Tire pressure sensor system with improved sensitivity and power saving
a sensor system and tire pressure technology, applied in vehicle tyre testing, instruments, roads, etc., can solve the problems of limited performance of such devices, limited sensitivity of the sensor circuit to the variable resistance range of the single strain gauge used, and relatively insensitive sensors to mechanical vibration. , to achieve the effect of extending the useful battery life, and reducing the risk of damag
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
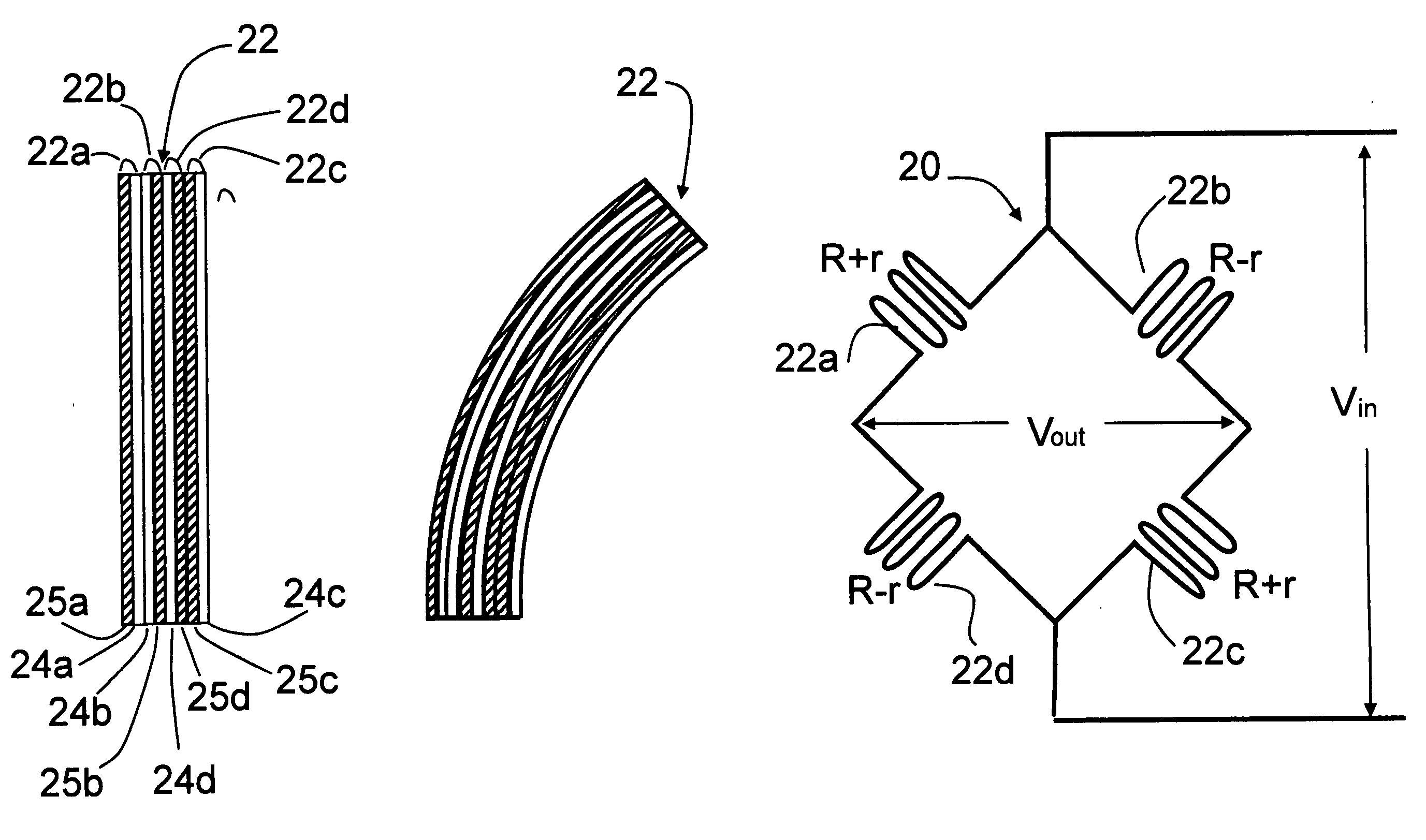
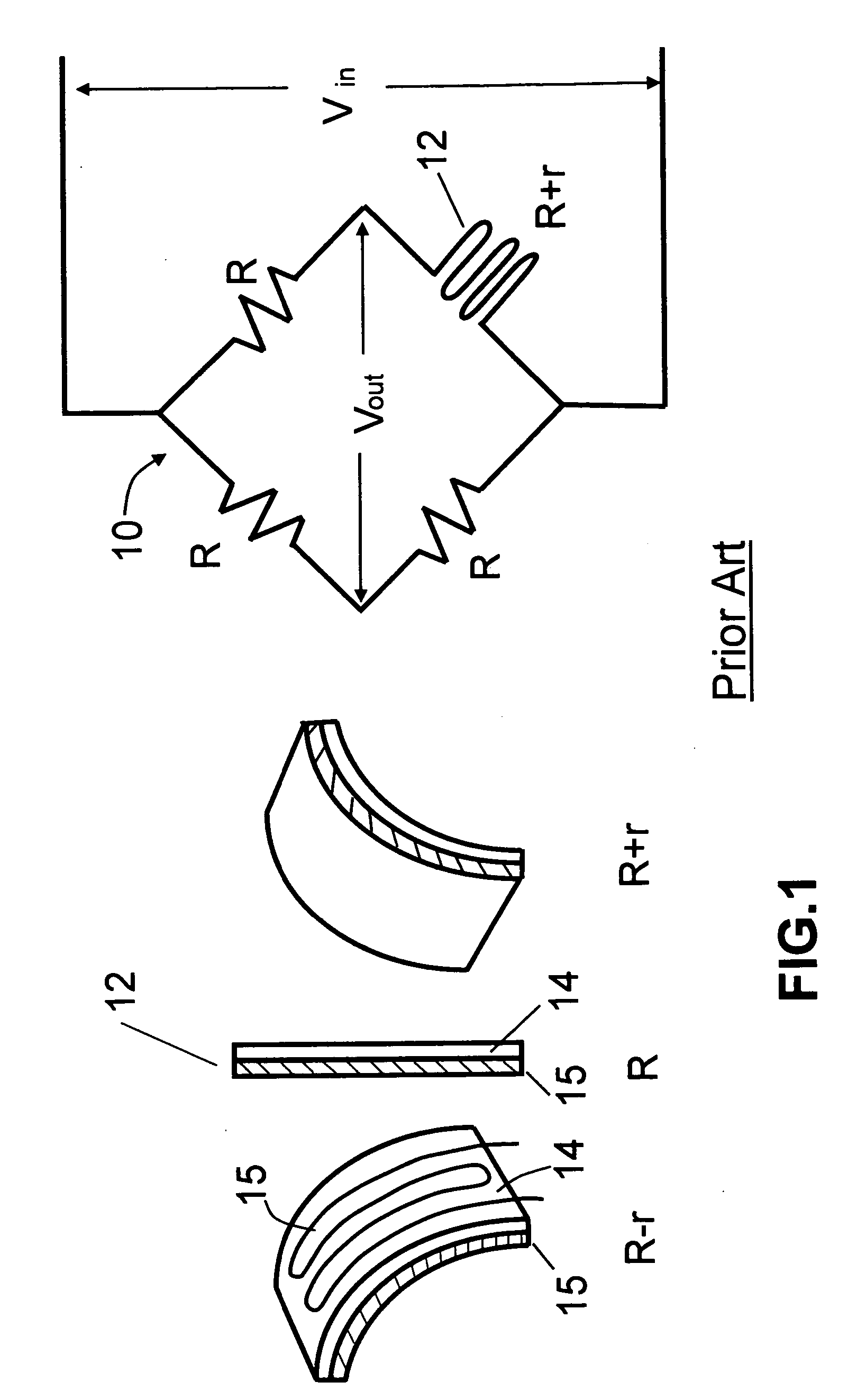
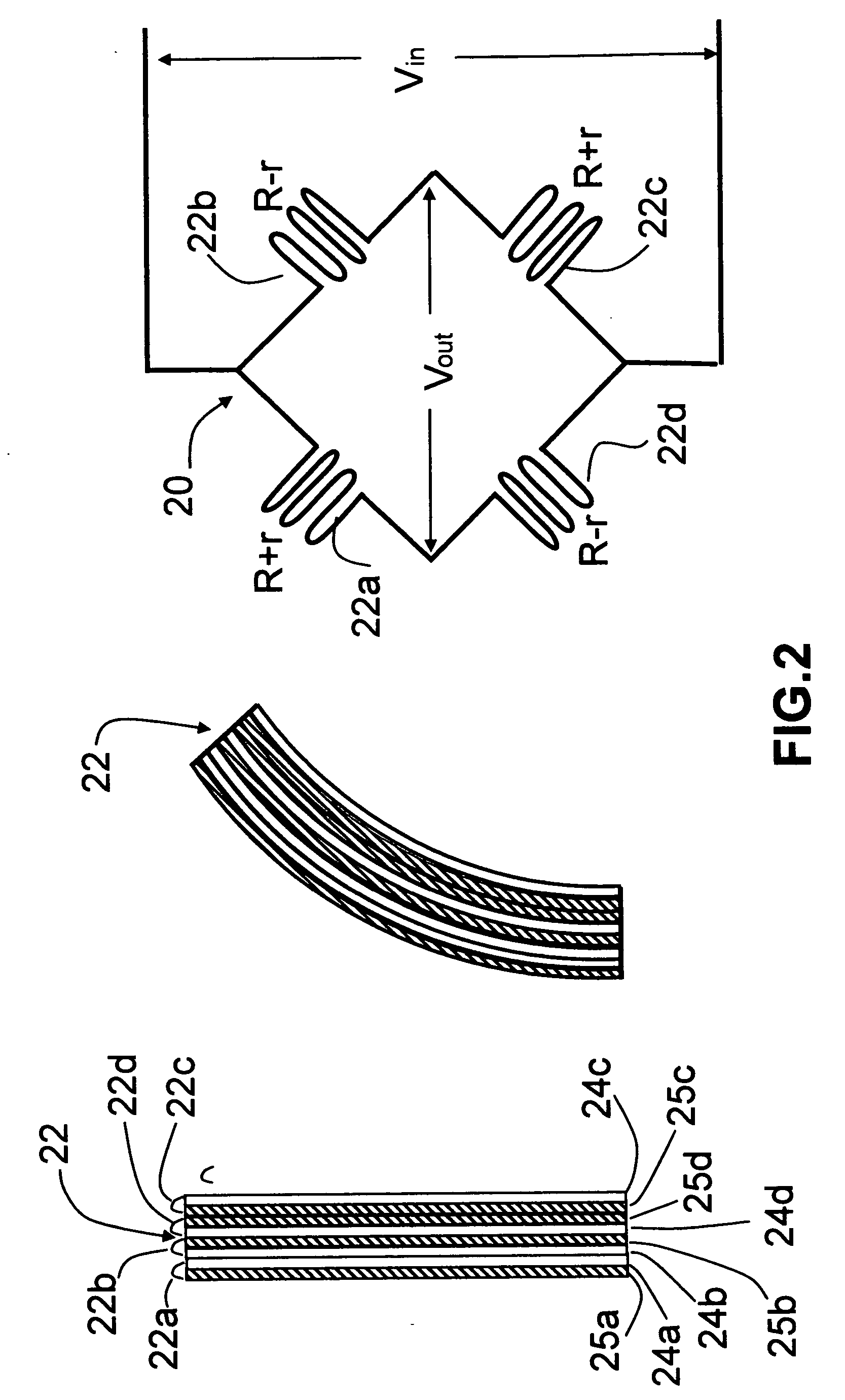
[0035] Turning now to the drawings, FIG. 1 is a schematic view of a prior art single tire pressure monitor circuit using a single stretch sensor in a bridge circuit. As seen in this Fig., the monitor circuit, generally designated with reference numeral 10, includes a single stretch sensor 12 ohmically connected in one branch of a bridge circuit having three additional branches each with a fixed resistance R ohmically connected as shown. Stretch sensor 12 is a known component having the property of an ohmic resistance which varies in a predictable amount with linear longitudinal displacement of the sensor body. Stretch sensor 12 has a first layer 14 on which a thin variable resistance element 15 is mounted; and a second, base layer which carries the first layer and provides additional mechanical strength for sensor 12. The fixed resistances R are all of equal value. A reference voltage Vin from a source of D.C. electrical power (not shown) is applied to two nodes of bridge circuit 10...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com