Methods, kits, and compositions for stem cell self-renewal
a technology of stem cell self-renewal and kits, applied in the field of hematopoietic stem cell population expansion, can solve the problems of pten in stem cell stem cell and tumorigenesis, recurrence of tumors heretofore not understood, and a risk of over-activation and expansion of stem cells,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
In Vitro Culture of Control and Mutant LSK Cells
Cell Culture
[0217]LSK or LSK Flk2− cells were sorted into 96-well U-bottom tissue culture plates at 100 cells / well with 200 μl media / well. Cells were incubated at 37° C., 5% O2, 5% CO2 (balance N2) for the indicated number of days. One-half total volume of media (see Table 1, below for the base media) was carefully pipetted from the top and replaced with fresh media every other day.
TABLE 1Base MediaComponentsSourceStemSpan Media: (Iscove's-modified Dulbecco'sStem Cellmedium (IMDM) supplemented with 1% bovineTechnologies;serum albumin, 10 μg ml−1 recombinant humanCat. No. 09600insulin, 200 μg ml−1 iron-saturated transferrin,0.1 mM 2-mercaptoethanol and 2 mM glutamine.)10 μg / ml HeparinSigma, Cat.No. H-31490.5X Penicillin / StreptomycinSigma, Cat.No. P433310 ng / ml recombinant mouse (rm) Stem CellBiovision, Cat.FactorNo. 4328-1020 ng / ml rm-ThrombopoietinCell Sciences,Inc, Cat. No.CRT401B
Double Mutant HSCs Expand Dramatically In Vitro and In ...
example 3
Transplantation Analysis of Pten and Pten:Ctnnb1 LSK Cells After 5 Weeks of Culture
[0220]For the following experiments, cells were cultured in the same manner as described in Example 2. As in Example 2, the base media of Table 1 was supplemented with 20 ng / ml rm-IGF-2 (R&D Systems, 792-MG) and 10 ng / ml recombinant human FGF-1 (Affinity BioReagents, ORP16010).
[0221]While Pten and especially Pten:Ctnnb1 cultures exhibited significant expansion in LSK cells, whether these cells were functional in vivo was determined.
[0222]At 5 weeks culture, Pten and Pten:Ctnnb1 LSK cultures were re-sorted and 1000 LSK cells (CD45.2+) from each were transplanted into lethally irradiated (10Gy) CD45.1+ recipient mice along with 2×105 congenic whole bone marrow competitor cells. Because wild-type cells did not survive 5 weeks culture, 1000 fresh wild-type LSK cells were also transplanted as a separate control group. Peripheral blood analysis at 4 weeks post-transplantation revealed robust repopulation in...
example 4
Differentiation Block and Dominant Phenotype of Pten:Ctnnb1 Mutant HSCs
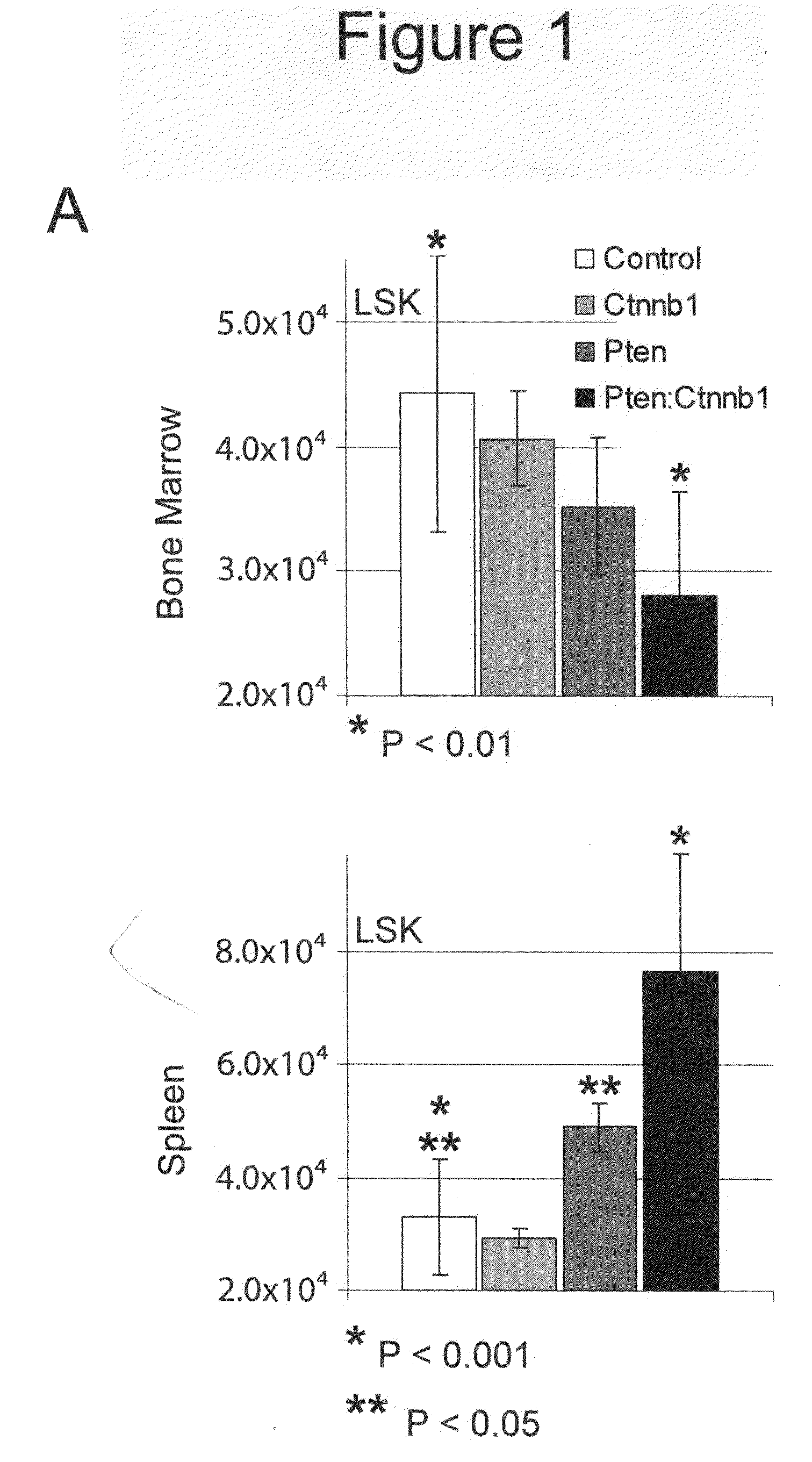
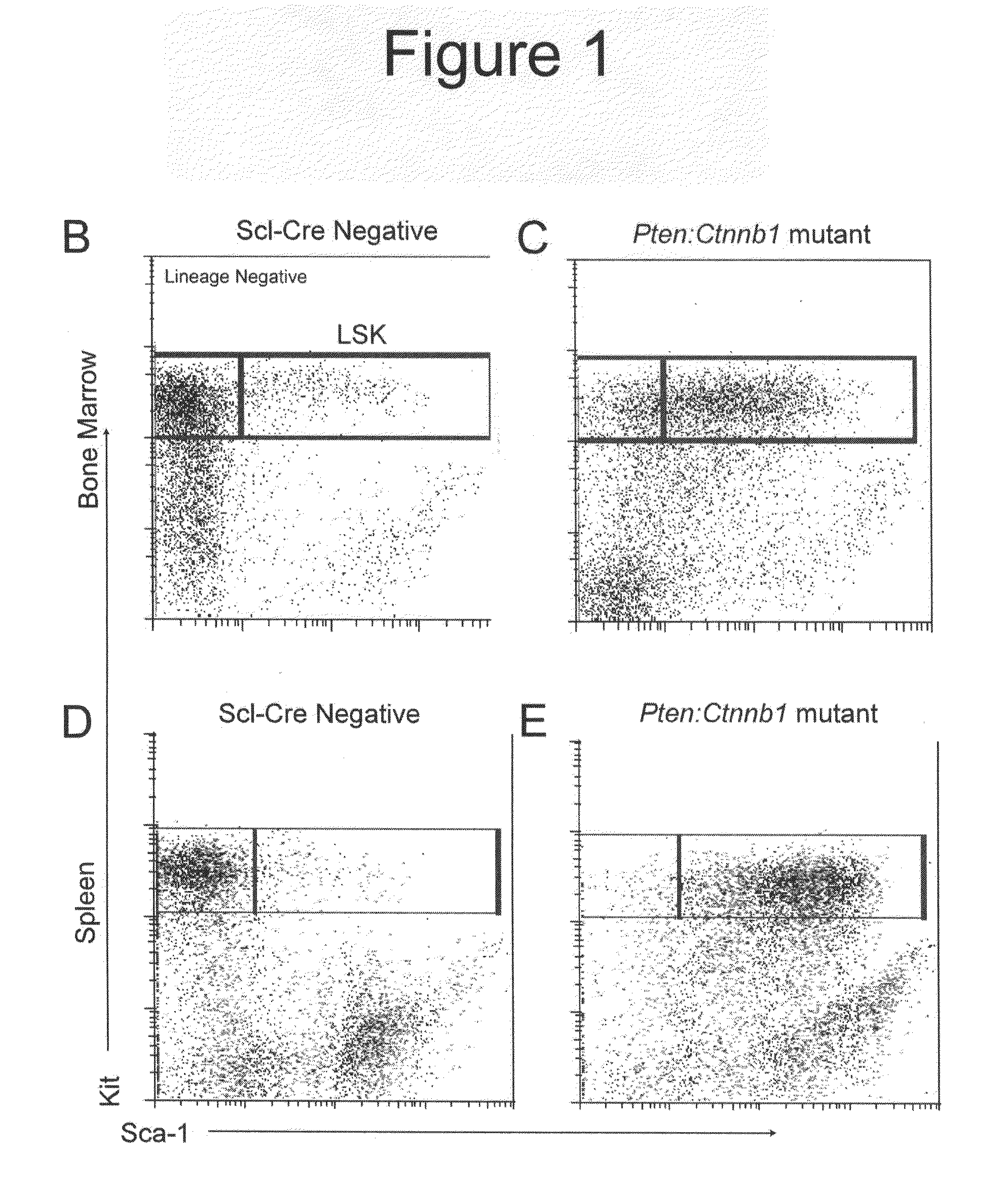
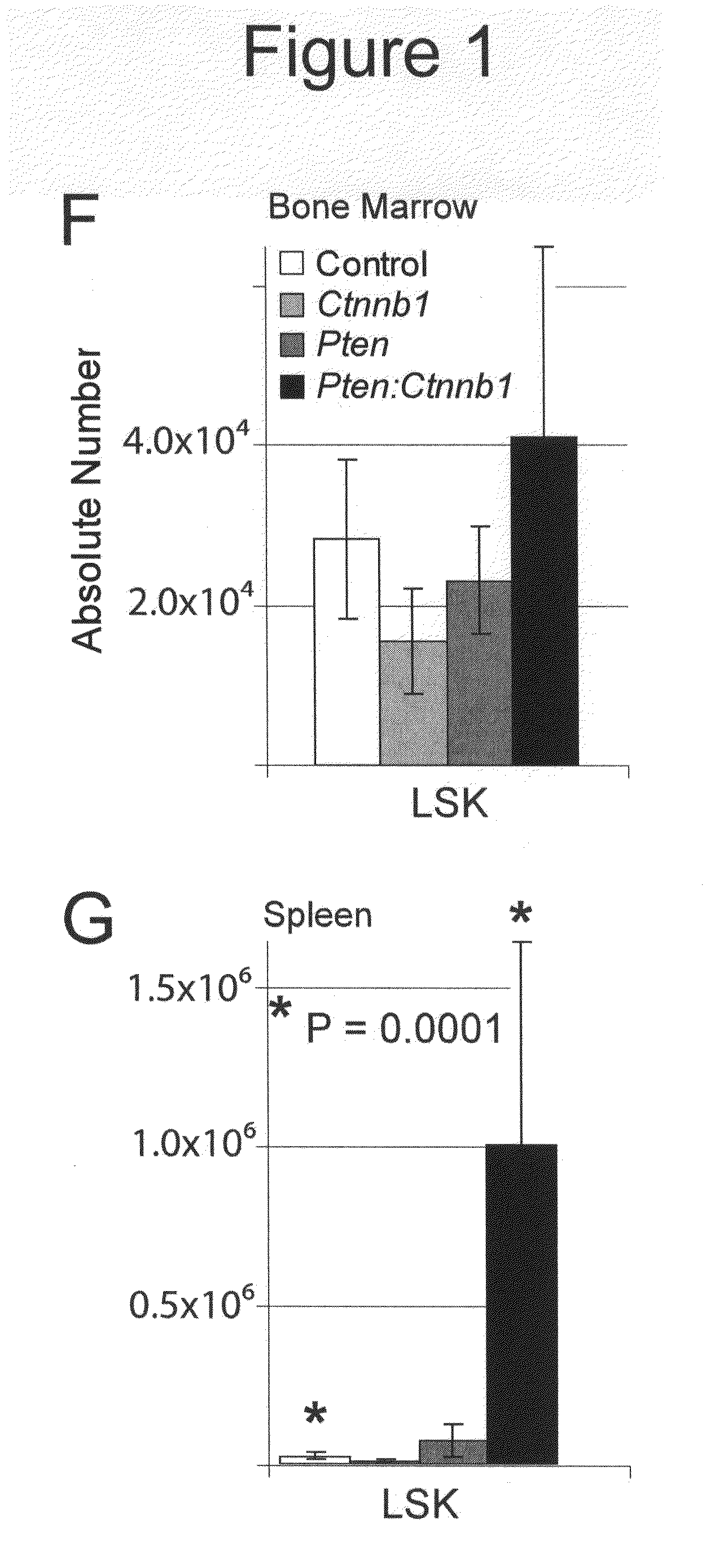
[0225]Initially, primary (non-transplanted) animals were used for phenotypic analysis. These mice eventually exhibited severe non-hematopoietic defects, including reduction of the marrow cavity and splenic fibrosis resulting in disruption of splenic niches (FIG. 16). Consequently, LT-HSC transplantations were used to verify Scl-Cre specificity (FIG. 10). Comparing these transplant groups with the initial data from primary mutants revealed an essentially identical phenotypic manifestation of defects between transplant and non-transplant groups, demonstrating that non-hematopoietic effects are due to interaction between the hematopoietic system and stroma rather than from defects arising from the stroma (FIG. 17 and data not shown).
[0226]The health of double mutants typically declined by 9 wpi (see below). LSK cells and early progenitors from control, single, and double mutant bone marrow and spleen at 9-10 wpi wer...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com