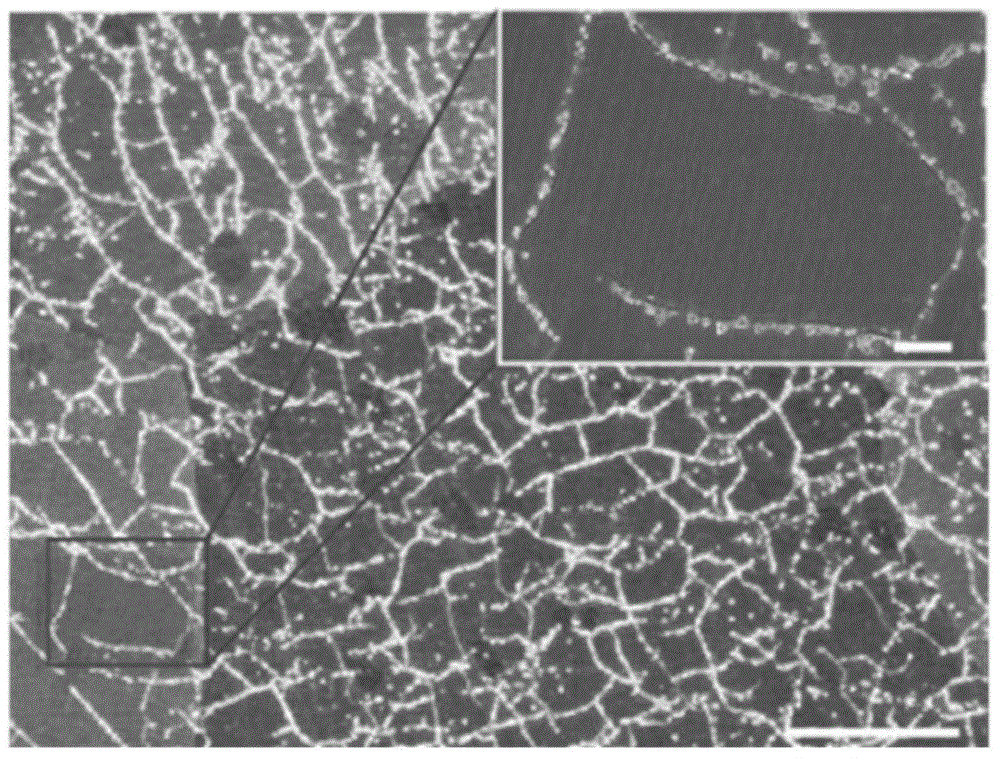
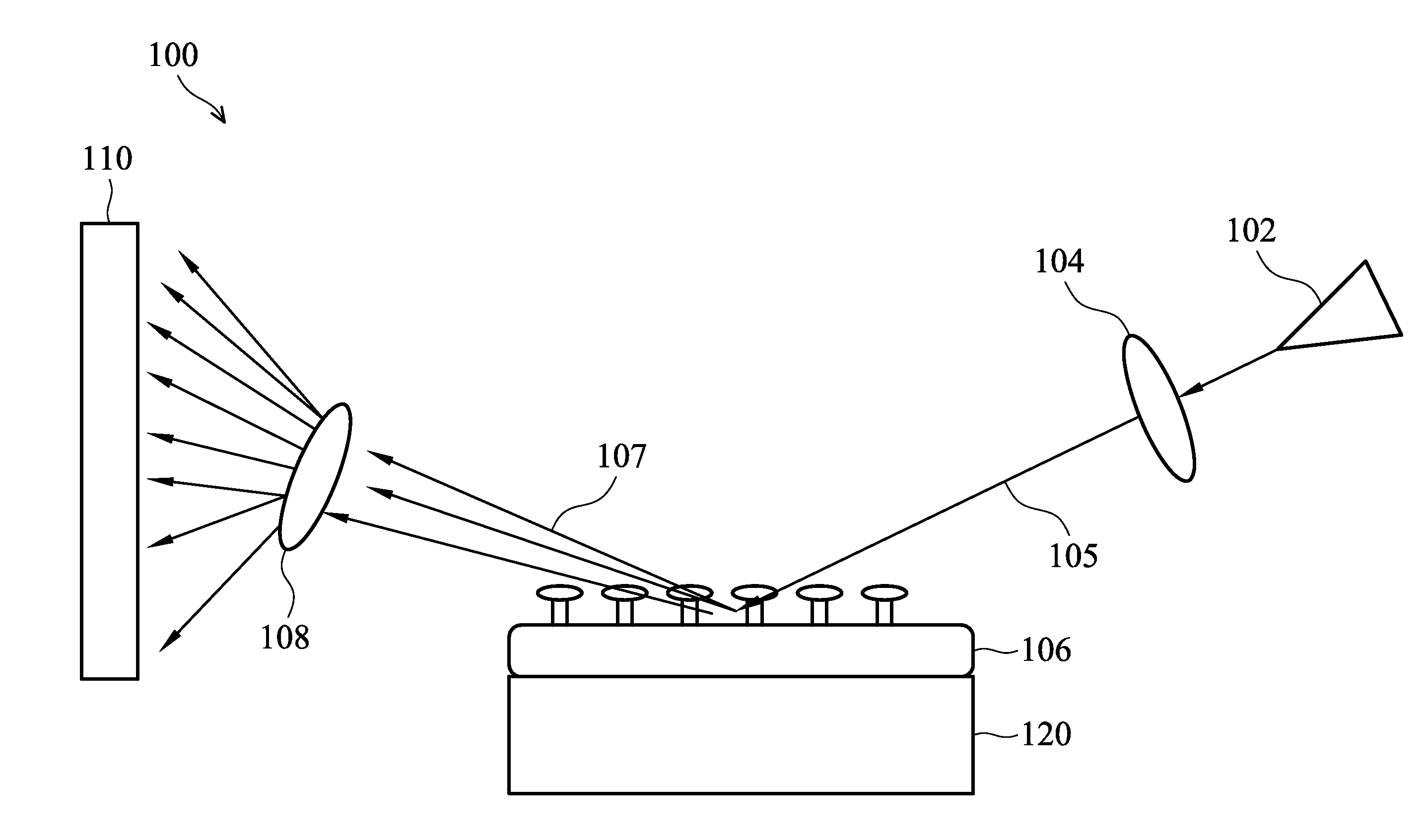
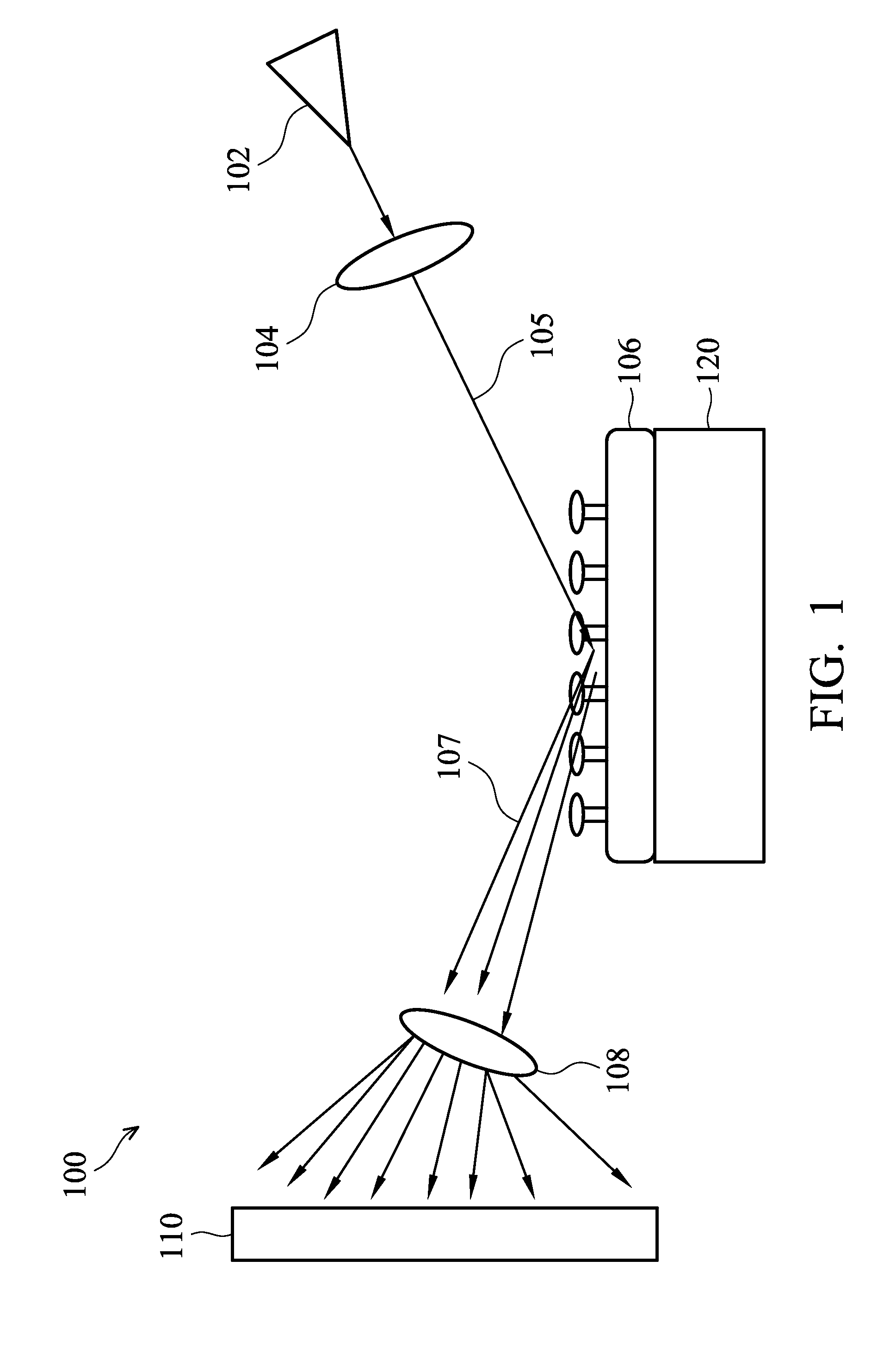
Apparatus and method of applying small-angle electron scattering to characterize nanostructures on opaque substrate
ActiveUS20150340201A1Sufficient angular resolutionReduce incidenceMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesProjection opticsElectron source
An apparatus and methods for small-angle electron beam scattering measurements in a reflection or a backscattering mode are provided. The apparatus includes an electron source, electron collimation optics before a sample, electron projection optics after the sample, a sample stage capable of holding the sample, and a electron detector module. The electrons emitted from the source are collimated and positioned to impinge nanostructures on the sample. The signals resulting from the interactions between the impinging electrons and the nanostructures are further magnified by the electron projection optics to reach a sufficient angular resolution before recorded by the electron detector module.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Forward Flux Channel X-ray Source
ActiveUS20150262783A1Improve conversion efficiencyIncreased x-ray flux outputX-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube windowsSoft x rayLight beam
This invention provides a source of x-ray flux in which x-rays are produced by e-beams impacting the inner walls of holes or channels formed in a metal anode such that most of the electrons reaching the channel impact an upper portion of said channel. A portion of the electrons from this primary impact will generate x-rays. Most of the electrons scatter but they continue to ricochet down the channel, most of them generating x-rays, until the beam is spent. A single channel source of high power efficiency and high power level x-rays may be made in this way, or the source can be of an array of such channels, to produce parallel collimated flux beams of x-rays.
Owner:STELLARRAY
Nanowire electron scattering spectroscopy
InactiveUS7547881B2Simple and direct electrical readoutEliminate requirementsRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationNanowireElectron injection
Methods and devices for spectroscopic identification of molecules using nanoscale wires are disclosed. According to one of the methods, nanoscale wires are provided, electrons are injected into the nanoscale wire; and inelastic electron scattering is measured via excitation of low-lying vibrational energy levels of molecules bound to the nanoscale wire.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
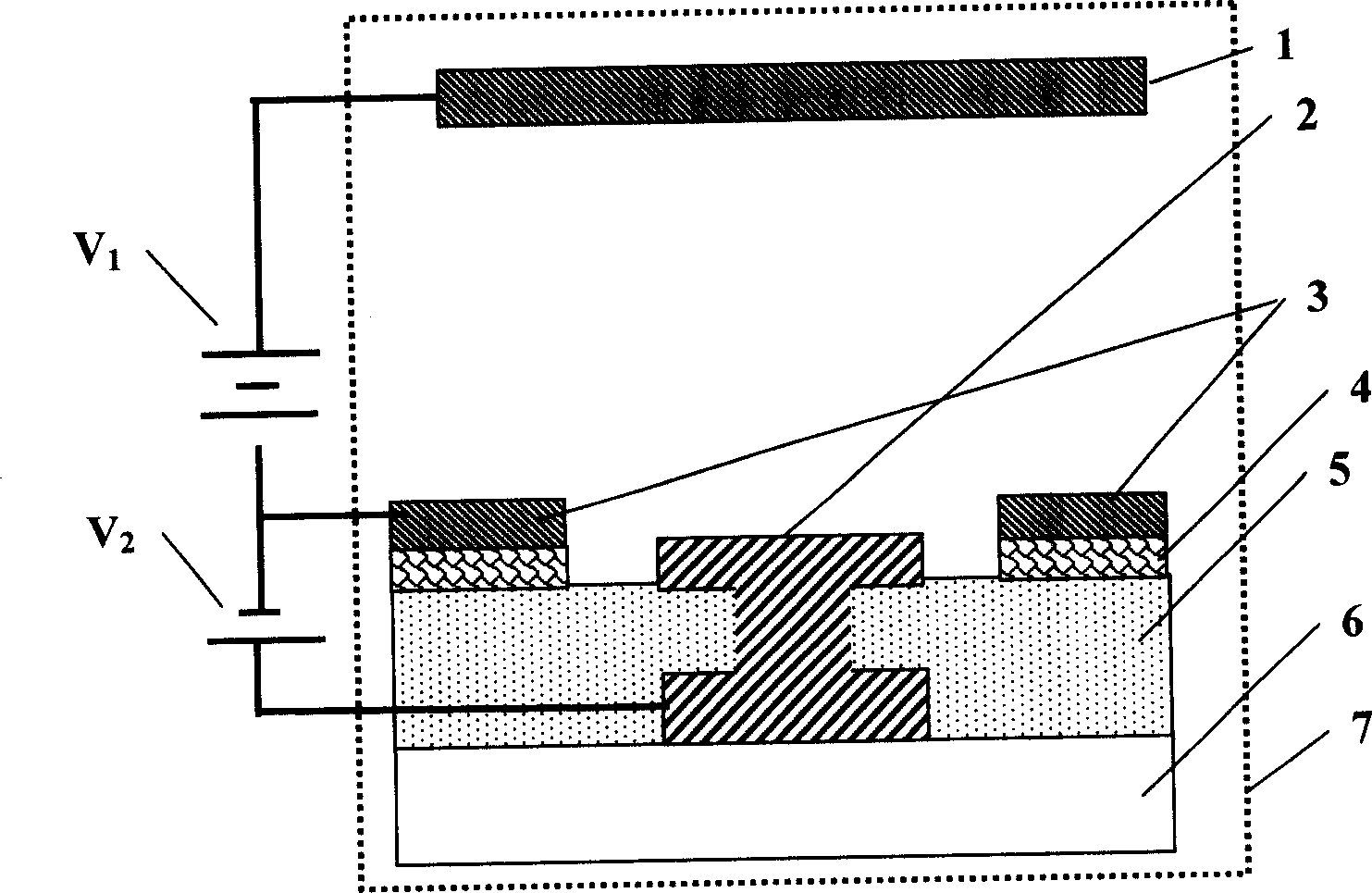
Surface conducting field emission electronic source device with convergent characteristic
InactiveCN1845287ASolve the lack of divergenceSimple processControl electrodesImage/pattern display tubesElectron sourceElectron scattering
The disclosed surface-conductive field-emission electron source device with convergence feature comprises a substrate with an inverted-T shaped or I-shaped grid, a cathode and an insulating layer, and an opposite anode fixed in a vacuum cavity. Wherein, arranging the grid between the insulating layer and the substrate, showing the grid through a hole to circle by the cathode; arranging an electron emission layer between the cathode and the insulating layer, and adding a layer of cathode between the emission layer and the insulating layer to form a sandwich cathode, as well as an electron scattering layer between the cathode and shown grid. This invention needs simple technique and low drive voltage, and has well electron convergence performance.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
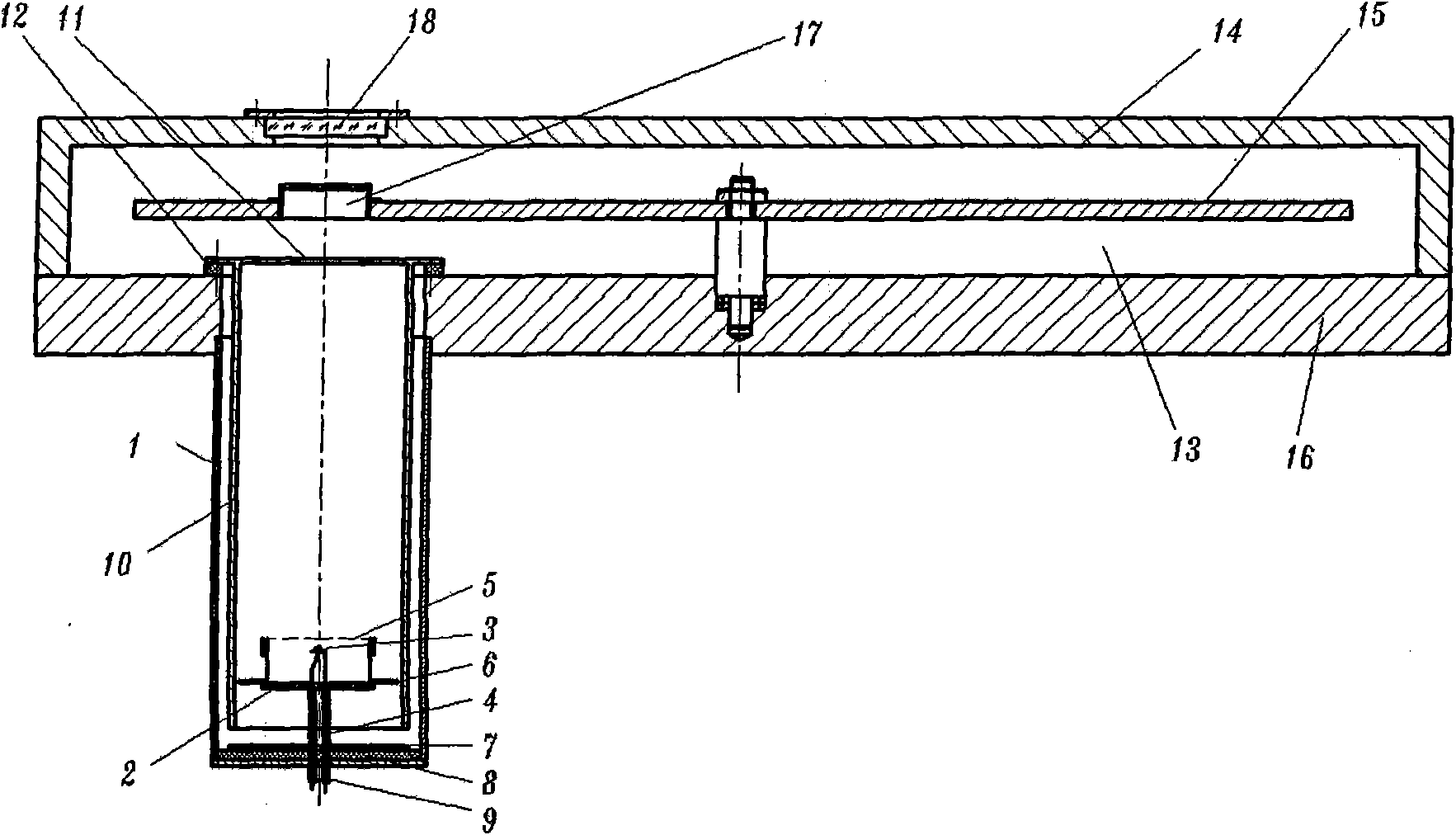
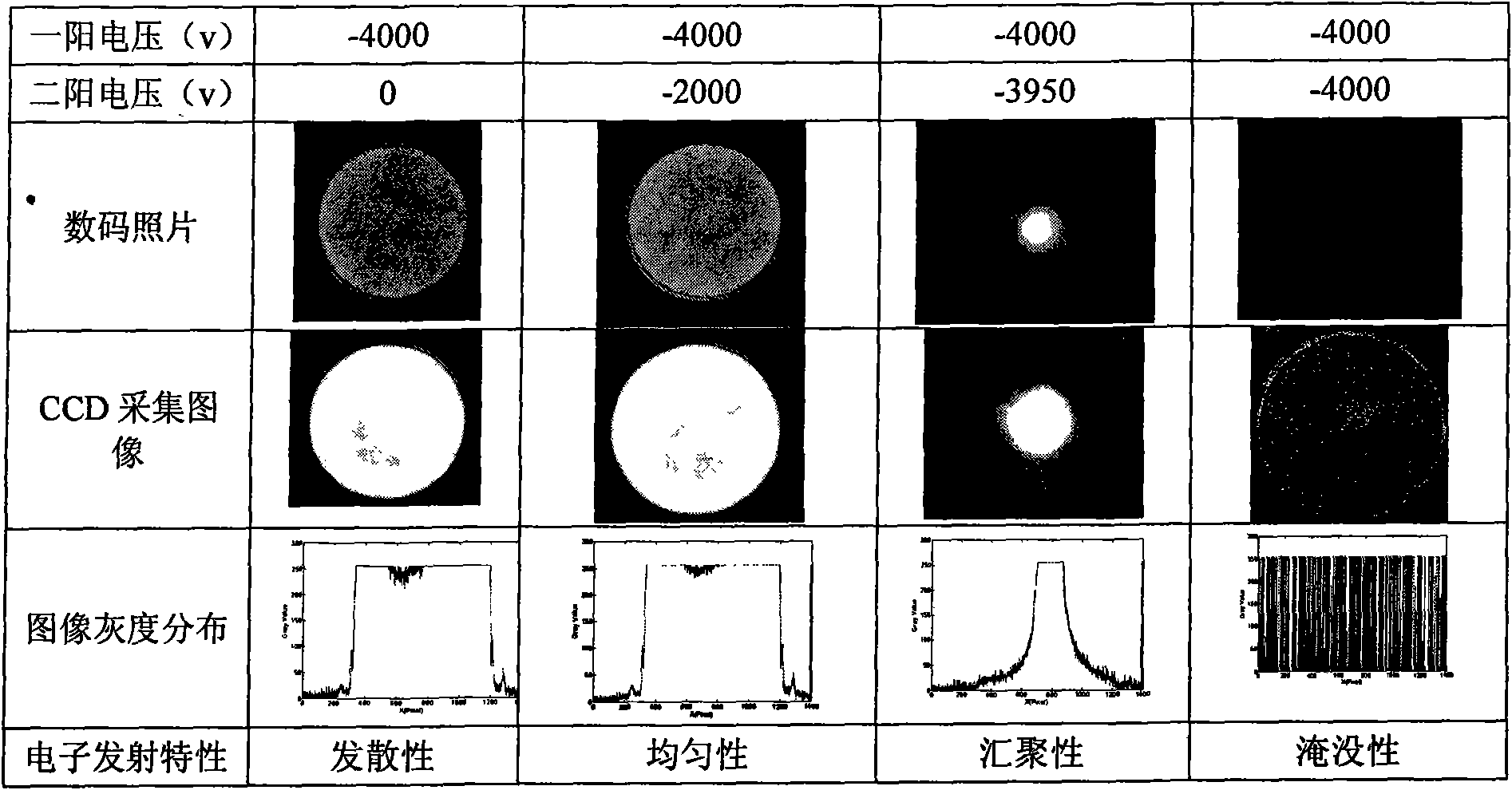
Thermal electronic surface emitting source for vacuum system
InactiveCN101685739AChange trackGather evenlyManufacture testing/measurementsTesting optical propertiesHigh energyElectron scattering
The invention discloses a thermal electronic surface emitting source for a vacuum system. In the invention, a first anode comprises a lamp holder, a lamp filament, a lamp filament wiring column, an electronic scattering mesh, a wiring column frequency shielding disk and a base frequency shielding disk, and a second anode is formed in such a way that a sleeve is added in a shell of the thermal electronic surface emitting source in a mutually insulating way; by the invention, an electronic track is effectively changed; after emitted electrons are accelerated by an electric field, the distribution of formed high-energy electronic beams can be controlled by changing the potential condition; the lamp filament is wound into a pane spiral shape by a tantalum wire; the lamp filament in the shape can generate the uniform high-energy electronic beams, finish the uniformization, gathering and submerging of the high-energy electronic beams and realize the detection of parameters of a fluorescent screen, such as uniformity, light emitting efficiency, afterglow, and the like; particularly, the detection error of the uniformity is smaller than + / -0.05; and the invention has multiple functions, simple structure and easy processing, can completely meet the test of all the parameters of the fluorescent screen and can be widely used for the quality detection of the fluorescent screens on variousimage intensifiers.
Owner:南京理工大学张家港工程院有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com