Semiconductor integrated circuit
a technology of integrated circuits and semiconductors, applied in pulse manipulation, pulse technique, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the operating speed reducing the reproducing quality of the class-d amplifier, and sacrificing the load or the class-d amplifier. , to achieve the effect of reducing the ringing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
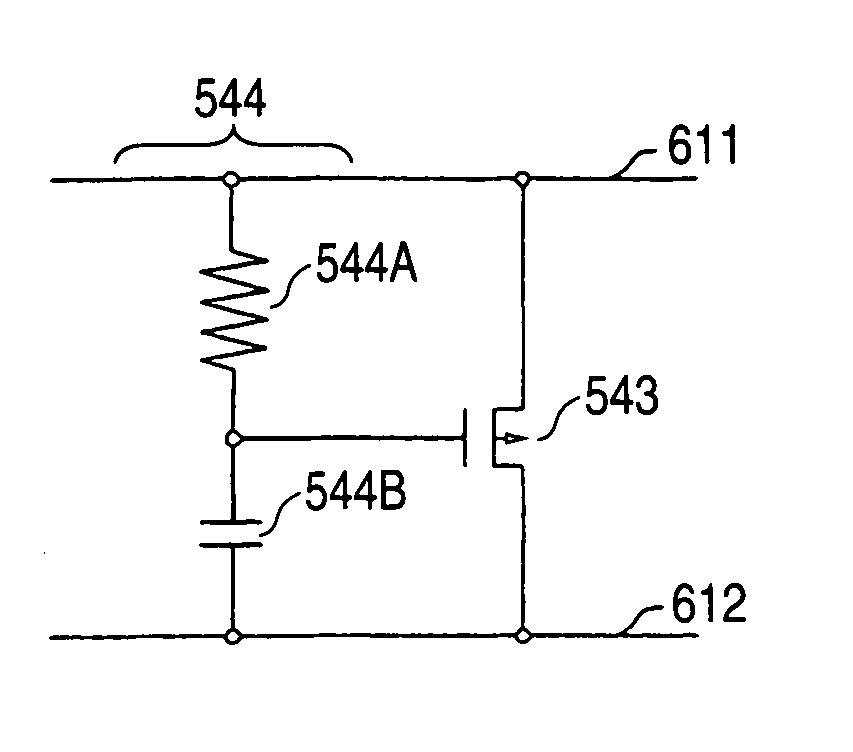
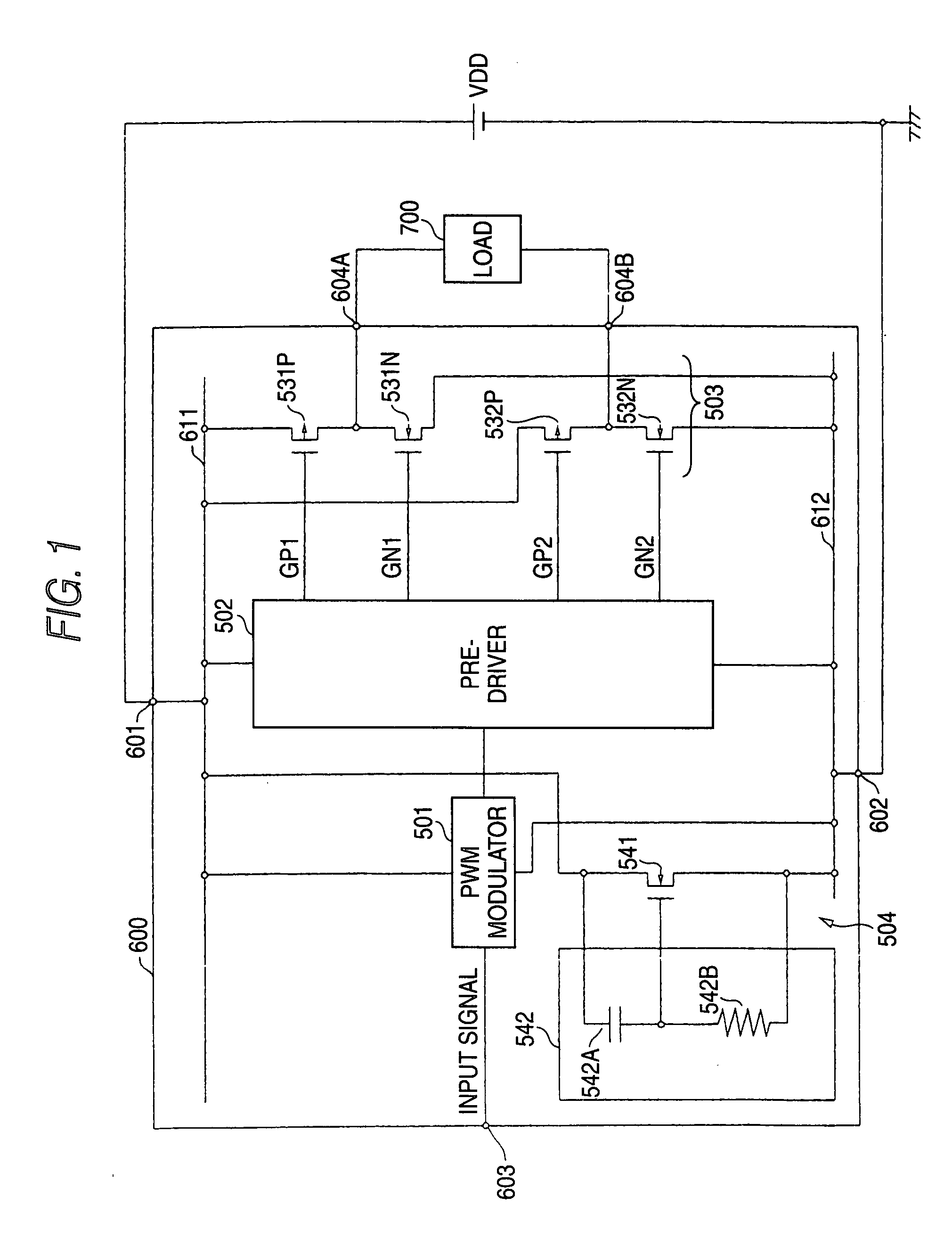
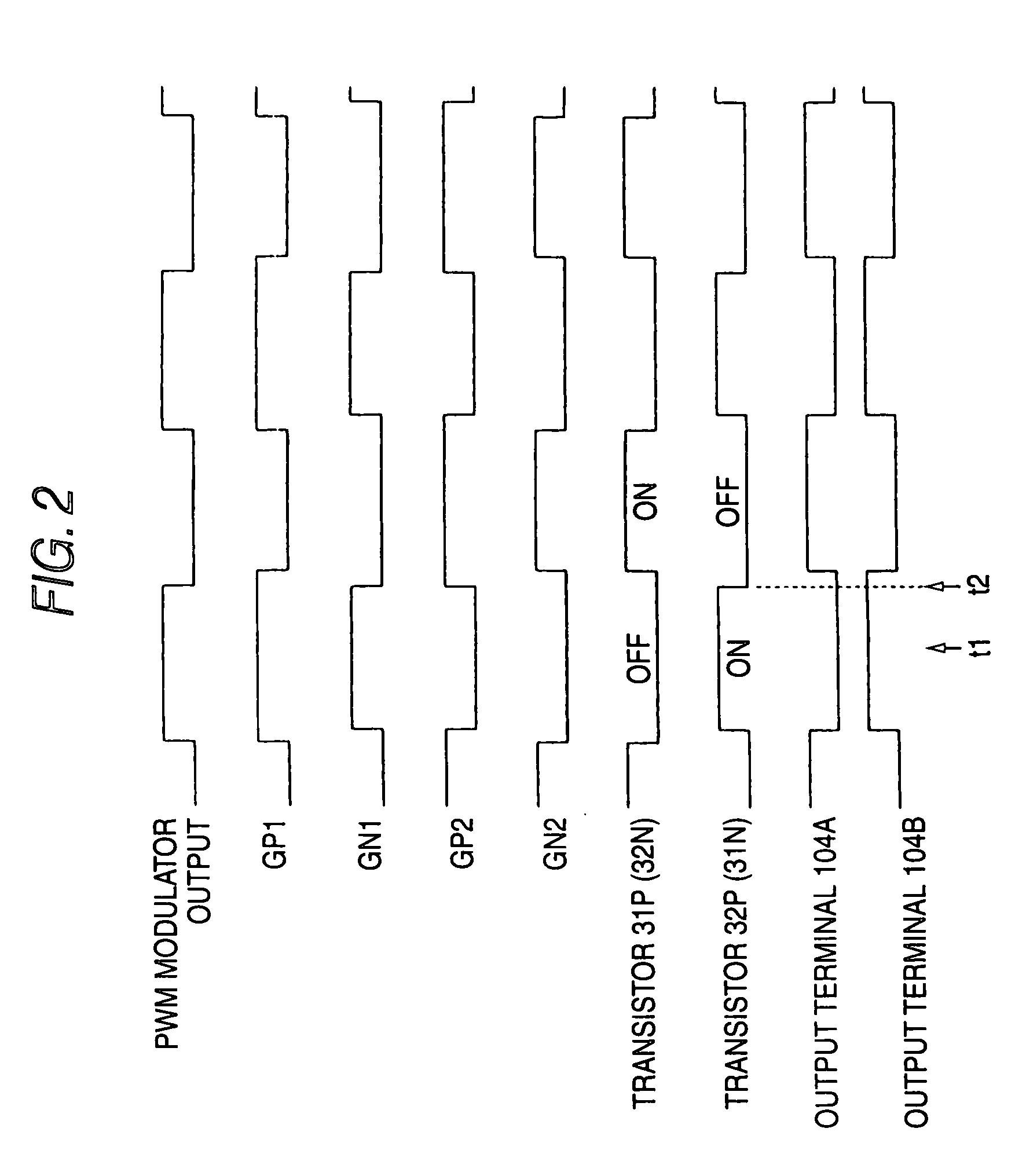
[0022]FIG. 1 is a circuit diagram showing a structure of a class-D amplifier 600 according to an embodiment 1 of a semiconductor integrated circuit in accordance with the invention. The class-D amplifier 600 has a high potential power terminal 601, a low potential power terminal 602, an input terminal 603, and output terminals 604A and 604B. The high potential power terminal 601 is connected to a positive electrode of a power supply VDD, and the low potential power terminal 602 is connected to a negative electrode of the power supply VDD and is grounded. In an example shown in the drawing, a single power supply is used. For this reason, the low potential power terminal 602 is grounded. In the case in which there is employed such a structure that a power supply for generating a positive source voltage and a power supply for generating a negative source voltage are used, however, it is preferable that the high potential power terminal 601 should be connected to an output terminal of t...
embodiment 2
[0033]FIGS. 6 and 7 are circuit diagrams showing the configuration of a class-D amplifier 100A having ringing reduction circuits 40NA and 40PA according to an embodiment 2 of the invention. FIG. 6 shows the circuit configuration of the ringing reduction circuit 40NA and FIG. 7 shows the circuit configuration of the ringing reduction circuit 40PA.
[0034] The class-D amplifier 100A has a high-potential power terminal 101, a low-potential power terminal 102, an input terminal 103, and an output terminal 104. The high-potential power terminal 101 is connected to the positive pole of a power source VDD via a high-potential power line 131 disposed outside the class-D amplifier 100A, and the low-potential power terminal 102 is connected to the negative pole of the power source VDD via a low-potential power line 132 disposed outside the class-D amplifier 100A and is grounded. In the illustrated example, the low-potential power terminal 102 is grounded because of the use of the single power ...
embodiment 3
[0045]FIGS. 9 and 10 are circuit diagrams showing the configuration of a class-D amplifier 100B having ring reduction circuits 40PB and 40NB according to an embodiment 3 of the invention. FIG. 9 shows the circuit configuration of the ringing reduction circuit 40NB and FIG. 10 shows the circuit configuration of the ringing reduction circuit 40PB. In FIGS. 9 and 10, components having corresponding components in FIGS. 6 and 7 referred to above are given the same reference symbols as the latter and will not be described.
[0046] In the embodiment 2, the comparators 410 and 420 which are the ringing detector detect occurrence of ringing in the output signal OUT by comparing the level of the output signal line 120 with the level PVDDI of the high-potential power line 111 or the level PVSSI of the low-potential power line 112.
[0047] However, when a switching current of the output buffer circuit 30 flows through the parasitic inductance 141 or 142, a large counterelectromotive force is indu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com