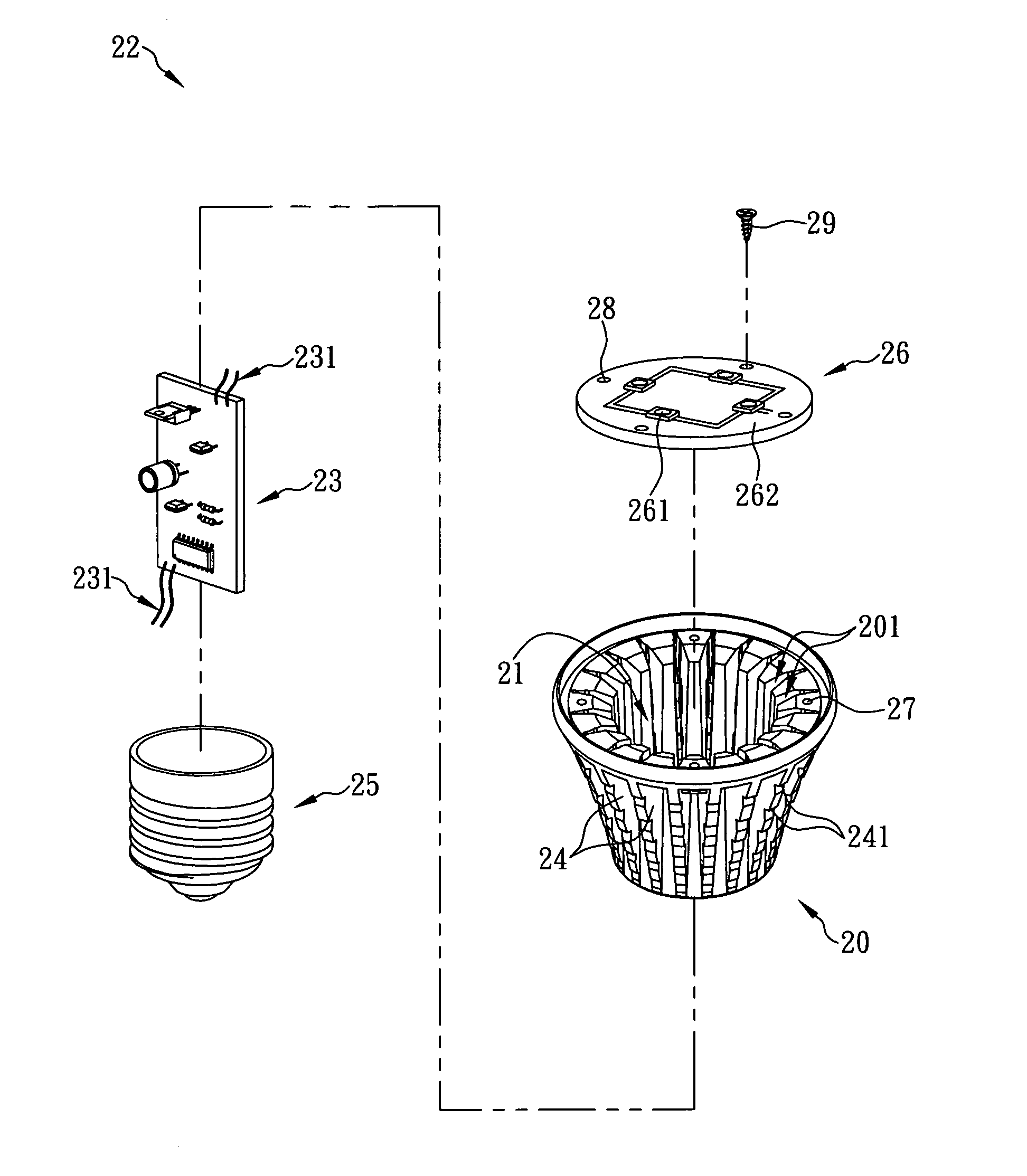
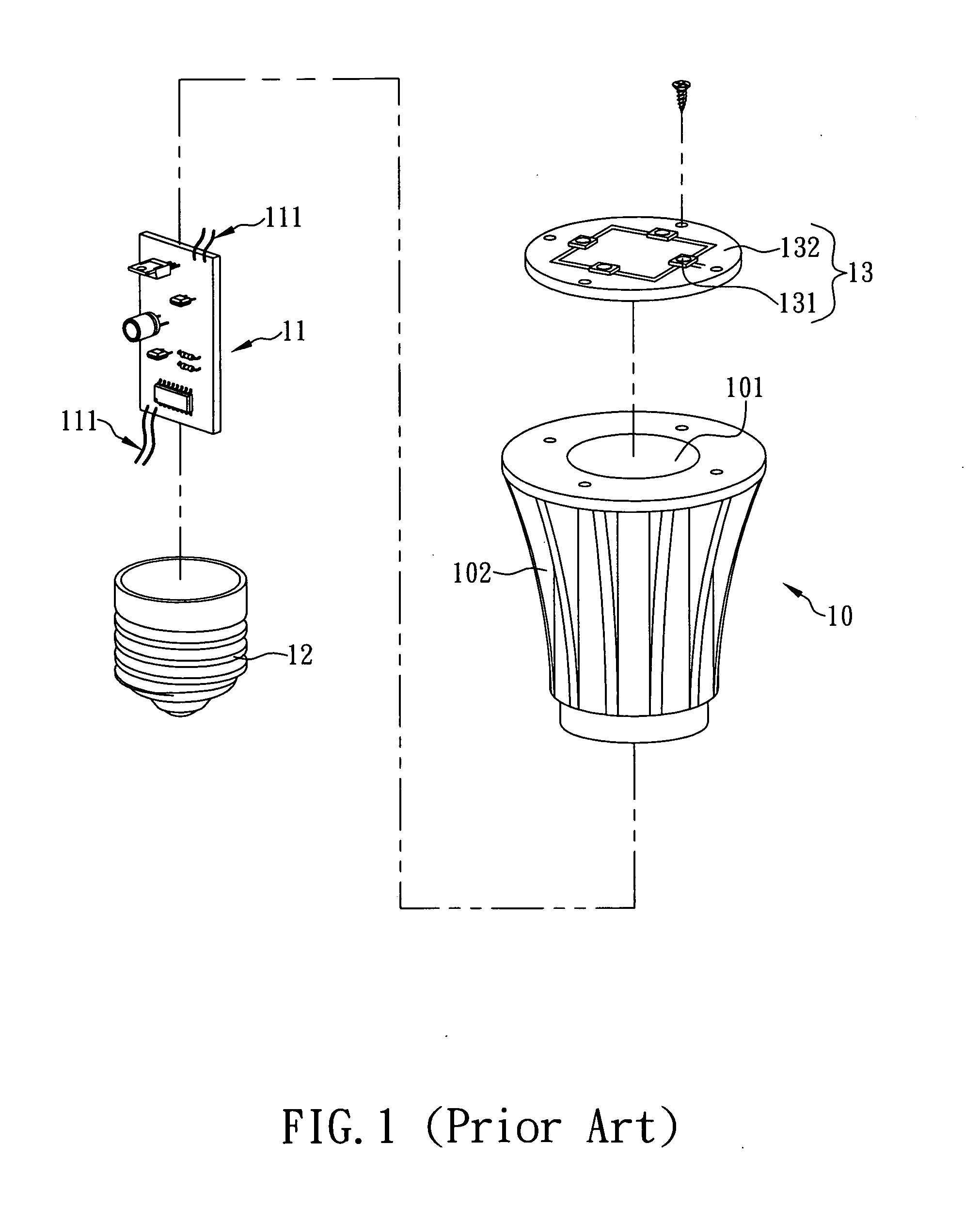
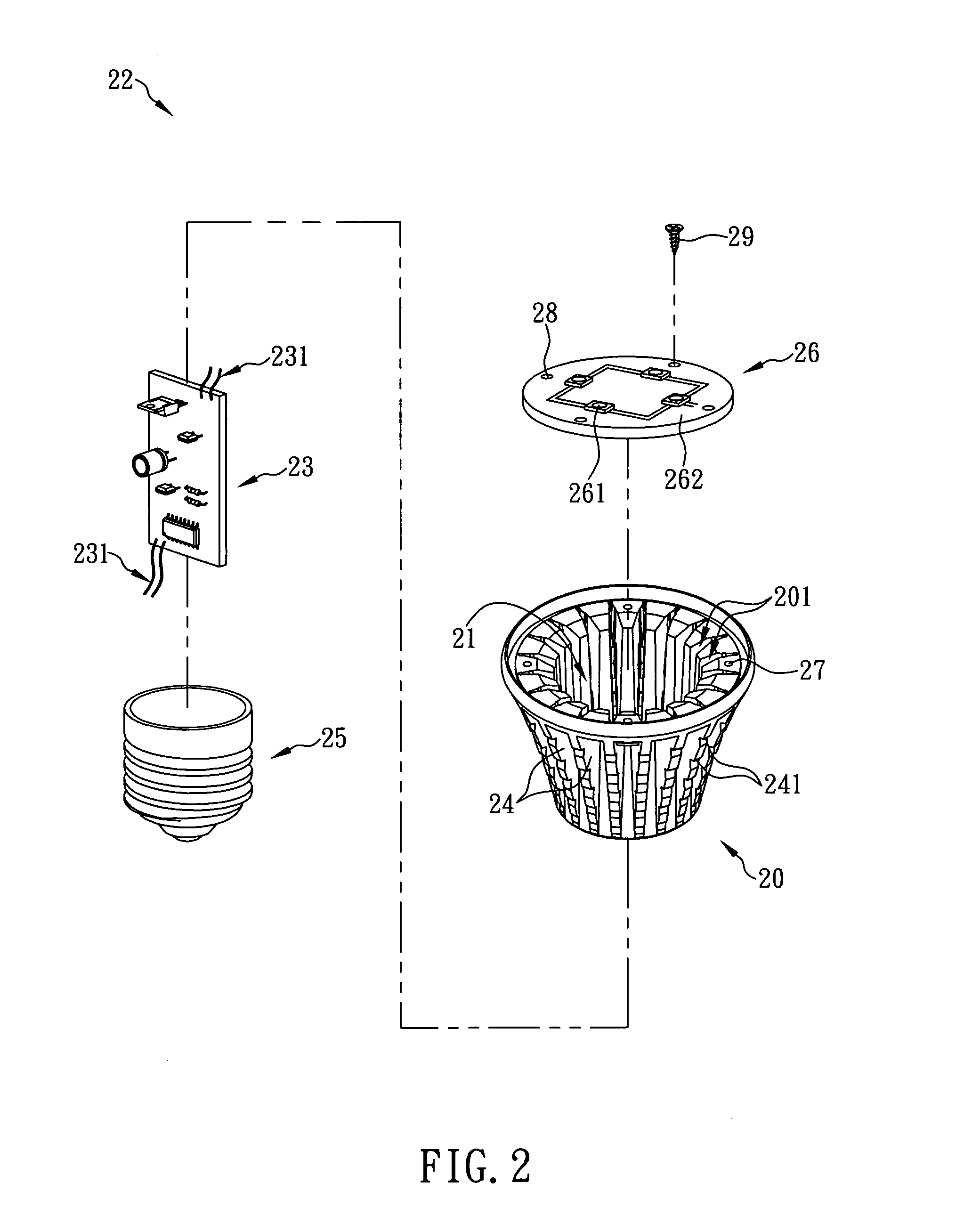
Heat dissipation housing for led lamp
a technology for led lamps and housings, which is applied in the field of housing for led lamps, can solve the problems of increasing the burden on the natural environment, reducing and reducing the use life of incandescent lamps, so as to improve the efficiency of air convection. efficiency, the effect of increasing the heat dissipation surfa
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
Generally, while a light emitting diode (LED) emits color light, the LED generates a large amount of heat. Thus, an LED lamp installed with LEDs is generally provided with a heat dissipation housing to dissipate heat generated by the LEDs to the ambient environment. Typically, the manufacturing methods of the heat dissipation housing can be classified into metal extrusion and metal casting. For a heat dissipation housing manufactured by metal extrusion, a pure metal plate (such as an aluminum plate) is extruded to integrate into one piece, so as to form the heat dissipation housing. However, the heat dissipation housing manufactured by metal extrusion has a rougher surface, so that the rougher surface must be finished by a secondary processing. It causes that the processing procedures are complicated and cost more time and manpower of manufacturers, so that the manufacture cost of the heat dissipation housing will be increased and the market competitiveness of the manufacturers will...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com