New fuse structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
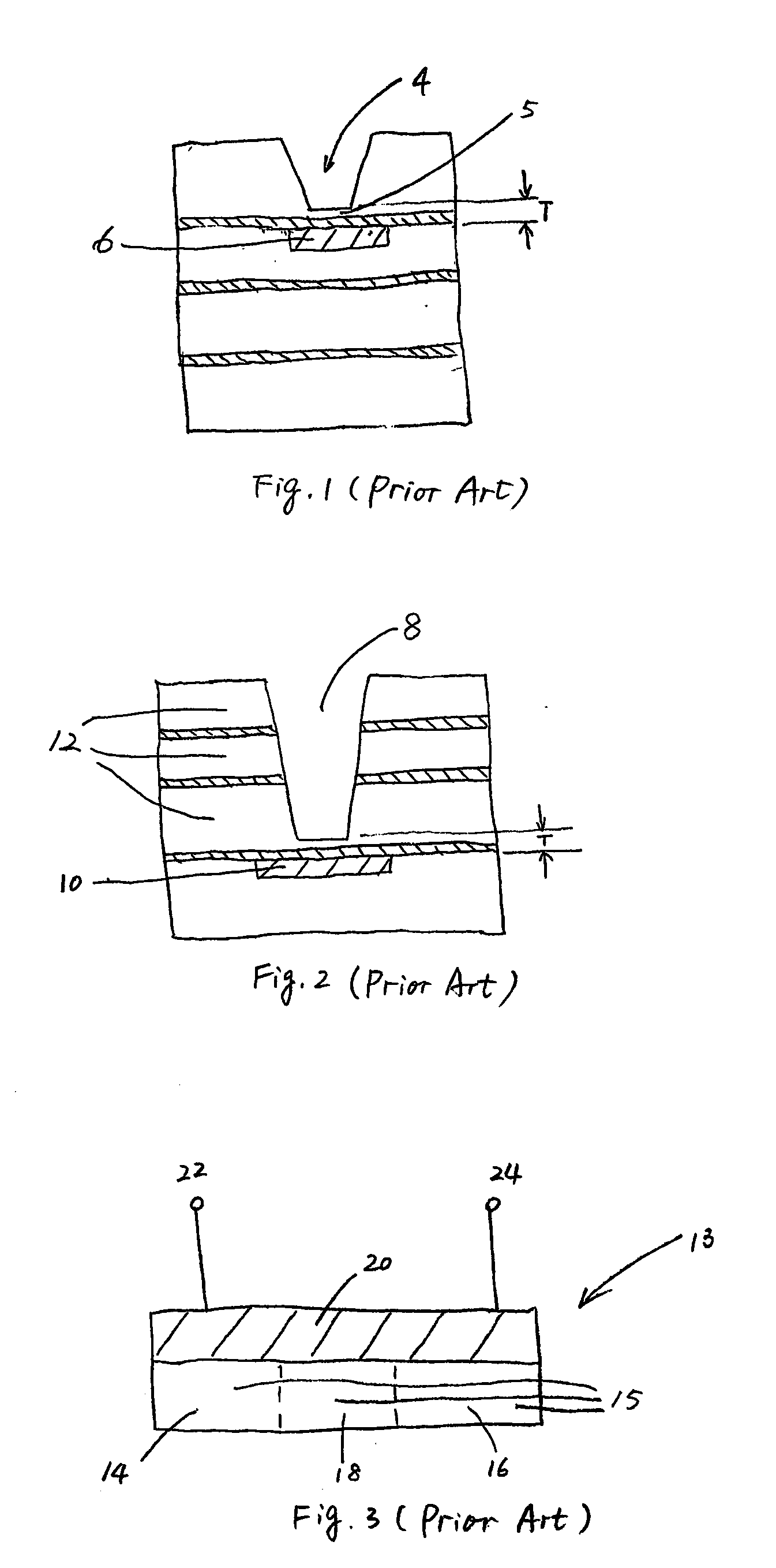
[0024] The making and using of the presently preferred embodiments are discussed in detail below. It should be appreciated, however, that the present invention provides many applicable inventive concepts that can be embodied in a wide variety of specific contexts. The specific embodiments discussed are merely illustrative of specific ways to make and use the invention, and do not limit the scope of the invention.
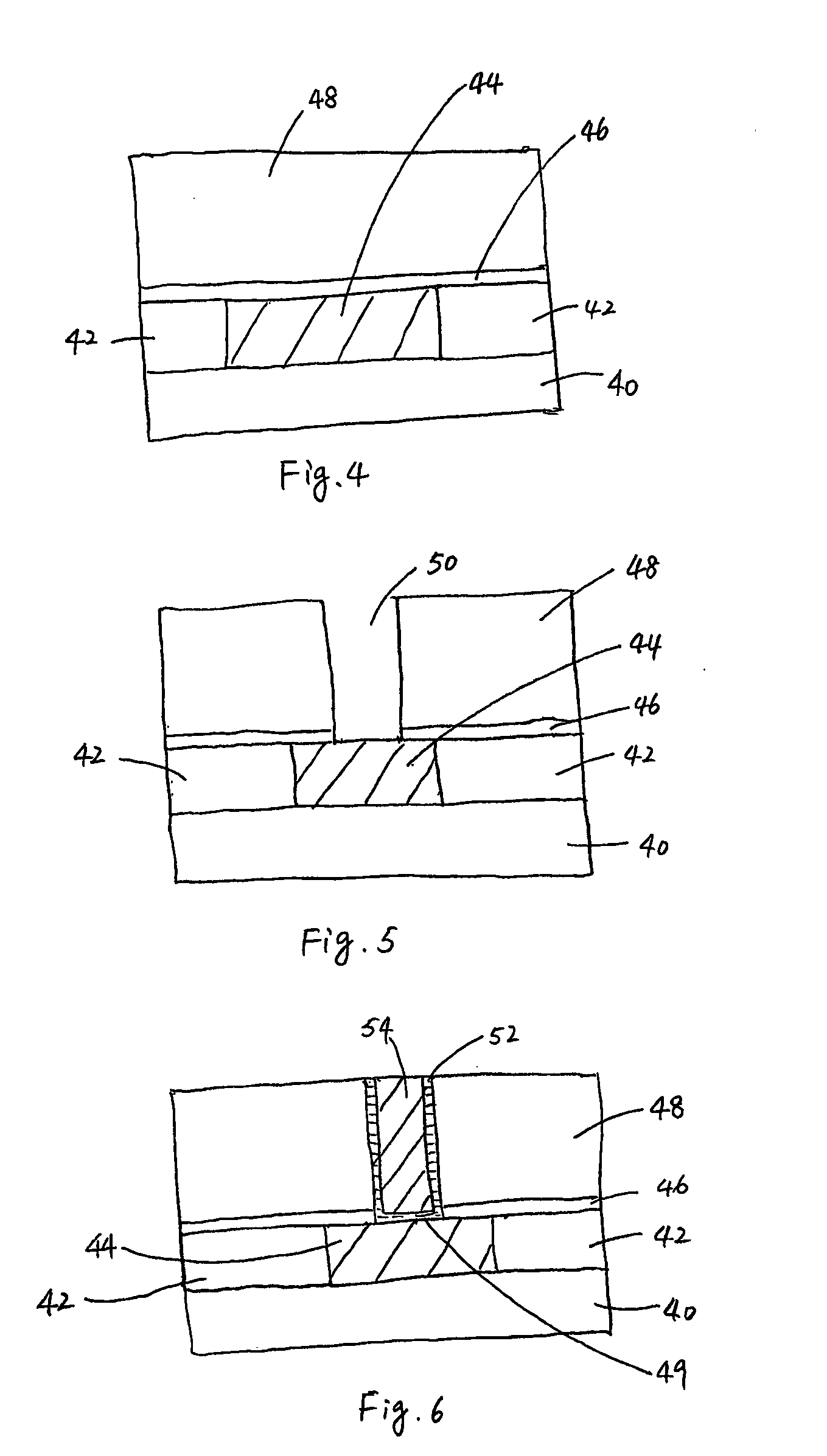
[0025] The preferred embodiments of the present invention present a novel method of forming e-fuses. A via connecting a lower-layer conductive line and an upper-layer conductive line is adapted to be an e-fuse. The e-fuse can be burned out by applying a voltage on external pads that are coupled to the lower-layer conductive line and the upper-layer conductive line. Throughout the description, conductive lines are also referred to as conductive layers.
[0026]FIGS. 4 through 7 are cross-sectional views of intermediate stages in the making of a preferred embodiment of the pres...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com