Microbially-mediated method for synthesis of non-oxide semiconductor nanoparticles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
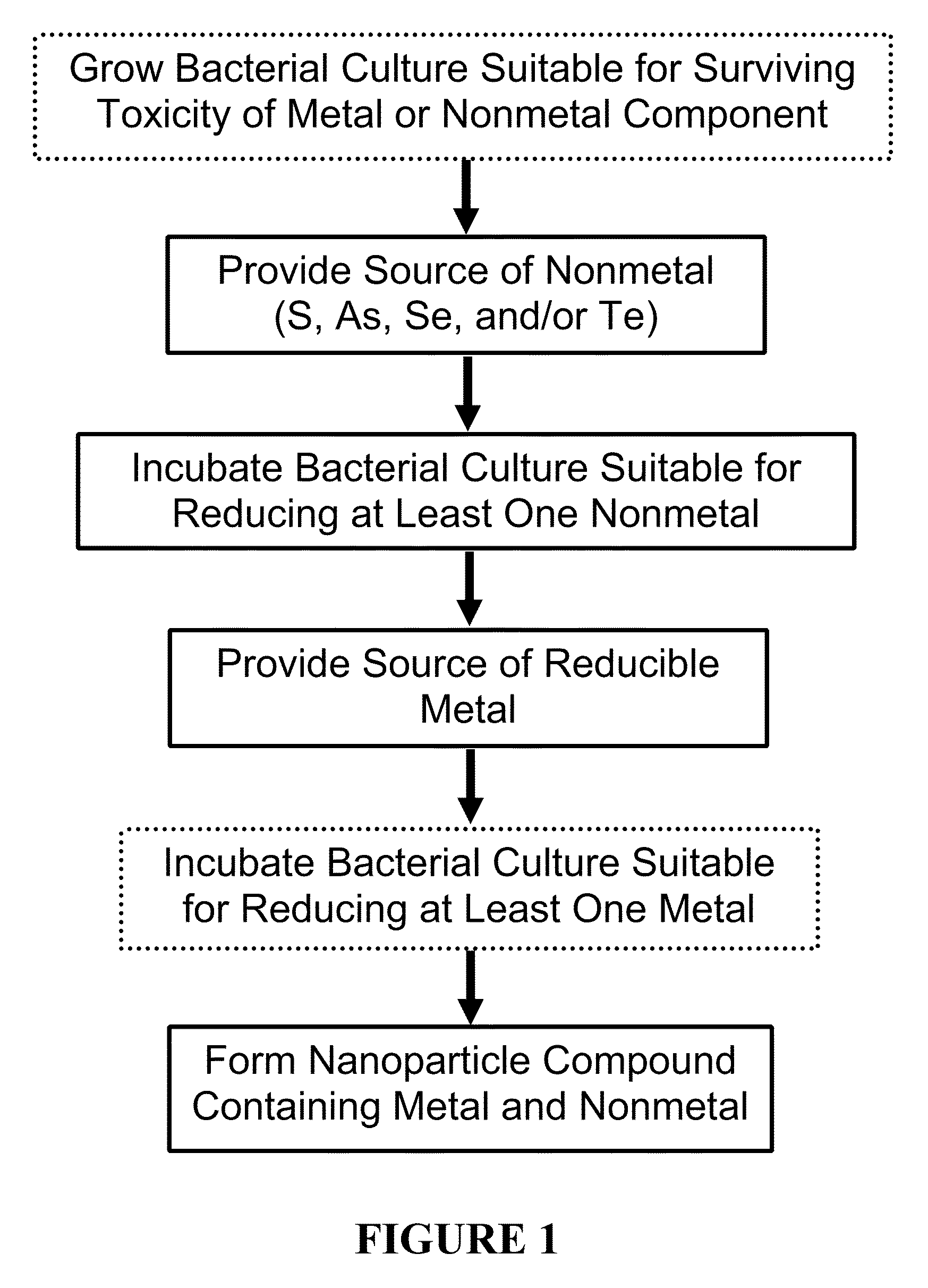
Method used
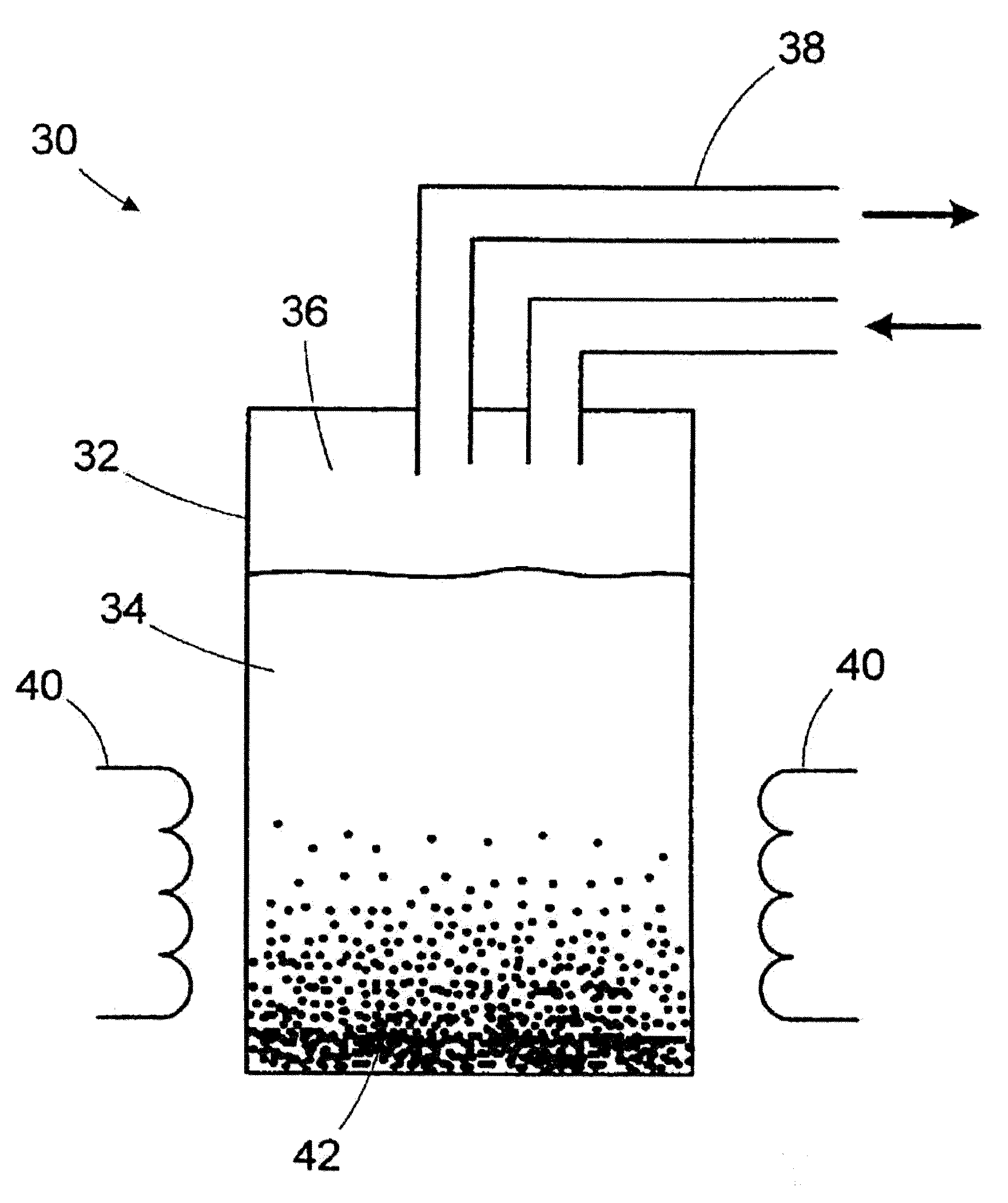
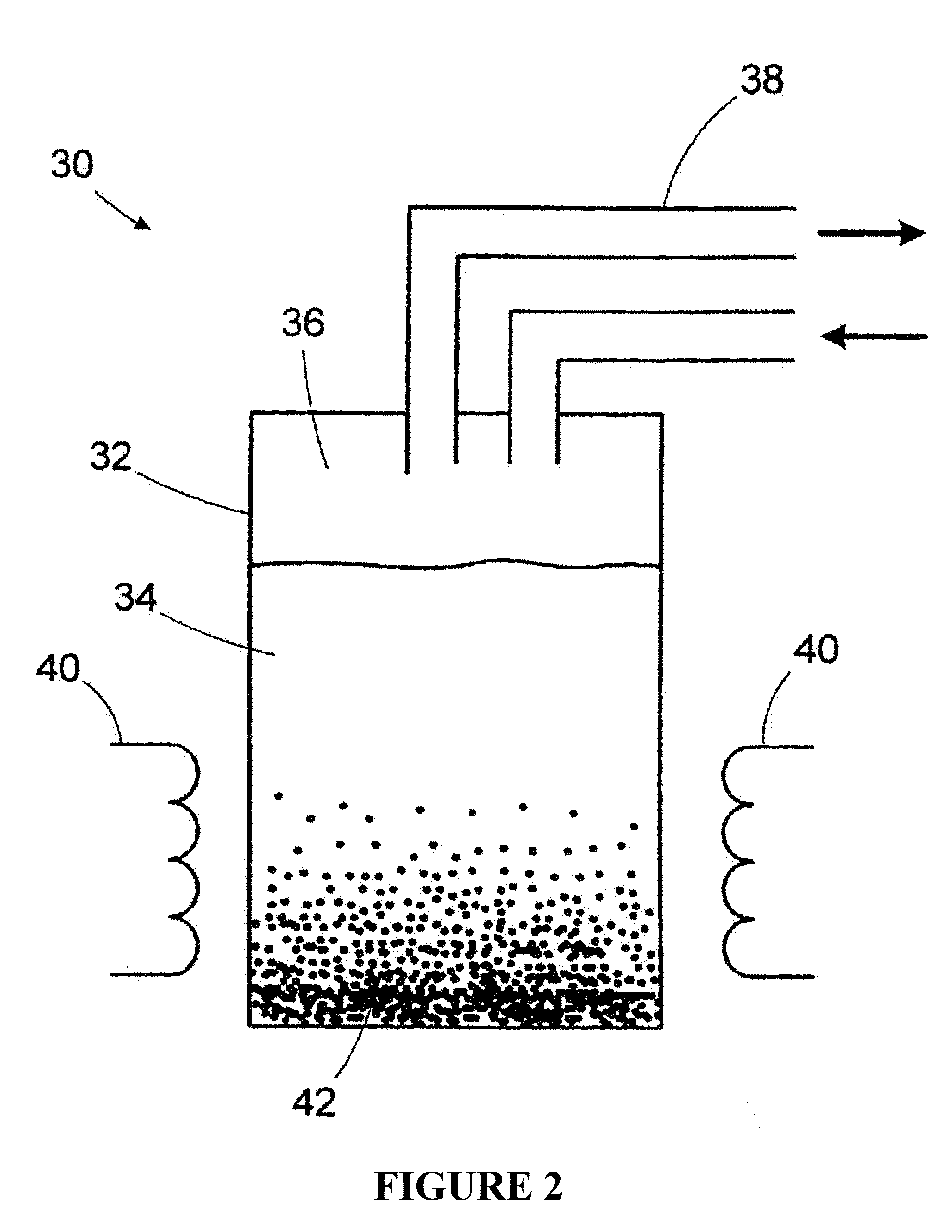
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of ZnS Nanoparticles Using Sulfate-Reducing Microbes
[0115]A mesophilic sulfate-reducing strain Desulfovibrio G-20 was grown in a lactate / SO4 culture medium as taught generally by Li et al., “Reduction of iron oxides enhanced by a sulfate-reducing bacterium and biogenic H2S”, Geomicrobiol. J., 23:103-117 (2006), the entire disclosure of which is incorporated herein by reference. Zn2+ was added as ZnCl2 at 0.2 mM and well-formed highly crystalline ZnS (sphalerite phase) nanoparticles were formed. Precipitated semi-conductor materials were harvested by repeated centrifugation followed by one or more times of washing with deionized water. Particle size was estimated at approximately 5.9 nm. A similar experimental run using standard medium containing nutrients, vitamins, trace elements, lactate as an electron donor at 50 mM, and Na2SO4 as a non-metal component with 50 mM and with Zn2+ added as ZnCl2 at 5 mM yielded ZnS particles estimated at approximately 3.7 nm in size.
[0116...
example 2
Preparation of CdS Nanoparticles Using Sulfate-Reducing Microbes
[0117]CdS nanoparticles were synthesized using the same mesophilic sulfate-reducing strain Desulfovibrio G-20. In this case, CdCl2 as a precursor metal component was added at 0.06 mM and a sulfur-containing non-metal compound as 0.06 mM Na2SO3 based on CO3-buffered medium containing nutrients, vitamins, trace elements, and lactate as an electron donor at 50 mM. Precipitated nanoparticles were harvested by repeated centrifugation followed by one or more times washing with deionized water. Well-formed highly crystalline CdS nanoparticles with an extremely sharp photoluminescent peak characterized by a full-width half maximum value of or less than 20 nm, as shown in FIG. 5C, were formed.
[0118]The foregoing example demonstrates that the sulfate-reducing strain G-20 was able to make the target CdS phase in the desired size range. Remarkably, the process showed no deleterious toxicity of Cd on the bacteria used. Again, the pr...
example 3
Preparation of ZnS Nanoparticles Using Metal-Reducing Microbes
[0119]In an effort to demonstrate the generality of the process, the following series of experiments were performed using a metal-reducing strain of bacteria rather than a sulfate-reducing strain. Fluorescent ZnS nanoparticles were synthesized using the thermophilic metal-reducing strain TOR-39 cultured in low-NaCl medium for one month. Because TOR-39 cannot efficiently reduce sulfate per se, sulfur-containing non-metal component was added in the form of thiosulfate. Zn was added as ZnCl2. One experiment used 5 mM thiosulfate and 5 mM ZnCl2, added as sequential aliquots (1 mM / day). A second experiment used 10 mM thiosulfate and 10 mM ZnCl2, added as sequential aliquots (1 mM / day). The two experiments produced highly crystalline ZnS quantum dots with average particle sizes of 6.5 nm and 12 nm, respectively.
[0120]This surprising result may be interpreted as follows. Although TOR-39 is a metal-reducing bacterium (e.g., typic...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com