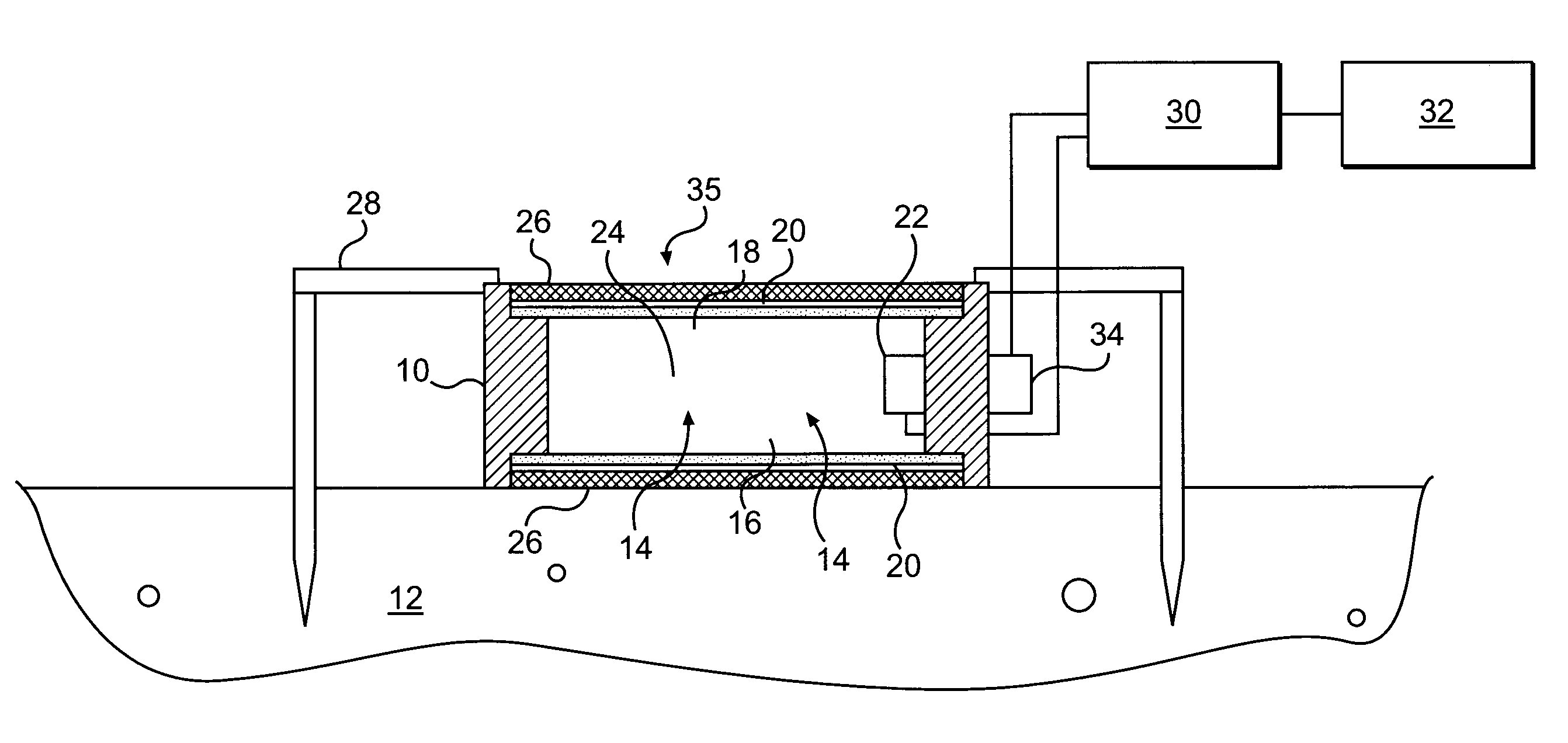
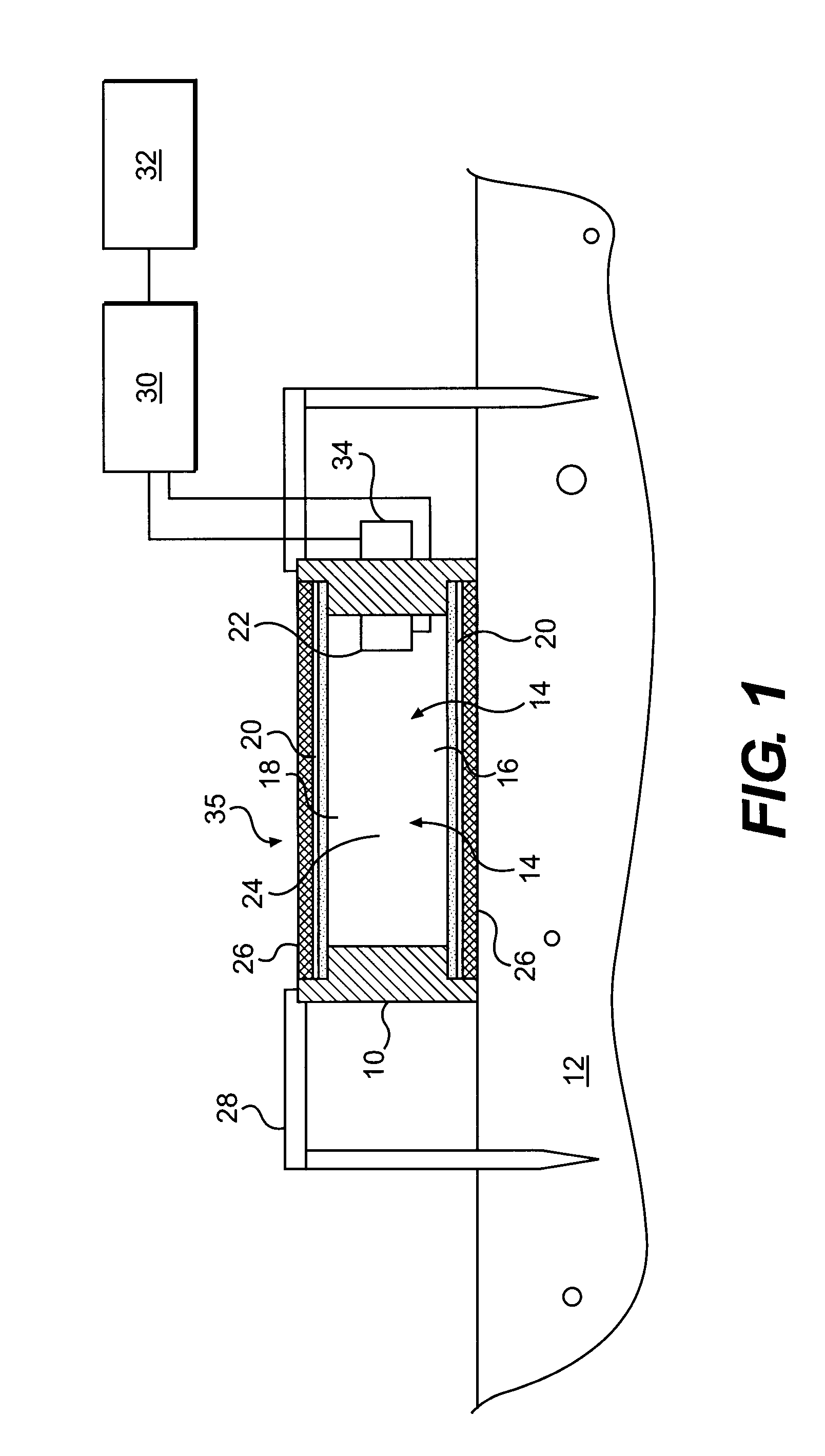
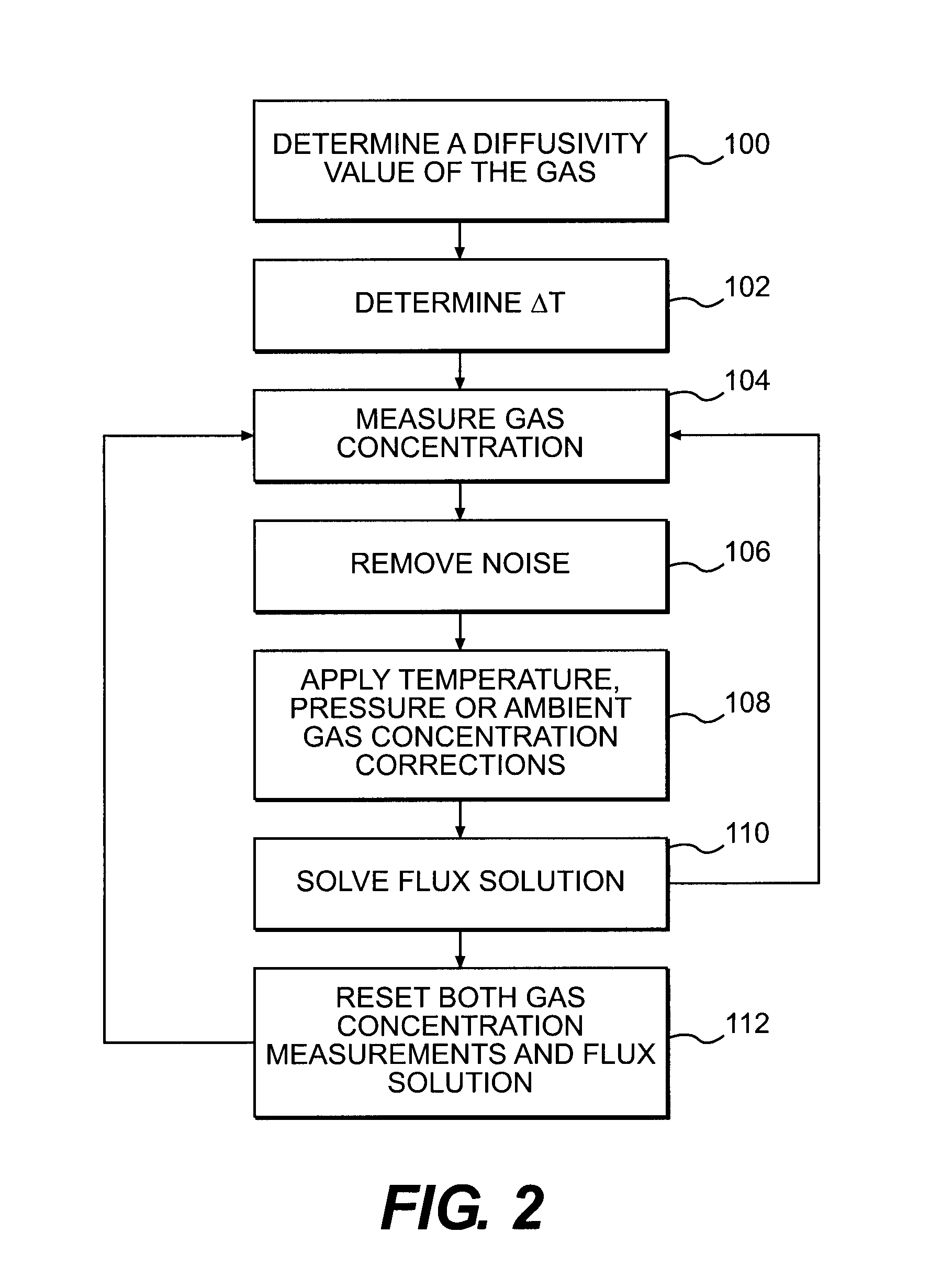
Method of measuring the flux of a soil gas
a technology of soil gas and flux, applied in the field of soil gas measurement, can solve the problems of affecting both the soil structure and the gas transport regime, prone to underestimating flux, and diffusivity models that perform better, so as to overcome or mitigate one or more disadvantages of known methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
second embodiment
[0062]the present invention is now described. Reference is made to FIG. 3. In this embodiment, a known measurement technique is used to measure soil gas concentration data over a large spatial scale. This system of measurement uses a semi-permeable polyvinyl tube 36 connected to a recirculating pump 38 and a gas analyzer 40. The tube 36 allows unrestricted diffusion of the soil gas into its interior, where it is circulated in a closed loop, allowing the tube 36 to reach equilibrium with its surroundings quickly. After equilibrium has been reached, the soil gas may be drawn off the loop and sampled by the gas analyzer 40. Since the tube 36 is constantly in equilibrium with its surroundings, small spatial variation in soil gas concentrations are averaged by the circulating air inside the tube 36. This averaging gives a representative gas concentration for the entire area with which the tube 36 is in contact, rather than a point measurement. Soil gas diffusivity must be measured with a...
third embodiment
[0063]A third embodiment is now described, with reference to FIG. 4. In the present embodiment, the single-point Flux Solution is coupled to a simultaneous measurement of soil gas diffusivity. Risk, in published U.S. patent application Ser. No. 10 / 419,082, describes an automated method and system for use in determining diffusivity values in-situ. However, rather than the described technique relying on a continuous flow membrane probe buried in the soil and coupled to an above ground control / measurement system, the probe 42 of the present embodiment is deployed at the soil-atmosphere interface to measure fluctuations in soil gas concentration, while still connected to a similar above ground control / measurement system 44. Diffusivity need be measured only infrequently, such as once per day, due to the slow changes in soil moisture that influences the diffusivity magnitude. This leaves significant periods where the probe 42, which is now a dual-purpose probe capable of both measuring s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com