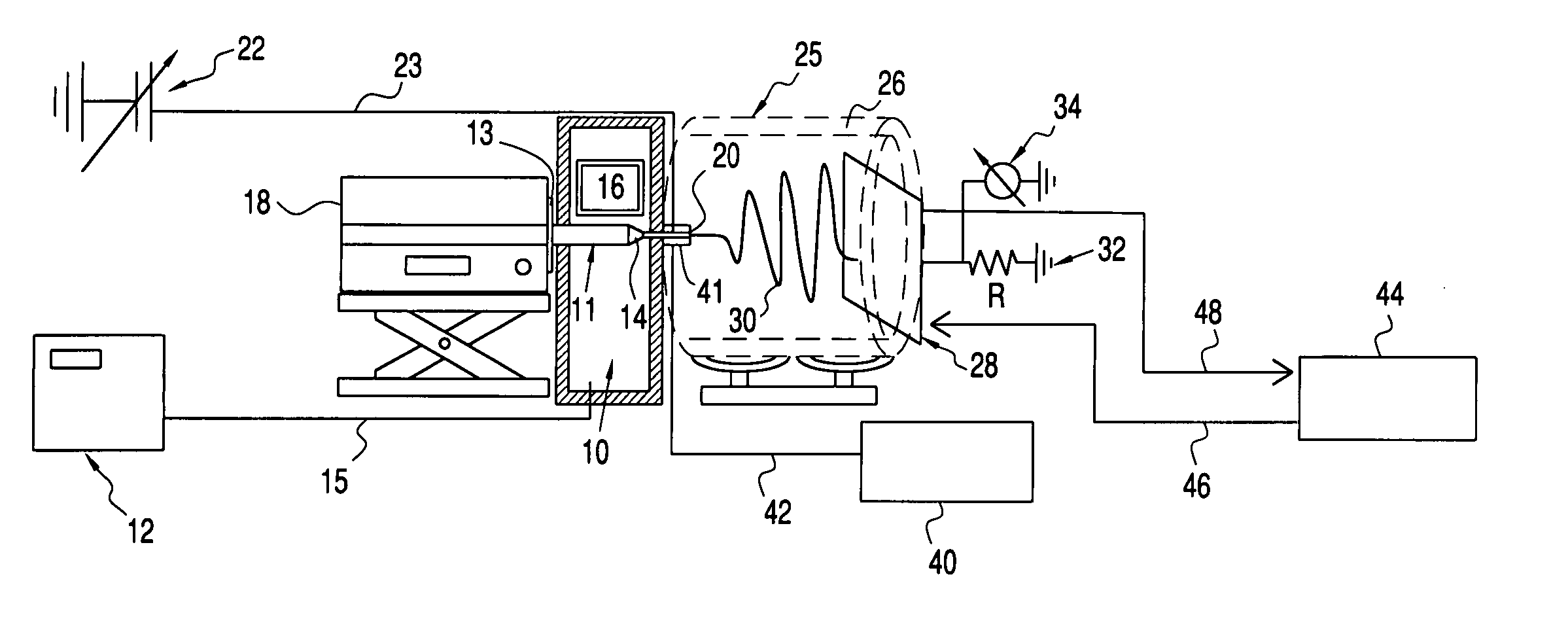
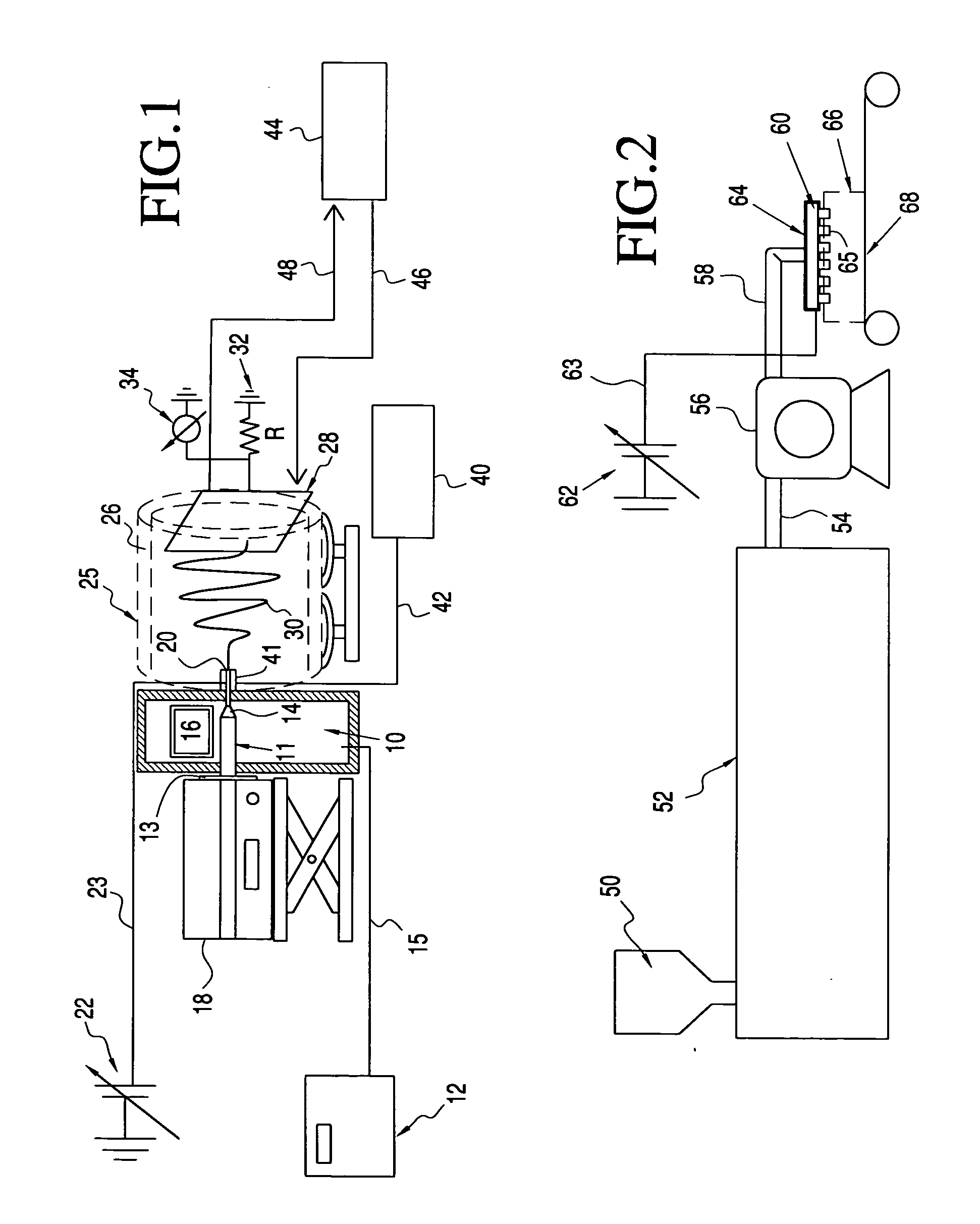
Apparatus and method for elevated temperature electrospinning
a technology of electrospinning apparatus and components, which is applied in the direction of dough shaping, manufacturing tools, auxiliary shaping apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of low production rate, inability to adapt to polymers, and requiring plurality regulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
working example i
Effect of Flow Rate, Distance and Applied Voltage on Fiber Diameter
[0066] The nozzle diameter was 0.84 mm. The temperatures used were T2=220° C., T3=100° C. and T4=60° C. Flow rates, distance between nozzle orifice and collector, voltage applied to the nozzle, are varied and results in terms of fiber diameter in μm are given in Table 1 below.
TABLE 1VoltageFlow RateDistance10 kV15 kV20 kV0.01 / ml / min3″3.23 ± 0.675.34 ± 0.6714.29 ± 2.83 6″7.65 ± 1.455.53 ± 0.918.21 ± 1.770.005 ml / min3″5.74 ± 1.454.85 ± 1.008.83 ± 1.666″6.67 ± 1.104.70 ± 0.944.46 ± 2.19
[0067] Except for one case with 10 kV and 3 inches, decreasing flow rate decreases the fiber diameter, possibly due to the increase in residence time (and thus, lower exposure to whipping motion).
[0068] At higher voltage setting (20 kV), the straight stable jet tends to extend longer and thus the whipping region is shortened, which leads to thicker fibers. Increasing the distance (from nozzle tip to collector) and thus increasing the ...
working example ii
Effect of Nozzle Temperature (T2) on Fiber Diameter
[0069] The nozzle diameter was 0.84 mm. The temperatures used were T3=100° C. and T4=60°; T2 was varied. Flow rate was 0.01 ml / min. Voltage was 15 kV. Distance between the nozzle and collector was 3 inches. The results are given in Table 2 below:
TABLE 2T2Fiber DiameterStandard(° C.)(μm)dev. (μm)2155.580.542256.172.191906.850.461609.491.131755.761.122055.361.70
The results show that if T2 is too high or too low, the fiber diameter tends to get thicker. Too low temperature freezes up the filament and thus less whipping motion can be induced. Too high temperature decreases the viscosity of the jet, and eventually continuous production of fiber would not be possible. High temperature (225° C.) also leads to poor size distribution. From the data it appears that T2 of above 215 to 220° C. leads to small fiber diameter with uniform size distribution.
working example iii
Effect of (T3) on Fiber Diameter
[0070] The nozzle diameter was 0.84 mm. The temperatures used were T2=220° C. and T4=60°; T3 was varied. Flow rate was 0.01 ml / min. Voltage was 15 kV, and distance between the nozzle and collector was 3 inches. The results are given in Table 3 below:
TABLE 3T3Fiber DiameterStandard(° C.)(μm)dev. (μm)2515.02.541005.340.67
[0071] The results show that increasing T3 decreases fiber diameter, and with T3=100° C., uniform size distribution is obtained.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com