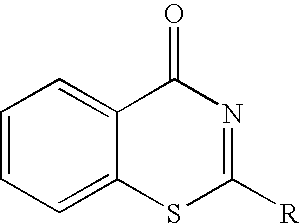
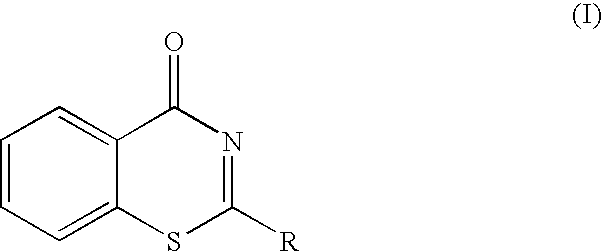
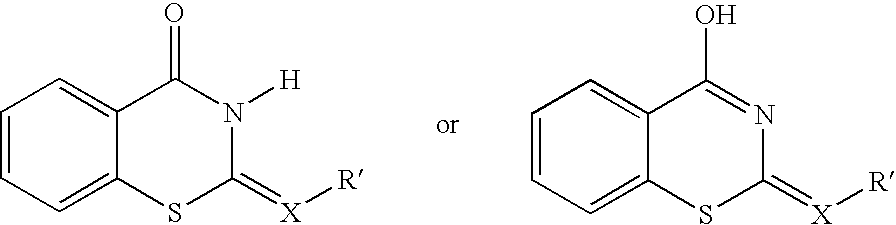
Cell death inhibitor
a cell death inhibitor and inhibitor technology, applied in the field of cell death inhibitors, can solve the problems of no report on the mechanism of cell death, the relationship between mif and cell death is unknown, etc., and achieve the effects of preventing myocardial cell death, preventing serum depletion-induced cell death, and increasing gene expression
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
reference example 1
2-(2-Pyridyl)-4H-1,3-benzothiazin-4-one (Compound 1)
[0122]
[0123] Methyl thiosalicylate (1.6 g, 9.51 mM) and 2-cyanopyridine (1.0 g, 9.60 mM) were dissolved in toluene (2 ml), and triethylamine (2 ml, 14.4 mM) was added to the solution. After heating for 8 hours under reflux, toluene was removed by distillation. Ethanol was added to the residue and the precipitates were taken out by filtration to give crude crystals (1.7 g). The crude crystals were purified by silica gel column chromatography (hexane: chloroform=5:1→chloroform) to give the title compound as crystals (1.0 g, 43.4%).
[0124] Elemental analysis as C13H8N2OS
[0125] Calcd. (%) C, 64.98; H, 3.36, N, 11.66.
[0126] Found (%) C, 64.93; H, 3.31, N, 11.59.
[0127]1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 7.50-7.75 (m,4H), 7.85-8.00 (m,1H), 8.50-8.60 (m,2H), 8.70-8.80 (m,1H).
[0128] IR (KBr): 1660 cm−1
reference example 2
2-(3-Pyridyl)-4H-1,3-benzothiazin-4-one
[0129]
[0130] Methyl thiosalicylate (1.8 g, 10.7 mM) and 3-cyanopyridine (1.1 g, 10.56 mM) were dissolved in toluene (5 ml), and triethylamine (2 ml, 14.4 mM) was added to the solution. After heating for 48 hours under reflux, the same procedures as in REFERENCE EXAMPLE 1 were carried out to give the title compound as crystals (1.1 g, 43.4%).
[0131] Elemental analysis as C13H8N2OS
[0132] Calcd. (%) C, 64.98; H, 3.36, N, 11.66.
[0133] Found (%) C, 64.97; H, 3.33, N, 11.63.
reference example 3
2-(4-Pyridyl)-4H-1,3-benzothiazin-4-one
[0134]
[0135] Methyl thiosalicylate (2.0 g, 11.9 mM) and 4-cyanopyridine (1.2 g, 11.5 mM) were dissolved in toluene (5 ml), and triethylamine (2 ml) was added to the solution. After heating for 22 hours under reflux, the same procedures as in REFERENCE EXAMPLE 1 were carried out to give the title compound as crystals (850 mg, 30.7%).
[0136] Elemental analysis as C13H8N2OS
[0137] Calcd. (%) C, 64.98; H, 3.36, N, 11.66.
[0138] Found (%) C, 65.07; H, 3.15, N, 11.62.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Antioxidant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Inhibition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com