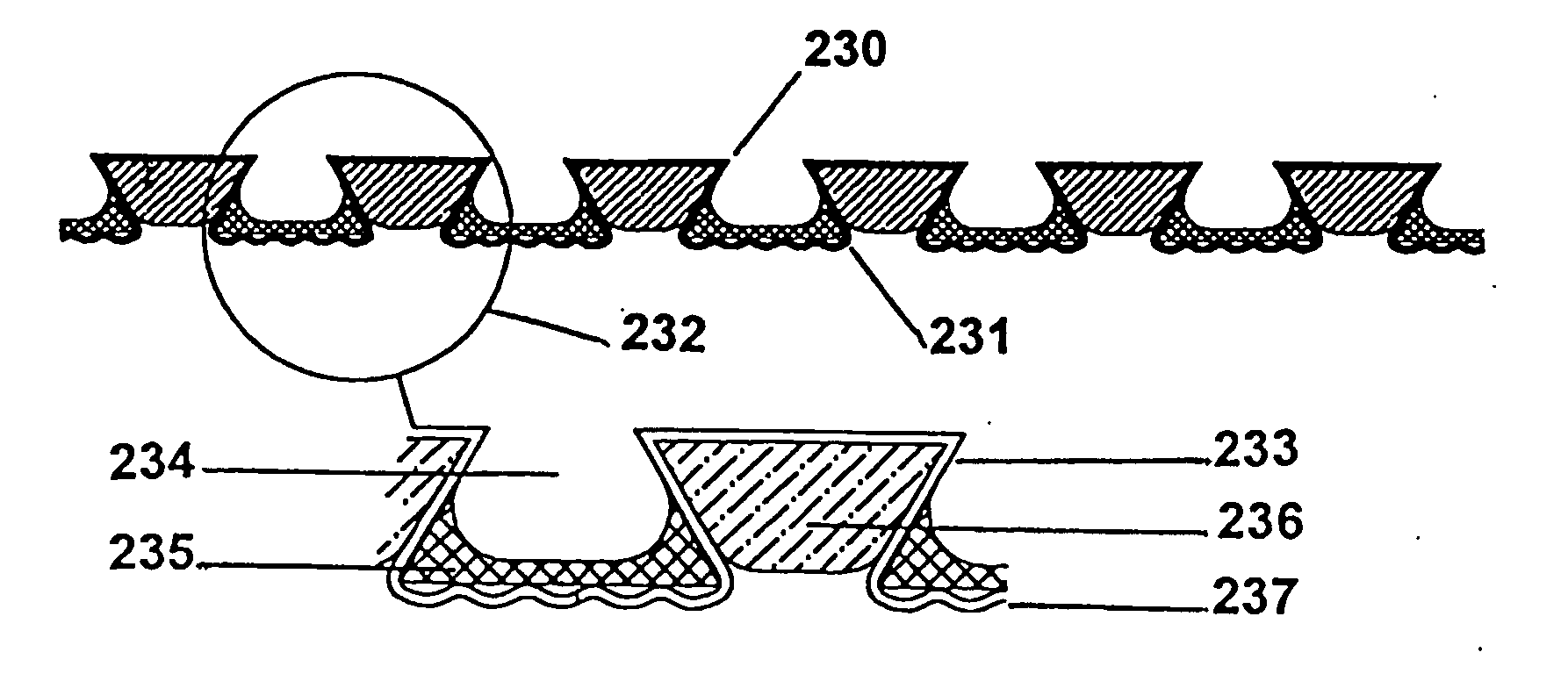
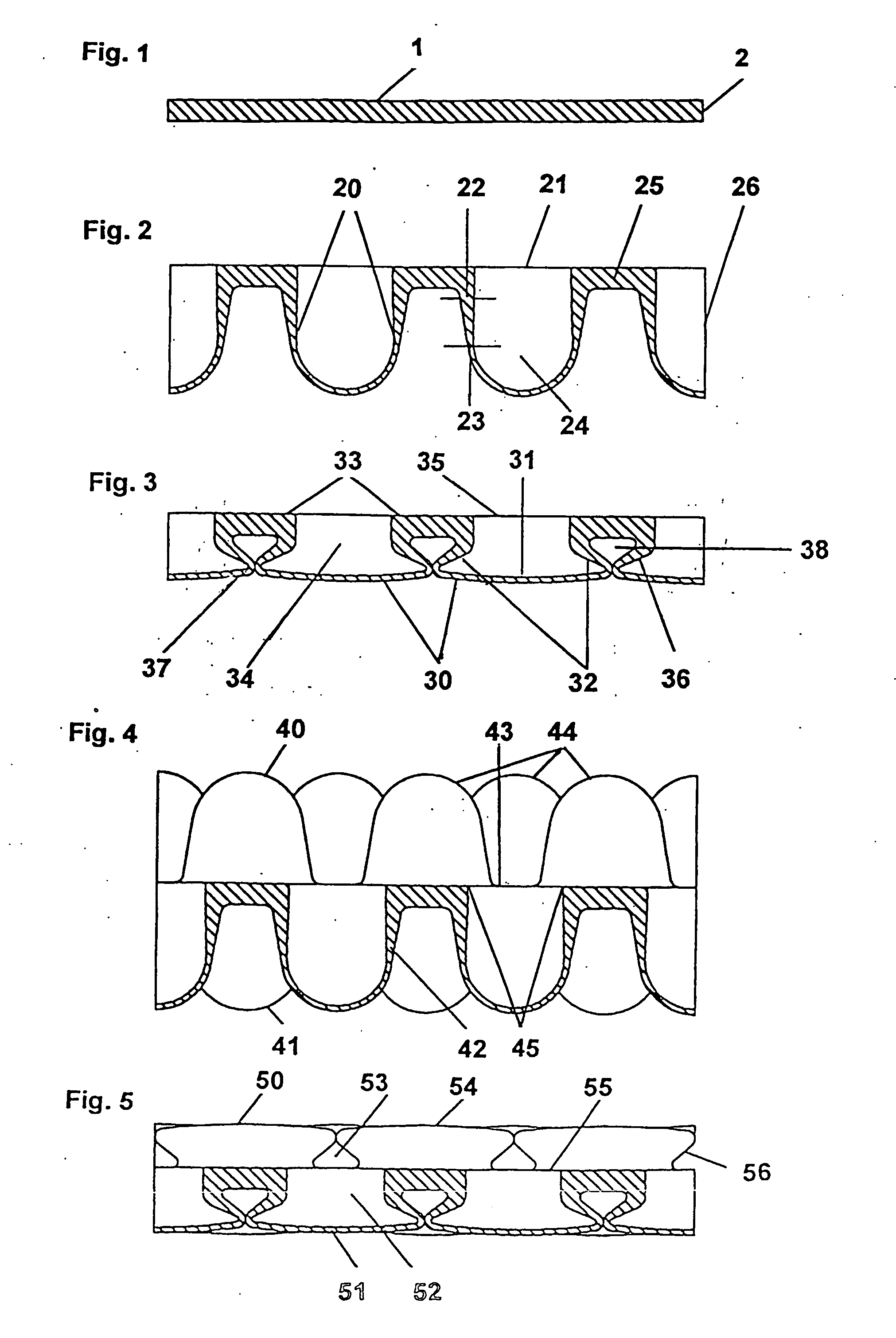
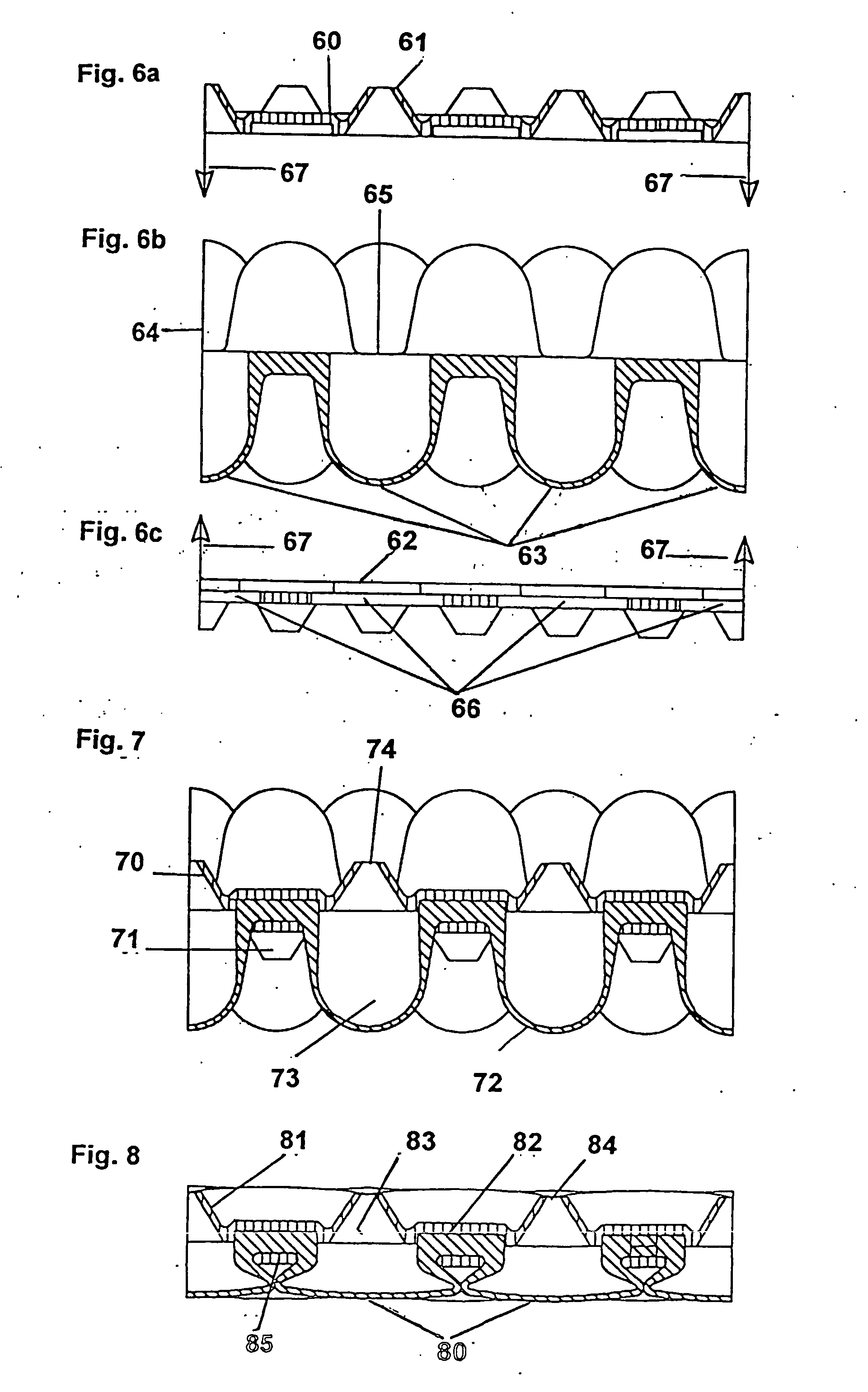
Flexible formed sheets for treating surfaces
a flexible, surface technology, applied in the direction of cleaning process and apparatus, application, domestic items, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to use, difficult to deal with fibre wipes, limitations in personal care cosmetics, domestic, institutional and industrial cleaning, etc., and achieve the effect of expanding the functionality of the tool
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0145] To vacuum draw an array use first tool set.
[0146] Test 1—Preparation: A 150 mm square 0.3 mm thick sheet was cut from general purpose LDPE blown film marked as grade 118W branded SABIC™, a trade mark of SABIC EuroPertochemicals Company, Poststraat 1, 6135 KR Sittard P.O. Box 5151, 6130 PD Sittard, The Netherlands. The material believed to have a Flexural Modulus between 200 and 600N / mm2. The cut sheet then placed between dies in Tool Set 1 and heated to 127° C. and the dies closed and left for 1 minute. The dies being of polished aluminium with recesses machined 3.5 mm deep overall with domed head and 3 mm diameter, and placed on 4.5 mm centres. A vacuum hole was placed at the top dead centre of each recess.
[0147] Test 1—Stage 1: An appropriate partial vacuum was drawn and maintained while the platens were cooled to about 75° C. The vacuum was released and the platens opened. The pre-form was removed from tooling at about 25° C. and was as shown in double-sided format in FI...
example 2
Tool Set 2 Employed a Wire Grid in Die Set with Flat Dies
[0155] Test 4 preparation: a 150 mm square 0.3 thick sheet of LDPE was cut from the same source as used in Example 1.
[0156] Test 4: the lower heated aluminium die had an air supply and diffuser located in a shallow recess approx 155 mm square and about 3.5 mm deep. A perforated sheet of aluminium 0.5 mm thick was cut to fit inside the recess to allow air to flow under the heated sheet. The sheet to be formed was laid into the recess on top of perforated sheet of aluminium and the wire grid placed over it as illustrated in FIG. 15—the wires being 2 mm thick and 154 mm long, and these rested on a ledge 2 mm down within the recess. A flat ton die was closed onto the wires generally as illustrated in FIG. 19, but without micro-roughness. A slight positive pressure of 0.2 bar was maintained as the sheet temperature within the tooling rose to 129° C. The pressure was then increased to 1 bar for 30 seconds and then relaxed back to ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com