Wire-bonding method for chips with copper interconnects by introducing a thin layer
a technology of copper interconnects and wire bonding methods, which is applied in the direction of electrical equipment, semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device details, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, high cost, and high cost of copper oxidation, and achieve the effect of improving the performance of deep sub-micron integrated circuits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
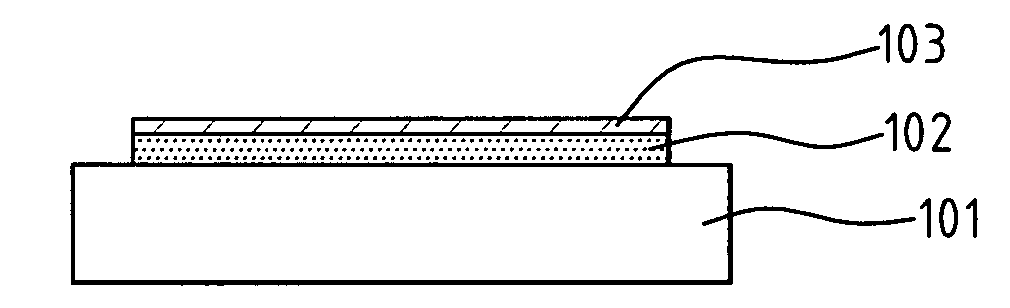
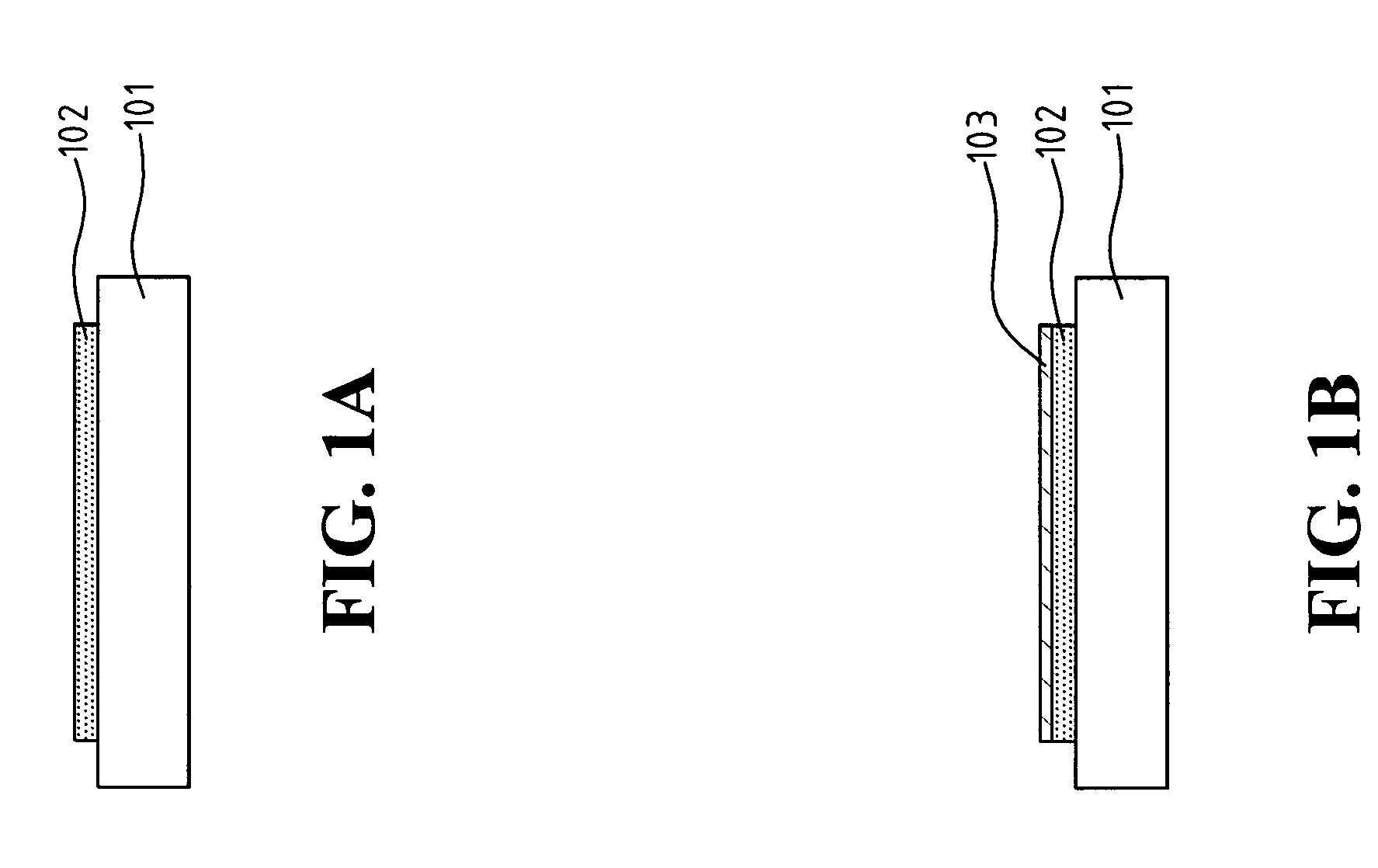
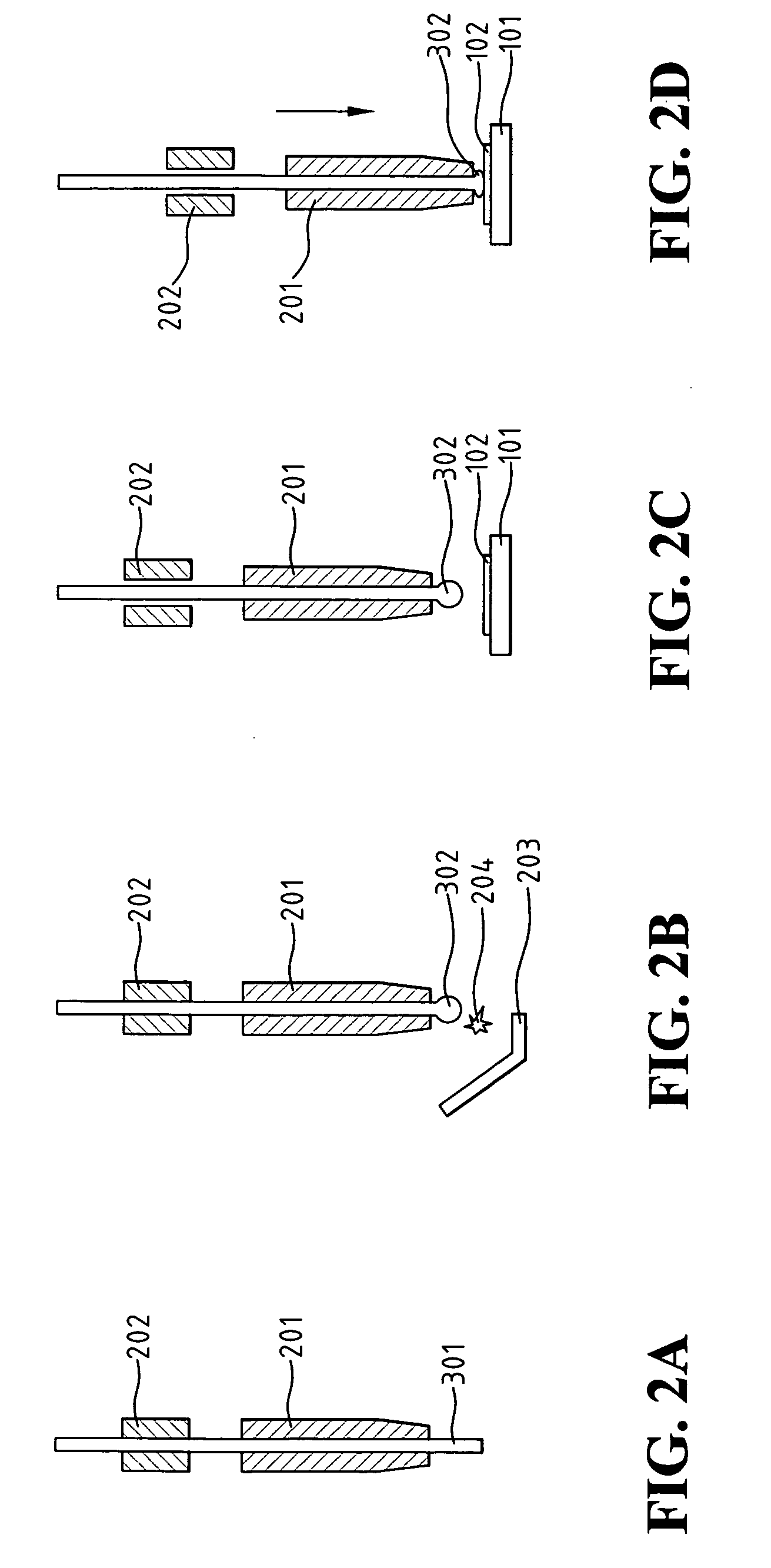
[0016] As shown in FIG. 1A, a chip 101 is provided thereon with a copper bonding-pad 102. The chemical reaction of copper in an aqueous solution is known as:
Cu⇄Cu++e− (1)
Cu⇄Cu2++2e− (2)
2Cu++H2O⇄Cu2O+2H+ (3)
[0017] According to the principle of Le Chatelier, a system would always react in such a way as to tend to counteract the original alteration when the system is in equilibrium and one of the factors, which determine the equilibrium point, is altered. It is understood from reaction (3) that H+ is supposed to move to the left side when its concentration is raised up. If the concentration of H+ goes up, the aqueous solution is becoming acidified and the pH value is lowered (the higher the H+, the lower the pH value), or vice versa. Therefore, it is possible to keep the reaction going toward the right hand to produce Cuprous oxide (Cu2O) should the concentration of H+ is controlled properly under a predetermined level. A preferred concentration of H+ below 10−5M / L, or a pH valu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| reaction time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com