Stent for neutron capture therapy and method of manufacture therefor
a neutron capture and neutron technology, applied in the field of intravascular neutron capture therapy, can solve the problems of clogging the vessel, inaccurate dose distribution, and several problems common to all devices for this type of intravascular, and achieve the effect of large capture cross-section and easy repeatability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
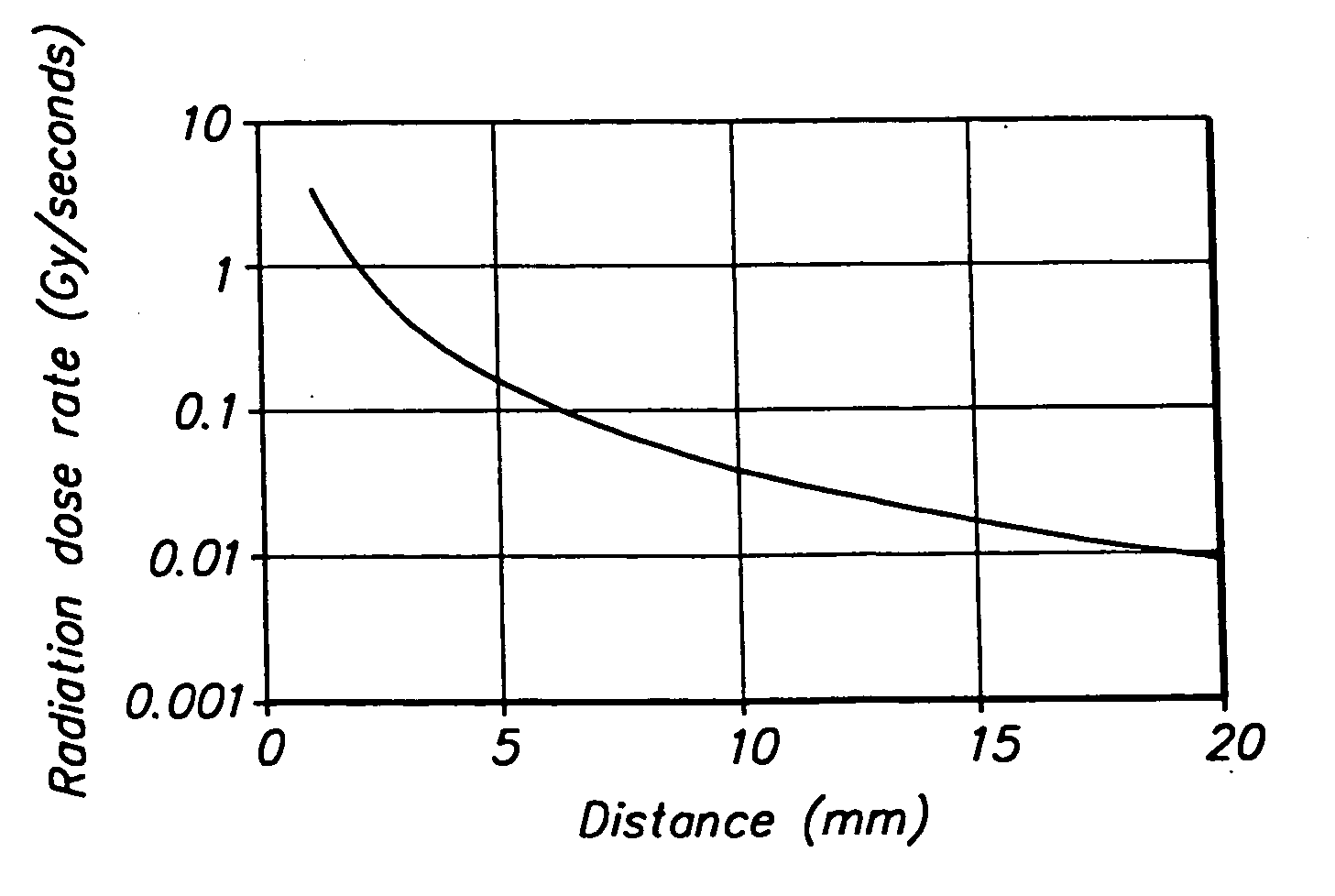
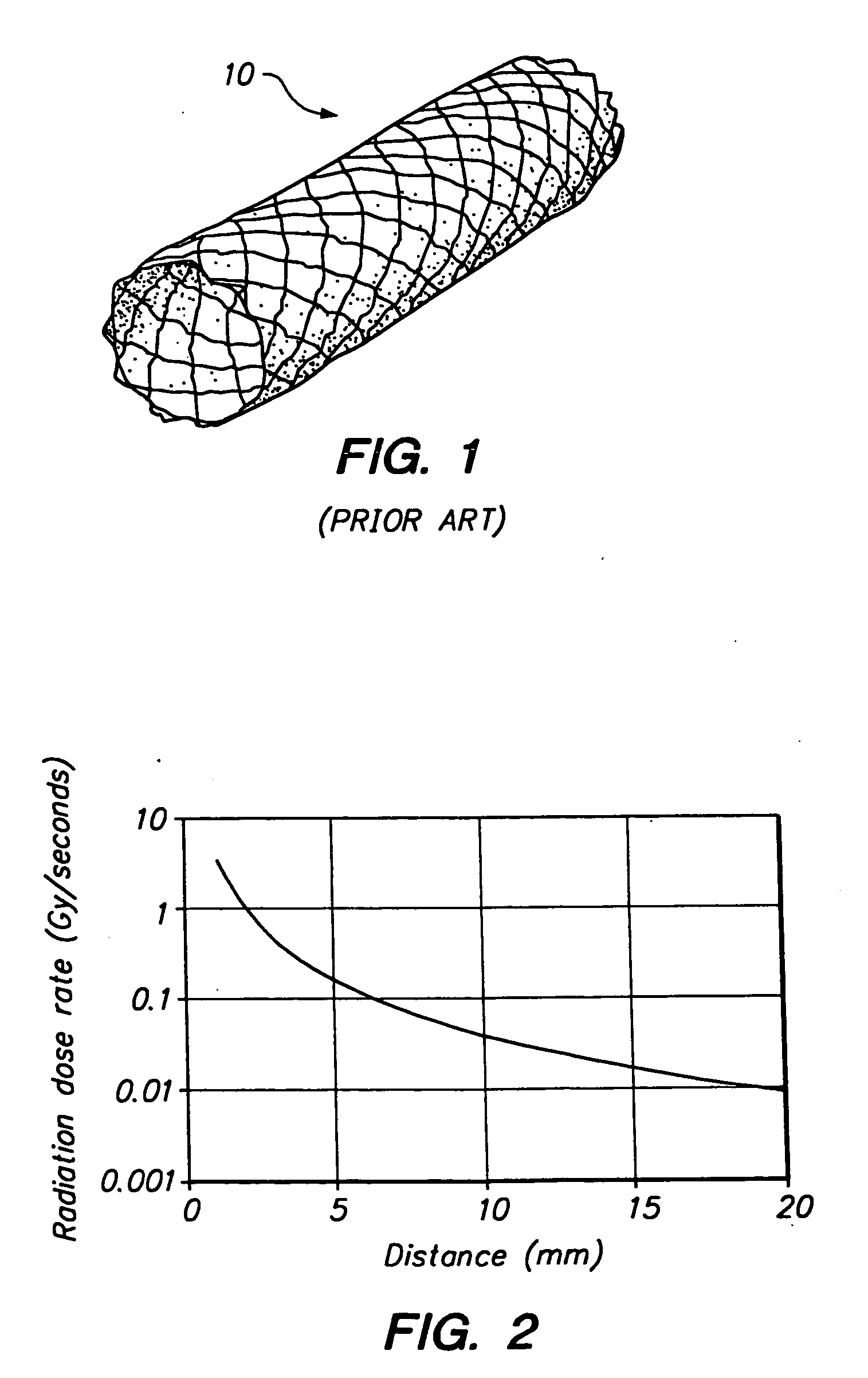
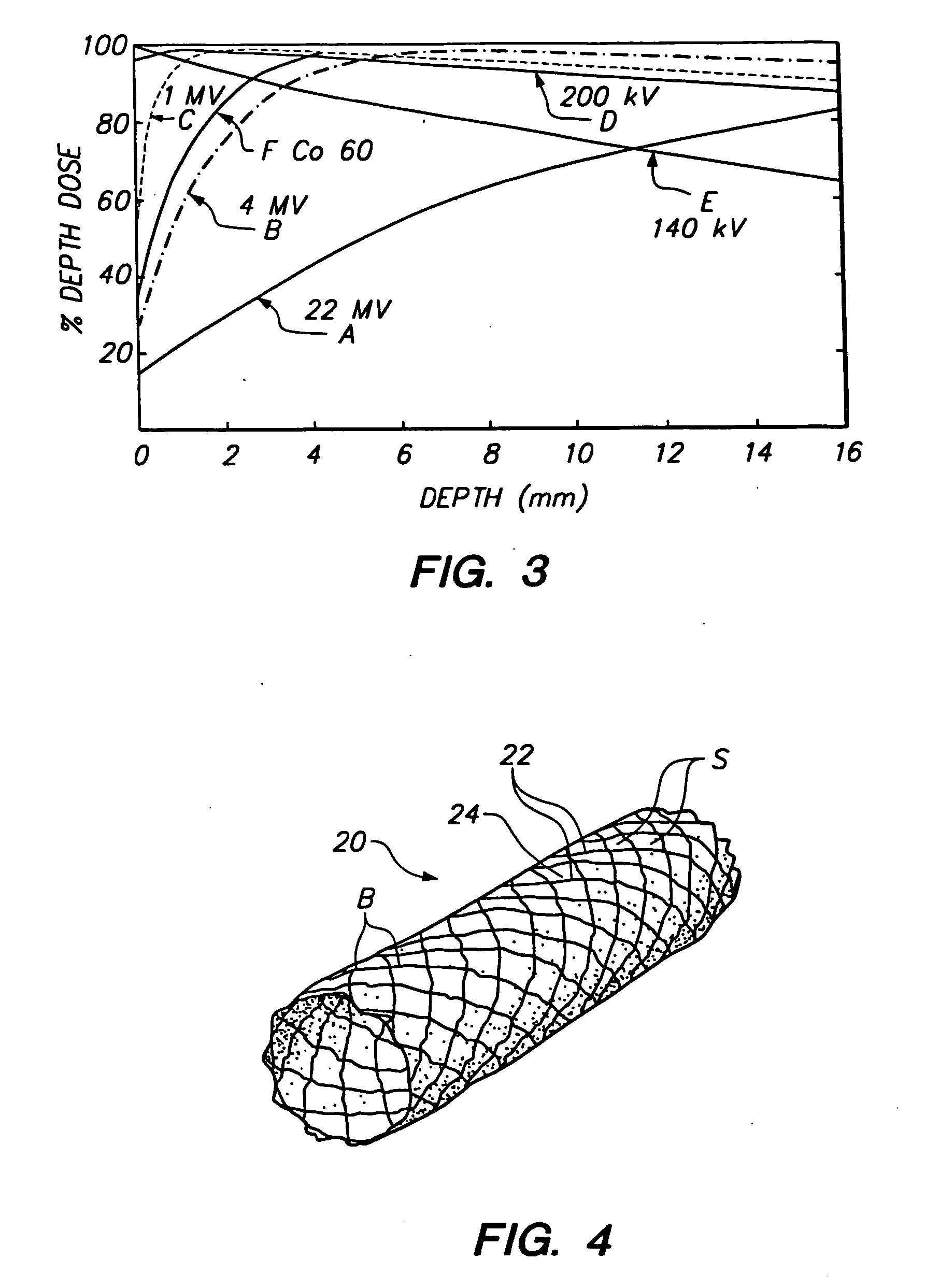
[0023] The present invention provides a stent comprising a stable nuclide element that may be externally activated by thermal neutrons, thereby providing localized neutron capture therapy in the vicinity of the vessel around the stent. Since radiation is applied by an external source, therapy may be delivered at any time after placement of the stent and easily may be repeated. Furthermore, unlike other known radiation techniques, the present invention ensures that neutron capture therapy is only provided to patients where radiation exposure is expected to provide therapeutic benefit.
[0024] In accordance with the principles of the present invention, a stent is constructed including a material having a high neutron capture cross-section, for example, greater than 103 barns, and that provides a high quality of radiation emission. As will of course be apparent, the irradiation dose provided by the stent after irradiation by an external source also depends upon the amount of stable nucl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com