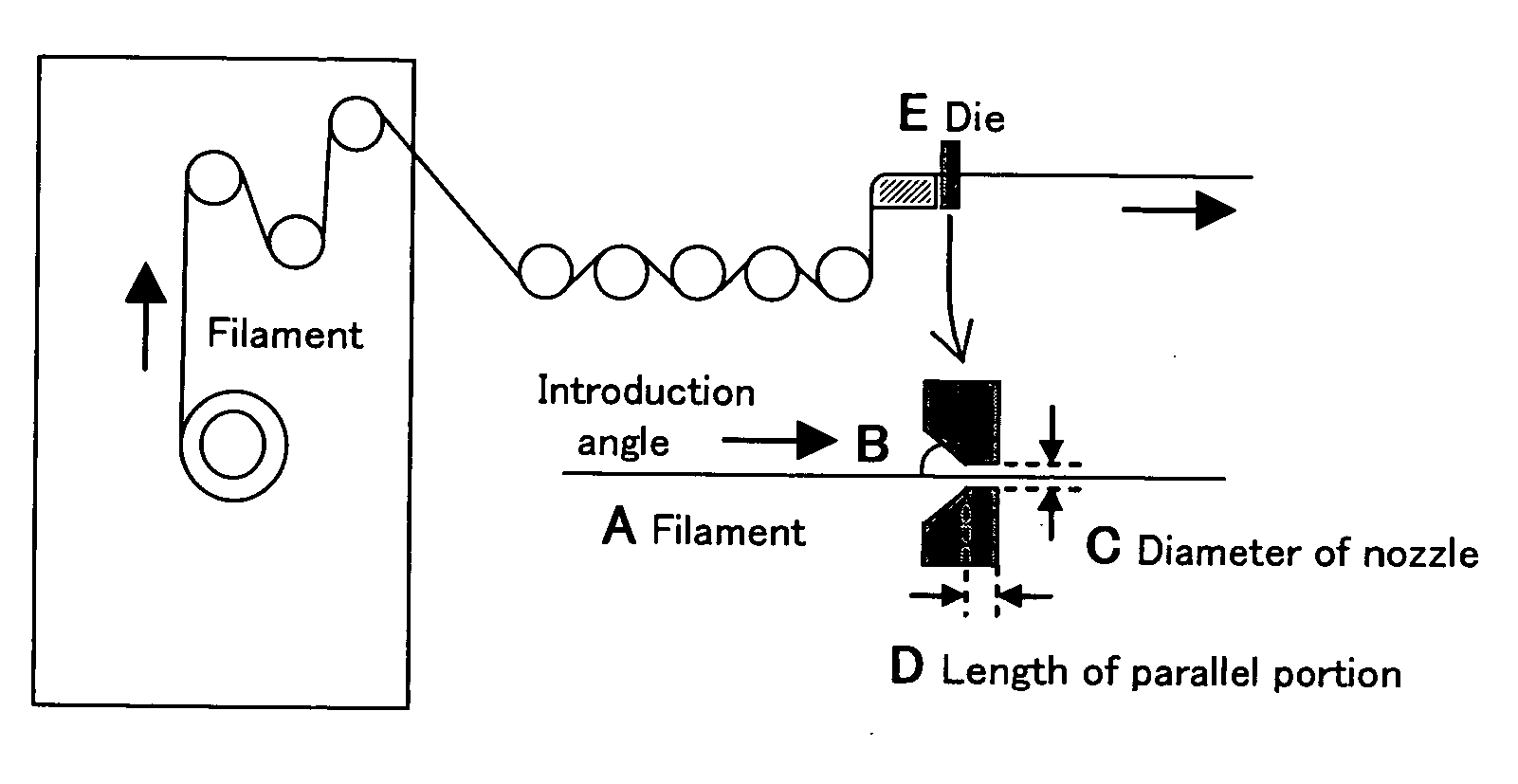
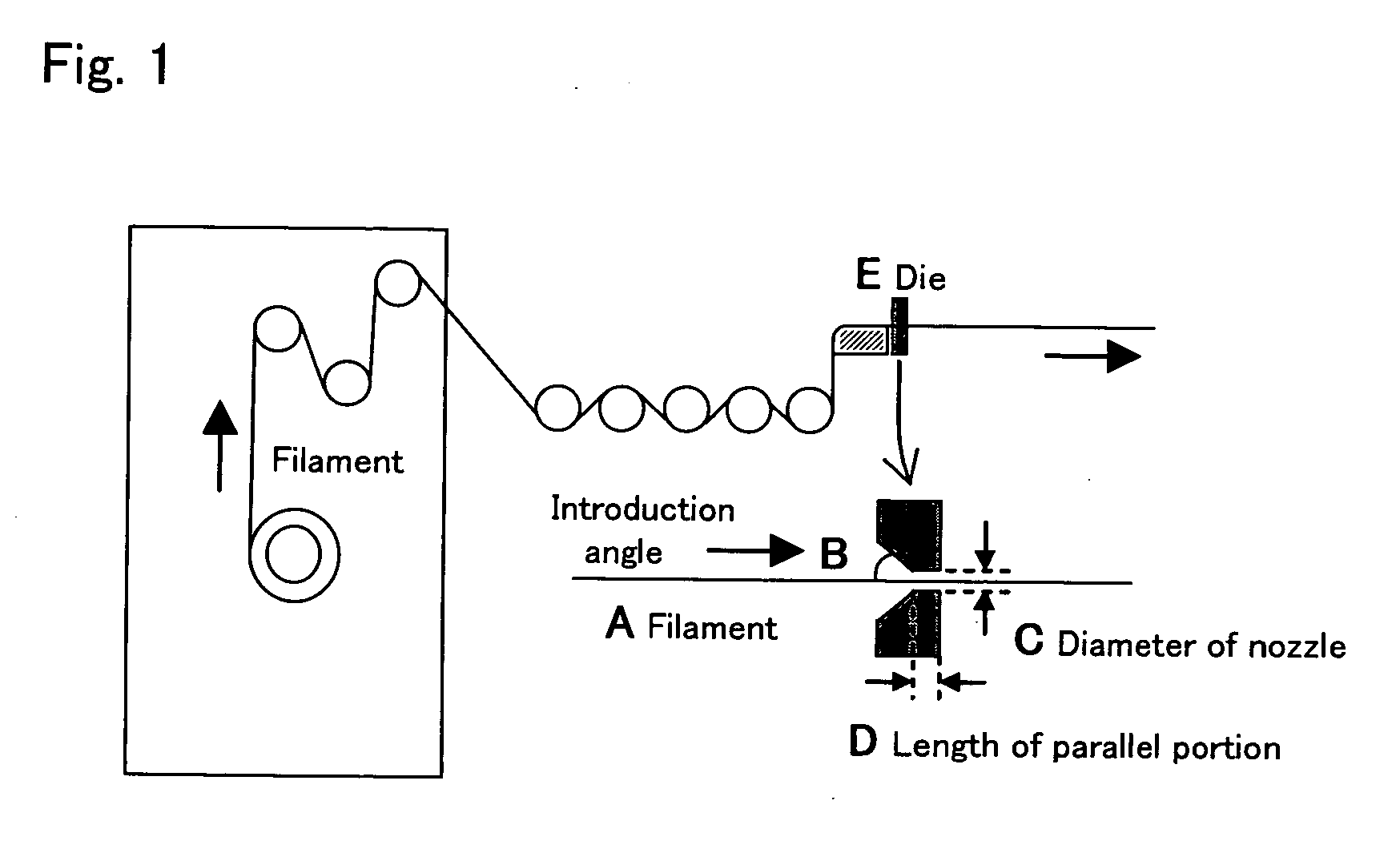
Polybenzazole fiber and article comprising the same
a technology of polybenzazole fiber and polybenzazole fiber, which is applied in the directions of yarn, textiles and paper, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of lower elastic modulus, poor impact resistance and fragility of carbon fiber, and carbon fibers, and achieves the effect of high heat resistance, very little decrease in the strength of such yarns, and durable yarns
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0099] Under a stream of a nitrogen gas, 4,6-diaminoresorcinol dihydrochloride (334.5 g), terephthalic acid (260.8 g) and 122% polyphosphoric acid (2,078.2 g) were stirred at 60° C. for one hour, and the mixture was gradually heated so as to be reacted at 135° C. for 25 hours, at 150° C. for 5 hours and at 170° C. for 20 hours. Threne (14.8 g) was added to the resultant poly(p-phenylenebenzobisoxazole) dope (2.0 kg) having an intrinsic viscosity of 29 dL / g at 30° C., measured using a methanesulfonic acid solution, and the mixture was stirred.
[0100] After that, the resultant dope was spun to make filaments each singly having a diameter of 11.5 μm and a fineness of 1.5 denier. That is, the dope was extruded through a nozzle having 166 holes with diameters of 0.18 mm at 175° C. to make the filaments, which were then dipped and solidified in a first washing bath so located as to converge the filaments at an appropriate position to make a multi-filament. A quench chamber was provided in...
example 2
[0113] Under a stream of a nitrogen gas, 4,6-diaminoresorcinol dihydrochloride (334.5 g), terephthalic acid (260.8 g) and 122% polyphosphoric acid (2,078.2 g) were stirred at 60° C. for one hour, and the mixture was gradually heated so as to be reacted at 135° C. for 25 hours, at 150° C. for 5 hours and at 170° C. for 20 hours. Copper phthalocyanine (14.8 g) was added to the resultant poly(p-phenylenebenzobisoxazole) dope (2.0 kg) having an intrinsic viscosity of 30 dL / g at 30° C., measured using a methanesulfonic acid solution, and the mixture was stirred.
[0114] After that, the resultant dope was spun to make filaments each singly having a diameter of 11.5 μm and a fineness of 1.5 denier. That is, the dope was extruded through a nozzle having 166 holes with diameters of 0.18 mm at 175° C. to make the filaments, which were then dipped and solidified in a first washing bath so located as to converge the filaments at an appropriate position to make a multi-filament. A quench chamber ...
example 3
[0127] Under a stream of a nitrogen gas, 4,6-diaminoresorcinol dihydrochloride (334.5 g), terephthalic acid (260.8 g) and 122% polyphosphoric acid (2,078.2 g) were stirred at 60° C. for one hour, and the mixture was gradually heated so as to be reacted at 135° C. for 25 hours, at 150° C. for 5 hours and at 170° C. for 20 hours. Copper phthalocyanine (14.8 g) was added to the resultant poly(p-phenylenebenzobisoxazole) dope (2.0 kg) having an intrinsic viscosity of 30 dL / g at 30° C., measured using a methanesulfonic acid solution, and the mixture was stirred.
[0128] After that, the resultant dope was spun to make filaments each singly having a diameter of 11.5 μm and a fineness of 1.5 denier. That is, the dope was extruded through a nozzle having 166 holes with diameters of 0.18 mm at 175° C. to make the filaments, which were then dipped and solidified in a first washing bath so located as to converge the filaments at an appropriate position to make a multi-filament. A quench chamber ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com