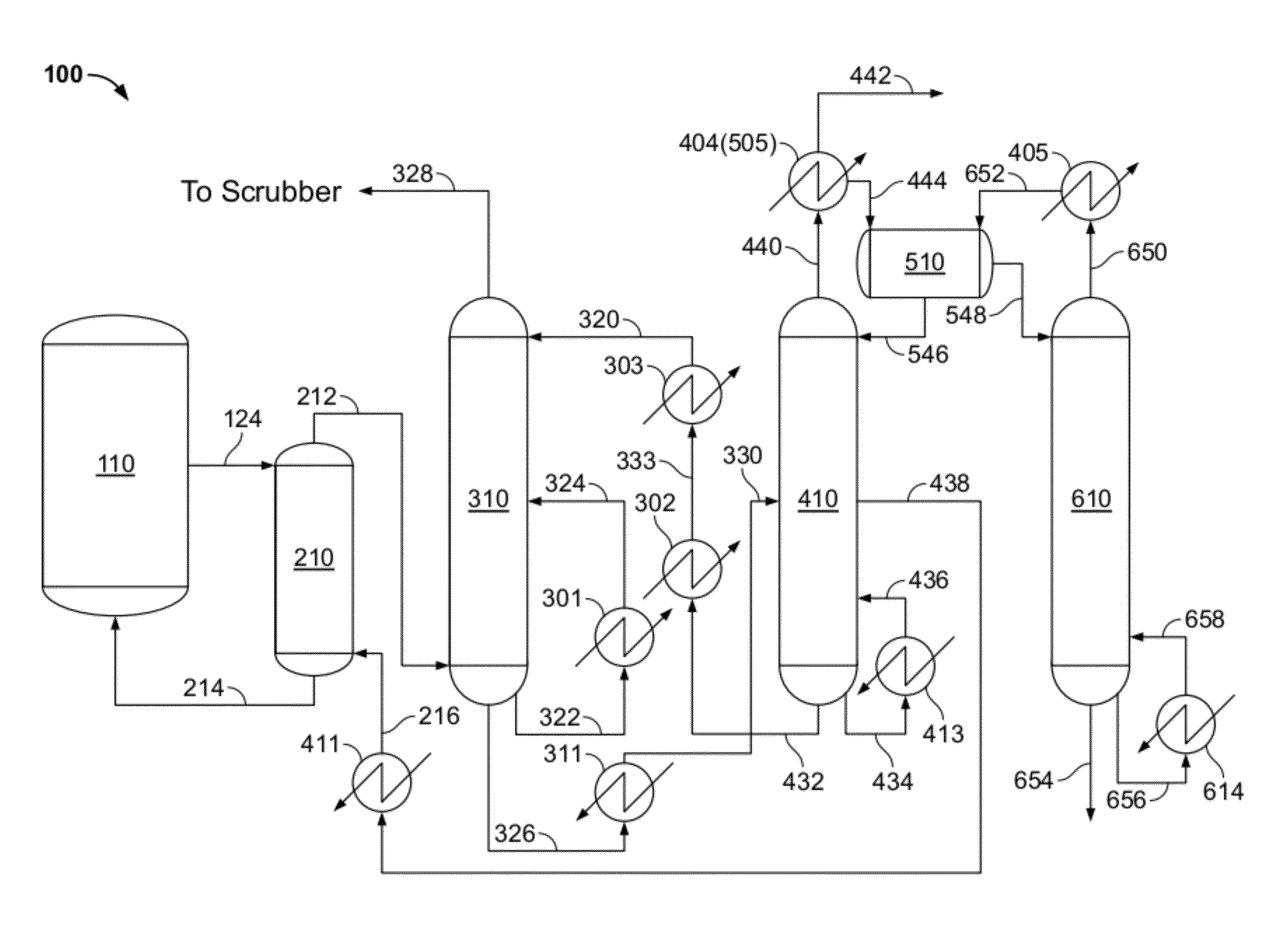
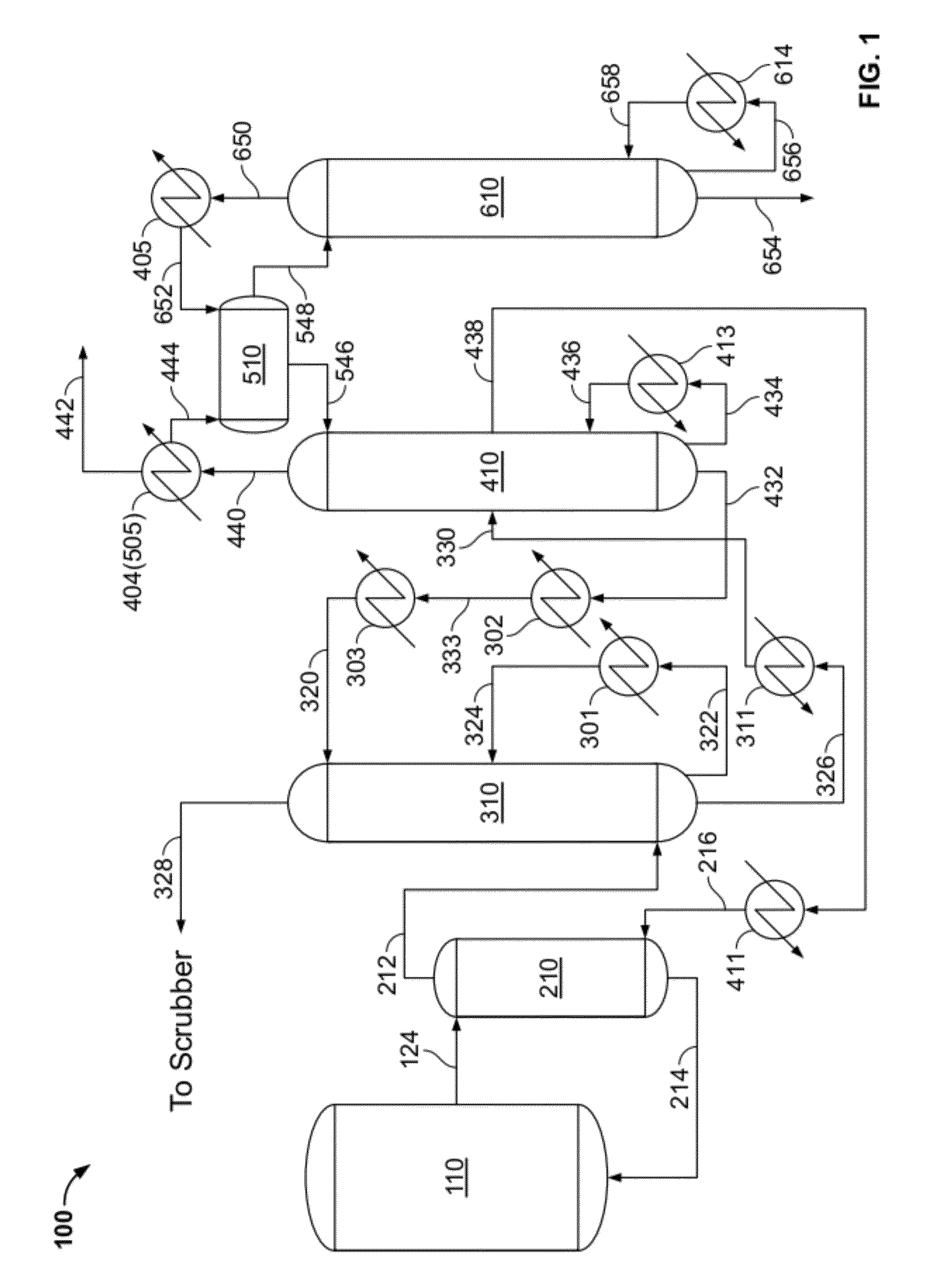
Process to remove product alcohol from a fermentation by vaporization under vacuum
a technology of product alcohol and vacuum, which is applied in the direction of separation process, separation machine, climate sustainability, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the cost and reducing the efficiency of the cooling medium
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Absorption Liquid MEA
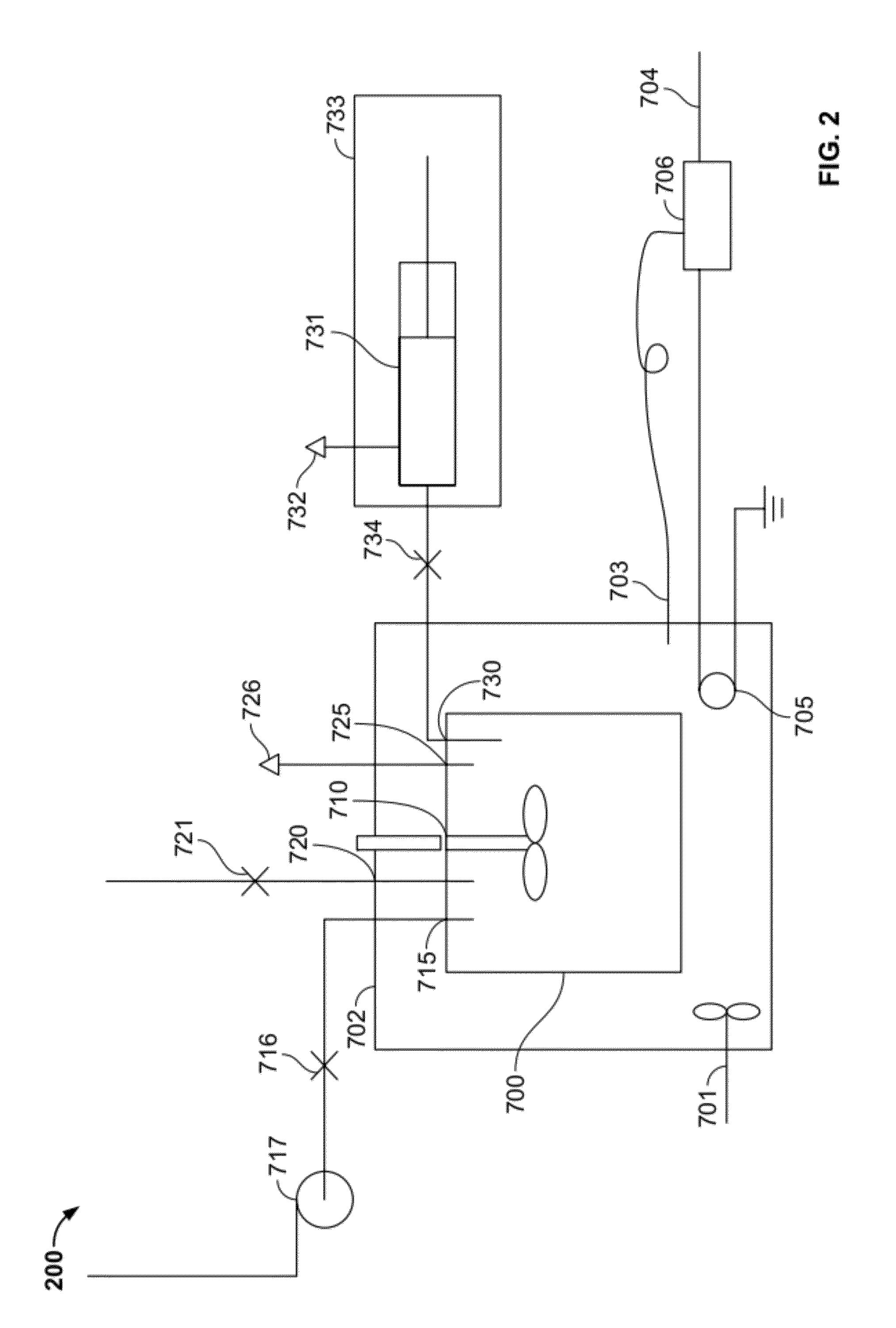
[0108]The pressure composition relationship at a known temperature was measured with the described apparatus 200 as follows:
[0109]51.967 grams of a mixture of 6.99% isobutanol, 20.01% deionized water and 72.99% MEA were charged to static cell 700 and magnetically driven mixer 720 was started. The cell operating temperature was 44.42° C. and the liquid charge was 51.967 grams. The liquid mixture was degassed slowly by opening valve 716 connected to vacuum pump 717 until the cell pressure did not drop further. Valve 716 was then closed. The degas procedure was repeated until the cell pressure did not change with time when valve 716 to vacuum pump 717 was closed. The absence of leaks was verified by observing constant, below atmospheric pressure, in static cell 700 for at least 10 minutes. Cell 700 was heated to a targeted temperature with bath 702.
[0110]A measured volume of carbon dioxide at known pressure and temperature was introduced to cell 700 and the cell co...
example 2
Absorption Liquid MEA
[0111]The procedures of Example 1 were repeated except the cell operating temperature was 44.46° C., the liquid composition was 7.24% Isobutanol, 20.57% water, 72.2% Monoethanolamine and the liquid charge was 49.925 grams. Results are given in Table 3.
TABLE 3Effect of MEA on vapor pressureGrams of CO2 added to cellVapor pressure in cell - psia00.6840.07390.6940.15770.7050.27980.7160.41210.7240.53620.7340.66570.7420.81860.7520.96790.7611.15210.772
example 3
Absorption Liquid MDEA
[0112]The procedures of Example 1 were repeated except the cell operating temperature was 44.45° C., the liquid composition was 4.99% Isobutanol, 12.01% water, and 83% methyldiethanolamine, and the liquid charge was 52.087 grams. Results are given in Table 4.
TABLE 4Effect of MDEA on vapor pressureGrams of CO2 added to cellVapor pressure in cell - psia00.6540.08330.9900.16781.50.30012.4280.39663.1530.50093.970.60584.8120.70585.6430.81646.5790.92207.501
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com