Matrix treatment of damaged sandstone formations using buffered HF-acidizing solutions
a technology of hf acidizing solution and matrix treatment, which is applied in the direction of fluid removal, chemistry apparatus and processes, and borehole/well accessories. it can solve the problems of limiting the productive (or injective) capacity of the well, affecting the process of dissolving siliceous minerals, and affecting the formation effect of the well
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0040] About 100 ml of BJSSA and mud acid containing 12% HCl and 3% HF was placed into separate beakers. Then 2 grams of carbonate chips was added into the acids, under static conditions, at room temperature and at 180° F. and left to stand for 24 hours. The solubility of calcium carbonate in the HF-based acids is set forth in Table I:
TABLE IACIDSYSTEMSOBSERVATIONSBJSSANo effervescence or precipitation even after 24 hrs whenexamined at room temperature and at 180° F.Mud AcidStrong effervescence and formation of white precipitateafter initial 15 minutes at room temperature as well asat 180° F.
[0041] Table I illustrates the low reactivity of buffered HF-containing acidizing solution versus the rapid reaction of mud acid with calcium carbonate and the subsequent precipitation of calcium fluoride. The solubility of calcium carbonate is limited partly by the higher-than-normal pH of the buffered HF-acidizing solution (which reduces acid attack on the carbonate) and partly by the low so...
examples 2-5
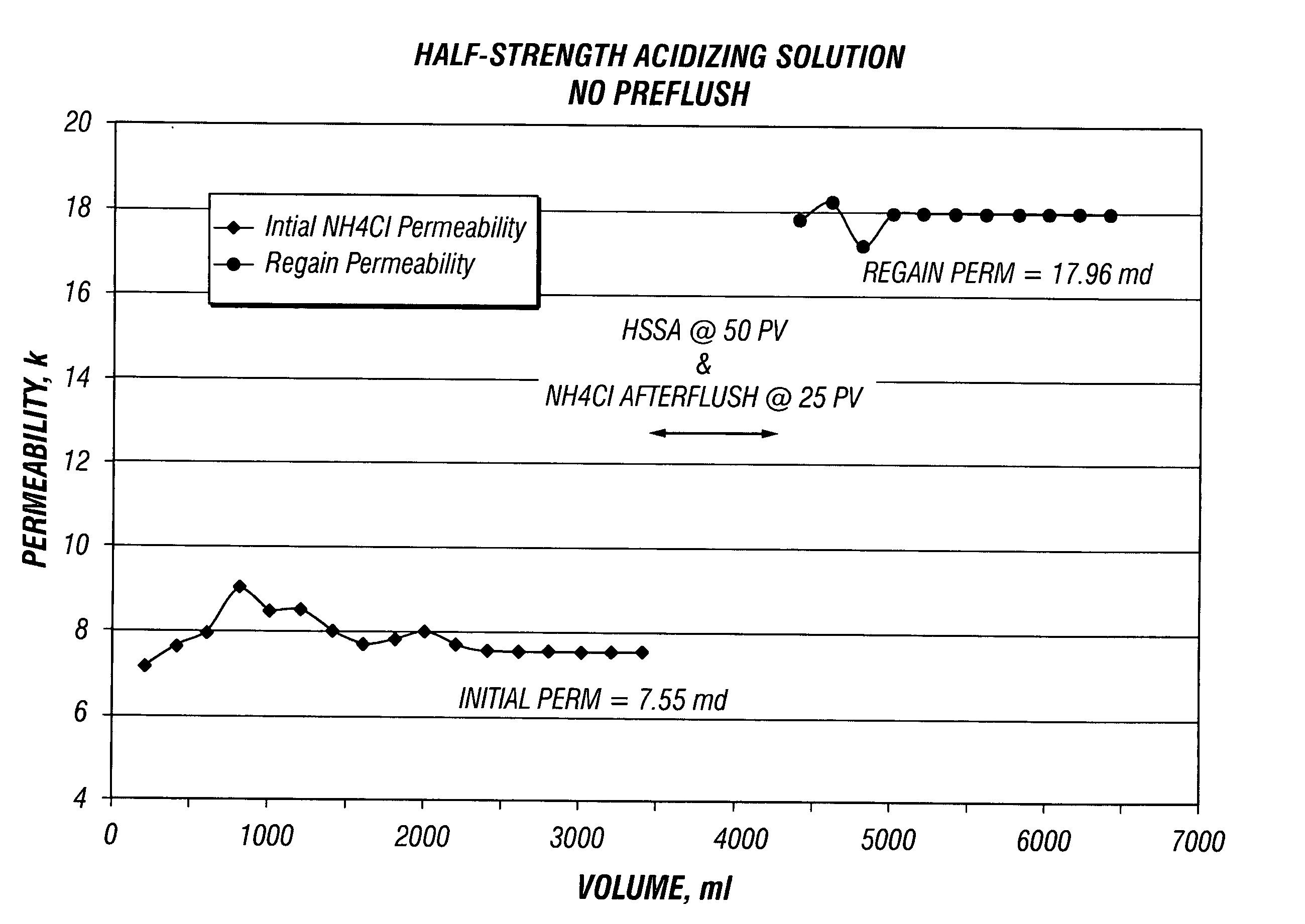
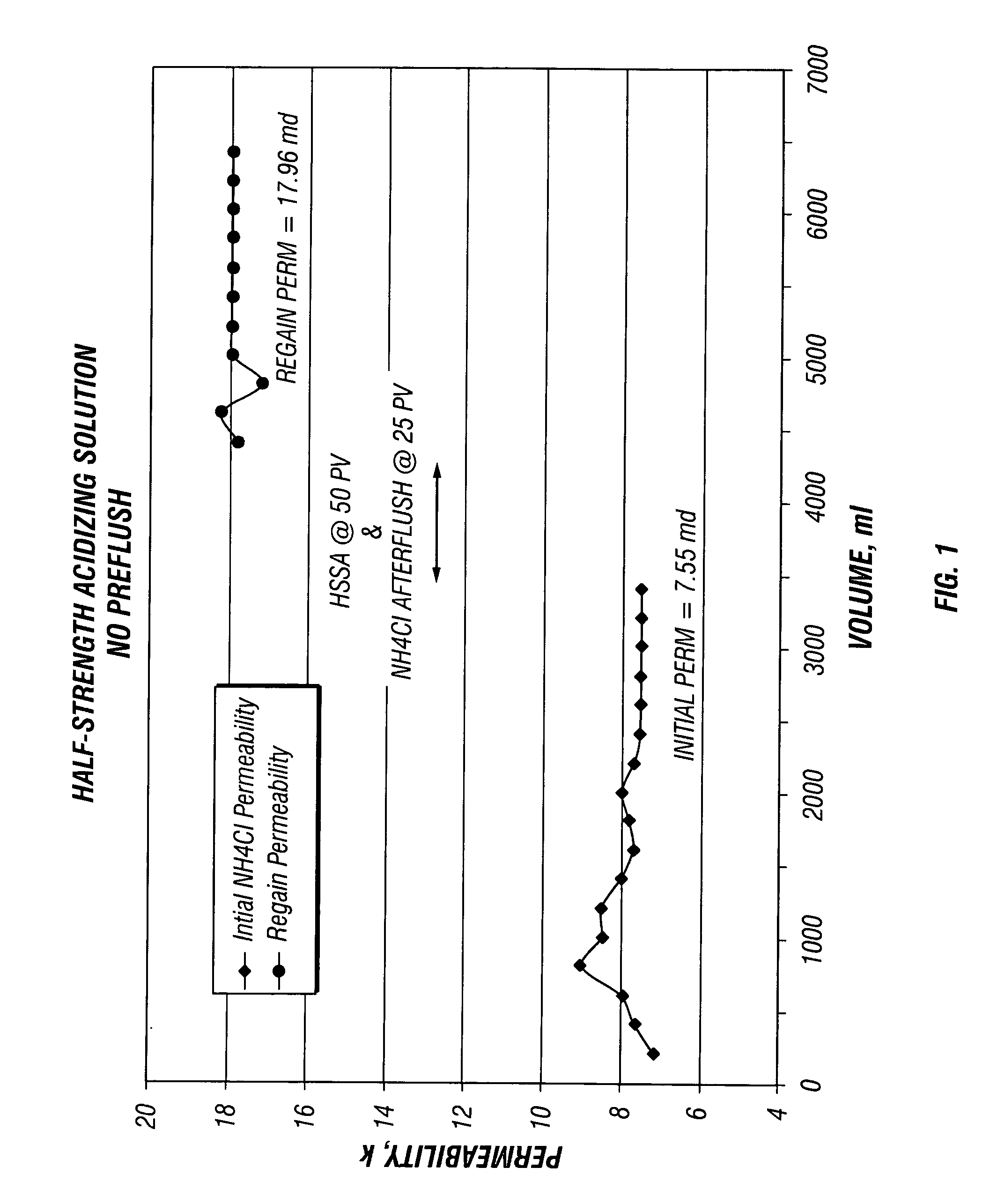
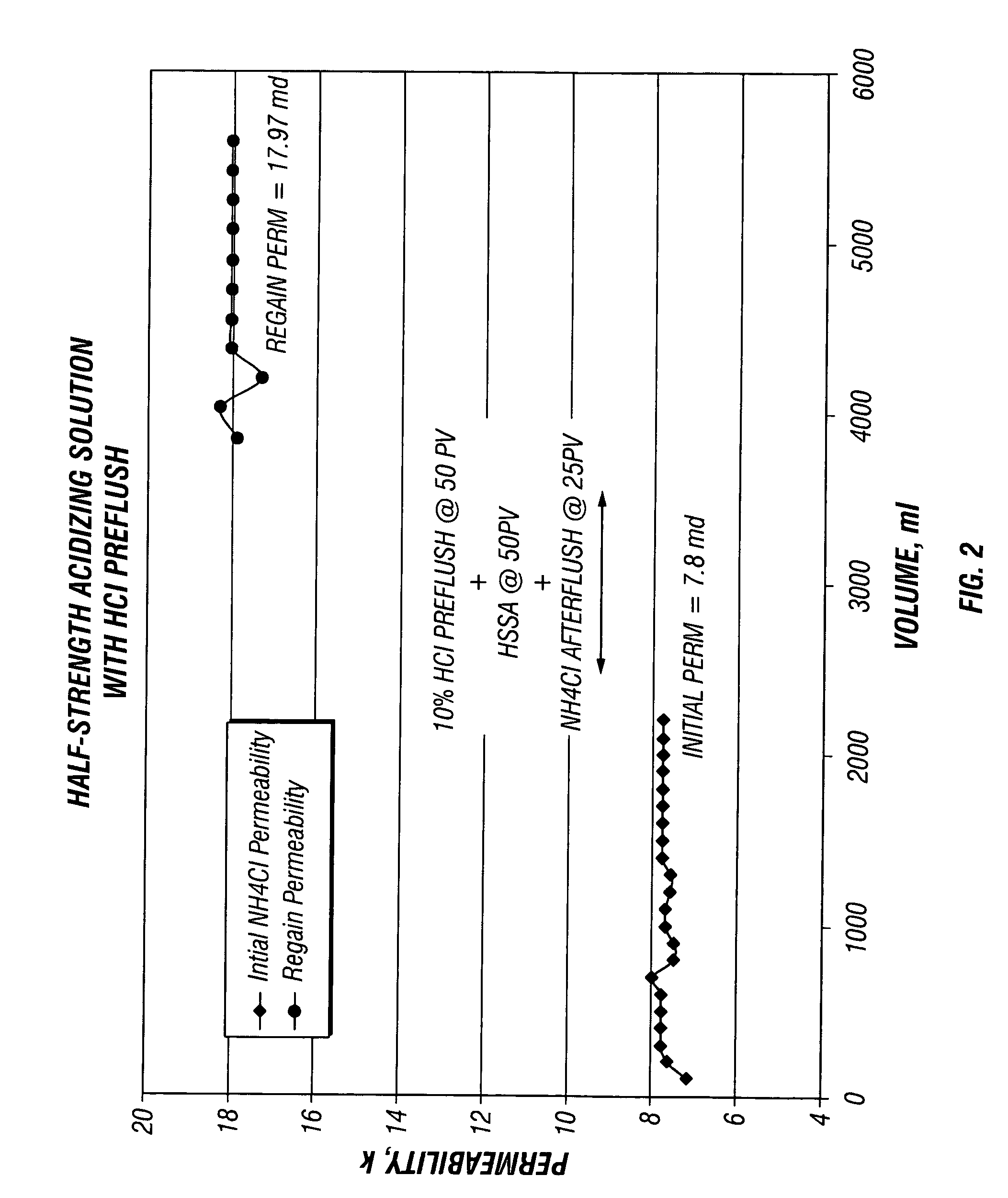
[0042] These Examples illustrate the effect of core flow testing using BJSSA on sandstone cores. Four separate core flow tests were conducted using 1.5 inch diameter and 2 inches length sandstone Berea core plugs with and without a preflush solution.
[0043] Prior to analysis, plugs were seated in rubber sleeves at 1000 psi confining pressure and flow saturated with filtered 3% NH4Cl containing a strongly water-wetting surfactant, NE-118 (a nonionic surfactant, a product of BJ Services Company) at 1 gpt. The surfactant was added to ensure that the sandstone was water wet and to avoid the formation of microemulsions.
[0044] The flow was established in an arbitrary formation to wellbore (production) direction with 3% NH4Cl brine to establish initial permeability. The flow was continued until a stable flow rate and permeability was obtained. [0045] 1. When flowing preflush, it was injected at 50 pore volumes in the reverse (injection) direction at constant flow rate of about 1 ml / min. W...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com