Data warehouse system and query processing method used in the system, and data collecting method and apparatus for the method, and charging method and apparatus in the system
a data warehouse and query processing technology, applied in database management systems, data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of high cost of processing those many queries, reduce the dependency of query processing on the network, reduce the load of each server, and shorten the response time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
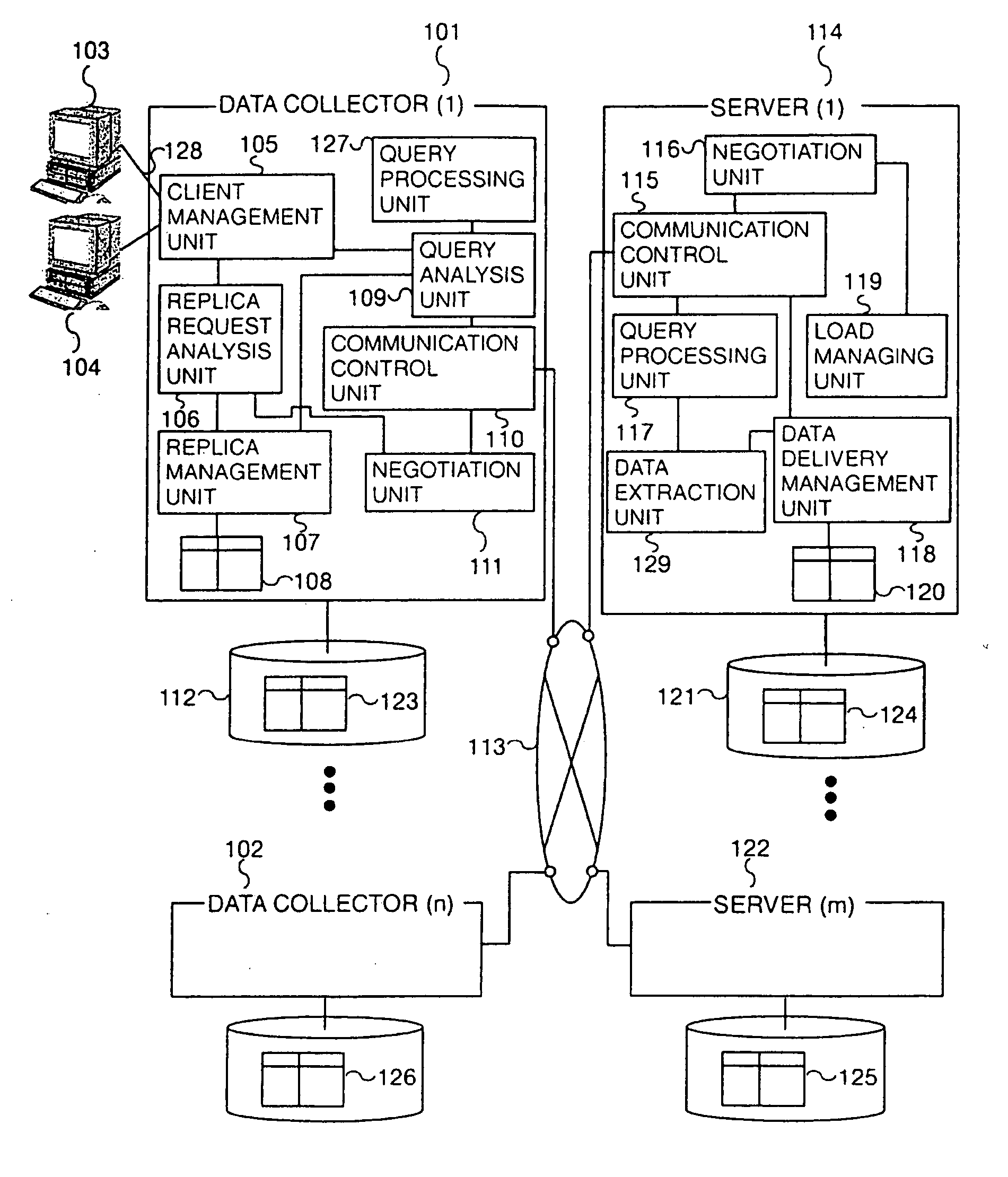
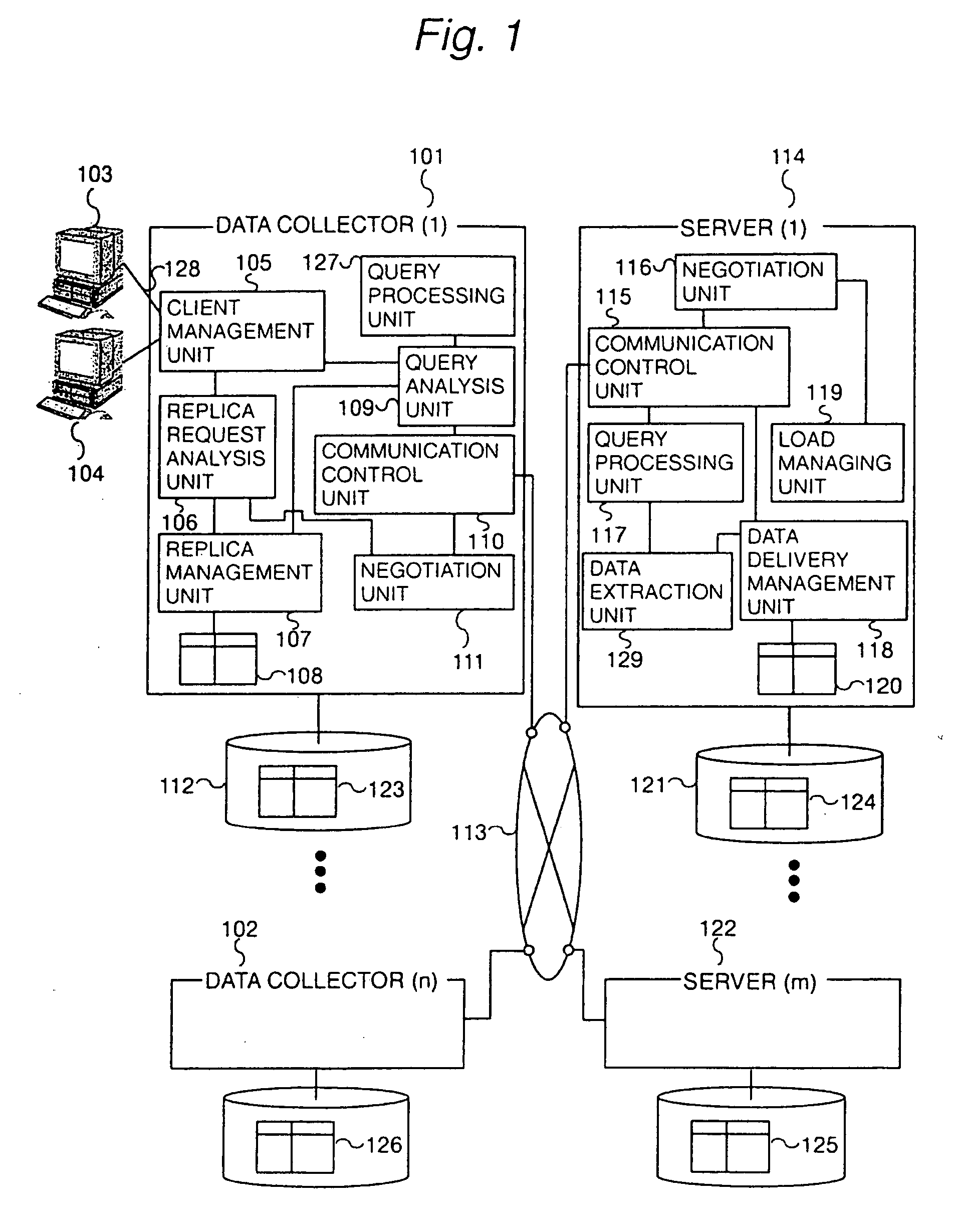
[0043]FIG. 1 shows a preferred embodiment of a data warehouse system in accordance with the present invention. Clients 103 and 104 are connected to a data collector 1 (101) via an infra-network 128.
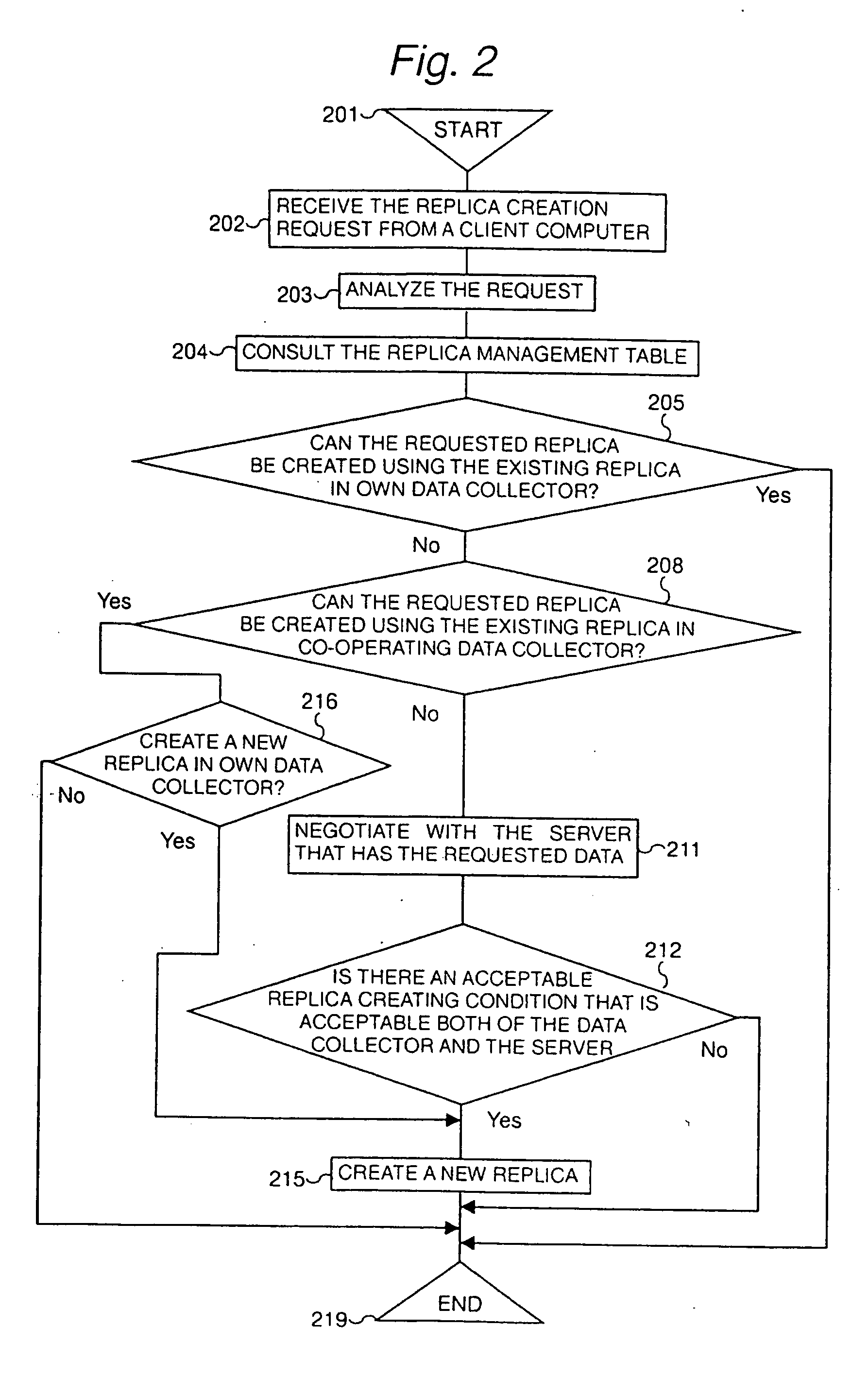
[0044] The intra-network 128 may be a local area network (LAN) connected through the Ethernet, optical fibers, and an FDDI. The clients 103 and 104 may be any computer systems such as personal computers including the Hitachi FLOPA, and Hitachi 3050 creative work stations. The data collector 1 includes a client management unit 105 which groups and manages a plurality of clients and accepts replica creation requests and queries from the clients and transfers replica creation requests to a replica creation request analysis unit 106 and queries to a query analysis unit 109; a replica creation request analysis unit 106 which decides whether to create a replica actually in response to a replica creation request from a client, then transfers the replica description, which is information related...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com