Trans-septal catheter with retention mechanism
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
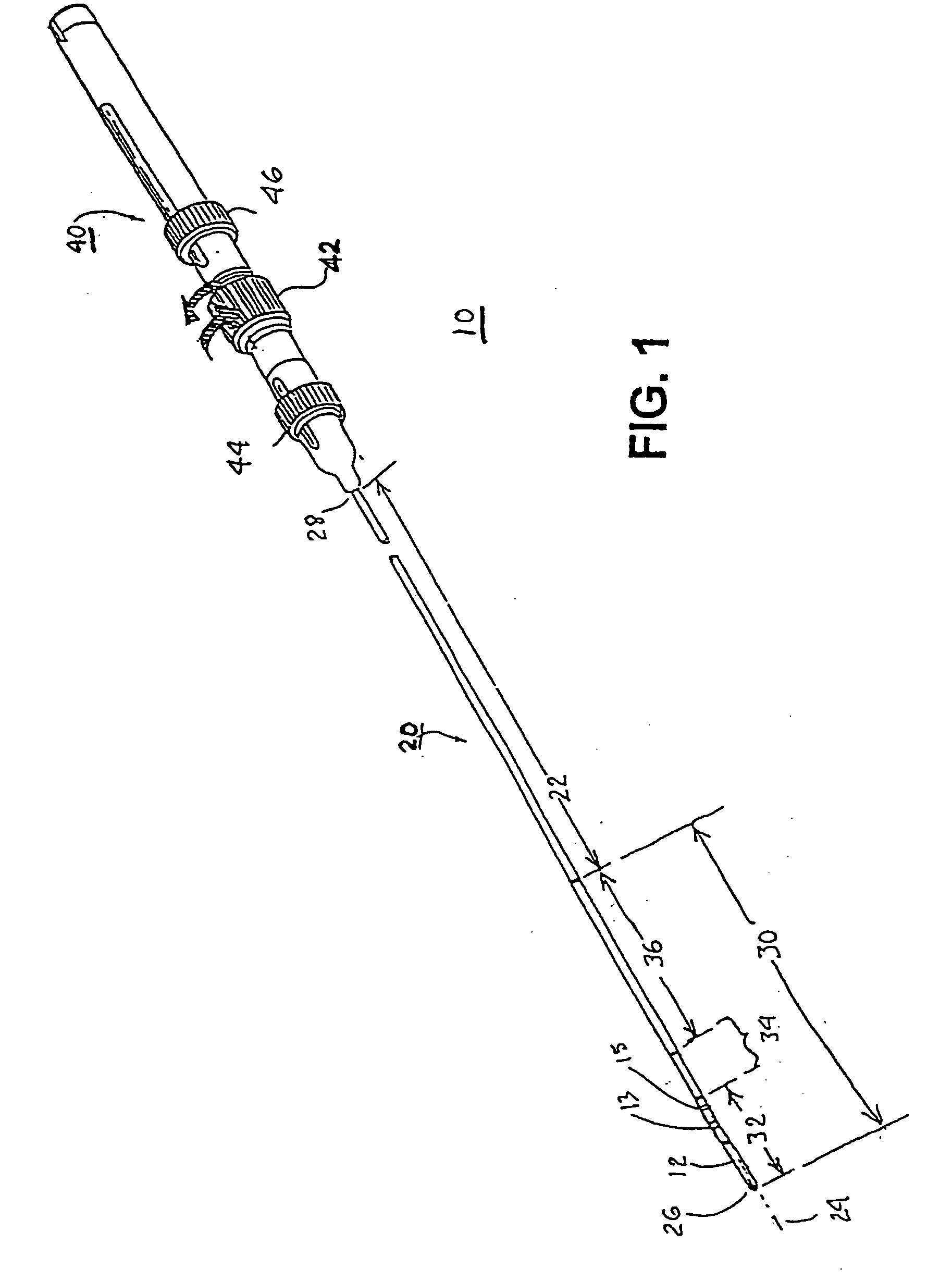
[0048]FIG. 3 is a simplified schematic illustration of a guide catheter 70 of the present invention having a deployable retention mechanism comprising an expandable balloon 78 expanded in the LA and drawn against the septal wall in the LA of the septum 66 to inhibit retraction of the guide catheter distal segment 76 into the RA. FIG. 4 is a cross-section view along lines 4-4 of FIG. 3 depicting the guide catheter lumen 72 and balloon inflation / deflation lumen 82 within the guide catheter body 80.
[0049] The inflatable balloon 78 is inflated and deflated through the inflation / deflation lumen 82 that extends within the guide catheter body 80 from a proximal inflation port 86 at the guide catheter proximal end 74 to a balloon inflation port 84 within the inflatable balloon 78. The inflation medium (preferably a fluid, e.g., saline or a radiopaque solution) is introduced through the balloon inflation / deflation lumen 82 to inflate the balloon 78 after the deflated balloon 78 is advanced t...
second embodiment
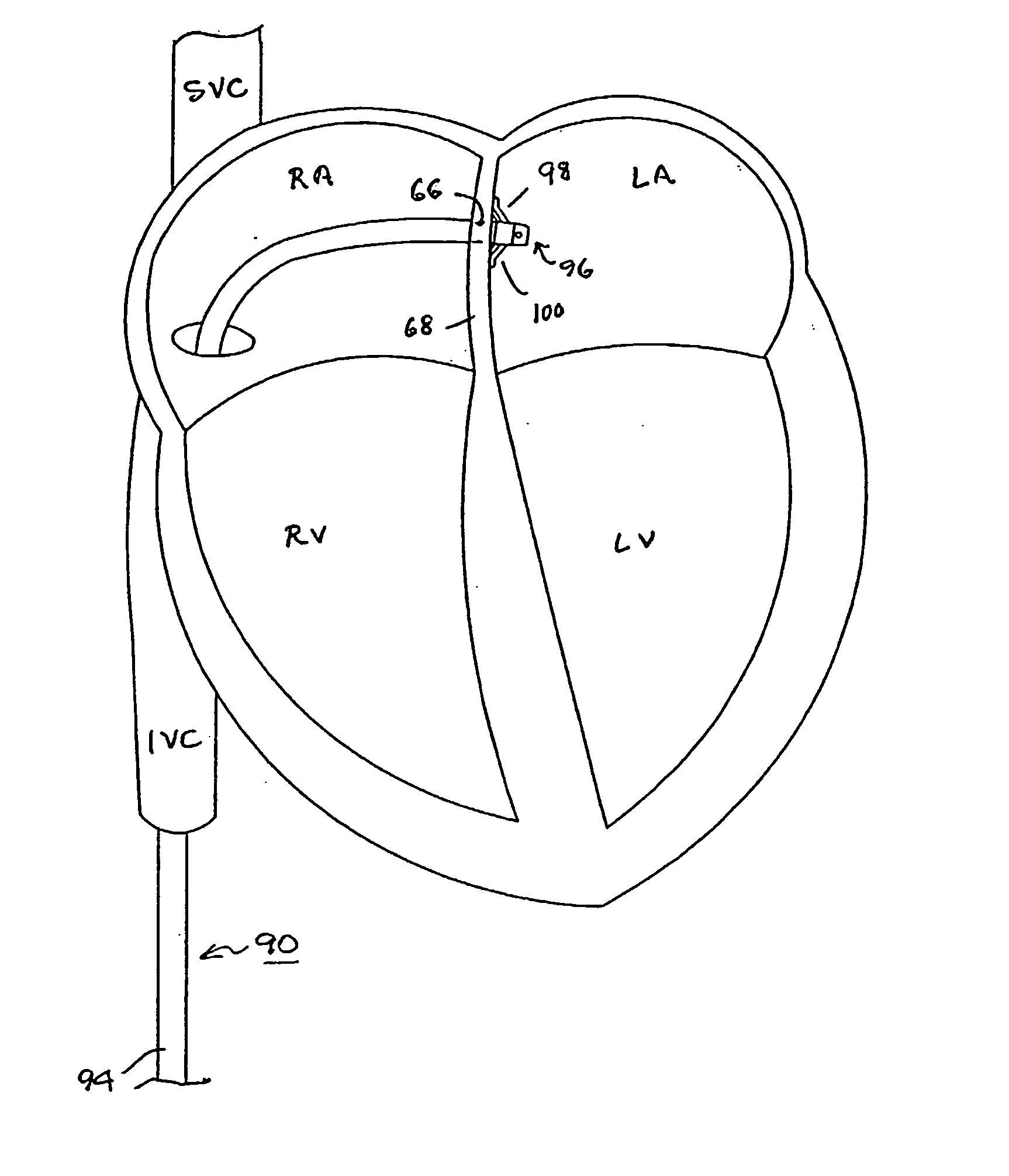
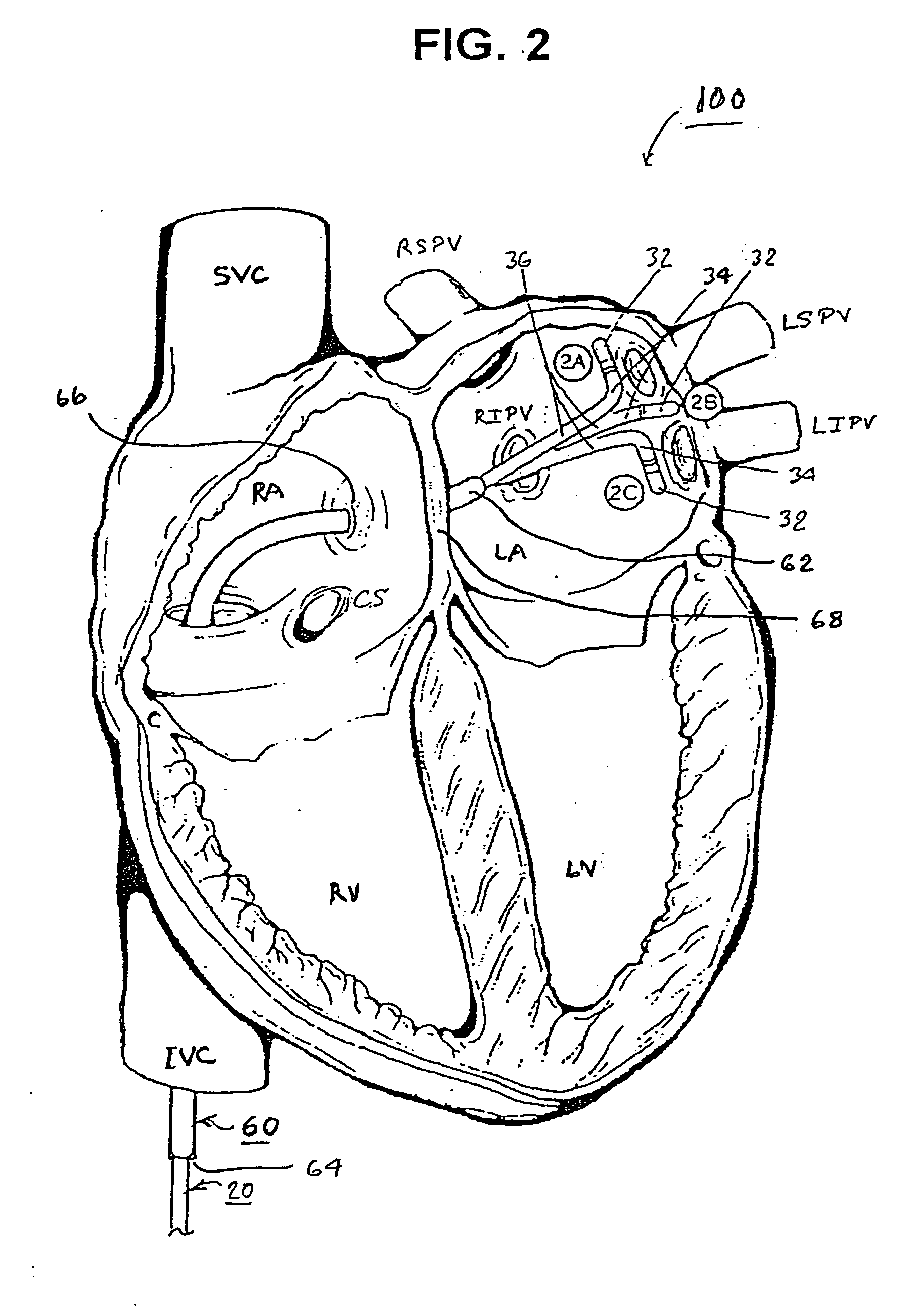
[0051]FIG. 5 illustrates a guide catheter 90 of the present invention having a self deployed retention mechanism that includes a plurality of pliant tines 98,100 drawn against the septum in the LA to inhibit retraction of the guide catheter distal segment 96 through the perforation 66 into the RA. FIG. 6 is an end view of the distal segment 96 of the guide catheter of FIG. 5 depicting the guide catheter lumen 92 and outwardly extending tines 98 and 100.
[0052] Each such flexible, pliant, tine 98,100 extends outwardly from a tine attachment 102,104 with the distal segment of the guide catheter body to a respective tine free end 106,108. Preferably, the flexible, pliant, tines 98, 100 extend proximally and outwardly from the respective tine attachments 102,104 with the guide catheter body 94 at an acute angle to the guide catheter body 94. The tines 98,100 can be rectangular or circular in cross-section and can be thinner or thicker than depicted and longer or shorter than depicted. Th...
third embodiment
[0055]FIG. 7 illustrates a guide catheter 110 of the present invention having a deployable retention mechanism that includes an extendable wire 112 that forms a wire coil 114 when extended from a wire deployment lumen 118 (shown in FIG. 12) into the LA and inhibits retraction of the guide catheter distal segment 116 into the RA. The catheter body 122 encloses a guide catheter lumen 124 (FIG. 12) adapted to receive a mapping / ablation EP catheter and the wire deployment lumen 118 extending between a deployment lumen proximal end opening and a deployment lumen distal end opening in the distal segment 120. FIG. 8 shows the extendable wire 112 that forms a wire coil 114 when extended into the LA retracted into the wire lumen 118 during introduction into or withdrawal from the RA of the distal segment 116 through the perforation 66 in the septum 68.
[0056] In use, the elongated retention wire 112 is extended at guide catheter proximal end 126 through the wire deployment lumen 118 to dispos...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com