Thermal power plant
a technology of thermal power plant and turbine, which is applied in the direction of machines/engines, mechanical energy handling, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the development cost and extending the development term, the strength of the rotational shaft (rotor) of the turbine made of stainless steel, which is currently used, and the inability to withstand, so as to improve improve the power generation efficiency. , the effect of improving the efficiency of the turbin
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
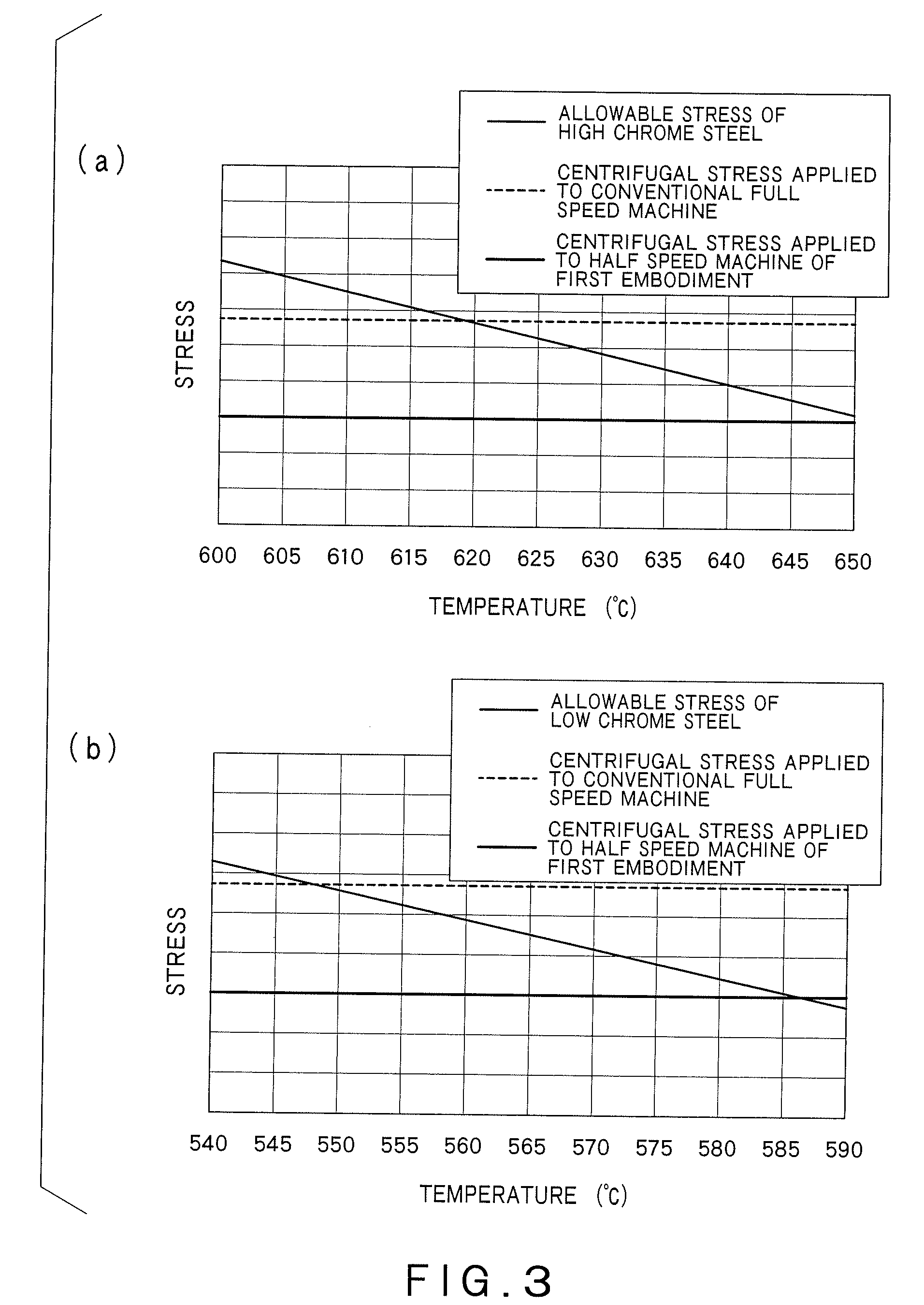
[0035]A thermal power plant in a first embodiment of the present invention is described below with reference to the drawings. FIGS. 1 to 4 show a first embodiment of the present invention.
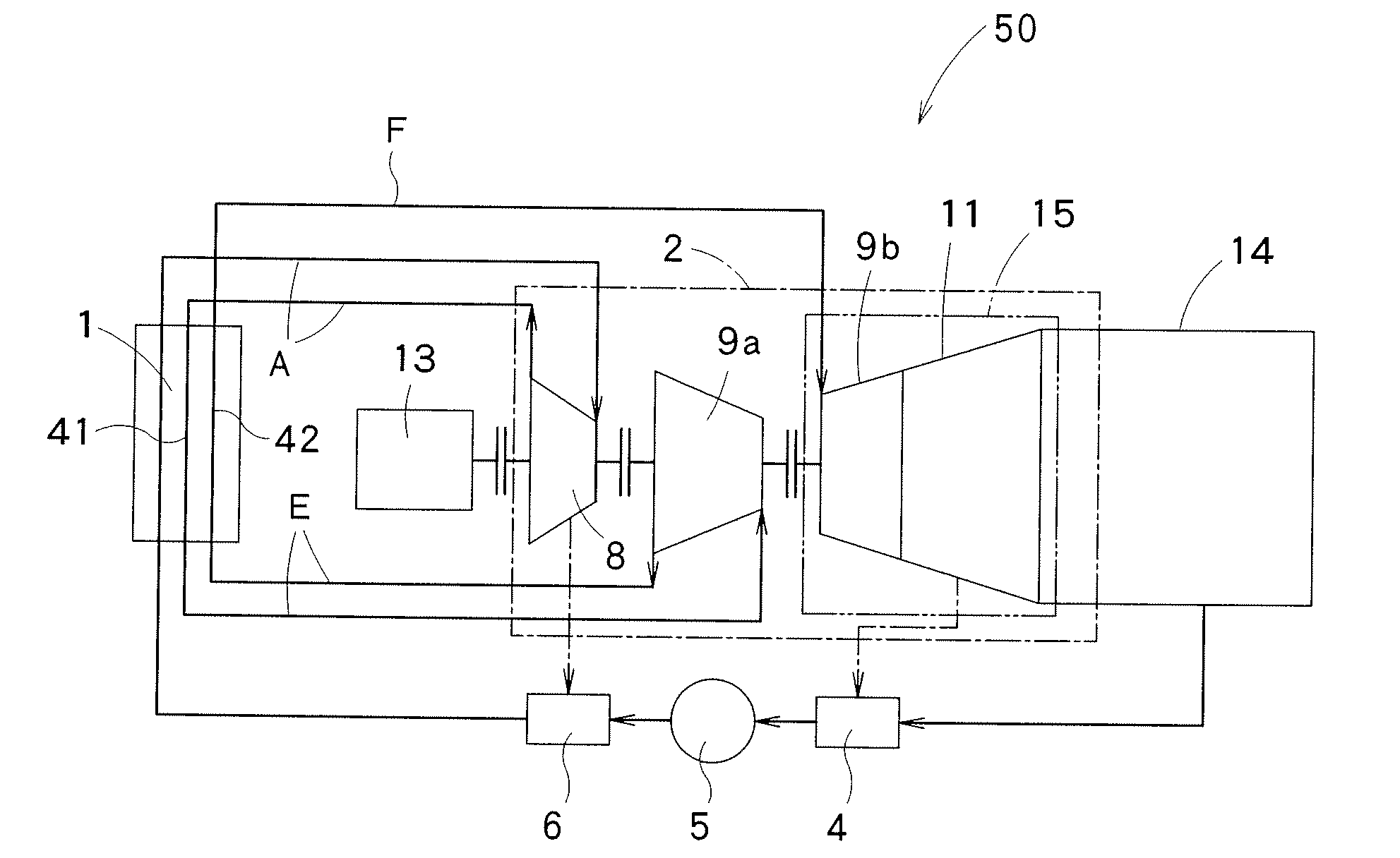
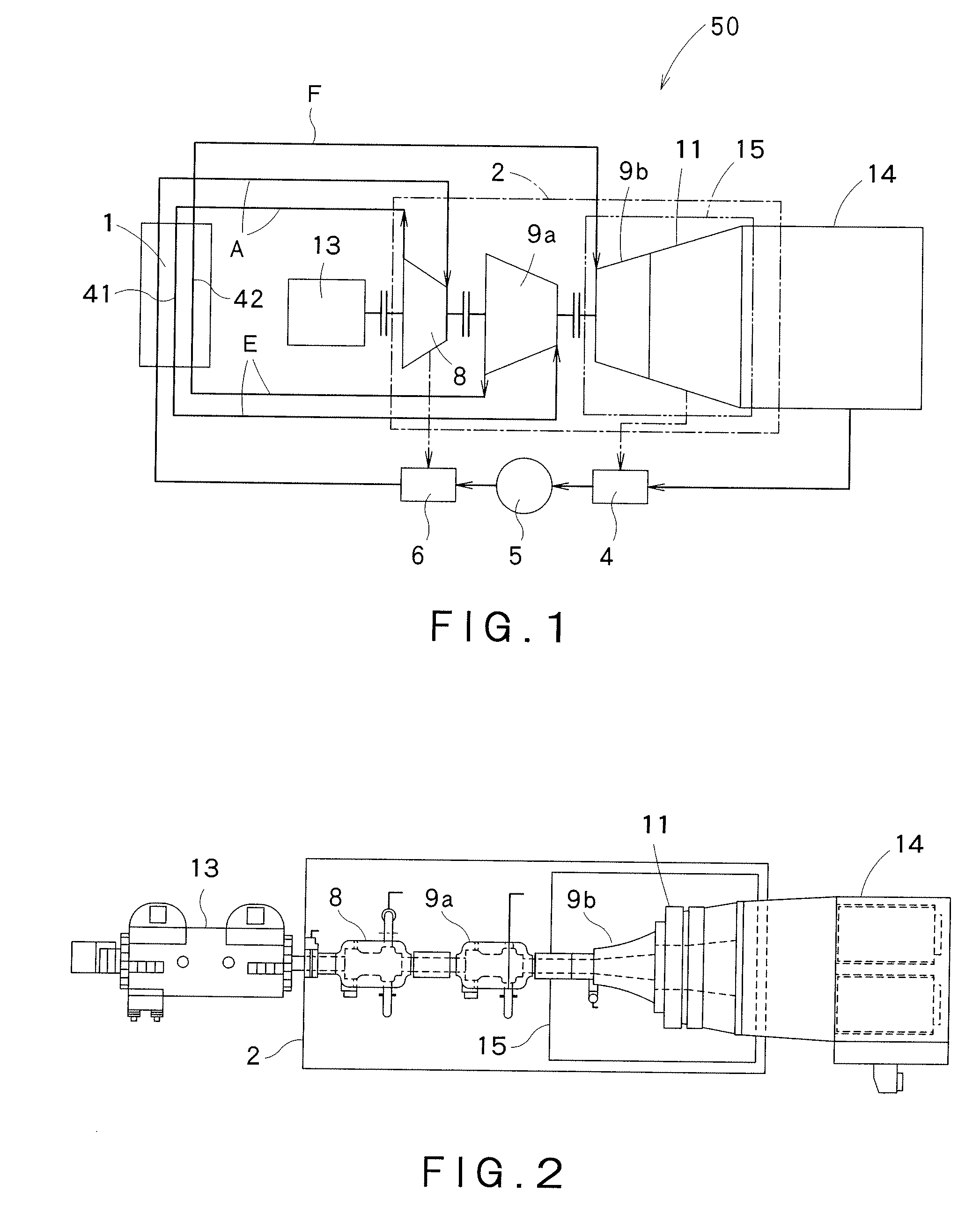
[0036]As shown in FIGS. 1 and 2, a steam turbine system 50 of a thermal power plant in a first embodiment of the present invention includes a boiler 1, a turbine 2, a condenser 14, and a 4-pole generator 13. The boiler 1 has a heater that heats a feed water by using a heat caused by combustion of a fossil fuel to generate a main steam A. In this embodiment, the boiler 1 is preferably a furnace utilizing coal or oil as a fuel. In this embodiment, the boiler 1 has a first reheater 41 and a second reheater 42, other than the heater that generates main steam A. First reheater 41 reheats the main steam A discharged from a high pressure turbine 8 so as to generate a first-stage reheated steam E. Second reheater 42 reheats the first-stage reheated steam E discharged from a first intermediate pressure turb...
second embodiment
[0098]Next, a second embodiment of the present invention is described with reference to FIGS. 5 and 6. The second embodiment shown in FIGS. 5 and 6 is a so-called combined cycle plant in which a gas turbine system 30 is combined with the steam turbine system 50 in the first embodiment shown in FIG. 1. The gas turbine system 30 includes: a compressor 31 that compresses air; a combustor 32 that burns a fossil fuel such as natural gas with the air compressed by the compressor 31 so as to generate a combustion gas; a gas turbine 33 that is driven by the combustion gas generated by the combustor 32; and a gas turbine generator 35 connected to the bas turbine 33. As a boiler for heating a feed water to generate a main steam by using a heat caused by combustion of fossil fuel, In this embodiment, steam turbine system 50 comprises heat recovery steam generator (HRSG) 20, in place of the boiler 1 in the first embodiment shown in FIG. 1. Heat recovery steam generator (HRSG) 50 has a heater th...
third embodiment
[0118]A third embodiment of the present invention is described with reference to FIGS. 7 and 8. The third embodiment shown in FIGS. 7 and 8 is a steam turbine system 50 of a single-stage reheating type, which only includes one intermediate pressure turbine 9a. In other words, steam turbine system according to this embodiment eliminates the first intermediate pressure turbine 9a from the first embodiment as shown in FIGS. 1 and 2. Other structure of this embodiment is substantially the same as that of the first embodiment shown in FIGS. 1 to 4. An intermediate pressure turbine 9 in this embodiment corresponds to the second intermediate pressure turbine 9b in the first embodiment. In this embodiment, only one reheater 45 is provided in boiler 1.
[0119]In FIGS. 7 and 8, the intermediate pressure turbine 9 and a low pressure turbine 11 received in a single casing constitutes an intermediate and low pressure turbine 15. The turbine into which a reheated steam is defined as the intermediat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com