Patents
Literature
231 results about "Electrode location" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
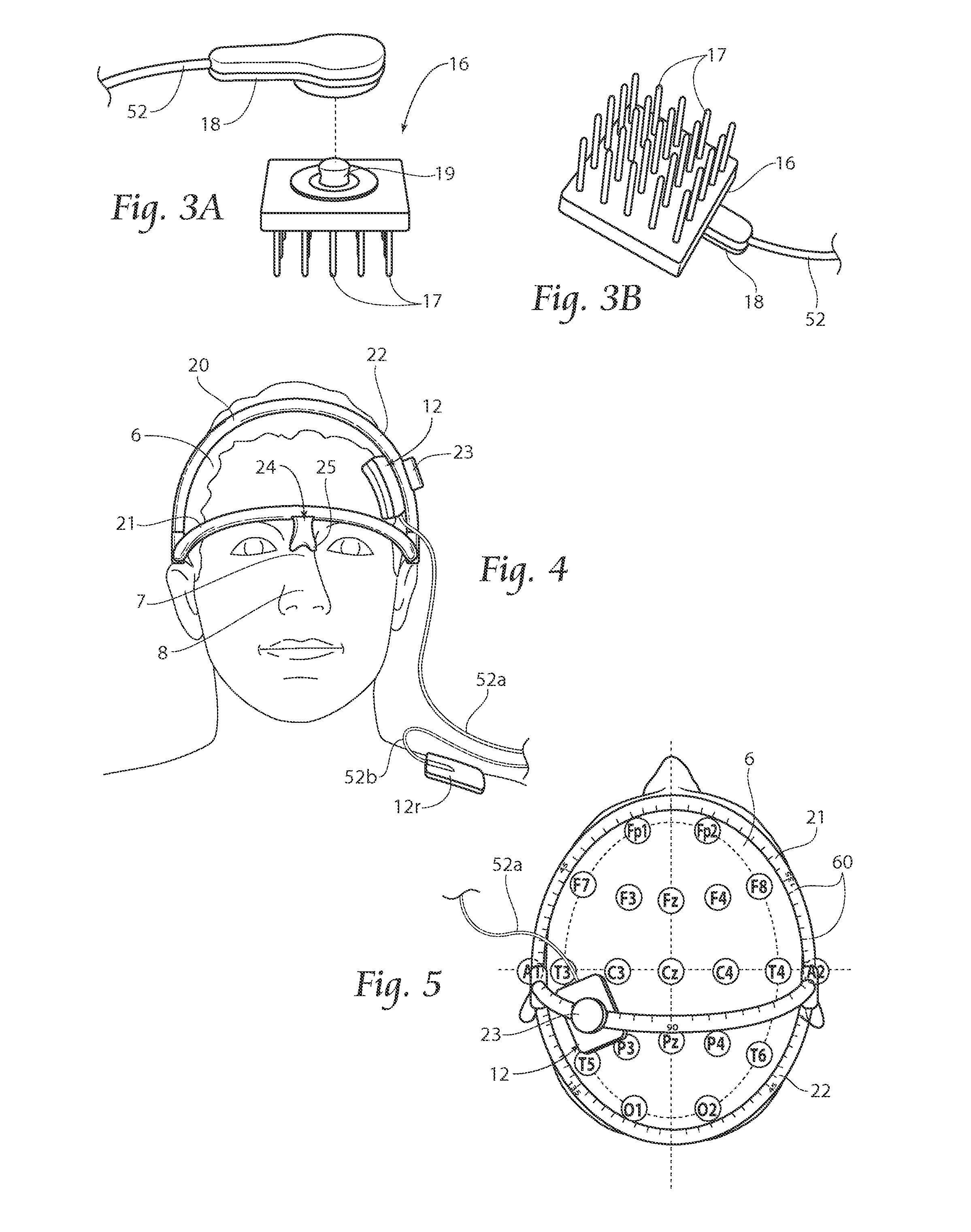
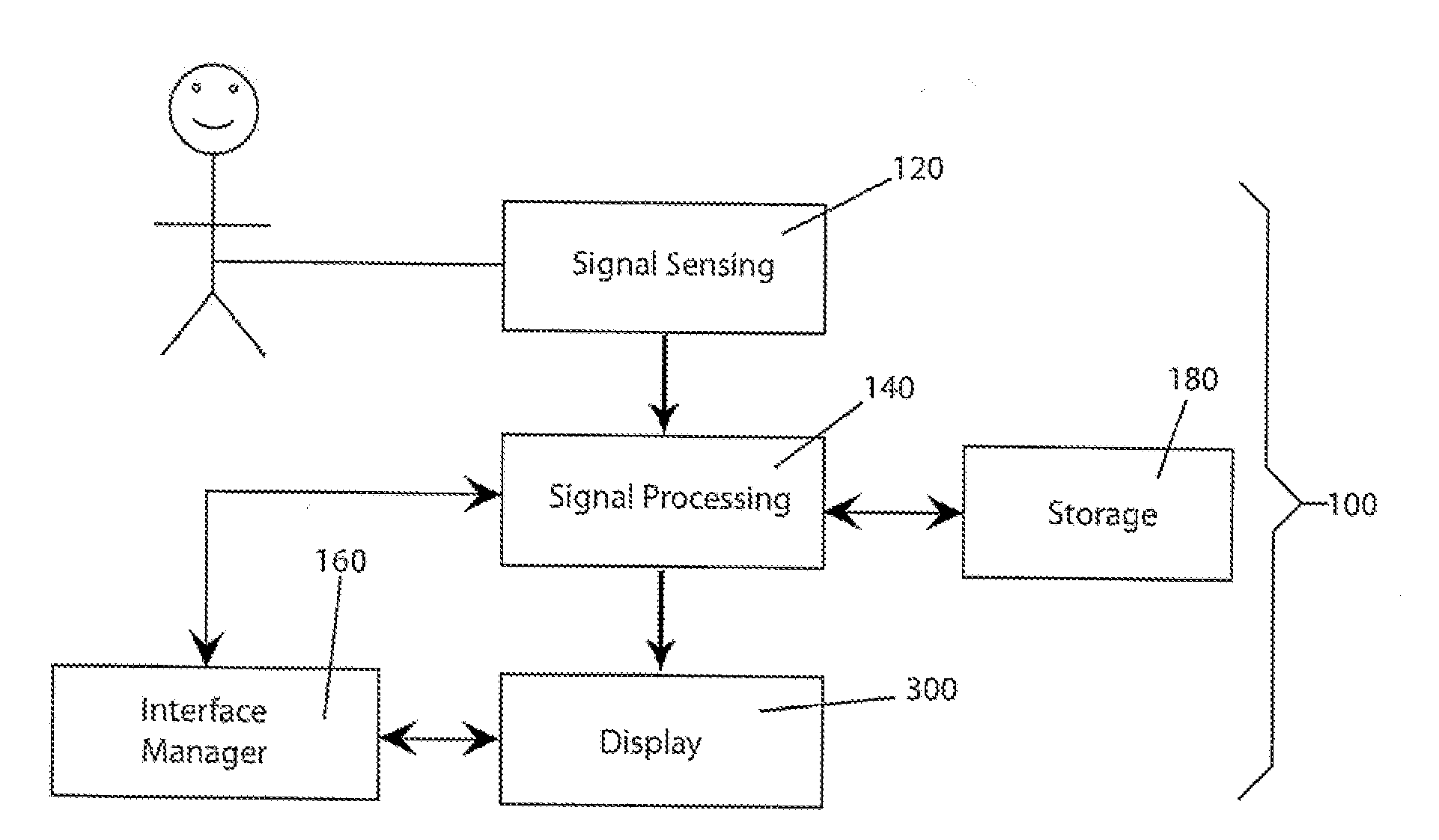
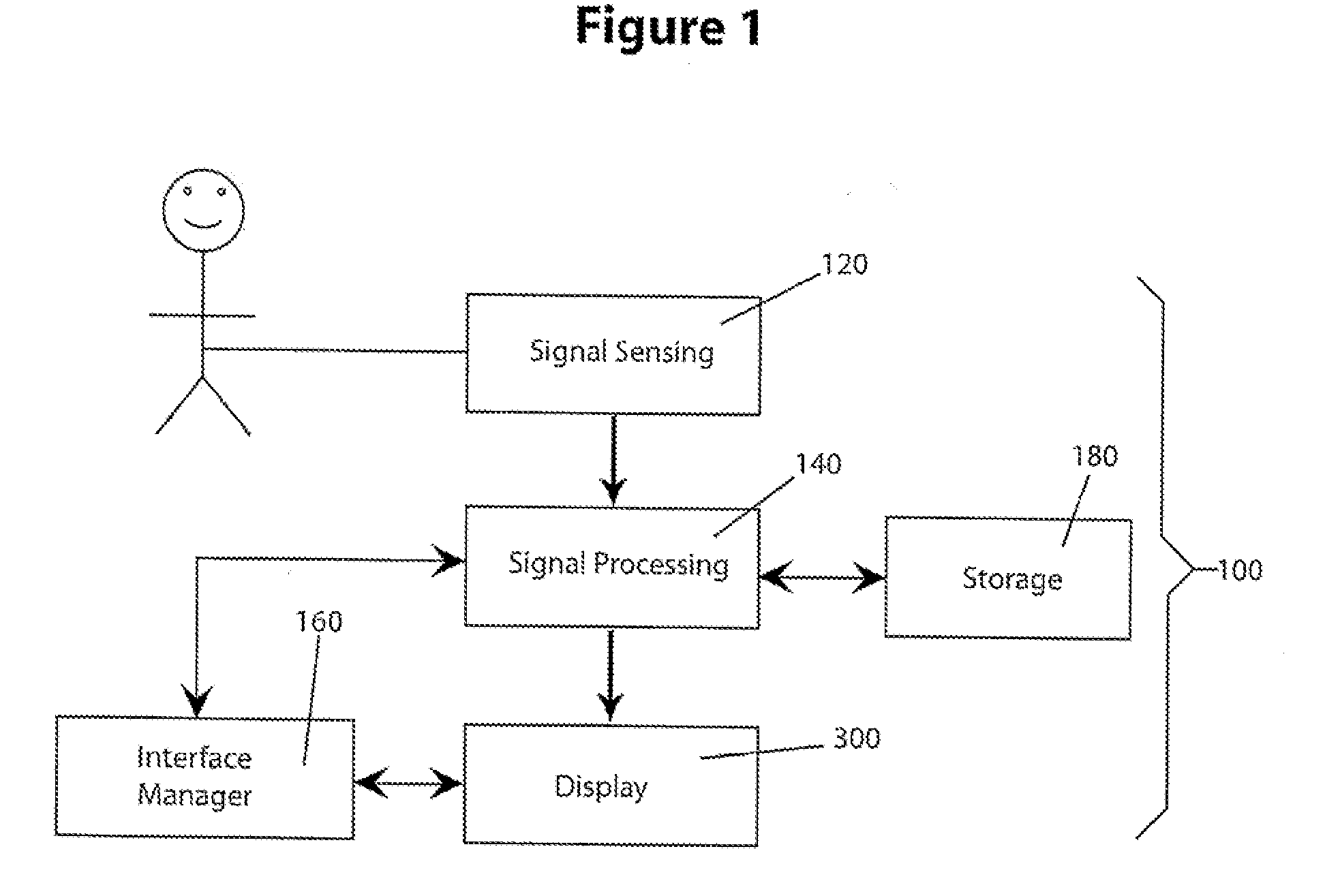
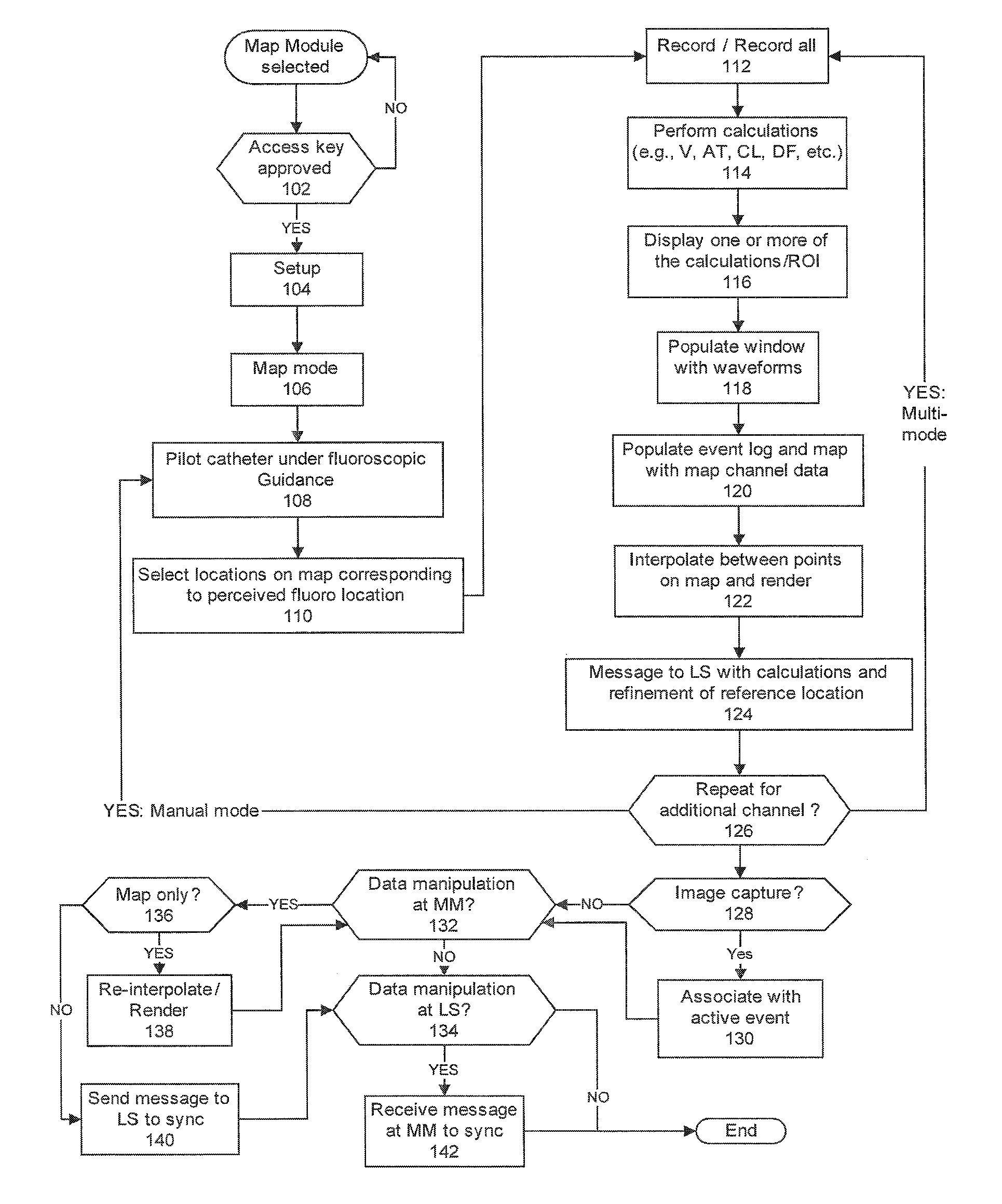
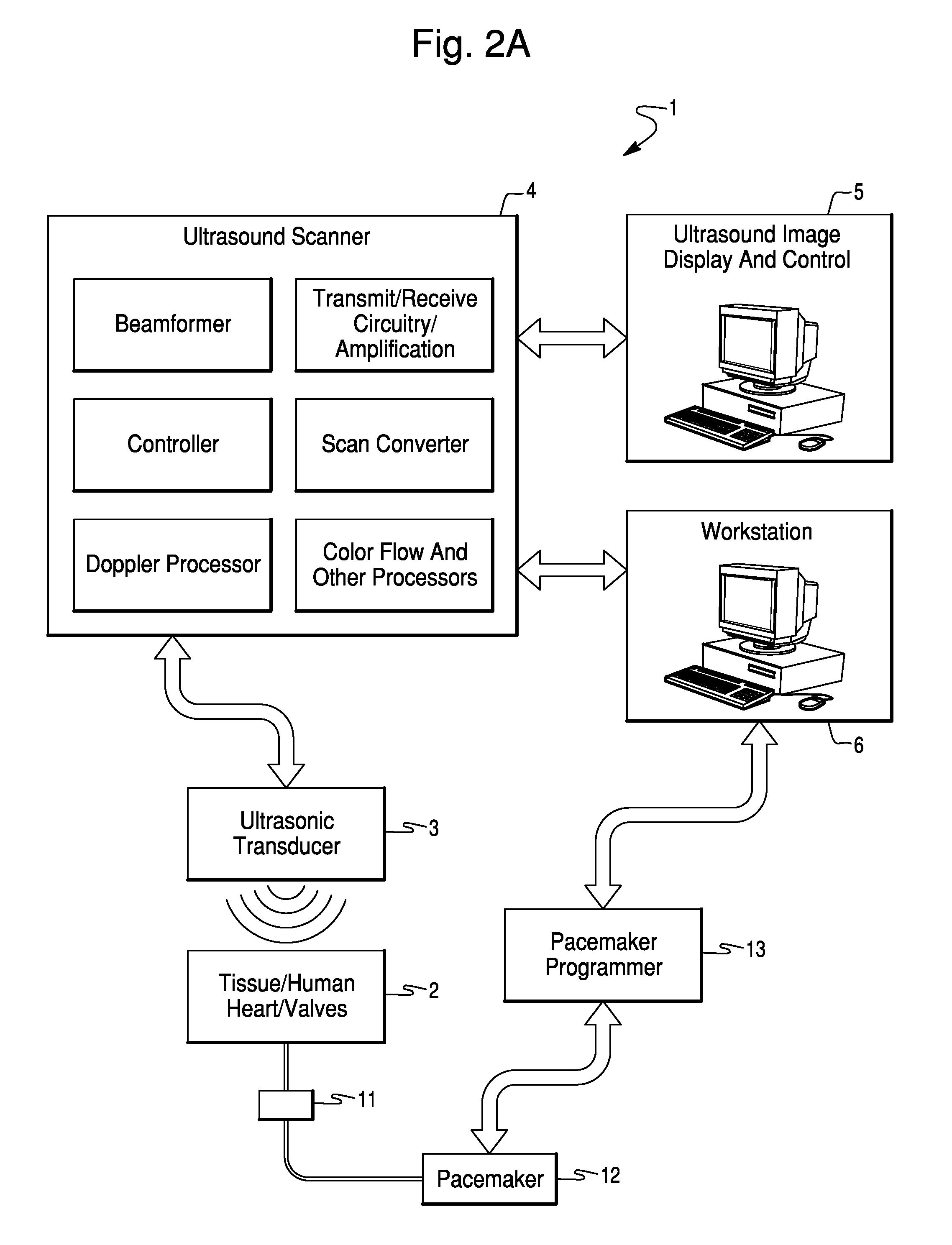
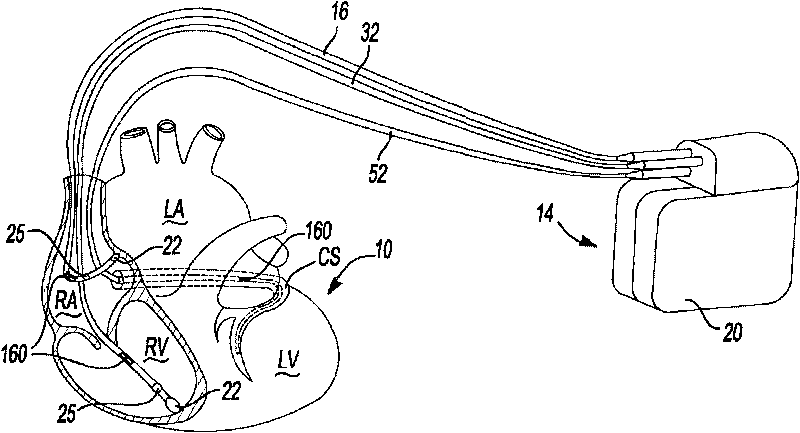
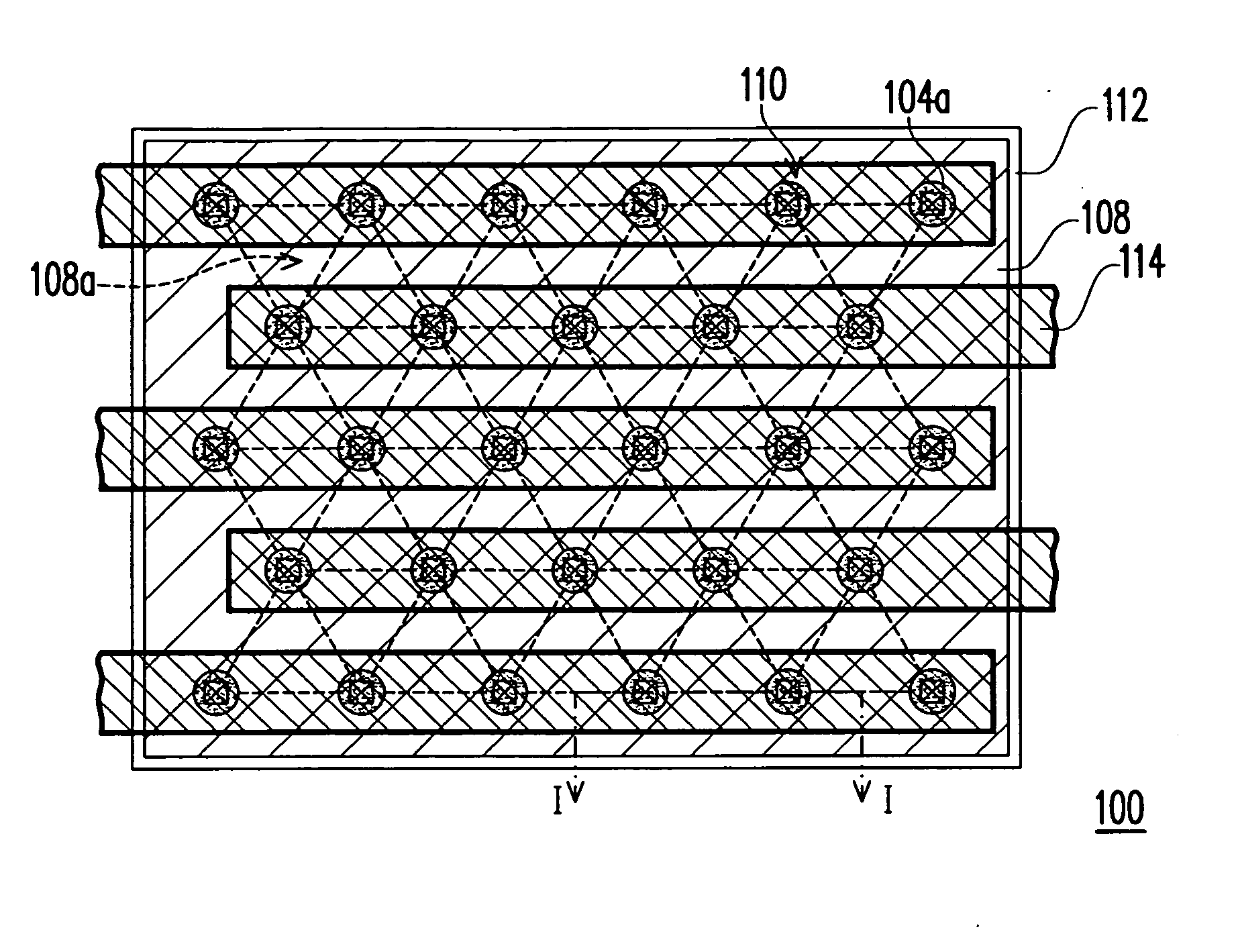
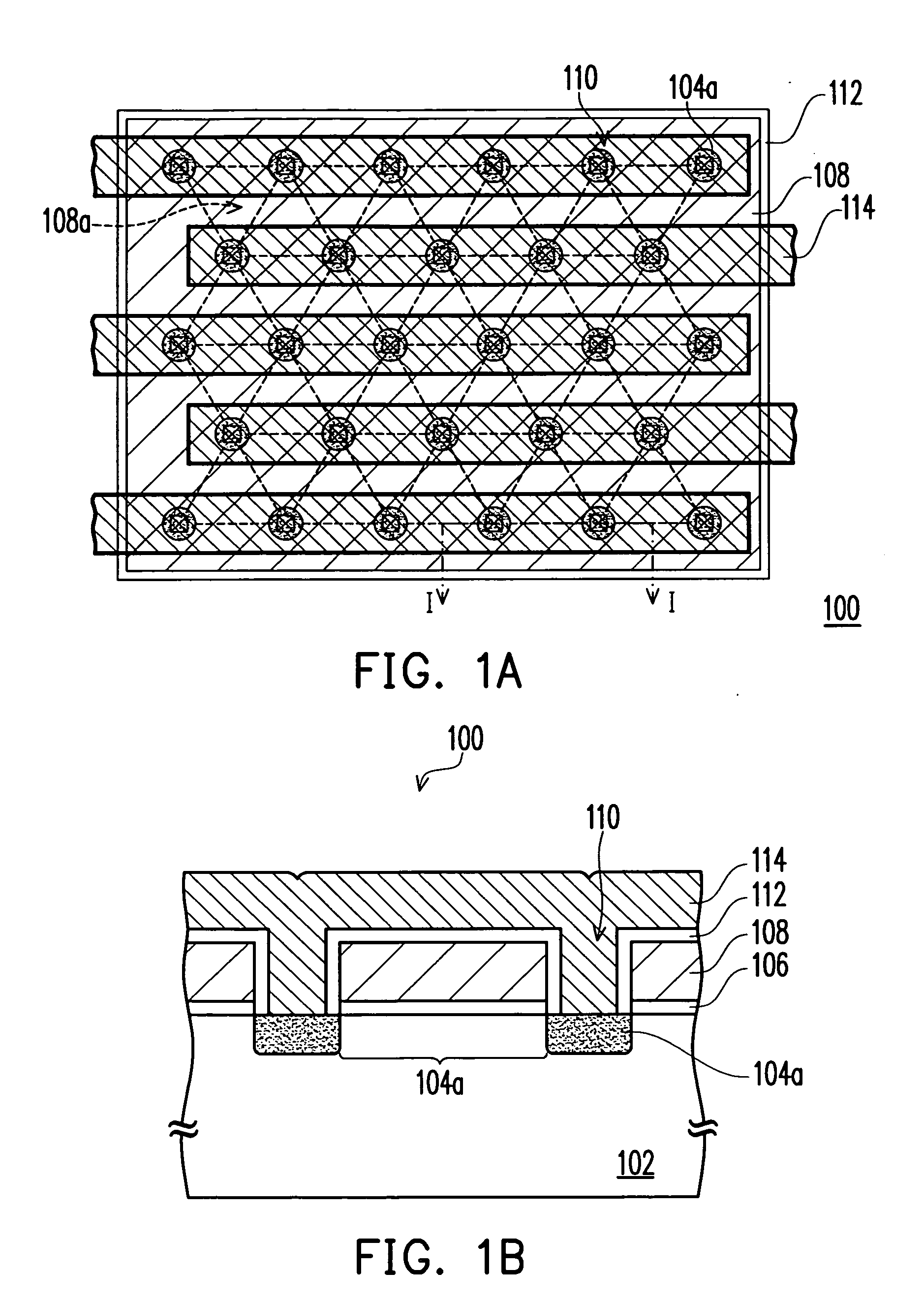
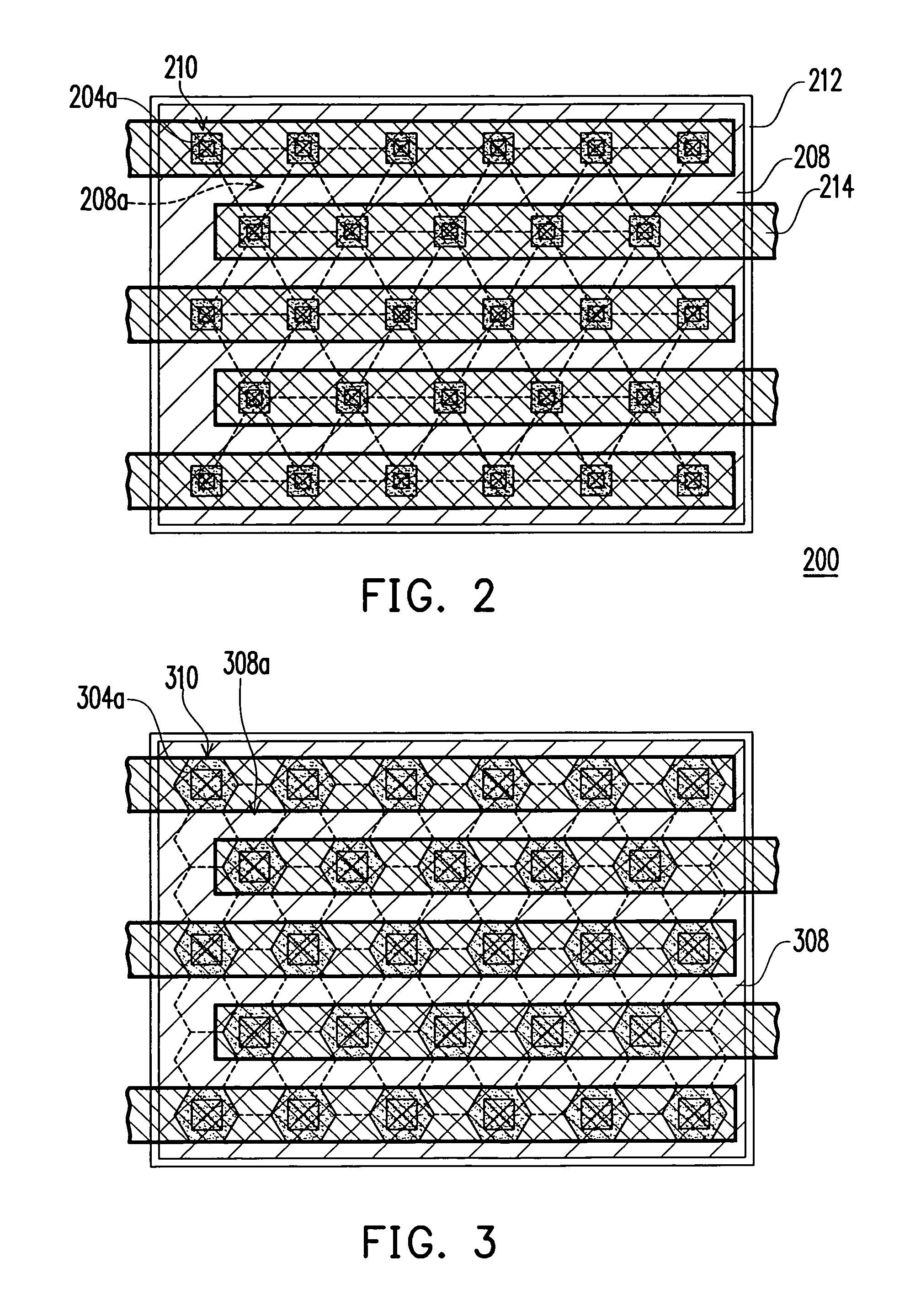
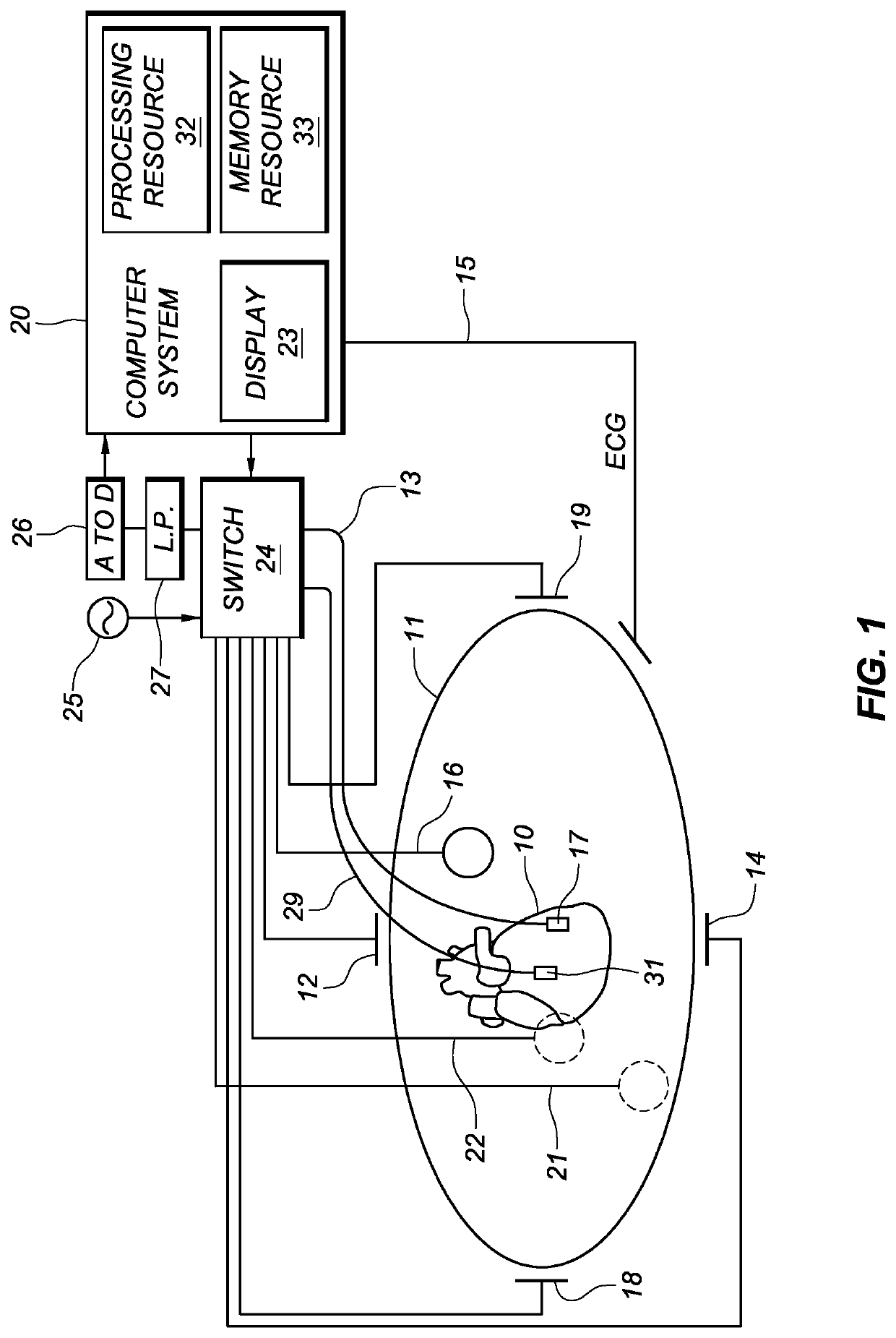
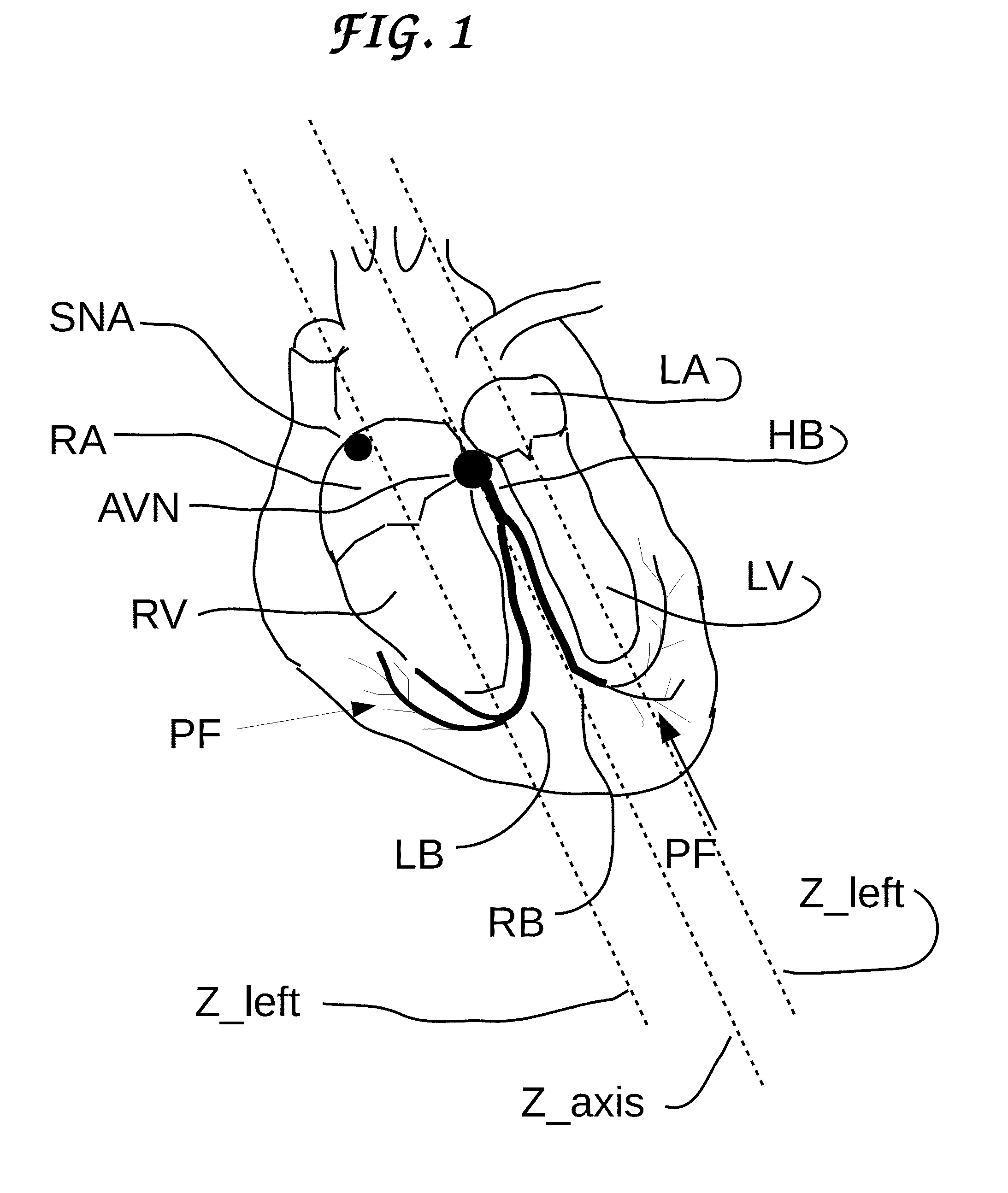
Method and apparatus for catheter navigation and location and mapping in the heart
InactiveUS7263397B2Enhance system functionsAccurate locationElectrocardiographyCatheterHeart chamberBiological activation
A medical system for finding and displaying the location of electrodes within the body. The electrodes may be used to measure the voltage on the heart wall and display this as an activation map on a geometry representing the heart chamber.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
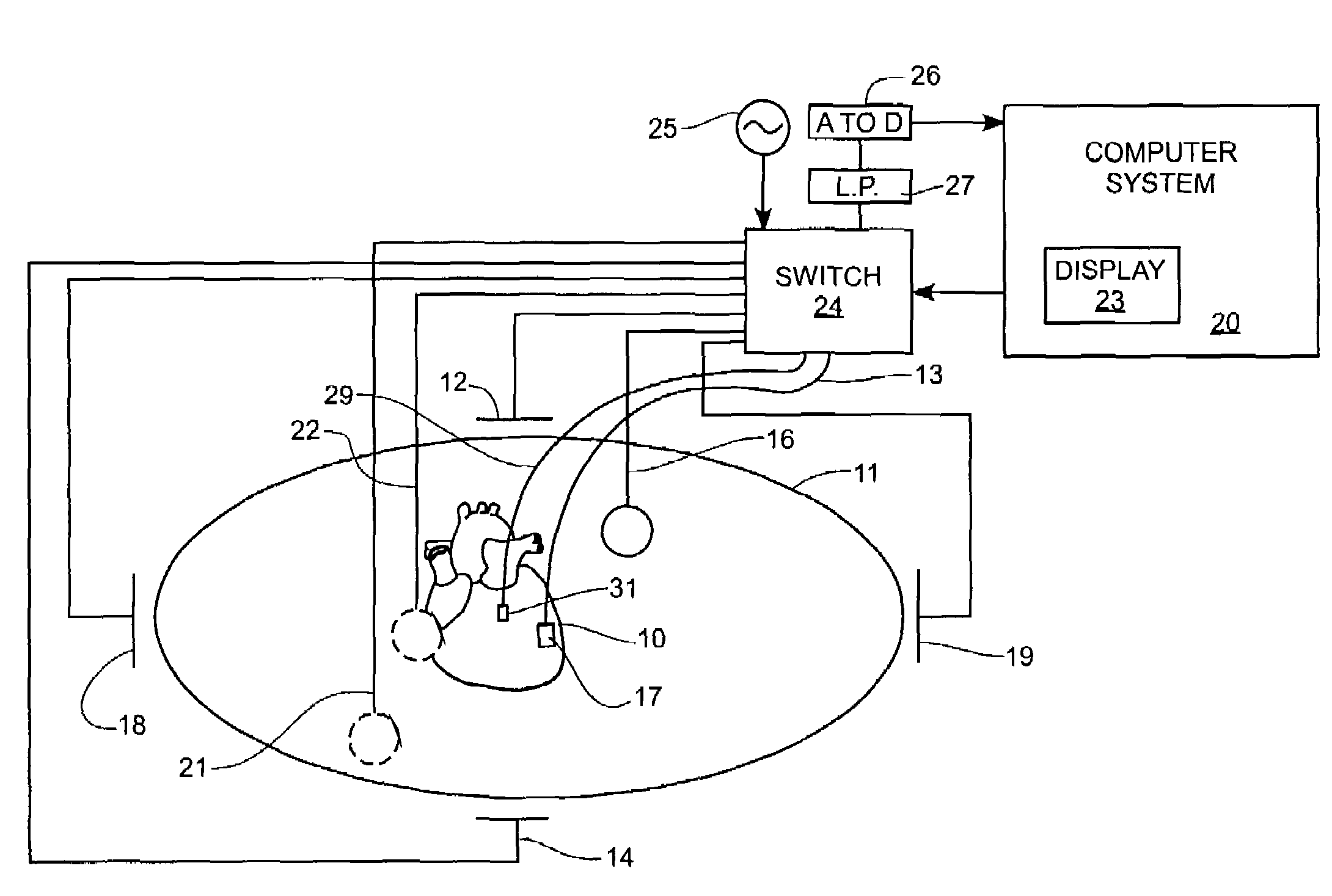
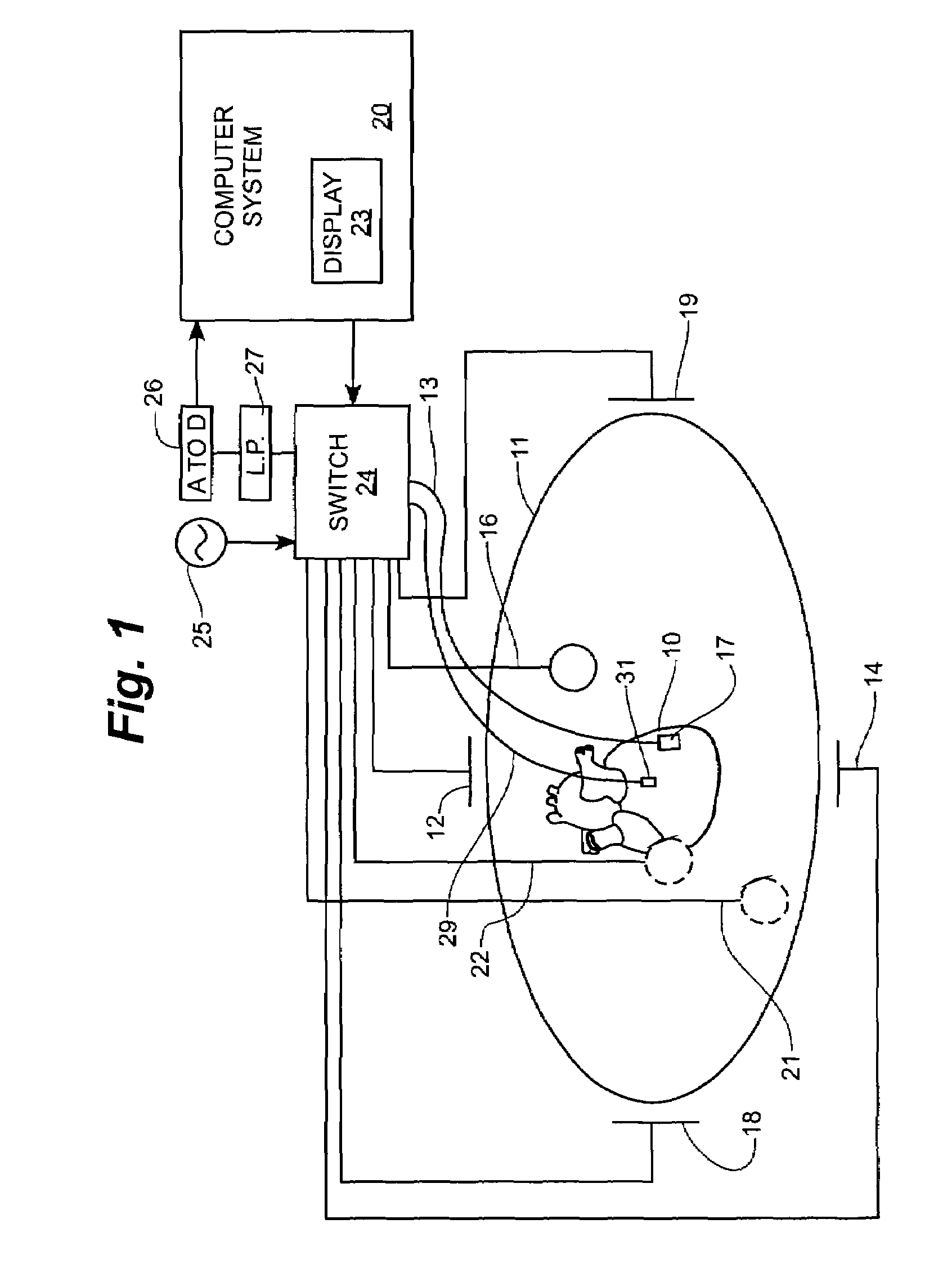
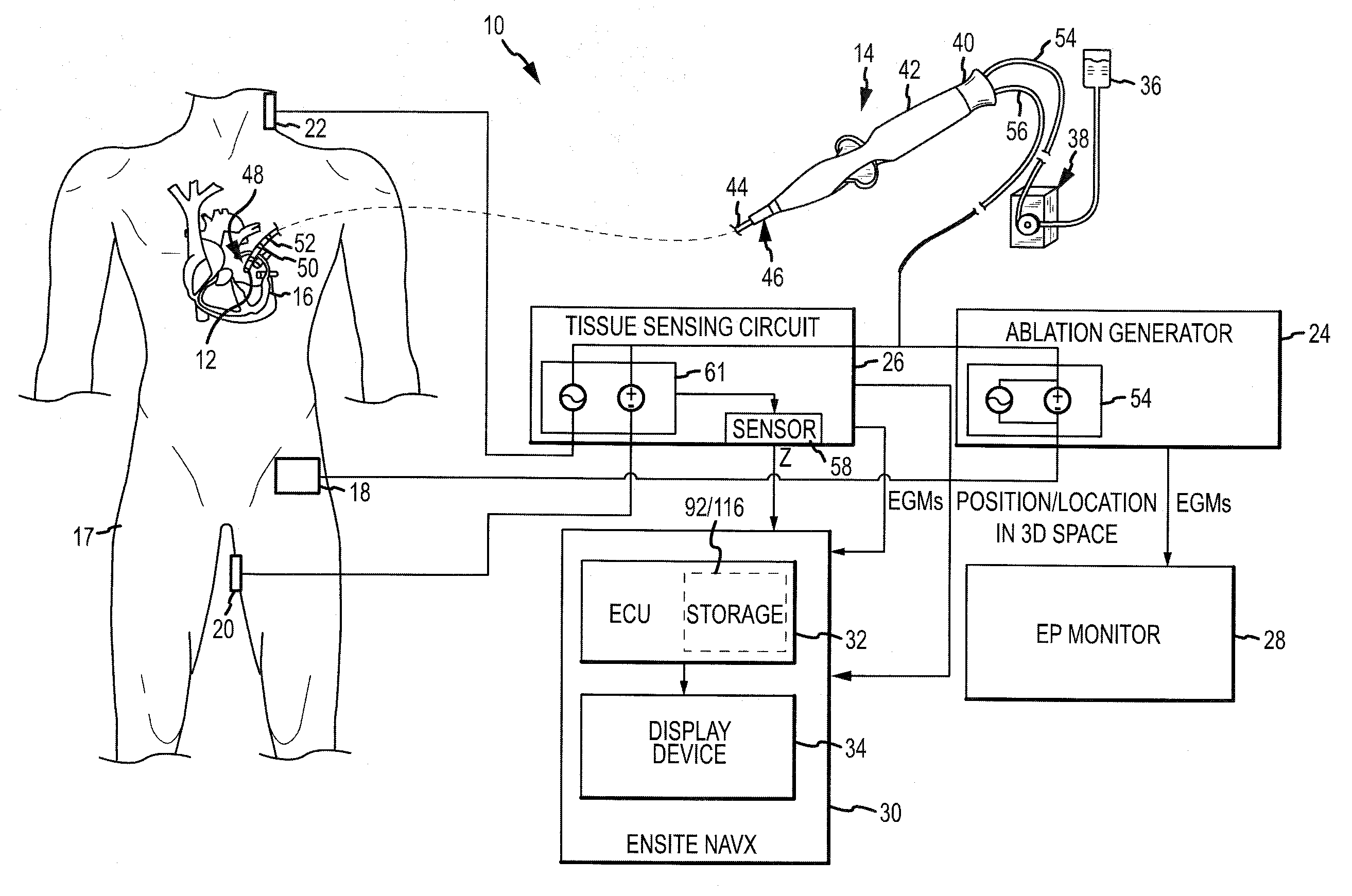
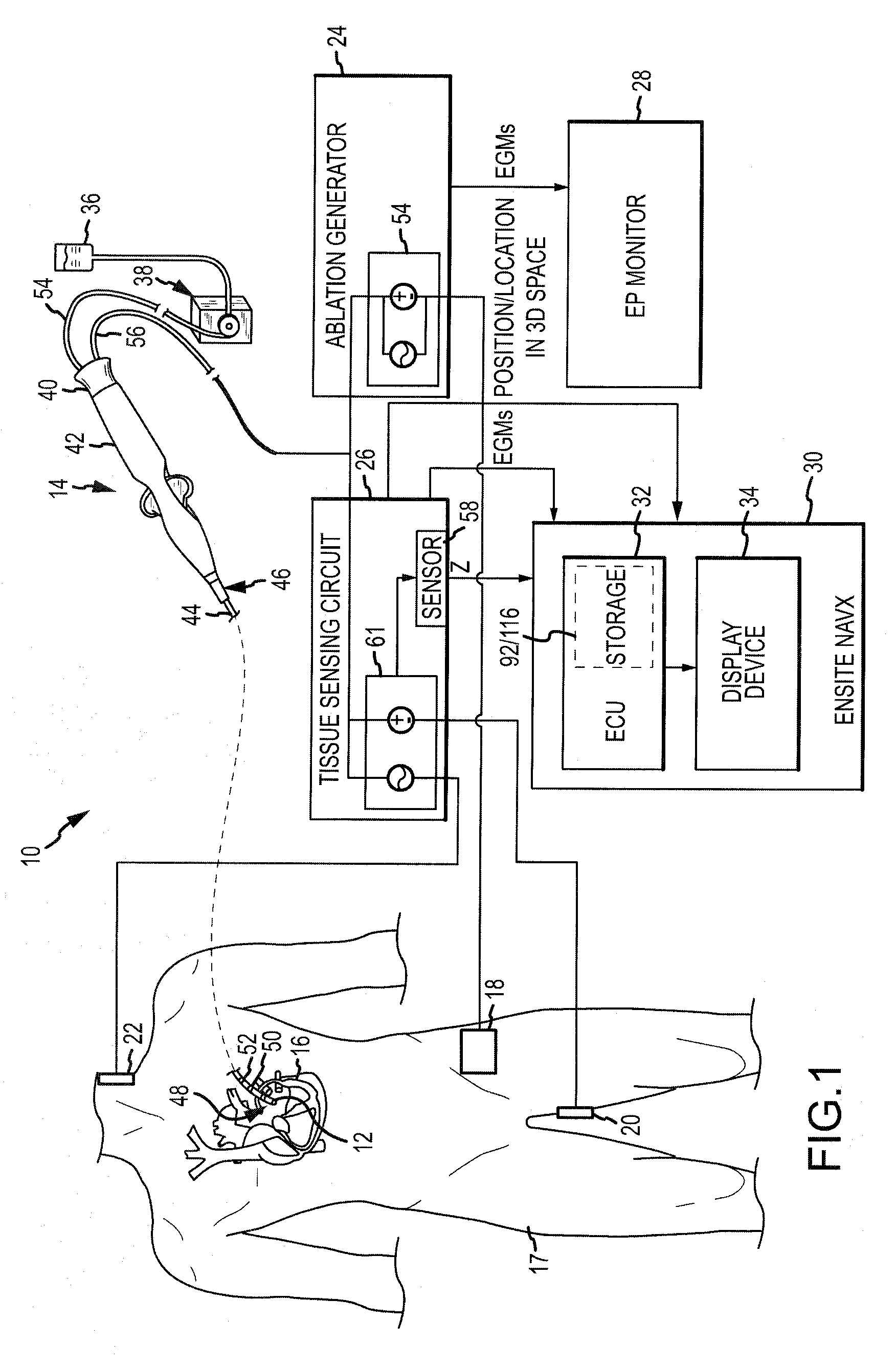
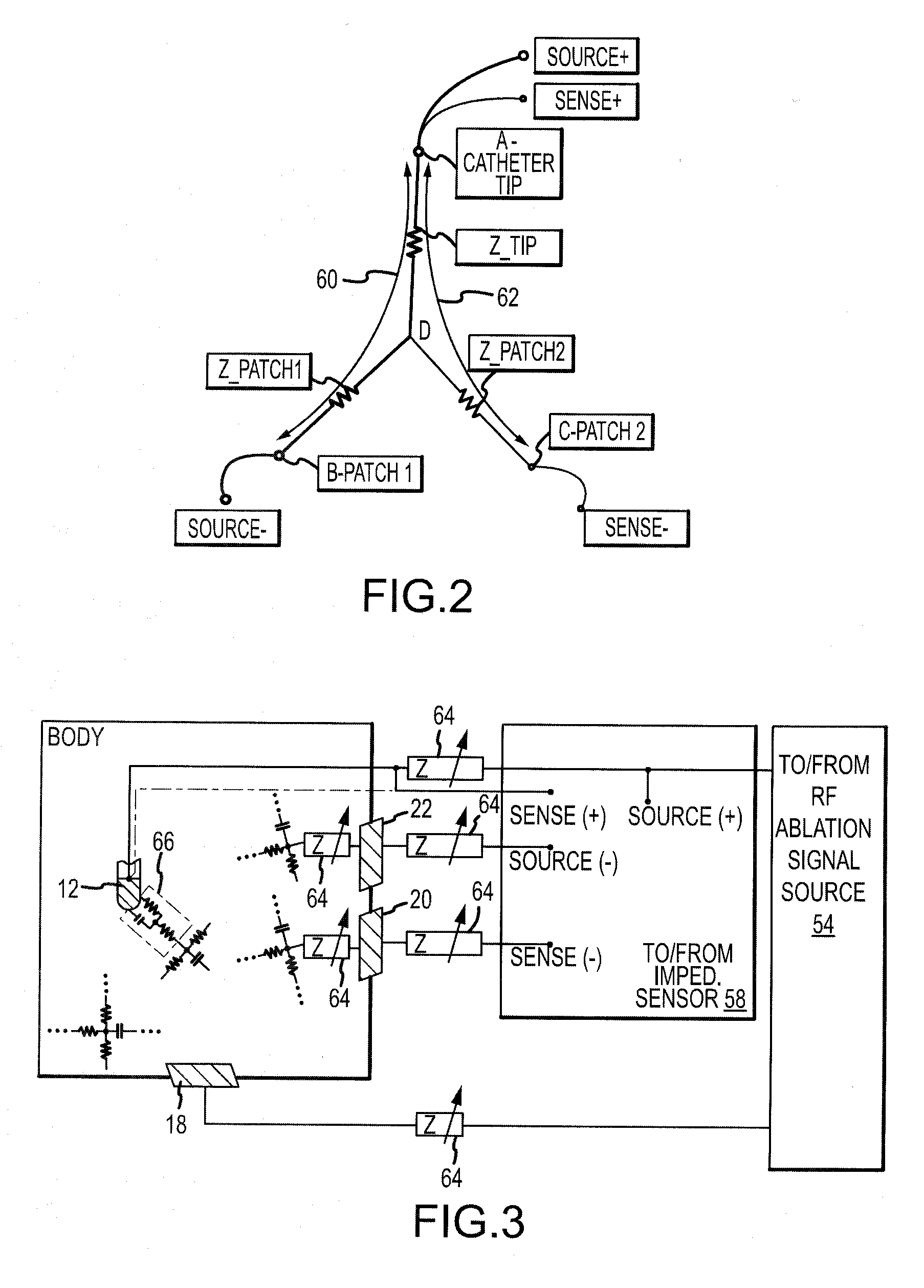
System and method for assessing the proximity of an electrode to tissue in a body
A method and system for assessing proximity between an electrode and tissue is provided. The system includes an electronic control unit (ECU). The ECU is configured to acquire values for first and second components of a complex impedance between the electrode and the tissue, and to calculate an electrical coupling index (ECI) responsive to the first and second values. The ECU is further configured to process the ECI to determine the proximity of the electrode to the tissue. The ECU may be configured to calculate an electrical coupling index rate (ECIR) based on the calculated ECI and information relating to the change in location of the electrode, and to assess proximity based on the ECIR. Alternatively, the ECU may be configured to assess the proximity using the calculated ECI, as opposed to the ECIR.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Method For Simultaneous Bi-Atrial Mapping Of Atrial Fibrillation
InactiveUS20070232949A1High resolutionFast informationElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyCardiac pacemaker electrodeDisplay device
A method for diagnosing and mapping atrial fibrillation correlates recordings of electrical activity from intracardiac multielectrode catheters with the locations of electrodes within the heart to obtain a global mapping of cardiac electrical activity. Time delay and / or amplitude information in the recorded electrical activities is fused with electrode location information to generate a display on a 3-D anatomical template of the heart. Time delay and / or amplitude information is displayed using color code and / or lines of equal value, to aid diagnosis and localization of electrical activity irregularities. Mapping of atrial fibrillation enables physicians to treat arrhythmia by ablation, pacing, shock therapy and / or drugs at initiation or during an episode based on therapy delivery at critical mapped locations for arrhythmia onset or maintenance. Locations for placement of pacing leads and pacemaker timing parameters may also be obtained from the display.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
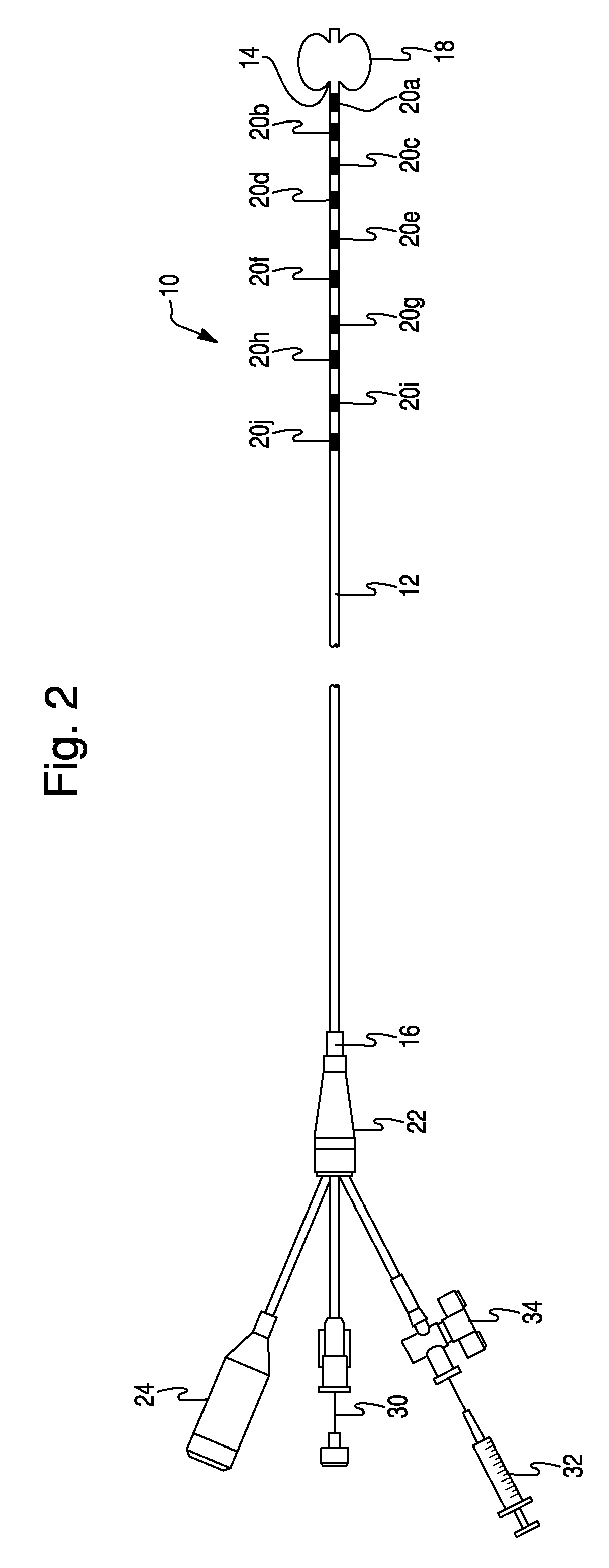
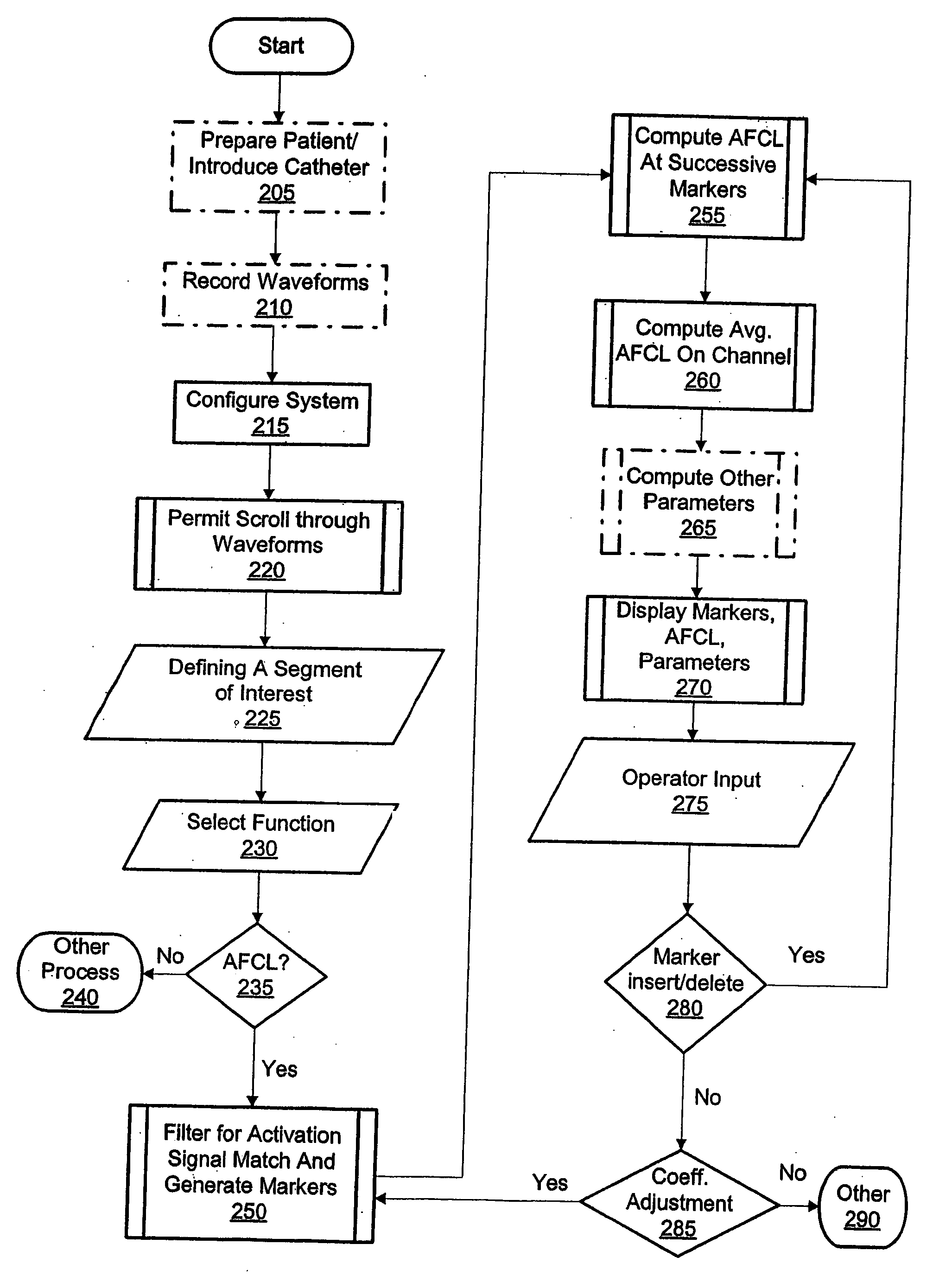
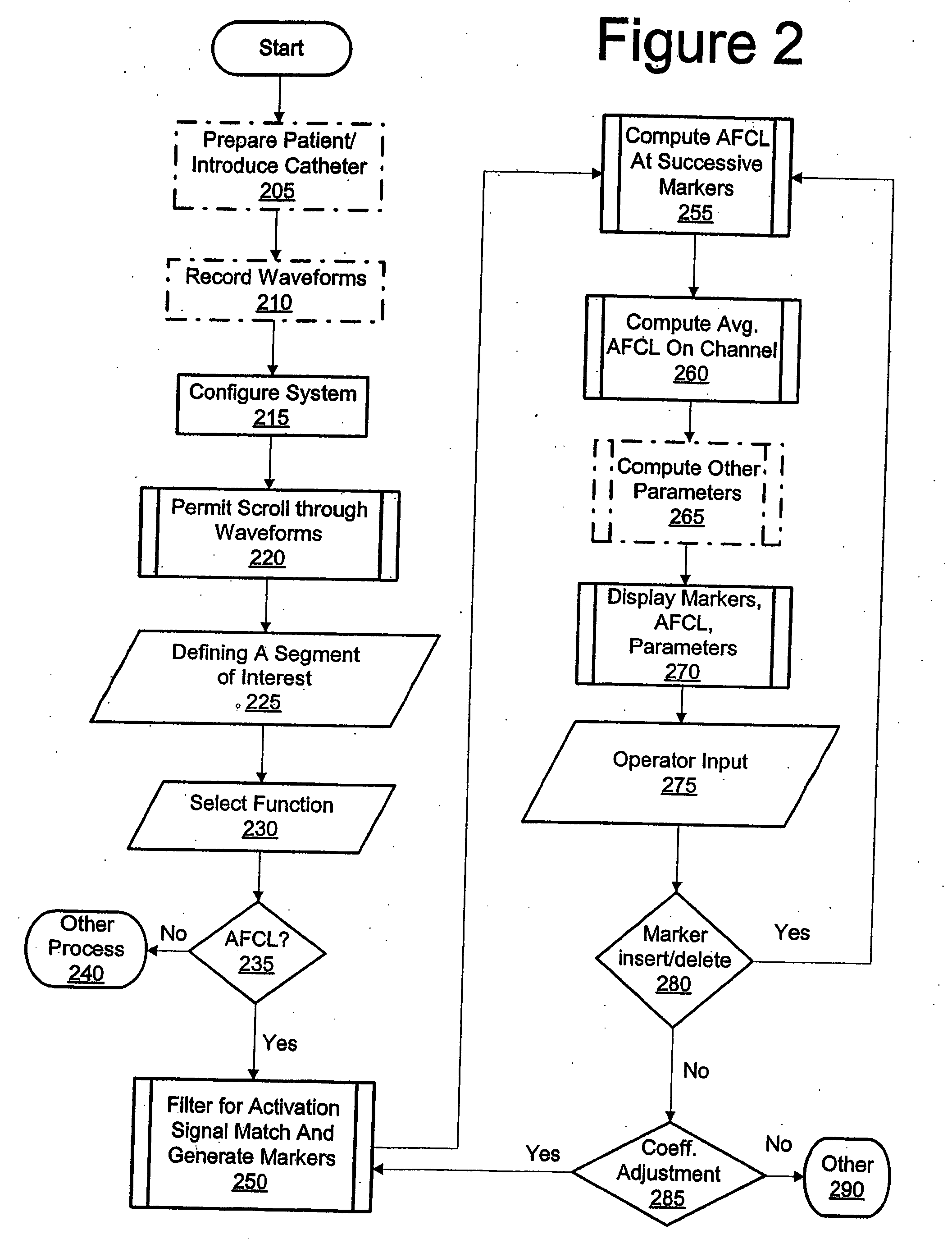
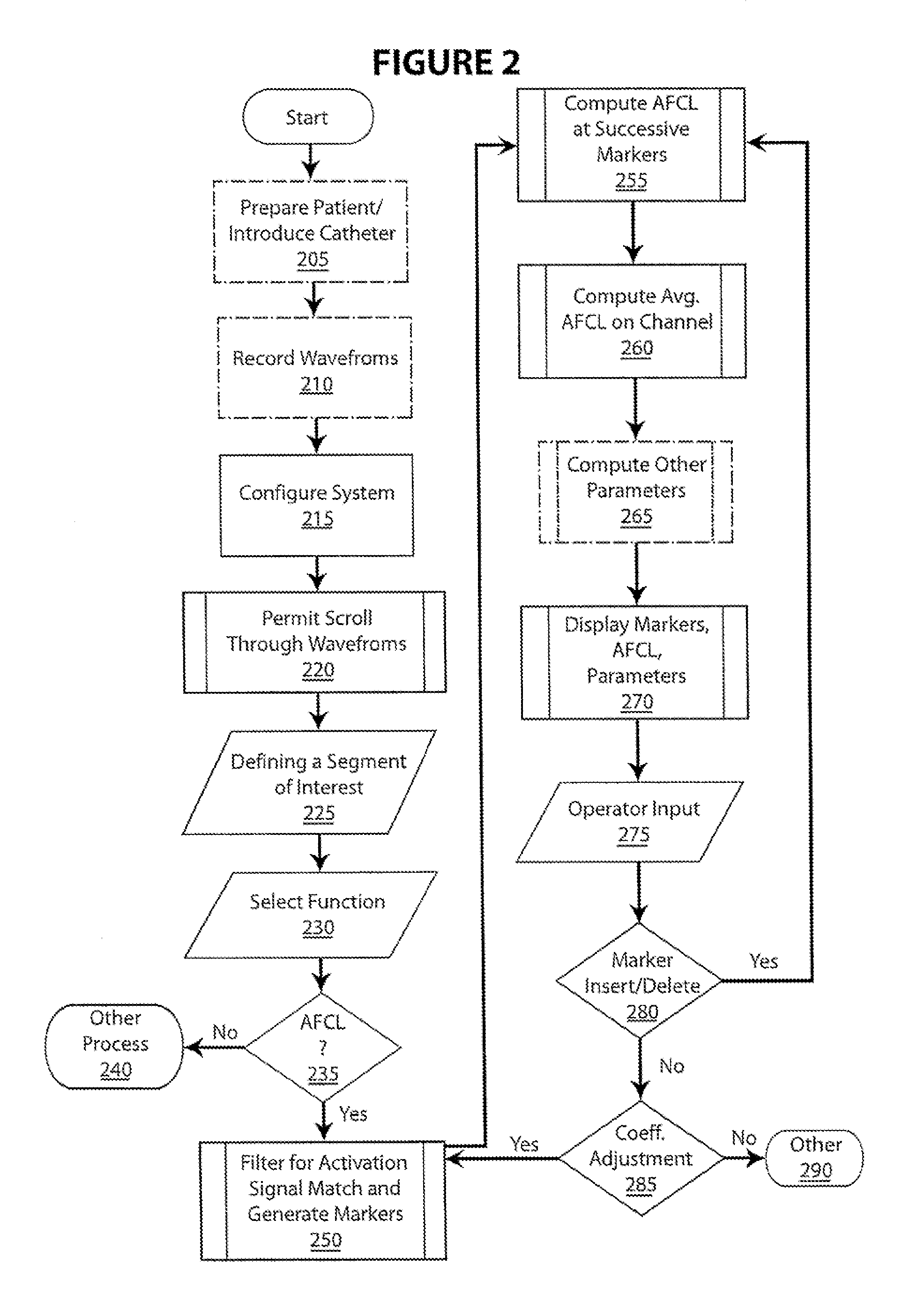
High density atrial fibrillation cycle length (AFCL) detection and mapping system
Systems and methods to assist in locating the focus of an atrial fibrillation include the association of atrial fibrillation cycle length values and statistics relating thereto with temporal locations on an electrogram of a given electrode, and / or the coordination of electrode locations with respective the spectral analyses of electrogram signals and further parameters and statistics relating thereto. Ablation therapy can proceed under guidance of such information.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
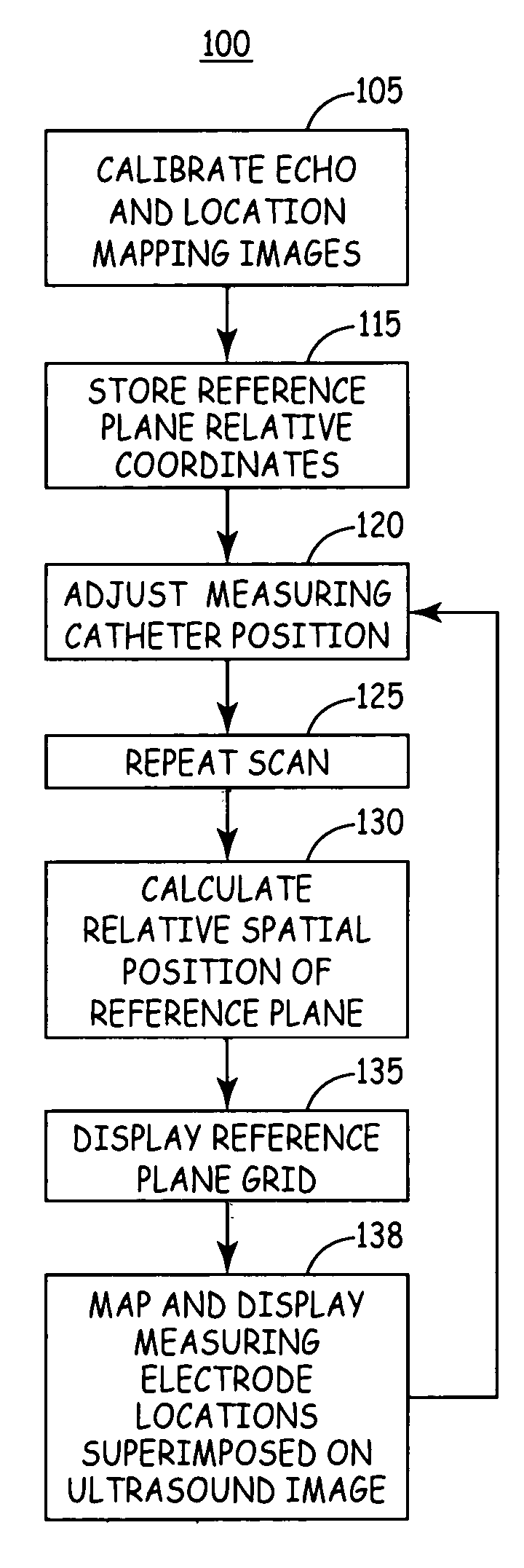
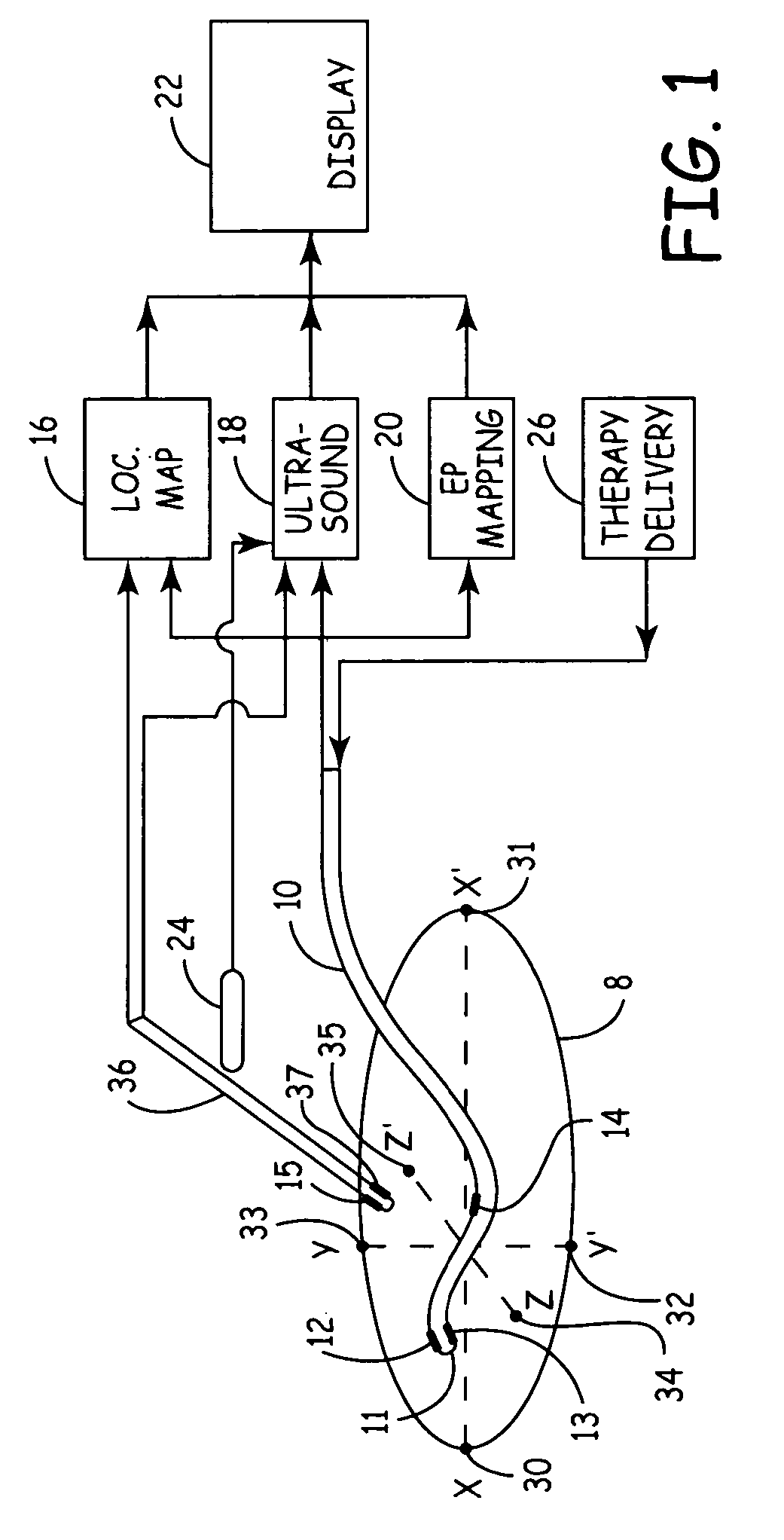
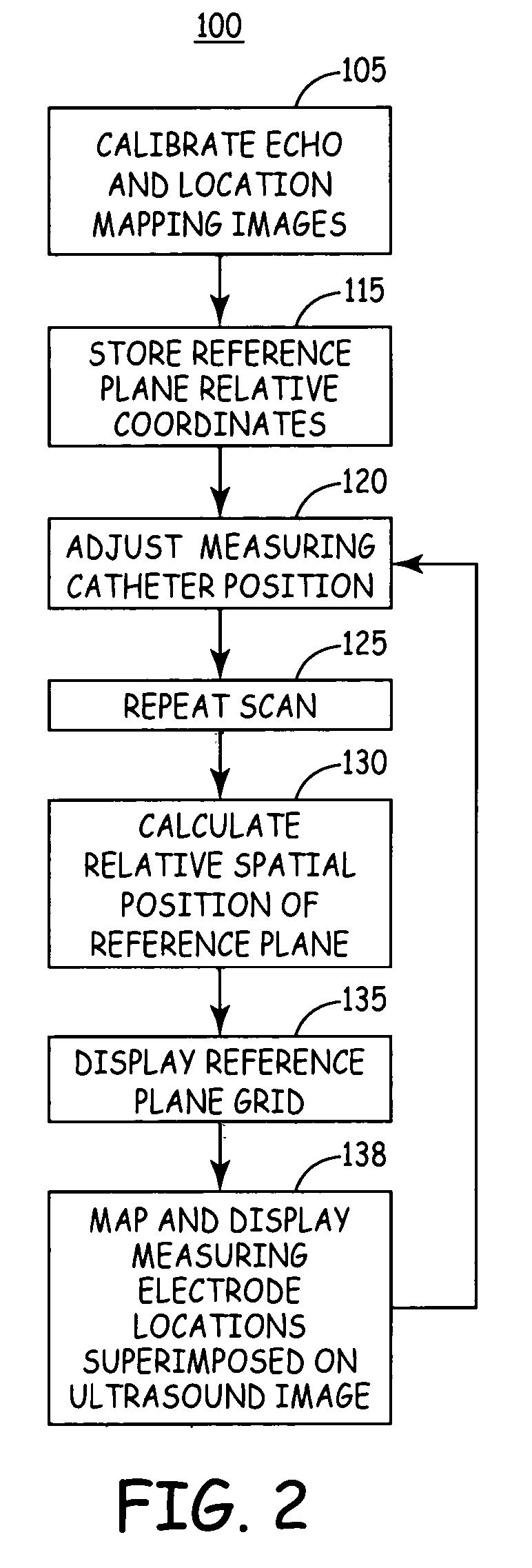
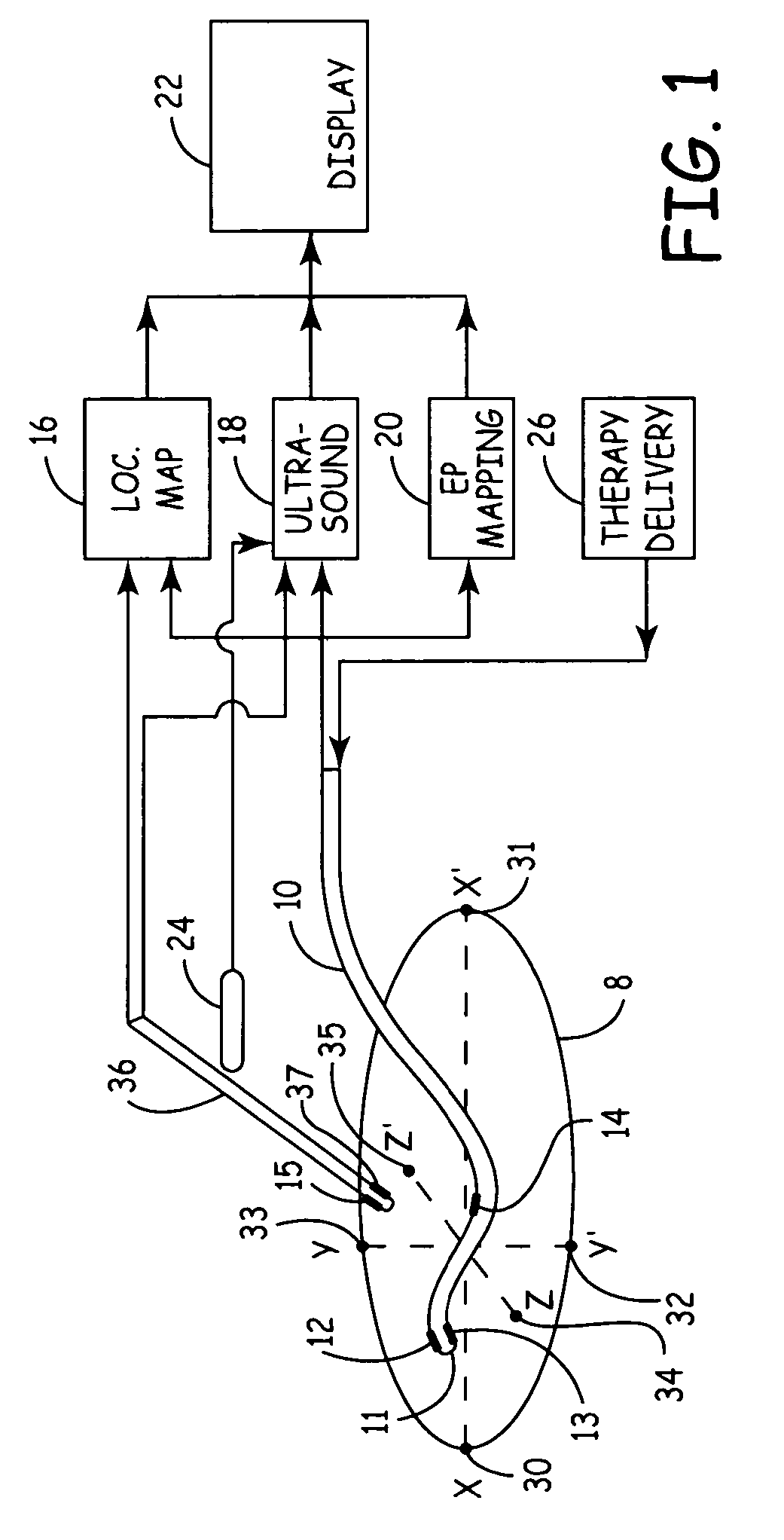
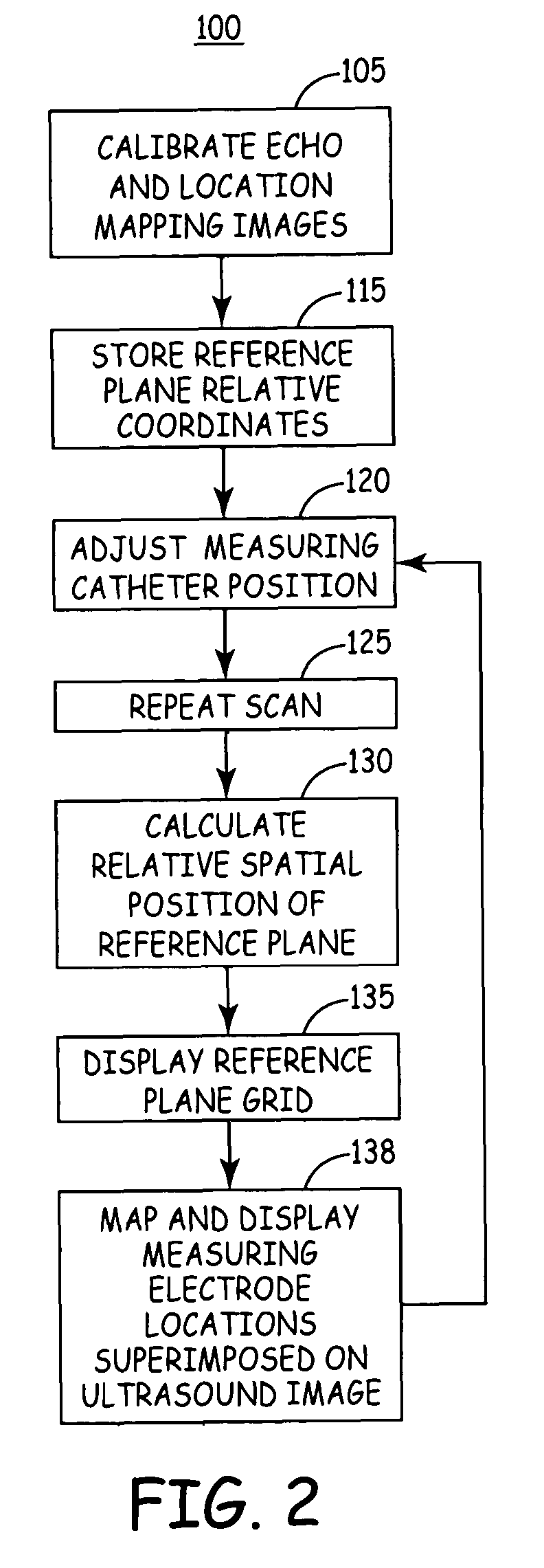
Electrode location mapping system and method
A mapped location of one or more electrodes within an electrical mapping volume is superimposed onto an ultrasound image corresponding to the electrical mapping volume.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
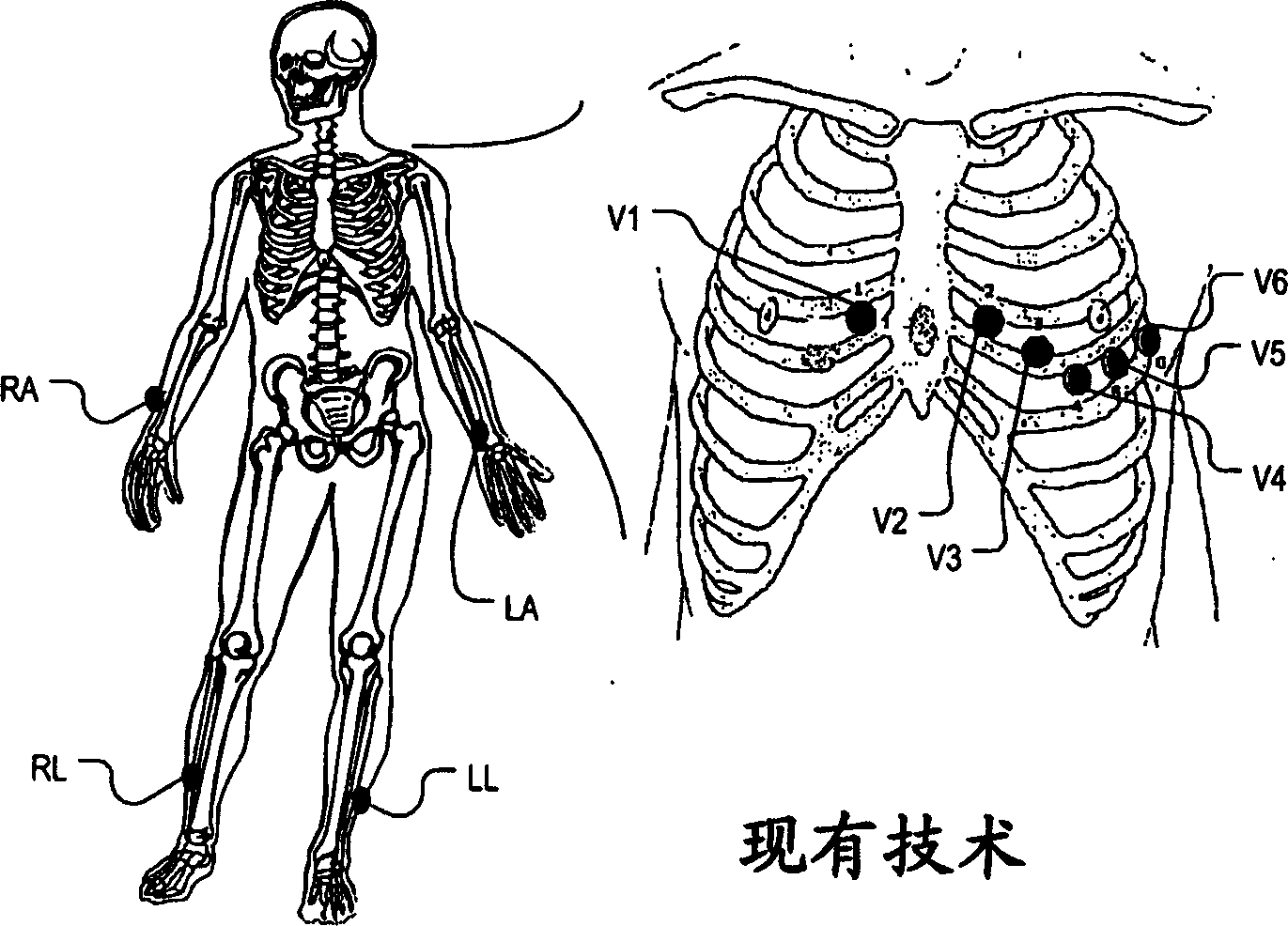
Methods and systems for electrode placement
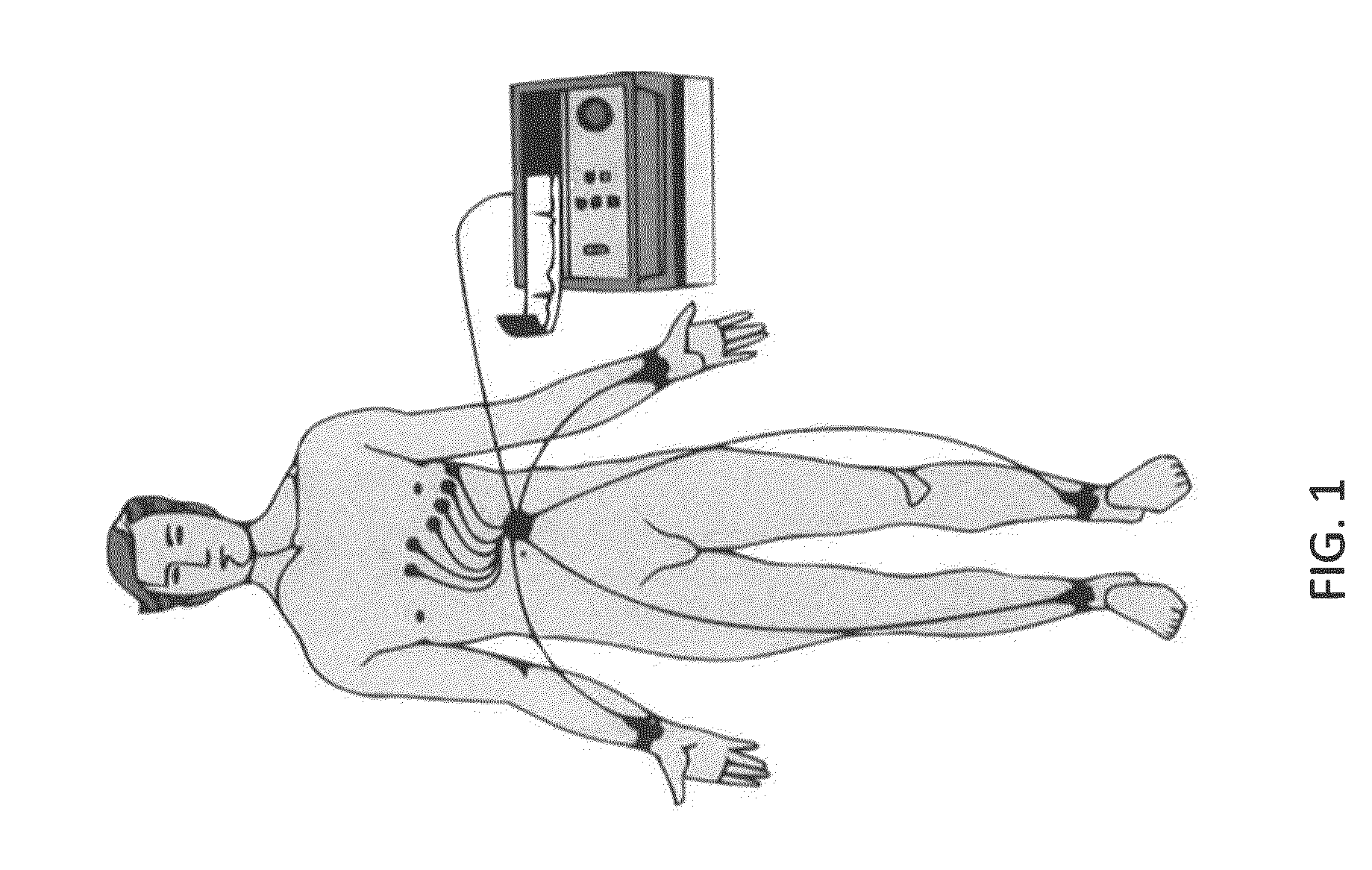
Described herein are systems, devices and methods for guiding placement of electrodes, and particularly ECG electrodes on a patient. A picture of the patient's body the patient can be analyzed to determine where on the patient's body to place electrodes according to a predetermined, conventional or standard placement pattern. The methods, devices and systems may then guide a user in positioning or correcting the position of electrodes on the patient. For example, an image of the patient may be provided showing the correct position of the electrodes, which may act as a patient-specific map or guide. The electrode placement positions can correspond to conventional or standard 12-lead ECG electrode positions.
Owner:ALIVECOR
Systems for and methods of transcranial direct current electrical stimulation
InactiveUS20130204315A1Reduce pointsSymptoms improvedImplantable neurostimulatorsArtificial respirationElectricityNervous system
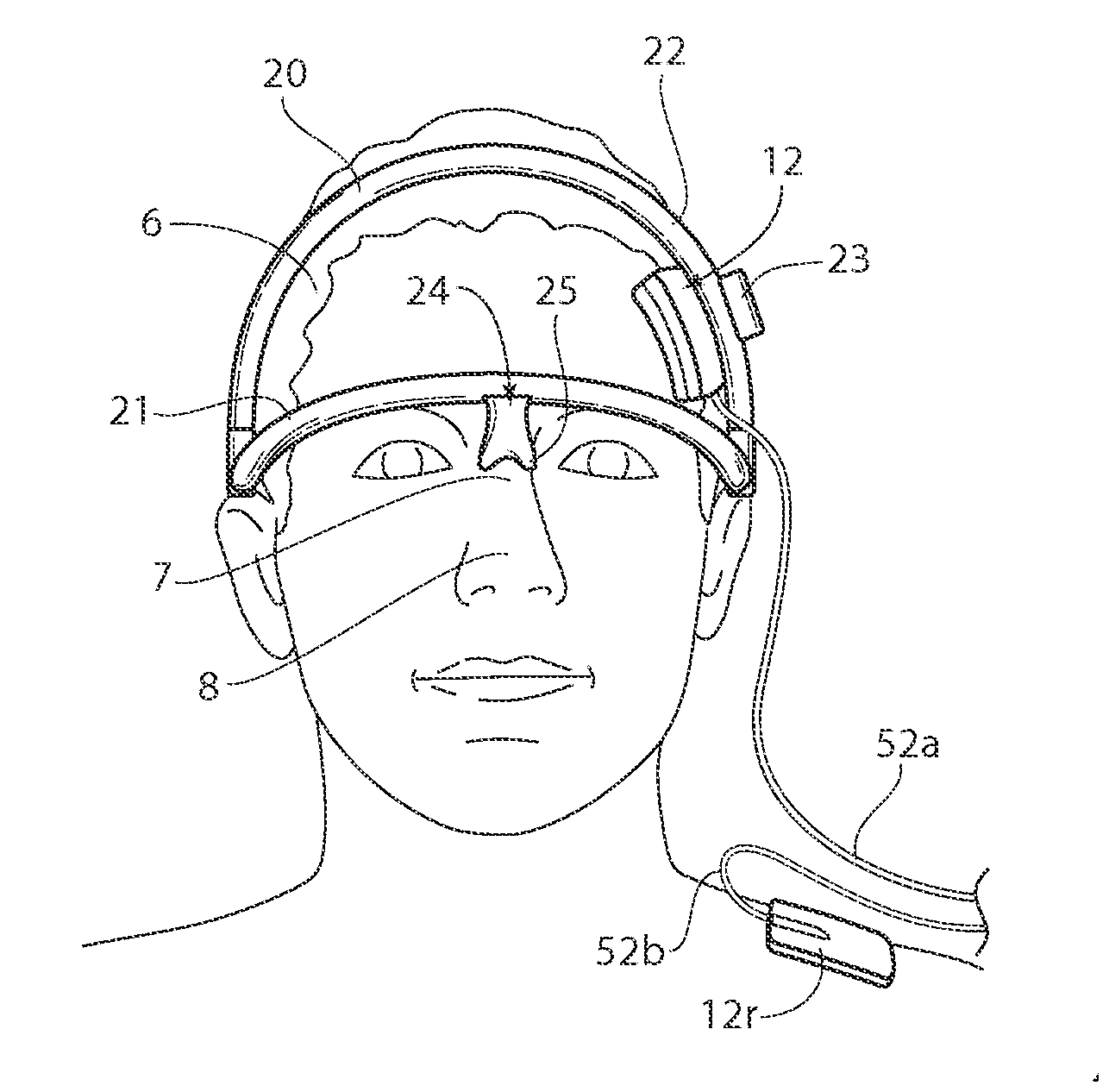
A system according to the present invention provides a portable, non-invasive device adapted to deliver electrical stimulation to a brain, such as to treat tinnitus. Such system is preferably a head-worn system configured to provide transcranial direct current electrical stimulation (tDCS) to a patient, where a therapy based at least partially thereon may be self-administered by the patient. tDCS is a non-invasive method of brain stimulation to treat tinnitus, or other neurological indications, that may provide significant relief. Methods according to the present invention include preferably brief sessions of anodal tDCS to assist in determining adequate electrode location and stimulus intensity by producing transient decreases in tinnitus intensity. Methods may also or alternatively include a number of sessions of cathodal tDCS at a confirmed electrode location and stimulus intensity to provide sustained tinnitus relief. Methods may also or alternatively include a number of maintenance sessions to prolong the sustained relief.
Owner:NDI MEDICAL
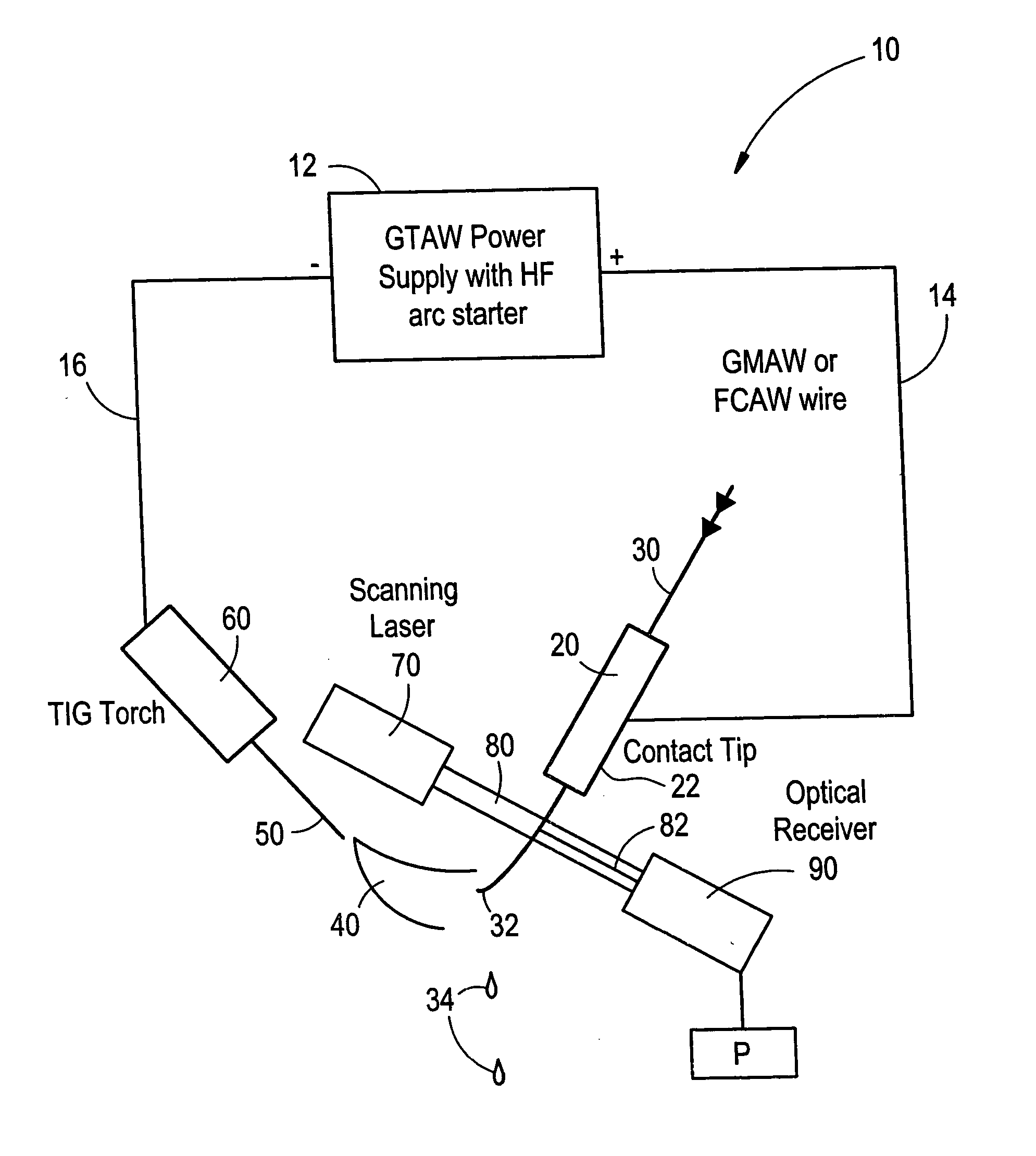
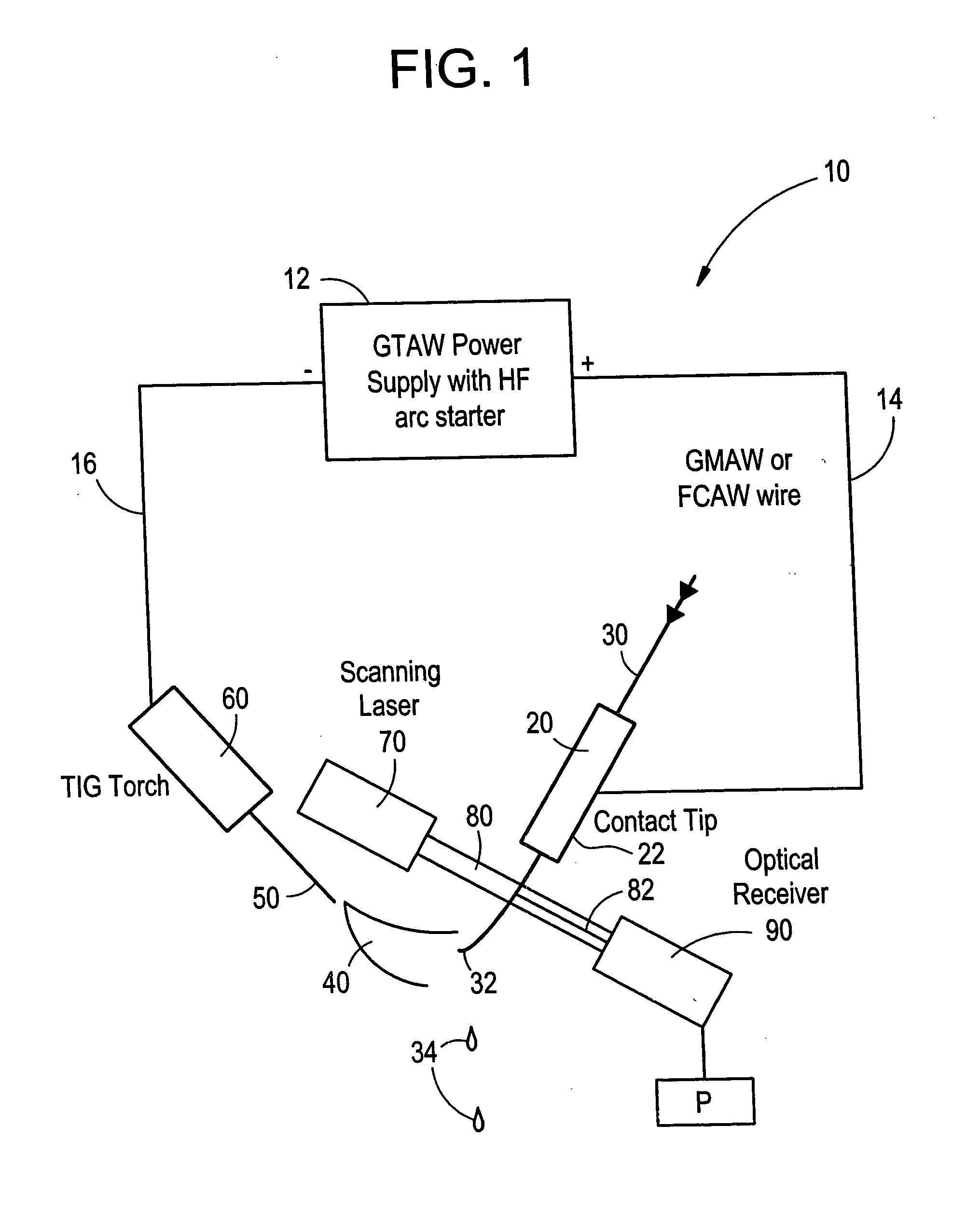
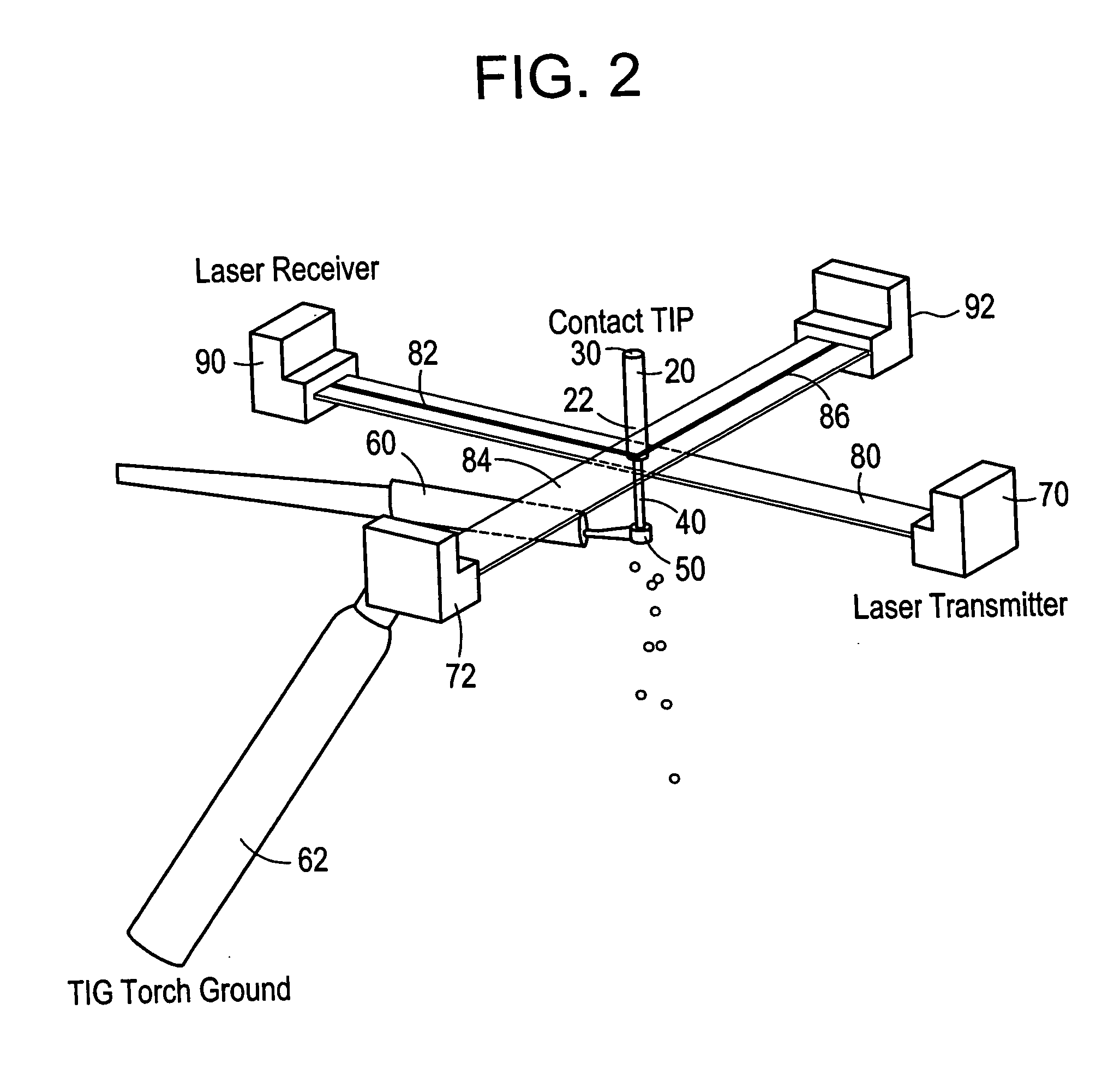
Welding wire positioning system
Owner:LINCOLN GLOBAL INC
High Density Atrial Fibrillatrion Cycle Length (AFCL) Detection and Mapping System
InactiveUS20090204113A1ElectrocardiographySurgical instruments for heatingHigh densityElectrode location
Systems and methods to assist in locating the focus of an atrial fibrillation include the association of atrial fibrillation cycle length values and statistics relating thereto with temporal locations on an electrogram of a given electrode, and / or the coordination of electrode locations with respective the spectral analyses of electrogram signals and further parameters and statistics relating thereto. Ablation therapy can proceed under guidance of such information.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Dynamic adaptive respiration compensation with automatic gain control
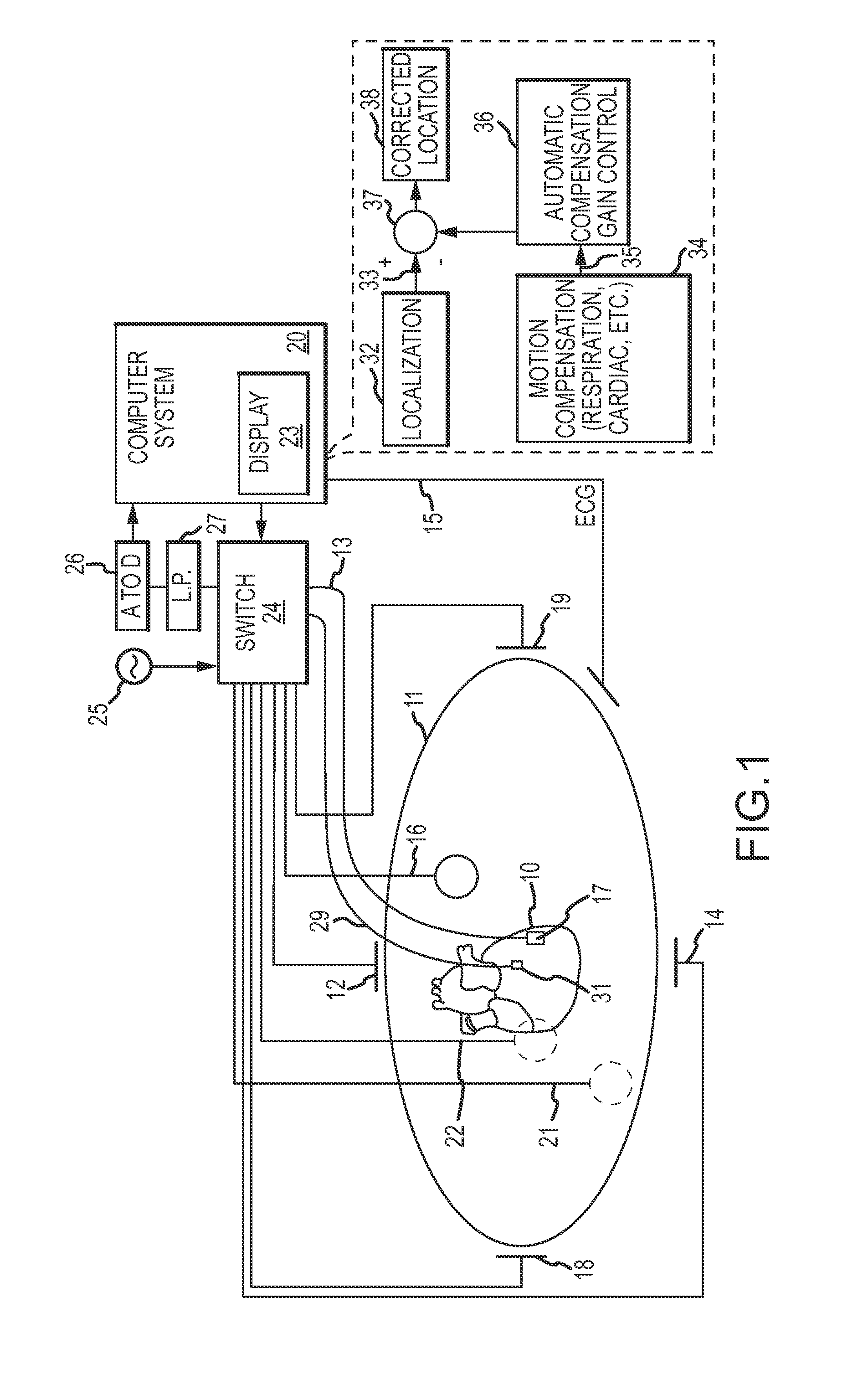
ActiveUS20120172702A1Reduce distractionsReduces the gain parameterSensorsBaseband systemsEngineeringCatheter
A system for determining a location of an electrode of a medical device (e.g., a catheter) in a body of a patient includes a localization block for producing an uncompensated electrode location, a motion compensation block for producing a compensation signal (i.e., for respiration, cardiac, etc.), and a mechanism for subtracting the compensation signal from the uncompensated electrode location. The result is a corrected electrode location substantially free of respiration and cardiac artifacts. The motion compensation block includes a dynamic adaptation feature which accounts for changes in a patient's respiration patterns as well as intentional movements of the medical device to different locations within the patient's body. The system further includes an automatic compensation gain control which suppresses compensation when certain conditions, such as noise or sudden patch impedance changes, are detected.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
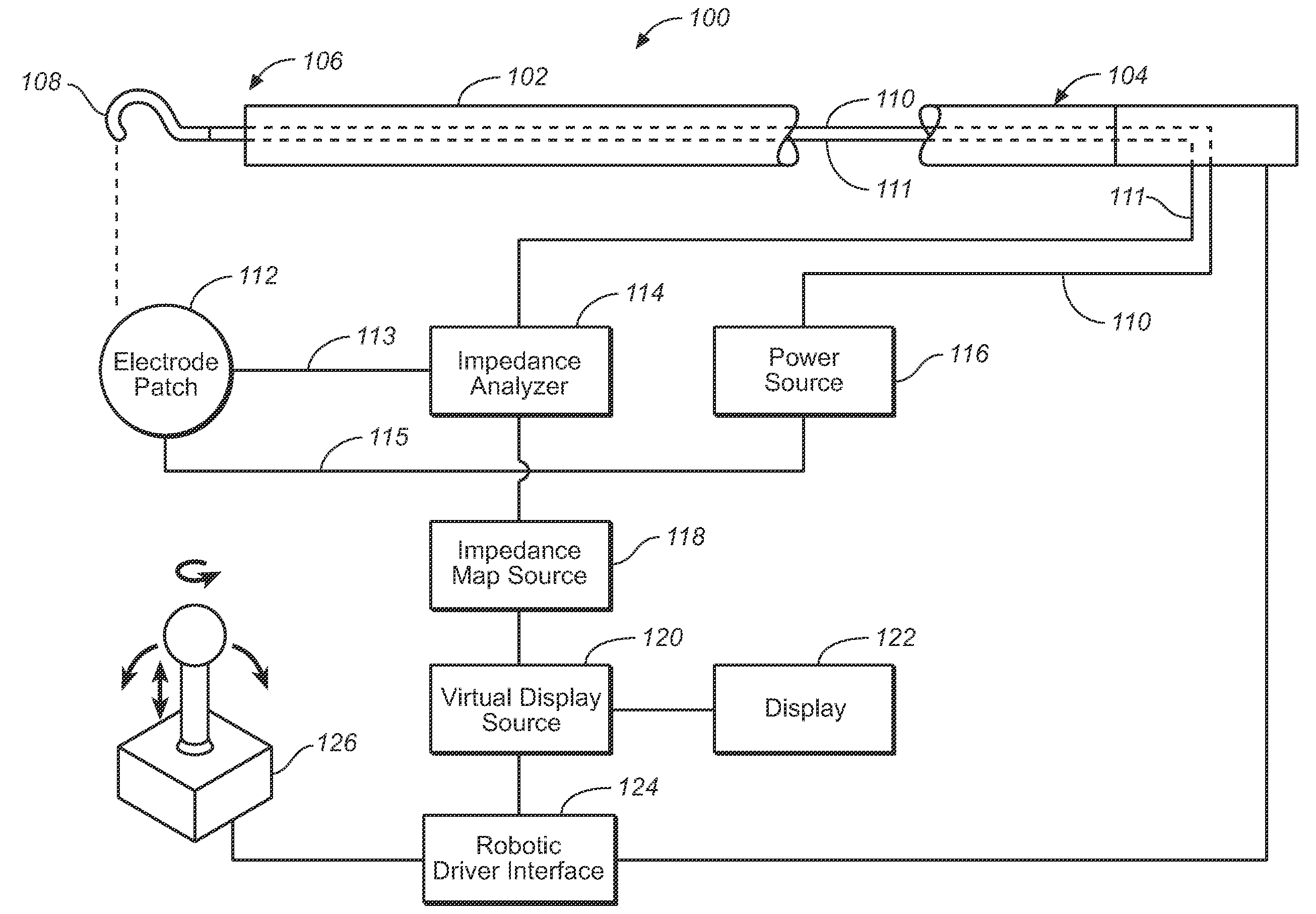
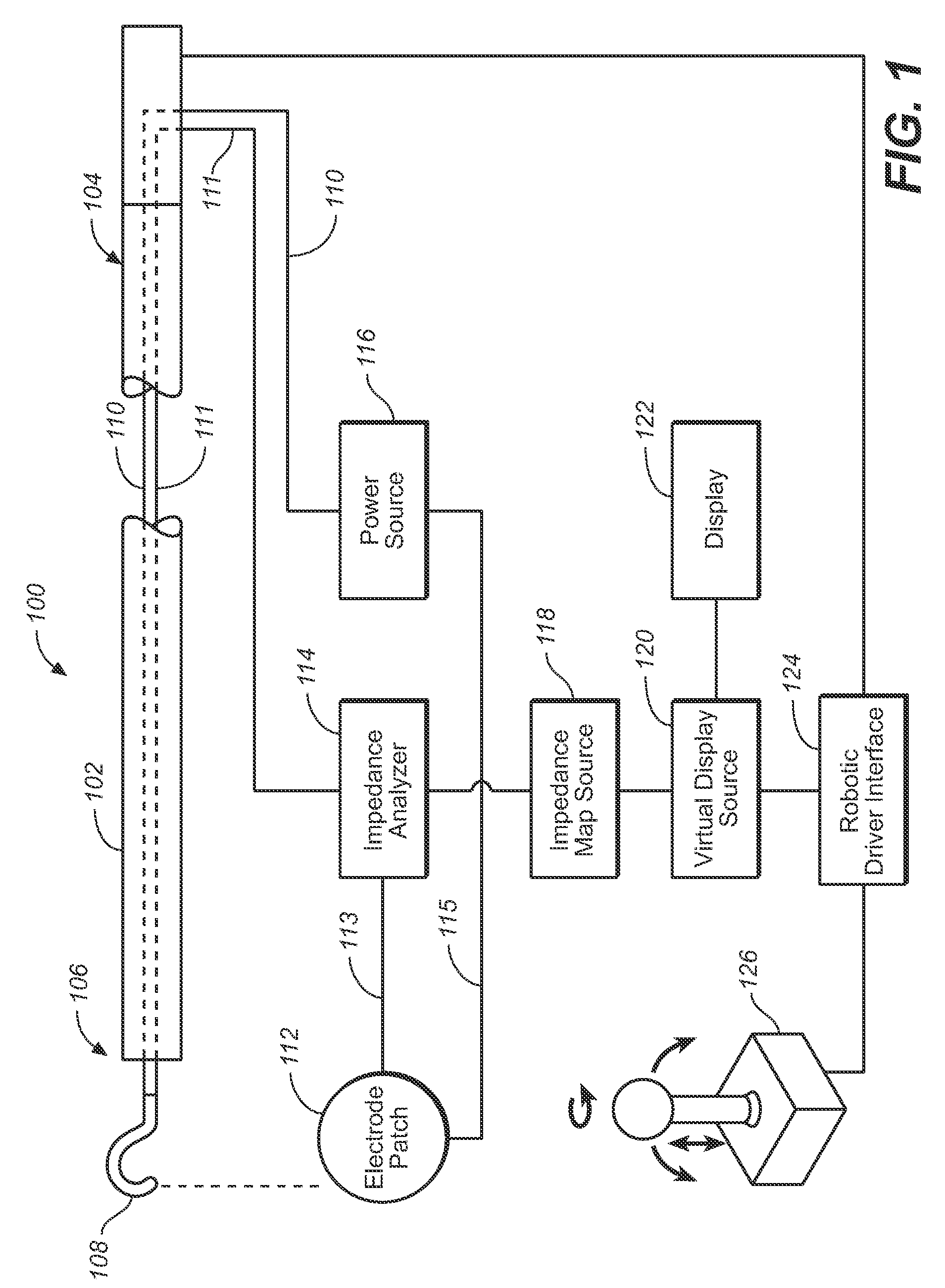
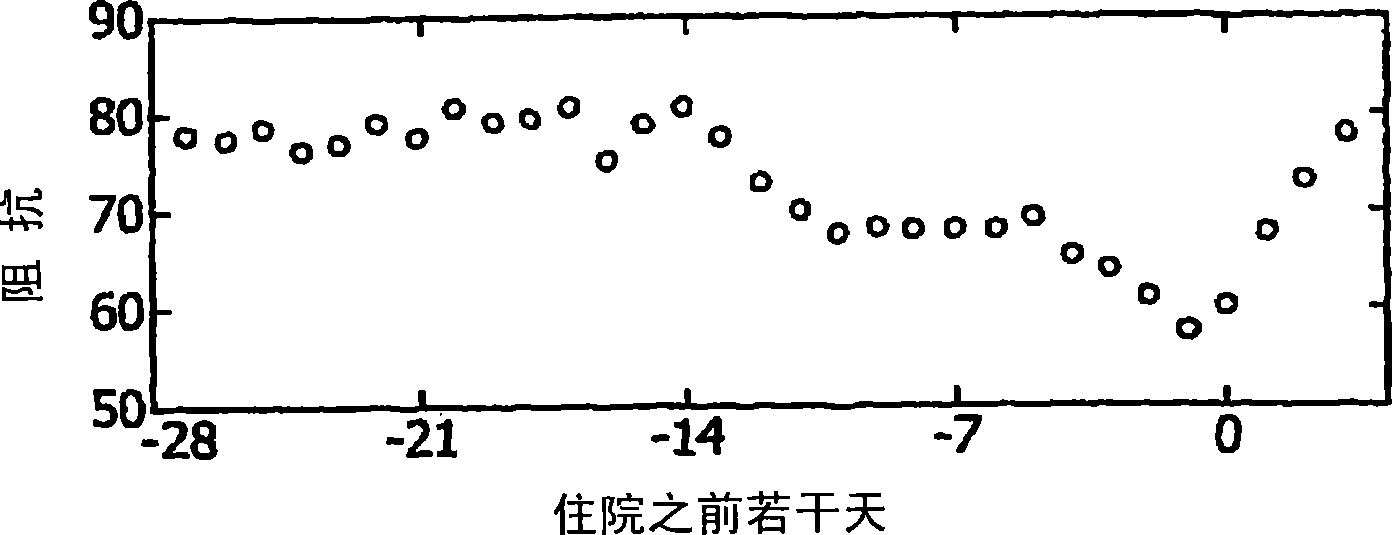
Robotic Fenestration Device Having Impedance Measurement
A method and system for real-time continuous impedance monitoring along the surface of a graft implanted within a main vessel to aid in optimally positioning an electrode at a branch vessel ostium. Due to the conductivity differences among various kinds of solid tissue and blood, a fenestration catheter system uses impedance monitoring as a tool to detect the location of branch ostia through graft cloth. Such information enables the fenestration electrode to be properly positioned for creation of a fenestration in the graft cloth in situ. In addition, the fenestration catheter system may utilize impedance information to avoid contact between the electrode and metal stent structures used to anchor the graft during an in situ fenestration procedure. The fenestration catheter system includes a catheter shaft, an electrode, one or more reference or indifferent electrodes, an impedance analyzer, a power source and an electrode position reference to record impedance measurements in relation to position.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
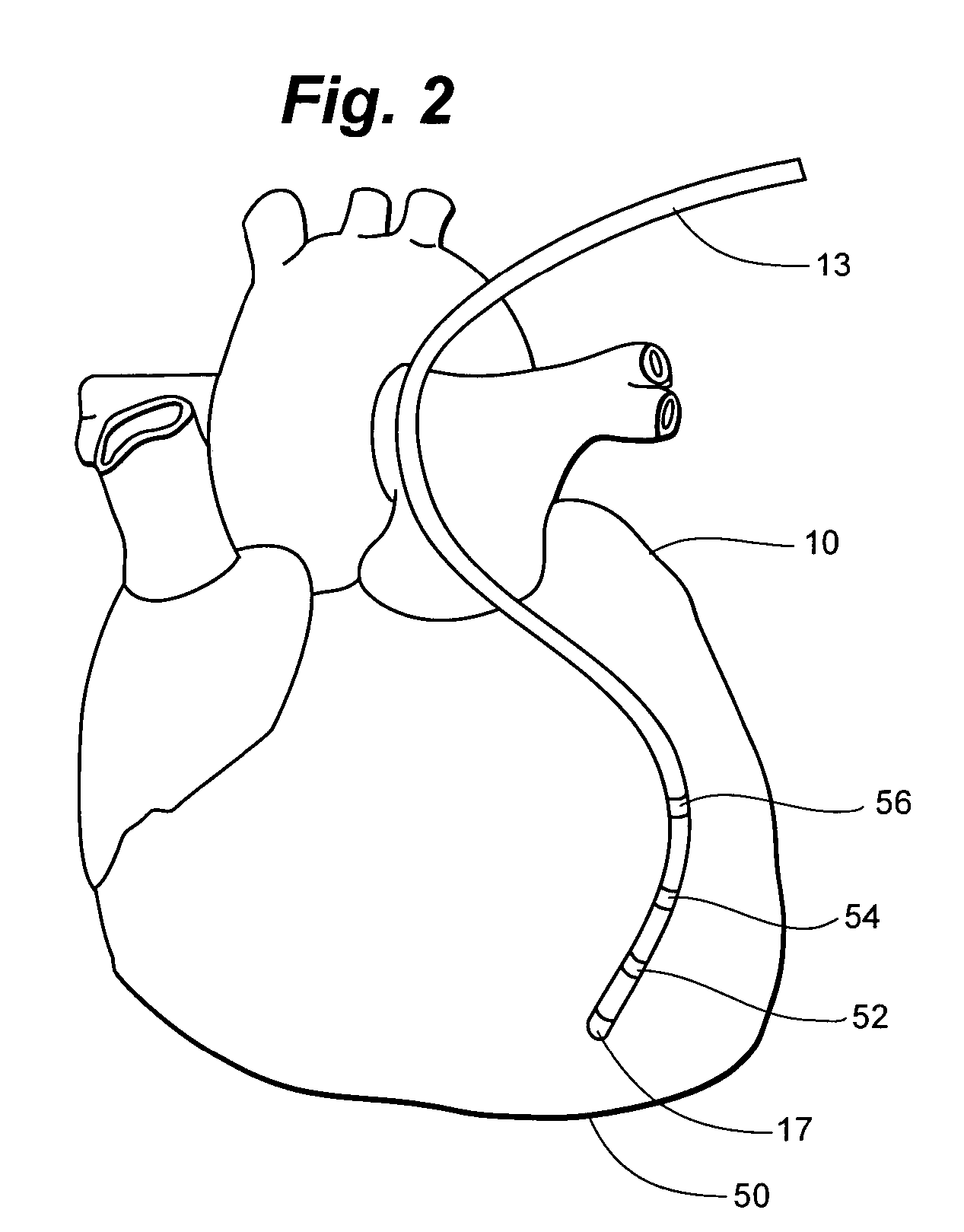
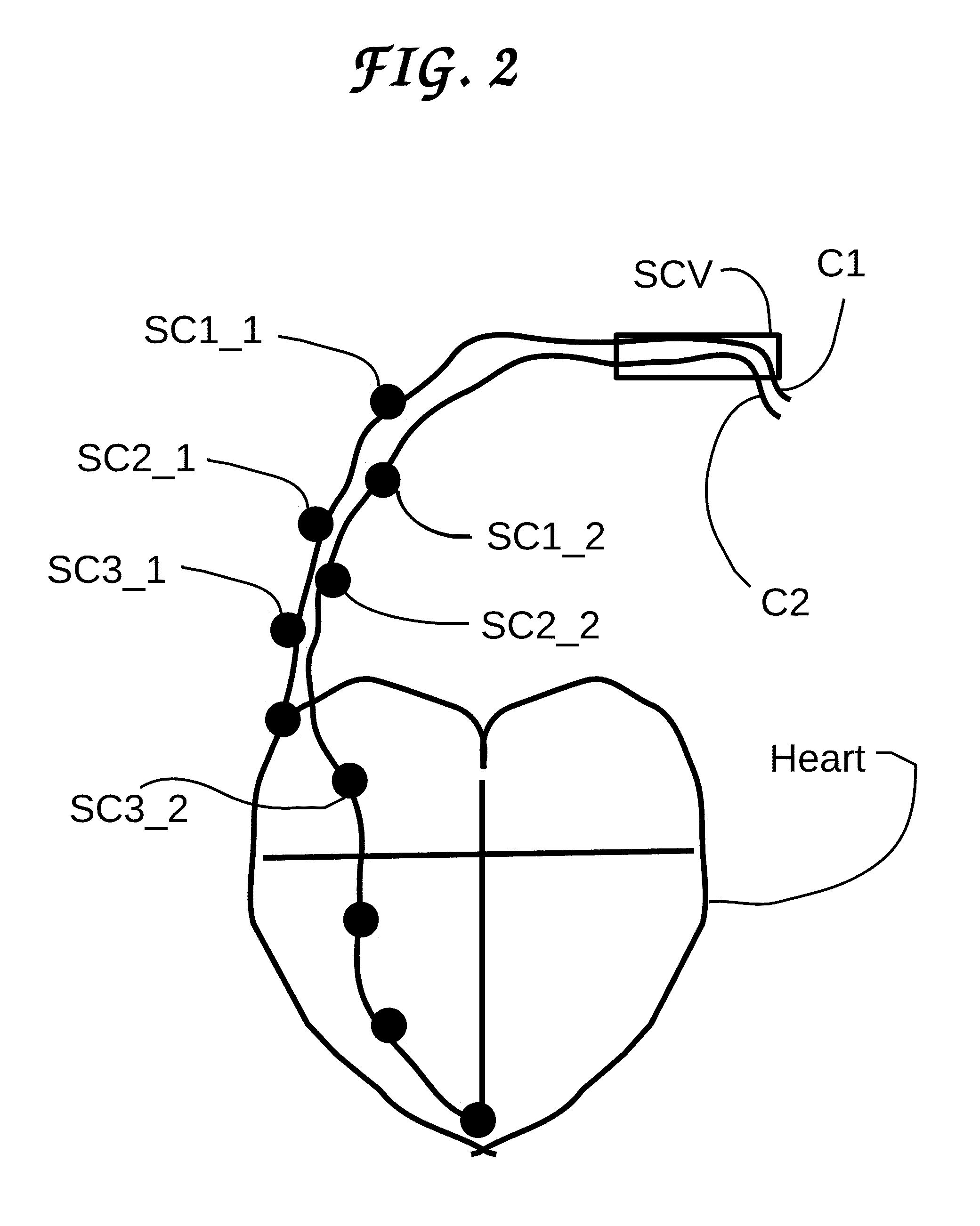
Multiple-electrode catheter assembly and method of operating such a catheter assembly
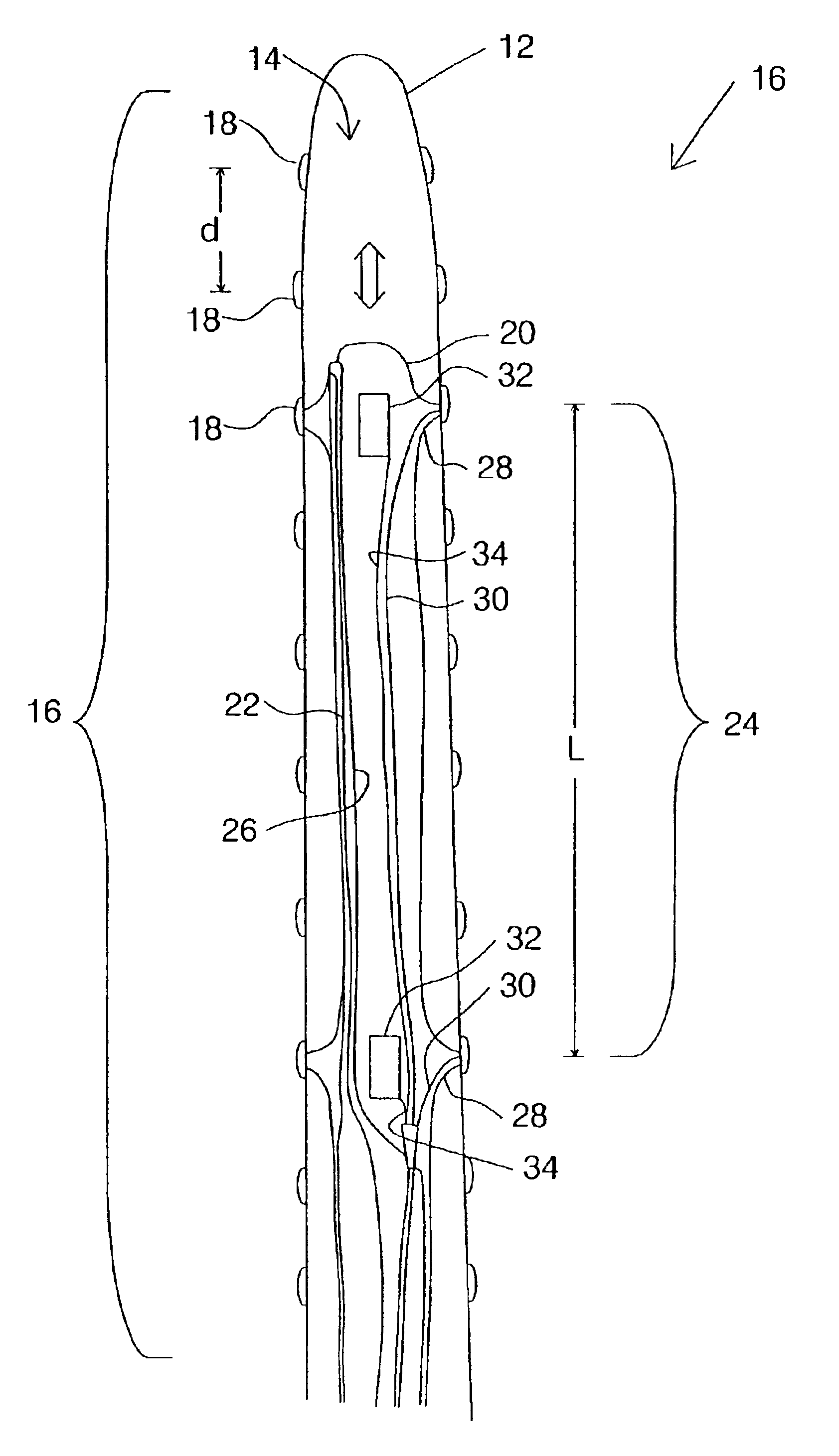
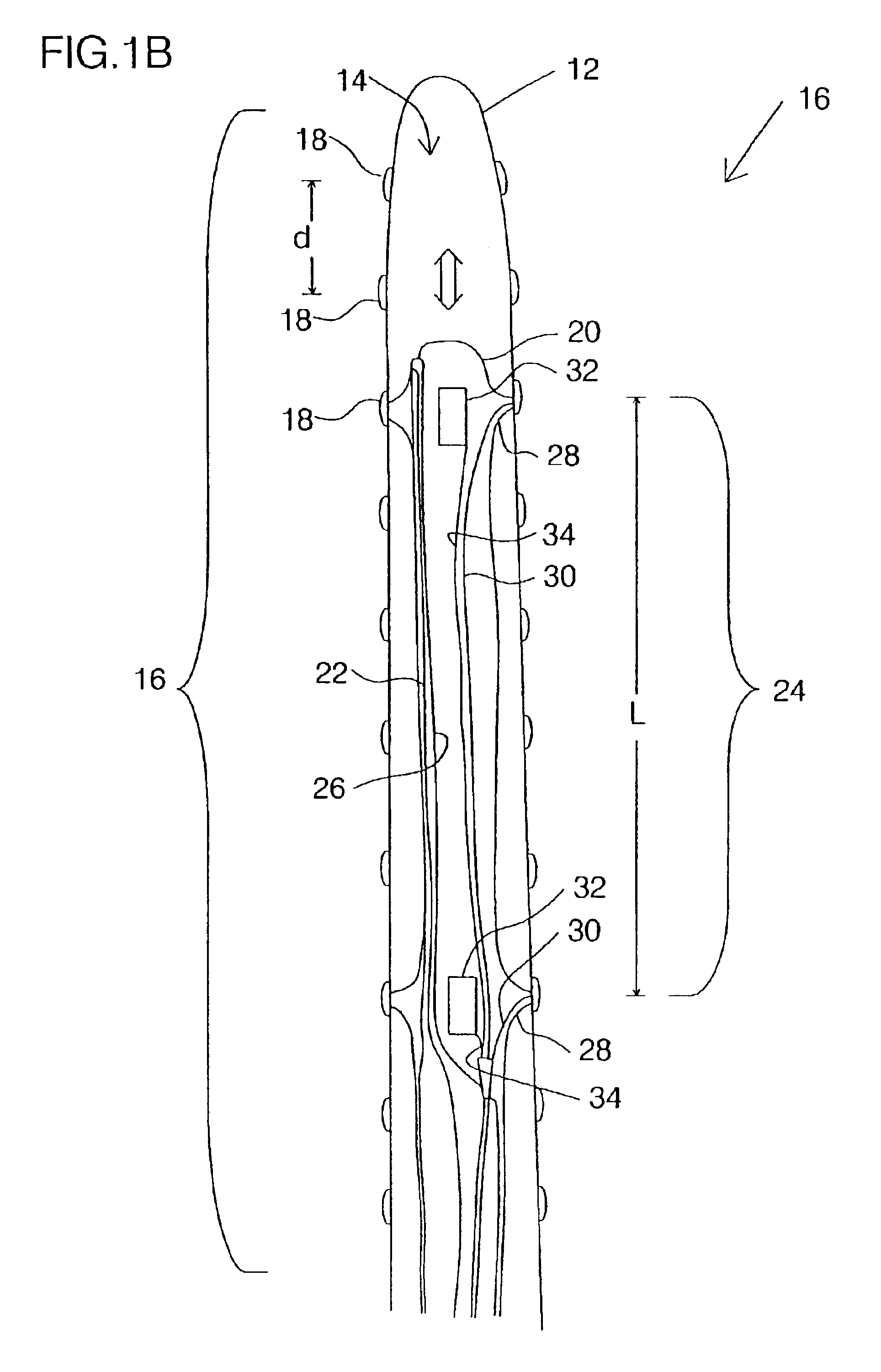
A multiple-electrode catheter assembly includes a hollow catheter having an internal elongated channel and a flexible distal portion. A number of electrodes are spaced along the flexible distal portion. An inner element, slidingly engaged within the elongated channel, has a steering mechanism configured for selectively deflecting a steerable distal portion of the inner element. According to additional, or alternative, features, the inner element includes sliding contacts for forming electrical connections with the electrodes, and displaceable locating elements for determining the position of an electrode during operation. Also provided is a method for operating such a catheter.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
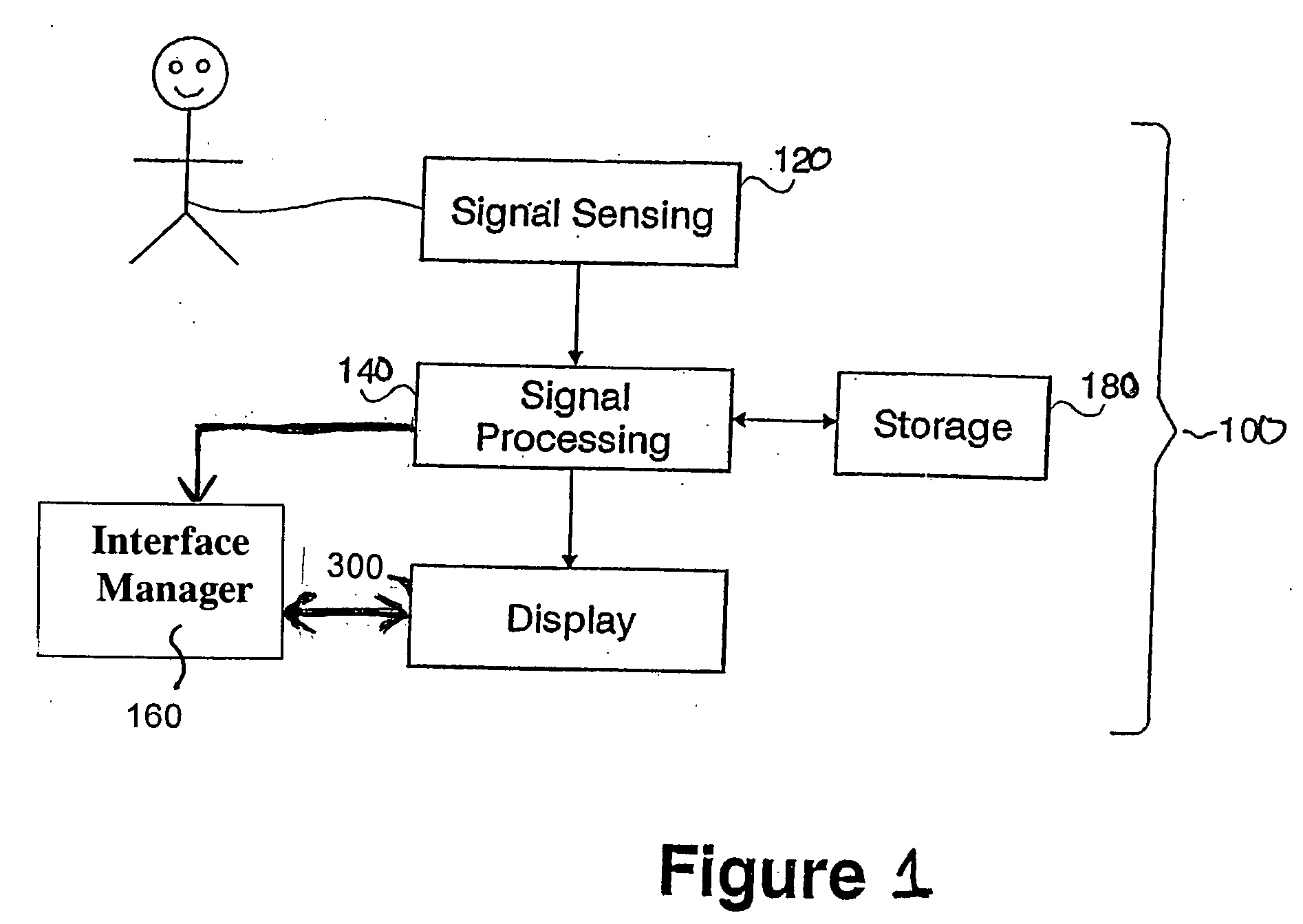
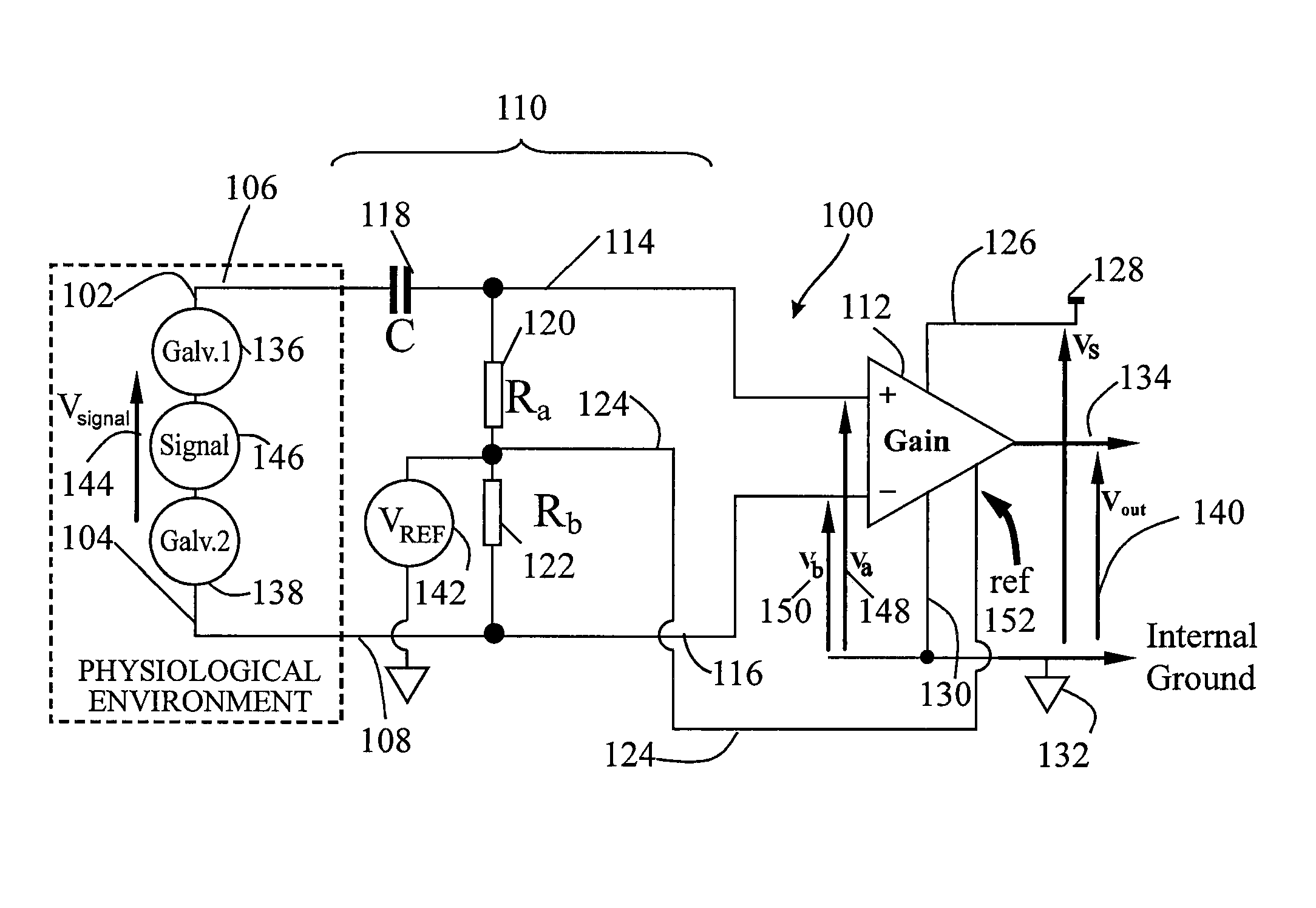
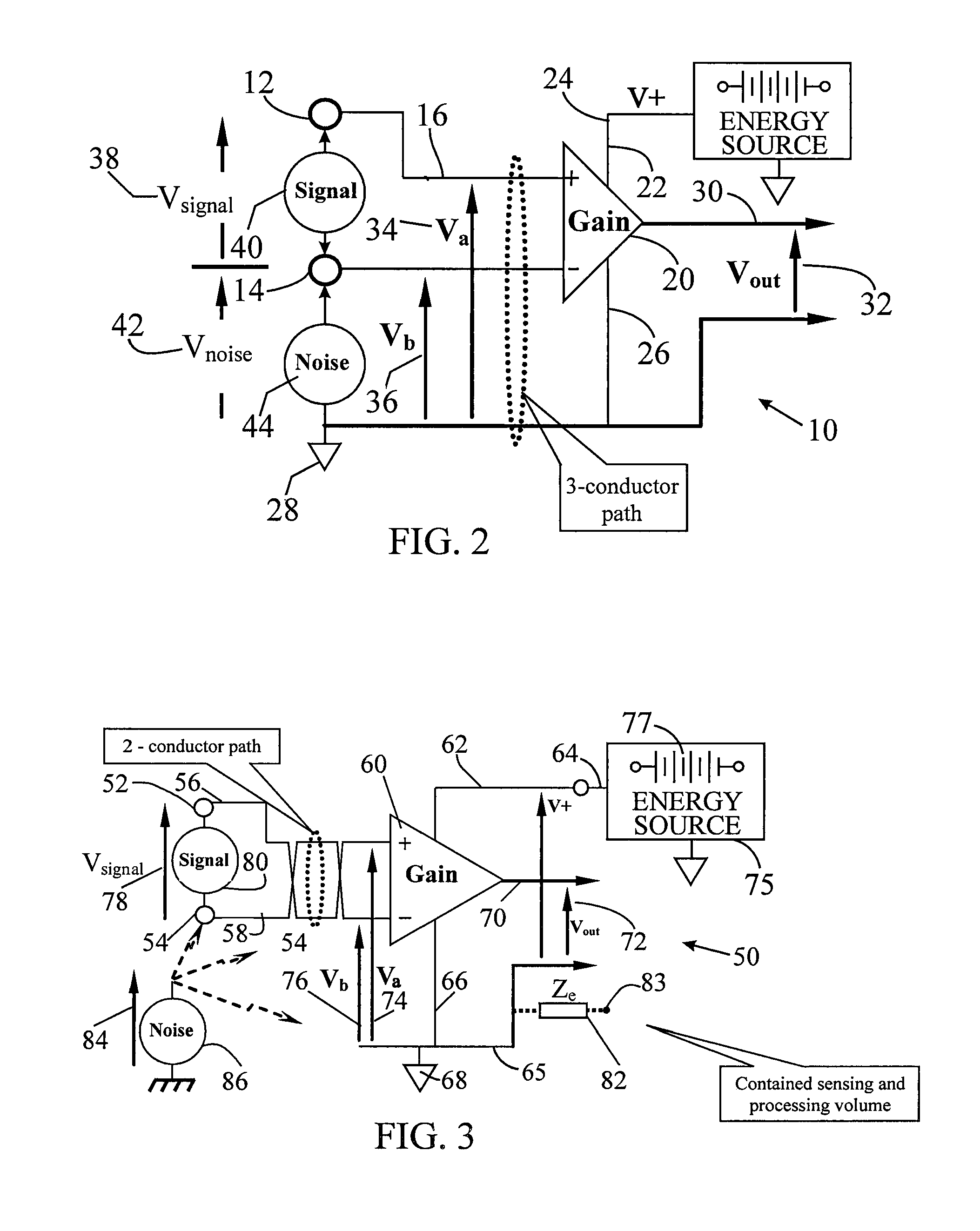
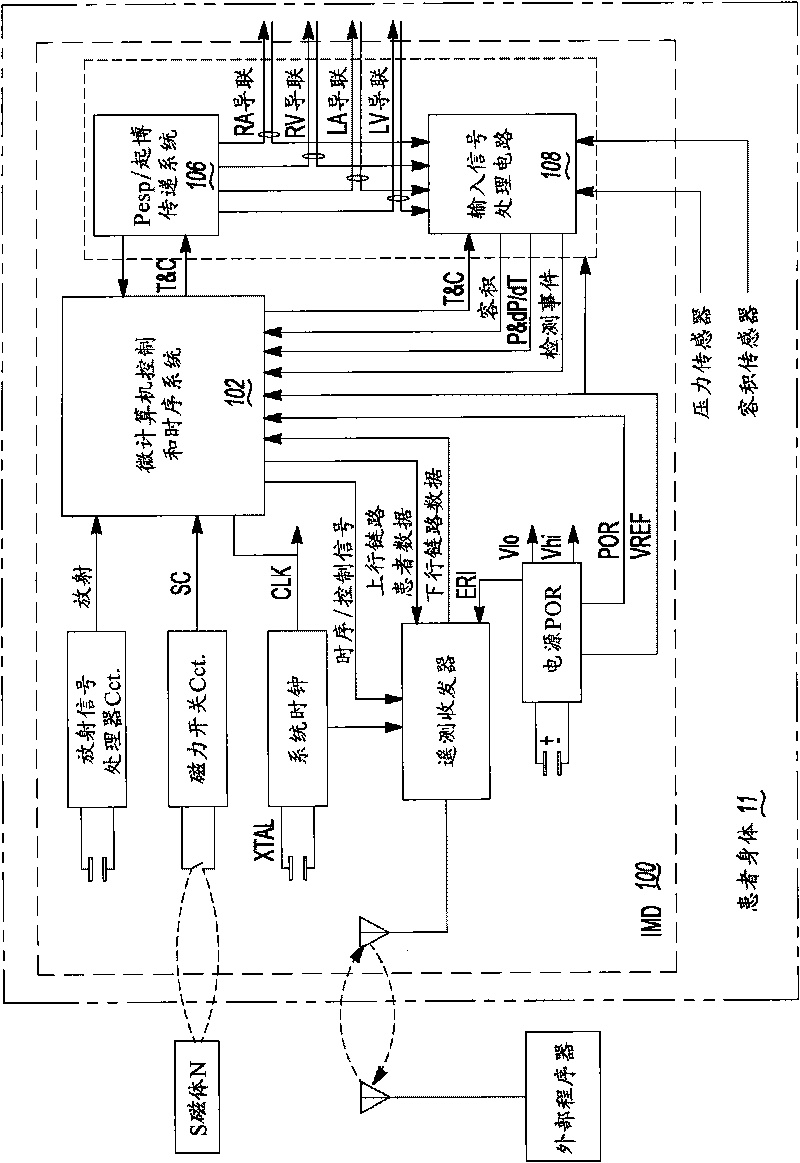
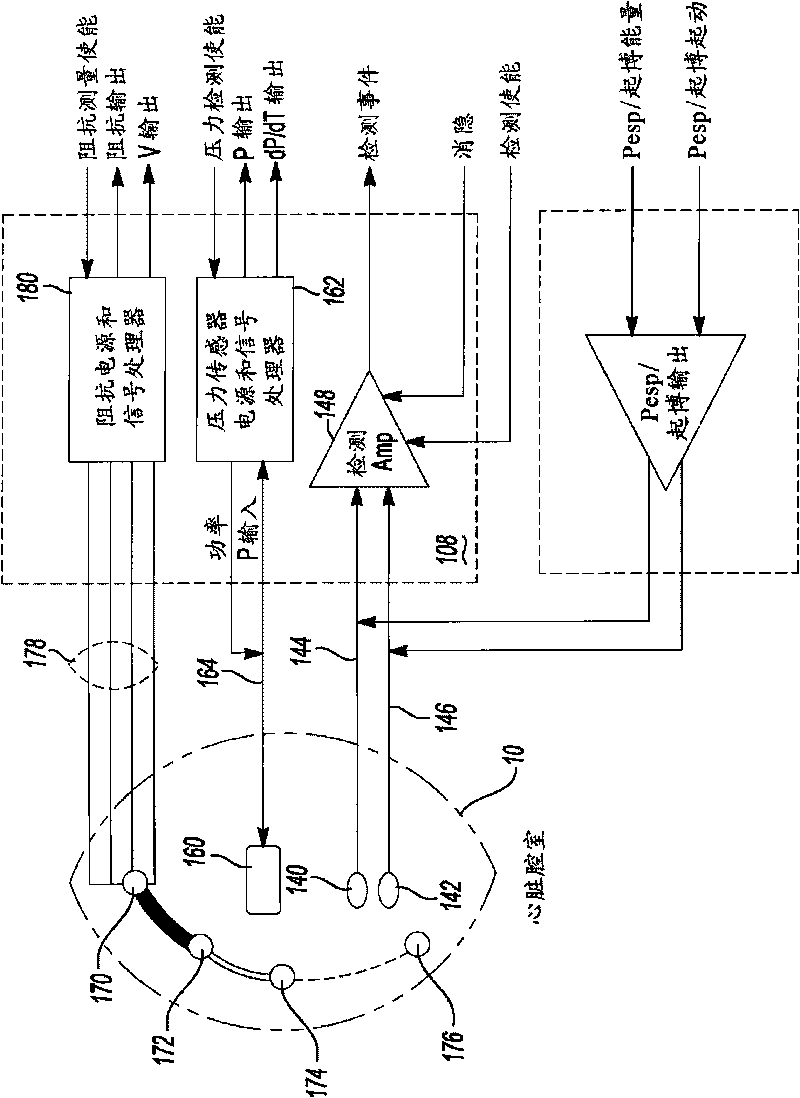
Signal sensing in an implanted apparatus with an internal reference
InactiveUS8366628B2Robust detectionPrevent pick-upElectrocardiographyAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesInstrumentation amplifierElectrical conductor
An implantable apparatus for sensing biological signals from an animal includes at least two electrodes disposed at locations to sense the biological signals. The electrode locations may be internal or external to the animal. Insulated conductors couple the electrodes via a passive network of filters to an instrumentation amplifier that has an internal voltage reference. Thus a sensed biological signal is filtered and amplified to provide an amplified differential signal. A signal analysis module processes amplified differential signal to determine at least one physiological parameter of the animal. The signal analysis module may include a first derivative zero detector for signal transition detection and feature detection and analysis. The apparatus may also comprise a signal presentation module to display amplified signals and physiological parameters associated with those signals.
Owner:KENERGY INC
Electrode location mapping system and method
A mapped location of one or more electrodes within an electrical mapping volume is superimposed onto an ultrasound image corresponding to the electrical mapping volume.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
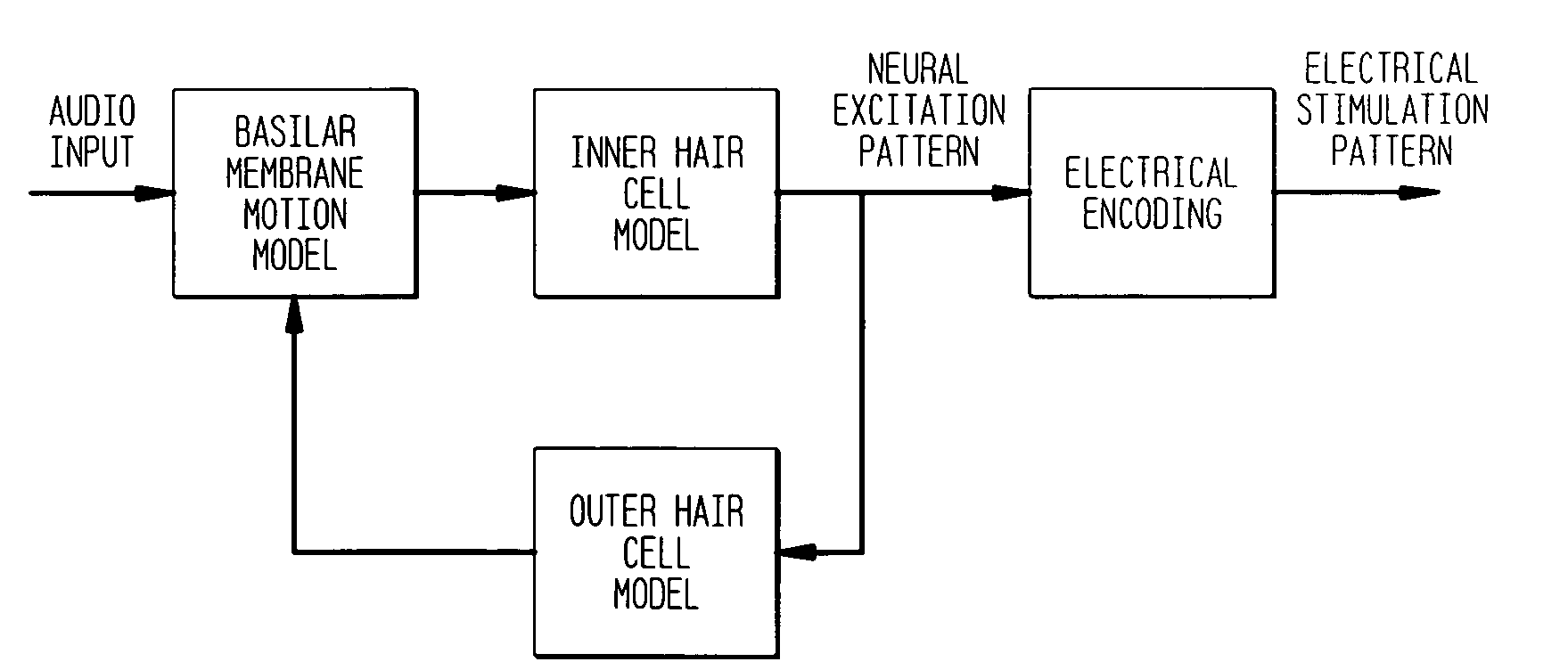
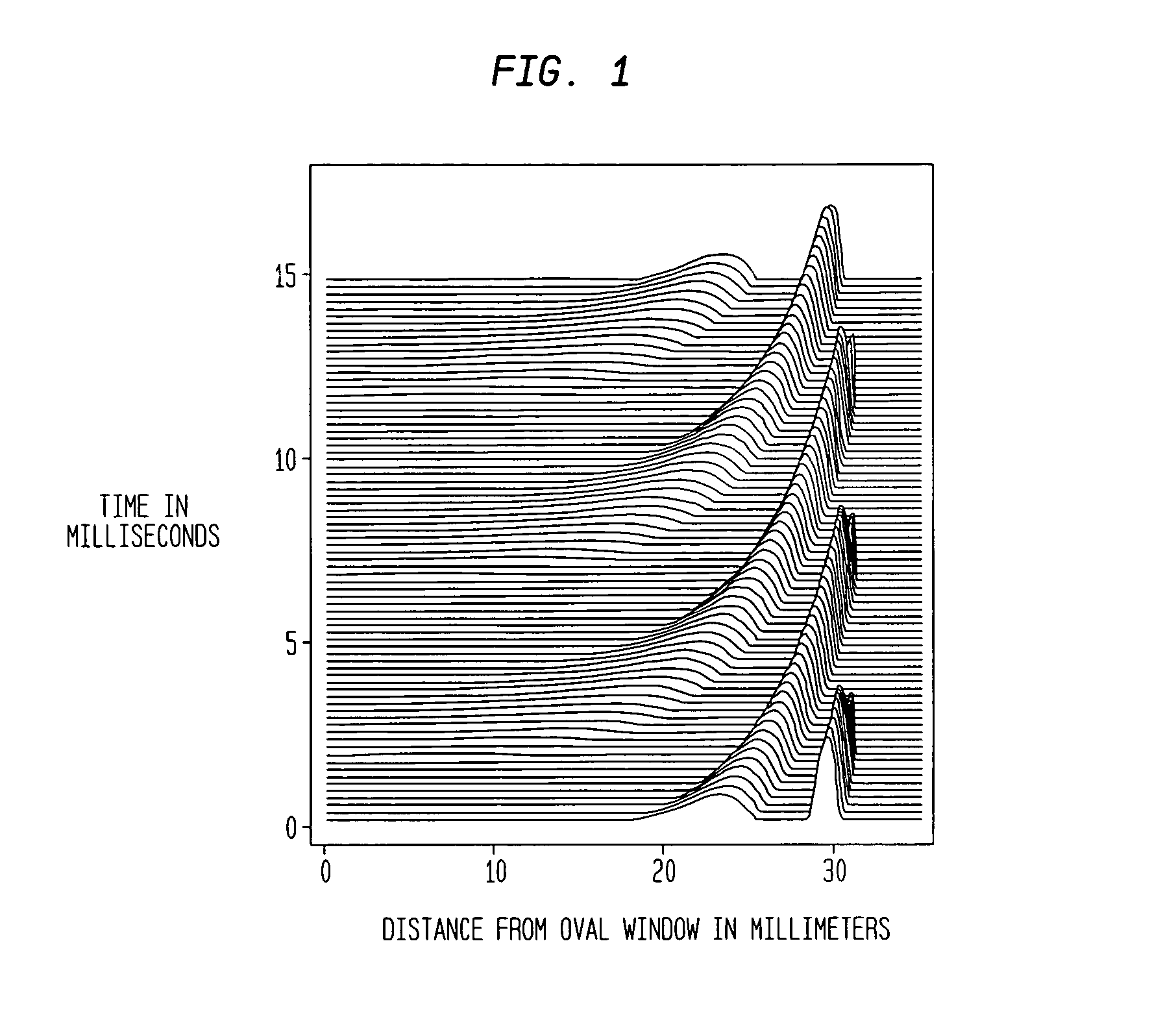
Sound processor for a cochlear implant
The sound processor and method uses a model of basilar membrane motion to select stimuli, based upon the predicted motion which the acoustic signal presented would produce in an acoustically excited normally hearing cochlea. The filter; used, in contrast to single channel per electrode approaches, cover multiple channels and overlap with each other. Consequently the stimuli presented produce a neural excitation pattern which approximates the spatio-temporal travelling wave observed on the basilar membrane in an acoustically excited normally hearing cochlea. Preferably, the predicted electrode stimuli are based upon the instantaneous predicted amplitude of the electrode location.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
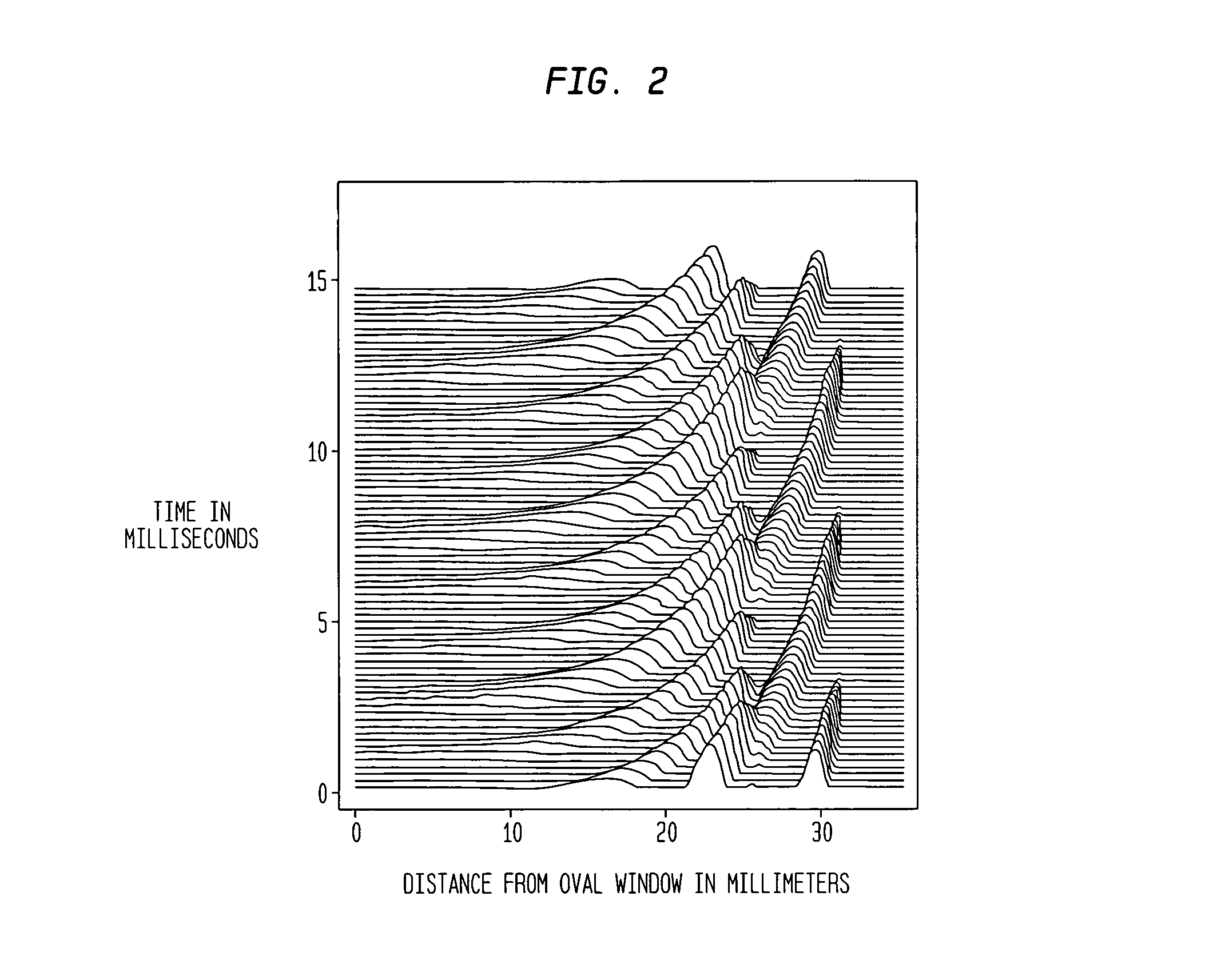
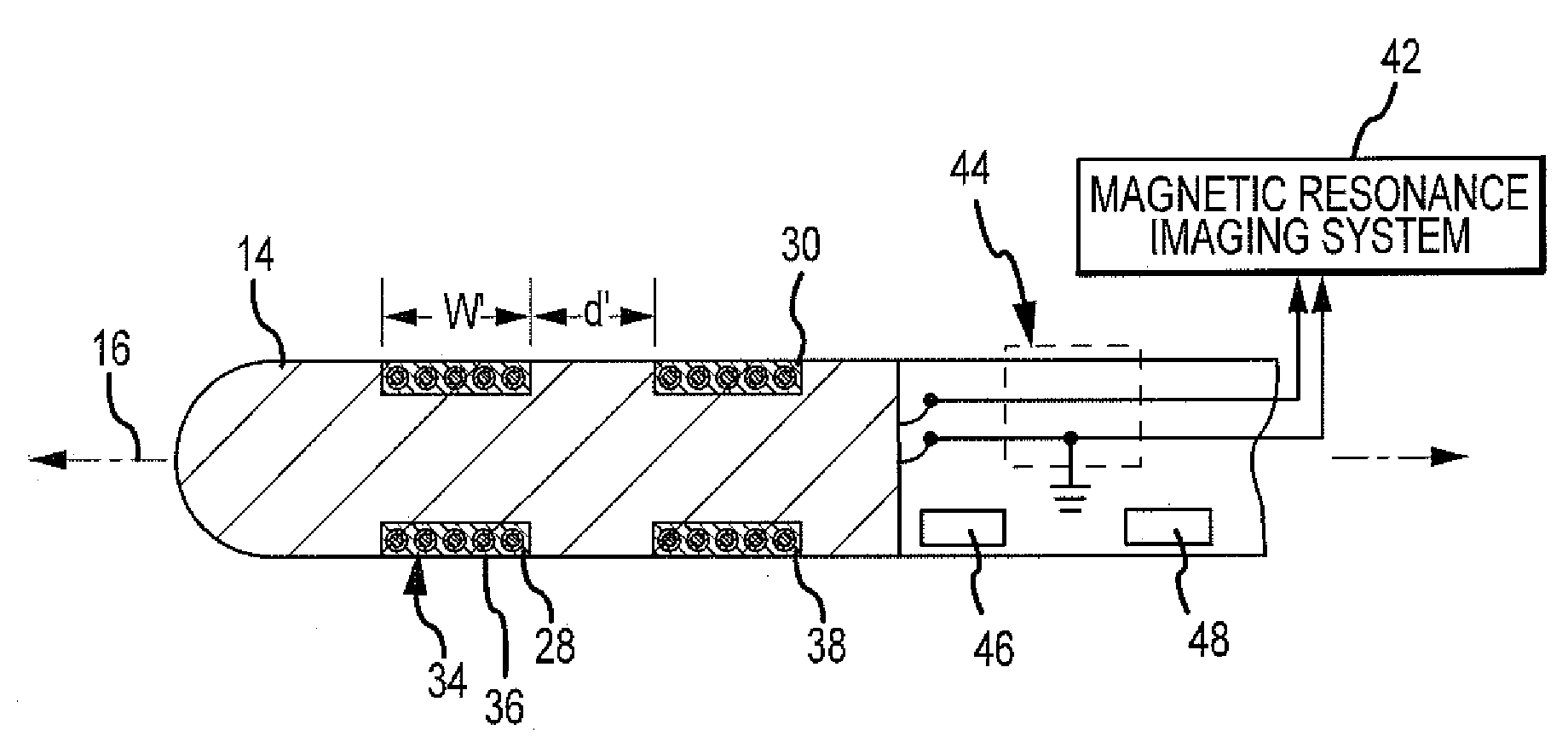
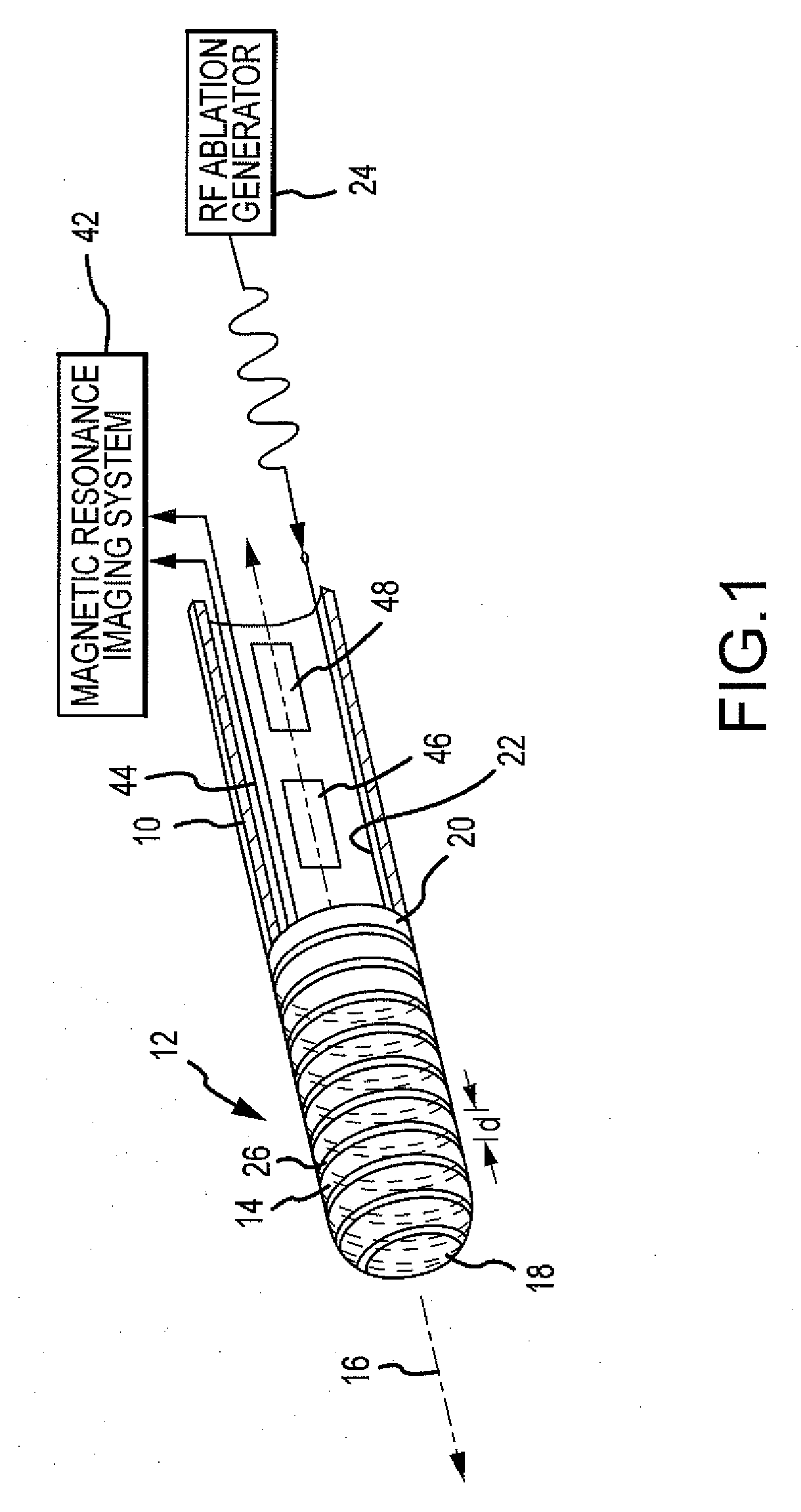
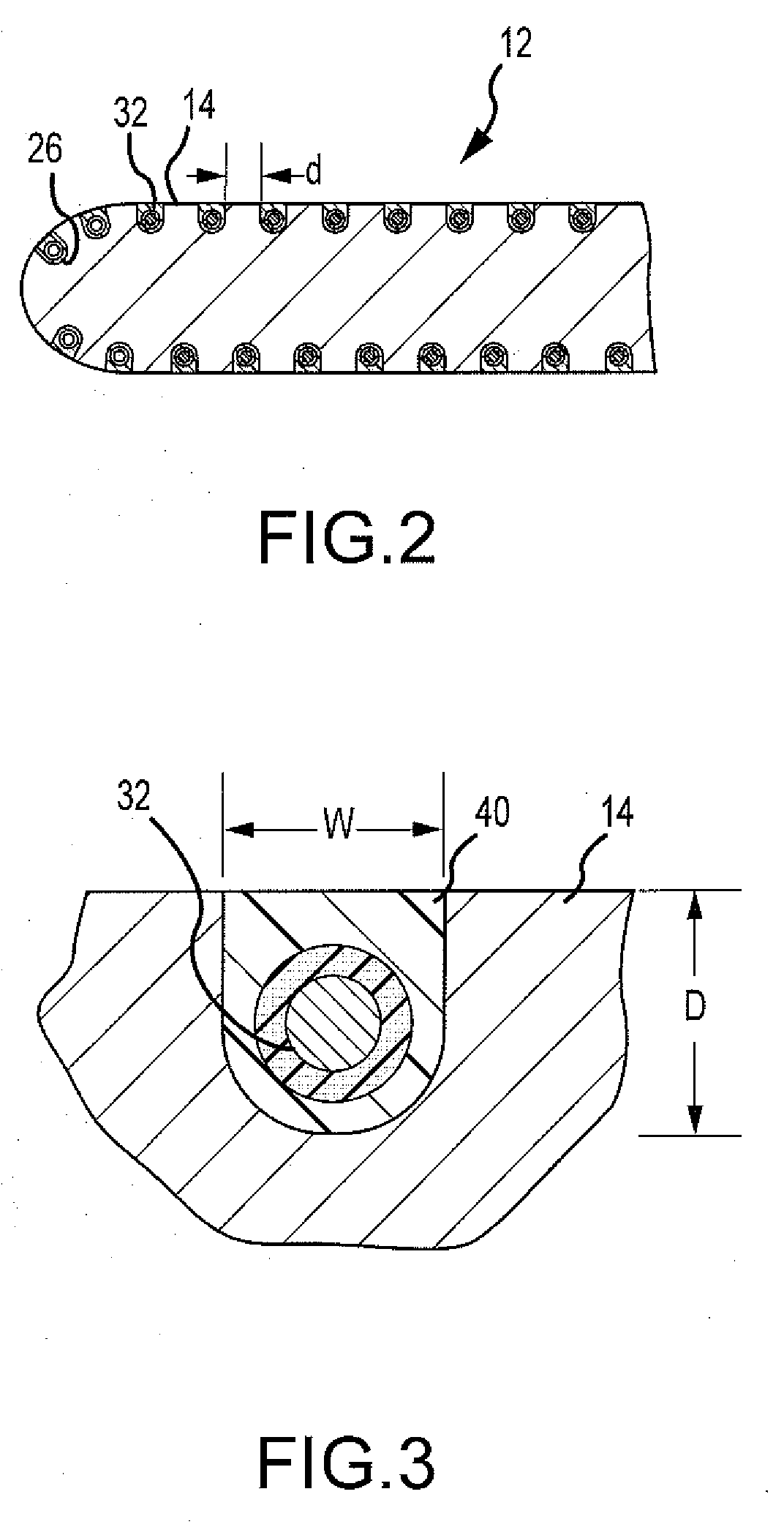
Catheter electrode that can simultaneously emit electrical energy and facilitate visualization by magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20090171187A1Reduce in quantityElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyEngineeringConductive materials
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
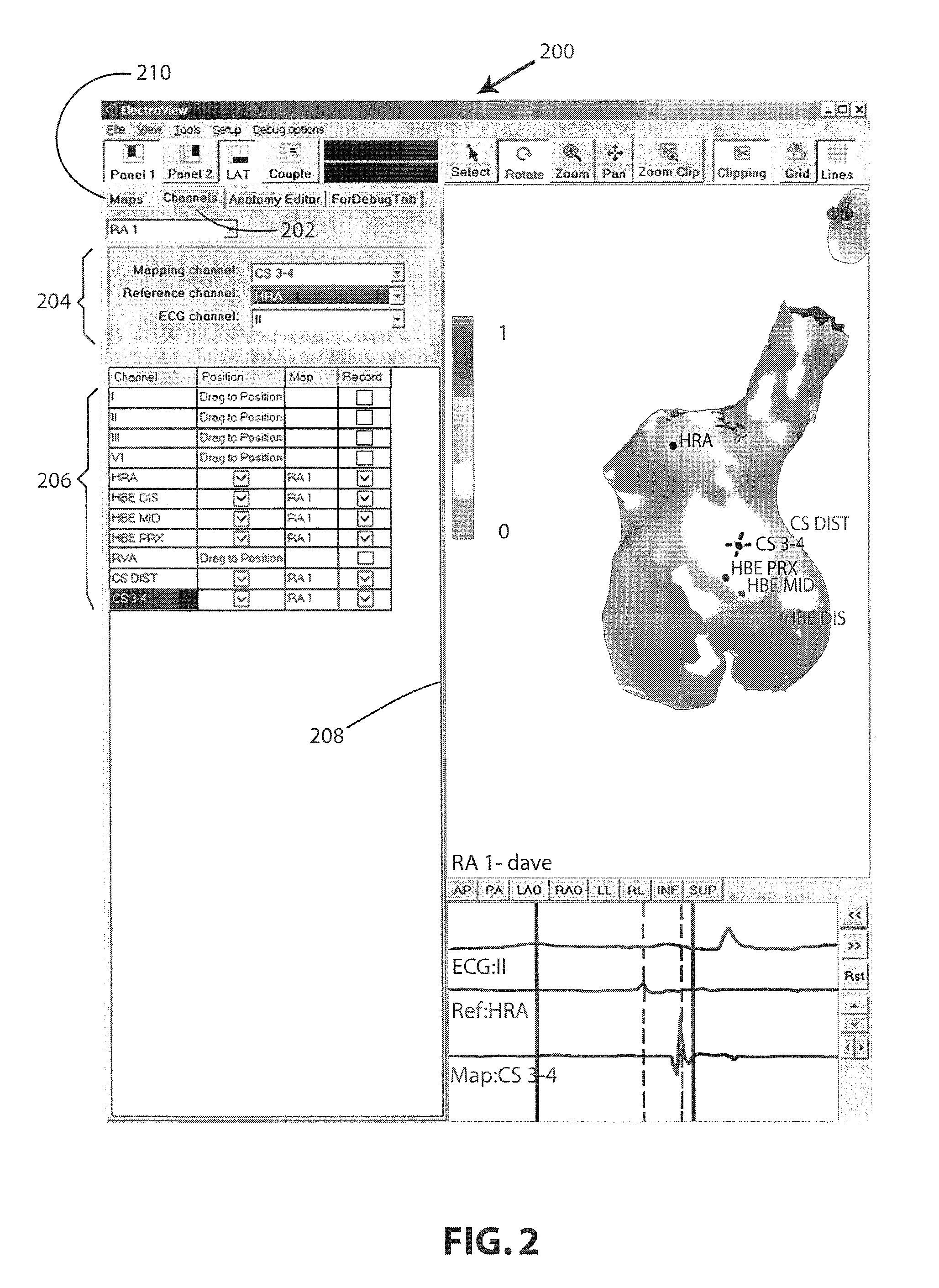
System for relocating catheter-supported electrodes on segmented model
Guidance to an operator to more accurately position electrodes upon a segmented heart model (SGM). The SGM is included in a map panel on a display screen. A catheter advanced into a beating heart supports one or more electrodes. During a single beat of the heart, an image is obtained with darkened portions corresponding to locations of the electrodes. The image is presented in the same map panel as the SGM. The current location of the electrodes is confirmed relative to the SGM, either manually or through automated software algorithms. EP data is captured that represents electrophysiological signals of the beating heart at the current location for each of the electrodes. A signal processing algorithm is applied to the captured EP data in view of the confirmed current location of the electrodes to result in a calculation that is mapped at the confirmed location of the electrodes.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
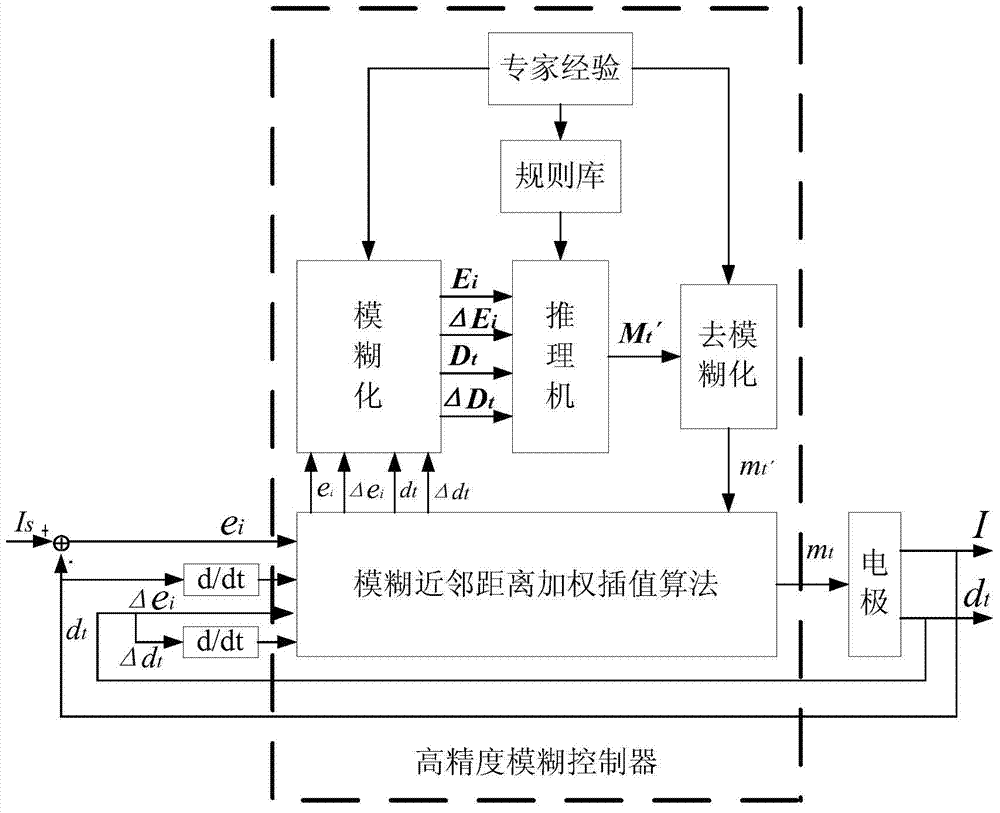
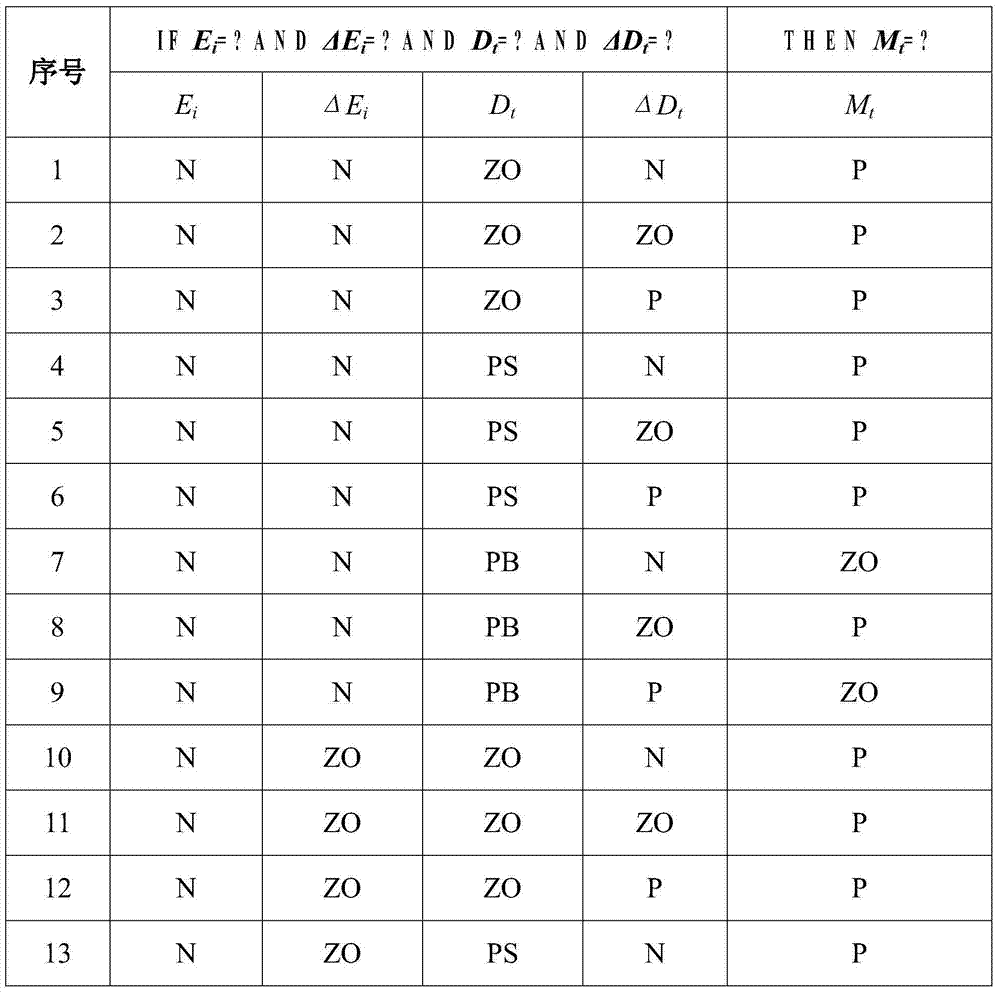
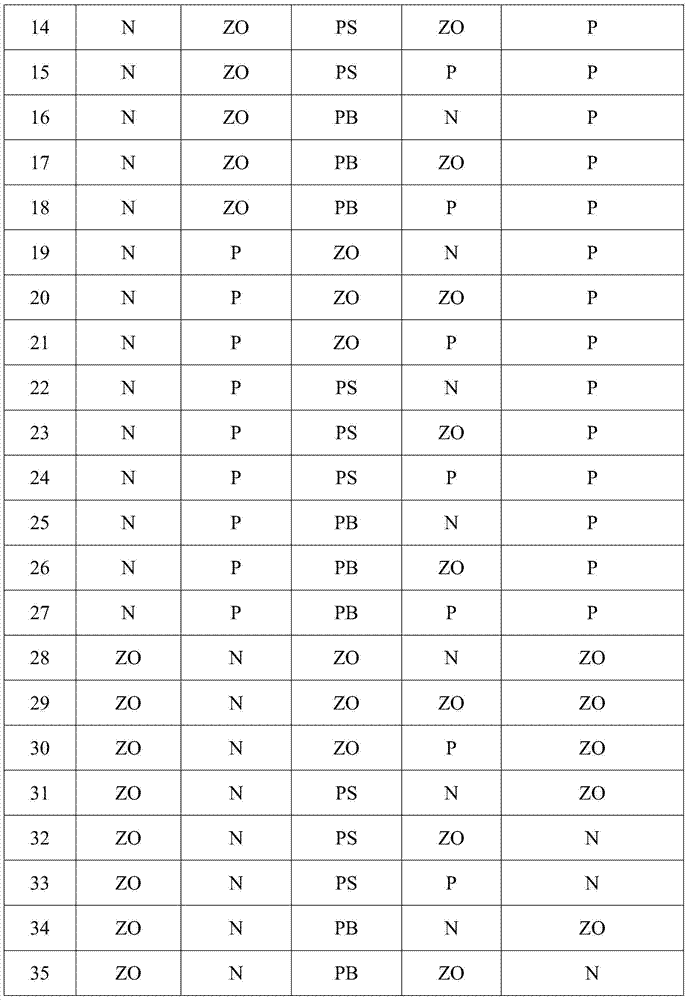
Automatic control method used for submerged arc furnace electrode and based on high-precision fuzzy control
InactiveCN103808159AHigh precisionSafe and stable operationControl devices for furnacesAutomatic controlHarmonic
The invention provides an automatic control method used for a submerged arc furnace electrode and based on high-precision fuzzy control. According to electrode current deviation ei, a change rate delta ei of the electrode current deviation, the depth dt of the electrode inserted into burden and a change rate delta dt of the depth of the electrode inserted into the burden, a high-precision fuzzy controller is adopted to adjust the variation mt of the position of the submerged arc furnace electrode, wherein a membership function and a fuzzy control rule of the fuzzy controller are obtained through expertise, and output of the controller is obtained through fuzzy neighbor distance weighted interpolation calculation, so that the control accuracy of the fuzzy controller is improved. The automatic control method used for the submerged arc furnace electrode and based on high-precision fuzzy control provides guarantee for safe and reliable operation of the submerged arc furnace which can operate in a stable manner, so that labor intensity of a worker can be reduced effectively, the maintenance quantity is reduced, the work environment is improved, and better conditions are provided for following harmonic suppression.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
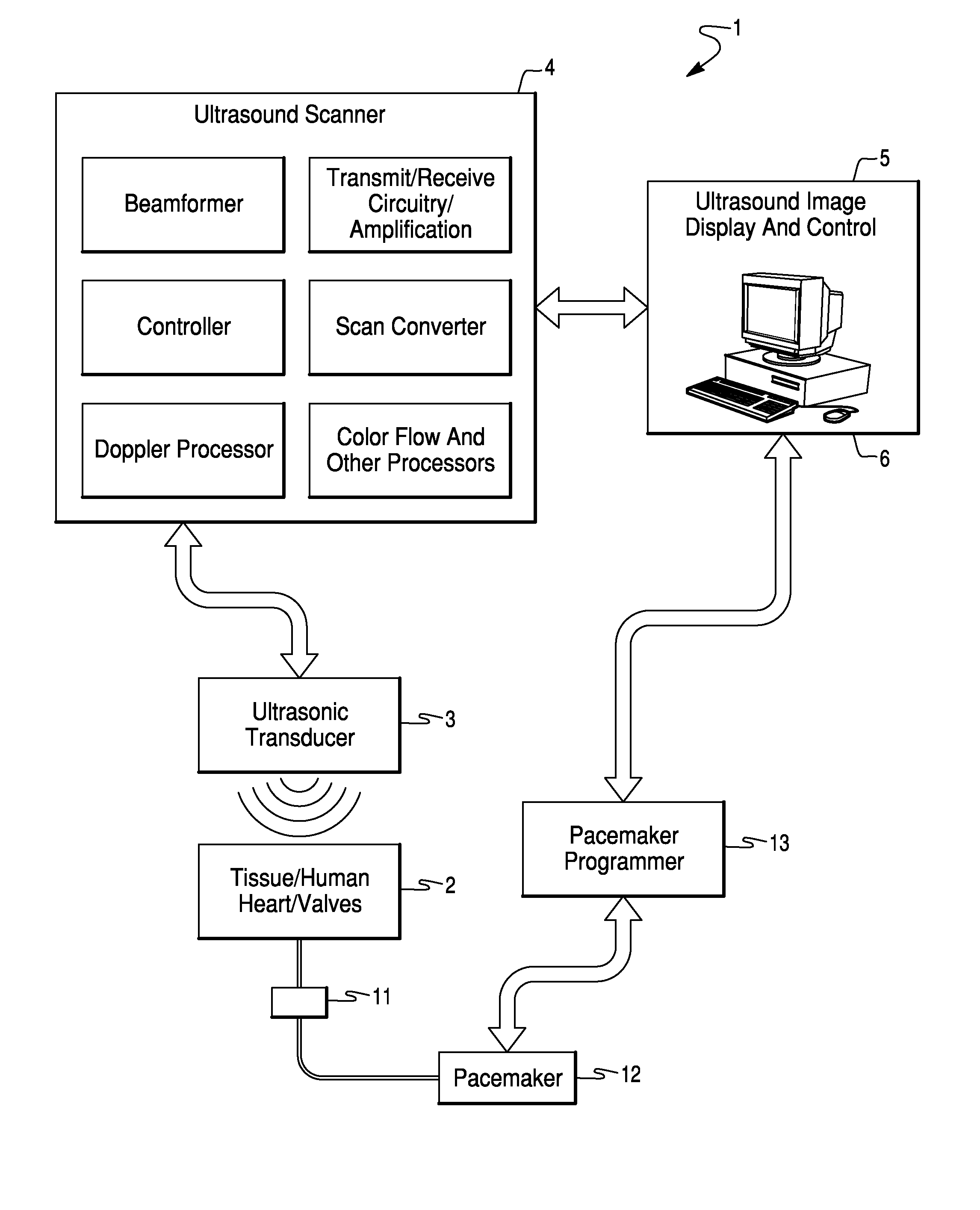
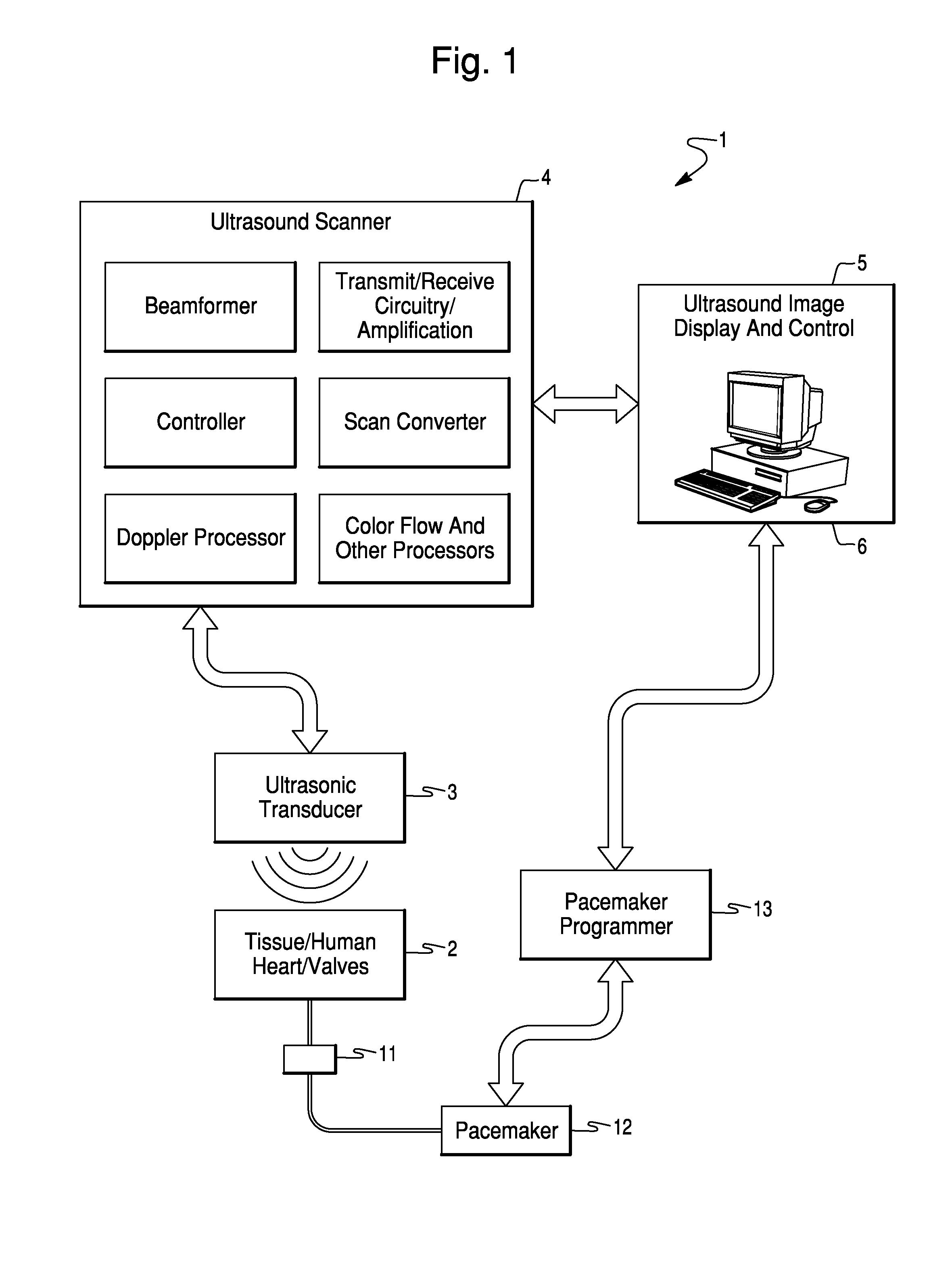
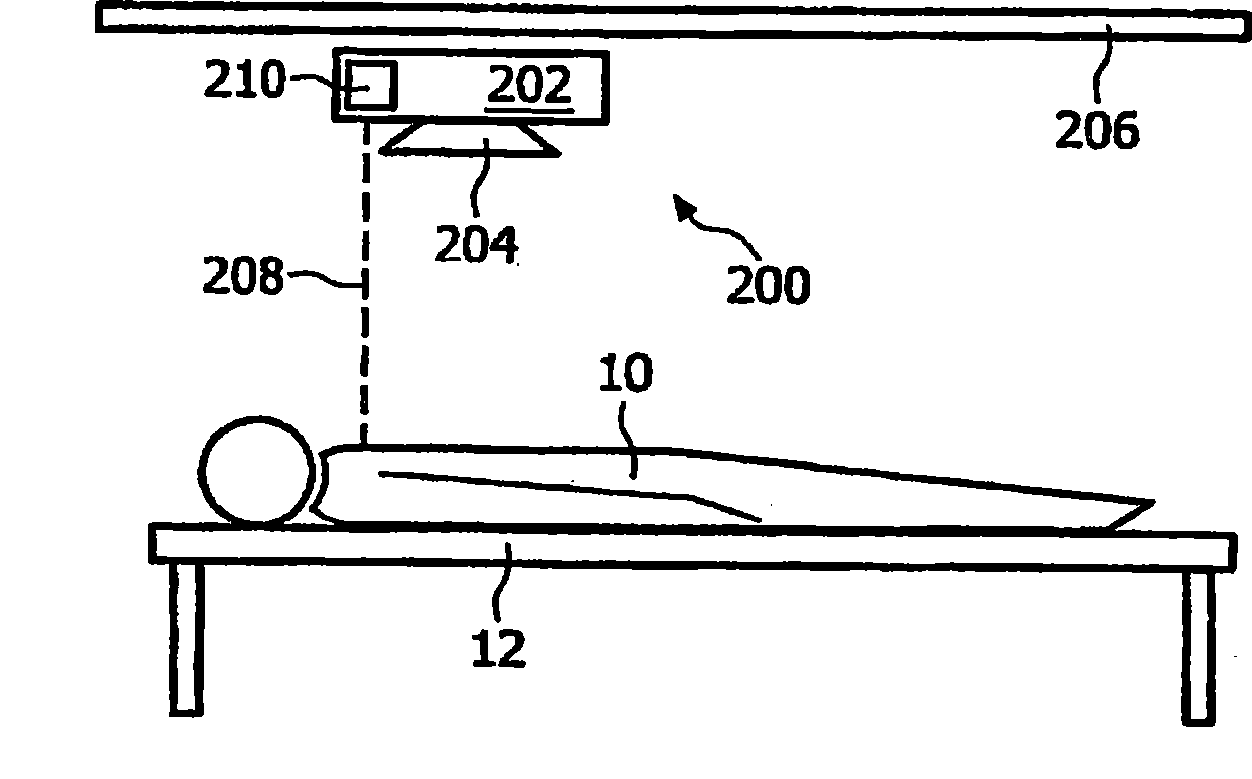
Method and System for Configuration of a Pacemaker and For Placement of Pacemaker Electrodes
InactiveUS20080146928A1Easy to compareEjection volume be maximizedBlood flow measurement devicesCatheterUltrasound imagingUltrasonic sensor
Ultrasound imaging methods and systems for assisting a clinician in configuring the operation of a pacemaker and for determining an optimal site for the pacemaker electrode are presented. The methods and systems provide a toolbox for analyzing and optimizing the effectiveness of the pacemaker and proposed electrode sites. The method includes a function which evaluates one or more electrode sites and pacemaker configurations. The function may be based, for example, on the activation voltage of the pacemaker, on an estimate of the volume of blood ejected from the heart and / or on the cardiac dysynchrony. The ejection volume and the dysynchrony may be estimated using an imaging cardiac catheter ultrasound transducer array and ultrasound unit.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
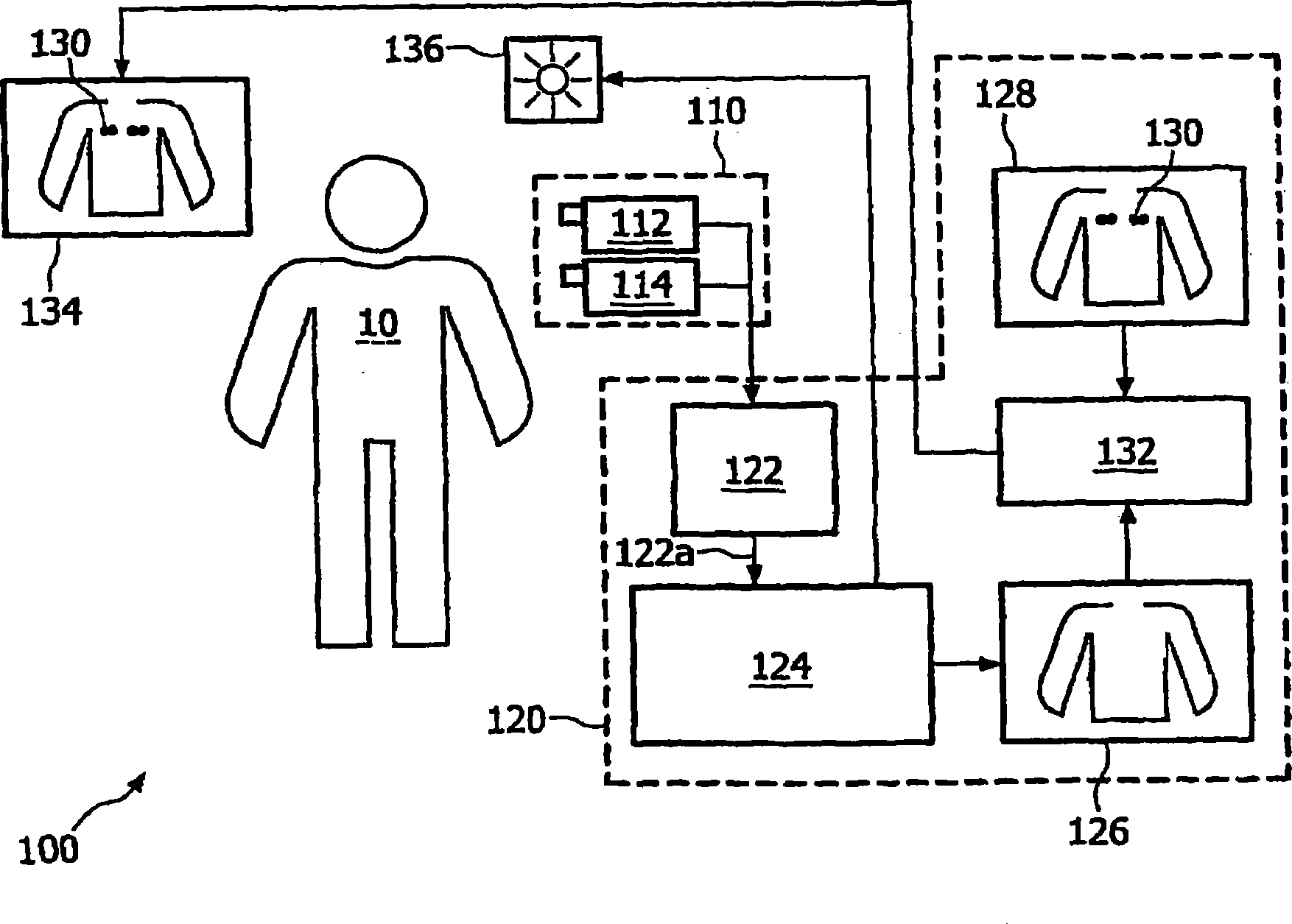
System and method for positioning electrodes on a patient body
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
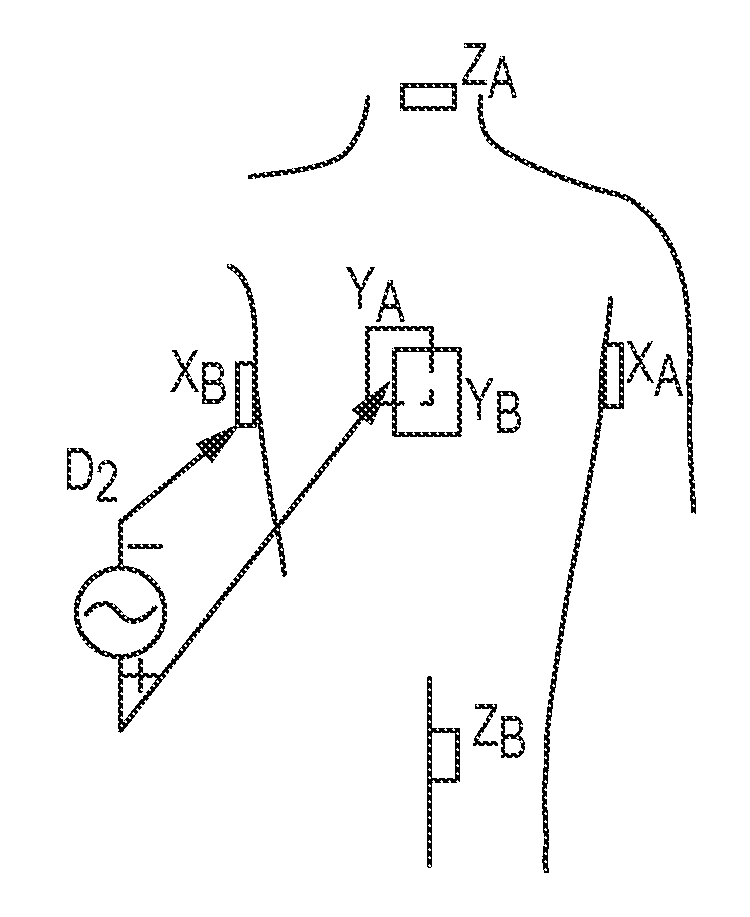
Chronically-implantable active fixation medical electrical leads and related methods for non-fluoroscopic implantation
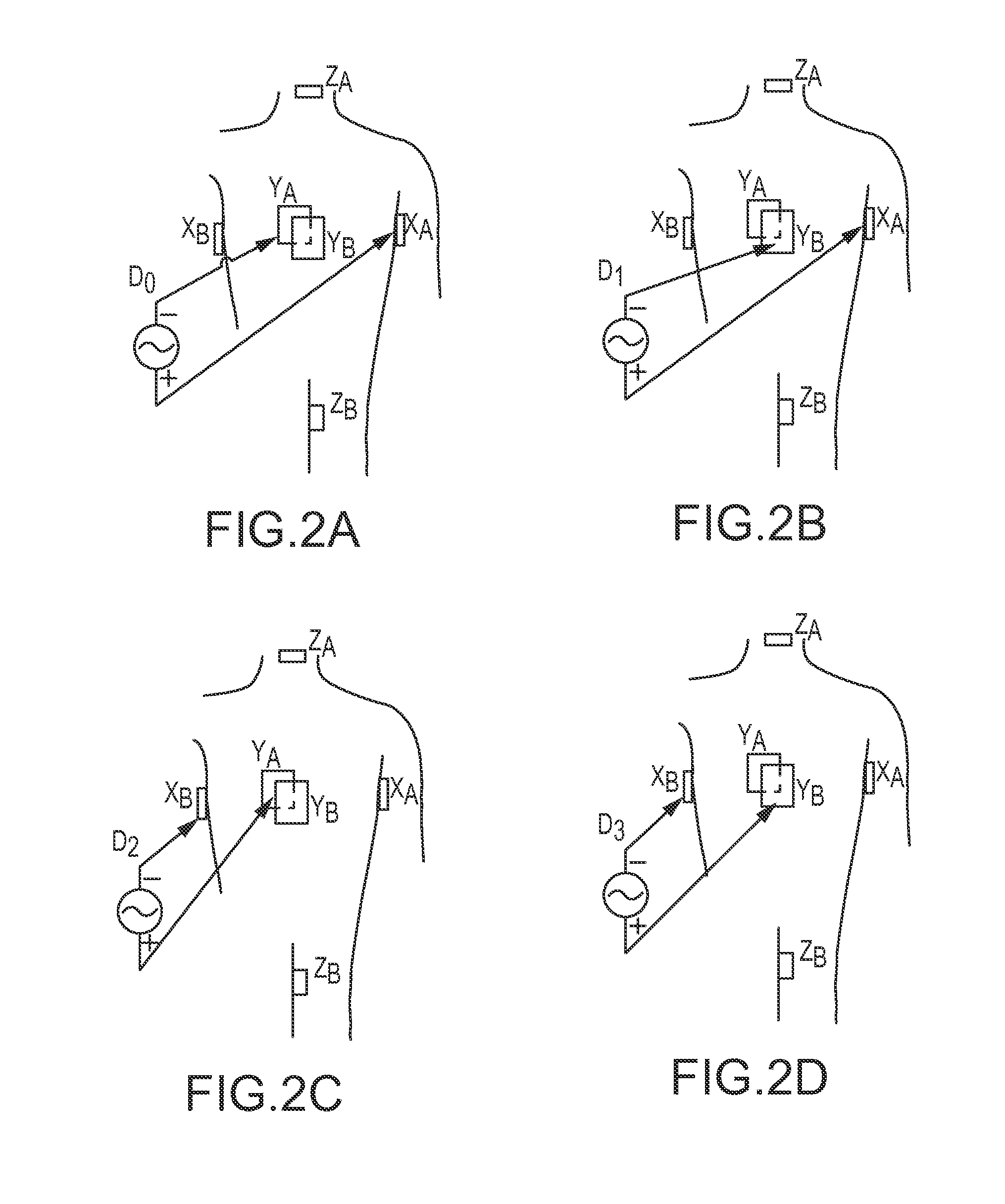
InactiveCN101711125ATransvascular endocardial electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringConductive materialsNavigation system
Bio-impedance may be used for navigation systems to chronically implant pacing and defibrillation leads in the heart using a non-fluoroscopic position sensing unit (PSU), such as a modified LocaLisa TM system from Medtronic Inc., which allows for variable frequency sampling of the position of electrode of a catheter. The PSU injects small AC signals via surface electrodes in three orthogonal axes, each on a slightly different frequency (e.g., near 30 KHz). Indwelling electrodes electrically connected to the PSU resolves the magnitude of induced voltage for each of the three frequencies, thus measuring voltage for each of the three axes. Voltages are divided by induced current to yield impedance in each axis for each electrode. Impedance is proportional to position within the body. Such a system requires that a conductive material, such as a retractable helical tip-electrode, be exposed during implantation. Since the tip is retracted during implantation, this disclosure provides a modified distal portion employing at least one aperture (or 'window') for fluid exposure of the helix-electrode and a deployable internal sleeve for covering the aperture(s) when the helix-electrode is extended.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
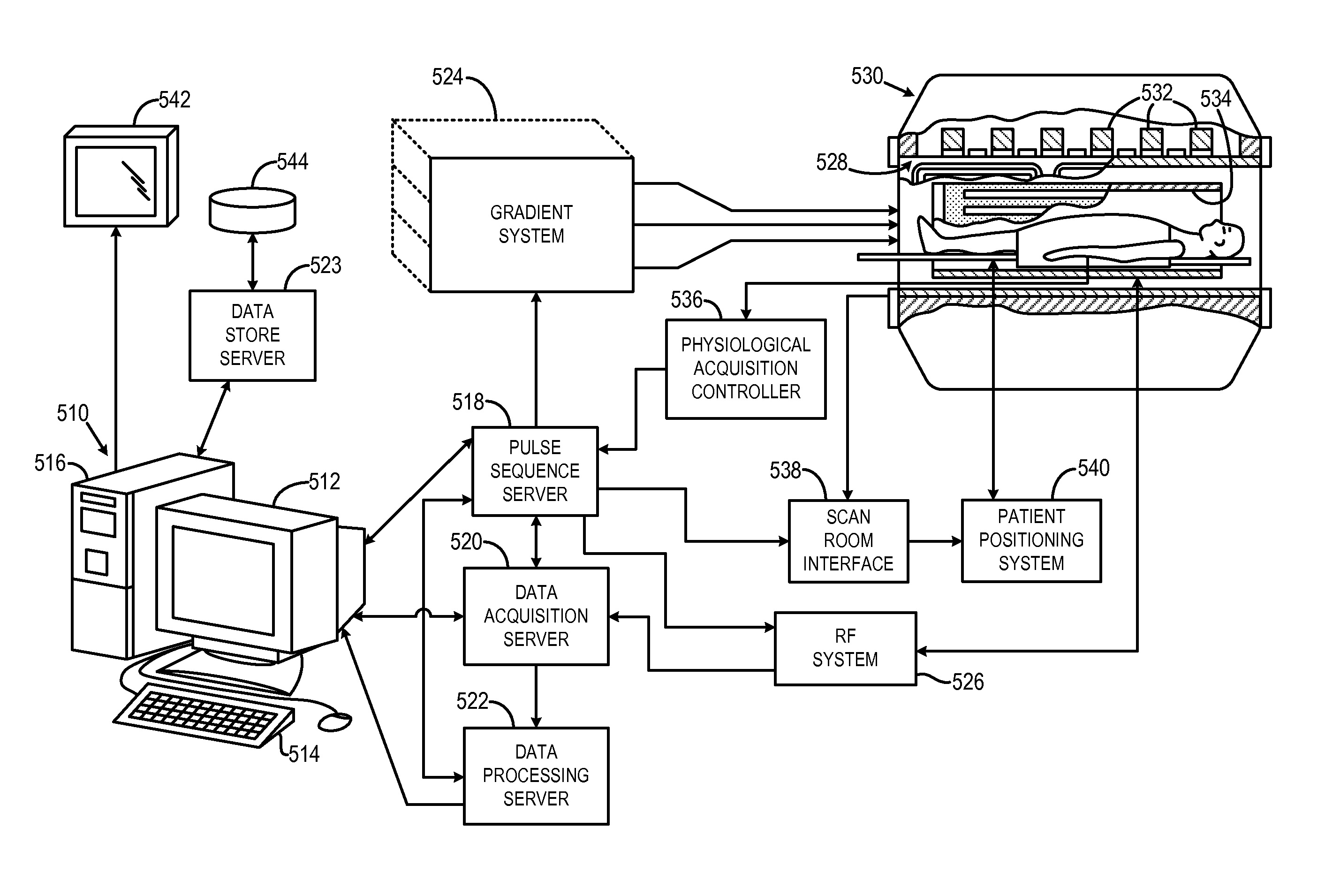
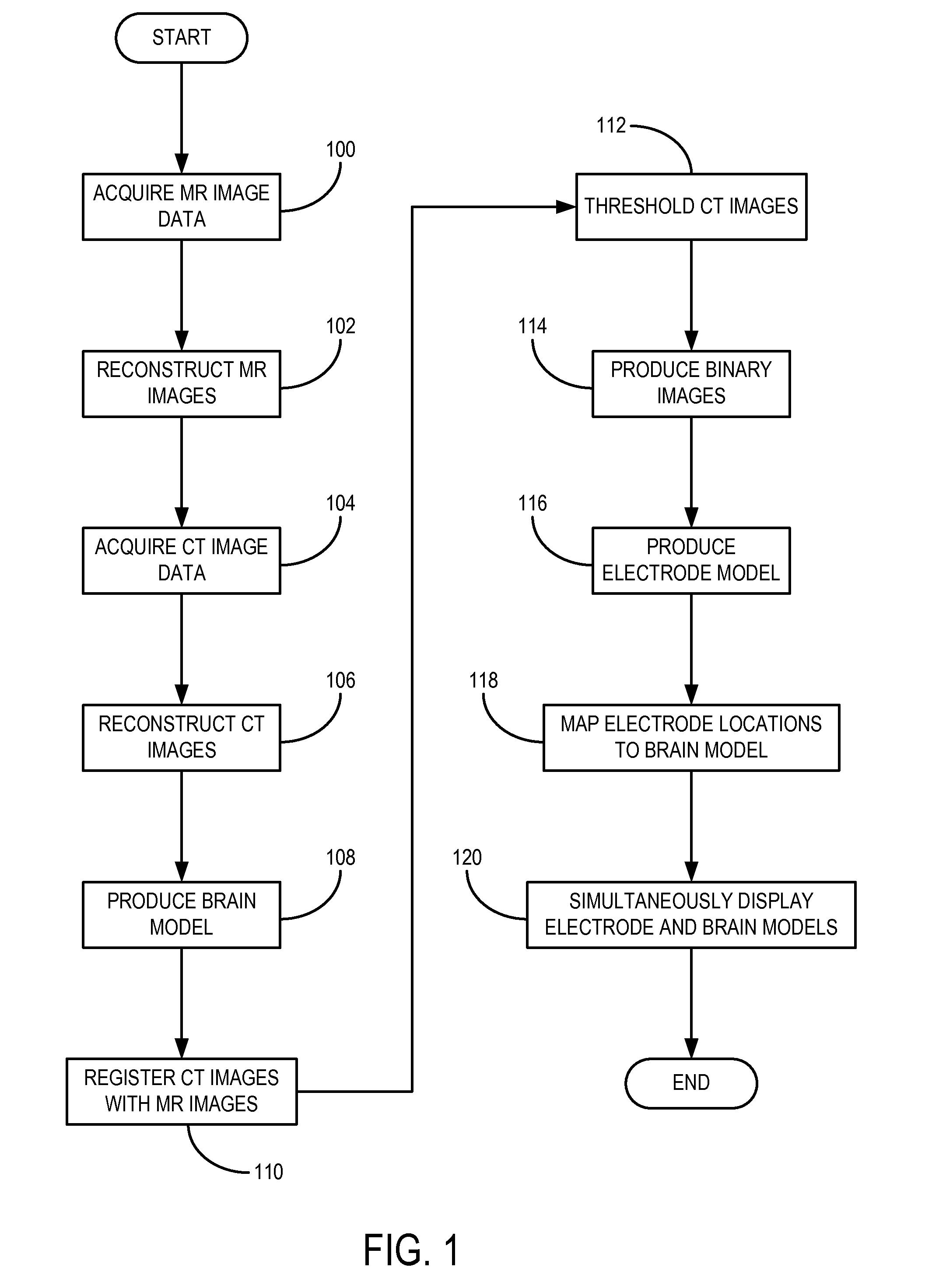
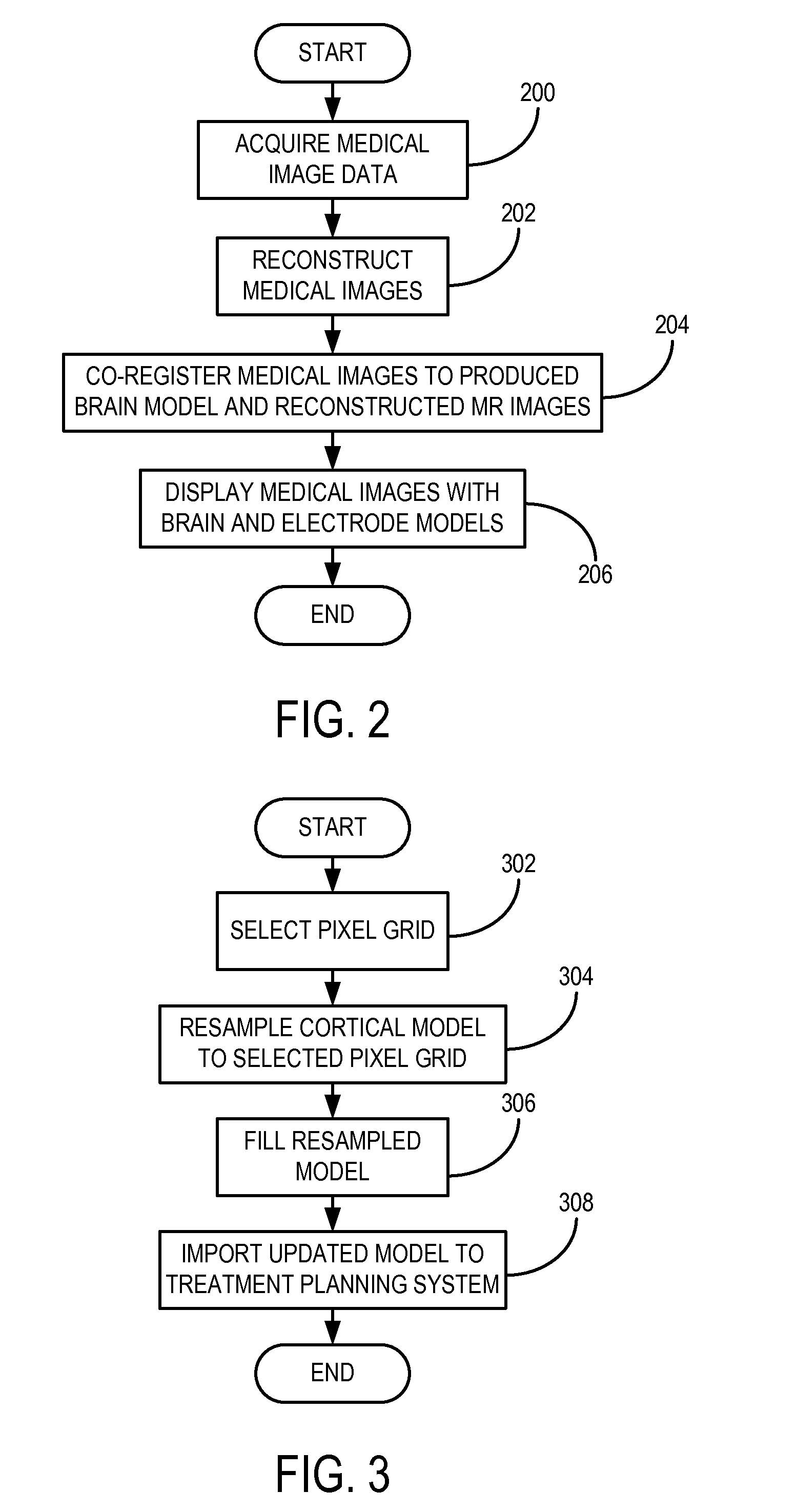
Method for Determining Locations of Implanted Electrodes with Medical Images
ActiveUS20120271151A1Overcomes drawbackError minimizationElectroencephalographyComputerised tomographsSurgical operationBrain section
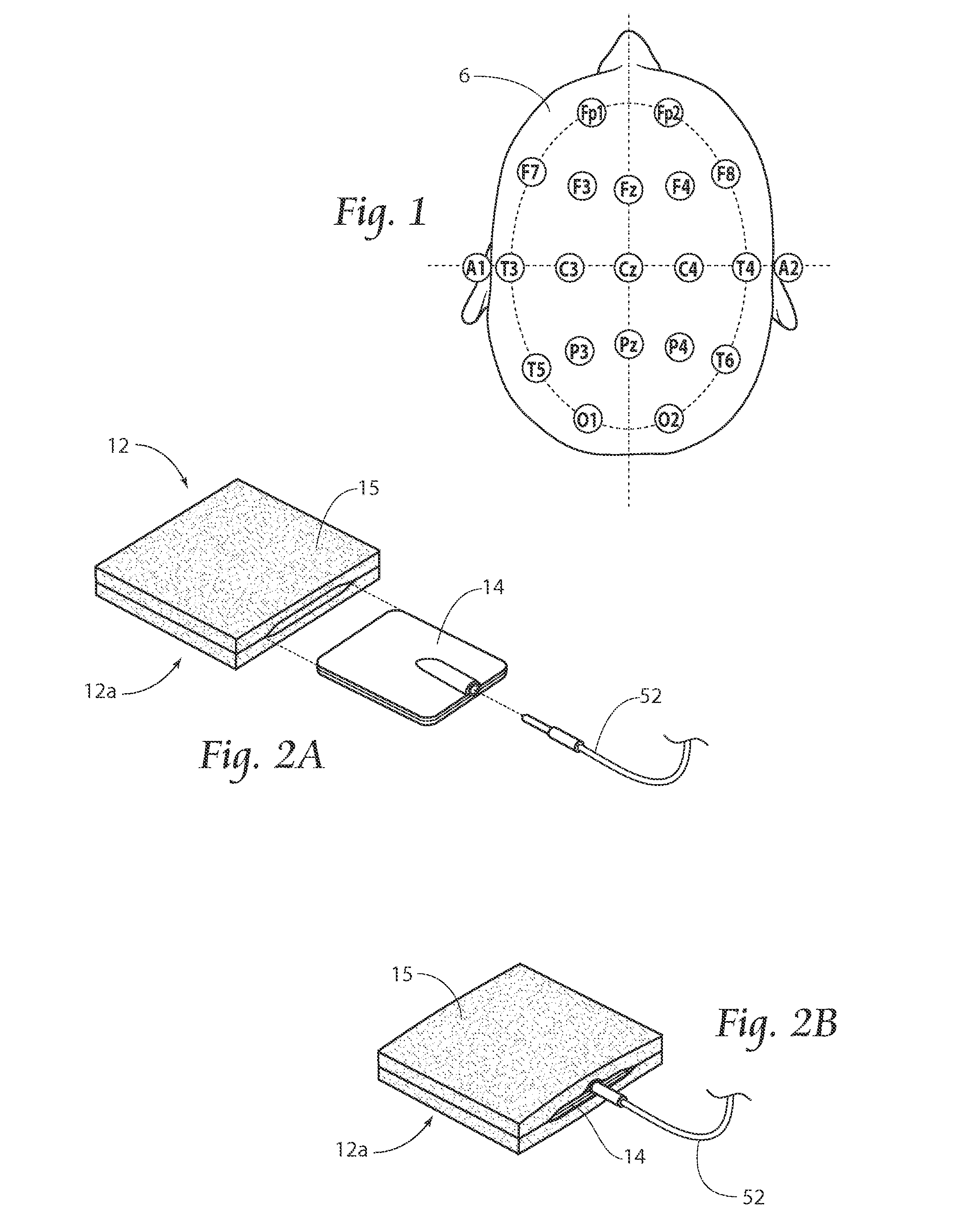
A method for accurate localization and visualization of implanted electrodes, such as implanted intracranial electrodes, is provided. More particularly, a realistic representation of intracranial electrode positions on patient-specific post-implantation MRI brain renderings is obtained. The resulting computer models provide an accurate depiction of electrode locations on three-dimensional brain renderings that are suitable for use in surgical planning of resection boundaries around, for example, epileptic zones. Electrodes placed inter-hemispherically are also visible with this method. In addition, a method for creating electrode “shadows” cast upon the brain model surface is provided. These electrode shadows are useful for estimating cortical areas sampled by iEEG and for locating electrodes that may straddle sulci and contact two adjacent cortical gyri.
Owner:THE MEDICAL COLLEGE OF WISCONSIN INC
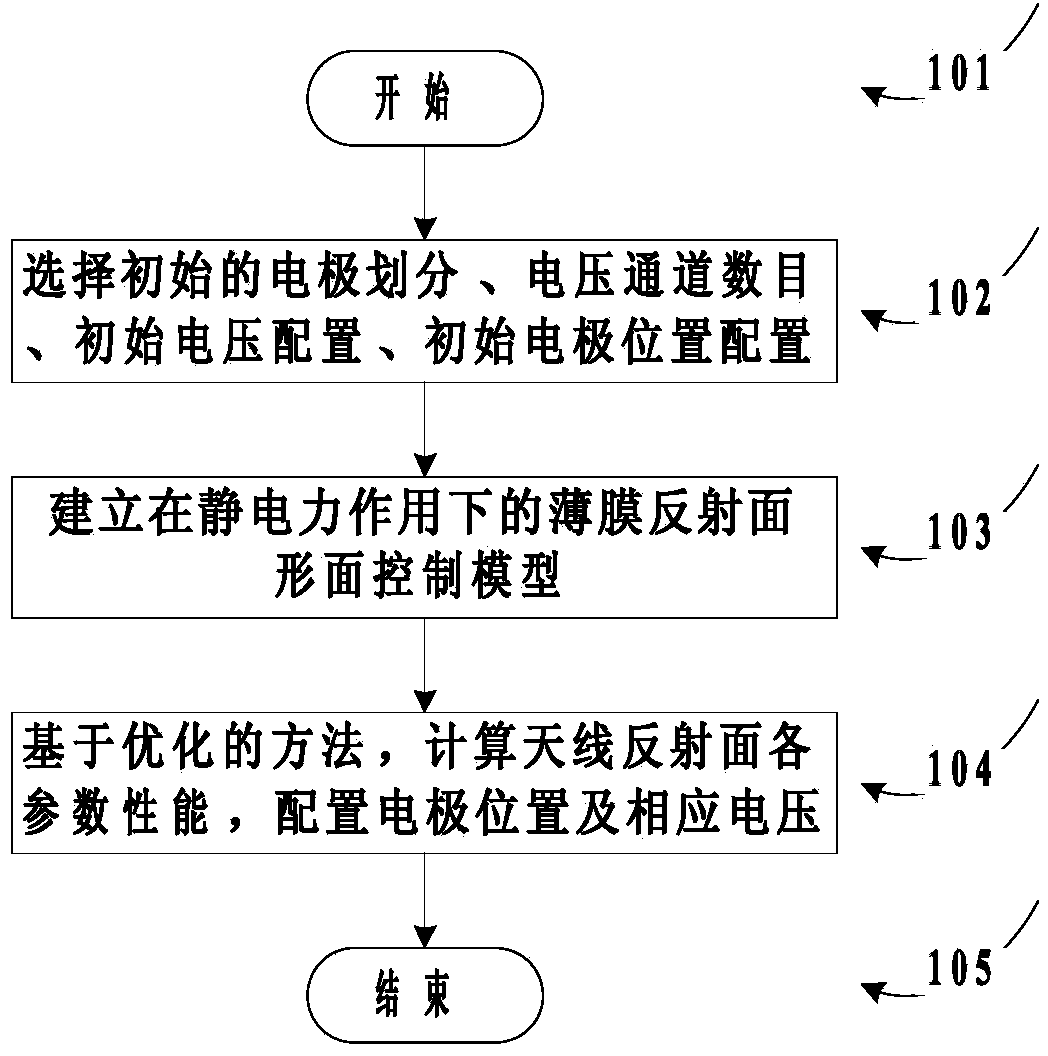
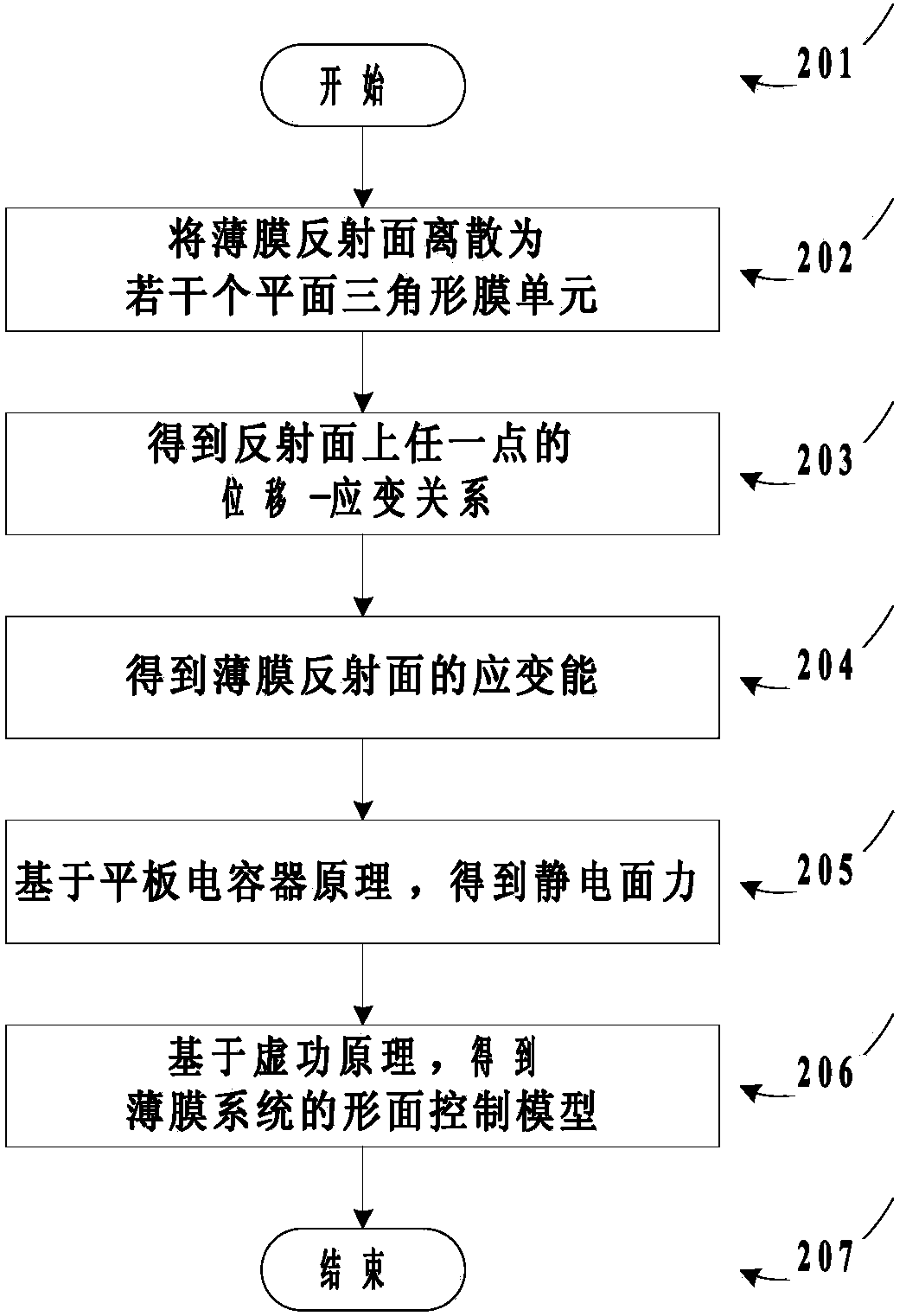
Electrode layout method of static formed film antenna
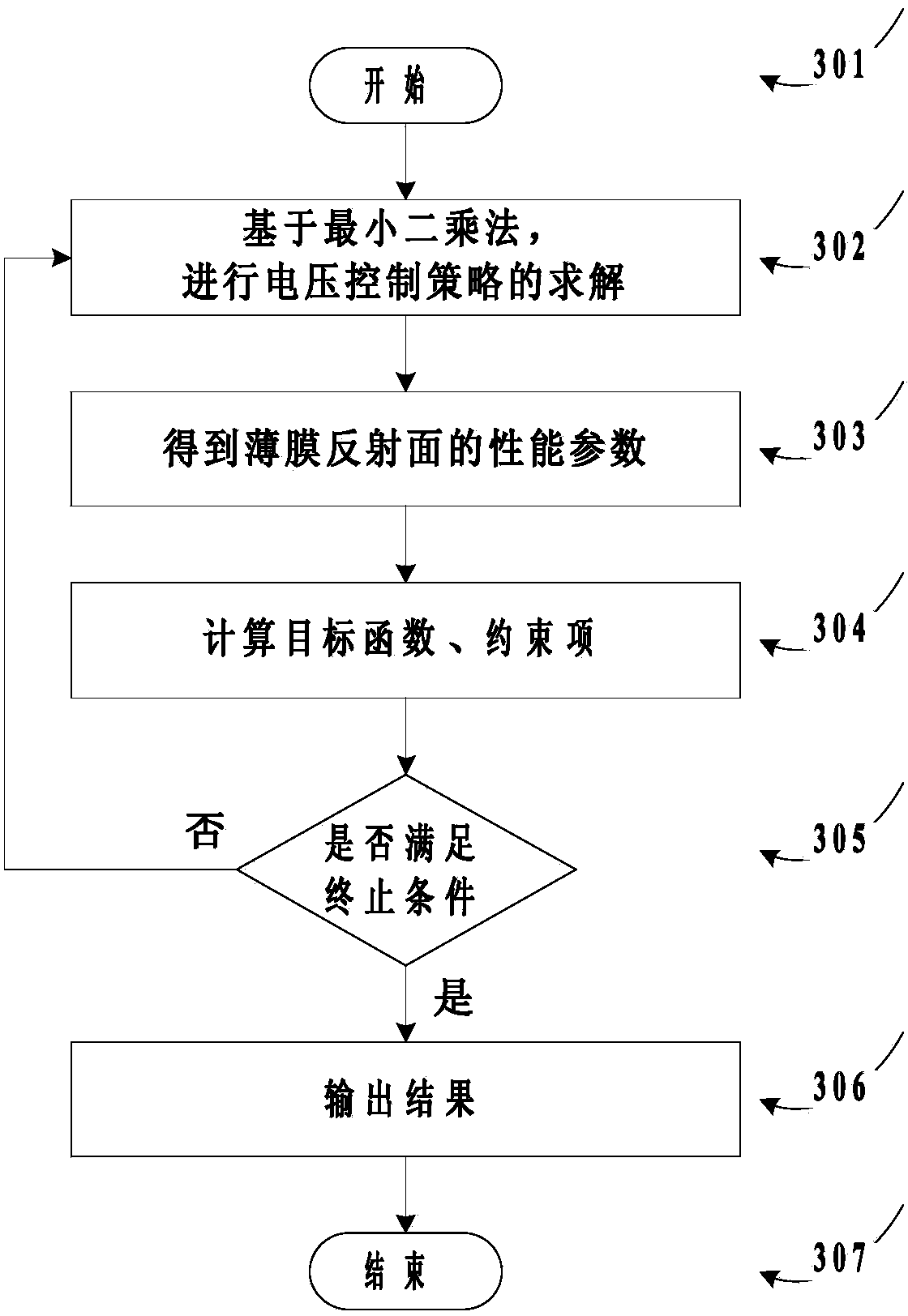
ActiveCN103678810AAchieve regulationImprove antenna performanceSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelEngineering
The invention aims at providing an electrode layout method of a static formed film antenna. A finite element model of a film reflecting face antenna is set up, corresponding optimal configuration are carried out on the position of an electrode and the voltage, thus the optimal electrode layout of the film reflecting face antenna is achieved. By means of the electrode layout method of the static formed film antenna, the face precision of a reflecting face can be effectively improved, wrinkling of the reflecting face is prevented and complexity of the system is relieved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Remotely reconfigurable system for mapping subsurface geological anomalies
ActiveUS20070299632A1High positioning accuracyAccurate calculationElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingElectric signal transmission systemsWireless controlRadio frequency
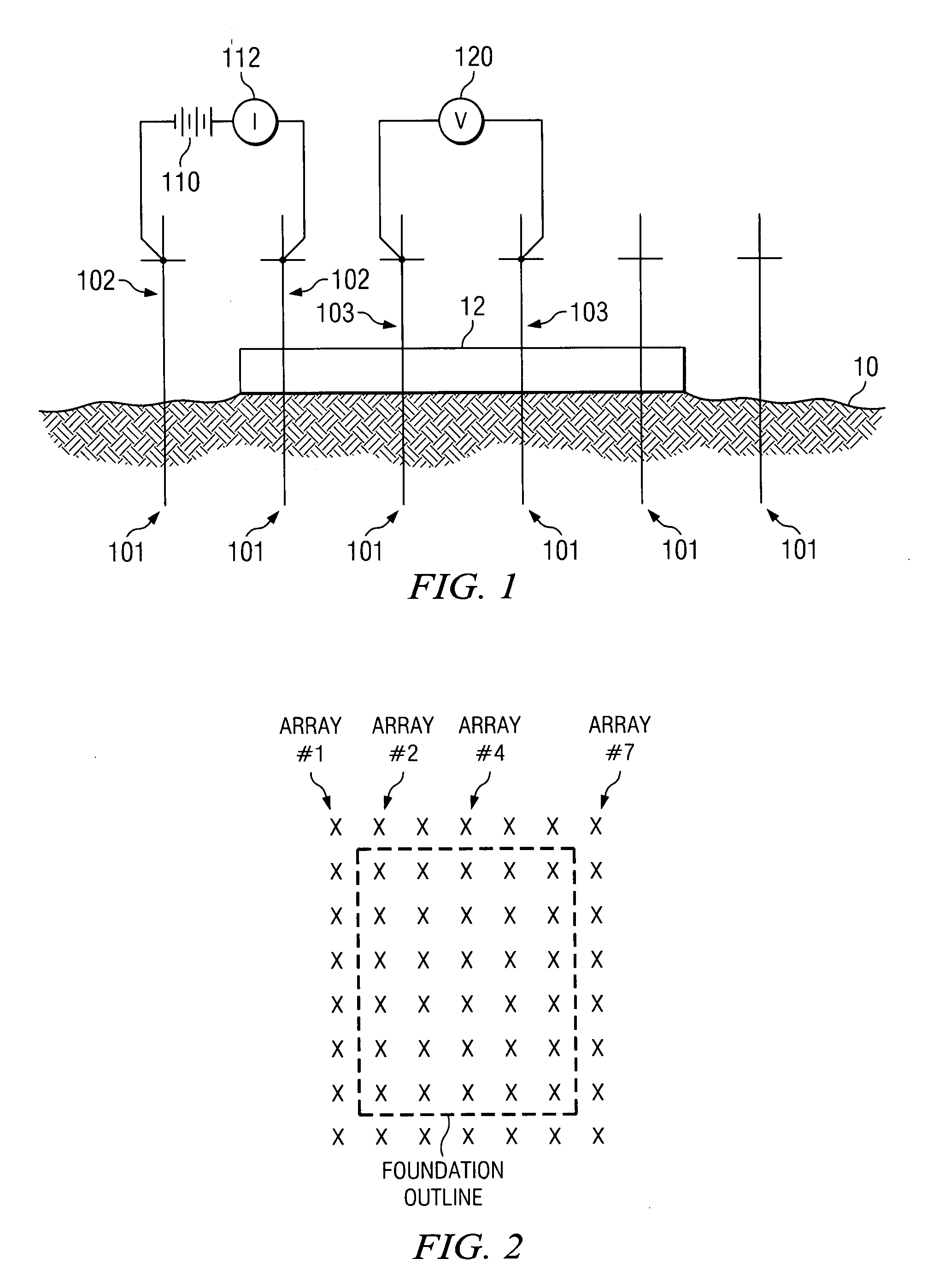
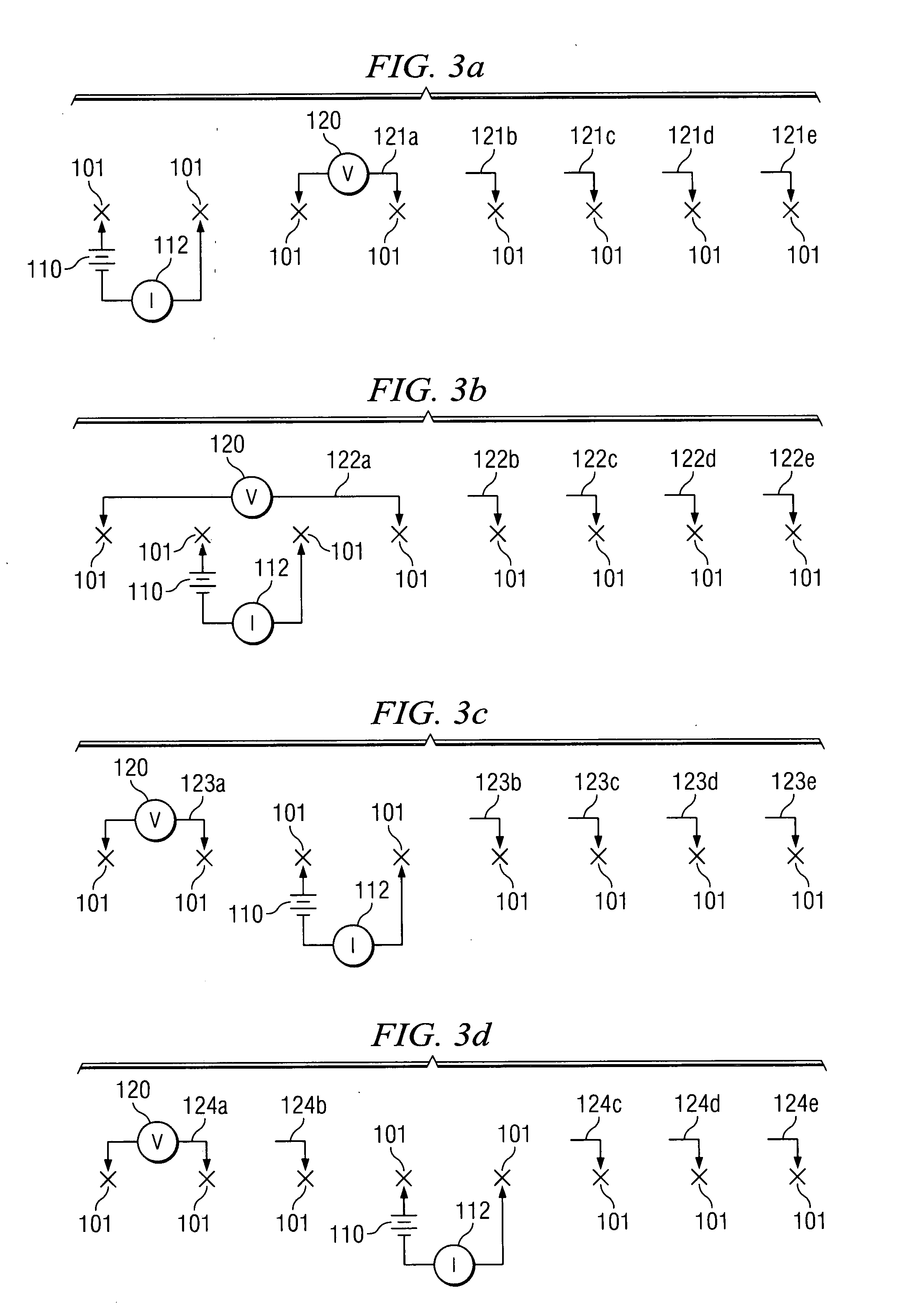
Methods and apparatus are provided for receiving, detecting and transmitting geophysical data from a plurality of electrodes placed in the soil utilizing a dynamically reconfigurable wireless control unit that is located on each electrode. Data from the control units is transmitted by a wireless signal to a centralized data processor for analysis. Control data is provided from a central control processor to the control unit by wireless transmission. The control unit, which is positioned, includes a multi-channel radio frequency transmitter / receiver and a processor to actuate relays and record data returns from the measured substrate soil for transmission to the central data processor. The control unit incorporates a changeable code or address to unambiguously identify itself, and its spatial relationship to other electrodes, to the central data processor and the central control processor. The control units are equipped with a GPS positioning device to allow for automatic transmission of electrode location and for electrode placement without a manual survey being required.
Owner:EARTHSYST TEHNOLOGIES INC +1
Varactor
ActiveUS20070246801A1Increase unit capacityHigh quality factorSemiconductor devicesElectrode locationDielectric layer
A varactor on a substrate is provided. The varactor comprises a bottom electrode, an upper electrode, a first dielectric layer and a conductive layer. The bottom electrode has several doped regions arranged in the substrate as an array with several rows and several columns, wherein the doped regions in adjacent columns are arranged alternatively. The upper electrode is located over the substrate and the upper electrode is composed of several electrode locations and has several openings, wherein each opening exposes the corresponding doped region. Furthermore, each electrode location is surrounded by three doped regions. The first dielectric layer is located between the substrate and the upper electrode. The conductive layer is located over the upper electrode, wherein the conductive layer and the upper electrode are isolated from each other and the conductive layer and the doped regions are electrically connected to each other.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Reliability determination of electrode location data
Embodiments of the present disclosure include a system for determining an error associated with an electrode disposed on a medical device. The system comprises a processor and a memory storing instructions on a non-transitory computer-readable medium. The instructions are executable by the processor to receive an electrode signal from the electrode disposed on the medical device. The instructions are further executable by the processor to receive a plurality of other electrode signals from a plurality of other electrodes disposed on the medical device. The instructions are further executable by the processor to determine that the electrode signal received from the electrode disposed on the medical device is an outlier in relation to the plurality of other electrode signals from the plurality of other electrodes disposed on the medical device, based on a comparison between the electrode signal and the plurality of other electrode signals.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
Balanced charge waveform for transcutaneous pacing
ActiveUS20110319950A1Minimizing hydrolysisAvoid harmful effectsHeart stimulatorsCardiac pacemaker electrodeExternal pacemakers
External pacemaker systems and methods deliver pacing waveforms that minimize hydrolysis of the electrode gel. Compensating pulses are interleaved with the pacing pulses, with a polarity and duration that balance the net charge at the electrode locations. The compensating pulses are preferably rectangular for continuous pacing, and decay individually for on-demand pacing.
Owner:PHYSIO CONTROL INC
Position detection sensor and input apparatus
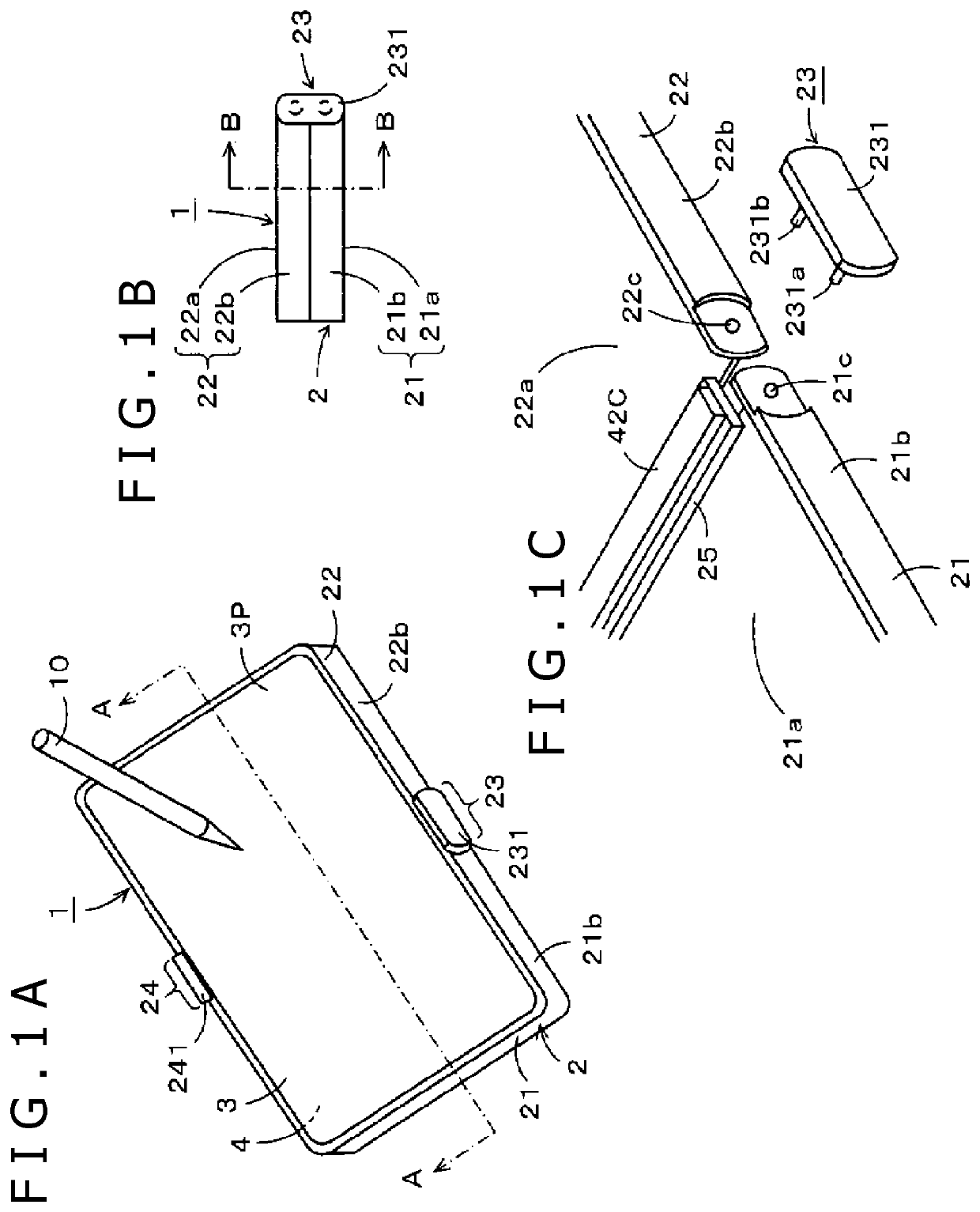
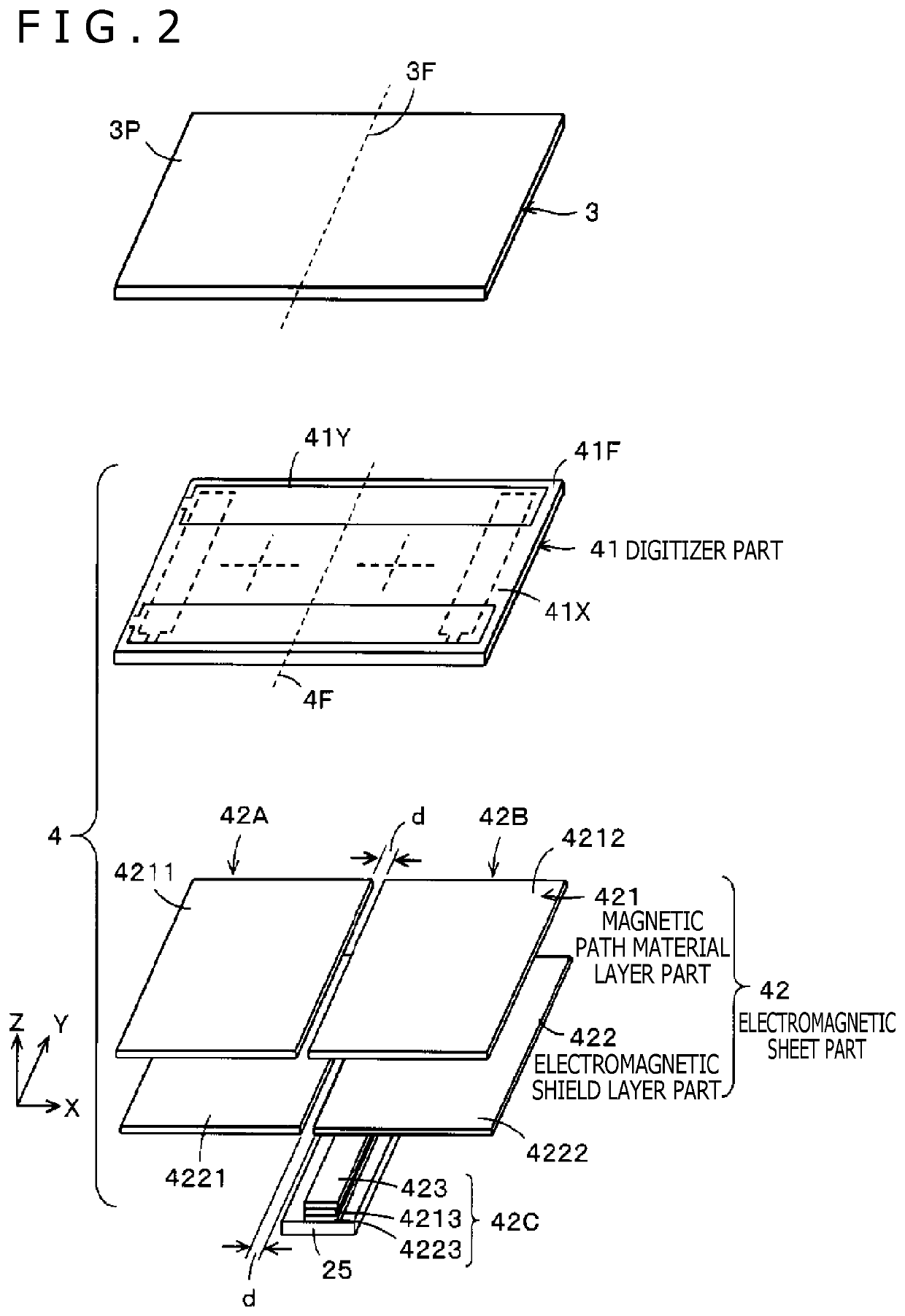
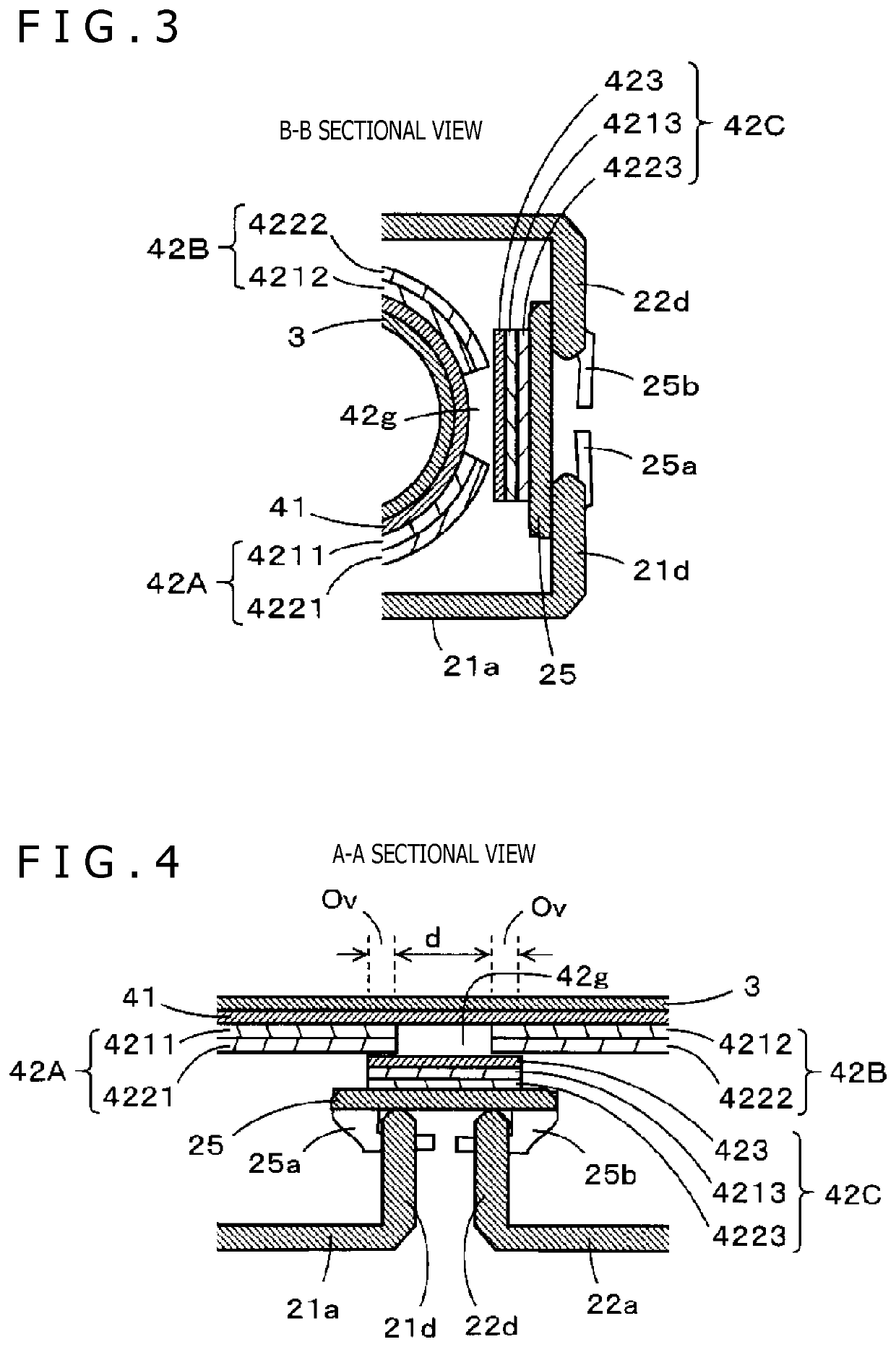
PendingUS20220129094A1Reduce bending stressReduce deteriorationDetails for portable computersInput/output processes for data processingElectromagnetic couplingLocation detection
A foldable position detection sensor operable by electromagnetic induction coupling is configured to alleviate the problem of the levels of electromagnetic coupling with an electronic pen locally changing at a bending portion of the sensor. The position detection sensor includes a digitizer that includes an electrode configured to couple with a position indicator by electromagnetic induction coupling. The position detection sensor includes multiple electromagnetic sheets disposed to cover a surface of the digitizer opposite to an input surface thereof for receiving input form the position indicator. The multiple electromagnetic sheets are spaced apart from one another along the surface of the digitizer at a bending location where the digitizer is bent. The electromagnetic sheets are configured such that when the digitizer is in an unfolded state the electromagnetic sheets overlap with one another at the bending location in a direction perpendicular to the input surface of the digitizer.
Owner:WACOM CO LTD
Cell electric stimulator with separate electrodes for electrical field shaping and for stimulation
An electric stimulator for heart, brain, organs and general cells with a possibly random shape and position of electrodes which enhances its performance for breaking the symmetry. Two types of electrodes are introduced: type-1, or active electrodes are similar to prior art, while type-2, or passive electrodes have not been used in this context. Passive electrodes are electrically insulated, being unable to inject current in the surrounding medium, but they are capable of shaping the electric field, which has consequence on the path of the stimulating currents injected by type-1 electrodes. The invention also discloses a supercapacitor-type passive electrode of type-2, which maximizes the stored charge on the electrode—therefore increasing the electric field magnitude created by it.
Owner:LEE CHONG IL +1
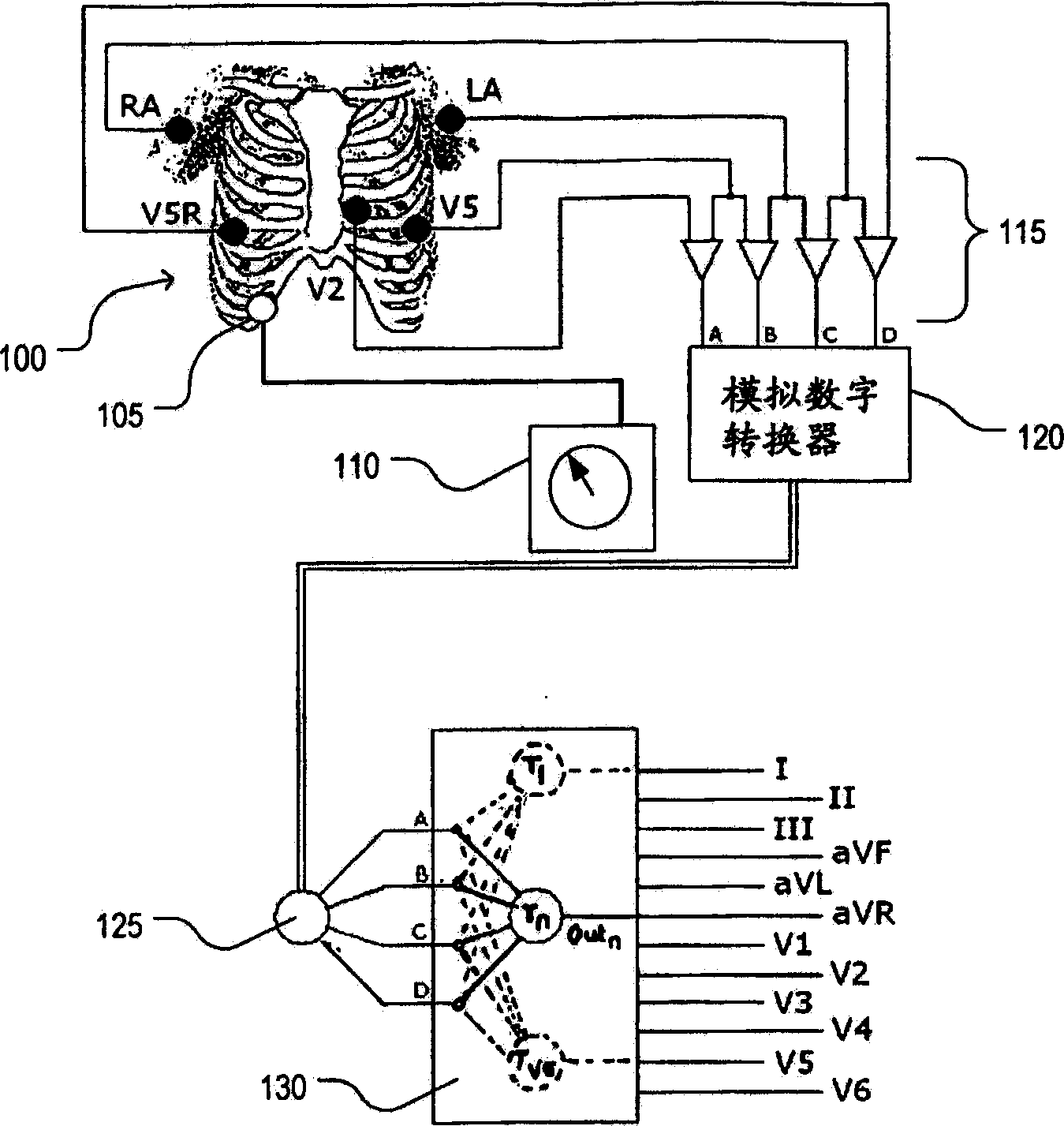
Reduced electrode electrocardiography system
A method for obtaining a set of electrocardiographic (ECG) signals by: receiving signals from a first group of electrodes connected to predetermined locations on a human body to acquire a first set of ECG signals; synthesising at least one further ECG signal using predetermined transformation (s) on said first set of ECG signals or a subset thereof to form a synthesised set of ECG signals, each synthesised signal corresponding to a location on the body (hereinafter referred to as the synthesised location); detecting the body's posture; and selecting or modifying the transformations used in said synthesising step on the basis of the detected body posture, so as to reduce posture-induced inaccuracies between each synthesised signal and a real signal that would be measured at the synthesised location in the detected body posture.
Owner:太空实验室保健有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com