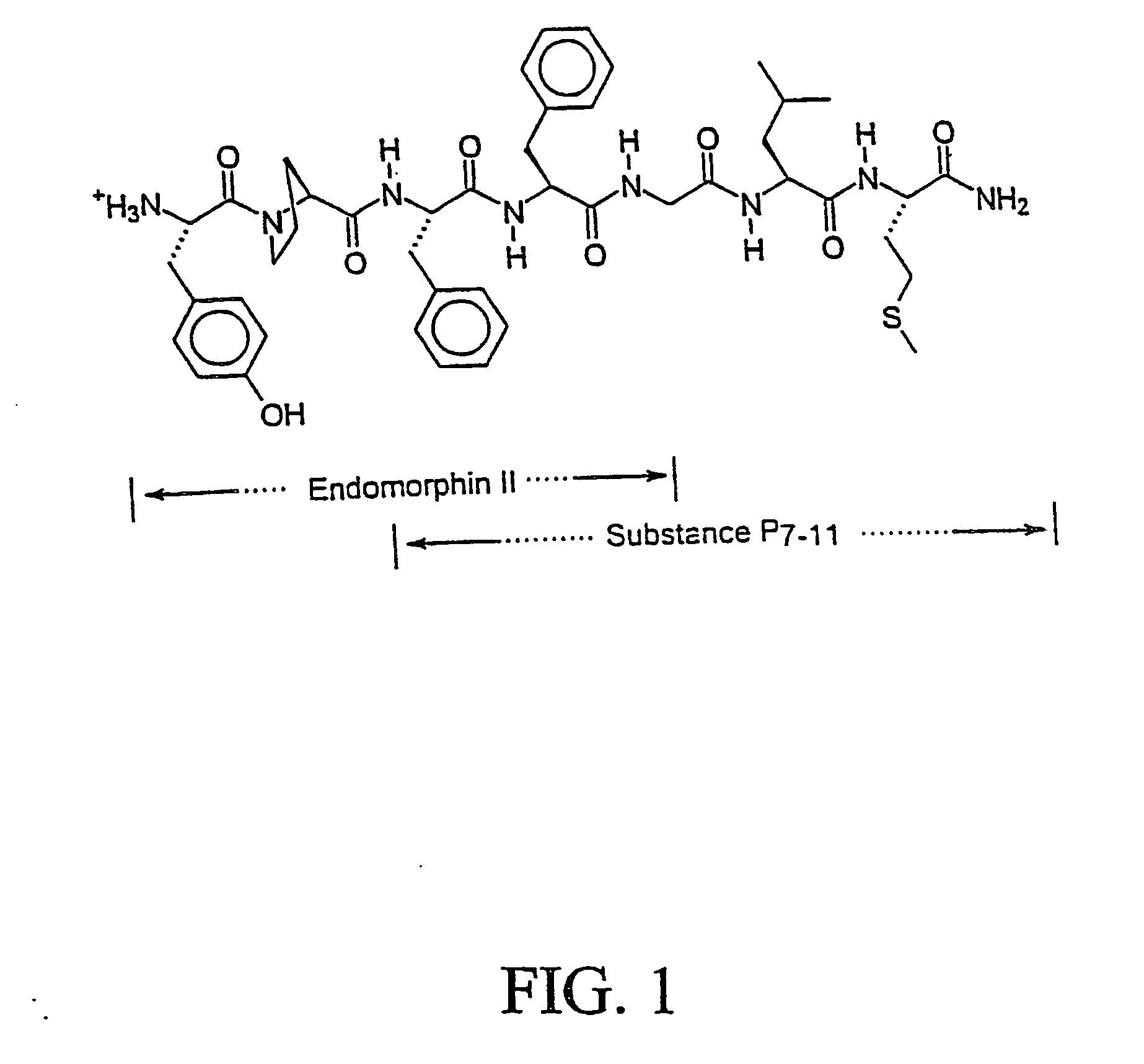
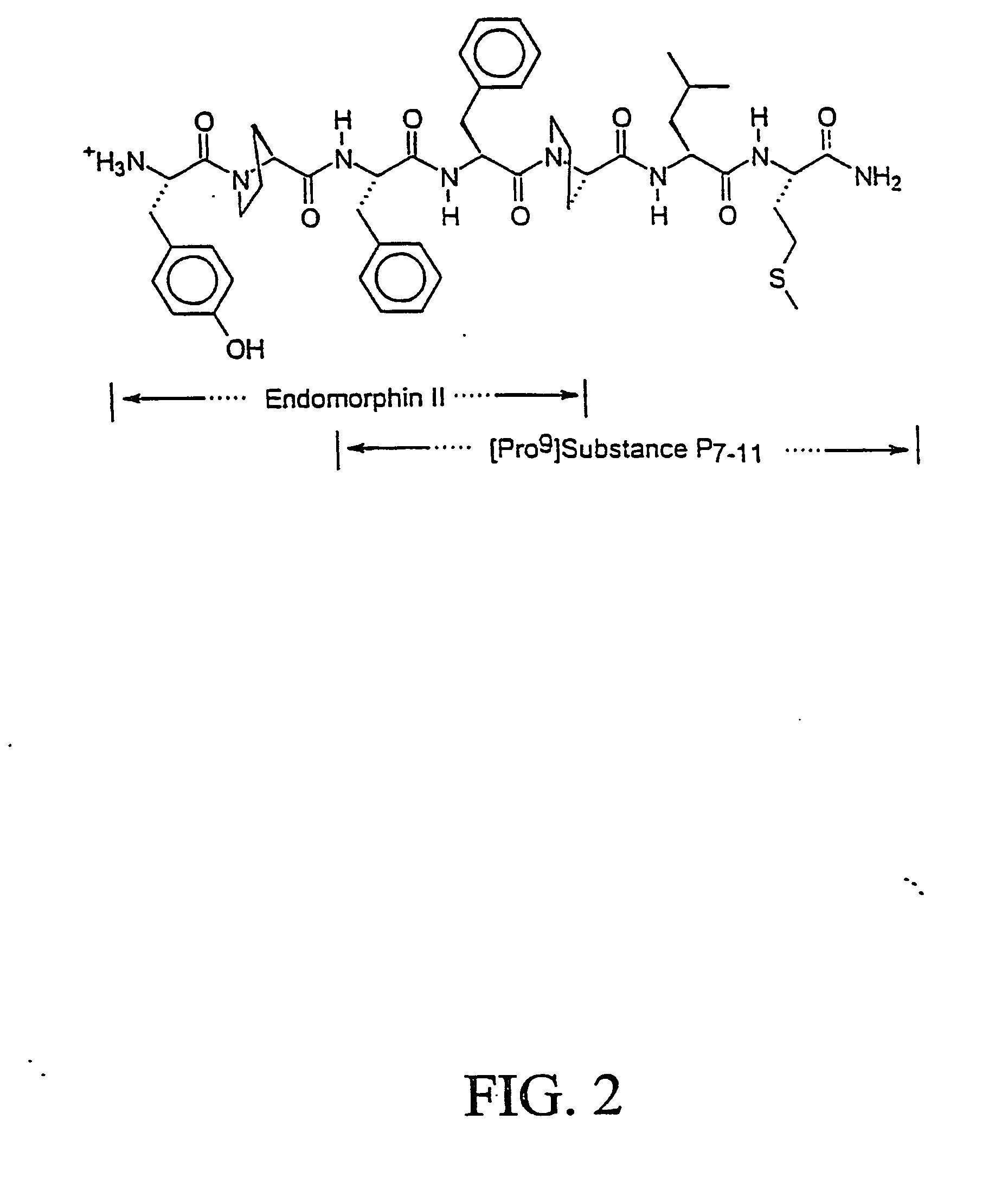
Novel chimeric analgesic peptides
a peptide and chimeric technology, applied in the field of pain treatment methods and compositions, can solve the problems of lowering the threshold for activation of nociceptors, frequent side effects, pruritis, etc., and achieves the effects of inhibiting the development of tolerance, enhancing the solubility of chimeric peptides, and reducing the risk of side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
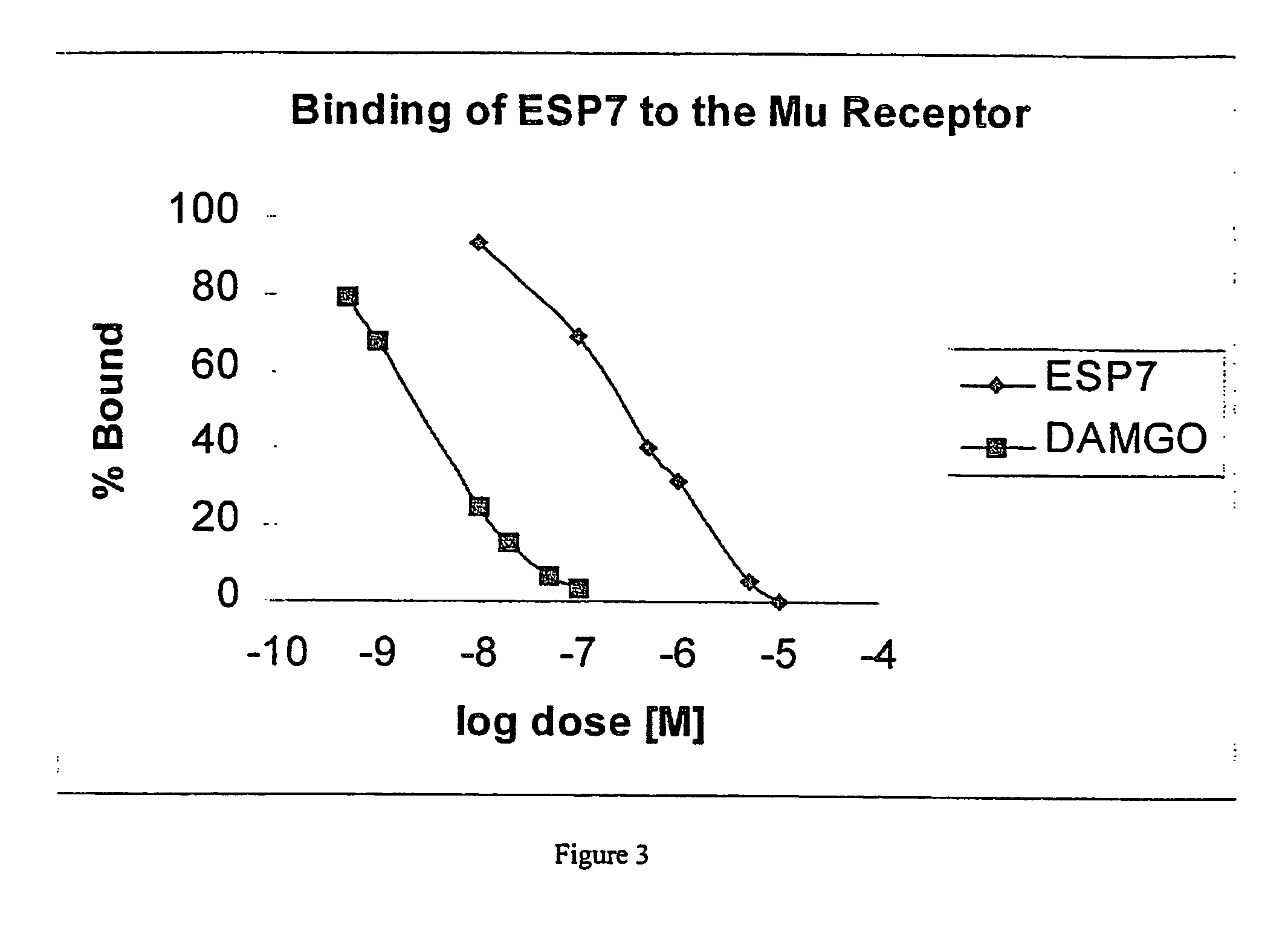
In Vitro Binding of ESP7 to Opioid and SP Receptors in Rat Brain Preparations
[0067] In order to assess the binding affinity of ESP7 to opioid and SP receptor, binding assays to opioid and SP receptors were performed with crude rat brain plasma membranes prepared using a modified procedure of Zadina Zadina et al., Life Sci, 55: 461-466 (1994). These assays showed that ESP7 has a strong affinity for both the μ receptor and the NK1 receptor in rat brain.
[0068] For binding assays to opioid receptors, frozen rat brains (−80° C.) were homogenized in 40 volumes of standard Tris buffer (50 mM Tris HCl (pH 7.4), 0.2 mg / ml BSA, 2.5 mM EDTA, 40 μg / ml bacitracin, 30 μg / ml bestatin and 5 mM MgCl1) and centrifuged at 15,000×g for 20 minutes. 100 mM NaCl was added to the buffer, in order to remove endogenous ligands, and the centrifugation was repeated After a wash with standard buffer, the membrane preparation was finally resuspended in 10 volumes of incubation buffer (standard buffer with 4 μg...
example 2
Characterization of the Analgesic Properties of ESP7
[0072] ESP7 was tested clinically in rats to determine analgesic effect and tolerance. The classical tail flick test was used to measure pain response and thermal pain was mimicked using a heat source. This system was controlled using standard opioids. The drug was administered with cyclodextran to increase solubility of the peptide in an aqueous solution.
[0073] 2.1 Intrathecal Administration of ESP7 in Rats and the Effects of Naltrexone and RP67580 Blockades
[0074] Intrathecal administration of ESP7 produced long-lasting analgesia without any significant development of tolerance. The opioid antagonist naltrexone blocked this analgesia, indicating that the analgesia was opioid in nature. Additionally, when the SP portion was antagonized with RP67580, an NK1 antagonist, tolerance to the drug developed within three days. These results indicate that the SP moiety of ESP7 does not contribute to the analgesia, but rather plays an inte...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com