Method of manufacturing semiconductor device, semiconductor device, and mounting structure of semiconductor device
a technology of mounting structure and semiconductor device, which is applied in the direction of semiconductor device, semiconductor/solid-state device details, electrical apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of lowering mounting reliability, reducing mounting cost, and resin (the adhesive) being unable to be prevented from remaining between the land and the bump, so as to achieve high-density mounting and reduce mounting cost. , the effect of enhancing mounting reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
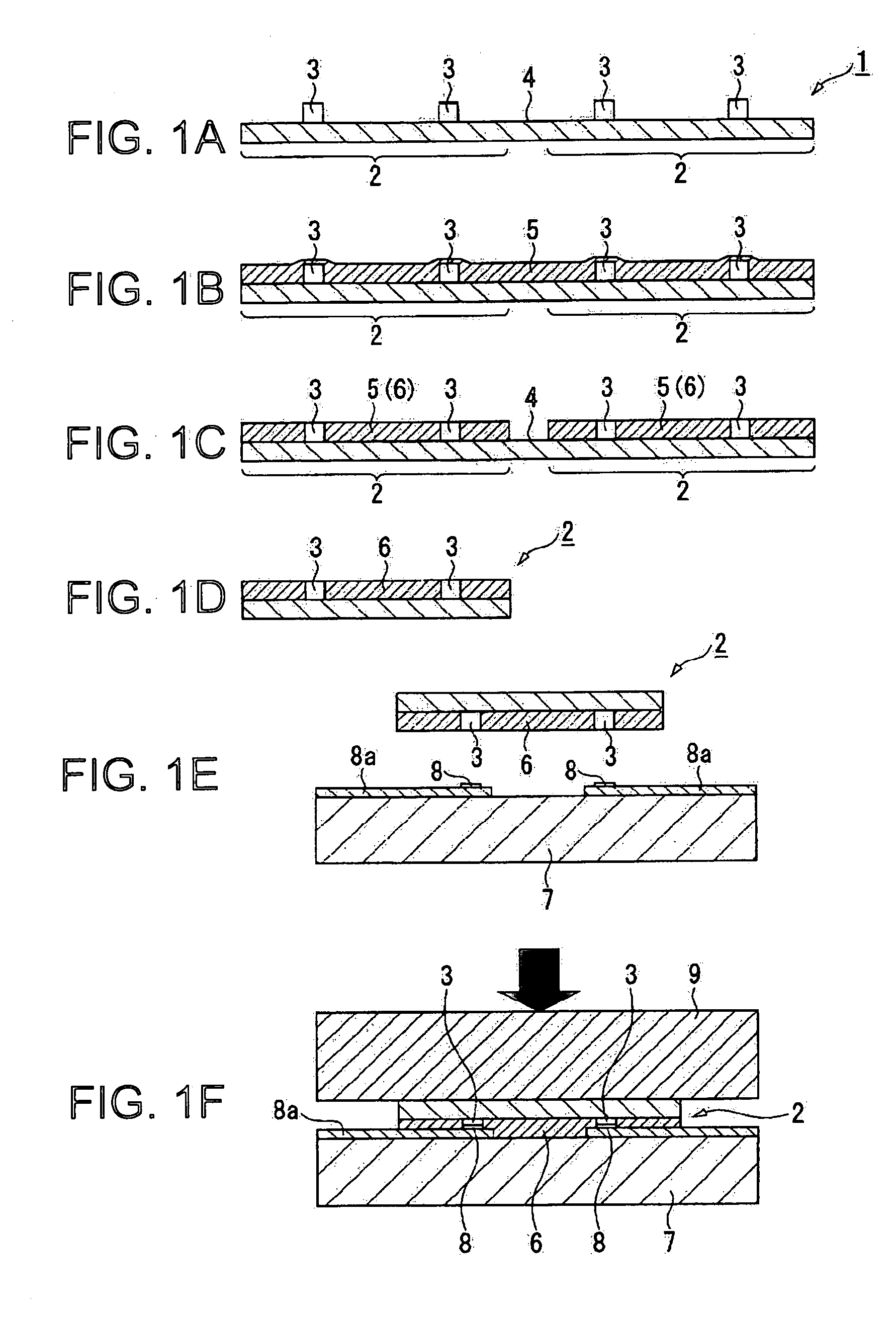
[0050] The invention will be explained hereinafter in detail. FIGS. 1A through 1F are schematic views for explaining processes of a mounting method of a semiconductor, which is an embodiment of the invention.
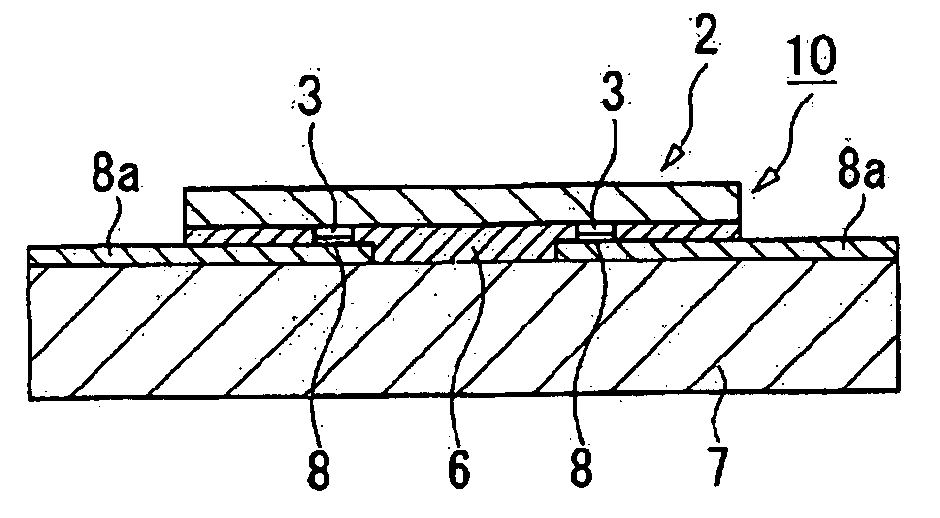
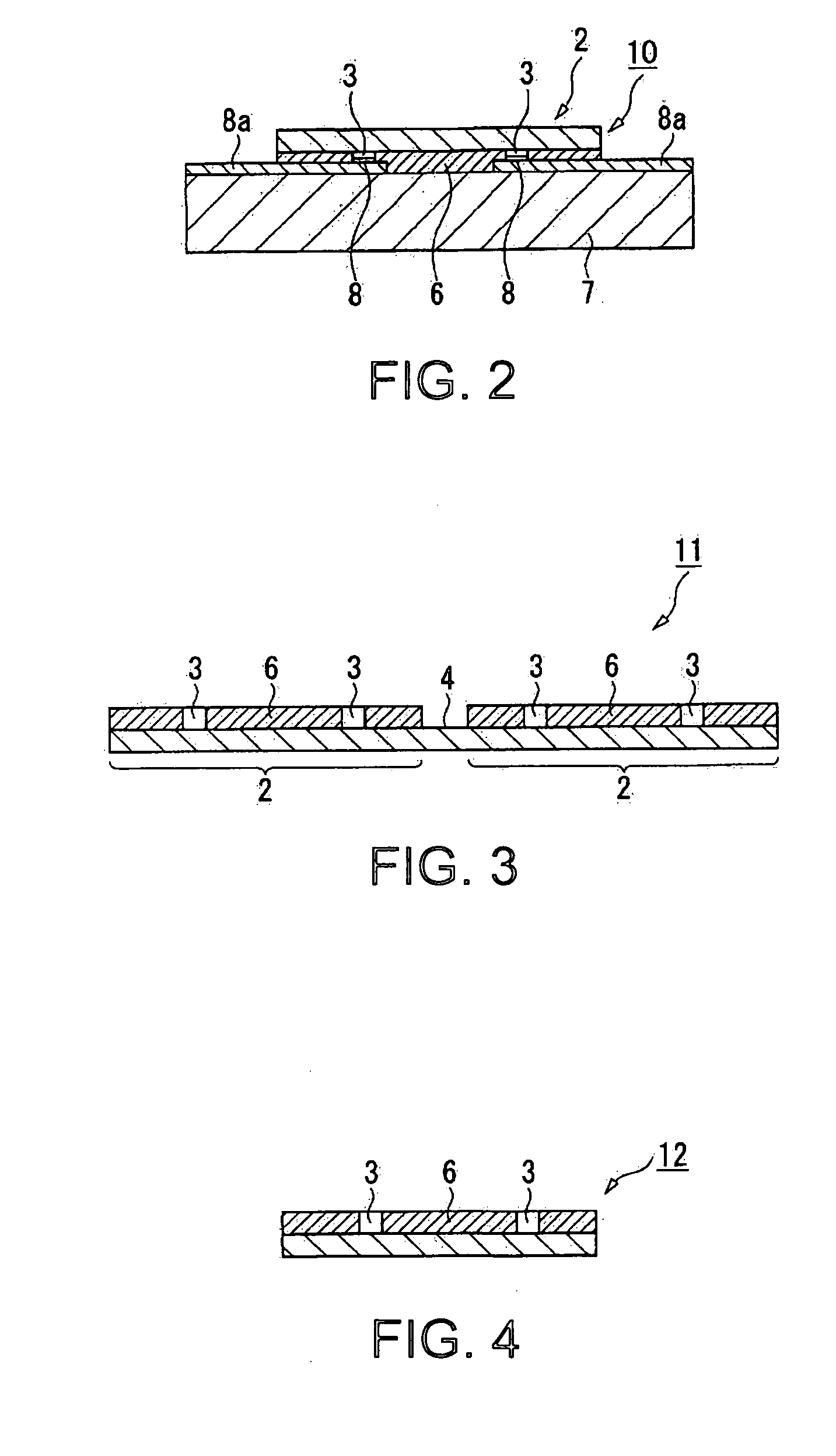
[0051] In the present embodiment, firstly a wafer 1 made of silicon is prepared as shown in FIG. 1A. In the wafer 1, there are a number of semiconductor chips 2 each equipped with various components formed thereon and further equipped with a number of bumps 3 formed on the side of the active surface. The bump 3 is formed of, for example, gold with an electrolytic plating process, or of a laminated structure of nickel and gold with an electroless plating process, and shaped like a cylinder or a prism having a height in a range of, for example, about 5 through 30 μm. Alternatively to the above, other known bumps such as a wire bump made by processing a gold wire to form a ball-shaped member, or a solder bump formed from solder can also be adopted.
[0052] In this case, the wafer 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com