Quantitative Assay for the Simultaneous Detection and Speciation of Bacterial Infections
a technology of simultaneous detection and speciation, applied in the field of clinical diagnosis, can solve the problems of false positives, amplification of exceedingly minor bacterial contamination, and long reporting tim
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Materials and Methods
Bacterial Species and DNA Isolation.
[0032]Fifteen common pathogenic microorganisms, all of which were eubacterial except one, Candida albicans, were obtained from the clinical laboratory (Division of Medical Microbiology, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, Md.). The species and their ATCC strain are listed in Table 1. Microorganisms were grown in standard cultures, and DNA extracted using the QIAamp DNA kit (Qiagen Corp., Santa Clarita, Calif.).
[0033]With regard to generating standard curves for starting DNA template quantification, Staphylococcus aureus was grown in Luria-Bertani (LB) broth at 37° C. with continuous shaking to an optical density at 600 nm of 0.6. Equal aliquots were then plated to determine colony-forming units (CFU) and subjected to DNA extraction with the QIAamp DNA kit. The isolated DNA was quantified based on optical density at 260 nm and then serially diluted. Analogous procedures were performed for Staphylococcus epidermidis.
TAB...
example 2
Specificity of Universal TagMan PCR
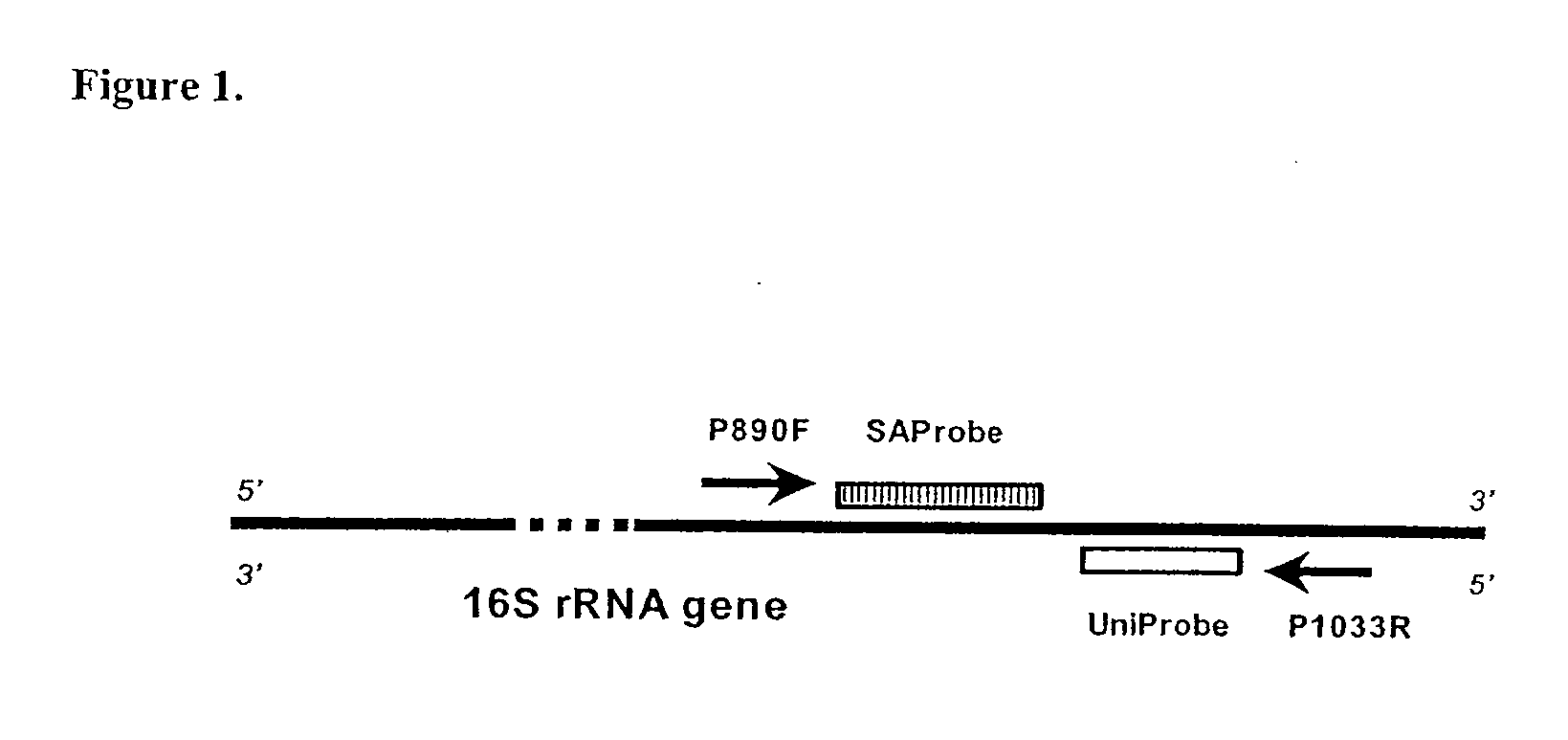
[0042]The specificity of the primers and probes used for universal amplification of eubacterial 16S rRNA gene was first assessed with genomic DNA extracts from 14 different bacterial species together with one isolate from Candida albicans (Table 2). In each PCR assay, 5 ng of purified DNA were used. The assay's positivity was determined by examination of the amplification plot (CT vs ΔRn) generated by the Sequence Detection Software (FIG. 1). All 14 bacterial species were correctly amplified and detected with CT values in the range of 19.2 to 21.8. No amplification (CT>40) was detected when DNA isolated from C. albicans was used. The assay results were further verified by subjecting reaction products to gel electrophoresis, with visualization of bands of the expected size (162 bp) (data not shown).
TABLE 2Specificity of the Taqman assay usinguniversal primers and probes.Isolated MicroorganismsStrain (ATCC)Taqman PCR resultsStaphylococcus aureus29213...
example 3
Theoretical Detection Limit of Taqman PCR
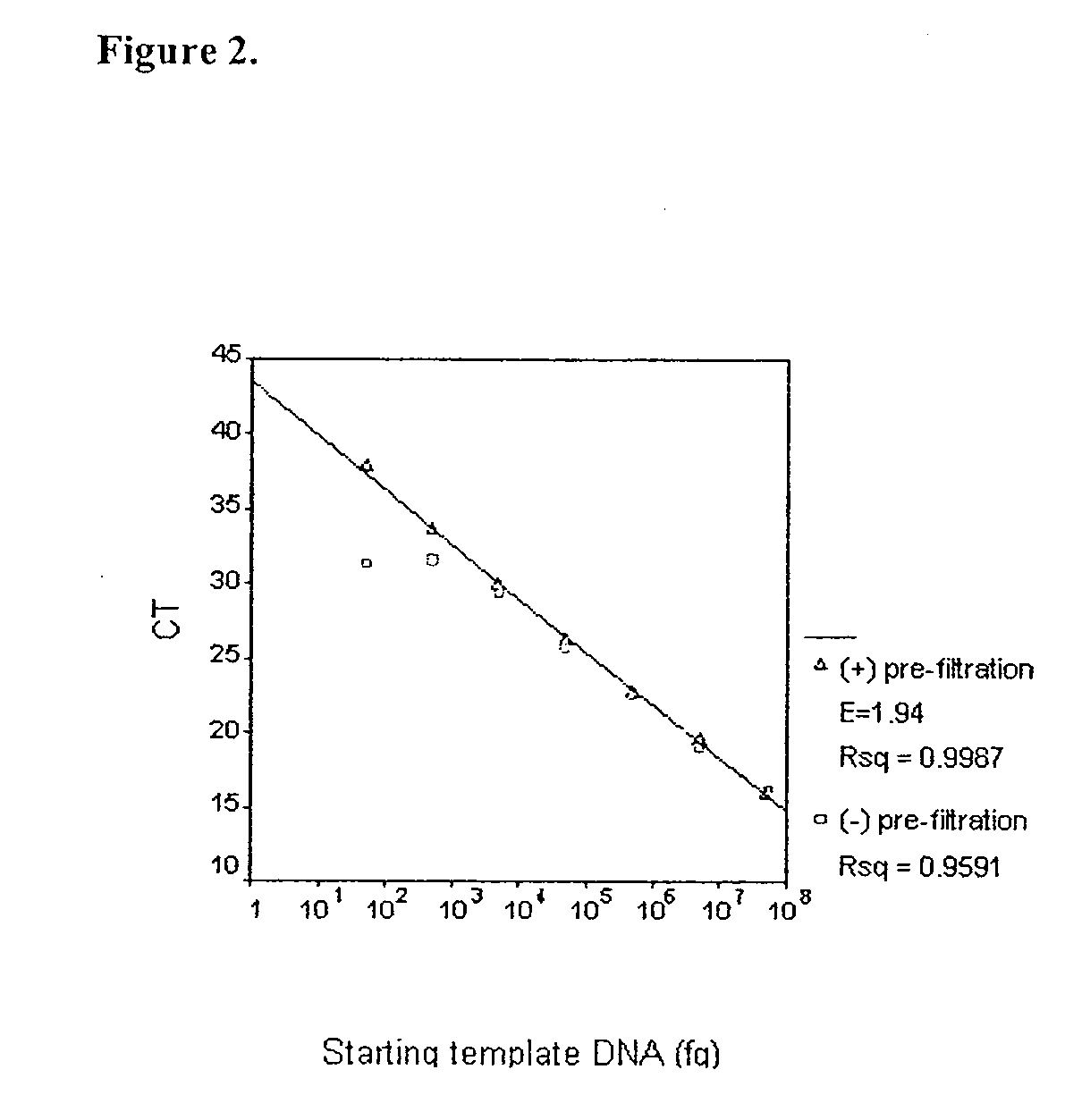
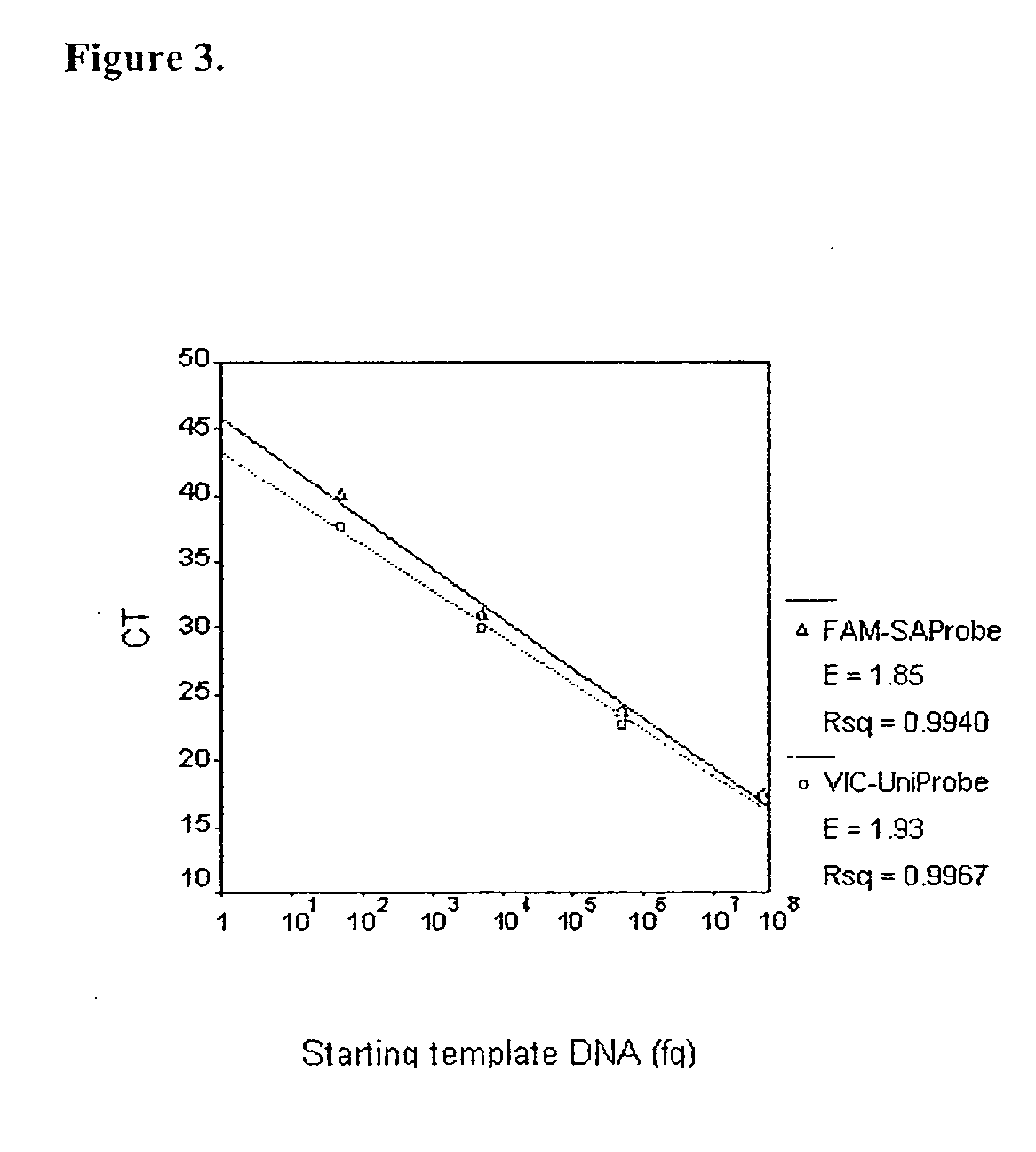
[0043]The sensitivity of the TaqMan assay was determined by amplifying serial dilutions of eubacterial DNA. The minimal detection limit of the TaqMan system was defined as the amount of template DNA at which the relationship between CT and starting template DNA became nonlinear. Serial dilutions of S. aureus DNA (50 ng to 5 fg) were added to PCR reactions with universal primers (p890F+p1033R) and probe (UniProbe). The results are shown in Table 3. The standard curve in which CT values were plotted against starting template DNA is linear between 50 ng to 5 pg (FIG. 2). At DNA levels below 5 pg, this relationship became non-linear, and the CT's were similar to the CT of the no template control (NTC). This suggested the presence of contaminating eubacterial DNA in the NTC. The minimal detection limit of the assay was thus 5 pg of S. aureus DNA.
TABLE 3Sensitivity of the Taqman Assay with or without pre-filtration.CT for the following template DNA...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| optical density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| emission spectra | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com