Methods for forming carbon nanotube thermal pads
a carbon nanotube and thermal pad technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device details, semiconductor devices, textiles and paper, etc., can solve the problems of large heat produced by devices that consume large amounts of power, messy thermal greases, and relatively low thermal conductivity of thermal greases
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
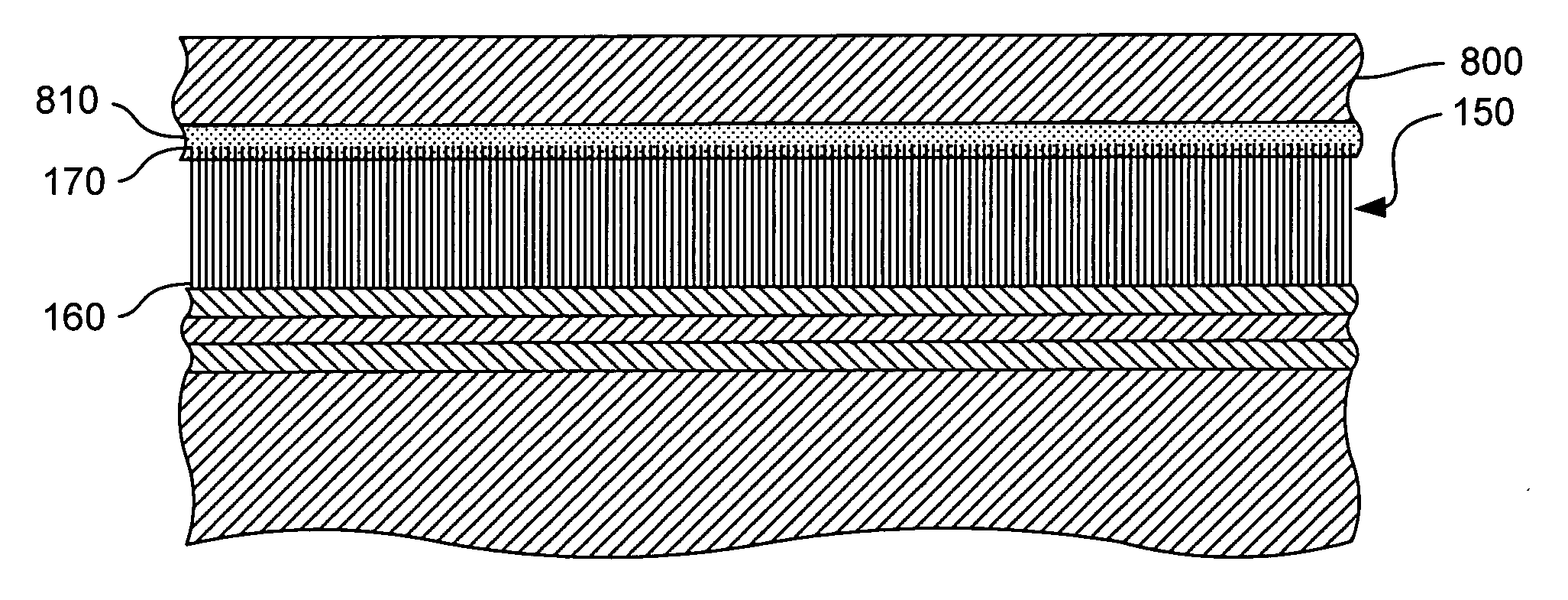
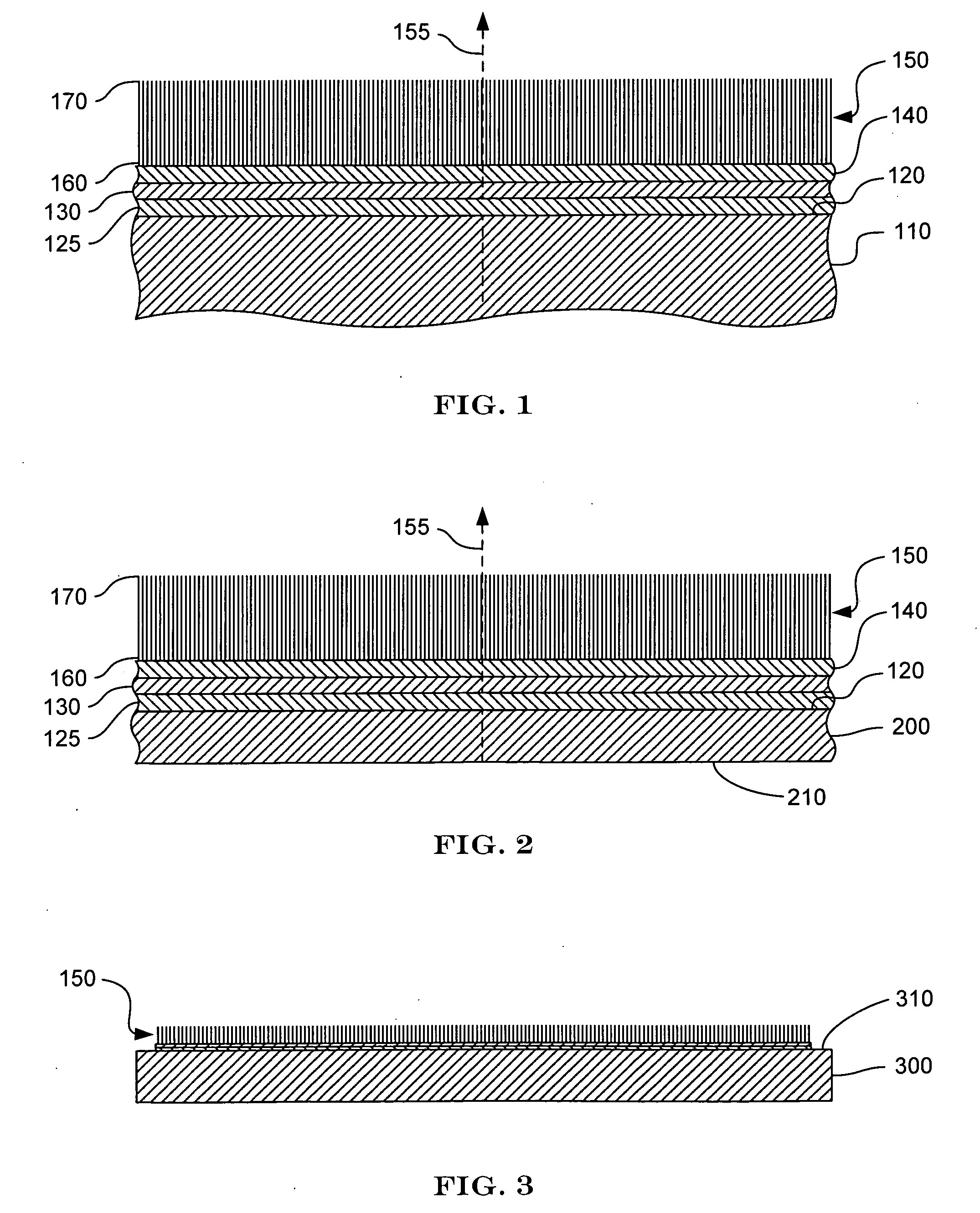
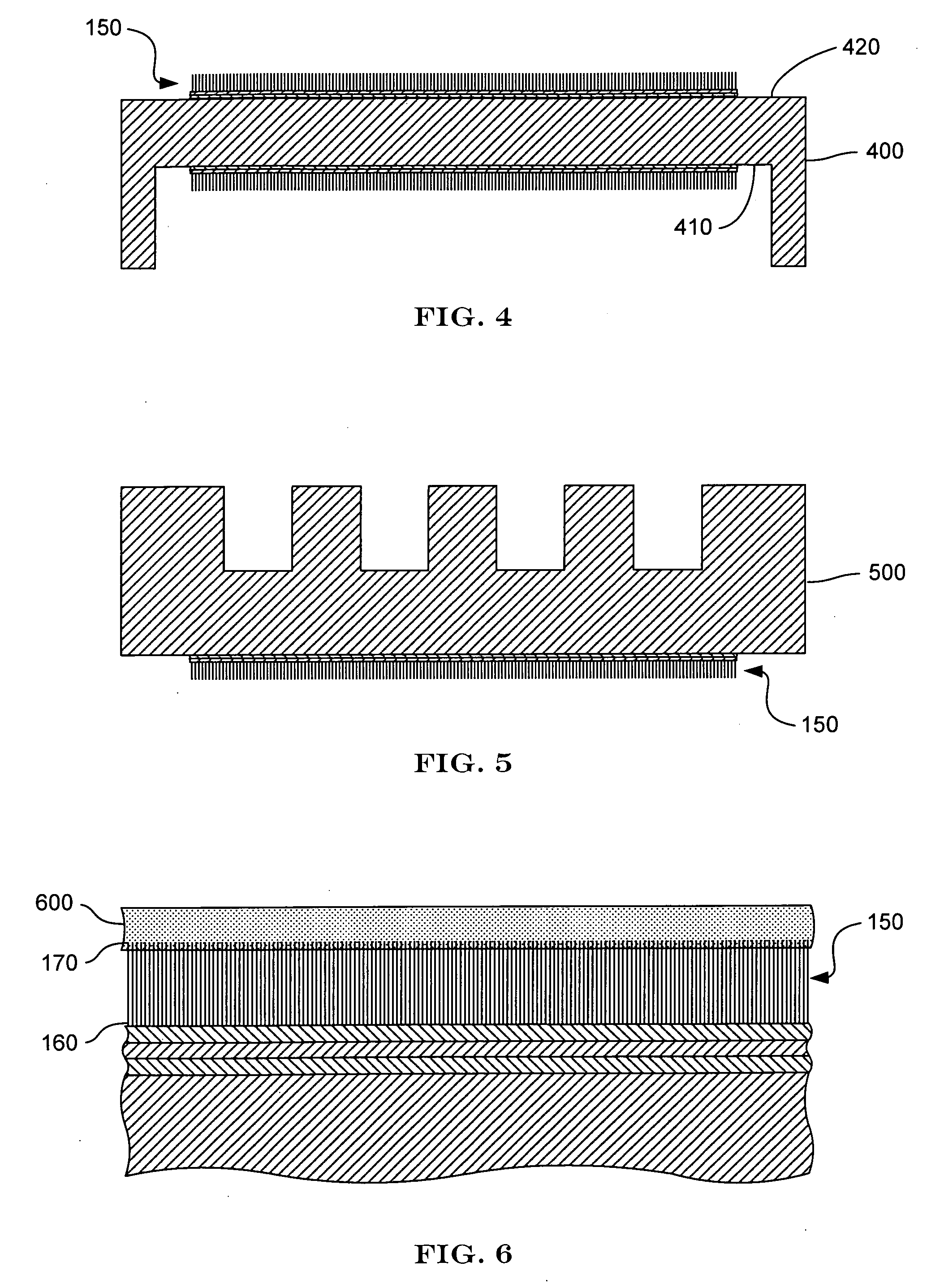
[0021] The present invention provides methods for fabricating carbon nanotube-based thermal pads. The thermal pads are characterized by an array of generally aligned carbon nanotubes disposed on a substrate, such as a foil, a thin metal sheet, or the surface of a component of a device. The carbon nanotubes are disposed on the substrate such that the direction of alignment is essentially perpendicular to the surface of the substrate on which the array is disposed. The alignment of the nanotubes allows the array to provide excellent thermal conduction in the direction of alignment. Accordingly, a thermal pad between a heat source and a heat sink provides a thermally conductive interface therebetween.
[0022] Some thermal pads are characterized by at least one, and in some instances, two very smooth surfaces. A thermal pad with a sufficiently smooth surface can adhere to another very smooth surface, such as the backside surface of semiconductor die, much like two microscope slides will ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com