Patents
Literature
94 results about "Pass the hash" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
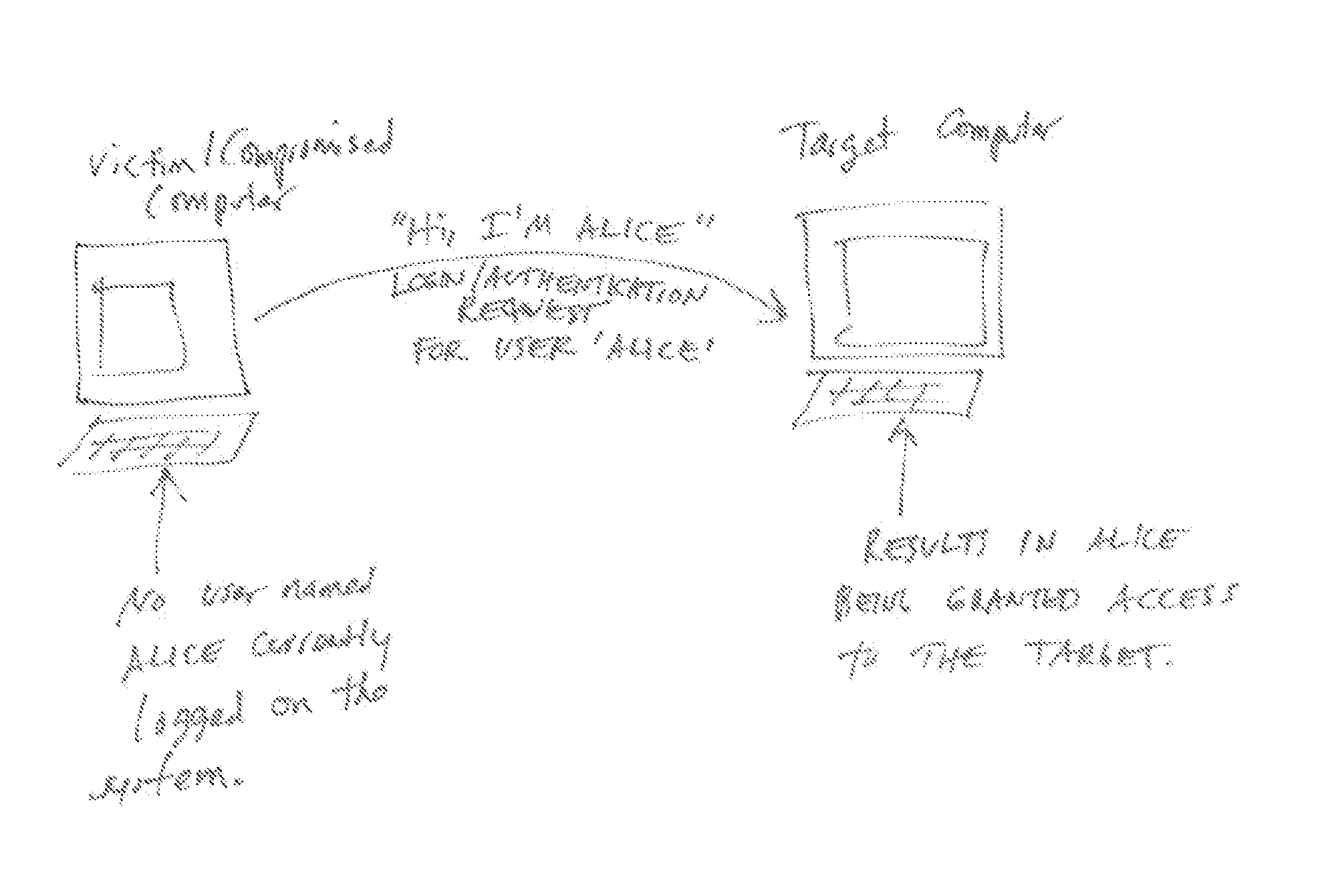
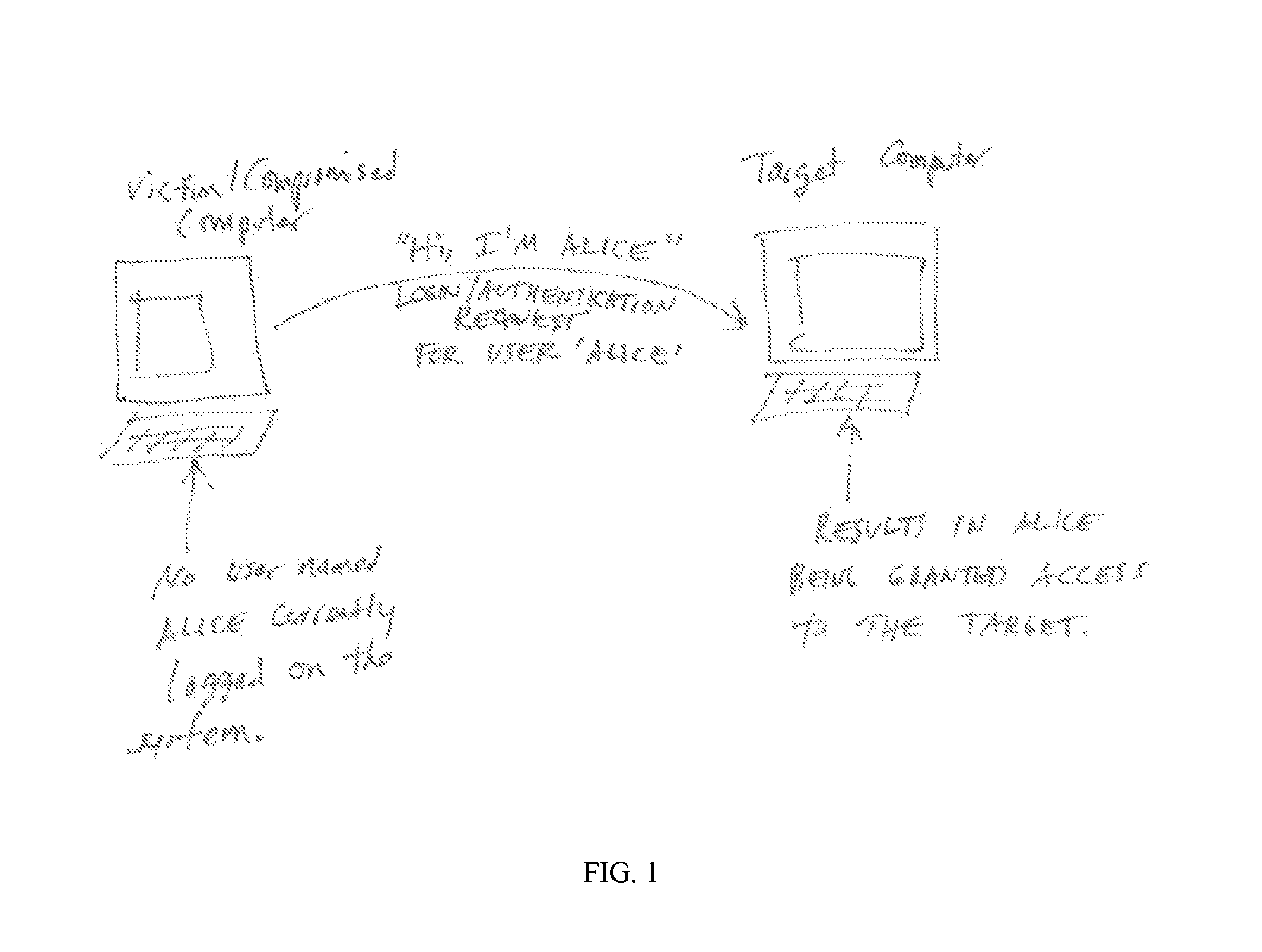
In cryptanalysis and computer security, pass the hash is a hacking technique that allows an attacker to authenticate to a remote server or service by using the underlying NTLM or LanMan hash of a user's password, instead of requiring the associated plaintext password as is normally the case. This is an example of security through obscurity, as it merely kicks the can down the road, by moving the goalposts. It replaces the need for stealing the plaintext password with merely stealing the hash and using that to authenticate with.
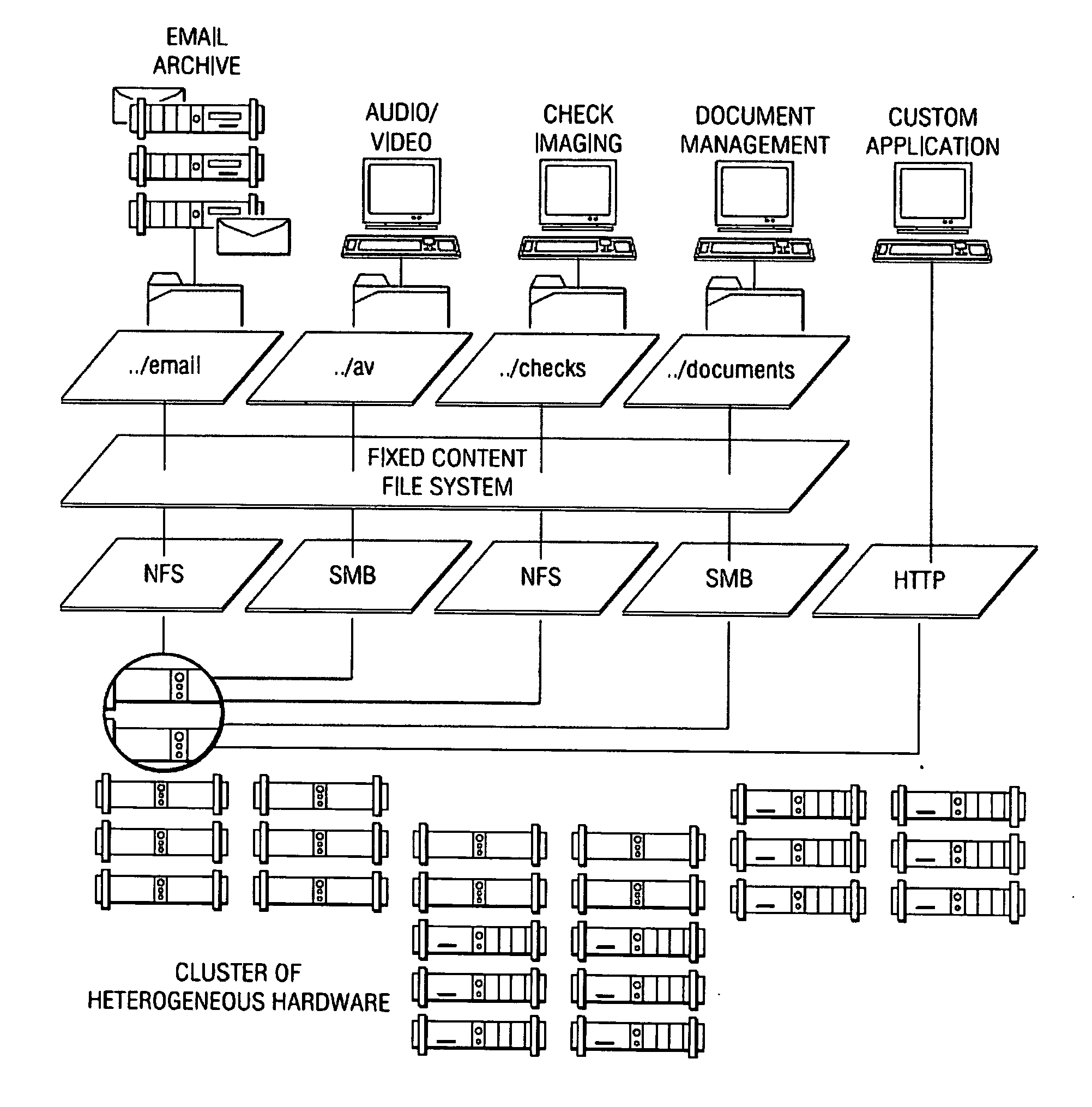
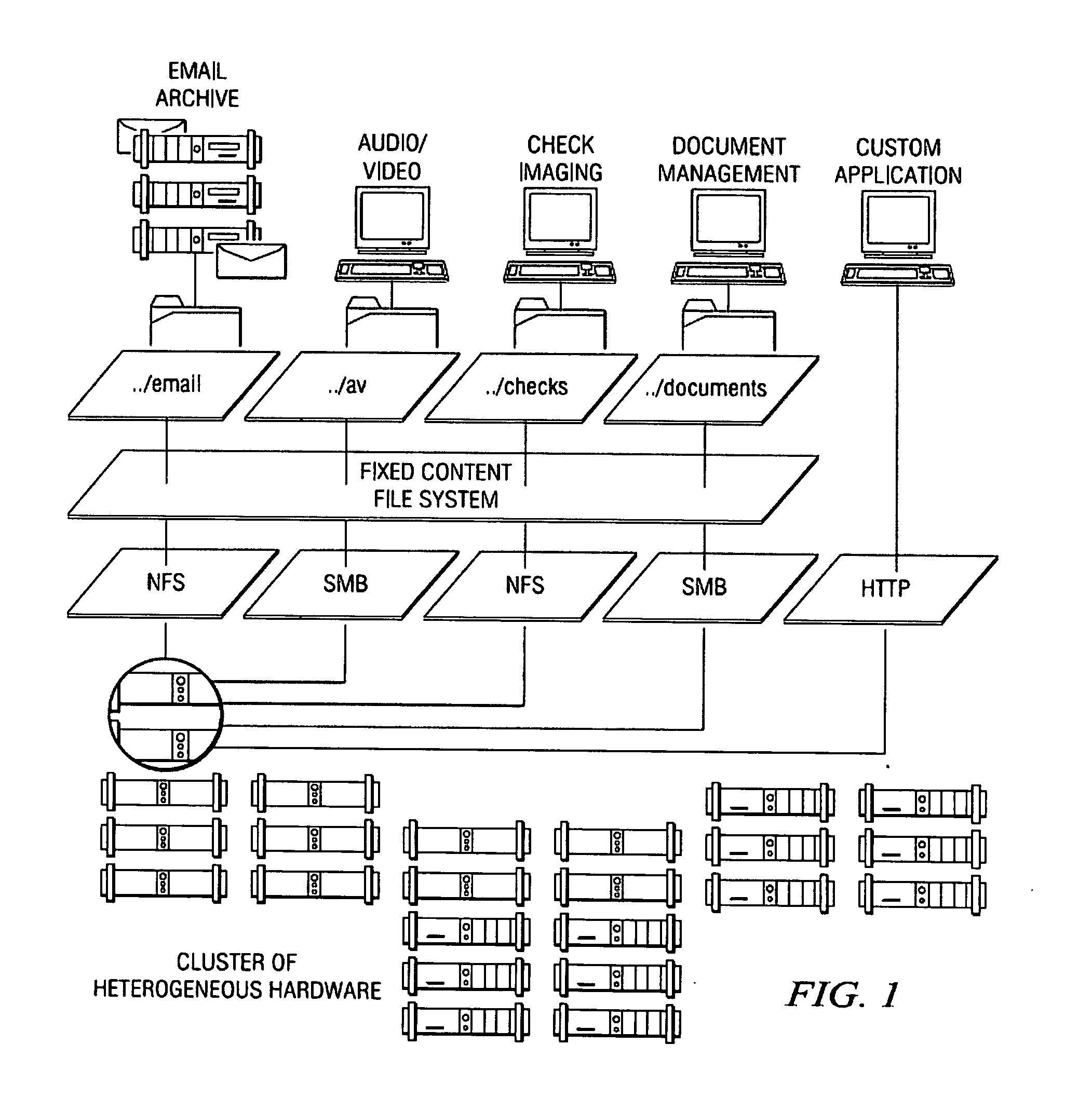
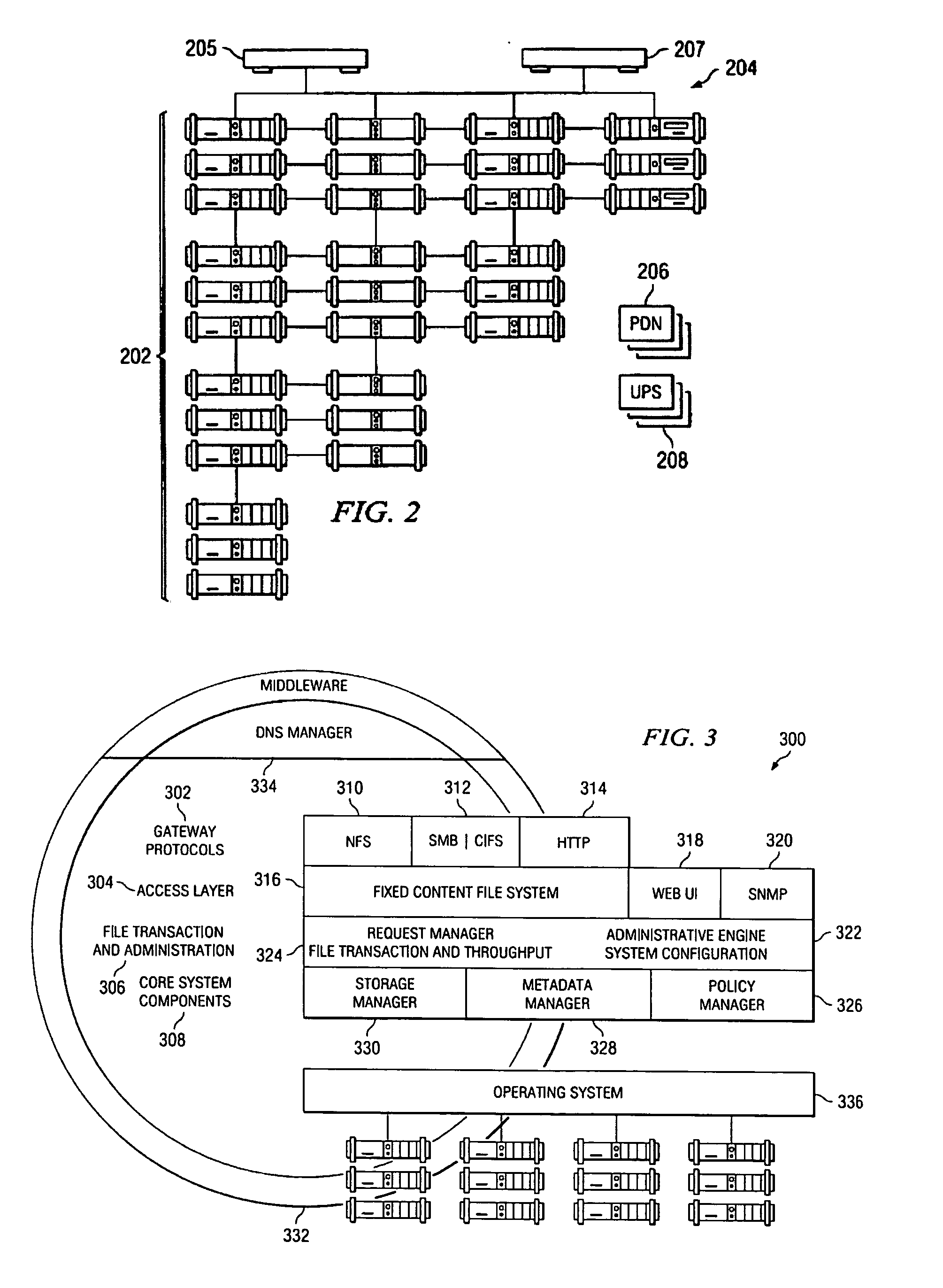
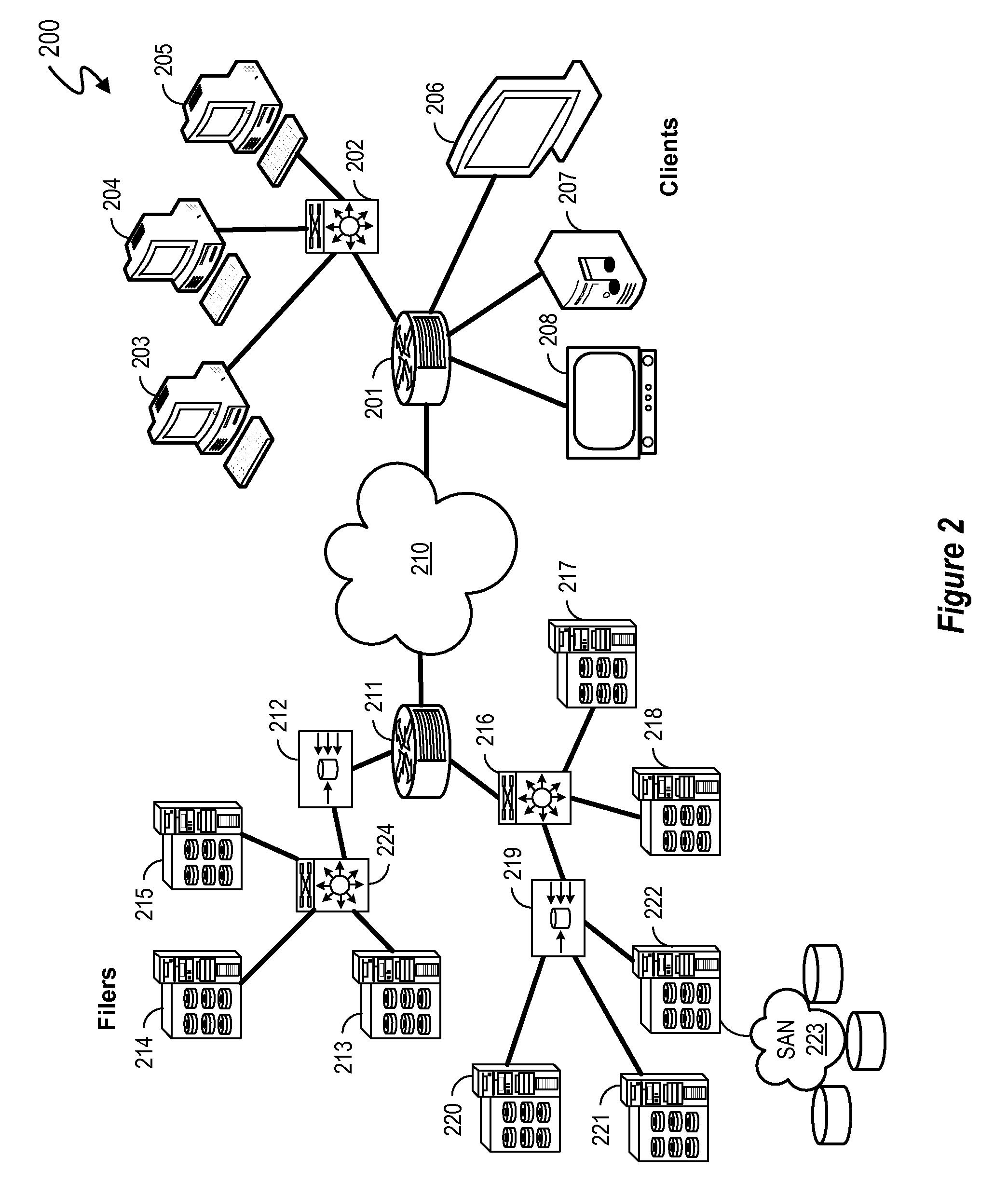
Metadata Management for fixed content distributed data storage
ActiveUS20060026219A1Improve usabilityDigital data processing detailsError detection/correctionMetadata managementDistributed data store
An archival storage cluster of preferably symmetric nodes includes a metadata management system that organizes and provides access to given metadata, preferably in the form of metadata objects. Each metadata object may have a unique name, and metadata objects are organized into regions. Preferably, a region is selected by hashing one or more object attributes (e.g., the object's name) and extracting a given number of bits of the resulting hash value. The number of bits may be controlled by a configuration parameter. Each region is stored redundantly. A region comprises a set of region copies. In particular, there is one authoritative copy of the region, and zero or more backup copies. The number of backup copies may be controlled by a configuration parameter. Region copies are distributed across the nodes of the cluster so as to balance the number of authoritative region copies per node, as well as the number of total region copies per node. Backup region copies are maintained synchronized to their associated authoritative region copy.
Owner:HITACHI VANTARA LLC
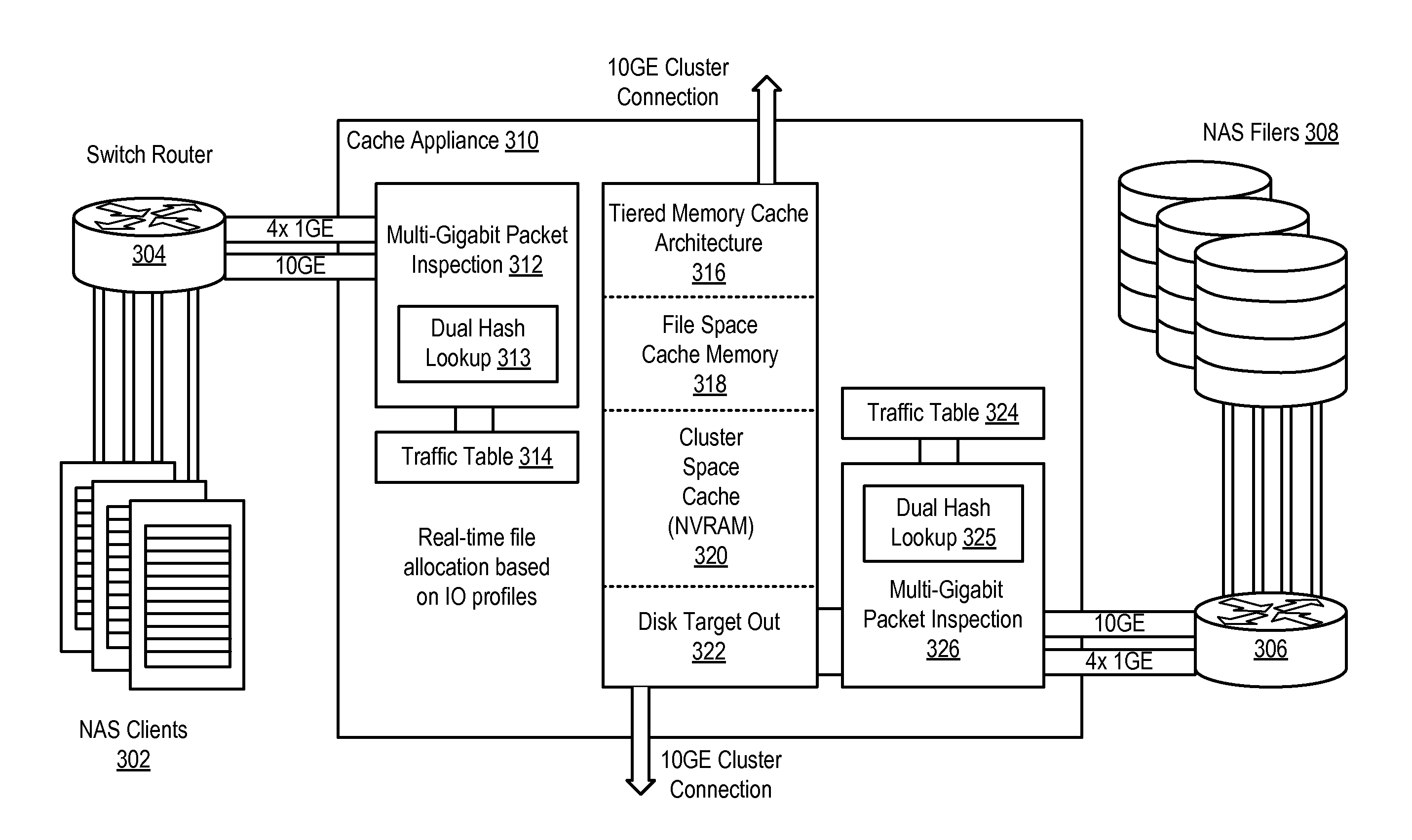
Dual Hash Indexing System and Methodology
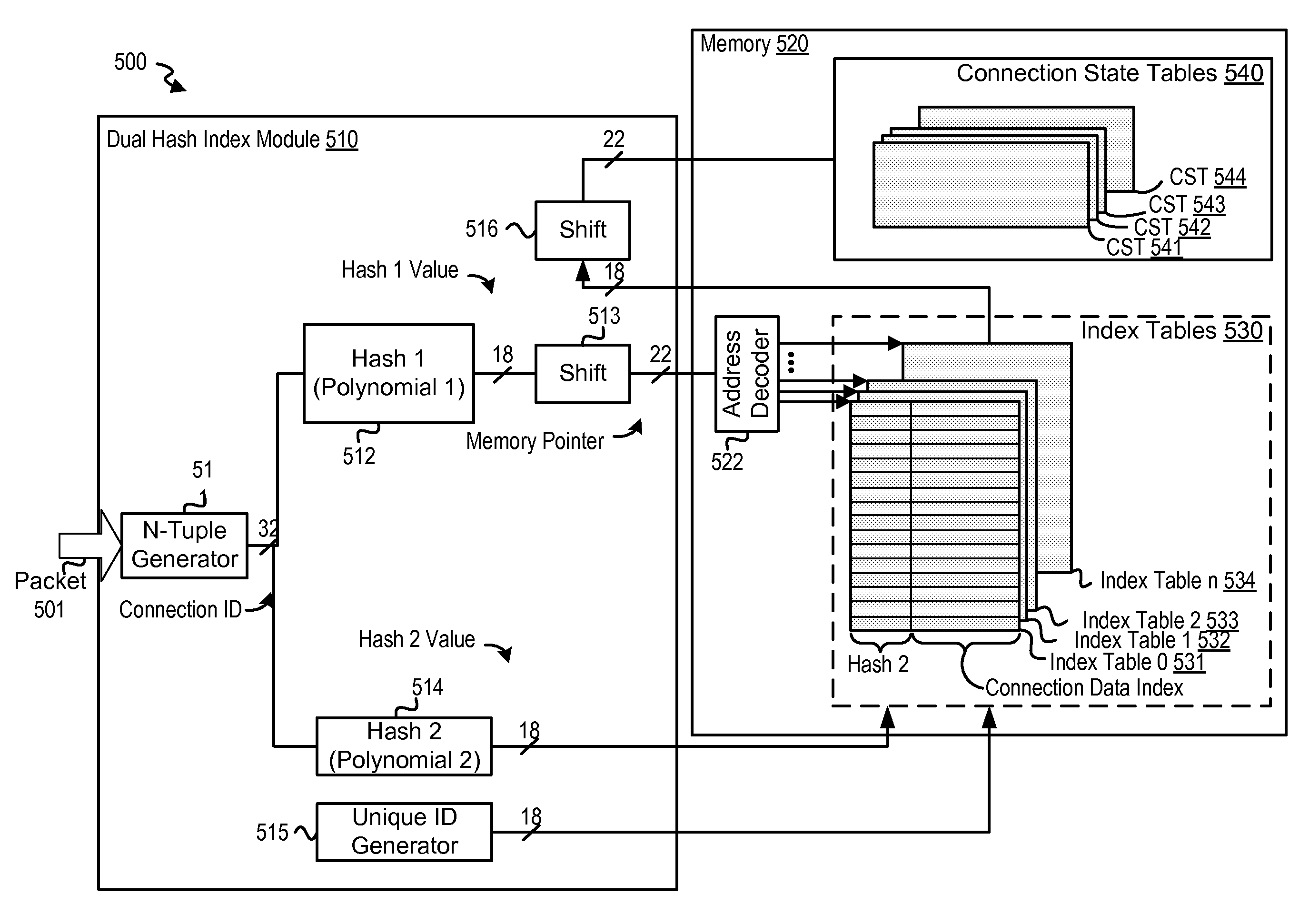
ActiveUS20100023726A1Fixed processing costFast computerMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityClient-side
A method, system and program are disclosed for accelerating data storage in a cache appliance that transparently monitors NFS and CIFS traffic between clients and NAS subsystems and caches files in a cache memory by using a dual hash technique to rapidly store and / or retrieve connection state information for cached connections in a plurality of index tables that are indexed by hashing network protocol address information with a pair of irreducible CRC hash algorithms to obtain an index to the memory location of the connection state information.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Memory efficient hashing algorithm
InactiveUS20050171937A1Efficient searchFew processing timeDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsTerm memoryComputer science
A technique efficiently searches a hash table. Conventionally, a predetermined set of “signature” information is hashed to generate a hash-table index which, in turn, is associated with a corresponding linked list accessible through the hash table. The indexed list is sequentially searched, beginning with the first list entry, until a “matching” list entry is located containing the signature information. For long list lengths, this conventional approach may search a substantially large number of list entries. In contrast, the inventive technique reduces, on average, the number of list entries that are searched to locate the matching list entry. To that end, list entries are partitioned into different groups within each linked list. Thus, by searching only a selected group (e.g., subset) of entries in the indexed list, the technique consumes fewer resources, such as processor bandwidth and processing time, than previous implementations.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
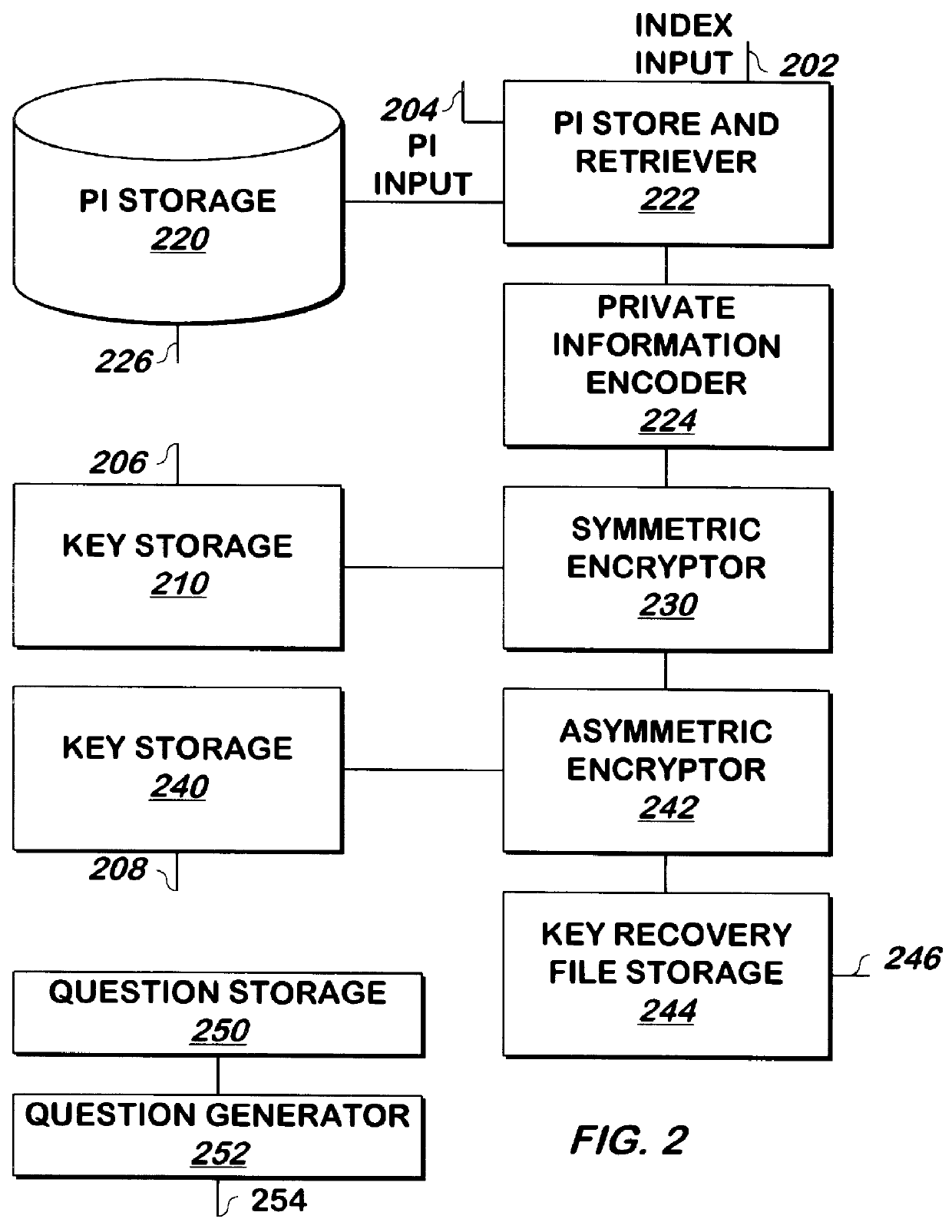
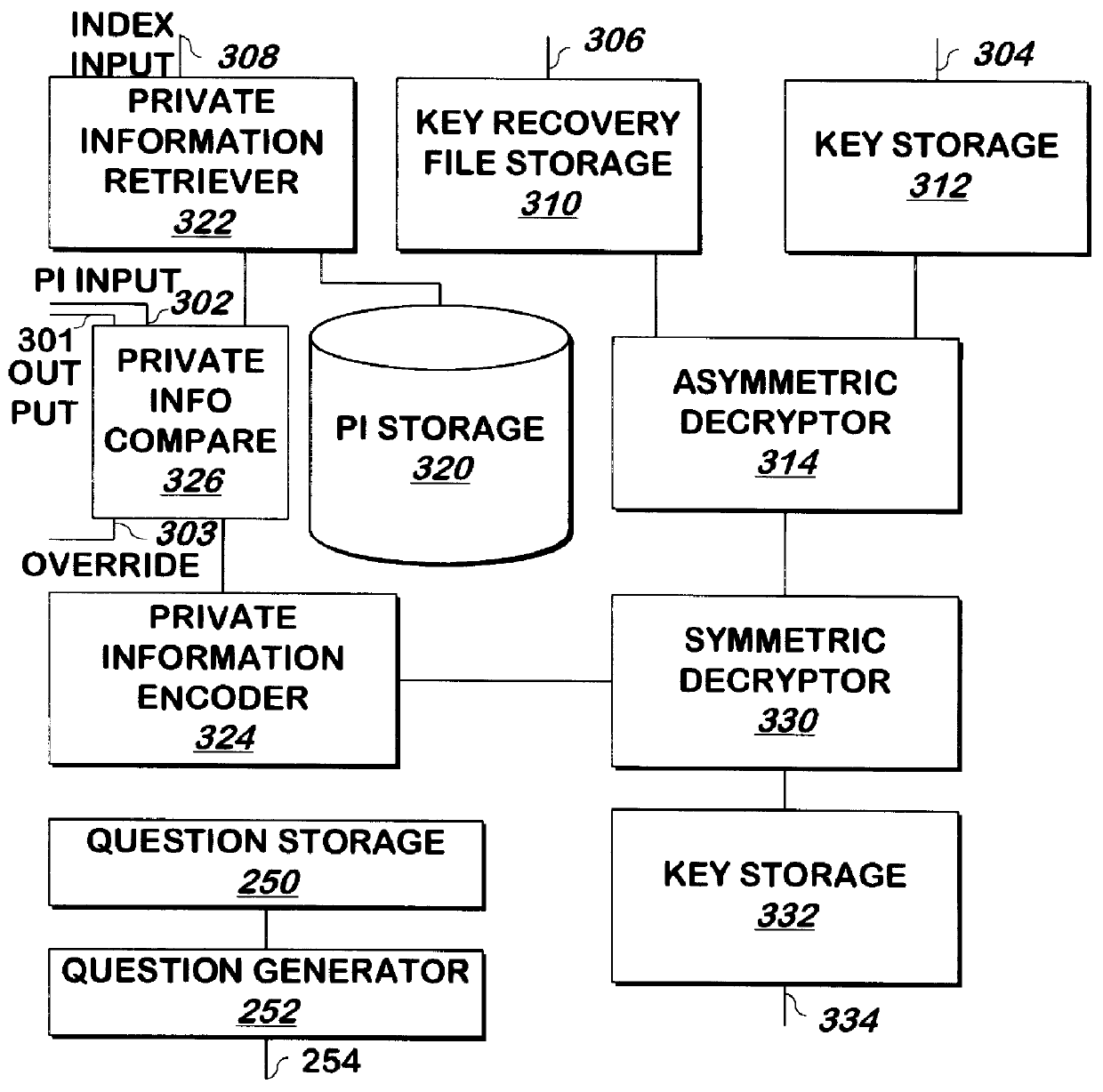
Methods and apparatus for recovering keys
A key such as a private key or key password of a private key is encrypted for storage, and may be decrypted if the private key becomes lost or unavailable. The key is encrypted by encoding, for example, by hashing, private information such as mother's maiden name and social security number, and the result is used as a key to encrypt the private key using DES or another symmetric encryption technique. The encrypted key is again encrypted, for example using asymmetric encryption, using the public key of a trusted party such as the certificate authority that generated the private key. The result may be stored as a key recovery file by the principal of the private key or another party. To decrypt the key recovery file, the private key corresponding to the public key used to encrypt the key recovery file is used to decrypt the key recovery file, for example by asymmetric decryption. The result is symmetrically decrypted using a key obtained by encoding, for example, by hashing, the private information in the same manner as was used to encrypt the key. The result of this decryption is the key.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
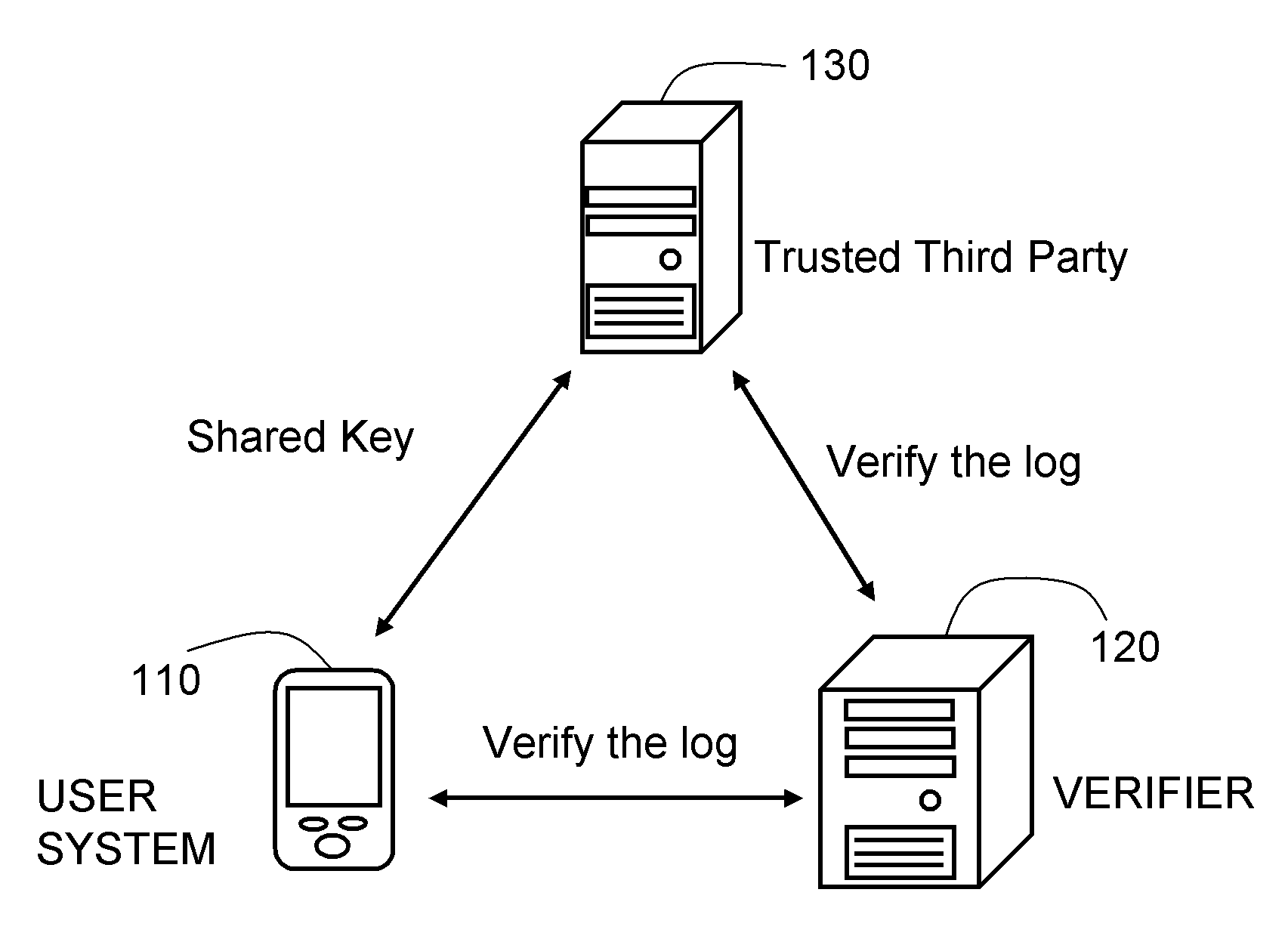
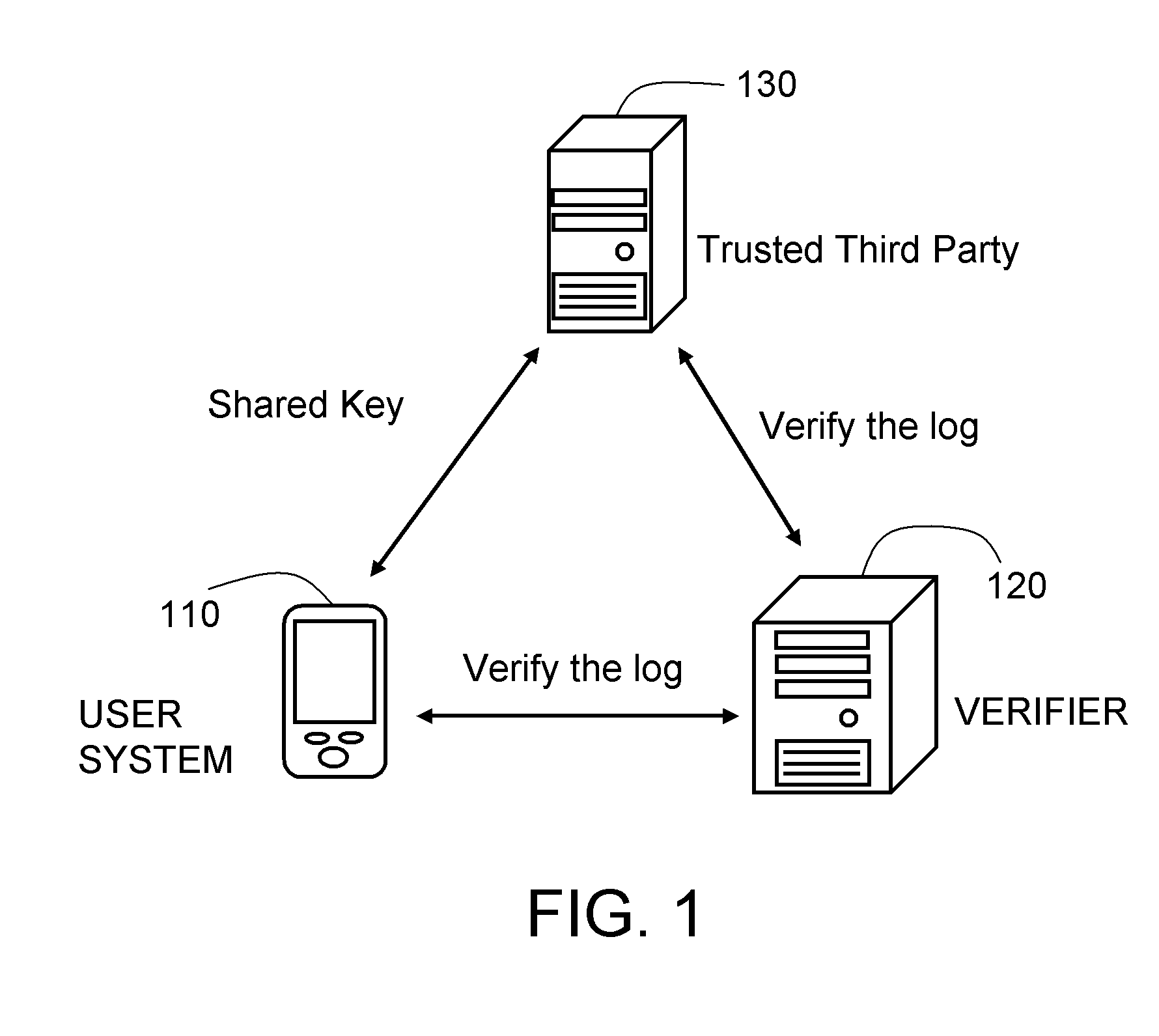
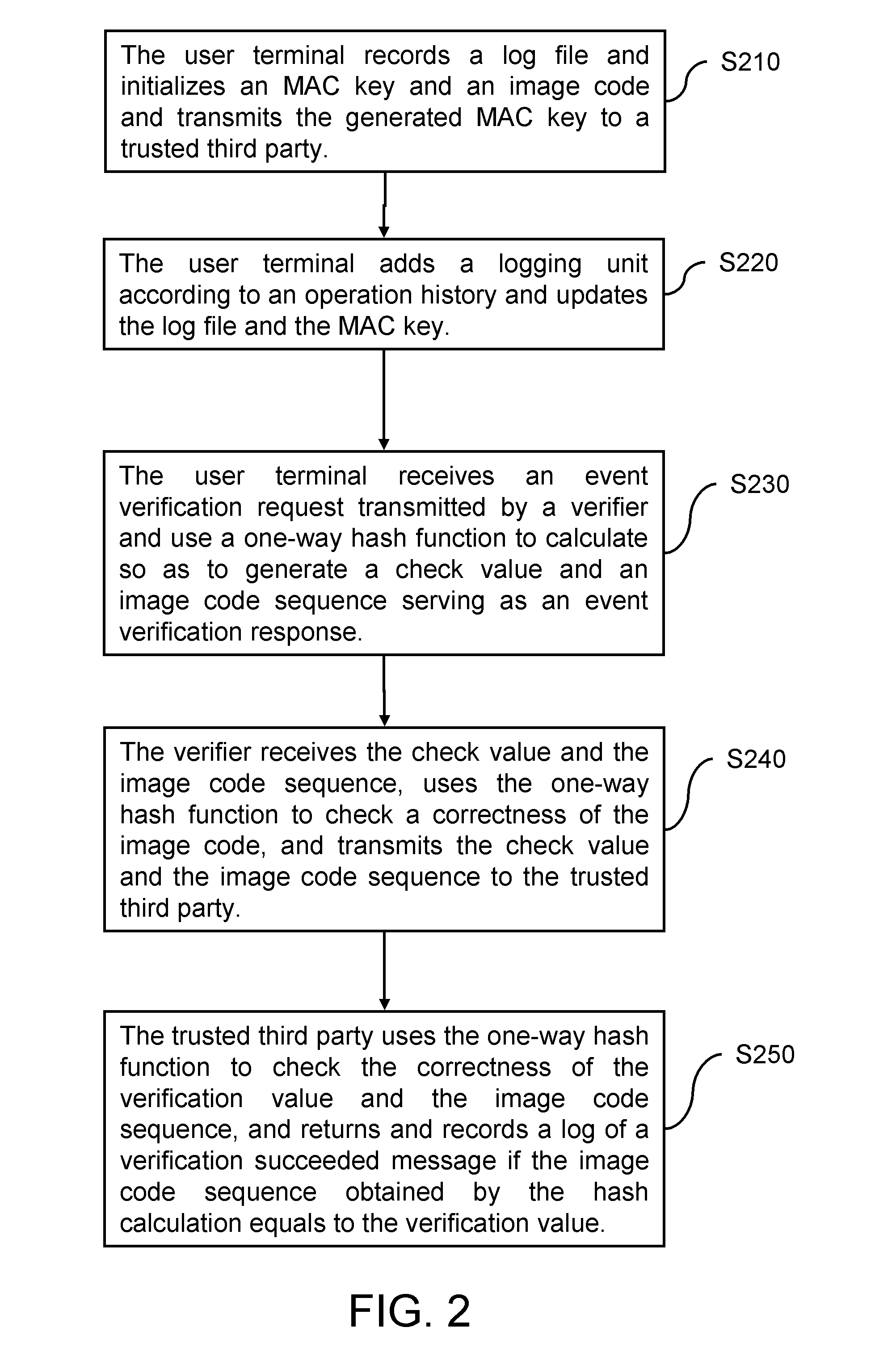
Logging system and method based on one-way hash function
A logging system and method based on a one-way hash function are described. The system includes a user system, a trusted third party, and a verifier. The method includes the following steps. The user system records a log file and initializes a message authentication code key and an image code. When the verifier requests the user system for a logging unit corresponding to an operation history, the user system uses a one-way hash function to calculate a check value and returns the check value and an image code sequence. The verifier then verifies the integrity of the check value and the image code sequence through the trusted third party. The trusted third party checks if the image code sequence obtained by the hash calculation equals to the check value through the one-way hash function, so as to verify that the log file of the user system has not been modified.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
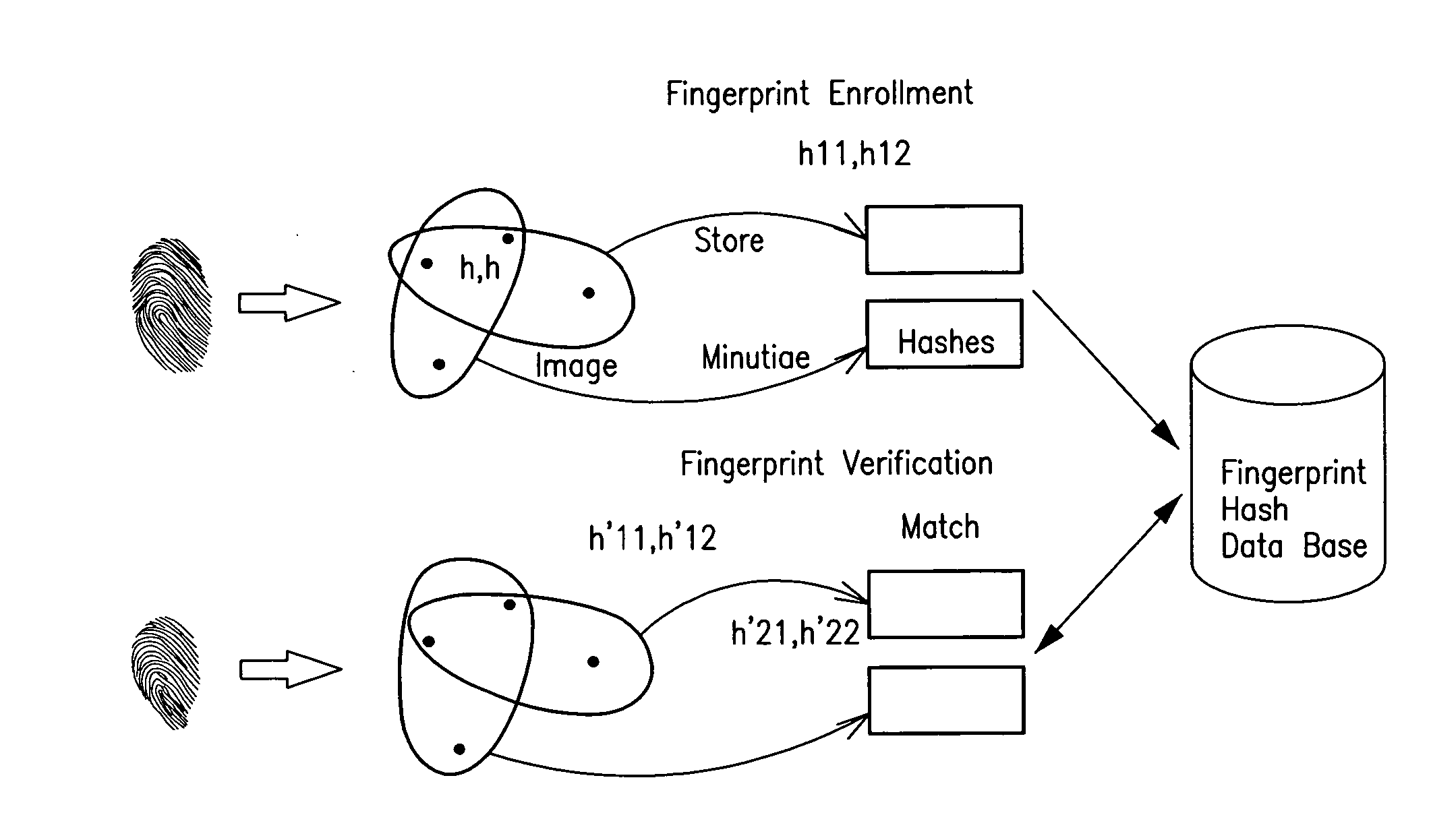
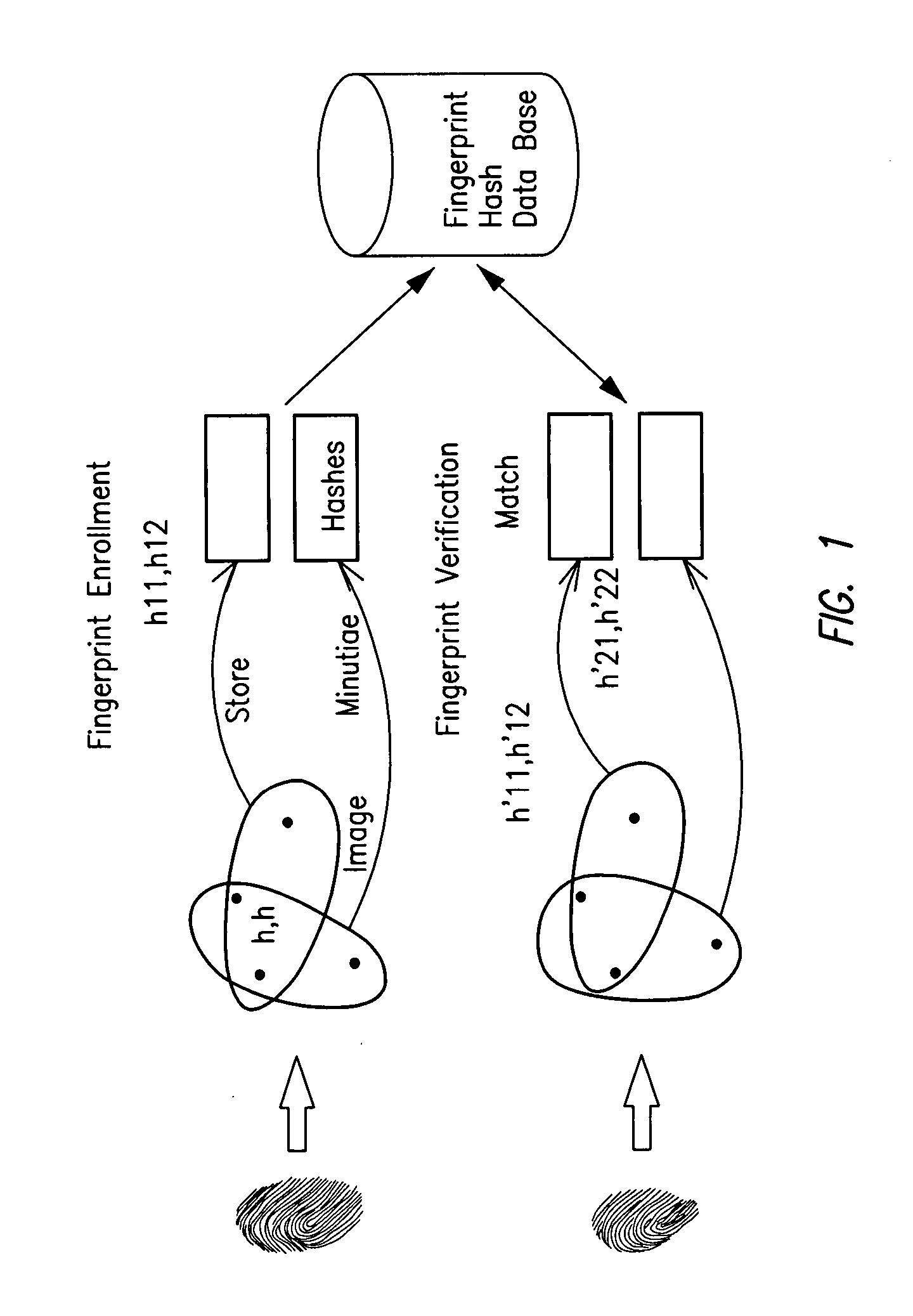
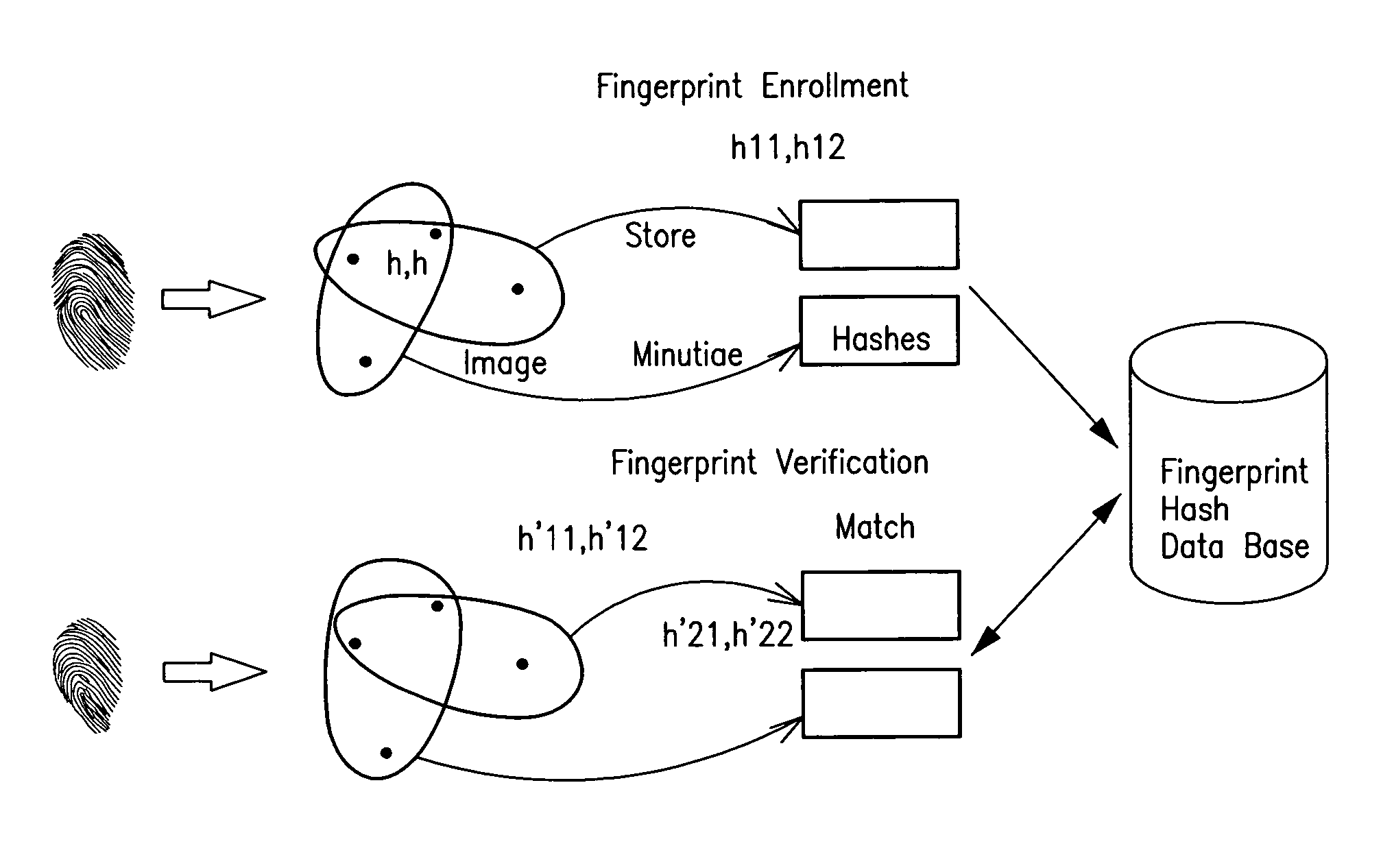
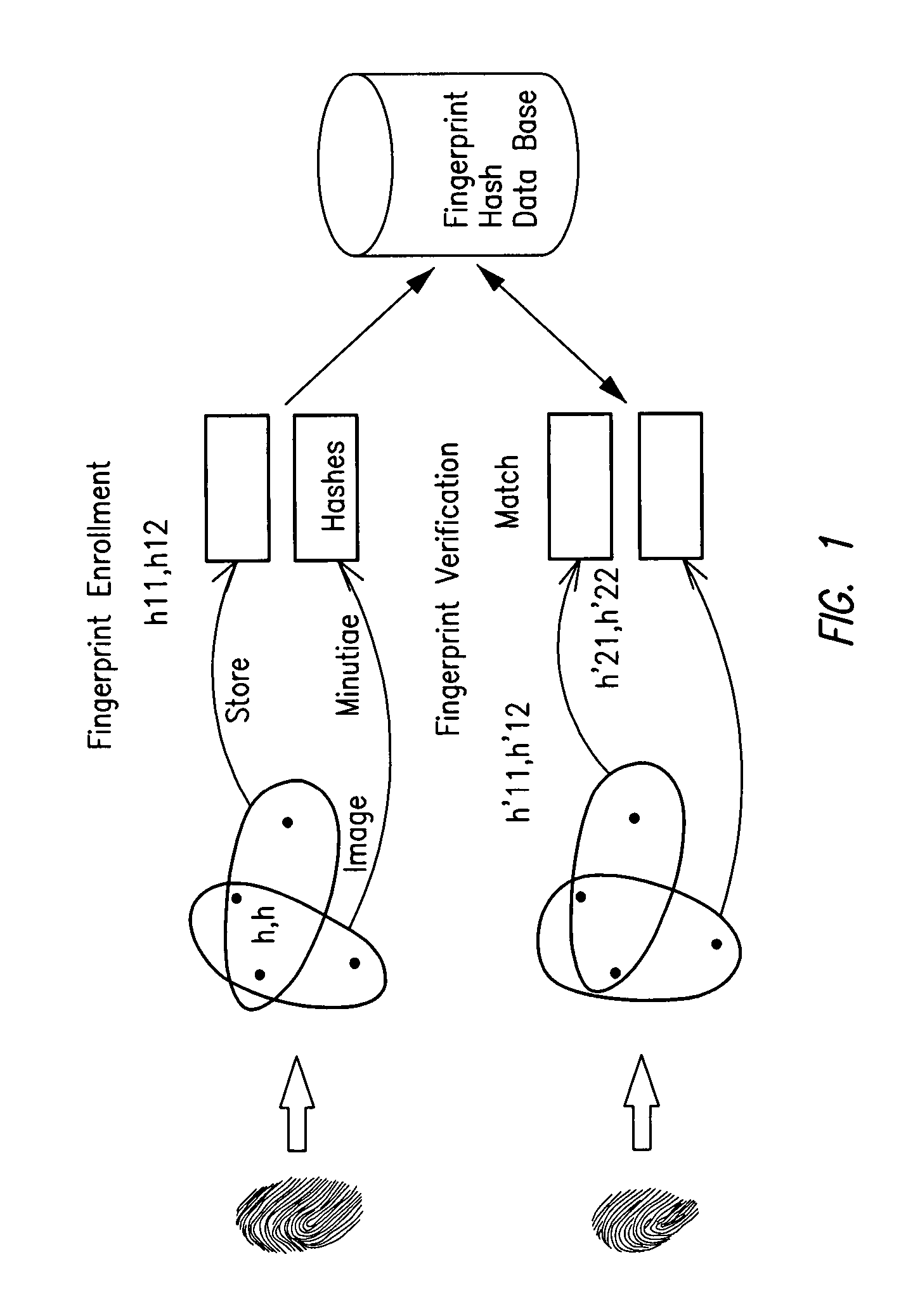
Secure fingerprint matching by hashing localized information
A method and apparatus for obtaining, hashing, storing and using fingerprint data related to fingerprint minutia including the steps of: a) determining minutia points within a fingerprint, b) determining a plurality of sets of proximate determined minutia points, c) subjecting a plurality of representations of the determined sets of minutia points to a hashing function, and d) storing or comparing resulting hashed values for fingerprint matching.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
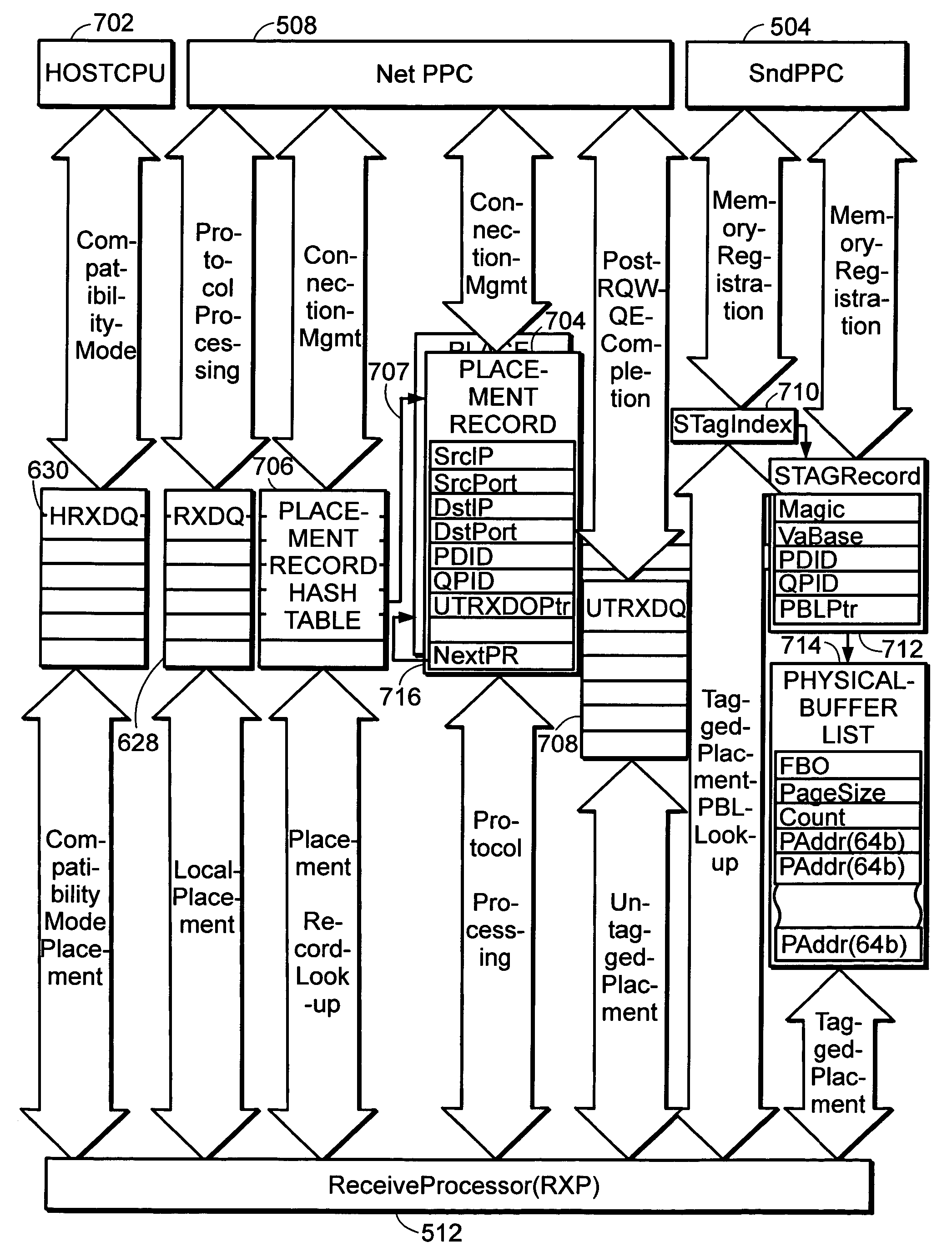
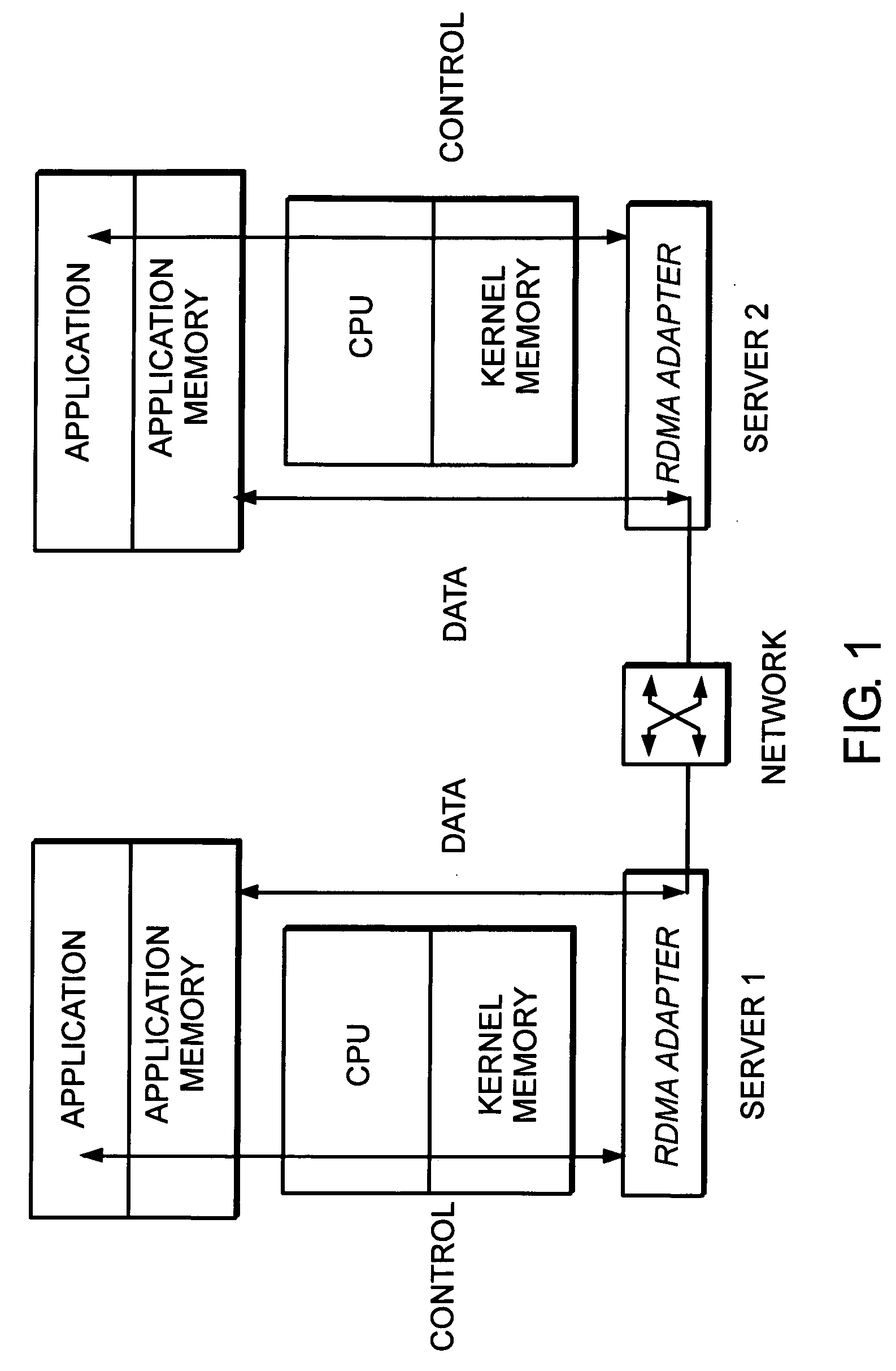
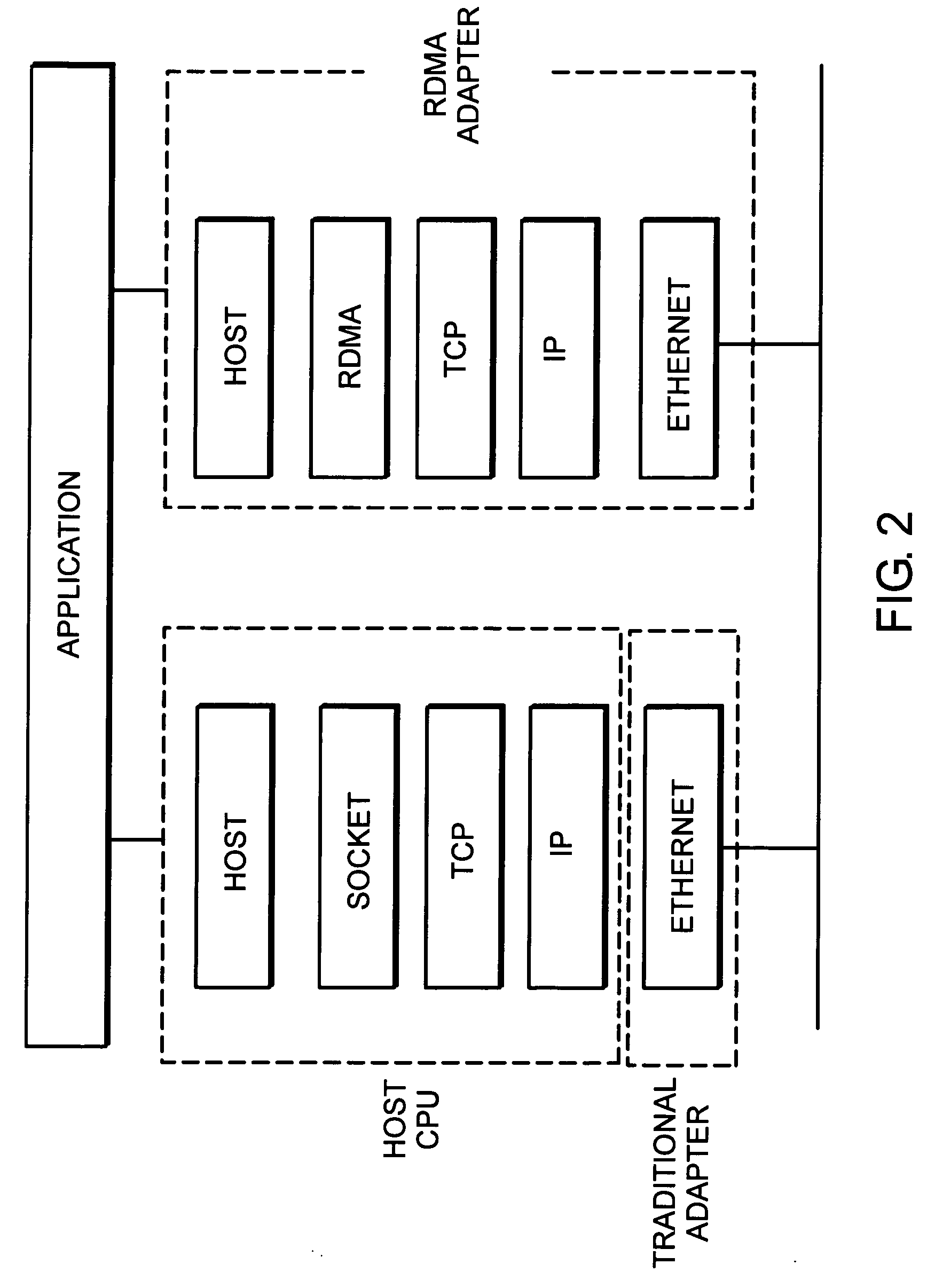
System and method for placement of RDMA payload into application memory of a processor system
InactiveUS20060067346A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationData switching by path configurationComputer hardwarePhysical address
A system and method for placement of RDMA payload into application memory of a processor system. Under one embodiment, a network adapter system is capable of use in network communication in accordance with a direct data placement (DDP) protocol, e.g., RDMA. The network adapter system includes adapter memory and a plurality of placement records in the adapter memory. Each placement record specifies per-connection placement data including at least network address information and port identifications of source and destination network entities for a corresponding DDP protocol connection. Placement record identification logic uniquely identifies a placement record from network address information and port identification information contained in a DDP message received by the network adapter system. Untagged message payload placement logic directly places the payload of the received untagged DDP message into physical address locations of host memory corresponding to one of said connection-specific application buffers. Tagged message payload placement logic directly places the payload of the tagged DDP message into physical address locations of host memory corresponding to the identifier in the received DDP message. According to one embodiment, the placement records are organized as an array of hash buckets with each element of the array containing a placement record and each placement record containing a specification of a next placement record in the same bucket. The placement record identification logic includes hashing logic to create a hash index pointing to a bucket in the array by hashing a 4-tuple consisting of a source address, a destination address, a source port, and a destination port contained in the received DDP message.
Owner:AMMASSO
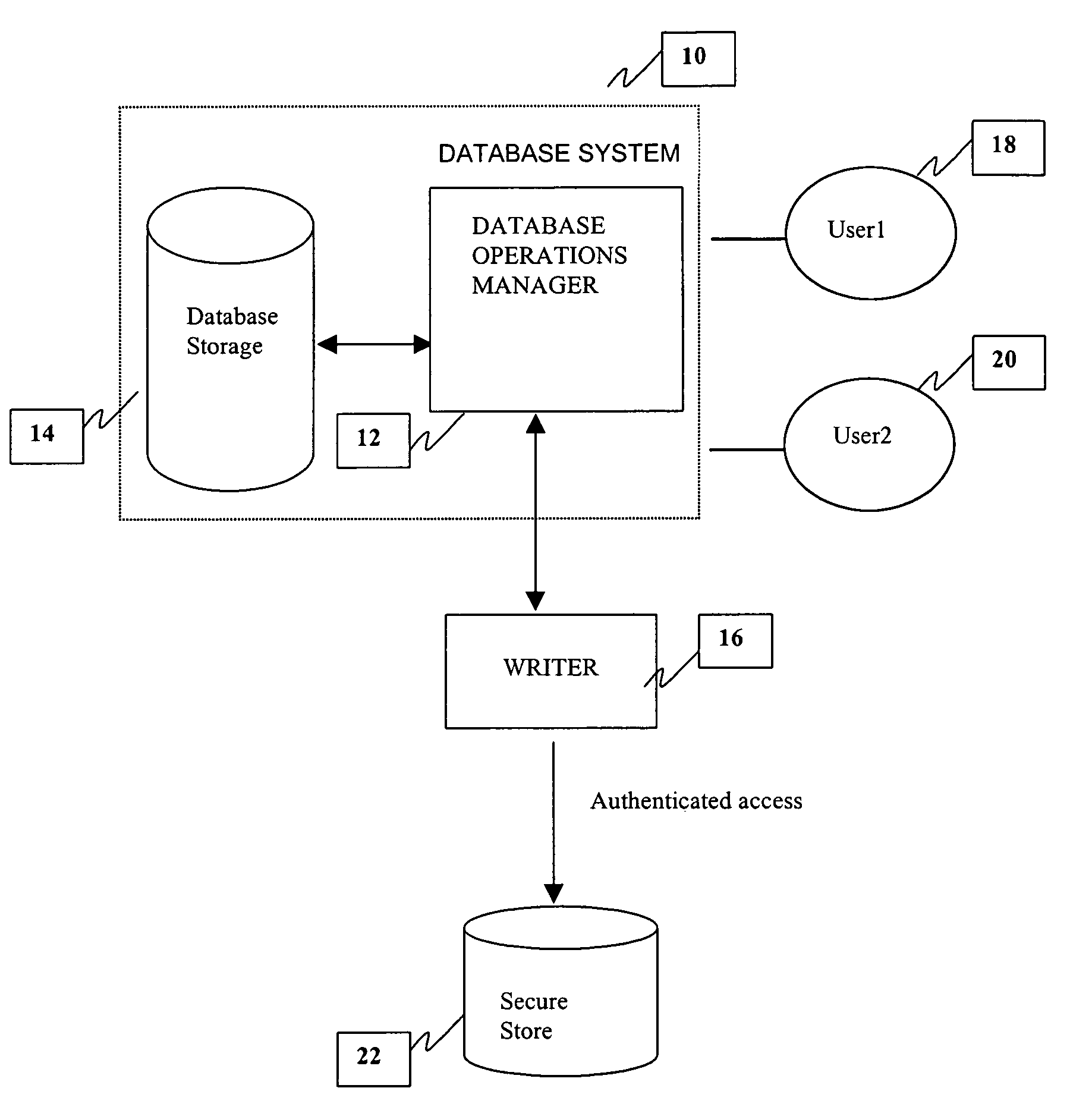
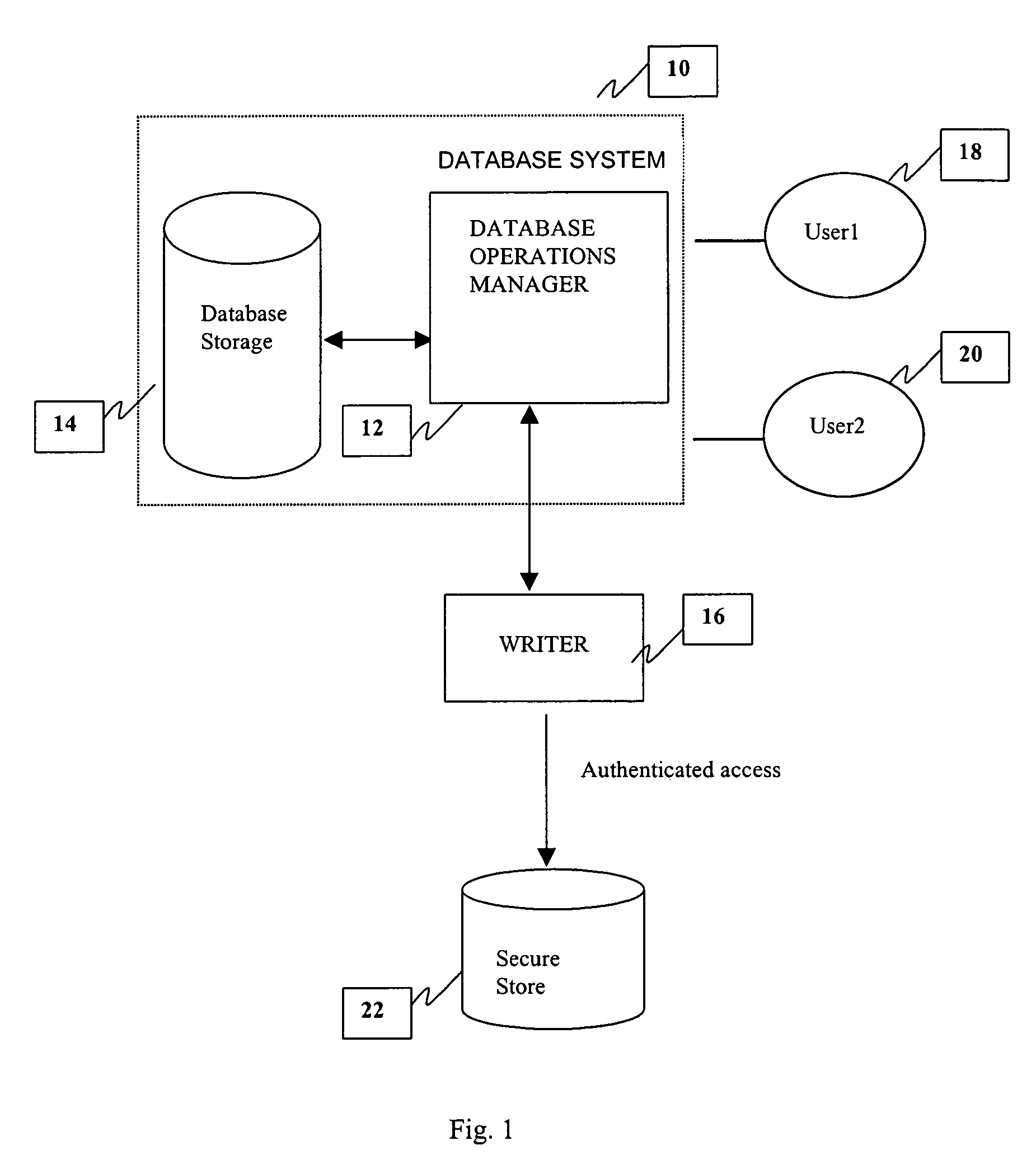
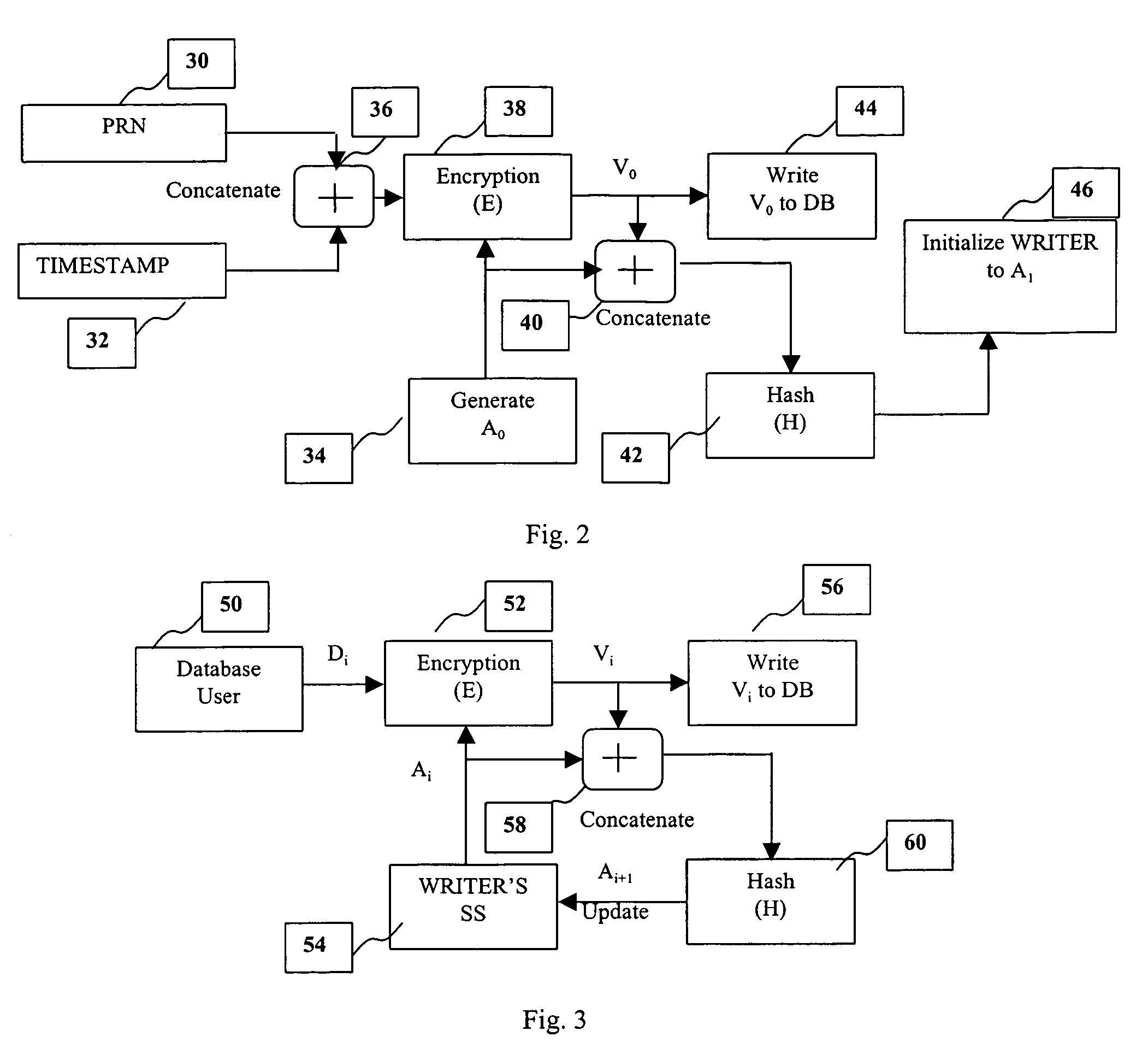
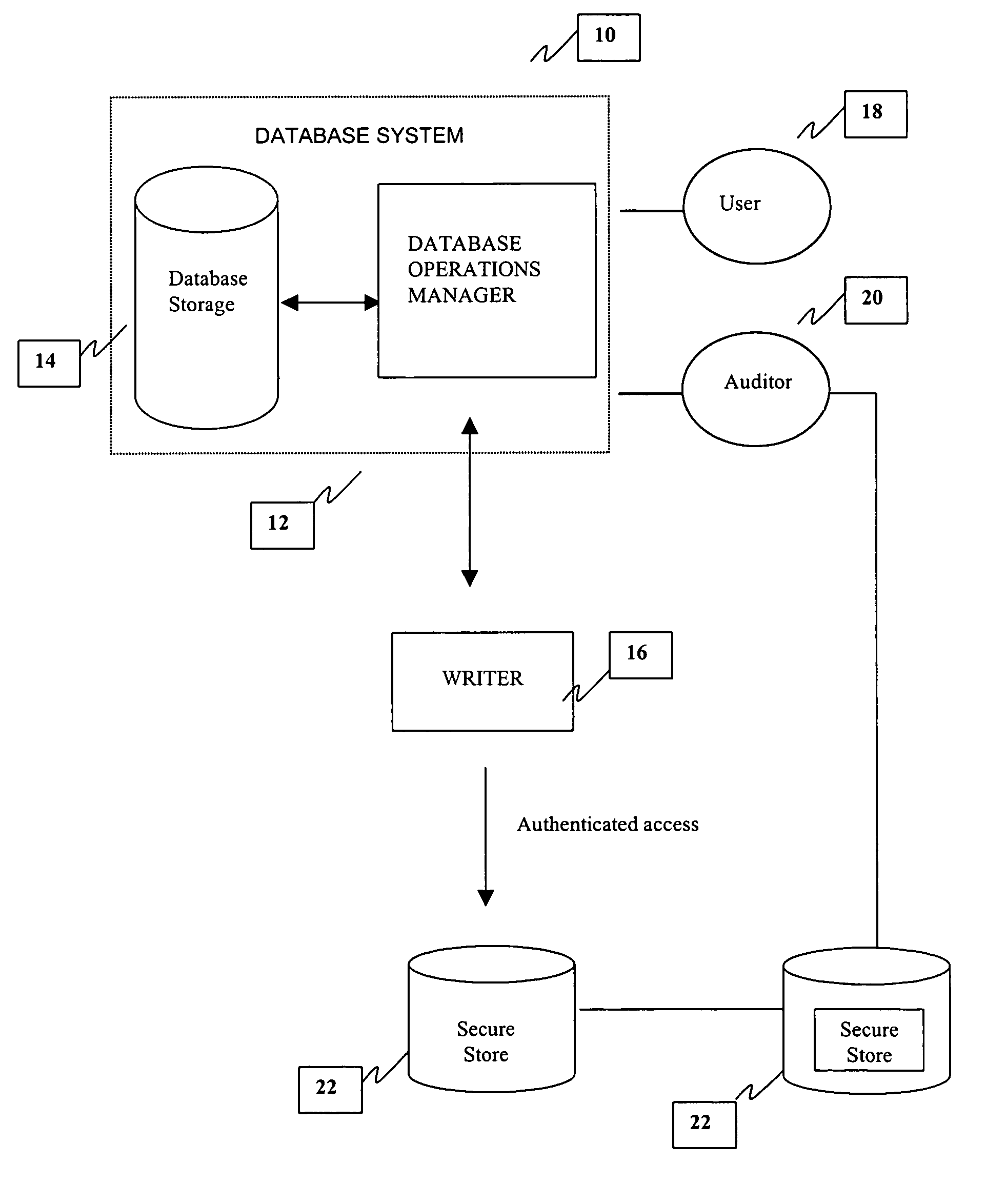
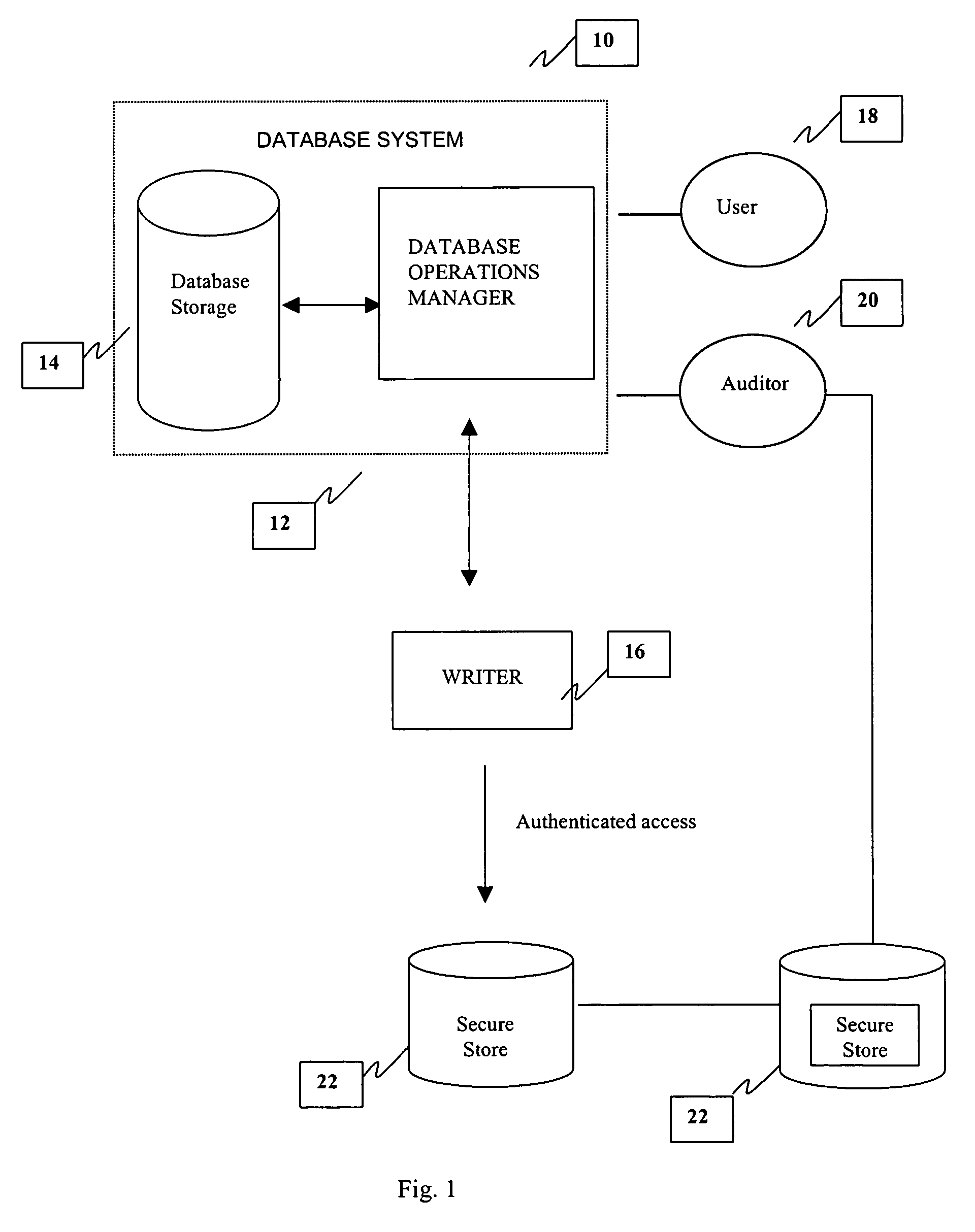
Method and system for providing a tamper-proof storage of an audit trail in a database
InactiveUS6968456B1Improve securityKey distribution for secure communicationData processing applicationsTamper resistanceDatabase administrator
A method and system is provided for a tamper-proof storage of one or more records of an audit trail in a database. Since the integrity of the database records may be vulnerable to actions taken by a user such as a privileged database administrator, a mechanism is provided to efficiently detect any changes made by him to the database records. The method creates one or more authentication tokens, and generates one or more validation tokens from the authentication tokens through a combination of a hashing process and an encryption process. Once the validation tokens are created, they are further integrated into the records in the database. The authentication tokens are written to a secured information storage in a predetermined format by a writing machine inaccessible by the user but accessible by the auditor. When an authorized person such as an independent auditor who needs to check the integrity of the records, he can detect a tampering of the records by comparing a validation token computed from the stored validation token with the validation token integrated in the record.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Electronic coin stick with potential for future added value
InactiveUS6341273B1Without incurring processing and communication overheadIncreased flexibility of useFinanceUser identity/authority verificationPayment transactionHash chain
In a digital payment transactions system, a broker generates and stores a secret number. The broker then generates a chain of hash values by successive operations of a hash function, using the secret number as the starting value. The broker then issues to the user a digitally encoded value from some way down the chain of hash values. The user generates a coin stick which comprises a chain of hash values starting with the value communicated by the broker. Subsequently, the broker can transfer further value to the user, without generating a new coin stick, by communicating a digitally encoded value from the broker's hash chain which precedes the value originally communicated to the user.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
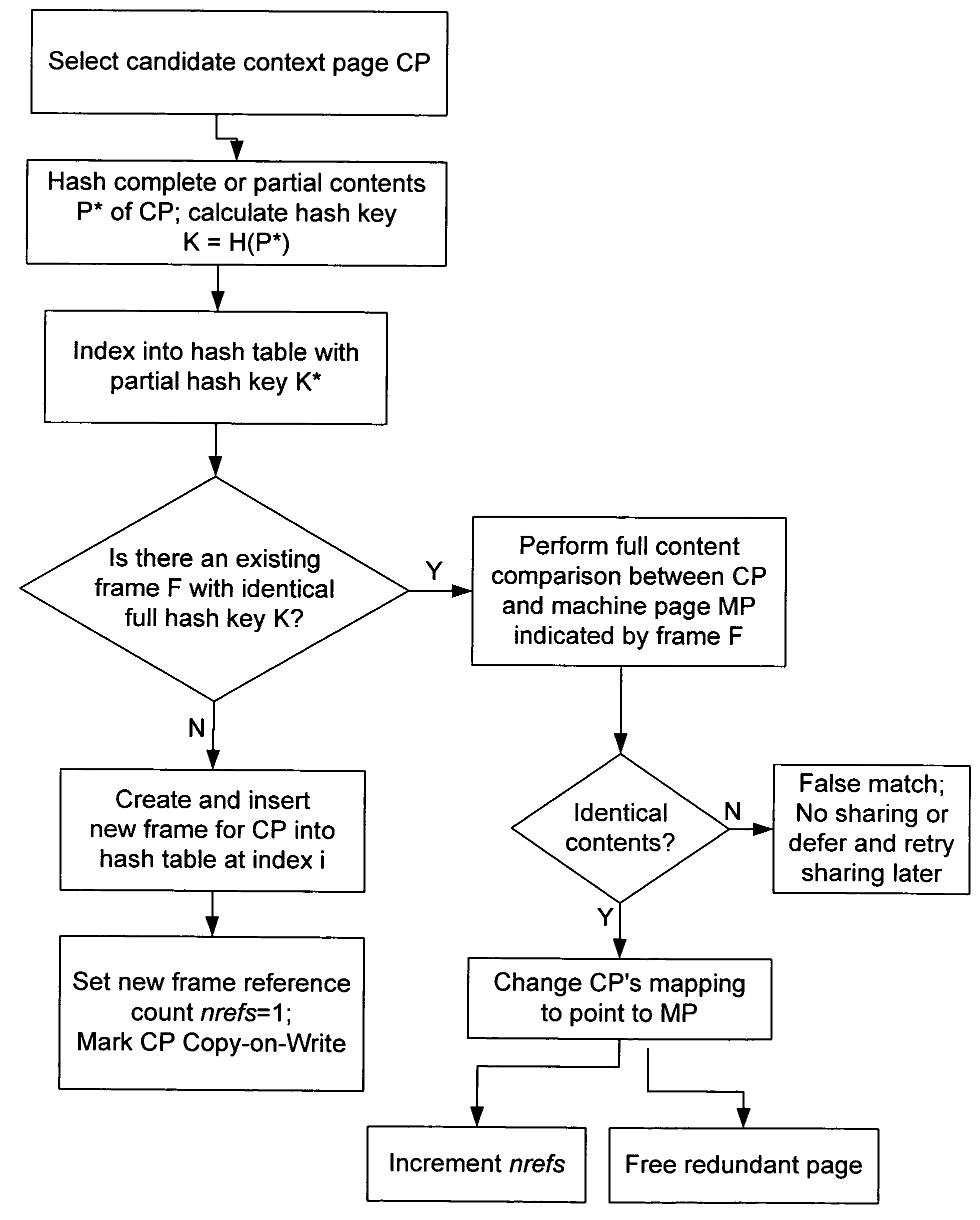
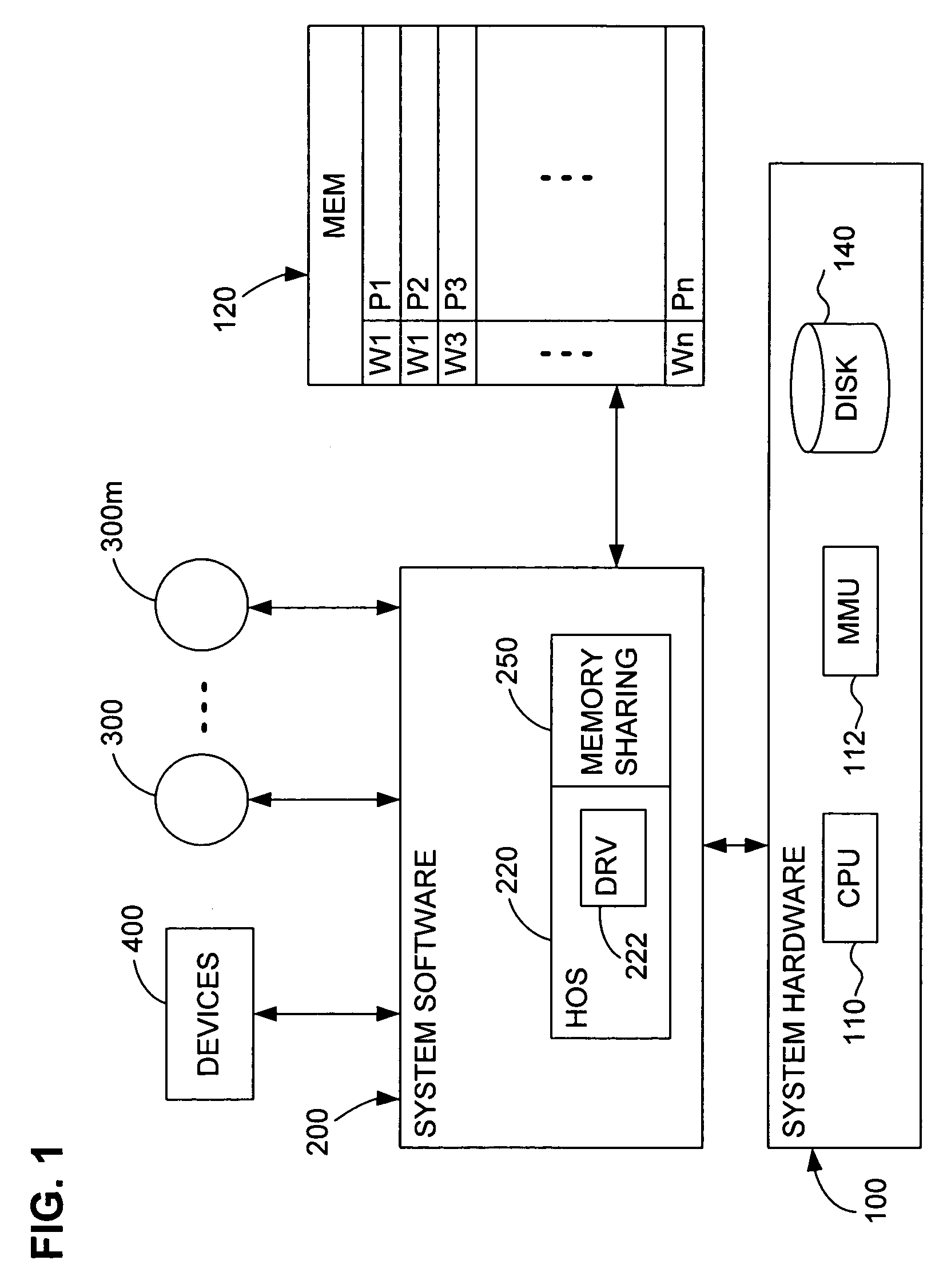
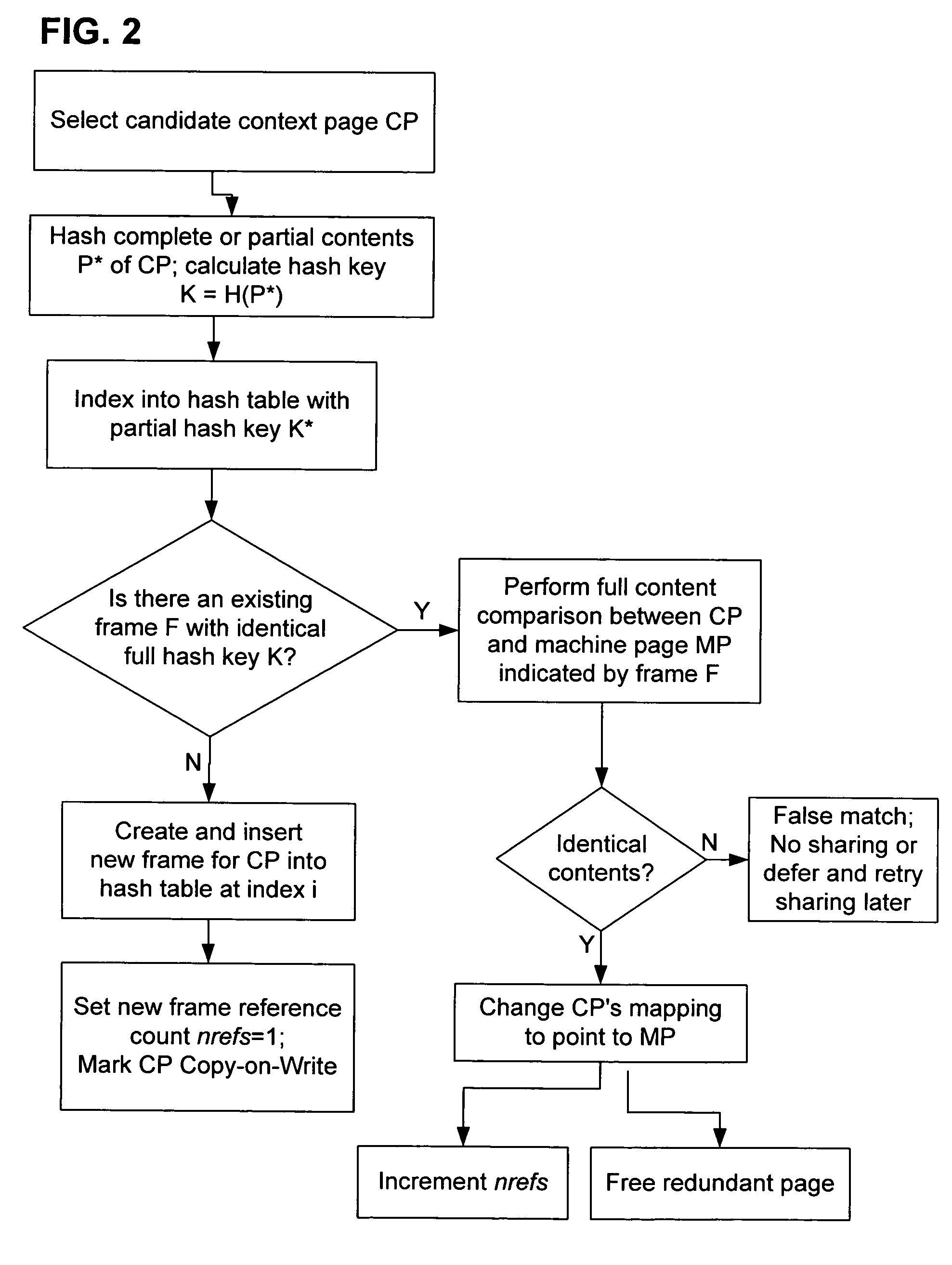
Transparent sharing of memory pages using content comparison
InactiveUS7620766B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMultiple contextVirtual memory
A computer system has one or more software contexts that share use of a memory that is divided into units such as pages. In the preferred embodiment of the invention, the contexts are, or include, virtual machines running on a common hardware platform. The contents, as opposed to merely the addresses or page numbers, of virtual memory pages that are accessible to one or more contexts are examined. If two or more context pages are identical, then their memory mappings are changed to point to a single, shared copy of the page in the hardware memory, thereby freeing the memory space taken up by the redundant copies. The shared copy is then preferably marked copy-on-write. Sharing is preferably dynamic, whereby the presence of redundant copies of pages is preferably determined by hashing page contents and performing full content comparisons only when two or more pages hash to the same key.
Owner:VMWARE INC
Secure fingerprint matching by hashing localized information
A method and apparatus for obtaining, hashing, storing and using fingerprint data related to fingerprint minutia including the steps of: a) determining minutia points within a fingerprint, b) determining a plurality of sets of proximate determined minutia points, c) subjecting a plurality of representations of the determined sets of minutia points to a hashing function, and d) storing or comparing resulting hashed values for fingerprint matching.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Cheap signatures for synchronous broadcast communication
InactiveUS20050182932A1Keep in syncSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesUser identity/authority verificationHash functionClient-side
A method and system are configured for synchronous broadcast communications by applying signature keys using hashing functions. Each subsequent transmission in a sequence includes a signature key that can be verified by hashing to a preceding signature key from a previous portion of the sequence. The first transmission in the sequence is signed using a signature key that is known by the client device, typically verified using some other mechanism such as asymmetric key signatures. Each client device can utilize an internal counter for the current time or the block number in the transmission sequence to maintain synchronized transmissions in the even that a particular portion of the sequence is missed, and to validate signature keys. Since the signature keys can be validated when they are received but not predicted before they are received, the transmission is difficult to attack while synchronization is maintained.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method to validate and authenticate digital data
InactiveUS20110231645A1Data can be securedDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationDigital dataDocument Identifier
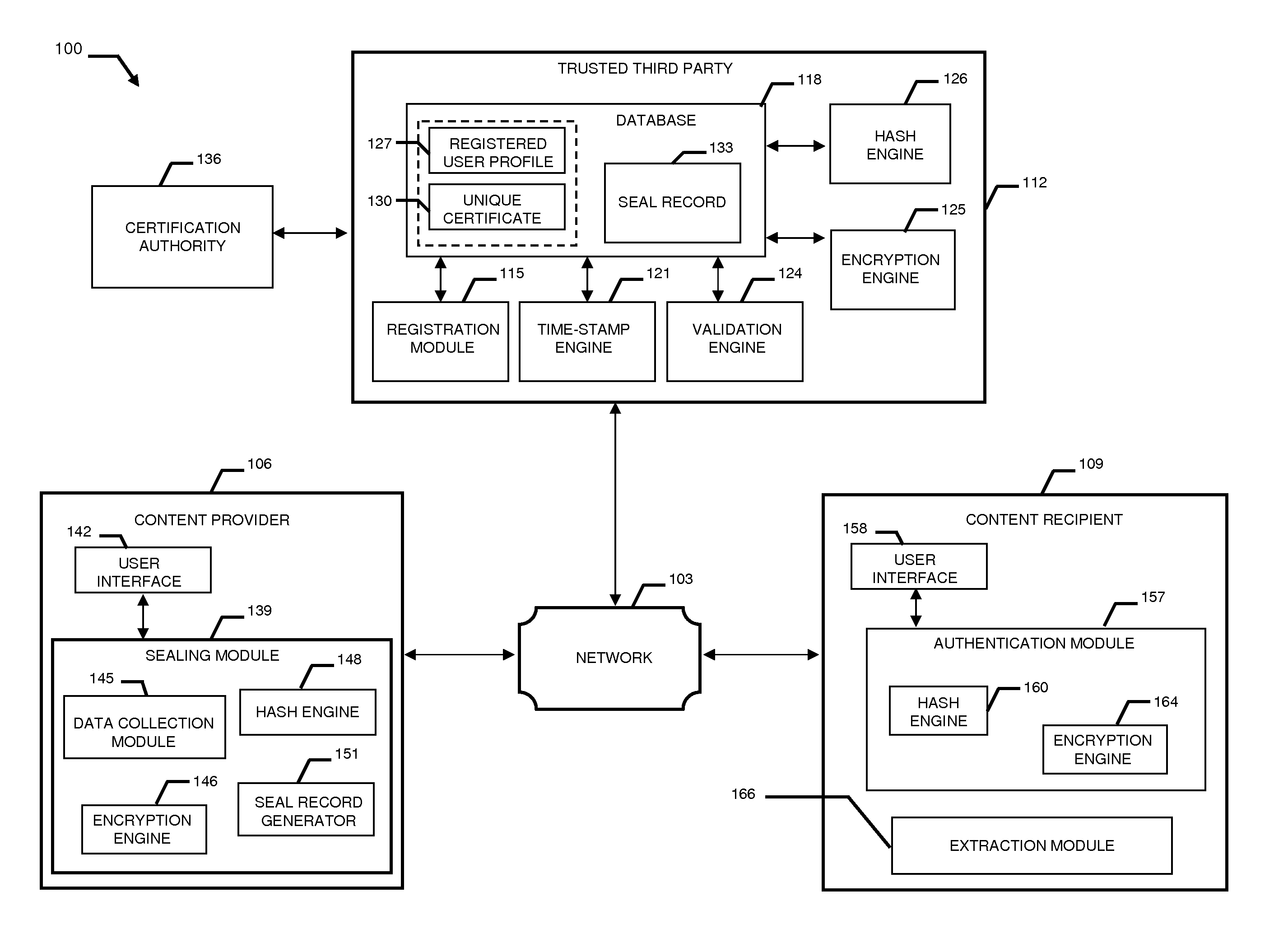
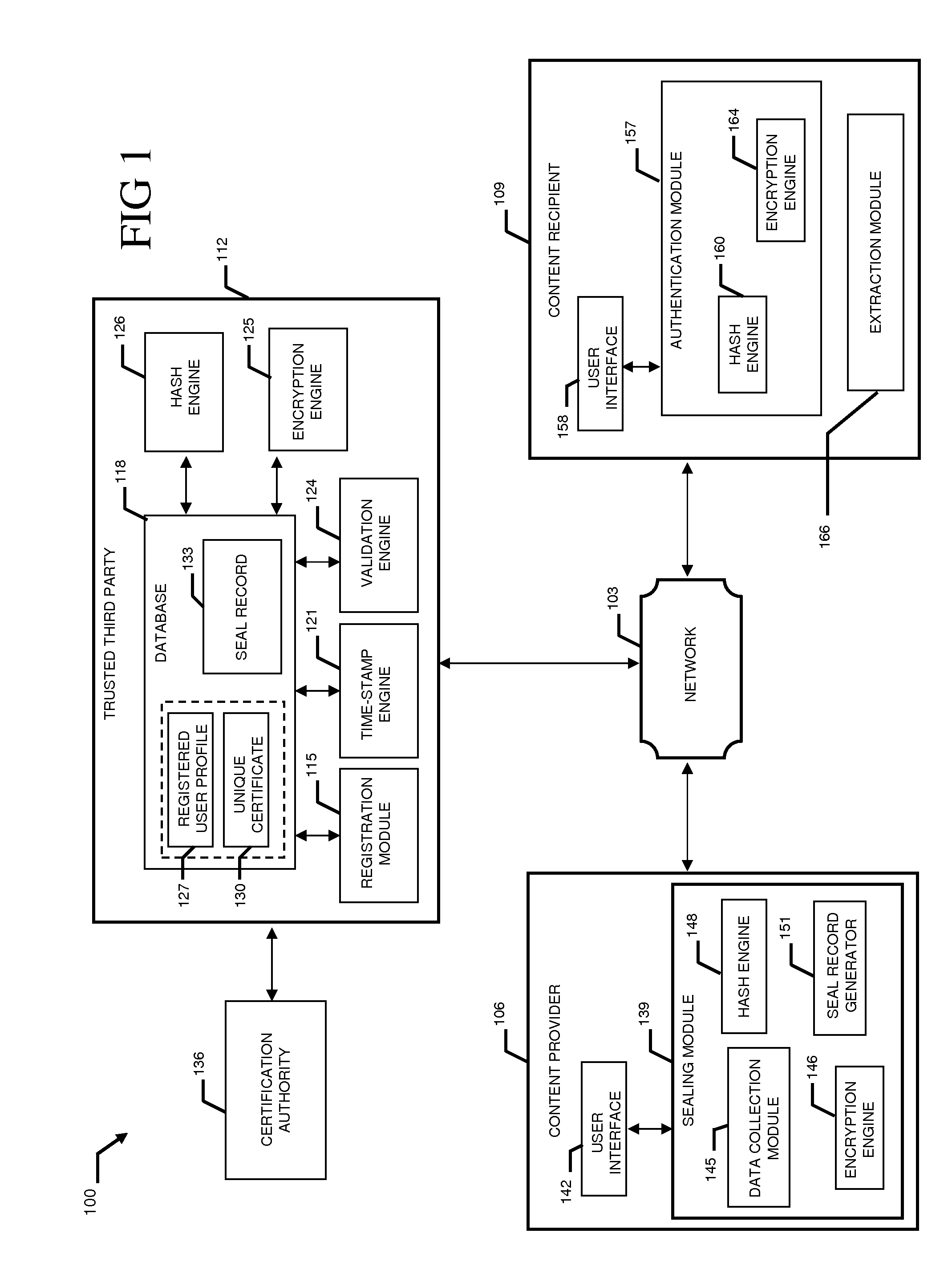
A system and method combining registration with a trusted third party, certificate generation, hashing, encryption, customizable file identification fields, and time-stamping technology with recognized “best practice” procedures to achieve the legal admissibility and evidential weight of any form of digital file or collection of digital files. Generally, the originator of the file (the first party) and the originator's employing organization are registered with a Trusted Third Party. The originator reduces the file, by means of a hashing algorithm, to a fixed bit length binary pattern. This provides a unique digital fingerprint of the file. The resultant hash value, the originator's identity details, the employing organization details associated and securely linked to the digital certificate, the title of the file, customizable file identification fields, and other relevant data are forwarded to a Trusted Third Party where the date and time from a known and trusted time source are added. The customizable file identification fields can provide the originator with a mechanism for configuring the seal to incorporate as much additional information as deemed necessary to prove the authenticity of the digital content and / or provide data for the purposes of adding value in functions such as source identification, sorting, analysis, investigation, and compliance. Such information could include, but would not be limited to, location / GPS coordinates, machine id, biometric information, smart-card data, reason for sealing. The original file does not leave the control of the originating party. When combined, the forwarded details and date and time create a Seal Record. The Seal Record is encrypted and hashed. The Seal Record along with all other relevant information are retained on a central secure server. The recipient of the file (the second party) can confirm the file has been received in an unaltered state with integrity retained and it is the authentic version by validating the file.
Owner:CYBERCUBE
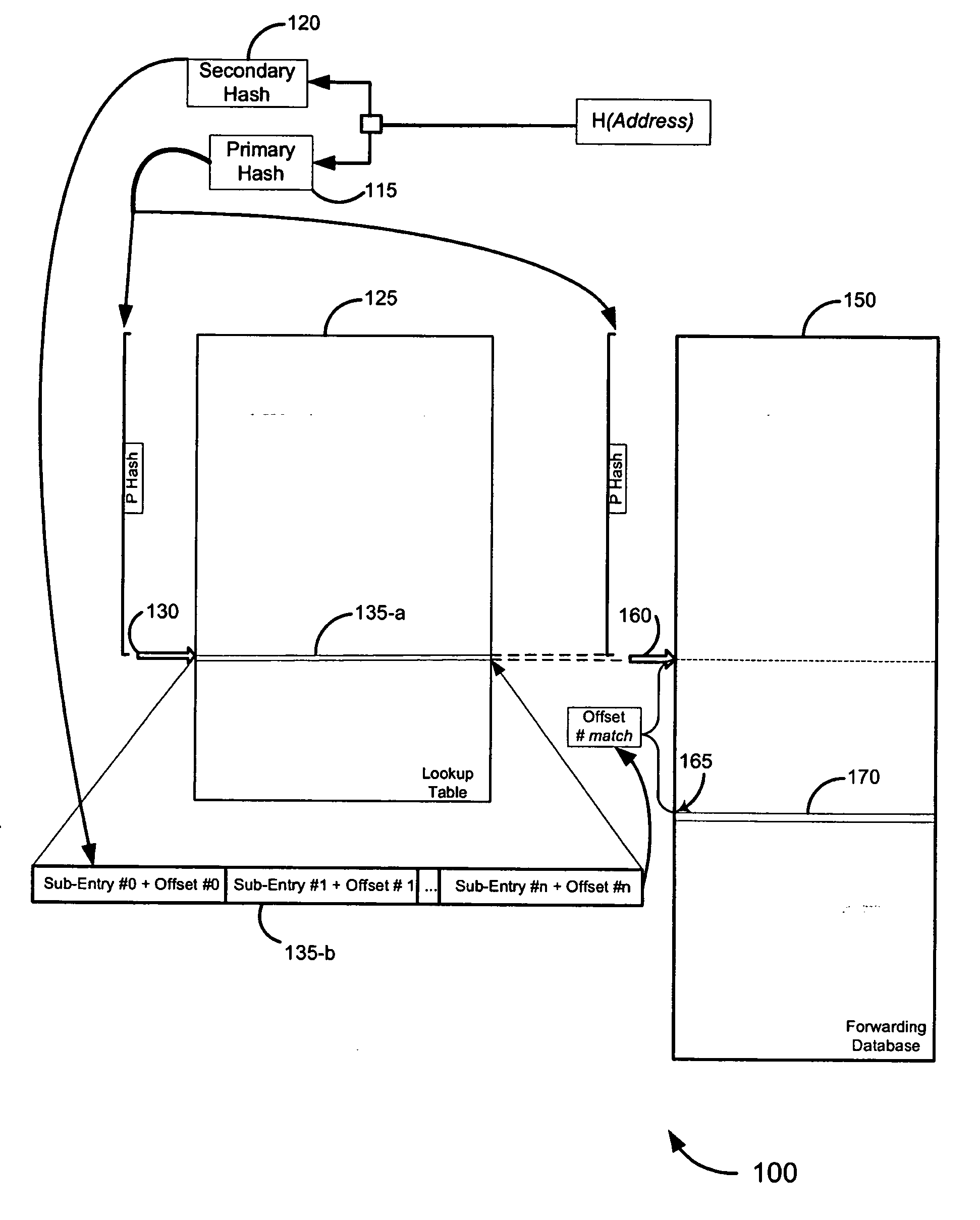
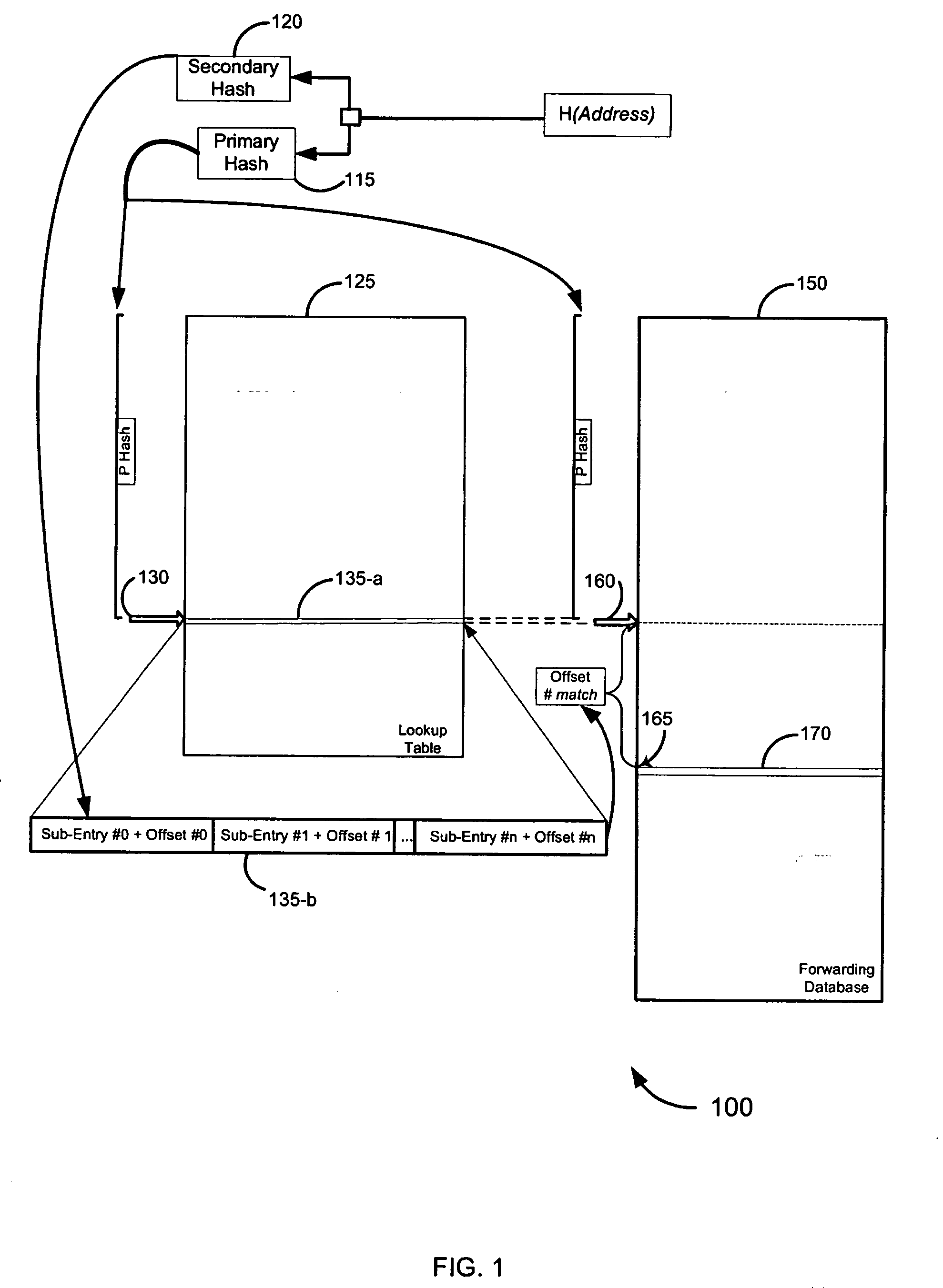
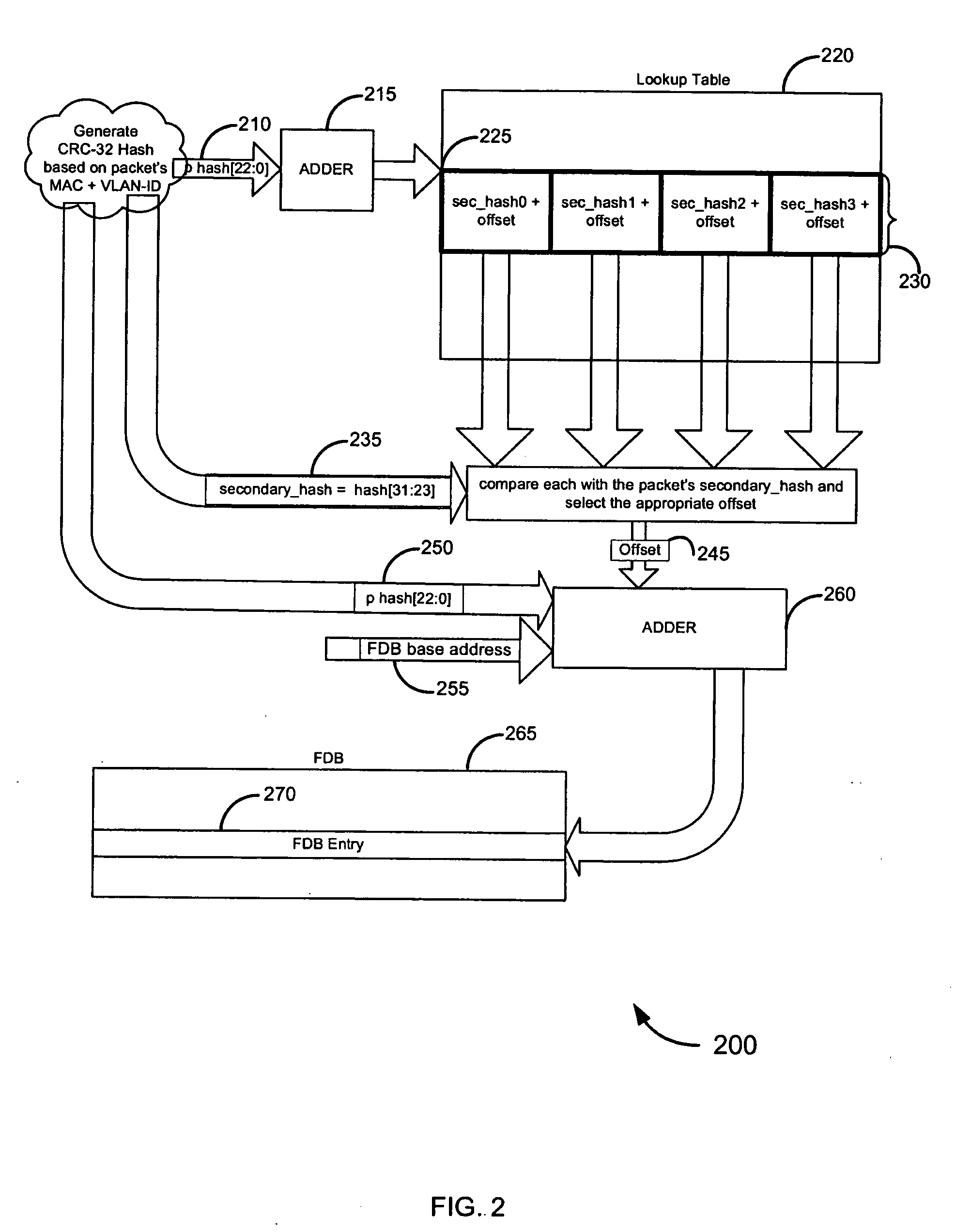
Double-hash lookup mechanism for searching addresses in a network device
A hash function is applied to a set of data to generate a hash. A first subset of the hash is used to lookup an entry in a lookup table for a forwarding database. A second subset of the hash is used to identify, within the entry, data comprising an offset. The offset is applied to a location identified in the forwarding database by the first subset of the hash to determine an entry in the forwarding database. Optionally, the lookup mechanism is used in conjunction with one or more other forwarding databases. A method of updating the forwarding database within the double hash lookup framework is also described.
Owner:MARVELL ISRAEL MISL
Anonymous Preservation of a Relationship and Its Application in Account System Management
InactiveUS20110078779A1Improve security levelDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsHash functionInternet privacy
Disclosed is a system or method of using hash functions to preserve a relationship. A relationship is anonymously preserved by storing the hash result of a relationship token that comprises a finite set of values of a plurality of objects. Specifically, an account anonymous identifier of an account can be produced by hashing a relationship token that comprises identity information of an owner of said account. A party that has enough knowledge of an account owner can independently produces said account anonymous identifier and therefore, securely communicates with a specific account without prior communication or a password. An account owner can further prove his / her ownership of an account by submitting related documents and a relationship token that comprises his / her identity information to an account system.
Owner:LIU SONG +1
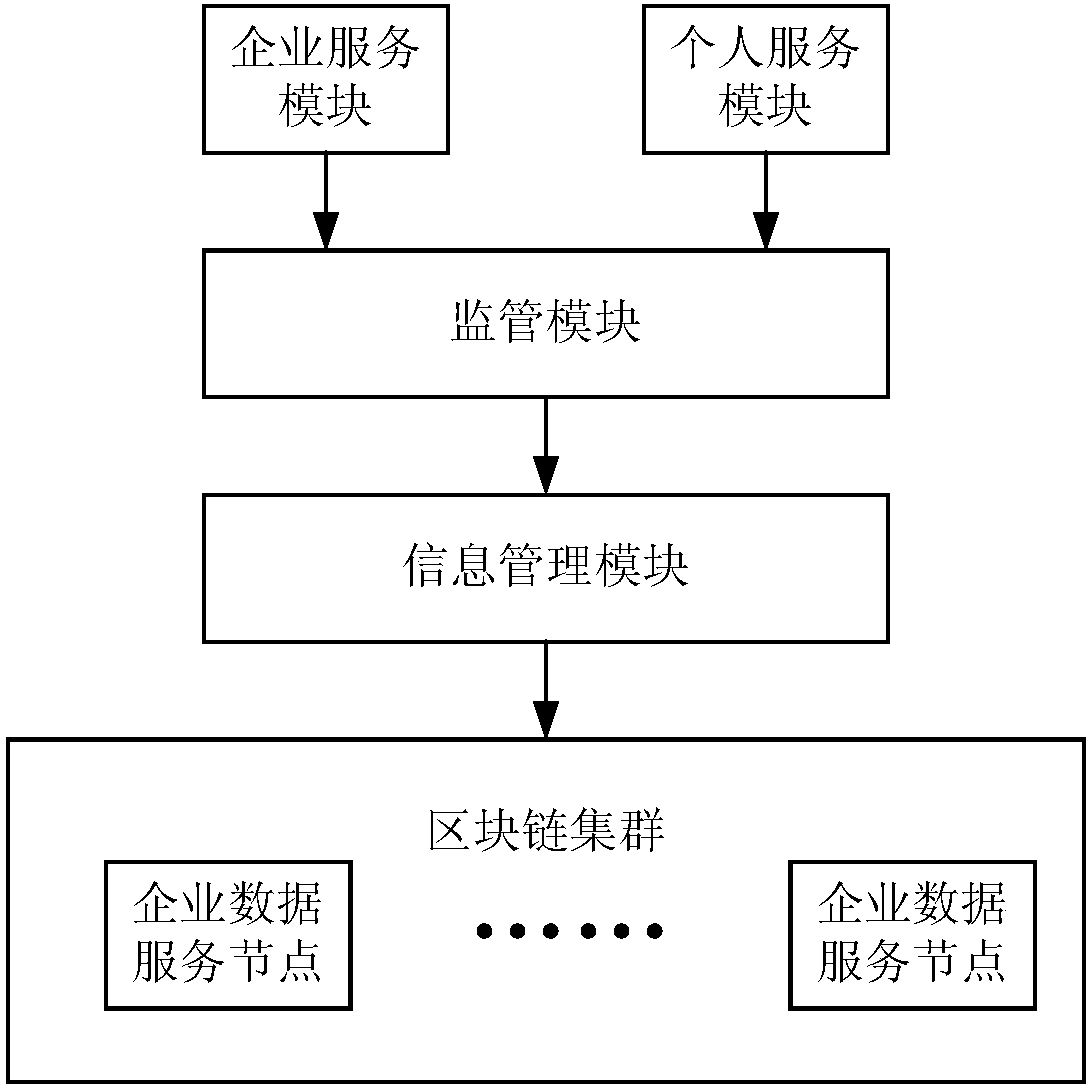
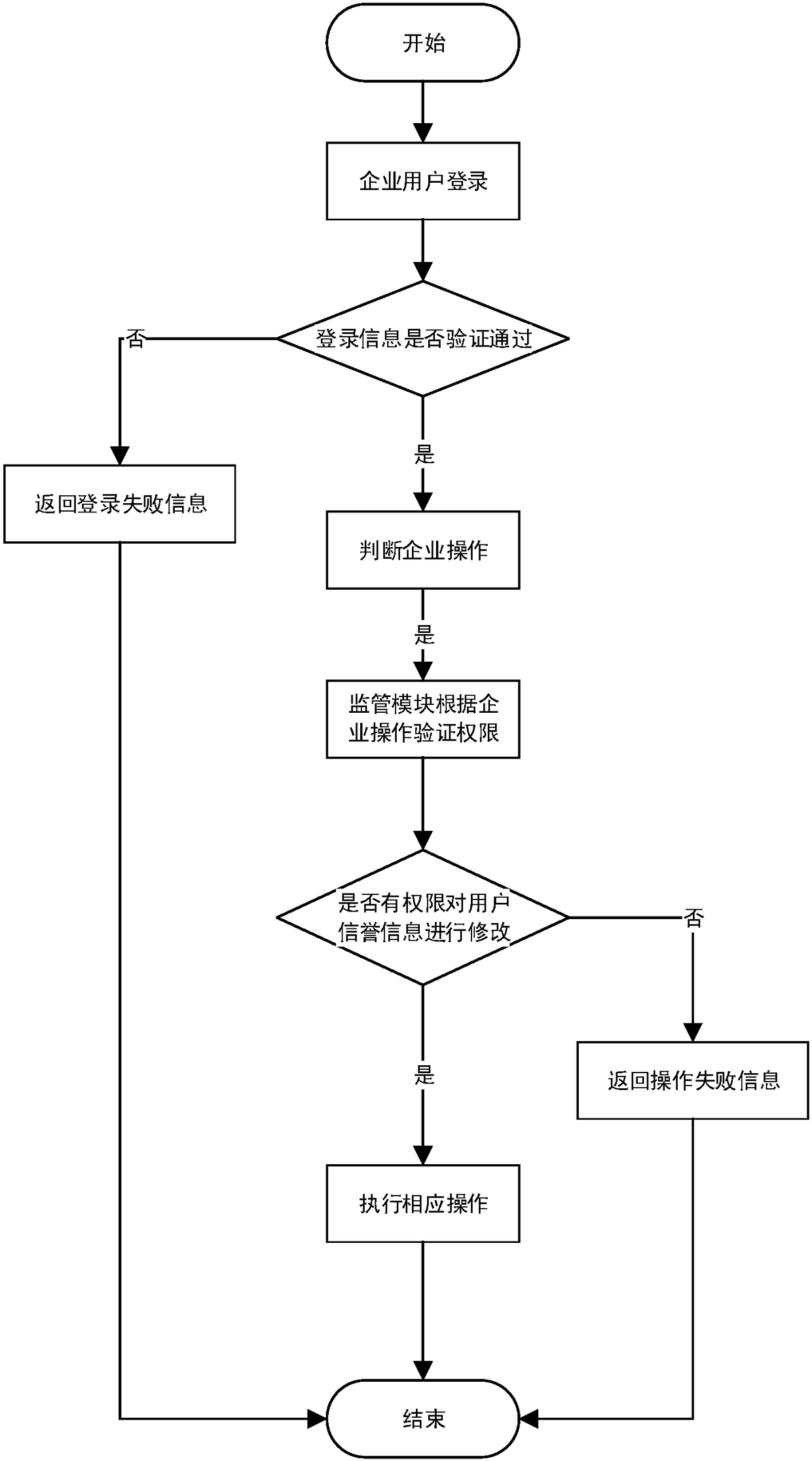
Personal credit information sharing system and method based on block chain
InactiveCN108234478ATrusted Shared ServiceExpress Sharing ServiceUser identity/authority verificationEnterprise servicesE-commerce
The invention discloses a personal credit information sharing system and method based on a block chain. The personal credit information sharing system based on the block chain comprises a block chaincluster, an enterprise service module, a personal service module, an information management module and a supervision module. The system is characterized in that the information management module is used for carrying out user information management comprising real-name authentication according to identity card information of a personal user and generation of a unique identity ID of the personal user through a hash algorithm and BASE64 code, creating assets on the block chain cluster, managing the assets on the block chain cluster and carrying out real-name authentication on the personal user; the enterprise service module is used for carrying out authentication on an enterprise user and distributing a login credential to an authenticated enterprise while providing relevant operation of thepersonal information for the enterprise user according to the authority provided by the supervision module, wherein the login credential comprises a private key and a digital certificate. The system and the method can be widely applied to the fields of banks, credit, games, electronic commerce and the like.
Owner:重庆小犀智能科技有限公司
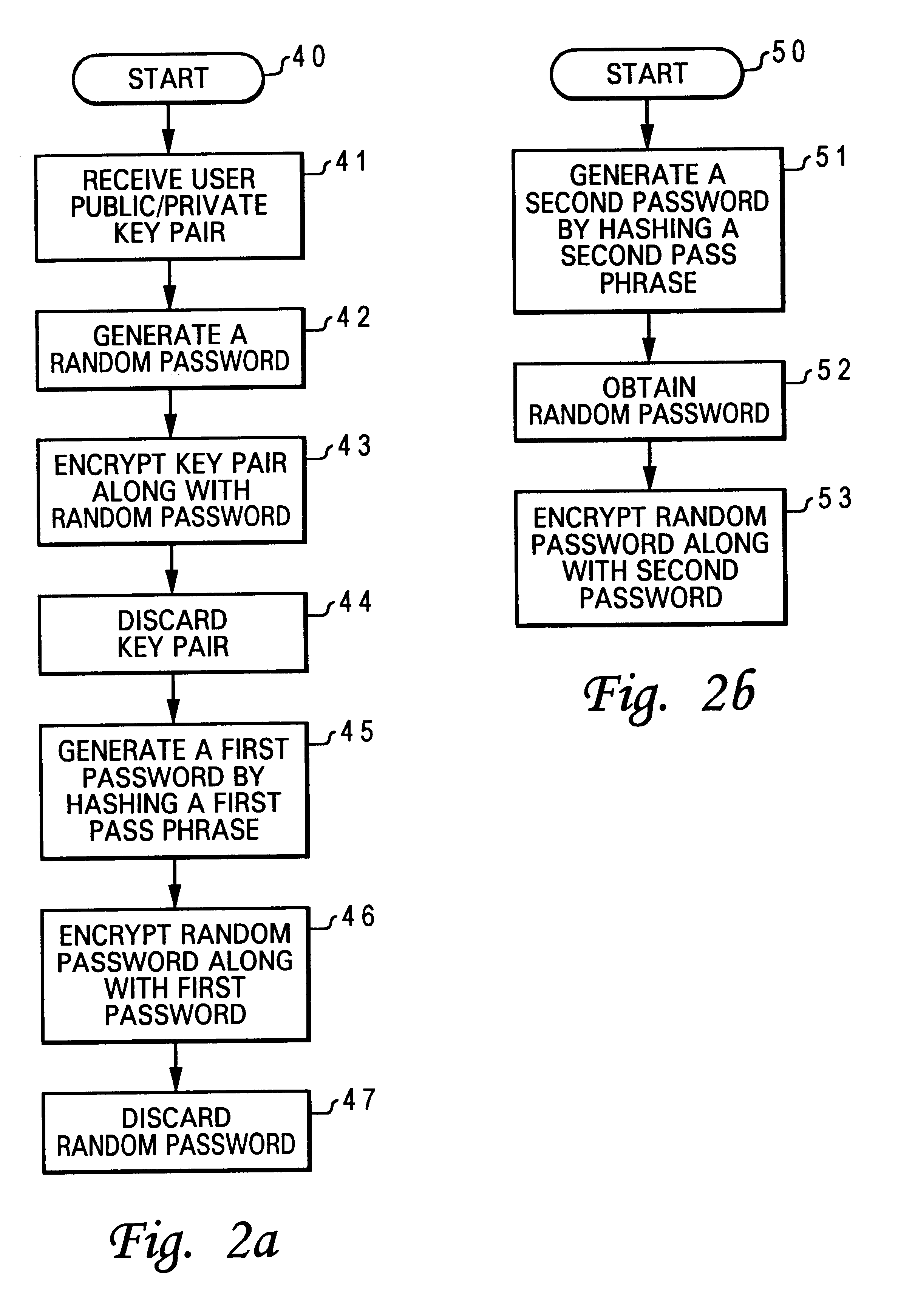
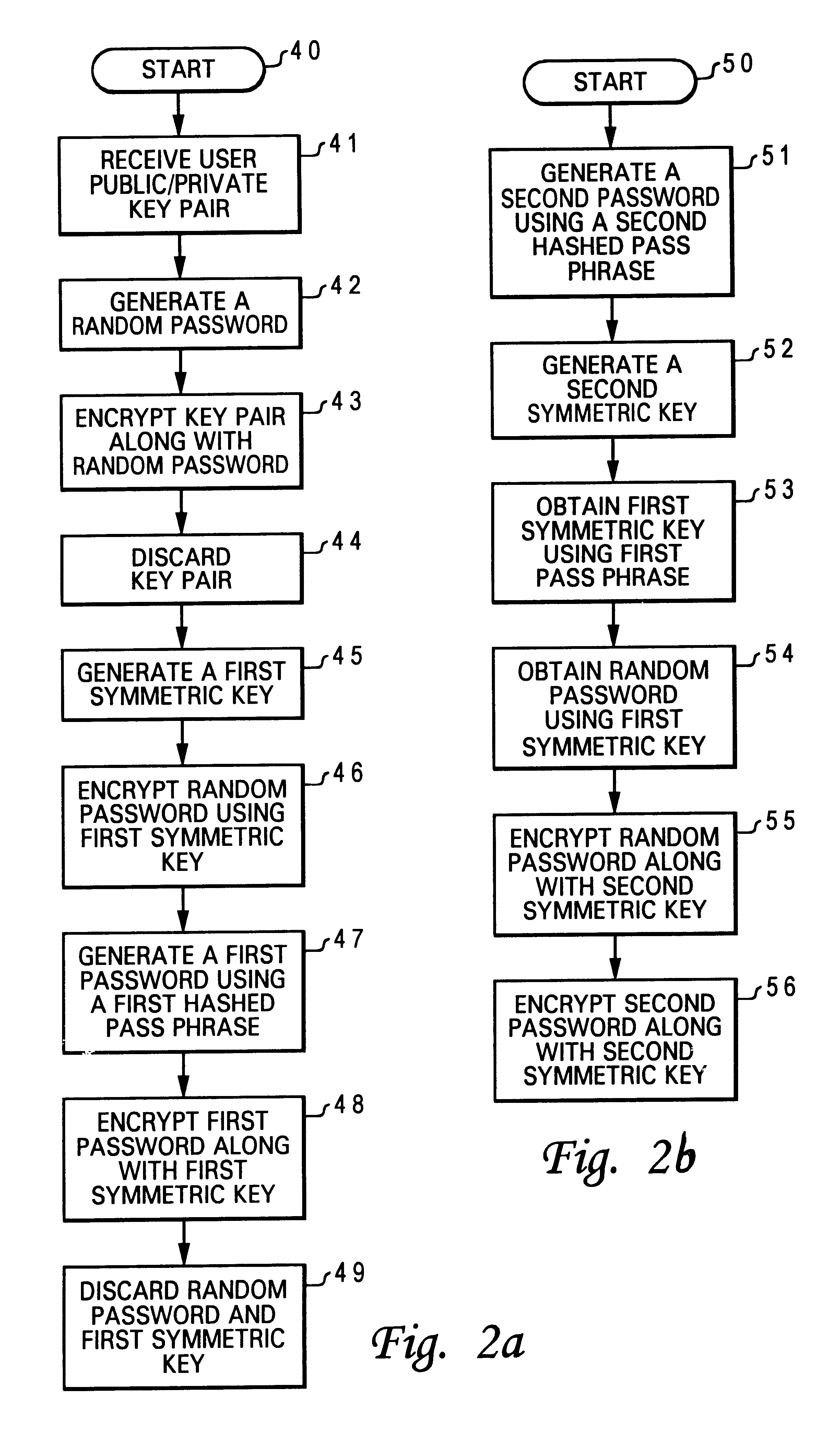
Method for associating a password with a secured public/private key pair
InactiveUS6718468B1Public key for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsPassphrasePassword
A method for associating a password with a secured public / private key pair is disclosed. A user public / private key pair is first established for a user. The user public / private key pair includes a user public key and a user private key. Then, the user public / private key pair is encrypted along with a random password, utilizing a chip public key. Next, a first password is generated by hashing a pass phrase. Finally, the random password is encrypted along with the first password, also utilizing the chip public key. As a result, a user can assess the user private key to perform an authentication function by providing the pass phrase.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
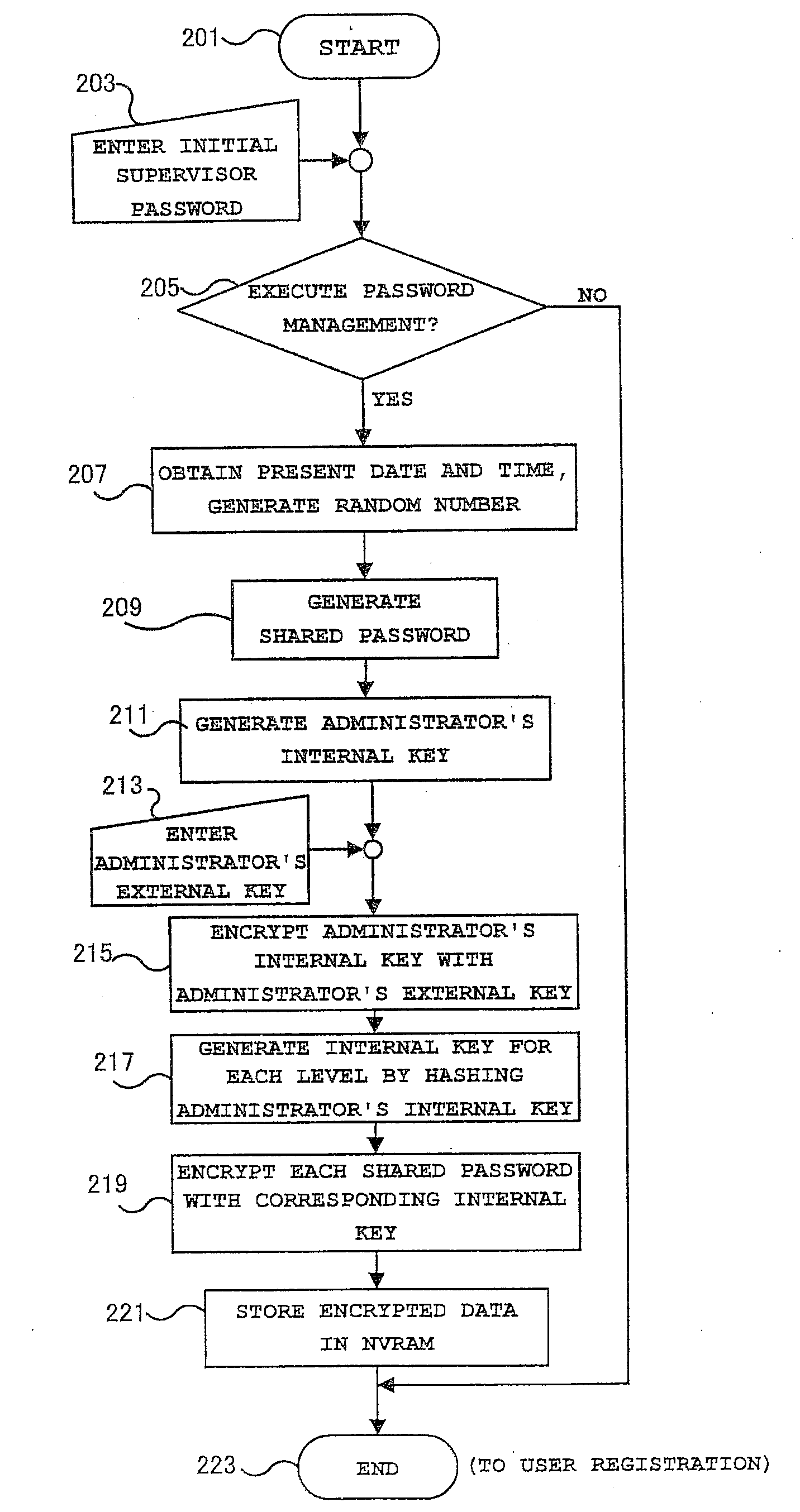
Method and Apparatus for Managing Shared Passwords on a Multi-User Computer
ActiveUS20080052777A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPasswordSecret code
A method for managing shared passwords on a multi-user computer system is disclosed. A set of shared passwords and an administrator internal key are initially generated. After the receipt of an administrator external key, the administrator internal key is encrypted with the administrator external key. For each user level within the computer system, an internal key is generated by hashing the administrator internal key. For each user level within the computer system, each of the shared passwords encrypted with a respective one of the internal keys. The internal keys and the encrypted shared passwords are then stored in a non-volatile storage device.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
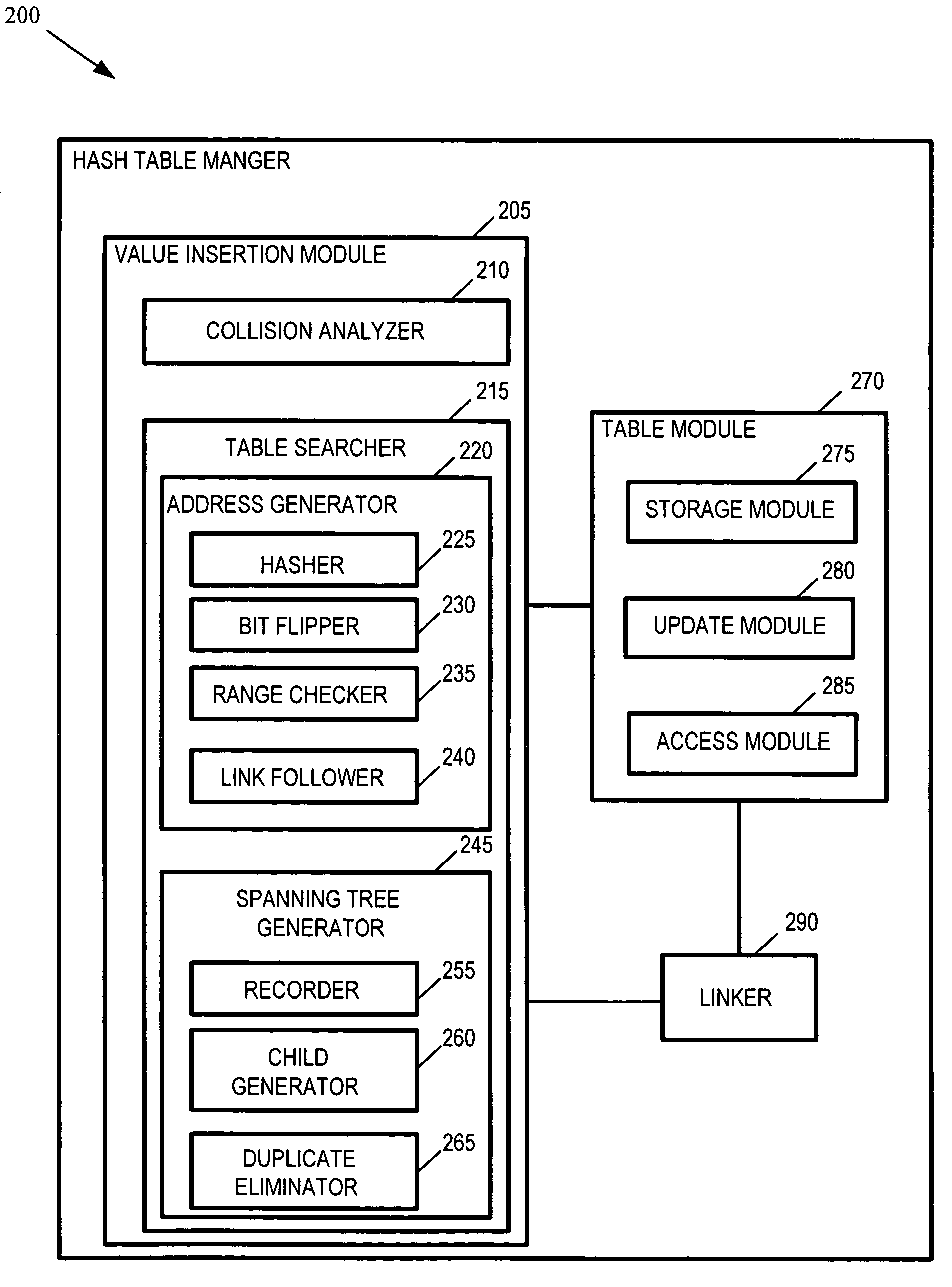
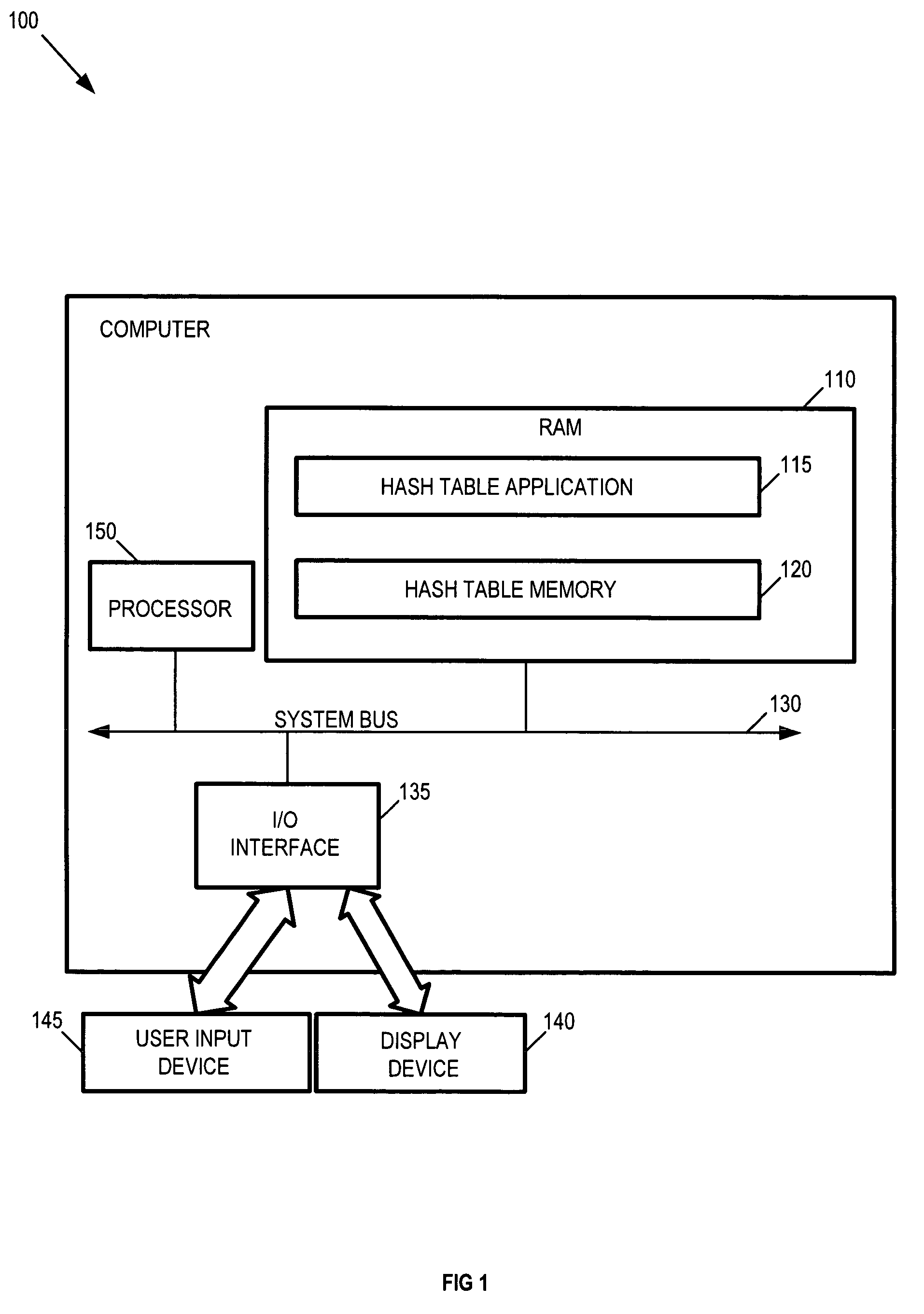
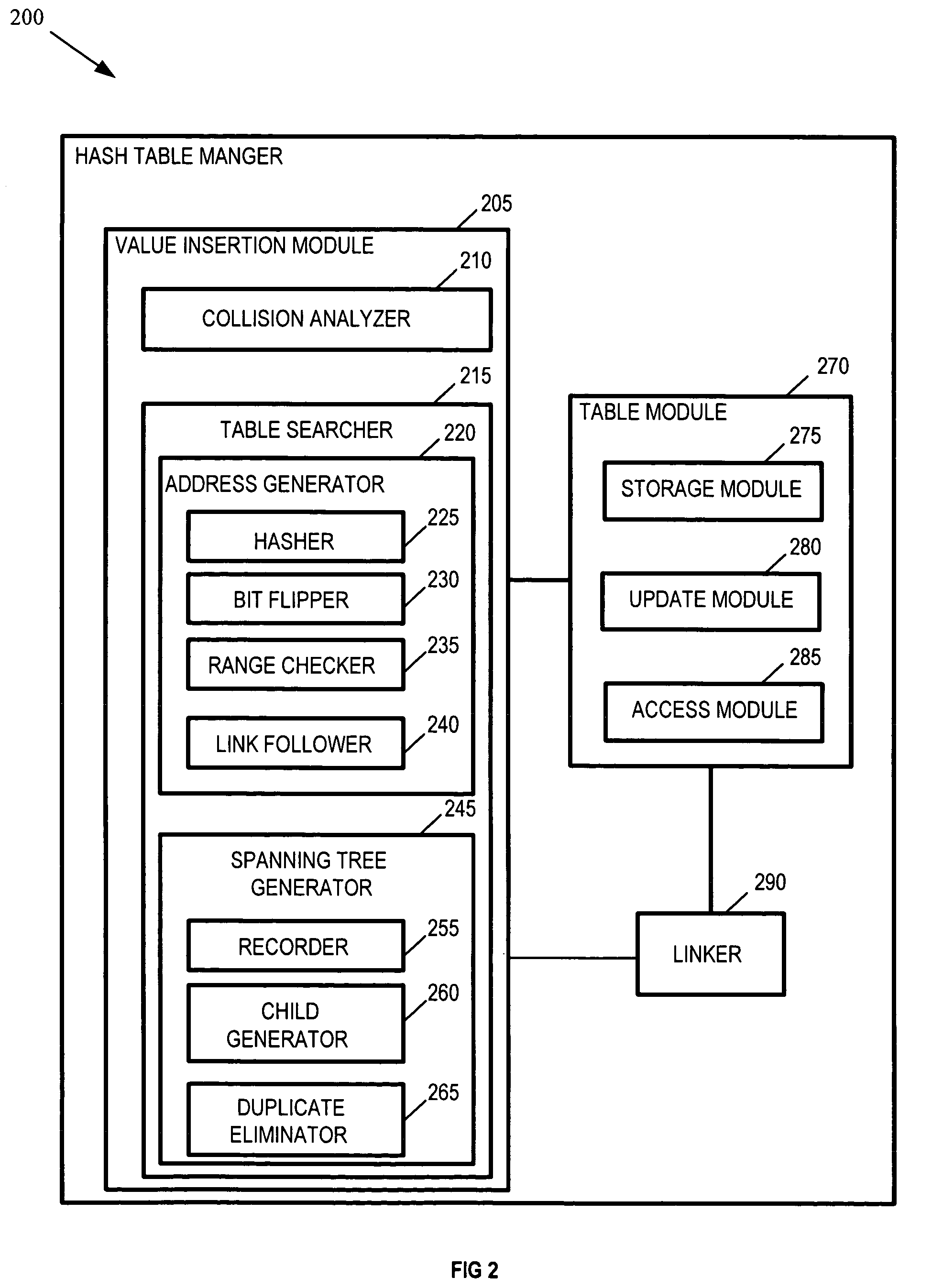
Methods and arrangements for inserting values in hash tables
InactiveUS7571299B2Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsTheoretical computer sciencePass the hash
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Asymmetric system and method for tamper-proof storage of an audit trial for a database
InactiveUS7000118B1Improve securityFulfil requirementsKey distribution for secure communicationData processing applicationsKey exchangeTamper resistance
An asymmetric key based method and system is provided for a tamper-proof storage of one or more records of an audit trail for a database. The asymmetric key based key exchange mechanism is employed to arrive at a common key, which is then used to obtain the authentication and the validation tokens. The method creates one or more authentication token values, and generates one or more validation token values from the authentication token values through a combination of a hashing process and an encryption process. Once the validation token values are created, they are further integrated into the records in the database. When an authorized person such as an auditor who needs to check the integrity of the records, he can detect a tampering of the records by comparing a validation token value newly computed by him independently with the validation token value integrated in the record.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
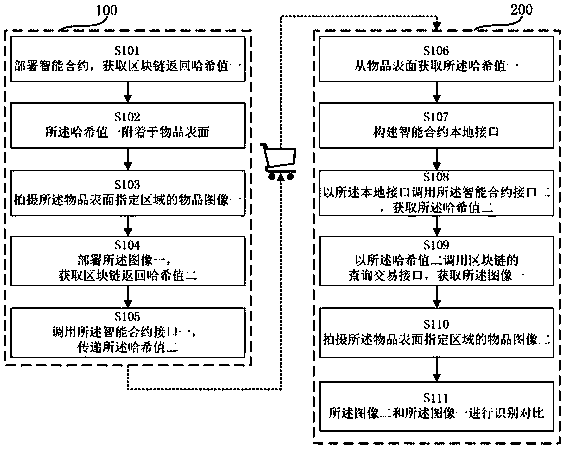
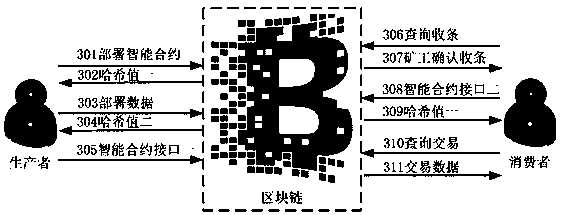
An article anti-counterfeiting and traceability method realized by using a block chain and an intelligent contract thereof
The invention discloses an article anti-counterfeit and traceability method realized by using block chain and intelligent contract thereof. On the production side, the producer publishes the transaction of the deployment intelligent contract to the block chain, obtains the hash value returned by the block chain, attaches the hash value to the surface of the article, then photographs the image of the designated area on the surface of the article, then publishes the transaction of the deployment image to the block chain, obtains the hash value returned by the block chain, and passes the hash value to the intelligent contract; after the goods reach the consumer end through the circulation link, a consume obtains a hash value one from that surface of the article, then, the hash value 2 is obtained through block chain and intelligent contract, and image 1 is obtained, image 2 of the designated area on the surface of the article is taken, and image 1 and image 2 are identified and compared,and the consistency of the article is checked through the consistency identification and comparison of the images, so as to realize the anti-counterfeiting and traceability of the article.
Owner:程昔恩
Method and system for authentication, data communication, storage and retrieval in a distributed key cryptography system
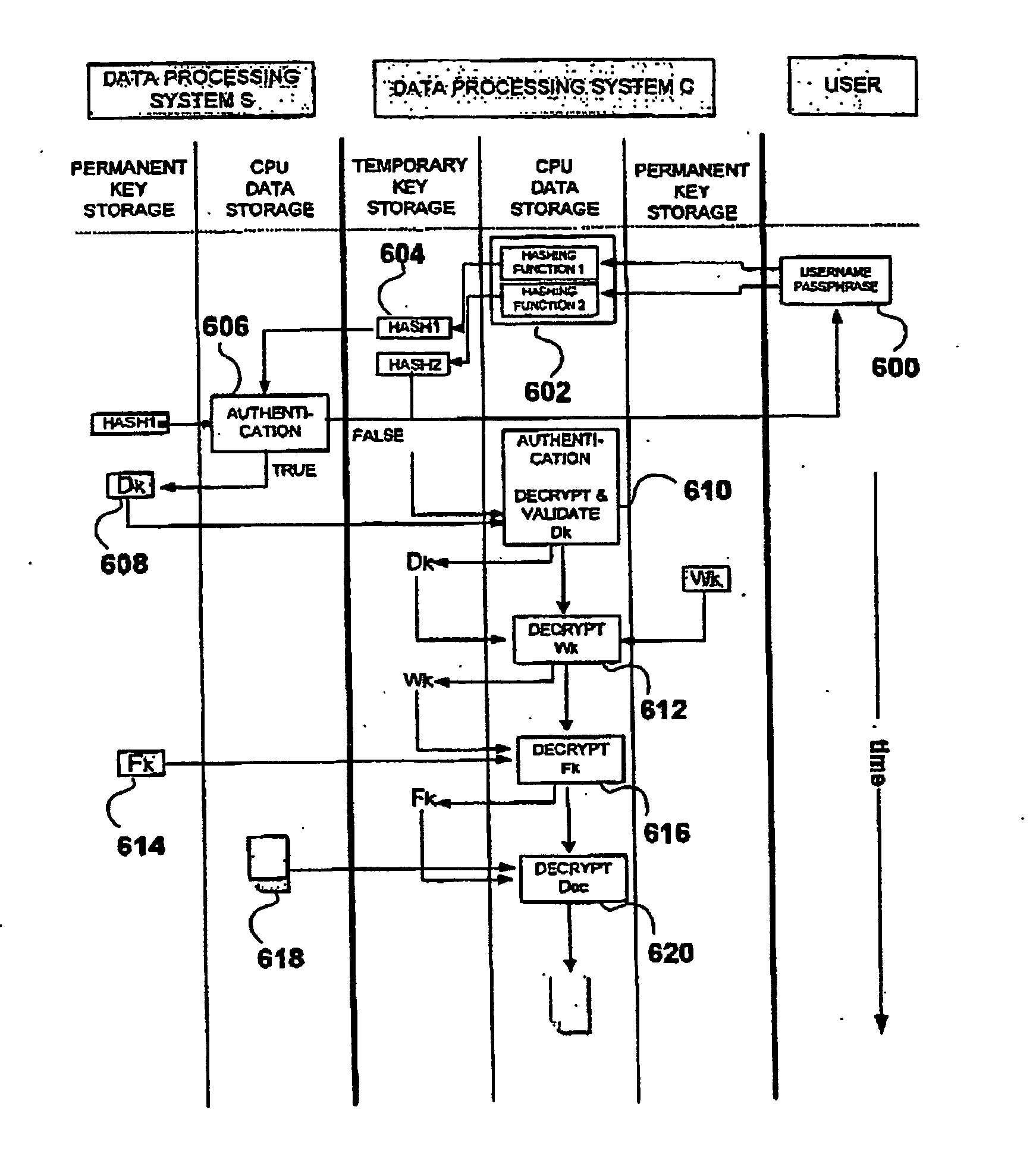
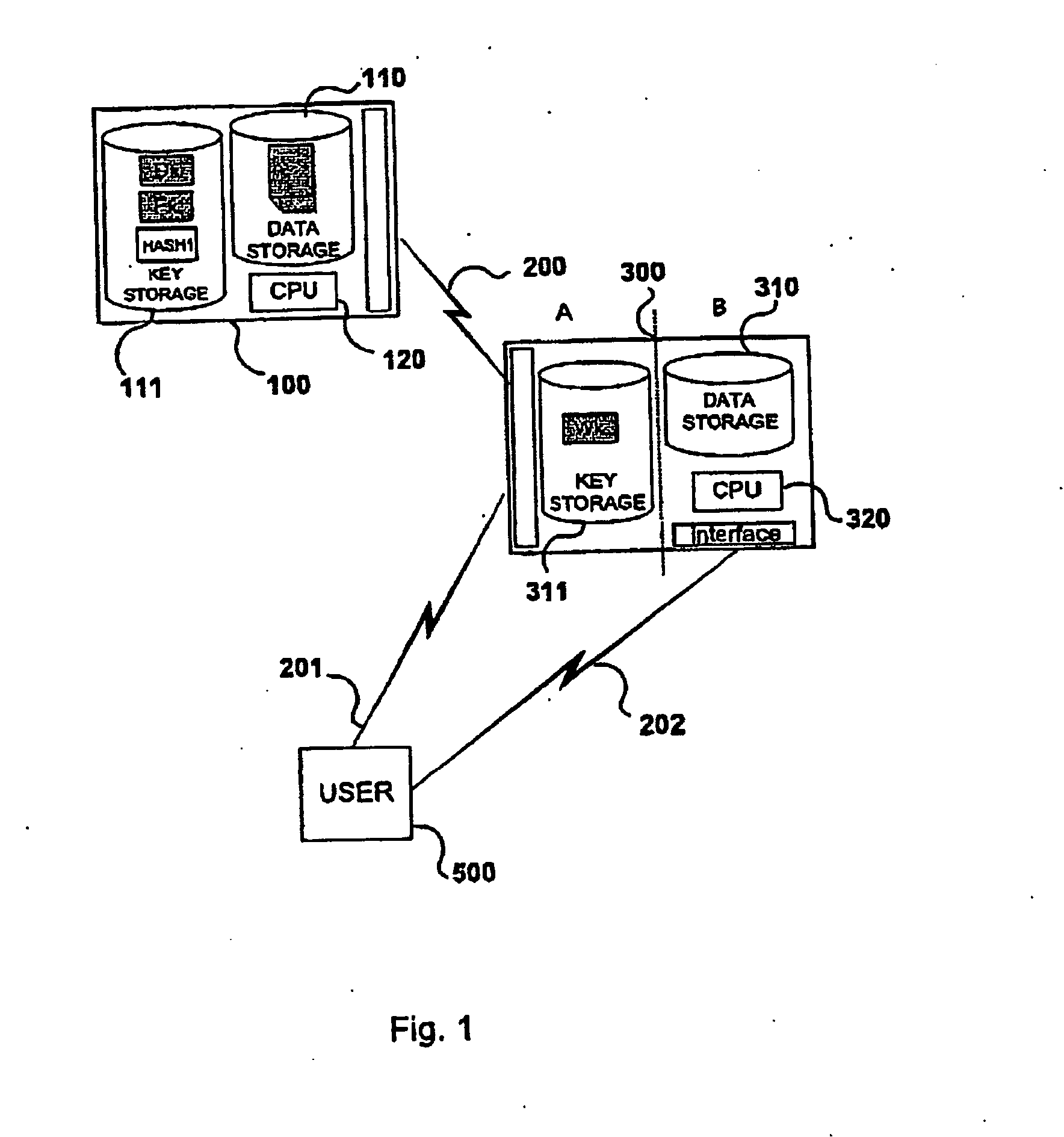
InactiveUS20050033963A1Improve securityUser identity/authority verificationPassphraseData processing system
A method for protecting the transfer and storage of data by encryption using a private key encrypted with a first key encrypting key, which is encrypted using a second key encrypting key. This latter key is encrypted using a hashed passphrase value, obtained by hashing a passphrase known only to the authorized user. Upon receipt of a request initiated by the user by entering a passphrase, a first hashed passphrase is transferred to a first data processing system, where it is compared with a predefined hash string. If they match, the first data processing system transfers to a second data processing system the encrypted second key encrypting key. A candidate key is obtained by decrypting the encrypted second key encrypting key using a second hashed passphrase. Upon successful validation of the candidate key, the passphrase is verified and the user is authenticated. After the user has been authenticated, the first data processing system transmits to the second data processing system the encrypted private key and the encrypted data. The second processing system then decrypts the encrypted first key encrypting key using the second key encrypting key, decrypts the encrypted private key using the first key encrypting key and finally decrypts the data using the private key.
Owner:EISST
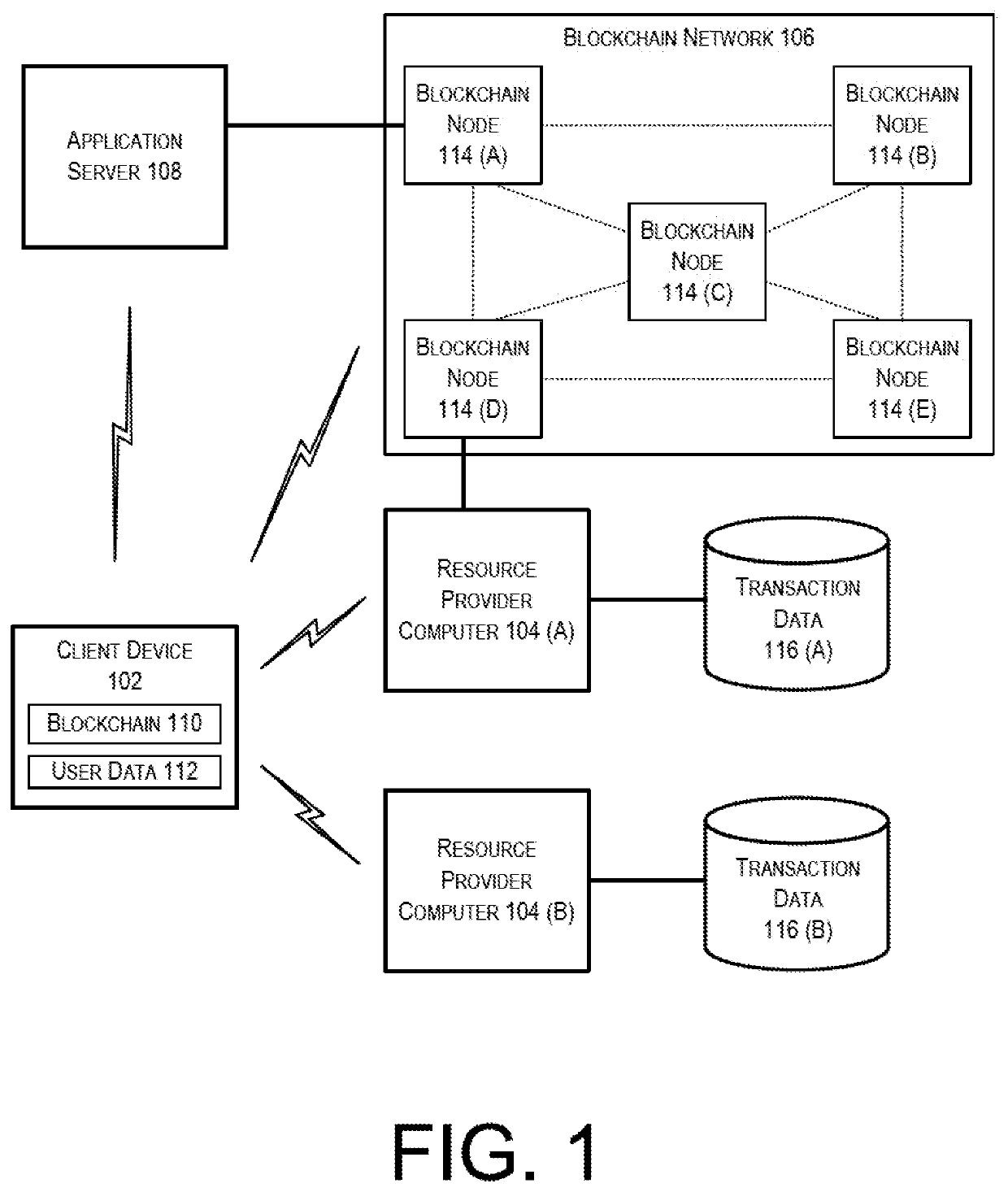
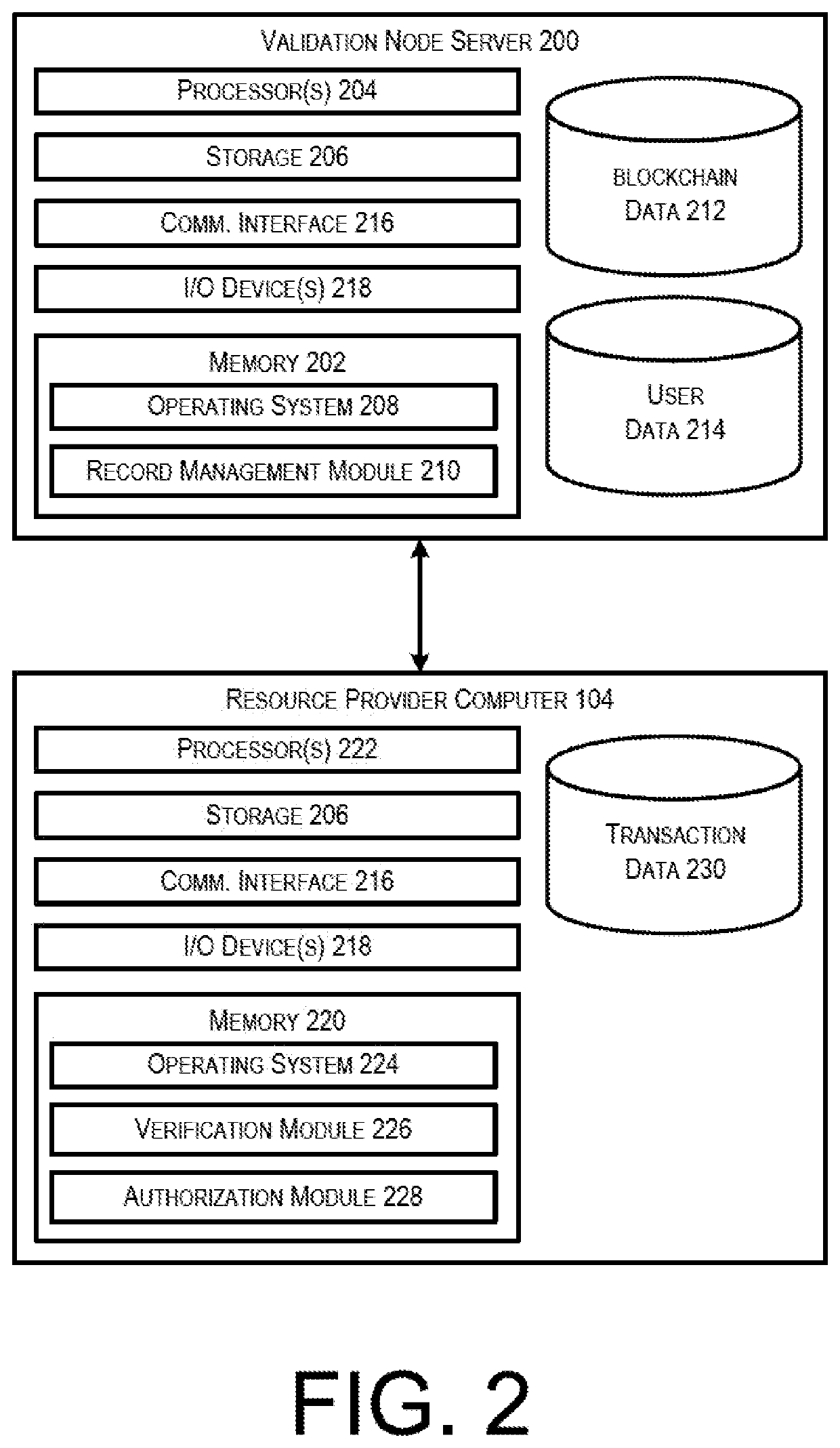
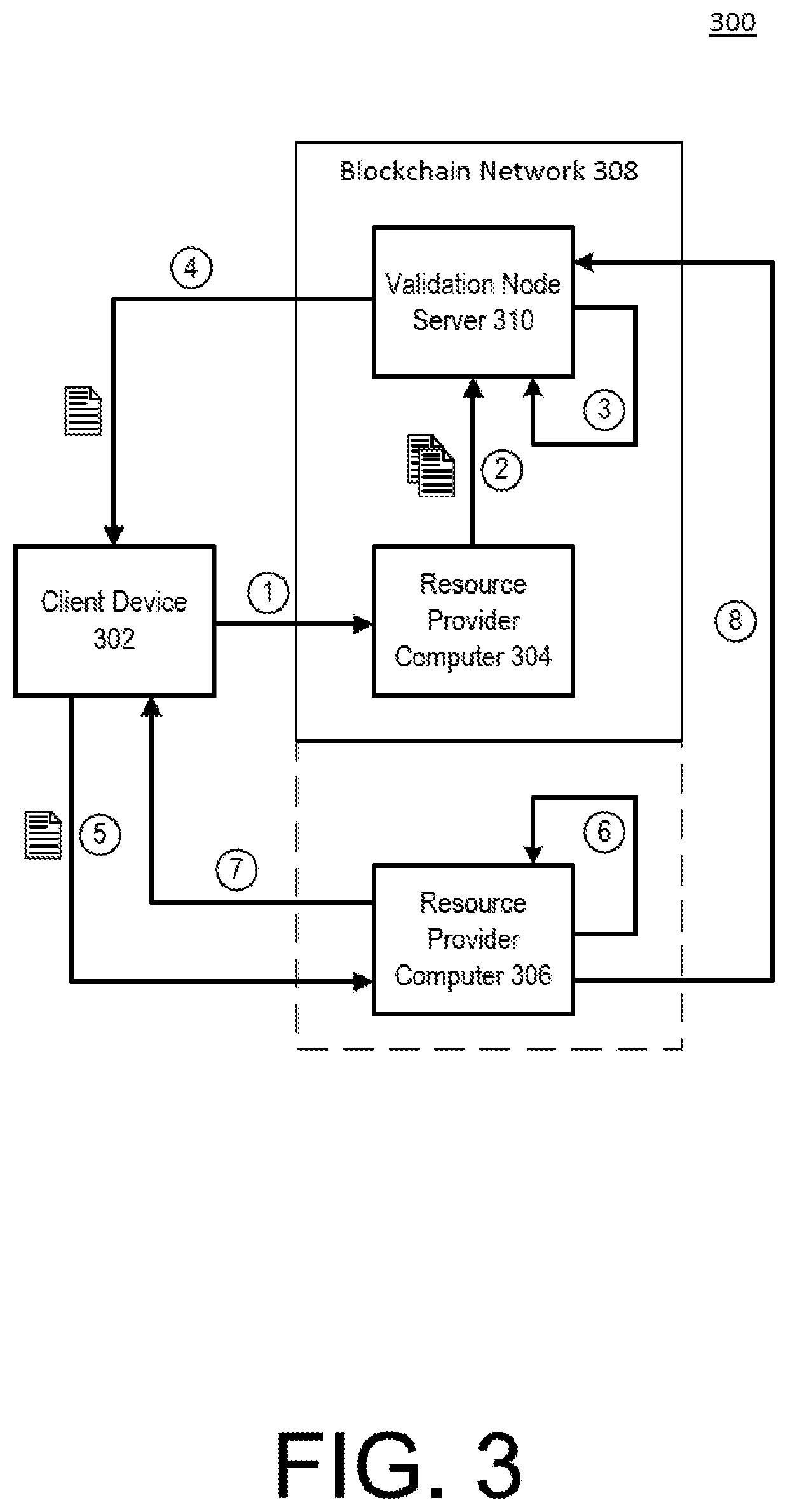
Blockchain architecture with record security
PendingUS20200250676A1Prevent unauthorized accessVerify authenticityKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesDigital signatureEngineering
Described herein is a system in which an electronic record is stored within a distributed environment. In this system, a validation node may receive a transaction record from an acceptance node. The validation node may verify that the acceptance node is authorized 5 to participate in a blockchain network, identify a user associated with the transaction record, and append the transaction record to an electronic record. The transaction record may be associated with a digital signature formed by hashing multiple data elements, and then encrypting the hashed data elements using a private encryption key.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
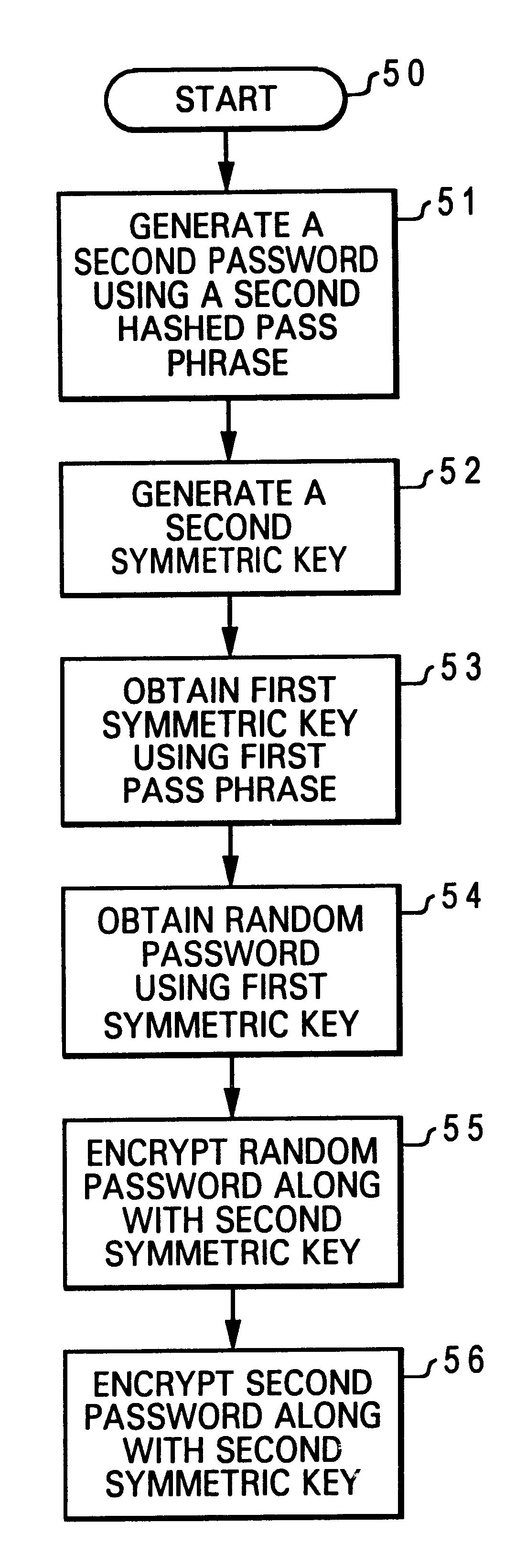
Method for associating a pass phase with a secured public/private key pair
InactiveUS6704868B1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPassphrasePassword
A method for associating a pass phrase with a secured public / private key pair is disclosed. A user public / private key pair is first established for a user. The user public / private key pair includes a user public key and a user private key. Then, the user public / private key pair is encrypted along with a random password, utilizing a chip public key. Next, a first symmetric key is generated. The random password is encrypted utilizing the first symmetric key. A first password is generated by hashing a first pass phrase. Finally, the first password is encrypted along with the first symmetric key, also utilizing the chip public key. As a result, a user can access the user private key to perform an authentication function by providing the first pass phrase.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
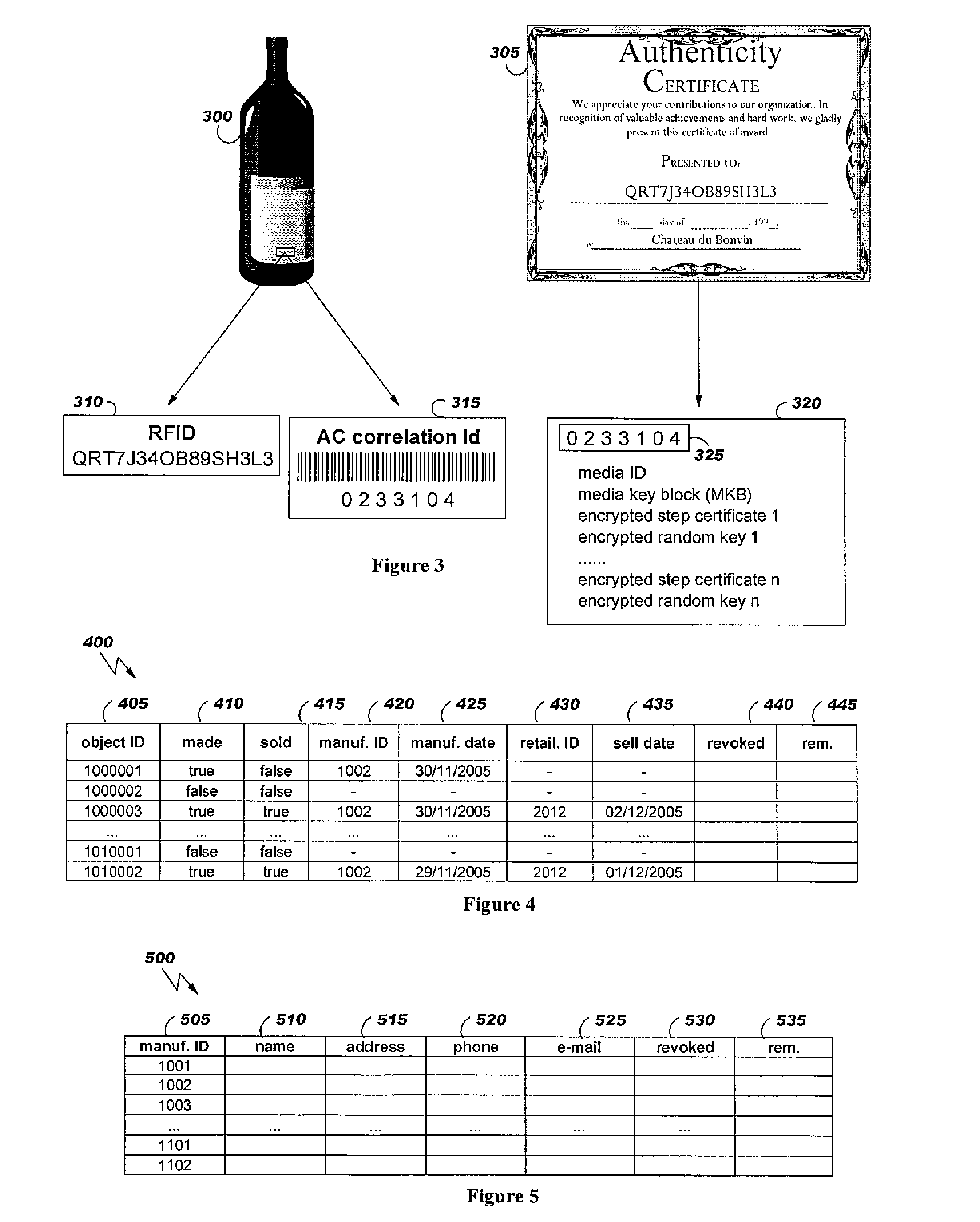
Using identifier tags and authenticity certificates for detecting counterfeited or stolen brand objects
A method and system for generating data for use in generating an authenticity certificate. A request is received for a step certificate that authenticates an involvement of the requester entity about an object. The request includes a media identifier, a media key block, an object identifier, a requester entity type of the requester entity, and a requester identity certificate of the requester entity. The object identifier is hashed. A signature is created. A hashing result is generated by hashing a concatenation of the object identifier, the requester entity type, the certifier entity certificate, the requester identity certificate, and the signature. The step certificate is generated and includes the hashing result. The step certificate is encrypted using a random key. The encrypted step certificate and an encrypted random key are sent to the requester entity for subsequent writing the step certificate and the encrypted random key on a media.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
System, apparatus and method for identifying and blocking anomalous or improper use of identity information on computer networks
InactiveUS20120151565A1Minimize potential for disruptionUndesirable activityDigital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsClient-sideComputer science
A system, apparatus and method is described for a security platform and / or identity platform for identifying, notifying, reporting and blocking pass-the-hash attacks and the anomalous or improper use of identity information on computer networks. The system, apparatus or method follows a policy of zero-trust, and does not rely on any client or server information to verify or confirm identity. Instead, the system, apparatus or method of the invention monitors communications between network devices, and when a first device transmits a communication of interest to a second device, the system, apparatus or method of the invention queries the first device directly to determine whether the transmission is authorized.
Owner:FITERMAN ERIC
Password encryption method and system, and cryptographic check method and system
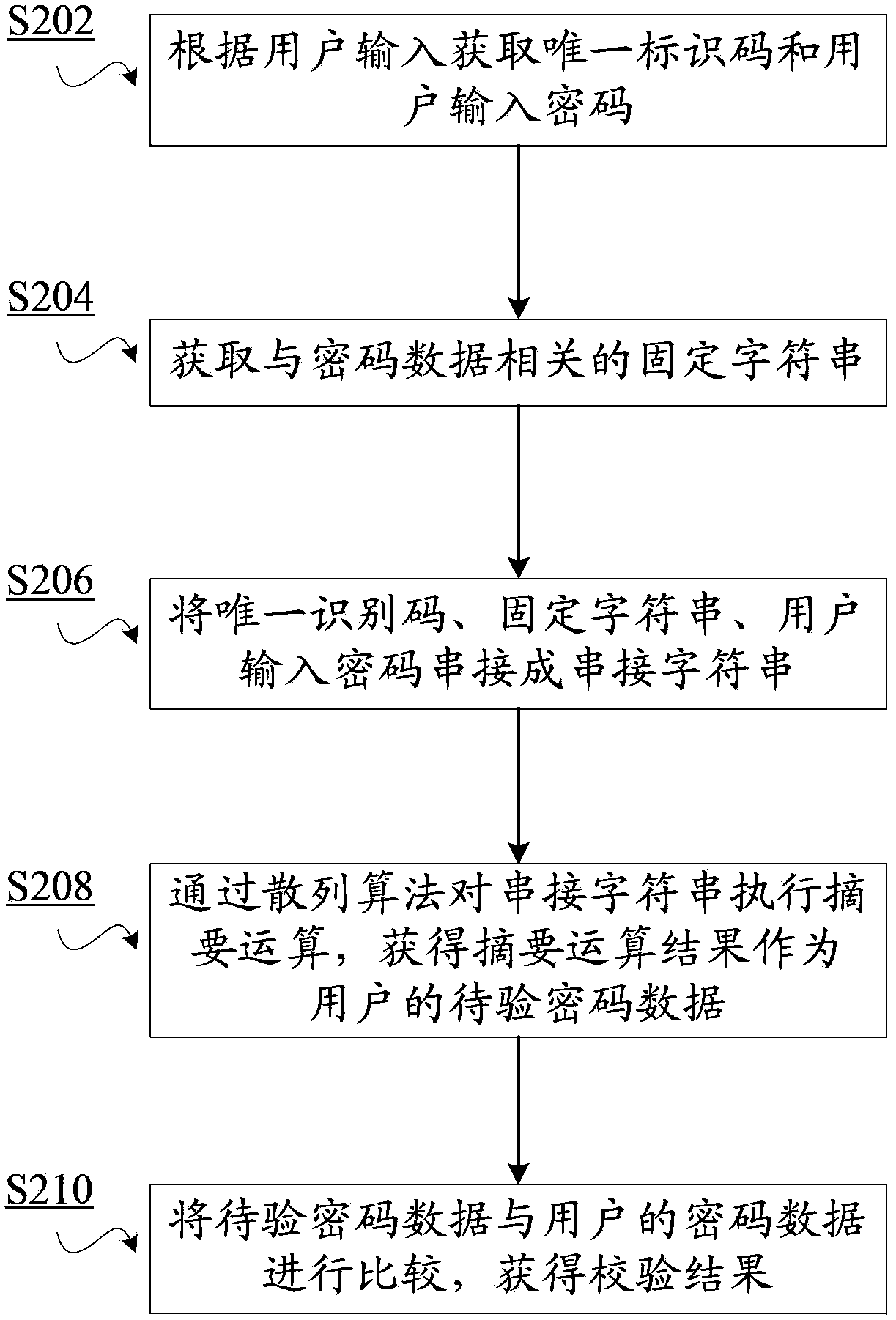
ActiveCN103780379AUniqueness guaranteedAdd unique factor - user unique identification codeUser identity/authority verificationChosen-plaintext attackPassword
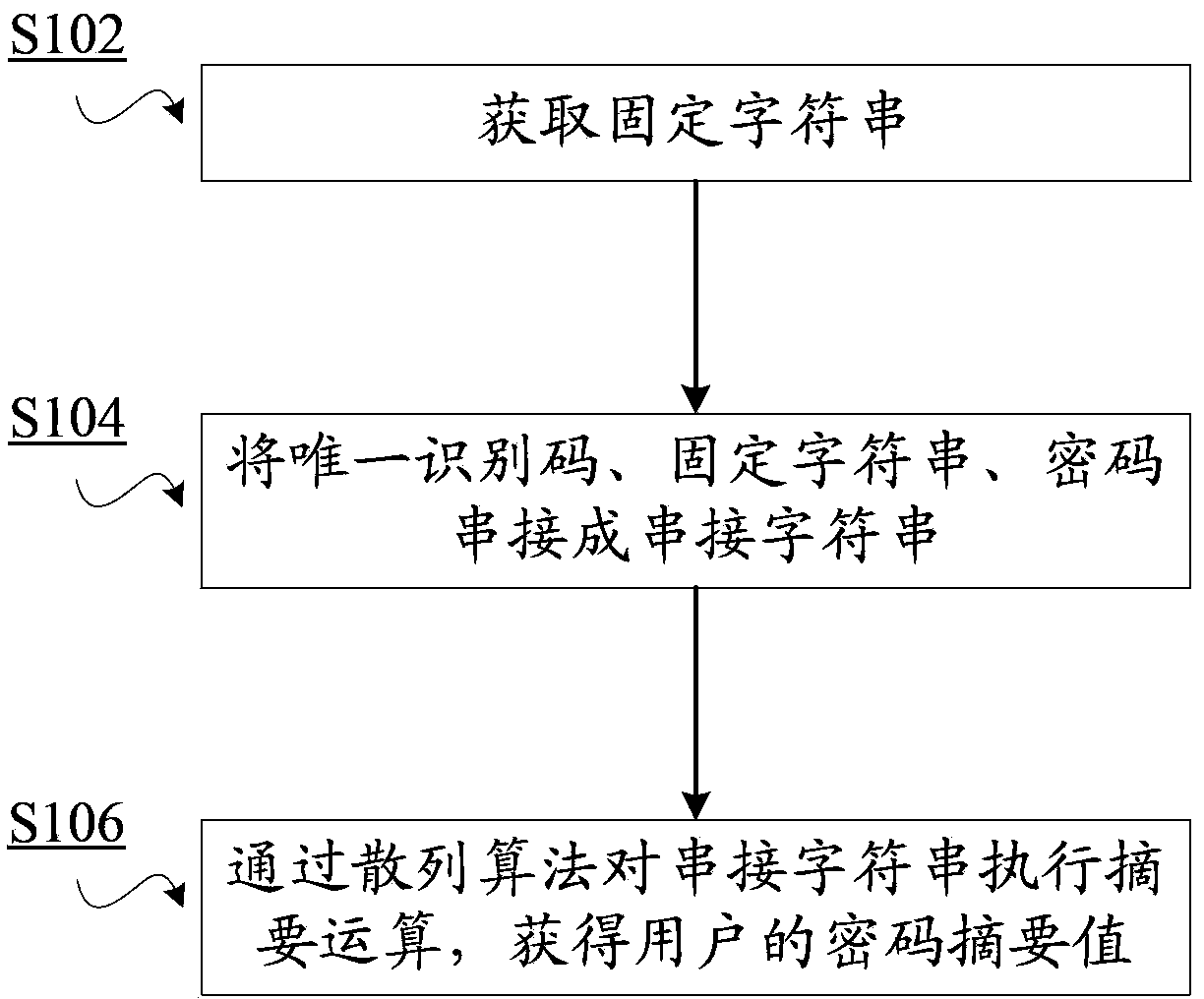
The invention discloses a password encryption method used for performing encryption on passwords of users, wherein each user has a unique identification code. The method includes the following steps: acquiring a fixed character string; cascading the unique identification code, the fixed character string and a password into a cascaded character string; and executing a digest operation on the cascaded character string through a hash algorithm and acquiring a password digest value of a user. Through application of the password encryption method and system, and a cryptographic check method and system, the methods and systems are applicable to card-password data protection and user security-problem answer protection and the like. Because in a user password digest operation process, a user unique factor, that is, the user unique identification code is added so that uniqueness of a user password digest value is ensured and thus password database files are endowed with capabilities of resisting chosen-plaintext attacks and beforehand chosen-plaintext attacks.
Owner:ADVANCED NEW TECH CO LTD
Dual hash indexing system and methodology
ActiveUS7979671B2Memory adressing/allocation/relocationData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityClient-side
A method, system and program are disclosed for accelerating data storage in a cache appliance that transparently monitors NFS and CIFS traffic between clients and NAS subsystems and caches files in a cache memory by using a dual hash technique to rapidly store and / or retrieve connection state information for cached connections in a plurality of index tables that are indexed by hashing network protocol address information with a pair of irreducible CRC hash algorithms to obtain an index to the memory location of the connection state information.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
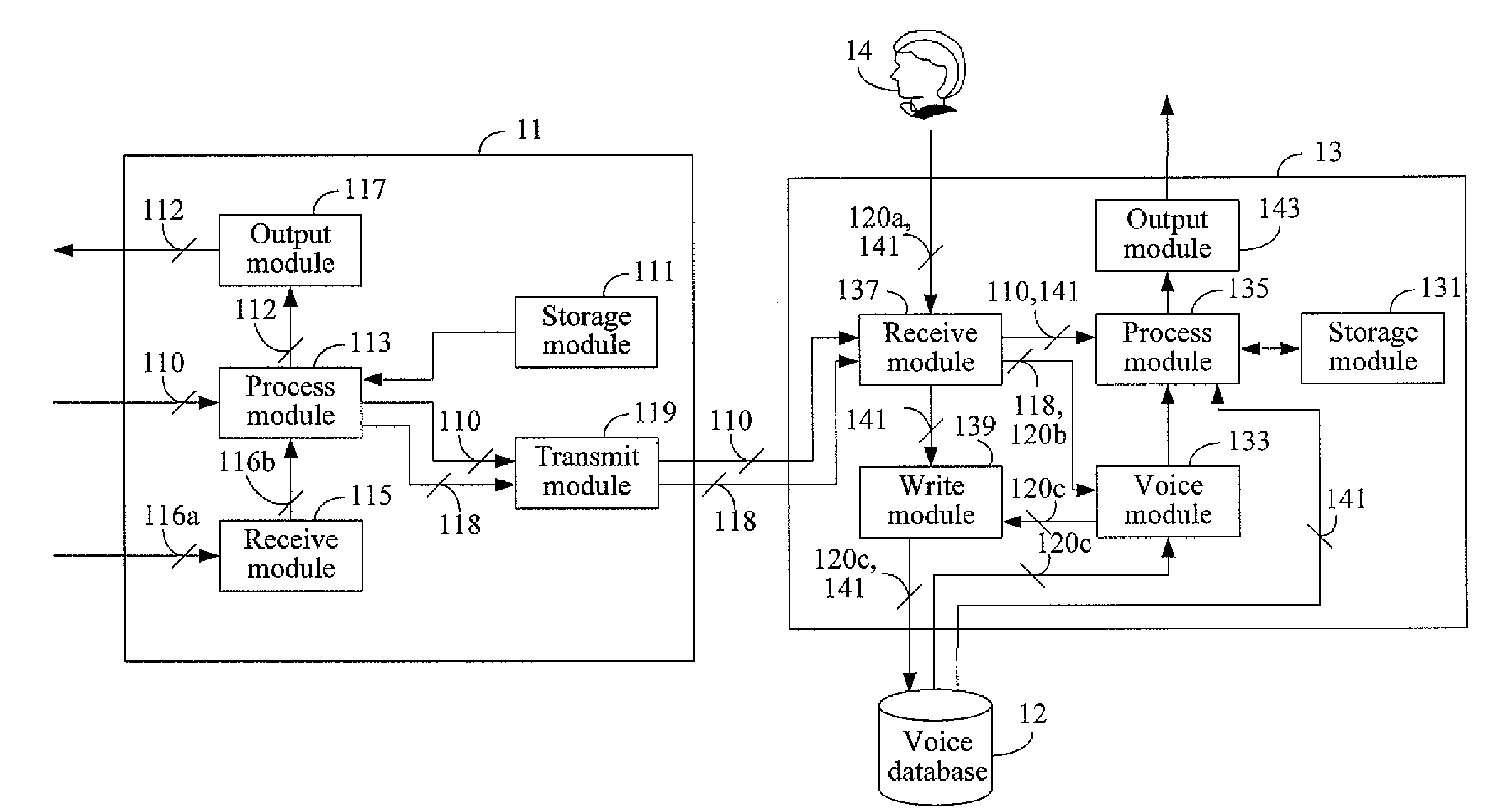
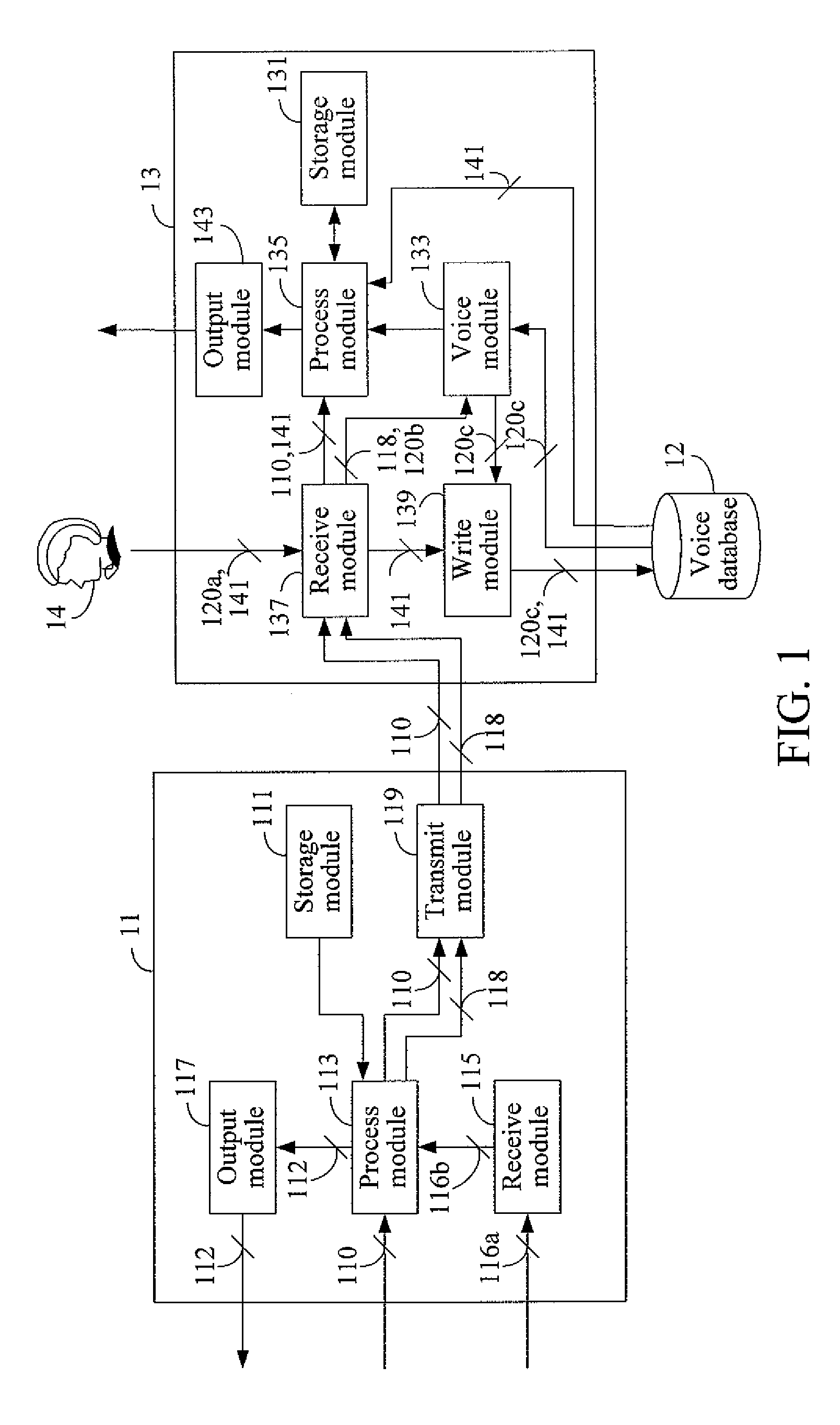
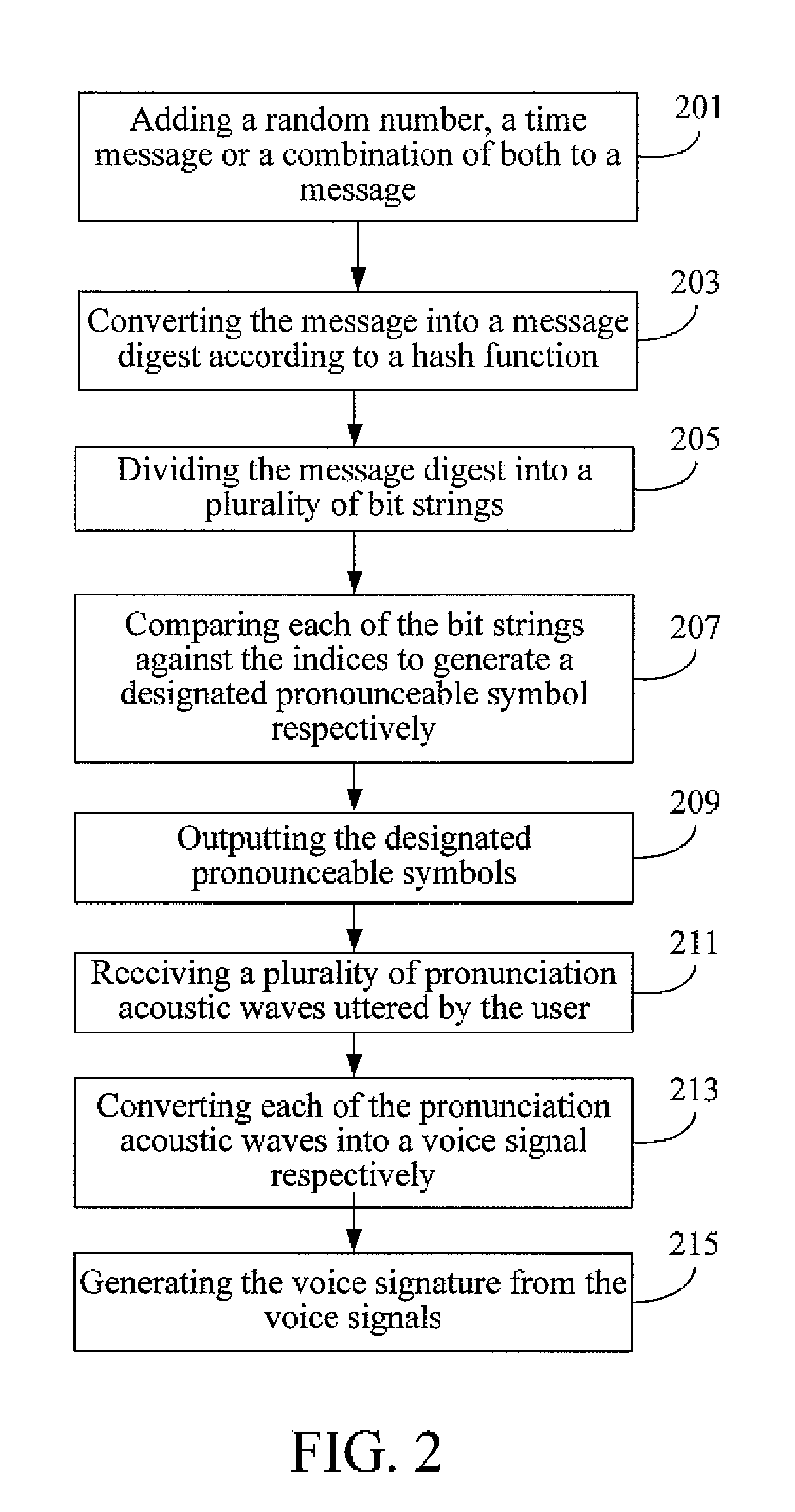
Apparatus and method for generating and verifying a voice signature of a message and computer readable medium thereof
InactiveUS20100131272A1Shorten the lengthReduce riskUser identity/authority verificationNatural language data processingHash functionSpeech verification
Apparatuses and methods for generating and verifying a voice signature of a message and computer readable medium thereof are provided. The generation and verification ends both use the same set of pronounceable symbols. The set of pronounceable symbols comprises a plurality of pronounceable units, and each of the pronounceable units comprises an index and a pronounceable symbol. The generation end converts the message into a message digest by a hash function and generates a plurality of designated pronounceable symbols according to the message digest. A user utters the designated pronounceable symbols to generate the voice signature. After receiving the message and the voice signature, the verification end performs voice authentication to determine a user identity of the voice signature, performs speech recognition to determine the relation between the message and the voice signature, and determines whether the user generates the voice signature for the message.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR INFORMATION INDUSTRY
Database concurrency control through hash-bucket latching
ActiveUS20180218023A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsConcurrency controlPass the hash
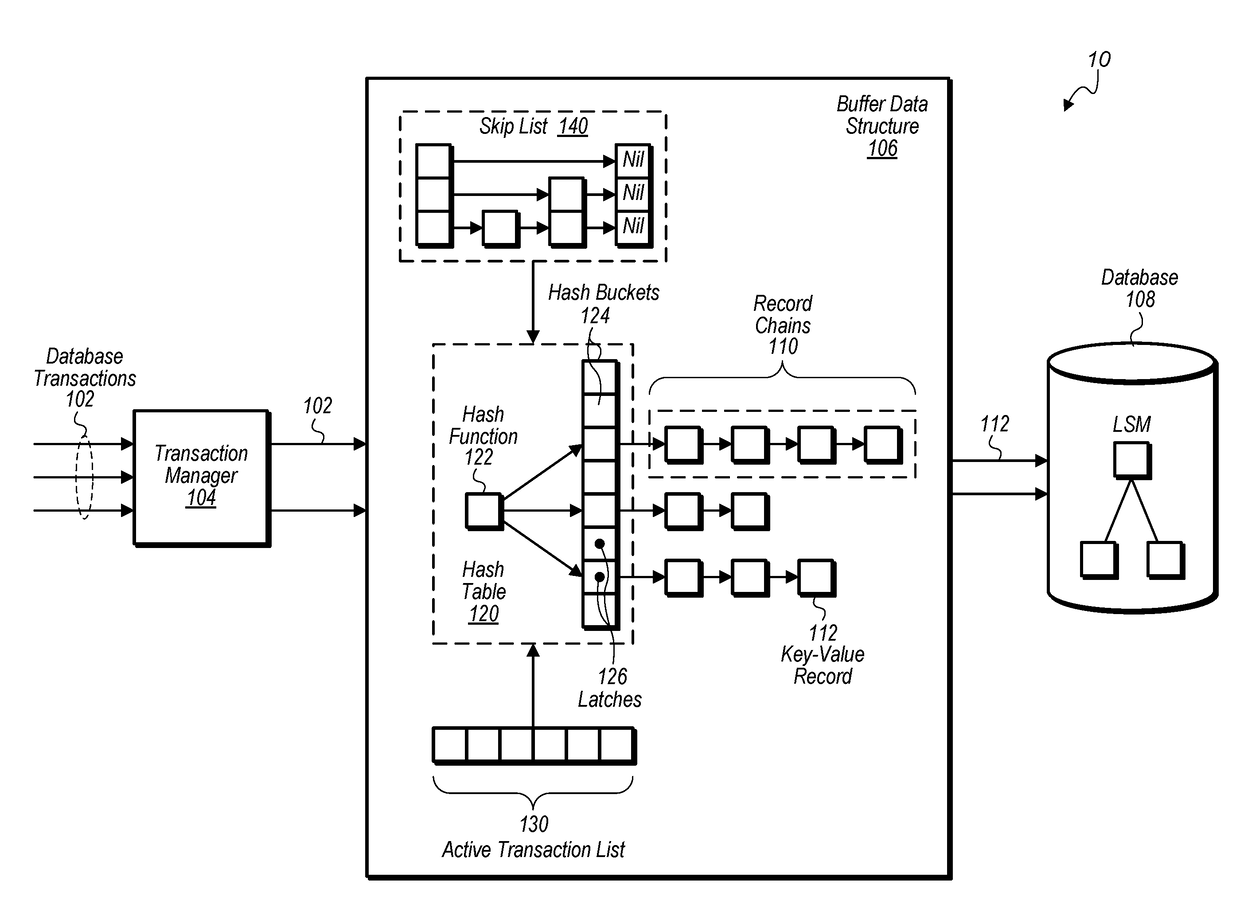
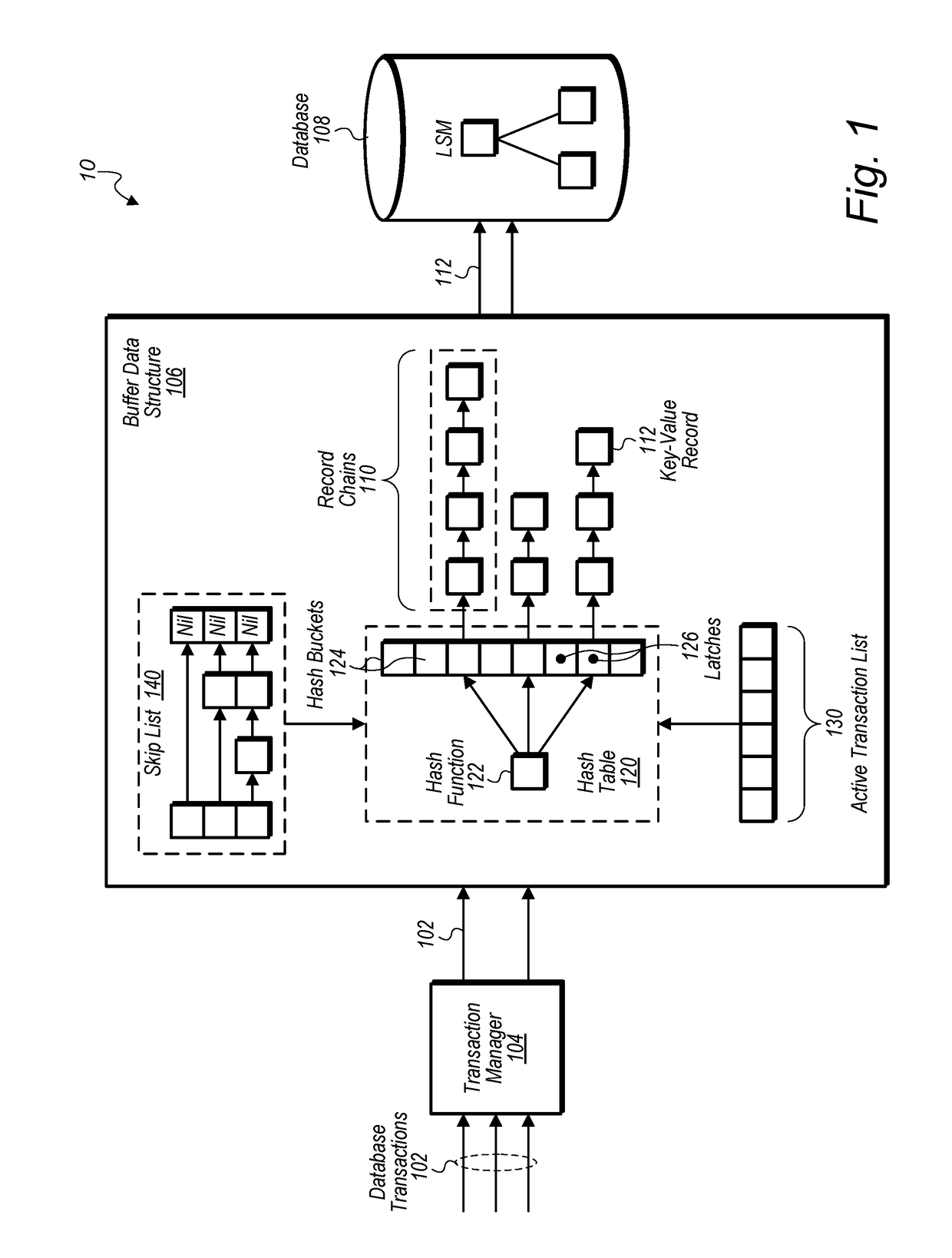
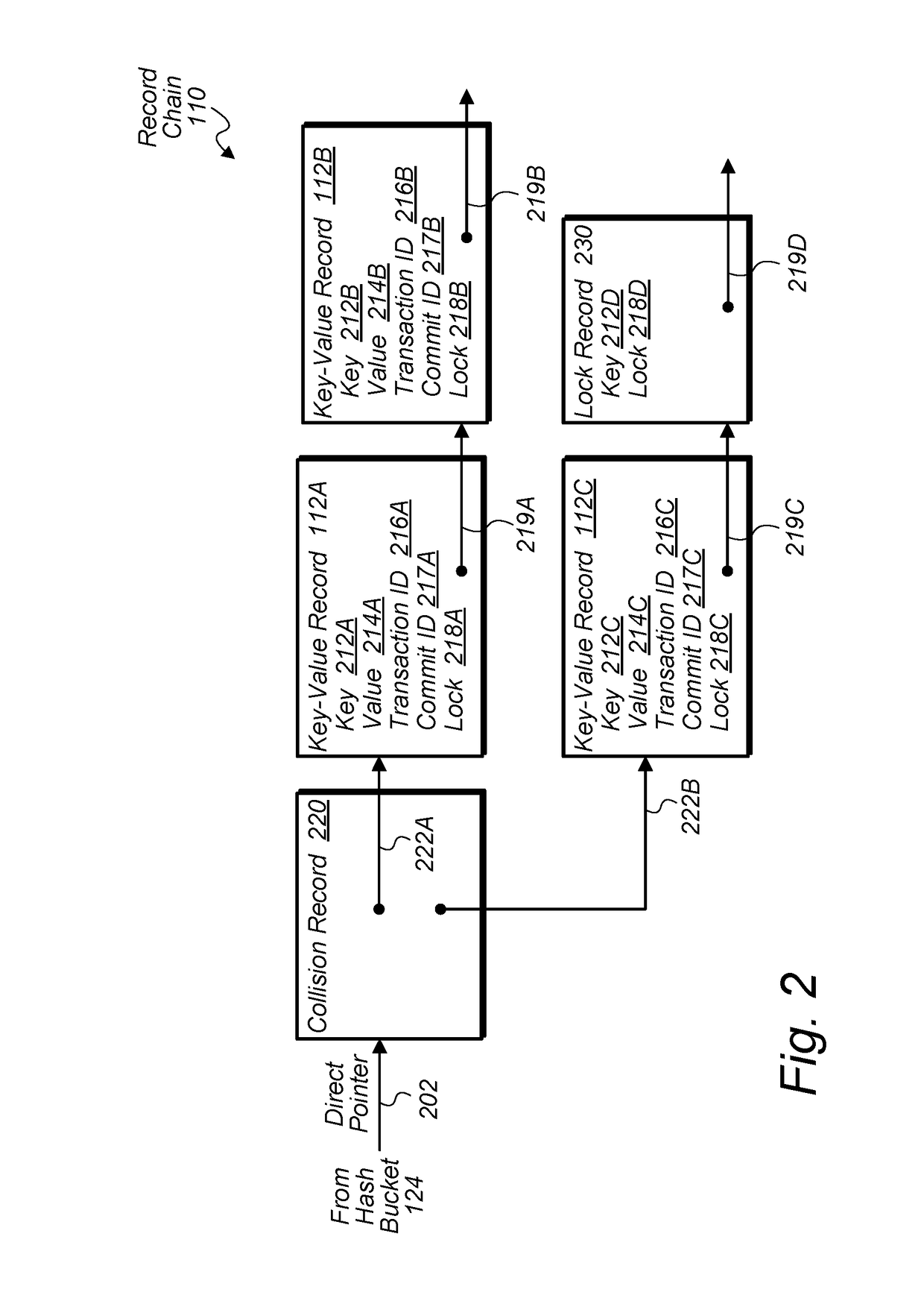
Techniques are disclosed relating to efficiently processing of concurrent database transactions. In one embodiment, a database system receives a first key-value pair for a database transaction and stores the key-value pair in a data structure for active database transactions. The storing may include indexing into a hash table of the data structure with a key of the key-value pair to identify a hash bucket of the hash table corresponding to the key, acquiring a latch associated with the identified hash bucket, and, based on a state of the acquired latch, appending, to the hash bucket, a record specifying the key-value pair. The database system may cause the key-value pair from the data structure to be committed to persistent storage in response to the database transaction being committed.
Owner:SALESFORCE COM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com