High density atrial fibrillation cycle length (AFCL) detection and mapping system
a high density atrial fibrillation and detection and mapping technology, applied in the field of intervention and treatment of heart conditions, can solve the problems of embolic stroke, limited ablating focal triggers, and heart stopping blood pumping,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
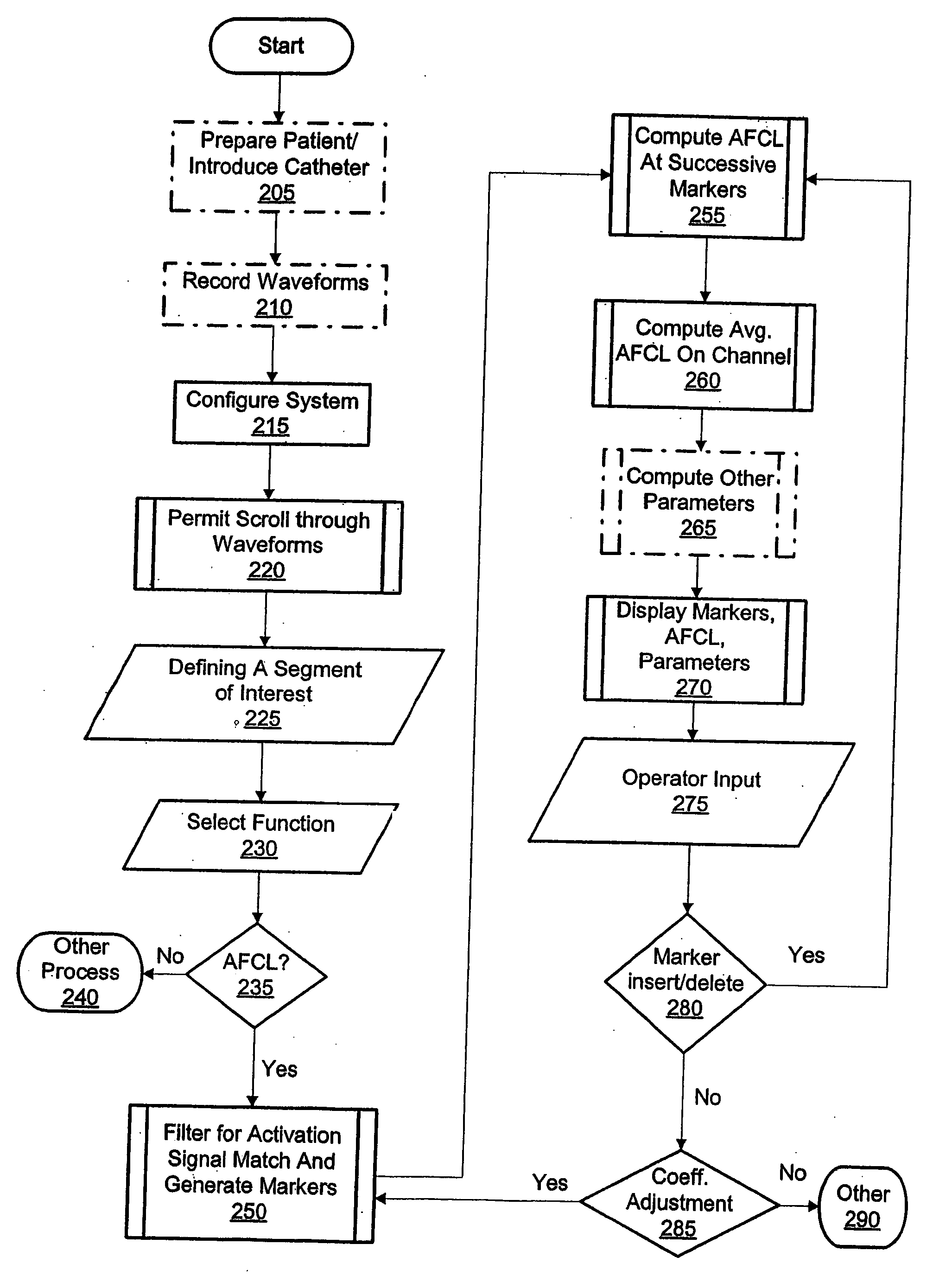
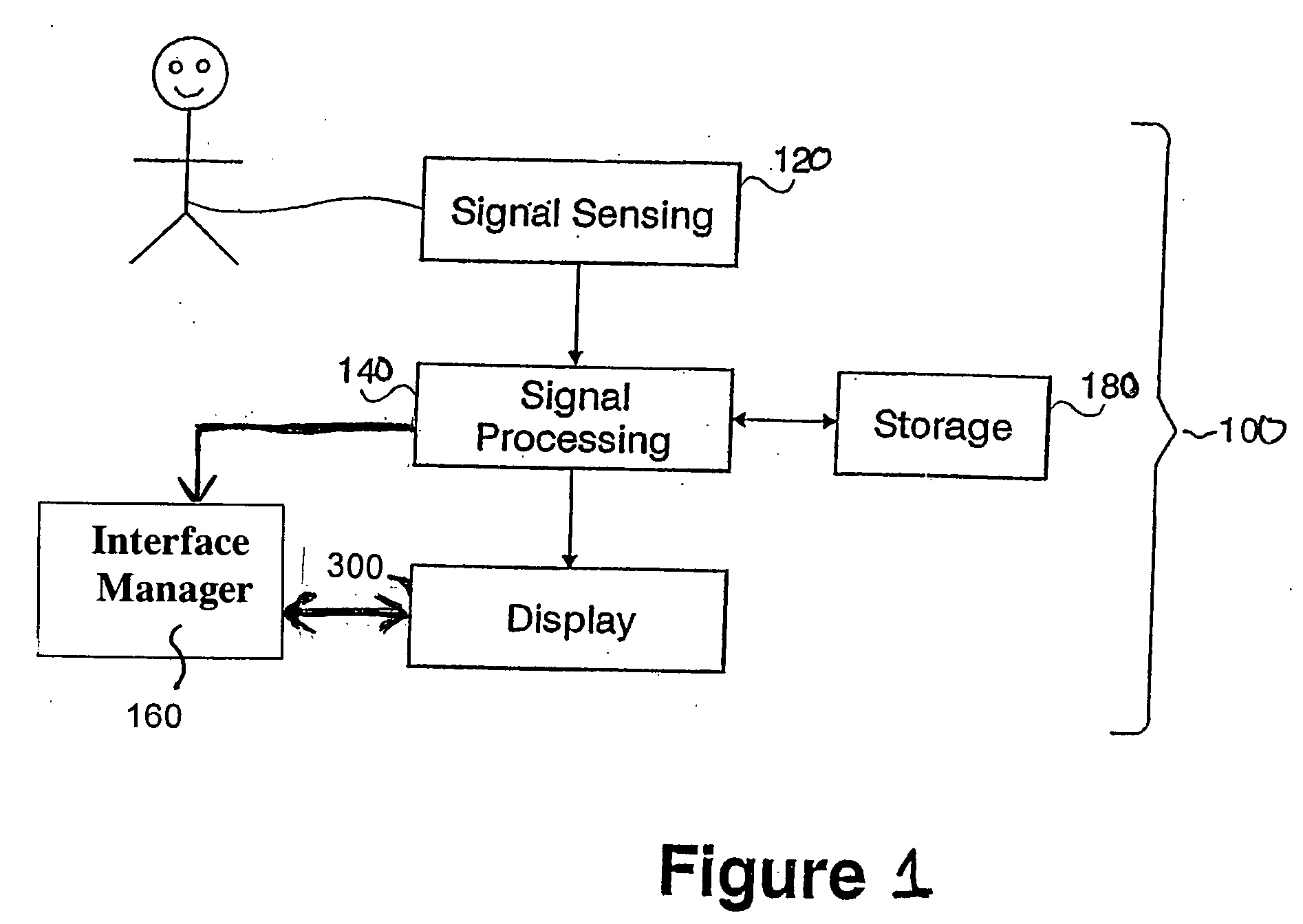
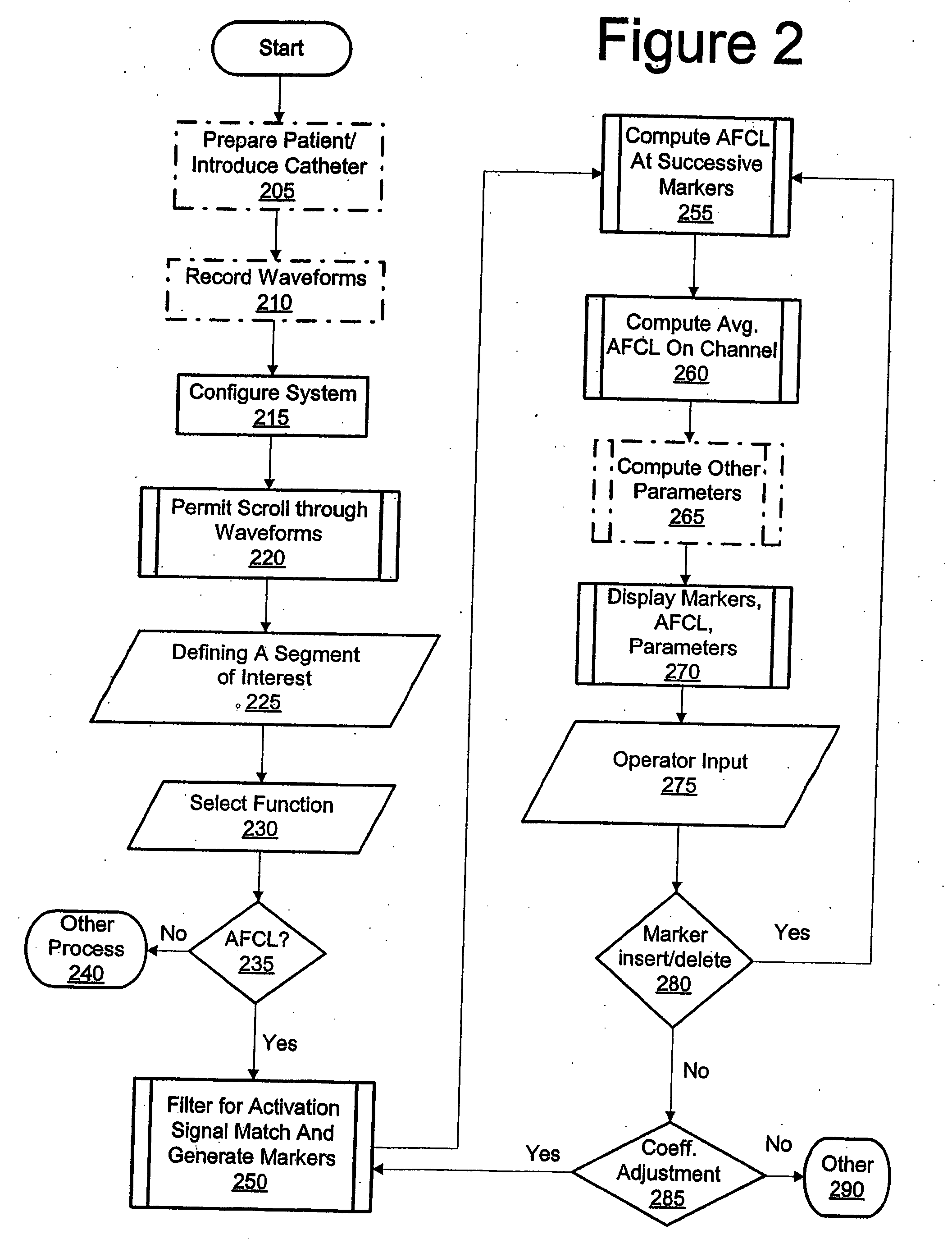
[0026] By way of overview and introduction, when heart cells are activated, the electrical polarization caused by the normal voltage difference of about 90 mV between the inside and outside of the cells collapses and the heart tissue is said to “depolarize.” Depolarized heart tissue which has not been given adequate time to re-establish its normal voltage difference and will not produce a new activation in response to a further intrinsic or extrinsic electrical stimulus is referred to as refractory tissue. After depolarization, heart cells begin to re-establish the normal voltage difference (“repolarization”). Tissue which has been afforded an adequate length of time to re-establish a sufficiently large voltage difference to once again become susceptible to depolarization is no longer refractory. The time interval which is required after a cell has been depolarized until it is again non-refractory is called the refractory period. In a fibrillating heart, depolarization wavefronts mo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com