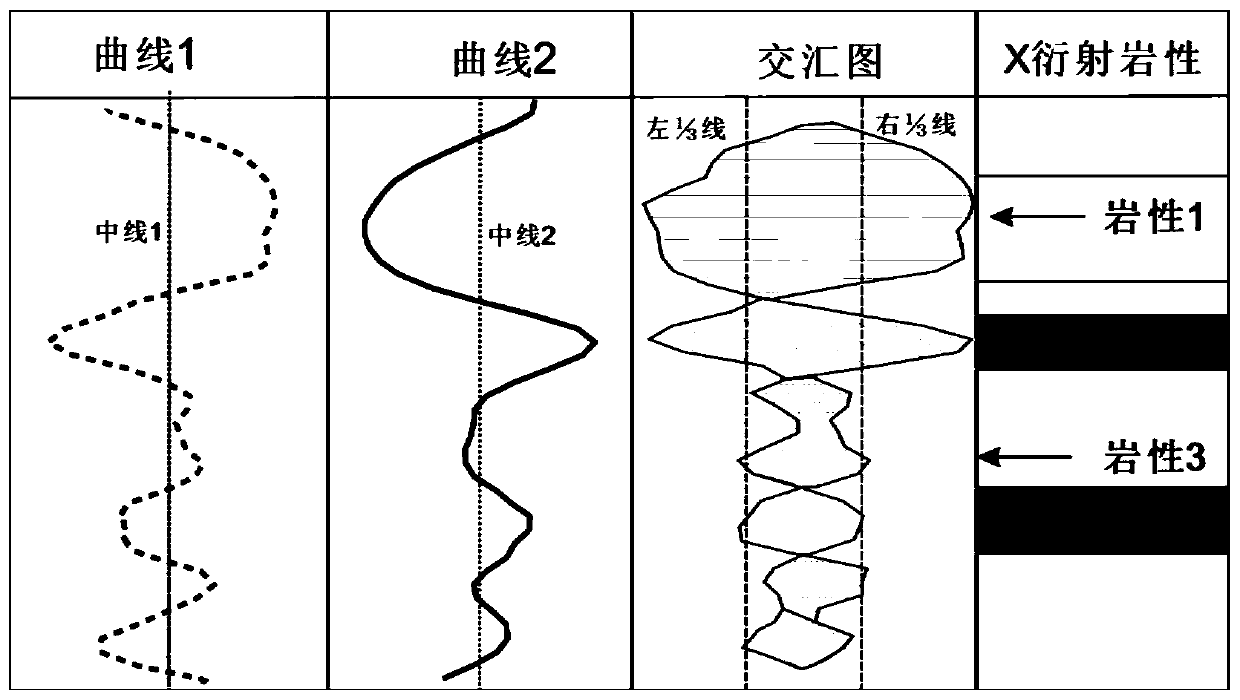
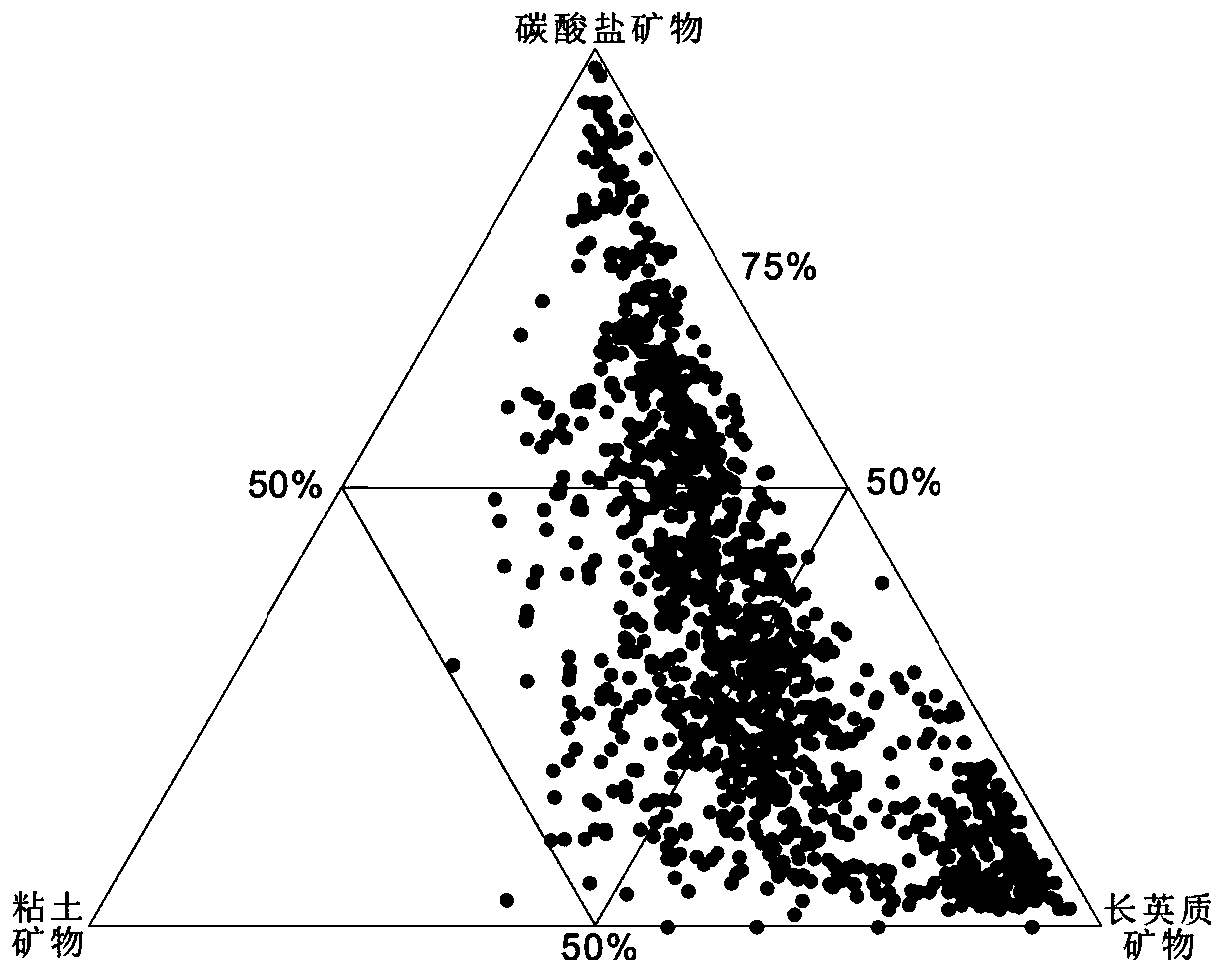
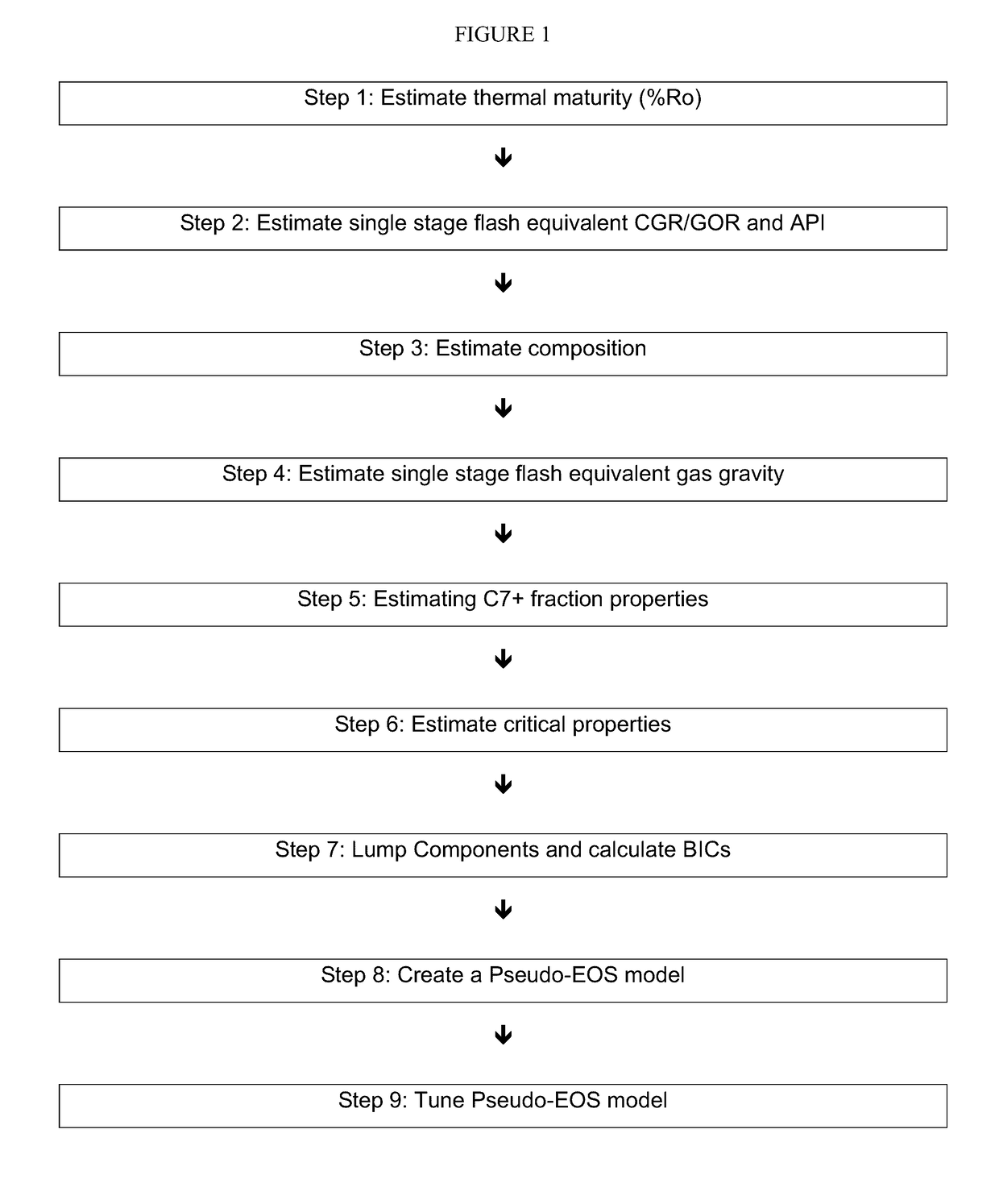
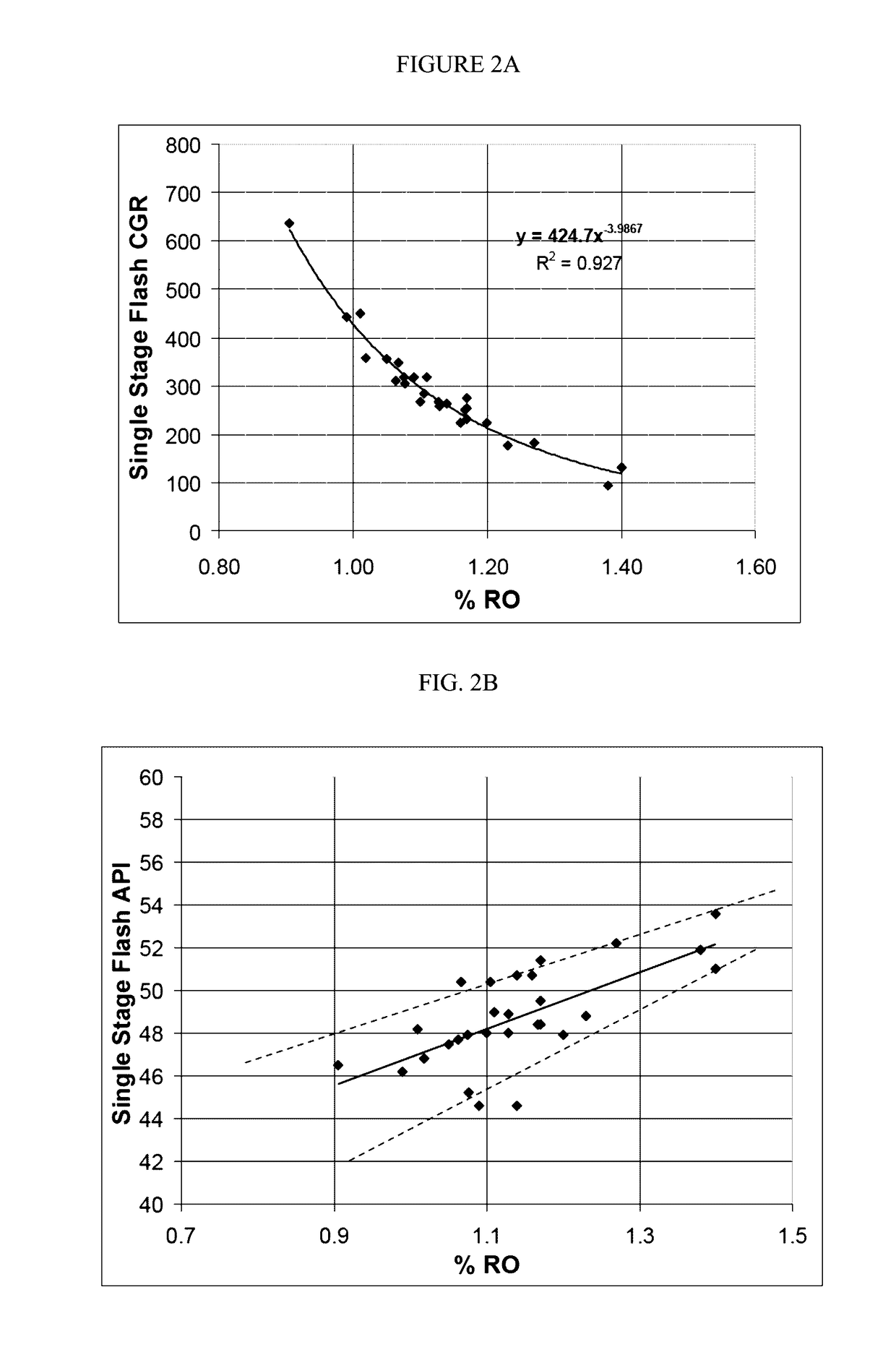
Patents
Literature
119results about "Prospecting/detection of underground/near-surface gases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
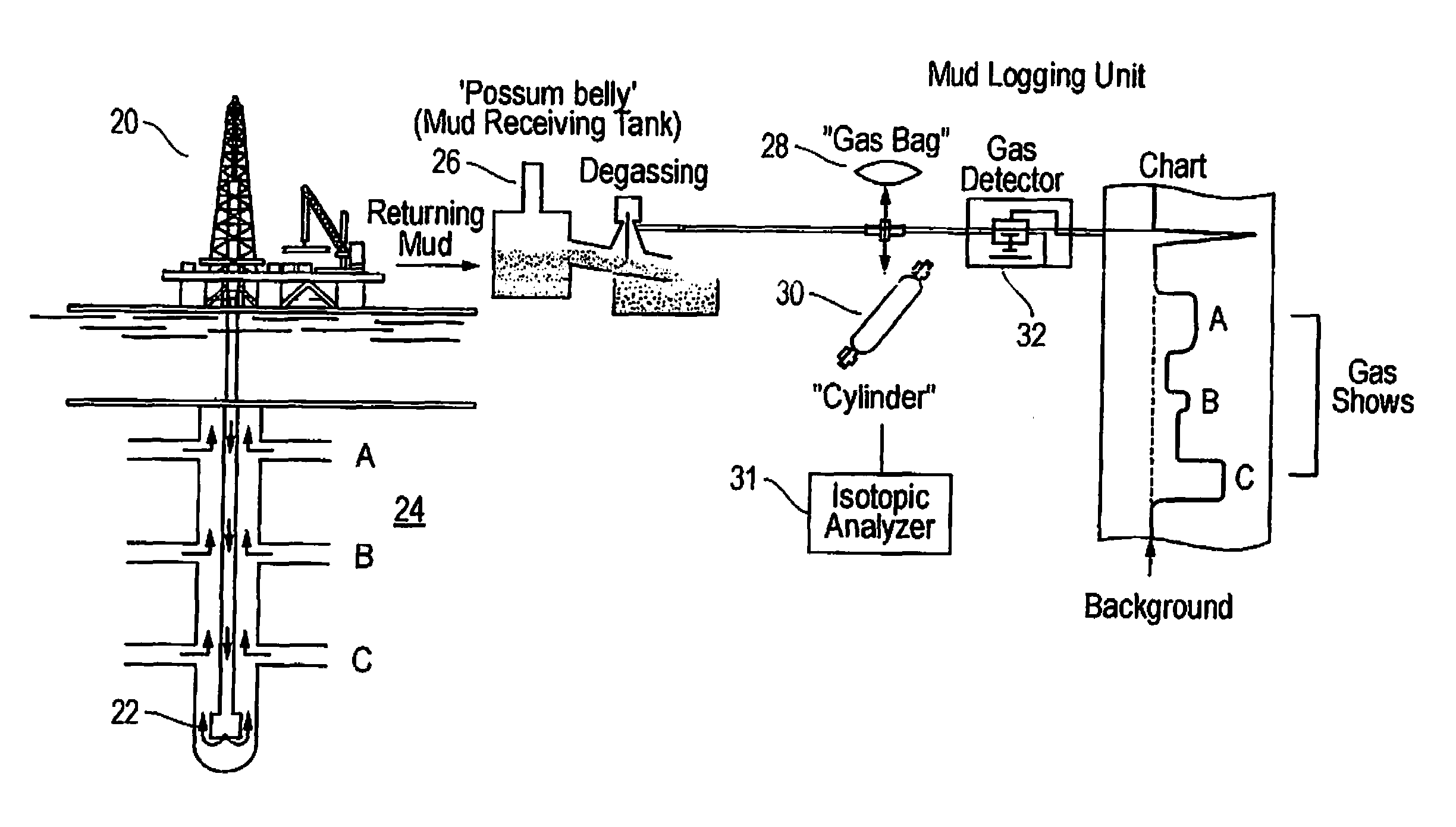
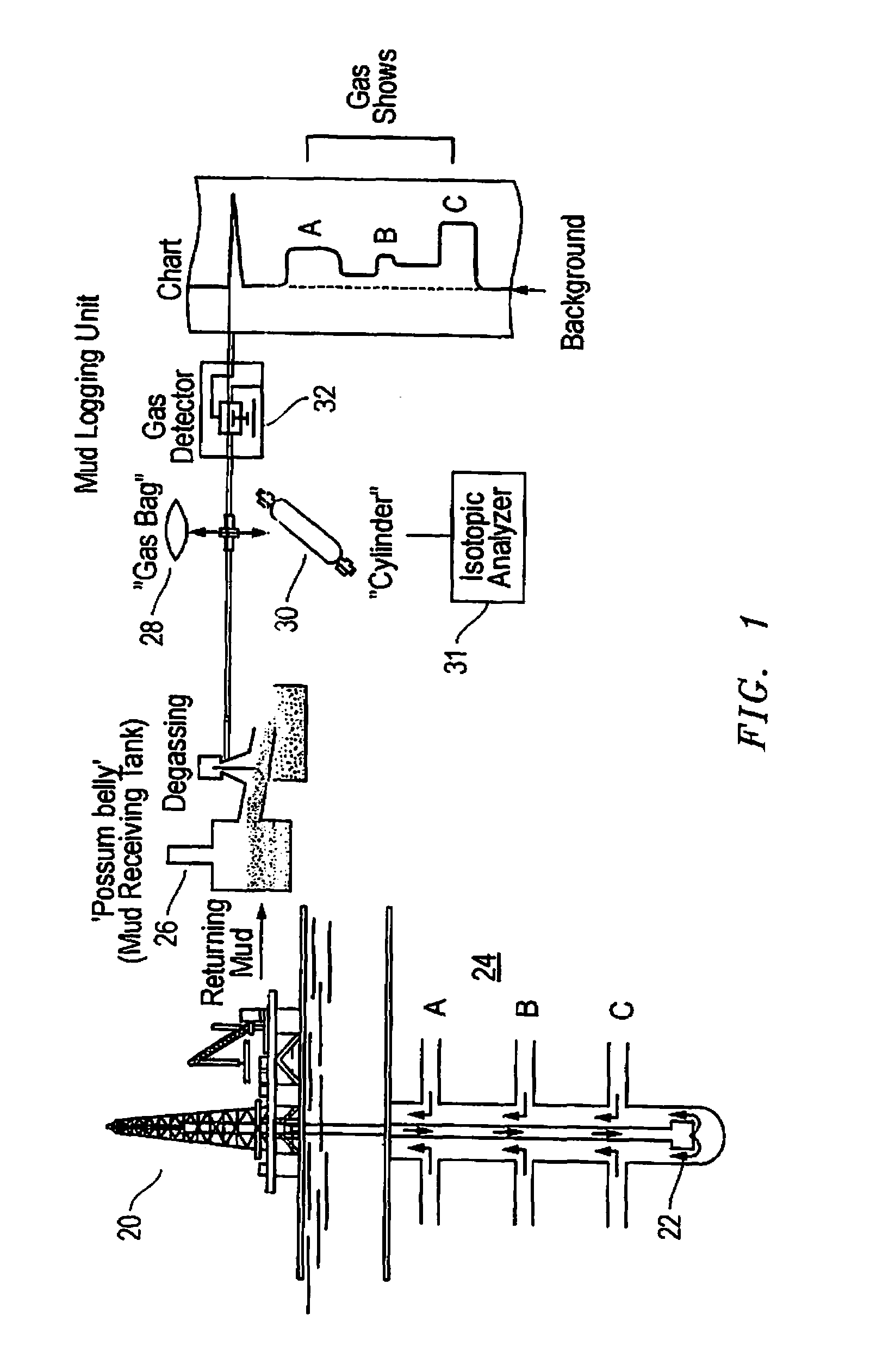
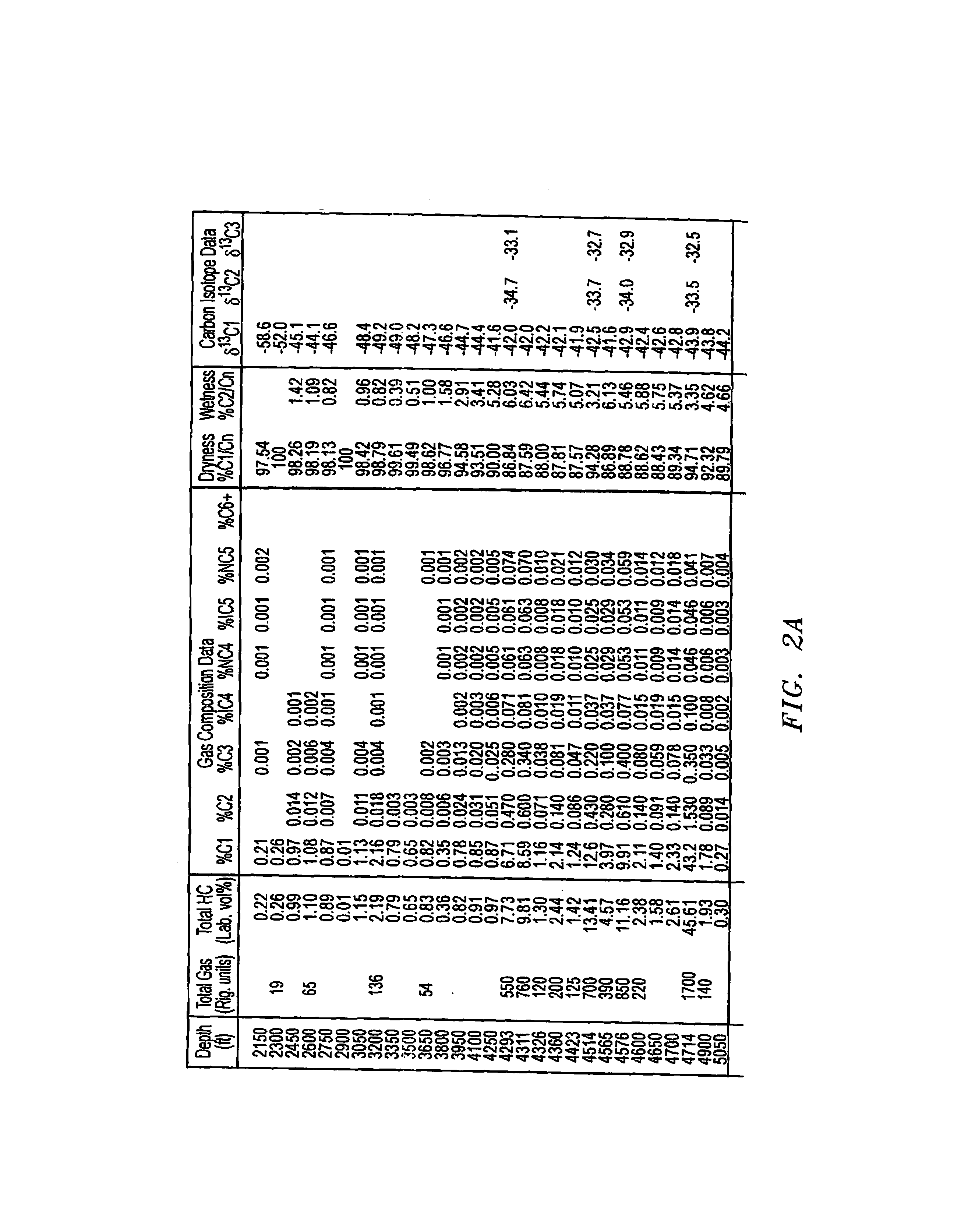
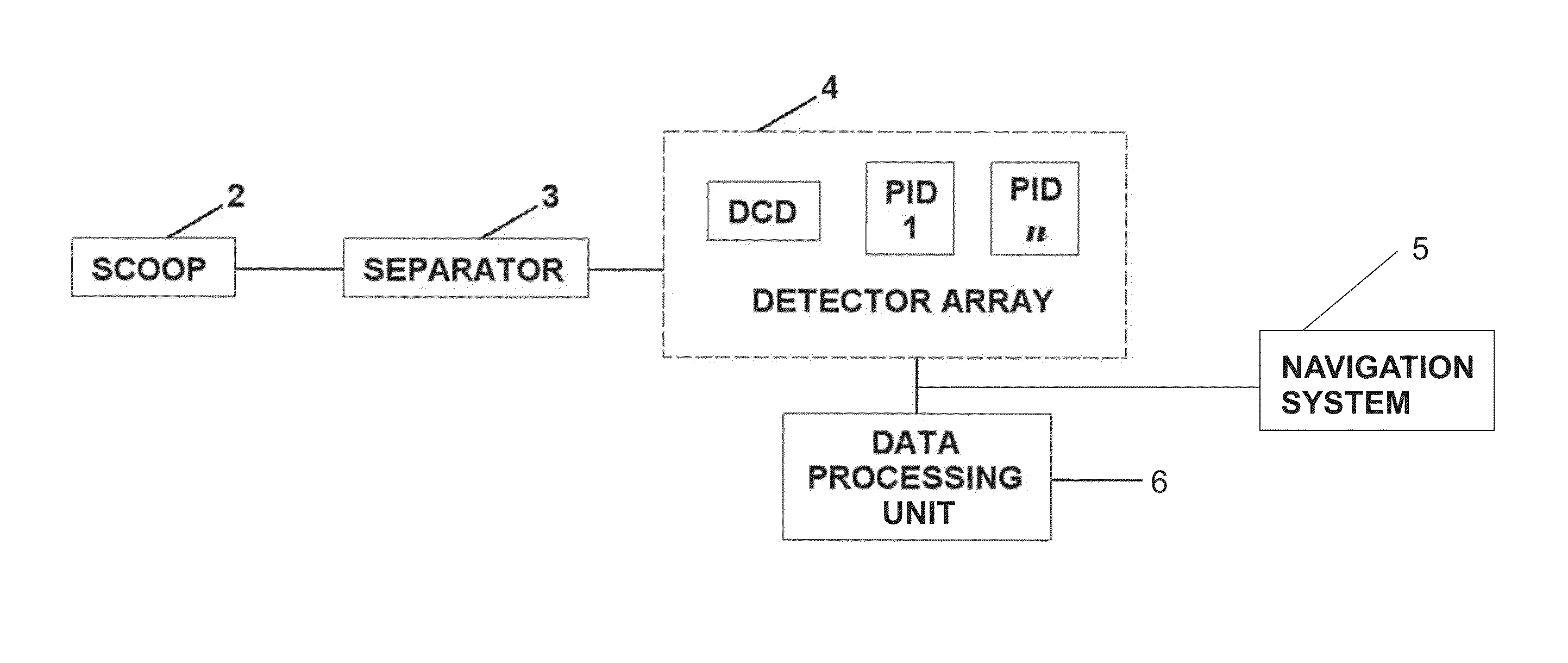
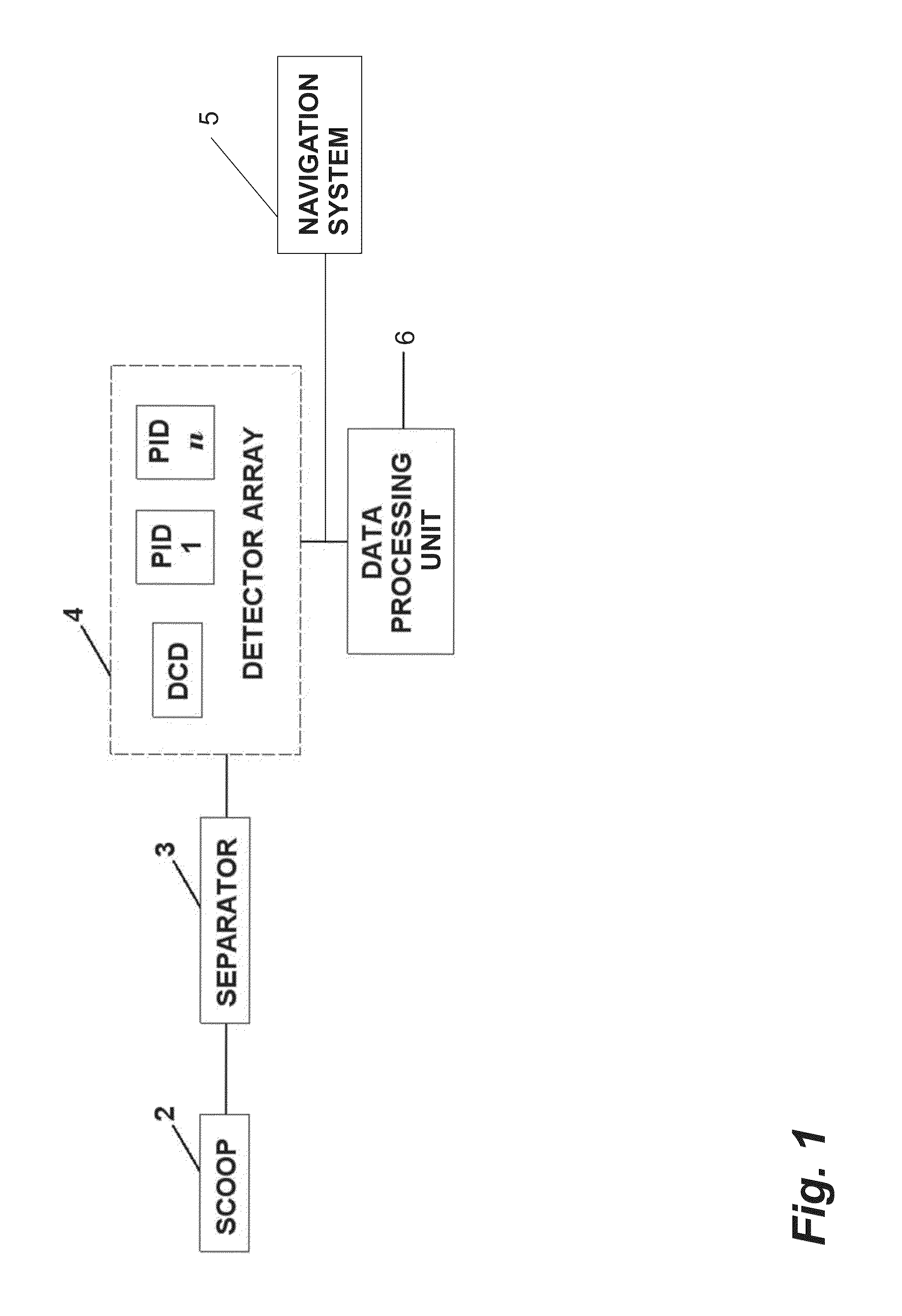
Method and system of processing information derived from gas isotope measurements in association with geophysical and other logs from oil and gas drilling operations
InactiveUS20080147326A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingProspecting/detection of underground/near-surface gasesWell loggingIsotopic composition
A system and method of interpreting well log isotopic information in a drilling operation of a target area. The method begins by inputting a template for indicating a trend from analyzed mud gas samplings into a computing system. Next, a plurality of mud gas samplings are profiled through a well bore at a plurality of incremental depths of the well bore. The plurality of gas samplings are analyzed to obtain a plurality of isotopic data points associated with hydrocarbon isotopic composition of the plurality of gas samplings. The plurality of isotopic data points includes data associated with a composition of ethane and methane or other gaseous components within each of the mud gas samplings. A trend associated with the template is determined by the computing system from the plurality of isotopic data points. The plurality of isotopic data points is analyzed to geochemically interpret the geological information.
Owner:ELLIS LEROY
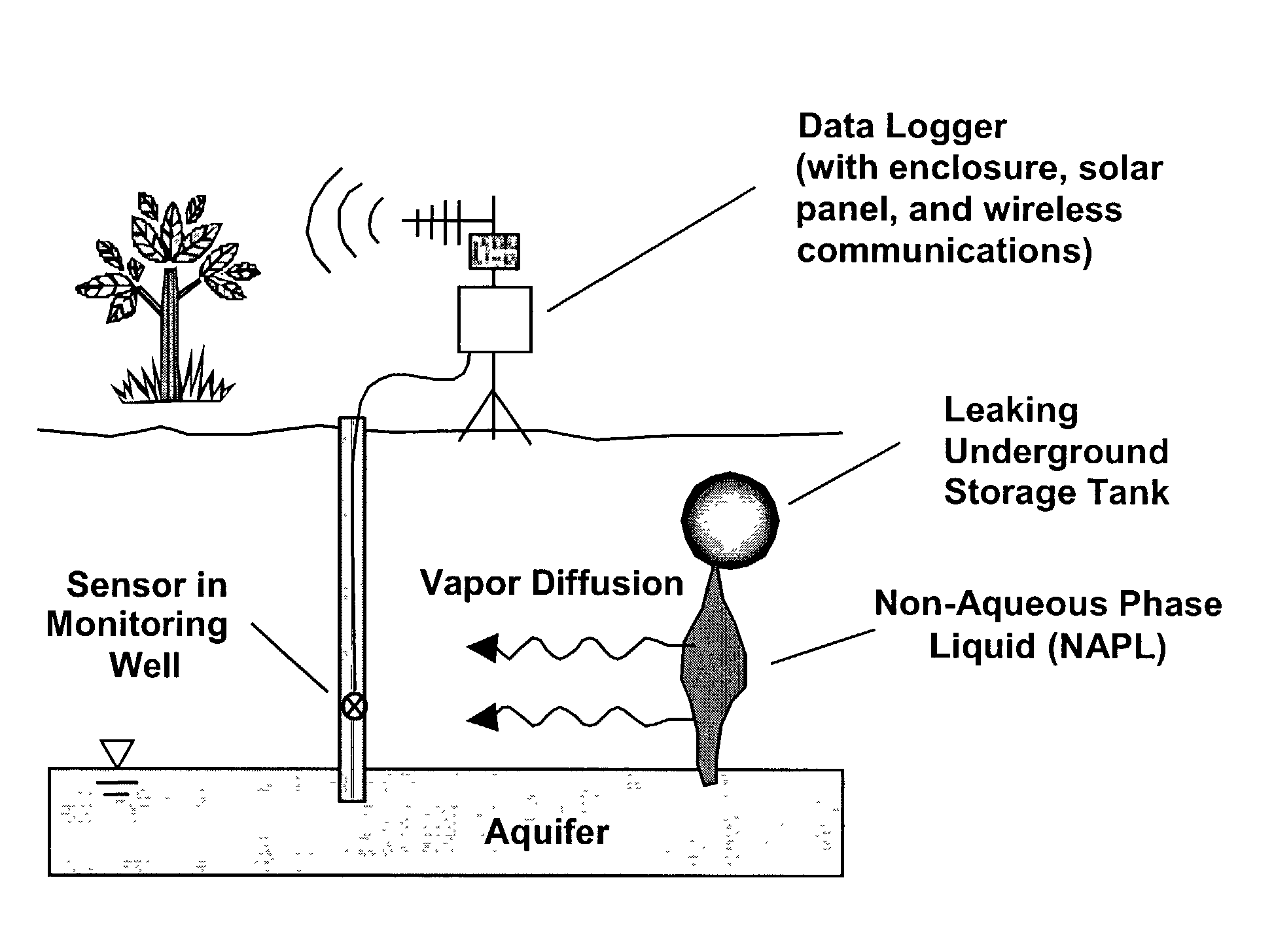
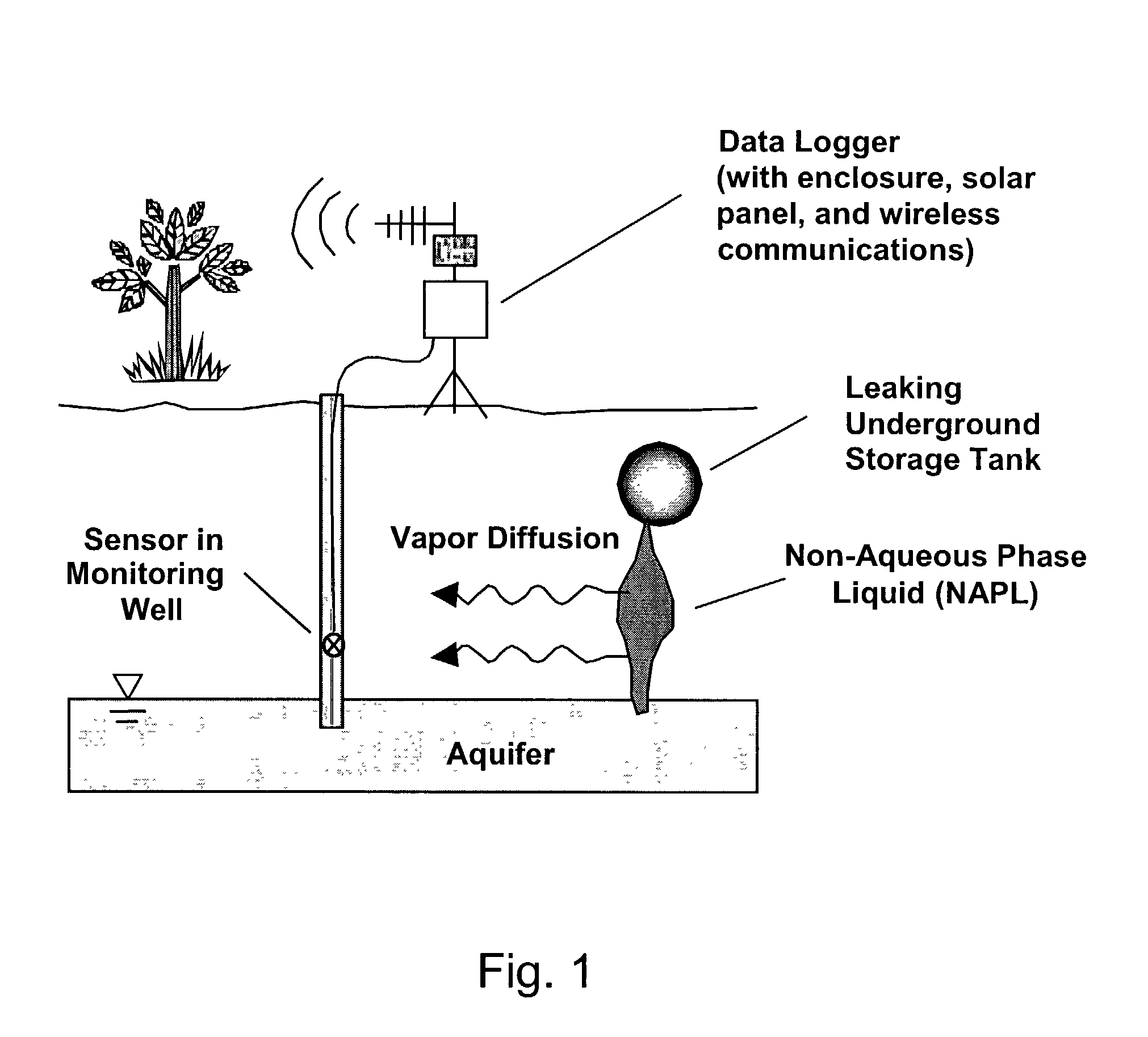
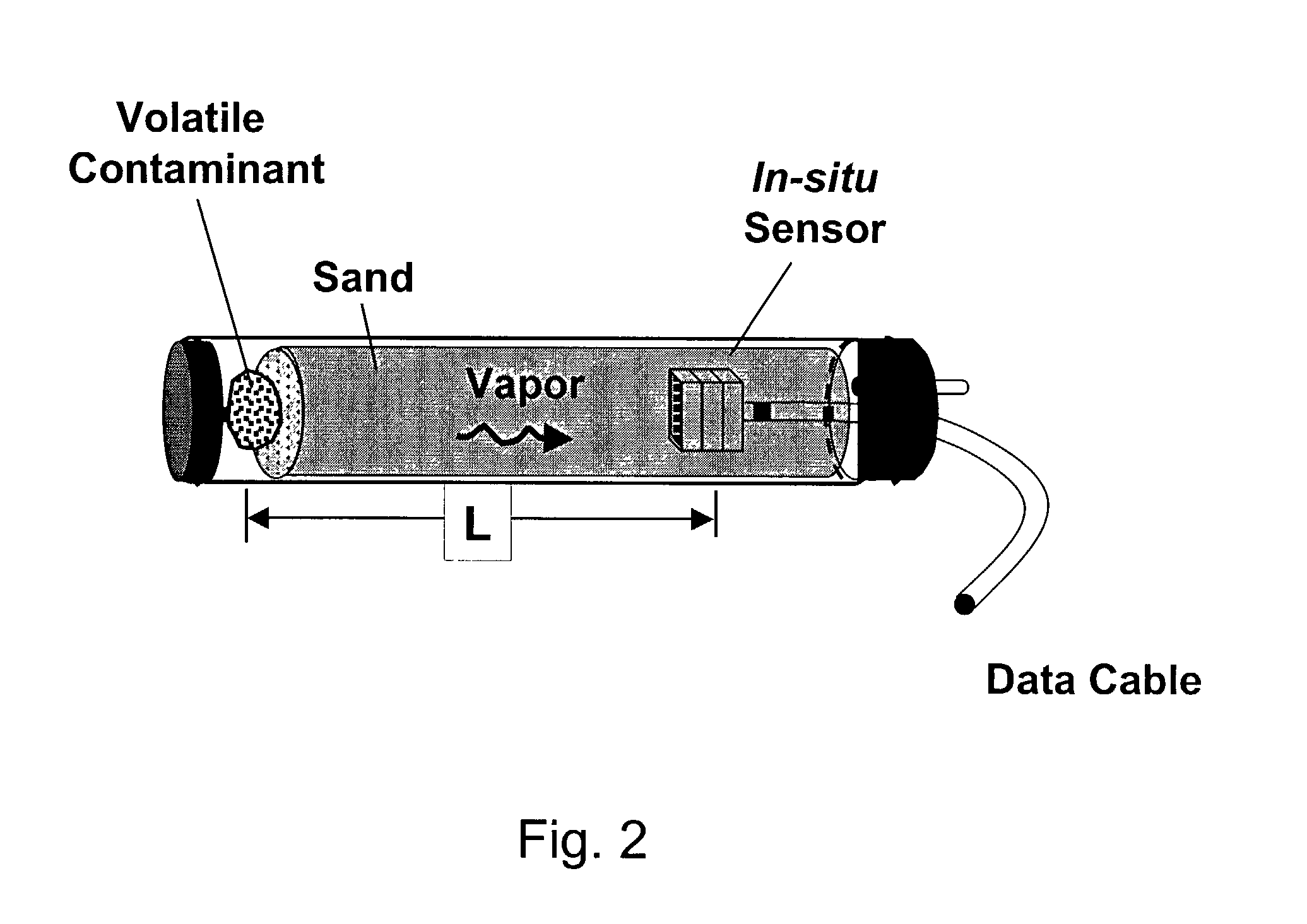
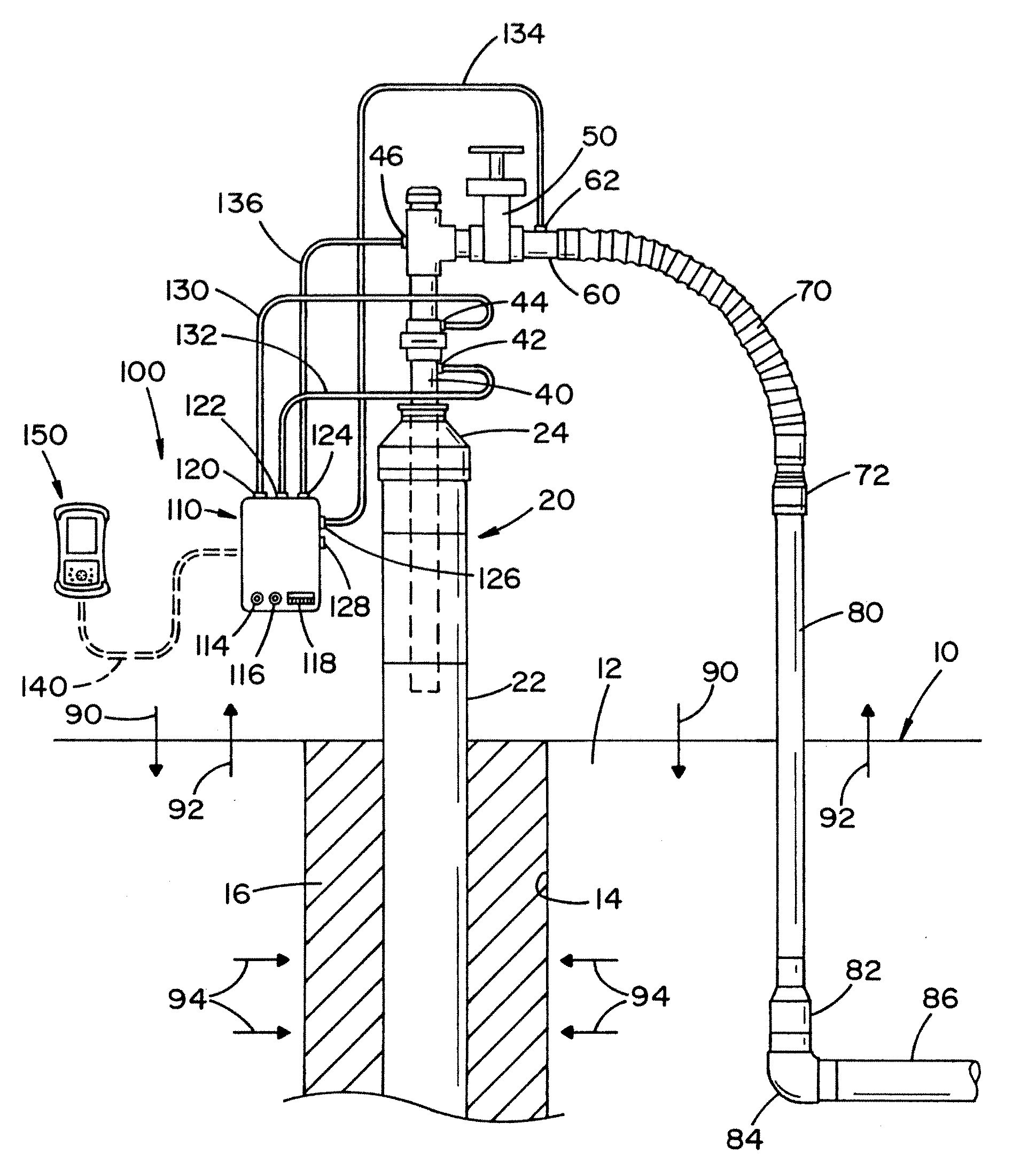
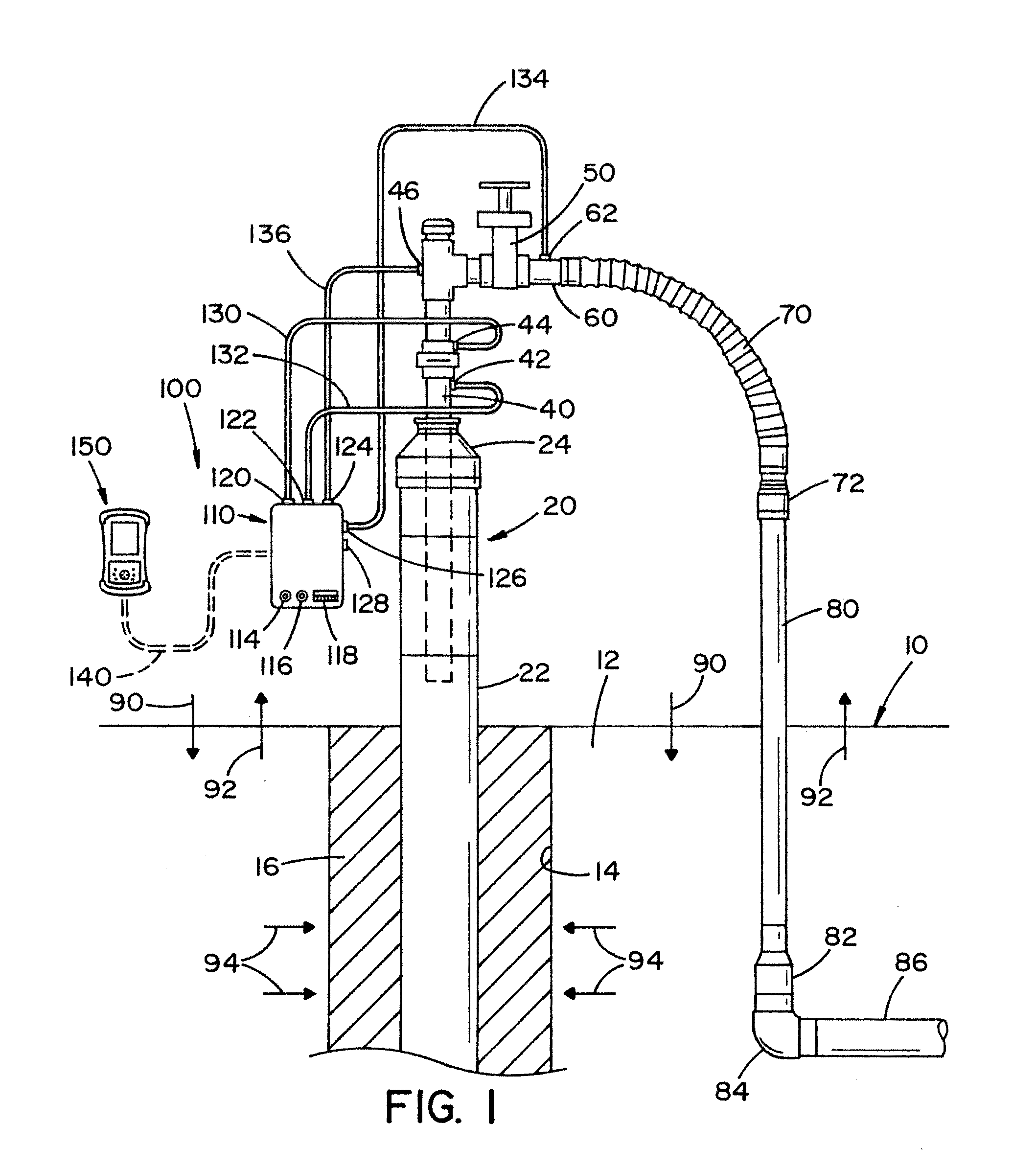
Methods for characterizing subsurface volatile contaminants using in-situ sensors
ActiveUS7003405B1Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConcentration ResponseTriangulation
An inverse analysis method for characterizing diffusion of vapor from an underground source of volatile contaminant using data taken by an in-situ sensor. The method uses one-dimensional solutions to the diffusion equation in Cartesian, cylindrical, or spherical coordinates for isotropic and homogenous media. If the effective vapor diffusion coefficient is known, then the distance from the source to the in-situ sensor can be estimated by comparing the shape of the predicted time-dependent vapor concentration response curve to the measured response curve. Alternatively, if the source distance is known, then the effective vapor diffusion coefficient can be estimated using the same inverse analysis method. A triangulation technique can be used with multiple sensors to locate the source in two or three dimensions. The in-situ sensor can contain one or more chemiresistor elements housed in a waterproof enclosure with a gas permeable membrane.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
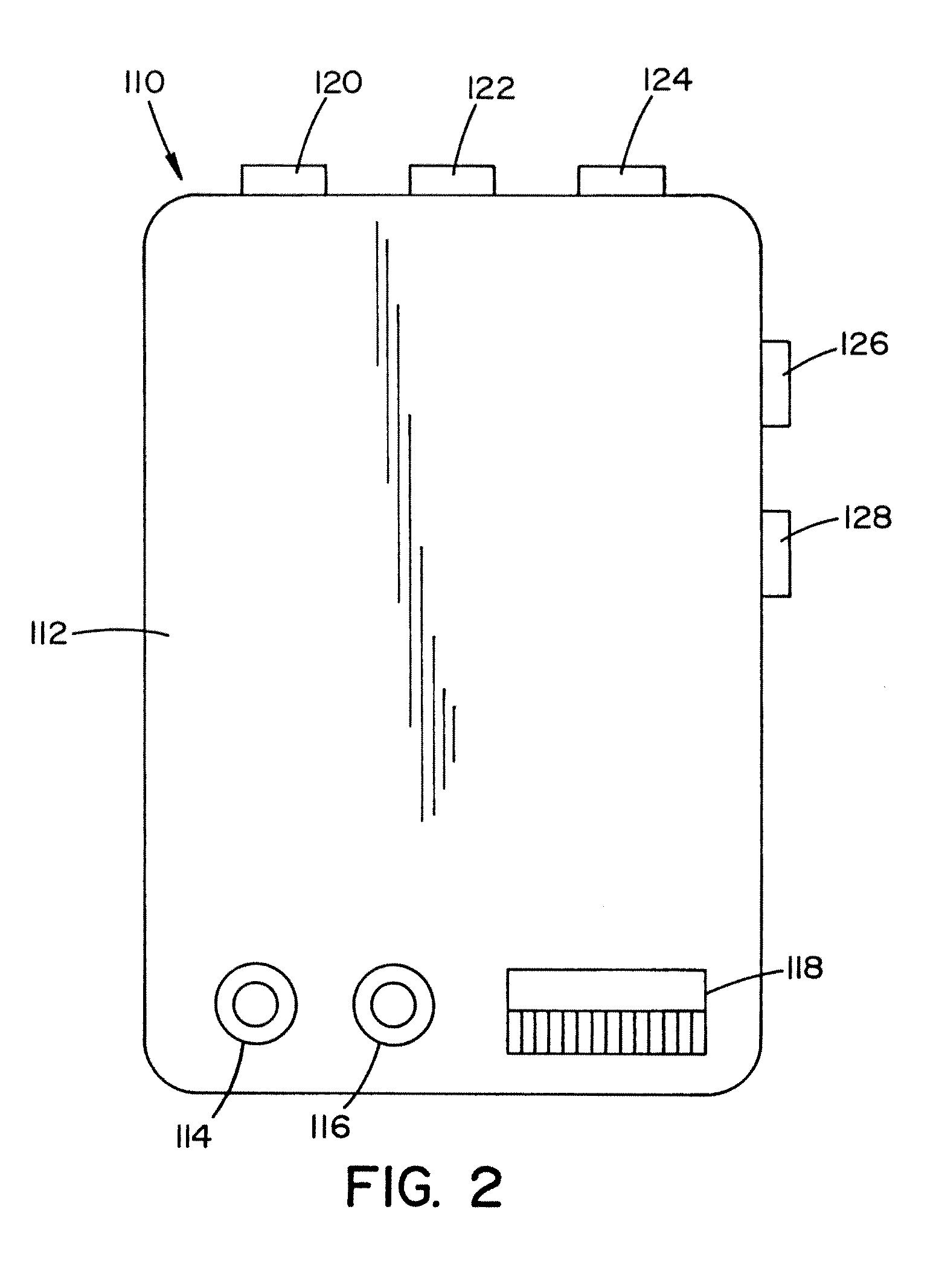
Portable gas monitor
InactiveUS20110231099A1Easy to identifyEasily obtain informationElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsEngineeringControl unit
A portable monitor used to measure landfill gas and landfill well parameters. The portable monitor includes a control unit and a measuring unit that can communicate wirelessly with one another. The control unit and / or measuring unit can include a heating arrangement to increase the temperature of one or more components in the control unit and / or measuring unit in cold environments.
Owner:ELKINS EARTHWORKS
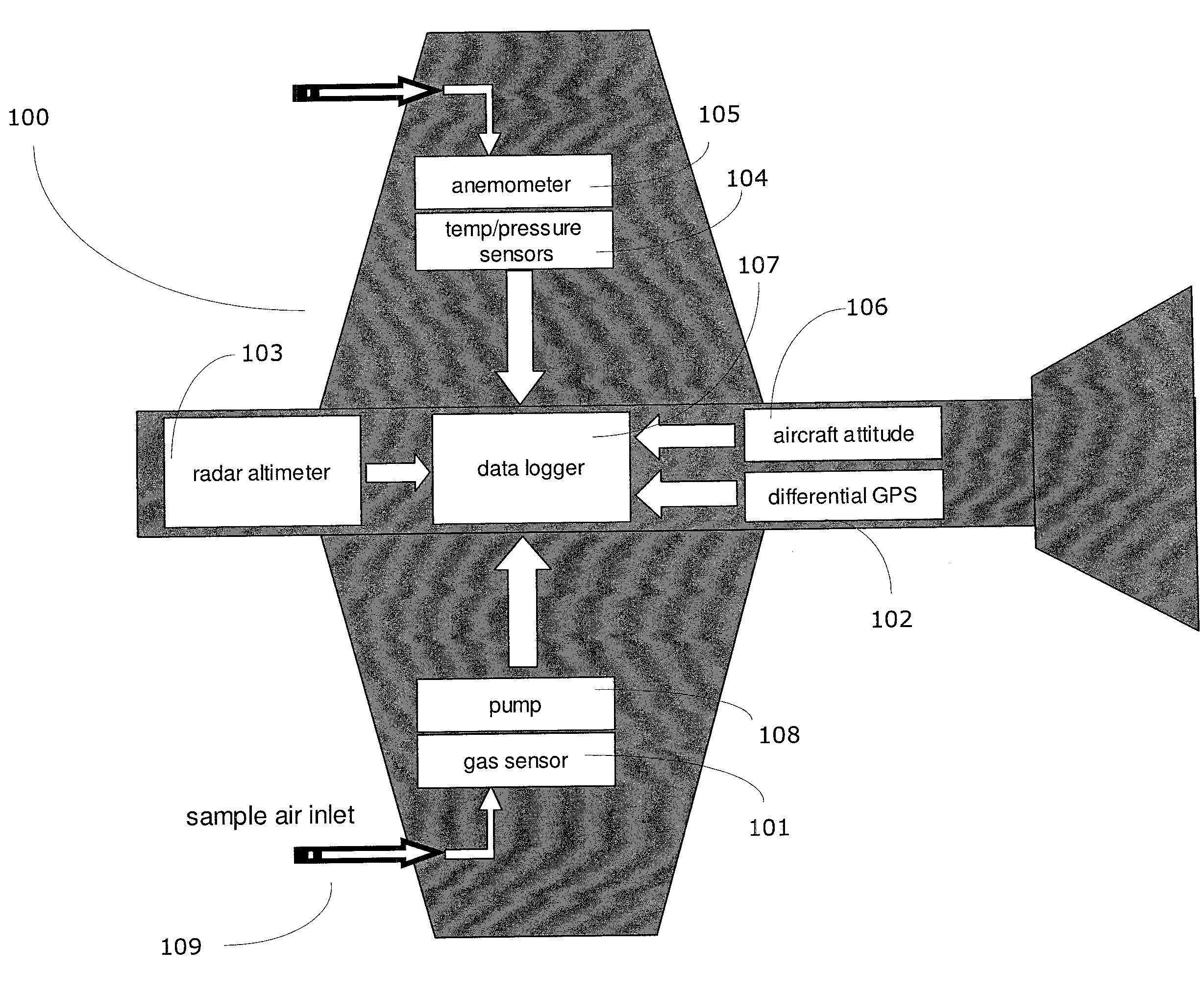
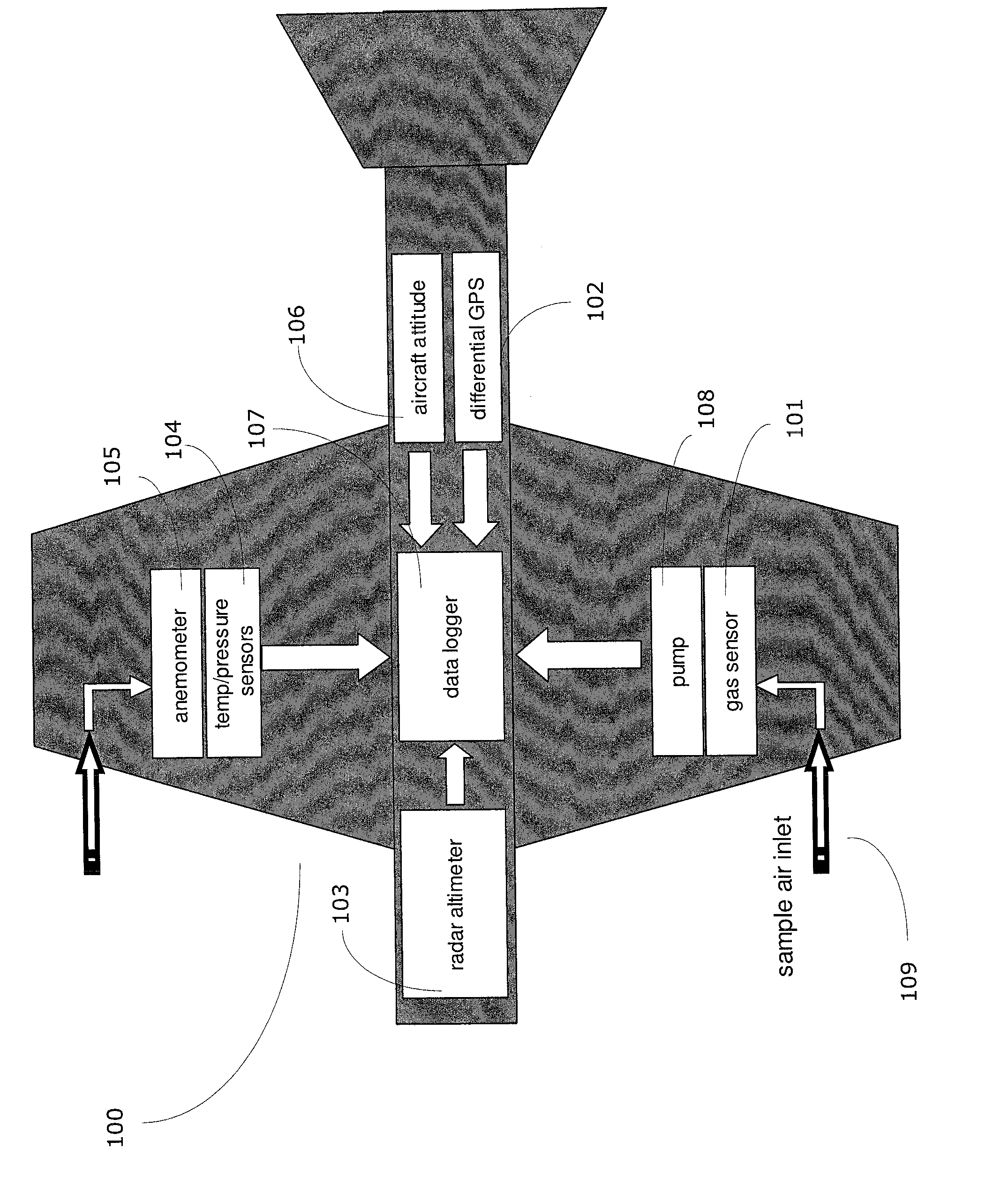
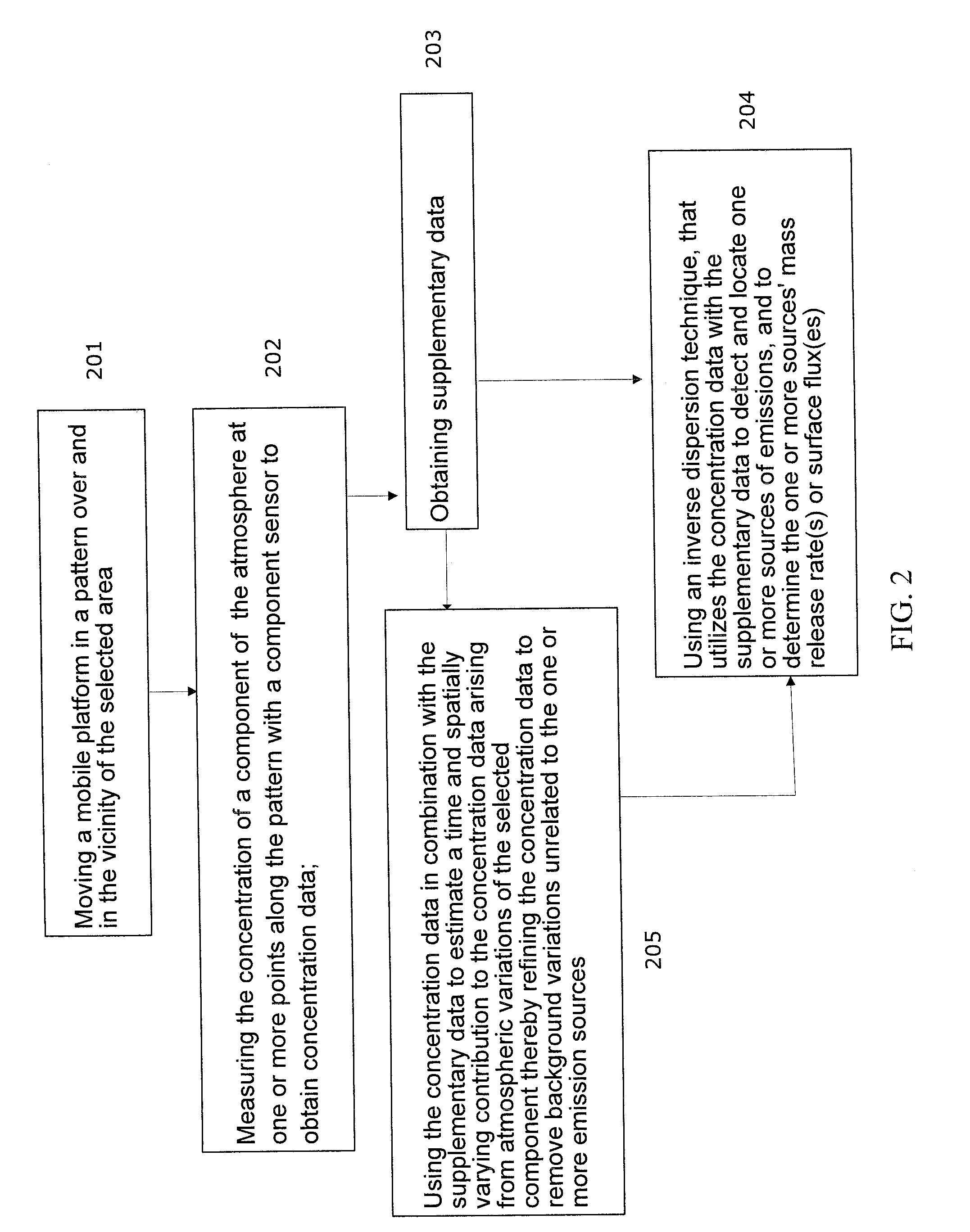
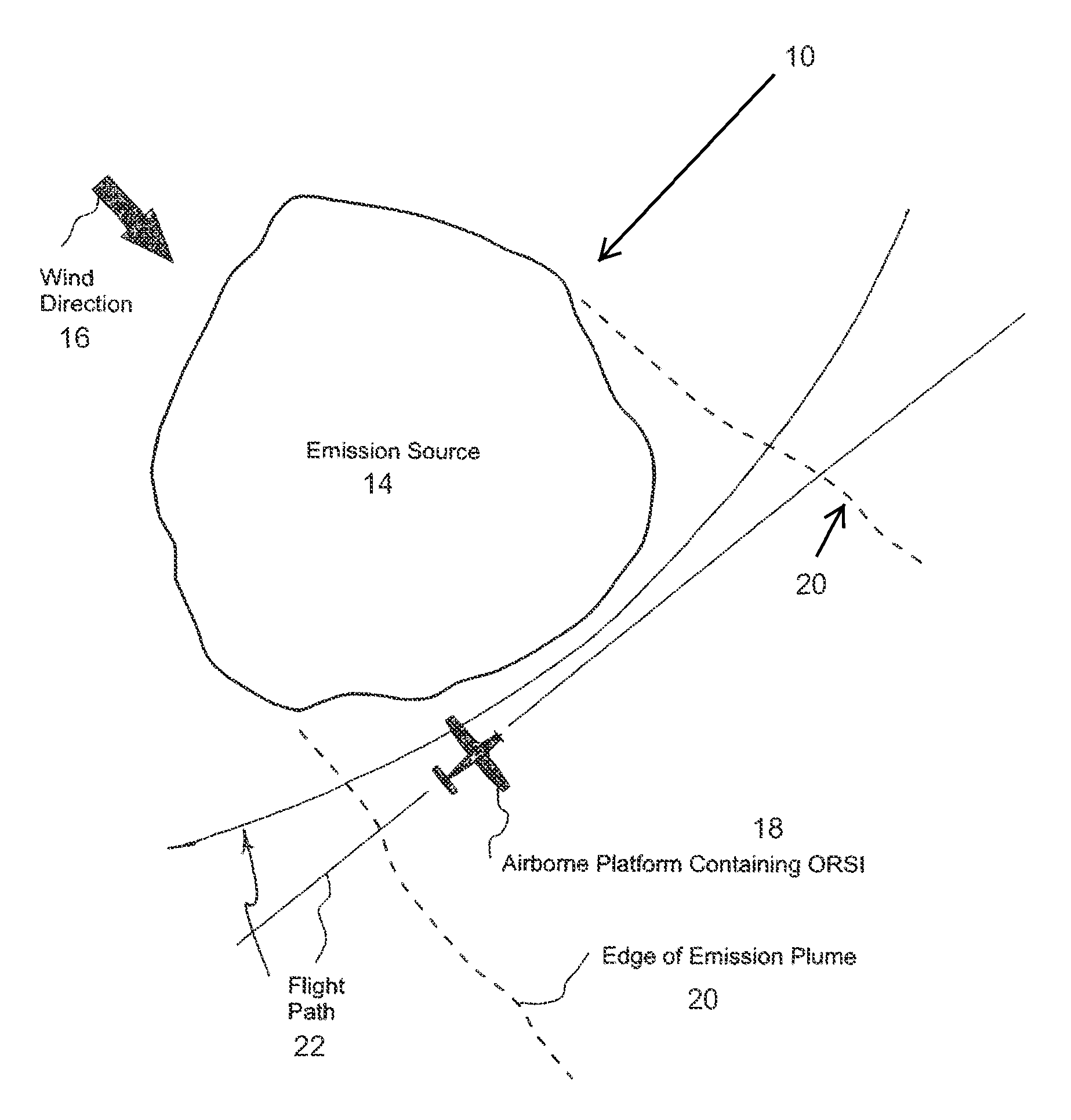
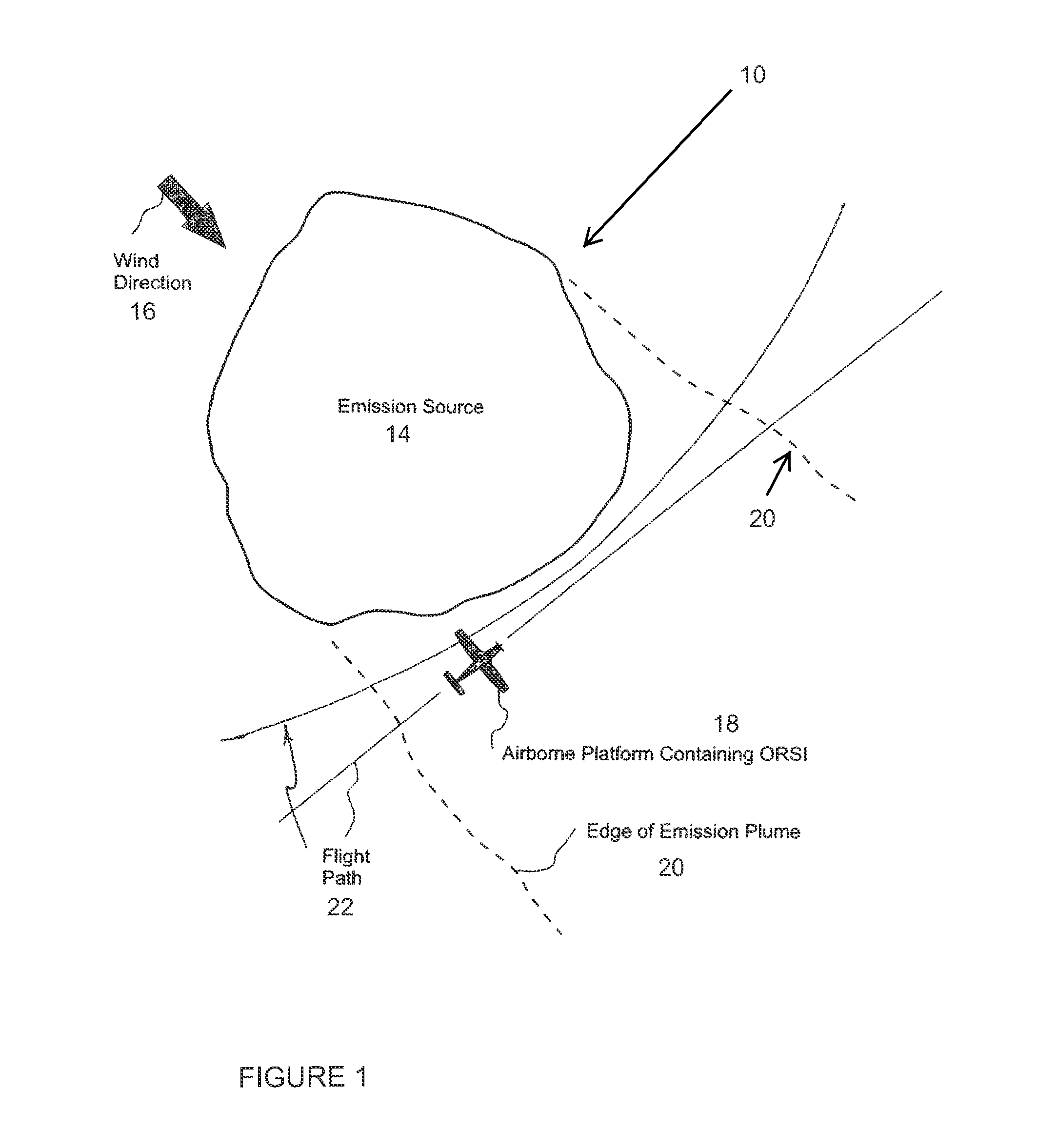
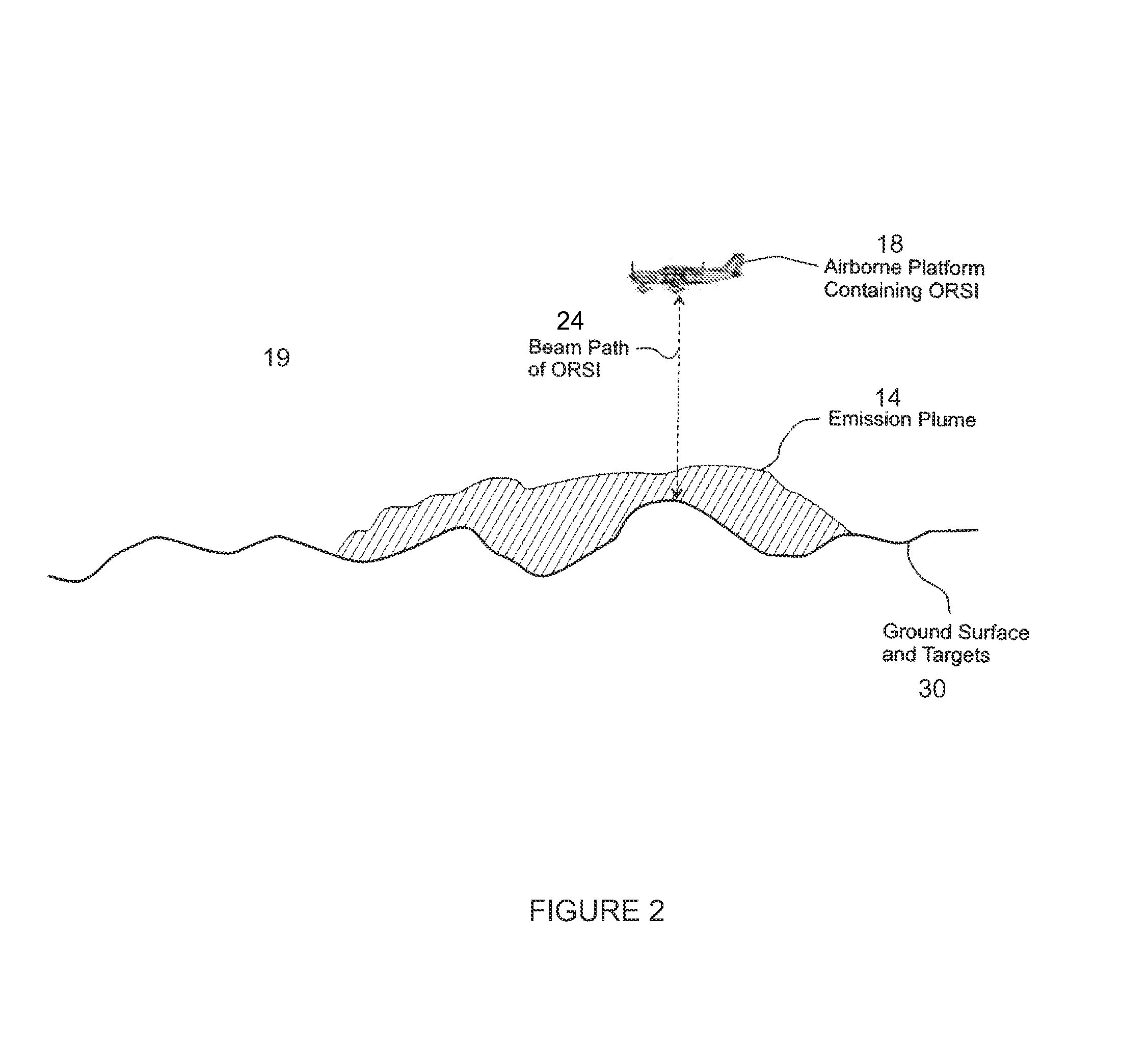
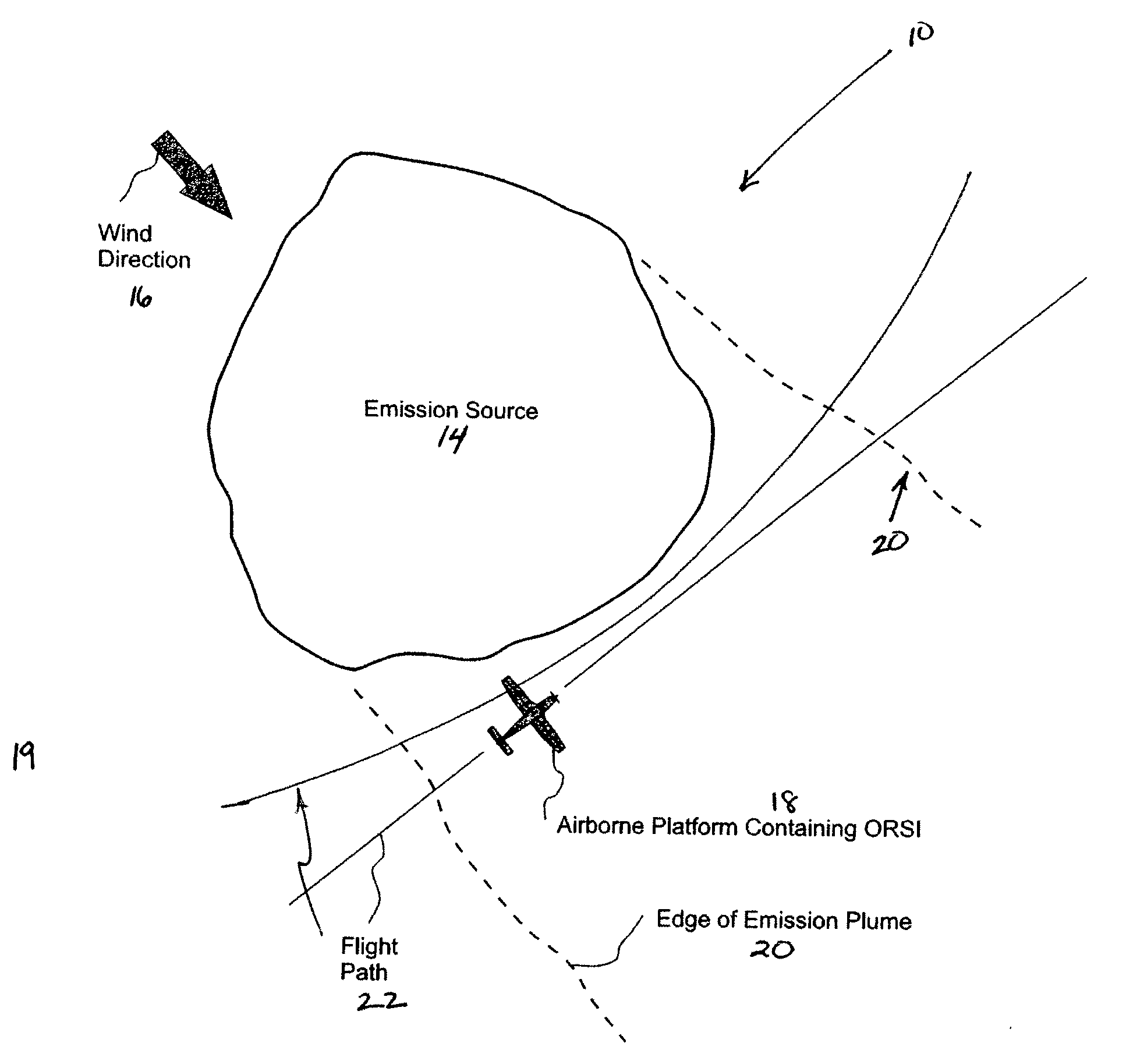
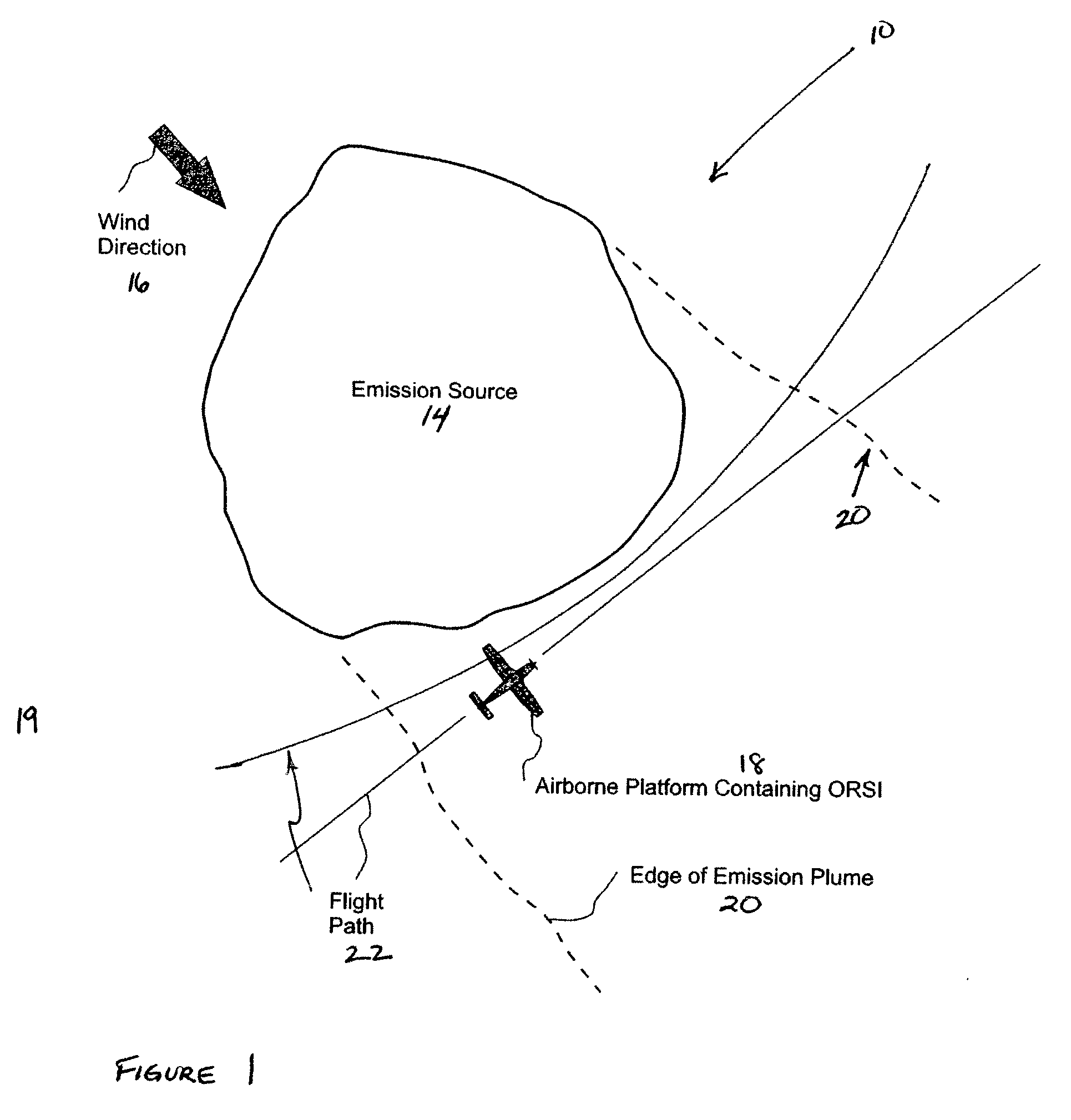
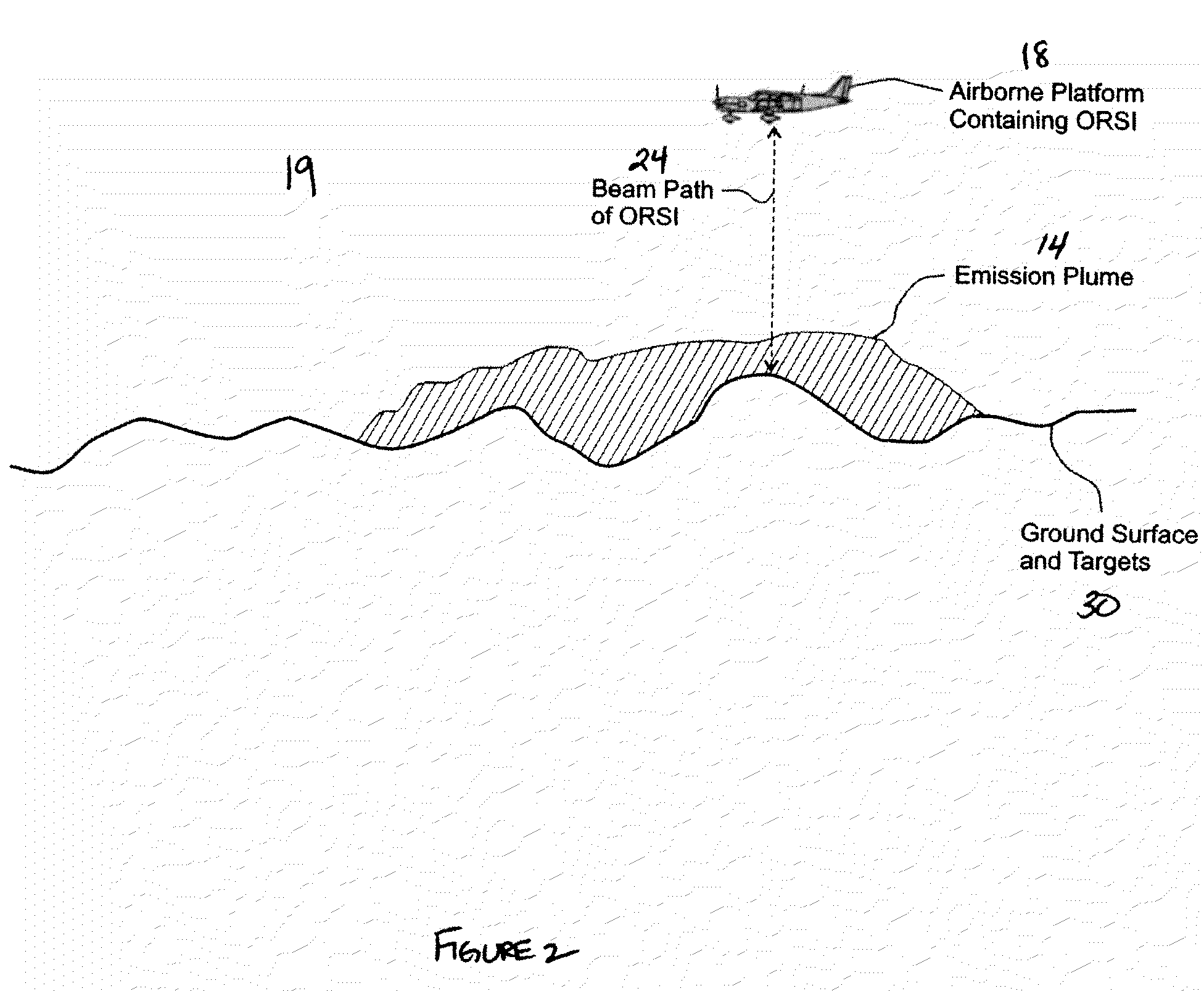
Method and system for screening an area of the atmosphere for sources of emissions
InactiveUS20110213554A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingProspecting/detection of underground/near-surface gasesEngineeringSupplementary data
A method for remotely screening a selected area of the atmosphere for the presence of emissions into the atmosphere comprises moving a mobile platform, such as an aircraft, which carries an atmospheric component sensor in a pattern over and in the vicinity of the selected area, measuring the concentration of a component of the atmosphere at one or more points along the pattern with the atmospheric component sensor to obtain concentration data, obtaining supplementary data, and using an inverse dispersion technique, that utilizes the concentration data with the supplementary data to detect and locate one or more sources of emissions, and to determine the emitted mass release rates and / or surface fluxes.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
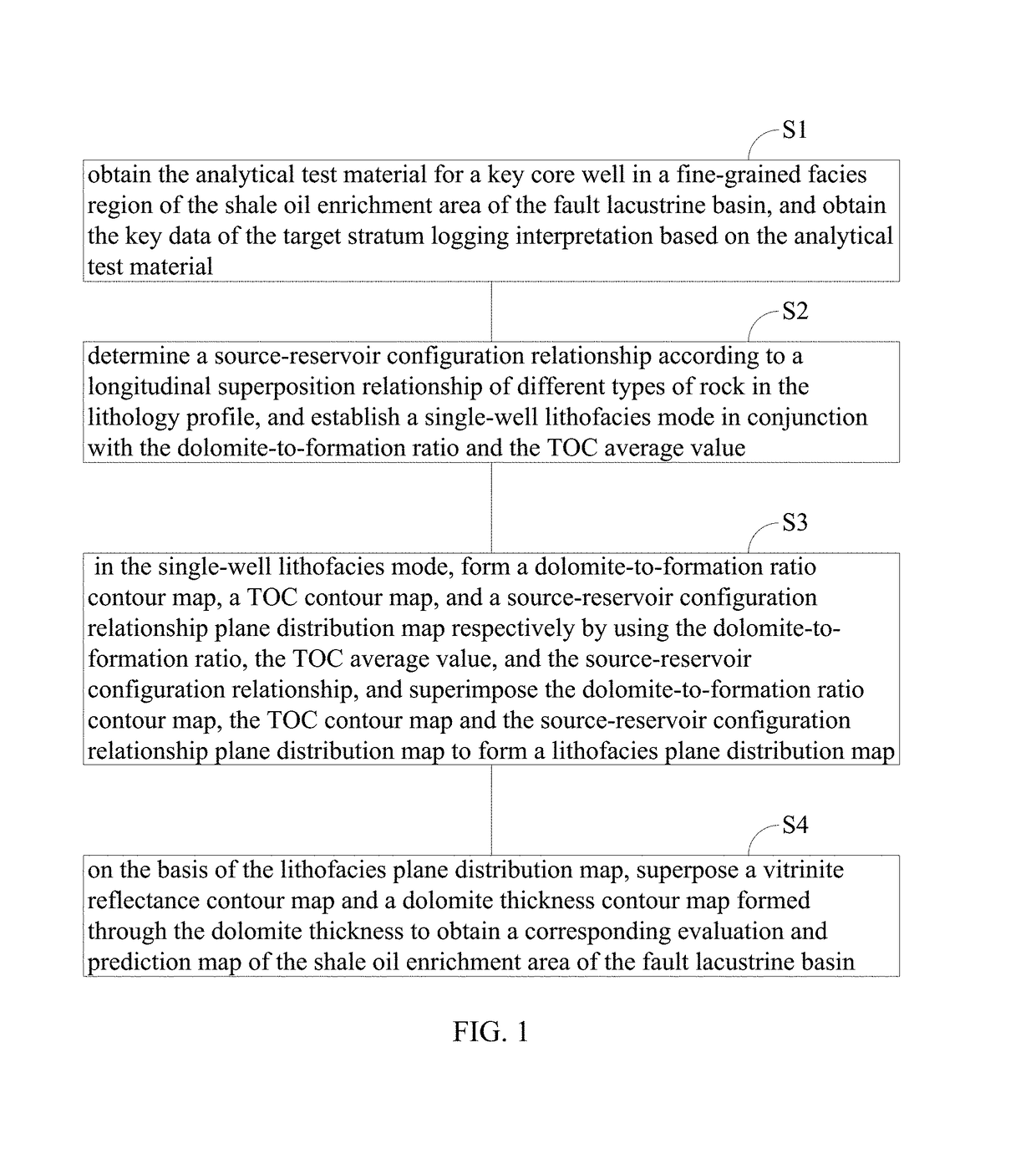
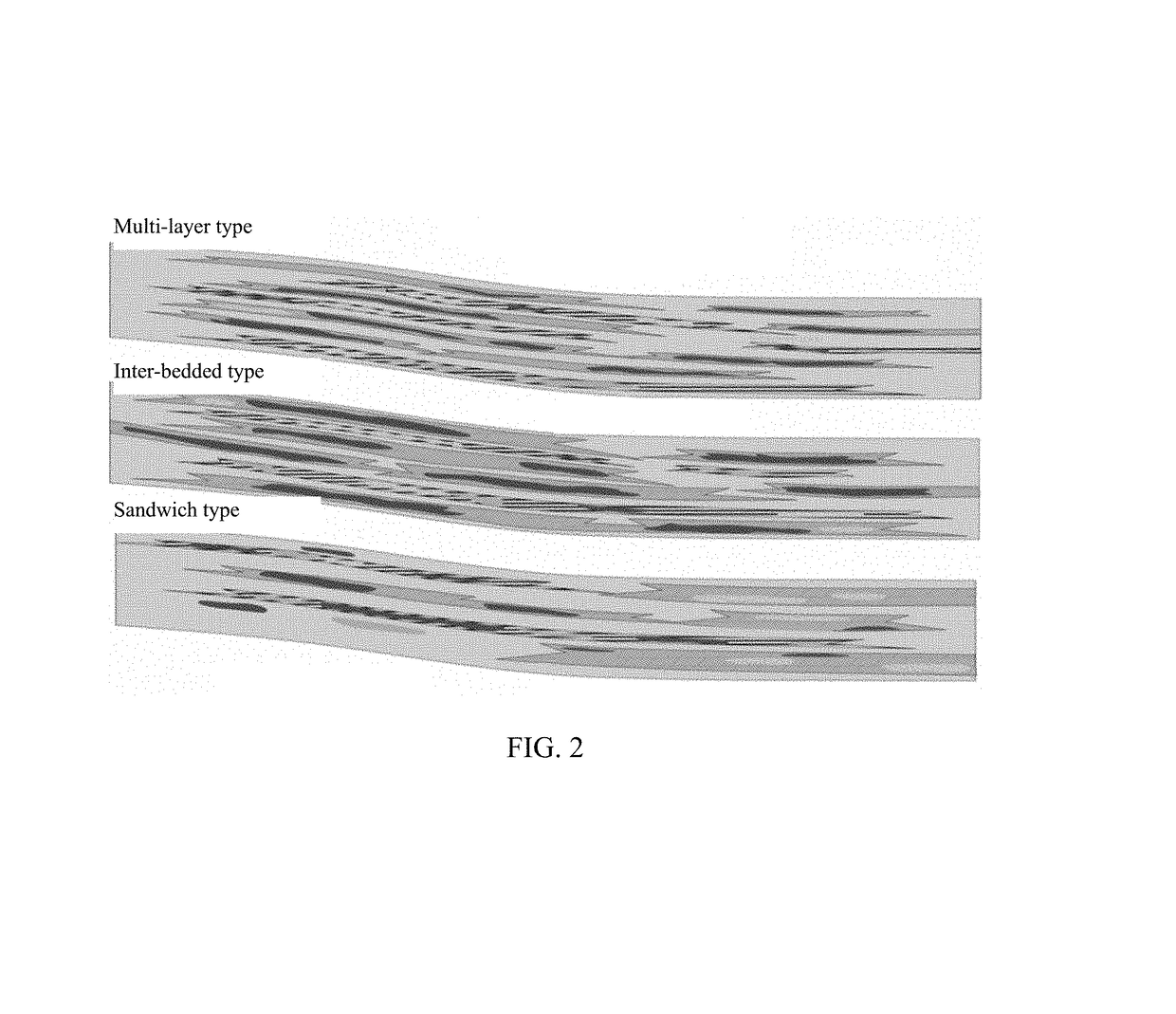
Method and device for evaluating and predicting a shale oil enrichment areas of fault lacustrine basins
ActiveUS10190998B1Reduce economic costsEasy to operateMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationEarth material testingLithologyDolomite
A method is disclosed for evaluating and predicting a shale oil enrichment area of a fault lacustrine basin, comprising: obtaining materials and key data; determining a source-reservoir configuration relationship according to a longitudinal superposition relationship of different types of rock in a lithology profile and establishing a single-well lithofacies model; in the single-well lithofacies model, using a dolomite-to-formation ratio and a TOC average value to form a dolomite-to-formation ratio contour map and a TOC contour map, and superposing the dolomite-to-formation ratio contour map, the TOC contour map and a source-reservoir configuration relationship plane distribution map to form a lithofacies plane distribution map; on the basis of the lithofacies plane distribution map, superposing a vitrinite reflectance contour map and a dolomite thickness contour map to obtain a corresponding evaluation and prediction map of the shale oil enrichment area of the fault lacustrine basin.
Owner:RES INST OF GASOLINEEUM EXPLORATION & DEV DAGANG OIL FIELD OF CNPC
Method for testing soil contamination, and probe therefor
The method is used for locally testing underground soil contamination by determining the generation rate of a first contaminant fluid in porous soil. The method includes the steps of making a hole of known dimensions in the soil, with the hole defining a first and a second spaced-apart portions; covering the hole, so as to define a closed volume in the hole; constantly injecting a second fluid in the hole at a constant given flow rate at said first portion of the hole, while simultaneously collecting fluid samples at the above-mentioned constant given flow rate at the second portion of the hole; measuring the concentrations of the first contaminant fluid from the fluid samples collected at known time intervals; and computing the generation rate of the first contaminant fluid, from the known volume of the hole and from the concentrations previously measured and originating from samples collected at the known time intervals. The probe used to carry out the above-described method has a rigid hollow body in which a semi-rigid tube is axially slidable. The probe can be driven through the ground and then partially retracted, to form a hole of known dimensions. The flexible tube is axially displaced so that its lower bored extremity is positioned near the bottom end of the hole, while the hollow rigid body of the probe has an annular opening about the tube at the upper end of the hole. The second fluid can then be circulated in the hole between the lower end of the tube and the annular opening of the probe rigid main body.
Owner:TARTRE ANDRE
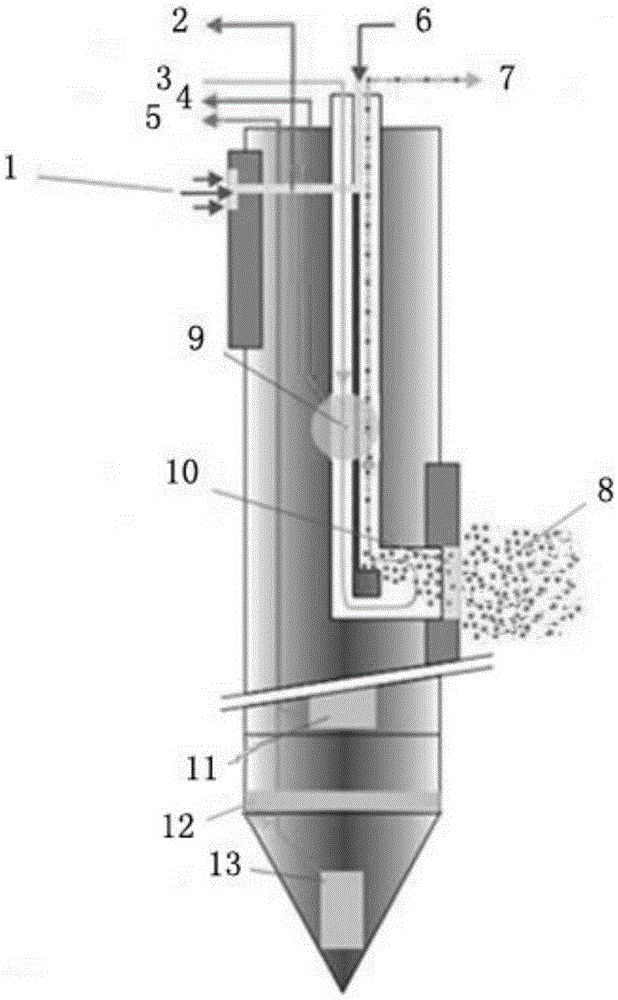
Seabed-based multipoint in-situ long-term observing system
ActiveCN106841311ARealize multi-point precise positioning functionSimplicity guaranteedMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSeismologyOcean bottomHydrate decomposition
The invention relates to a seabed-based multipoint in-situ long-term observing system which comprises a platform frame, a floating body material, an underwater sound communication apparatus, a beacon receiver, a monitoring cabin, a control cabin, a release control cabin, a central rotary table, a balancing weight and a microelectrode probing system. A main body of the platform frame is of a cylindrical shape and is divided into four layers from top to bottom; the floating body material, the underwater sound communication apparatus and the beacon receiver are mounted in the first layer, the monitoring cabin, the control cabin and the release control cabin are mounted in the second layer, the central rotary table is mounted in the third layer, and the balancing weight is mounted in the fourth layer. The seabed-based multipoint in-situ long-term observing system provided by the invention effectively realizes a multipoint precise positioning function so as to acquire data of a plurality of probing points in a probing region as required. Finally, spatial distribution information of an active diffusion field can be analyzed to provide an important data support for marine environment effect estimation of oil spill and aquo-complex decomposing process, thereby providing support and service for key projects such as submarine oil extraction and pilot production of natural gas hydrates.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF MARINE GEOLOGY
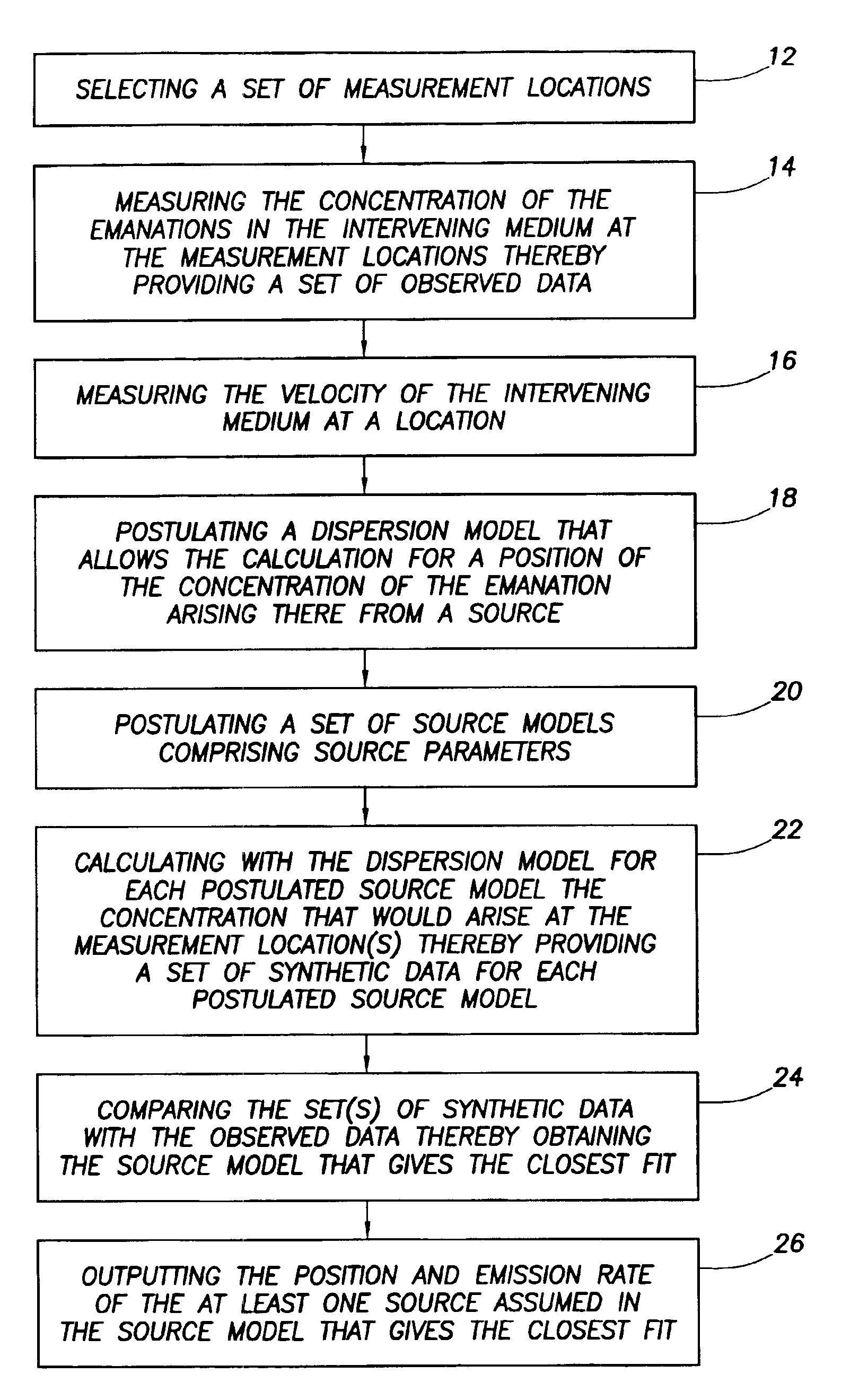
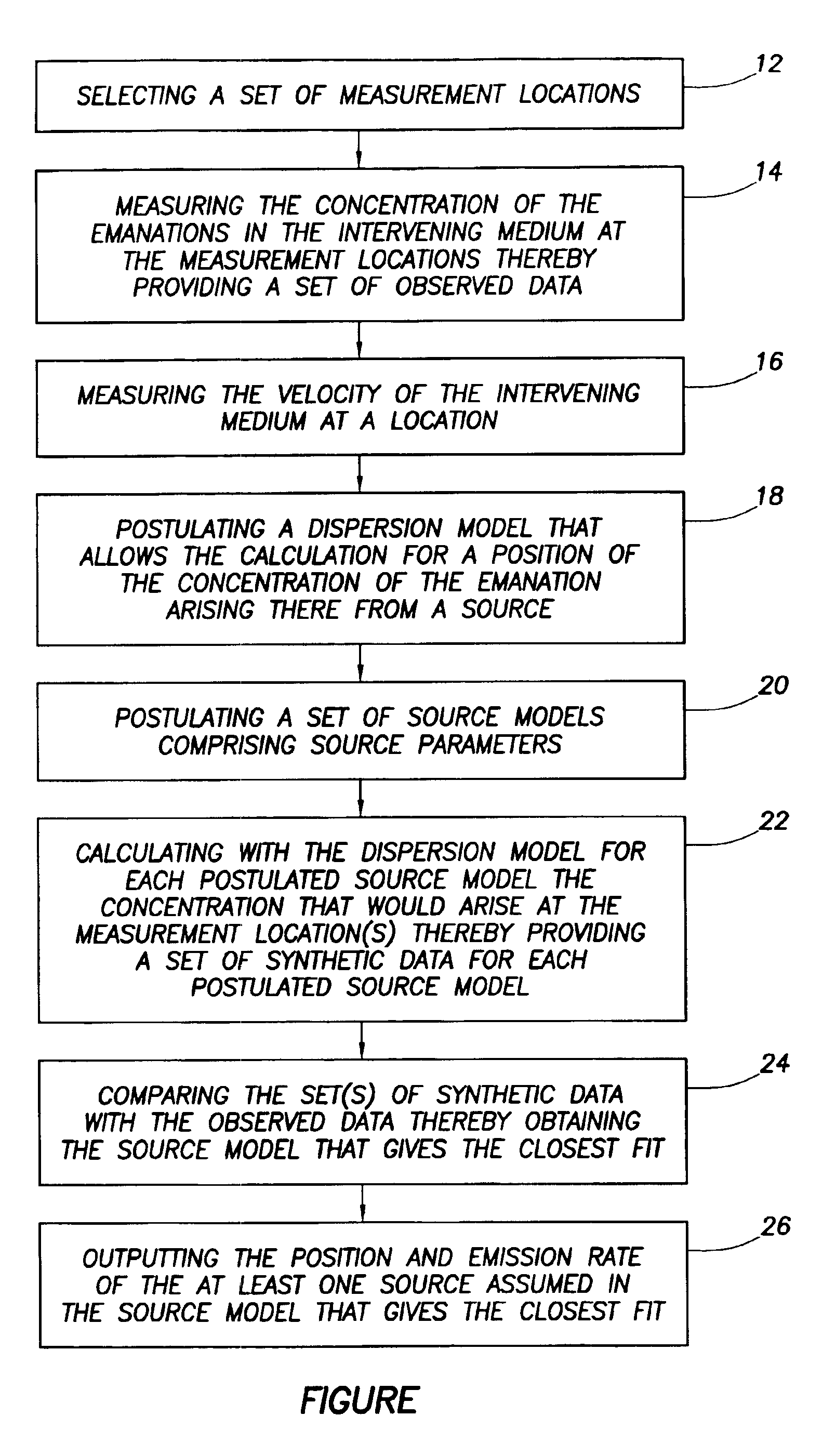
Locating a source of emanations
InactiveUS6895335B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingProspecting/detection of underground/near-surface gasesEmissivitySynthetic data
A method of determining the position and emission rate of at least one source of emanations into an intervening medium, which method comprises measuring the concentration of the emanations in the intervening medium at selected measurement locations to obtain observed data, and measuring the velocity of the intervening medium; postulating a dispersion model; postulating a source model containing source parameters, such as the position(s) of assumed source(s) and assumed emission rate(s); calculating with the dispersion model for a postulated source model the concentration that would arise at the measurement location(s) to obtain synthetic data for the postulated source model; comparing the synthetic data with the observed data to obtain the source model that gives the closest fit; and outputting the position and emission rate of the at least one source assumed in the source model that gives the closest fit.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Methods and systems for evaluation of hydrocarbon reservoirs and associated fluids using biological tags and real-time PCR
InactiveUS20100015612A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsSurveyReal-Time PCRsHydrocotyle bowlesioides
This invention relates in general to characterizing hydrocarbon reservoirs and / or determining flow properties of fluids associated with the reservoir-including fluids introduced into the reservoir to provide for hydrocarbon extraction-using biological tags and real-time polymerase chain reactions for tag detection. In embodiments of the present invention, one or more biological tags may be added to one or more liquids associated with the hydrocarbon reservoir and subsequently one or more liquid samples may be taken from locations associated with the hydrocarbon and the presence of the one or more biological tag may be qualitatively and / or quantitatively tested for in the samples using real-time PCR.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
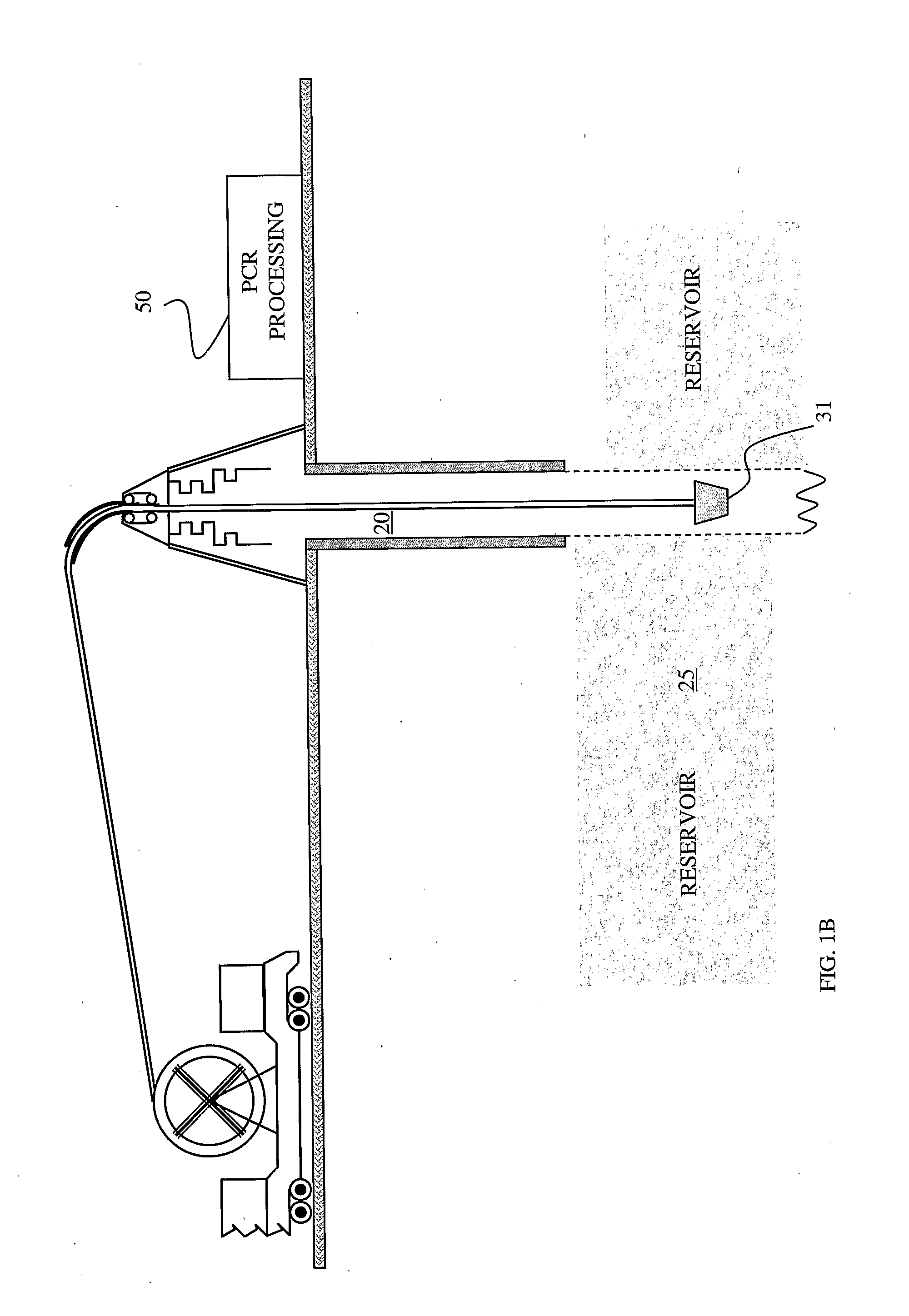
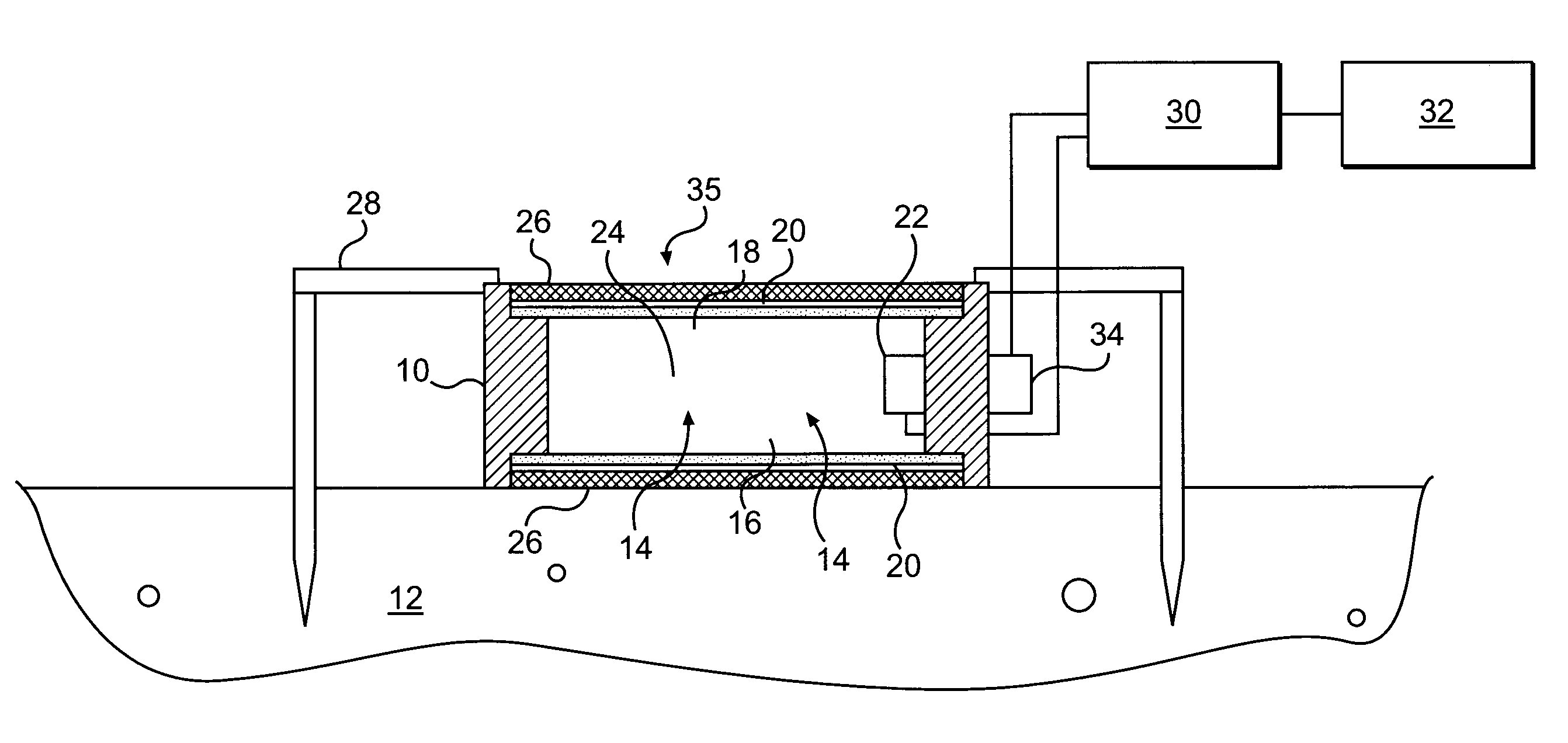
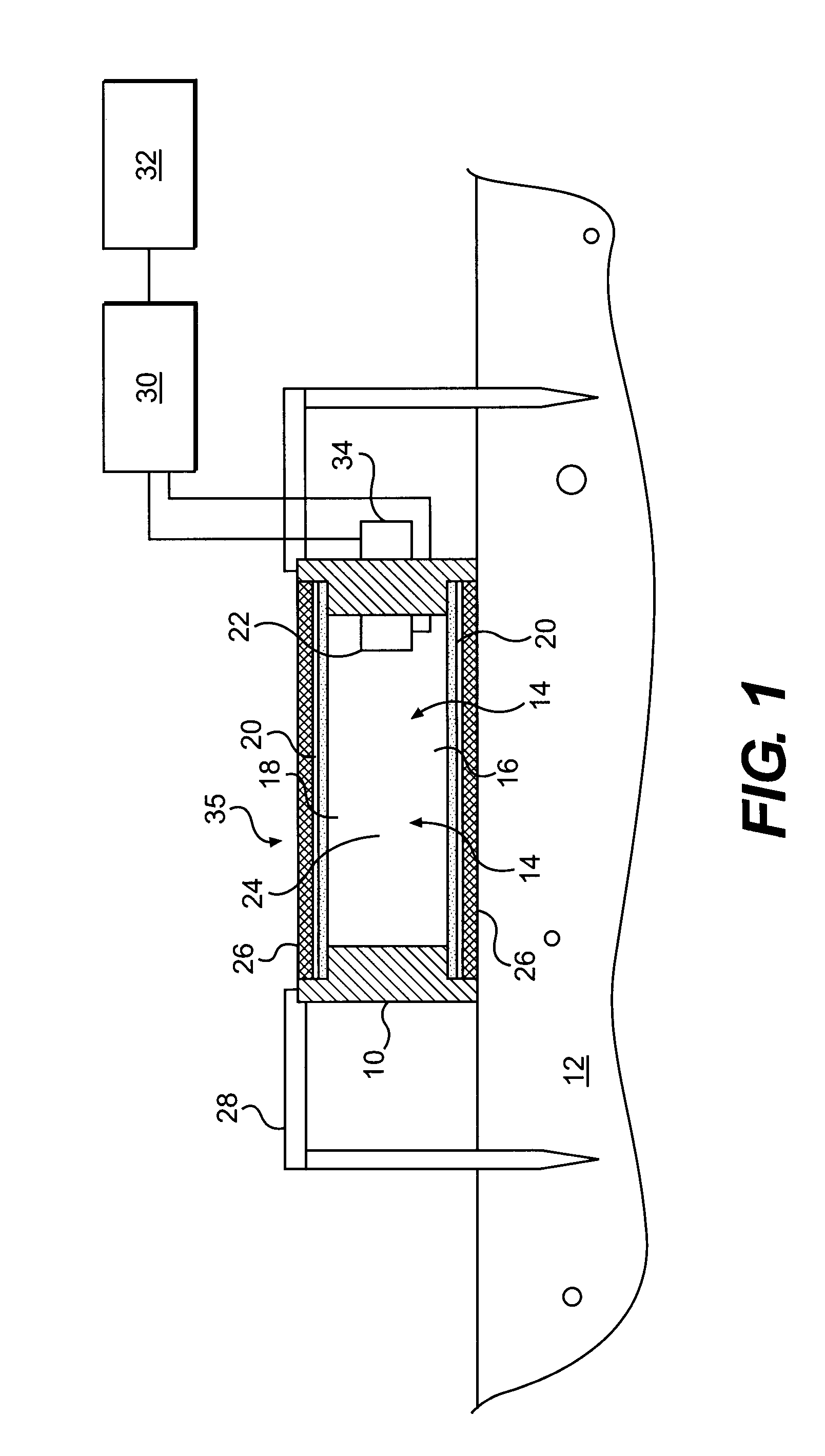
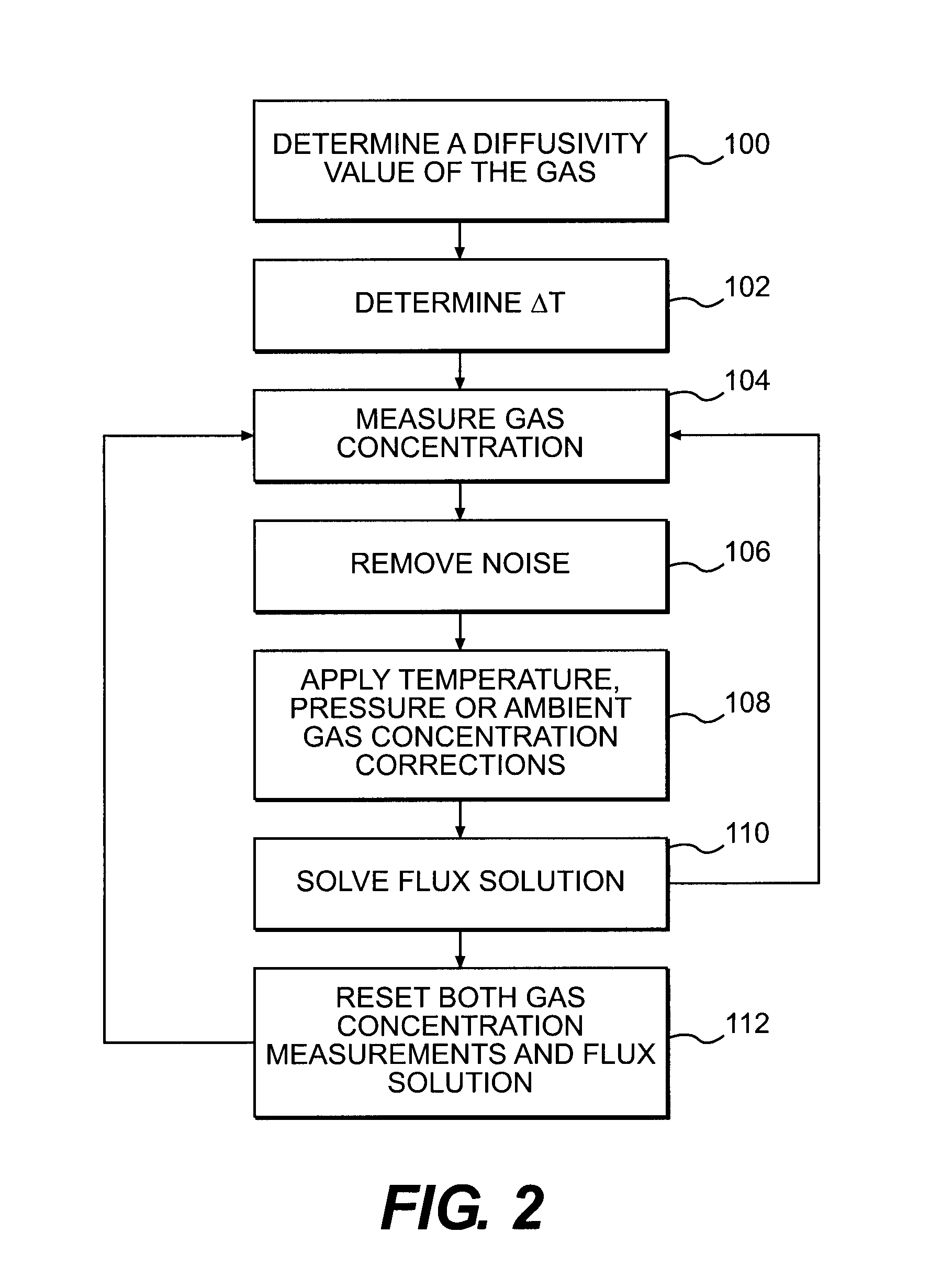
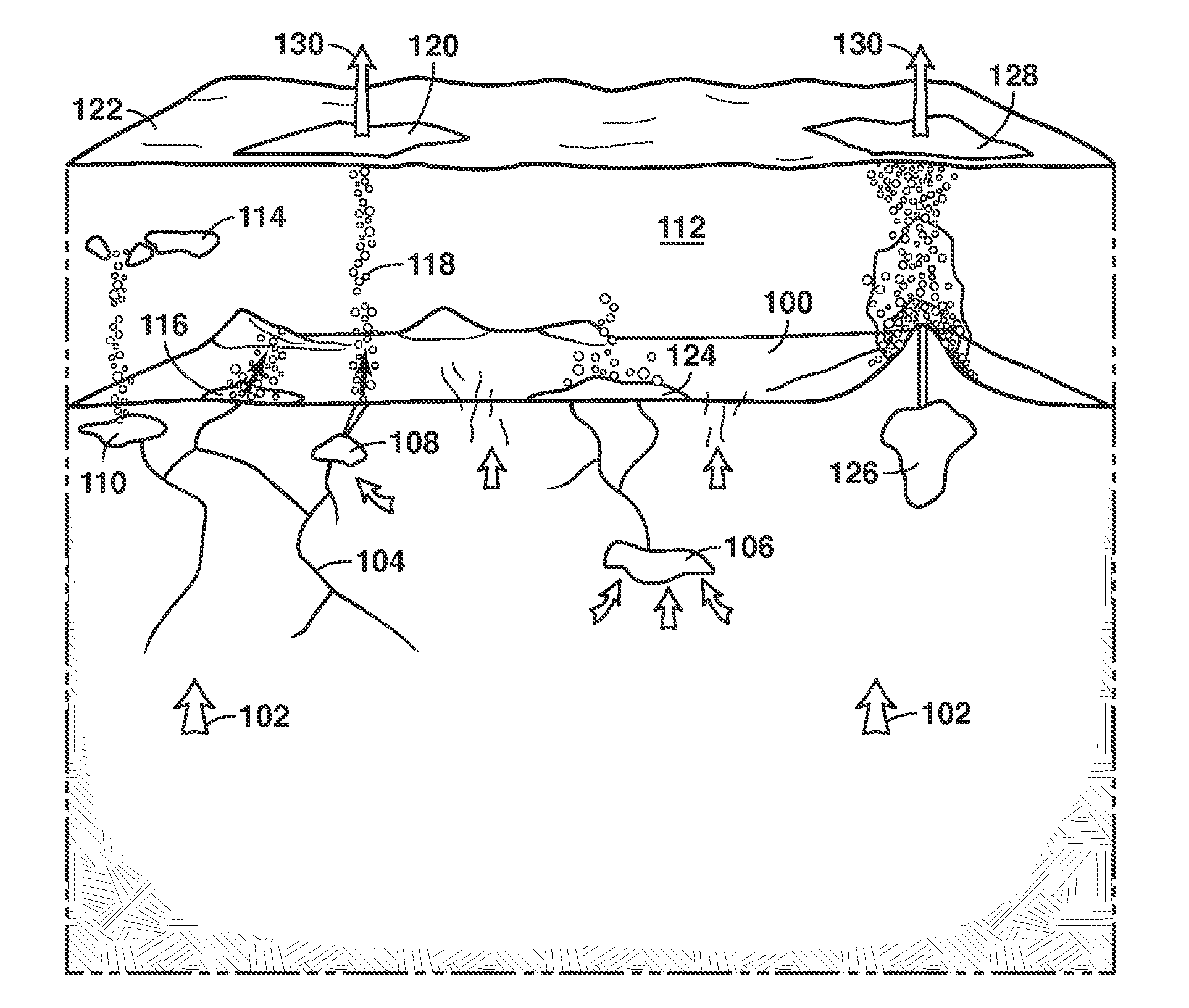
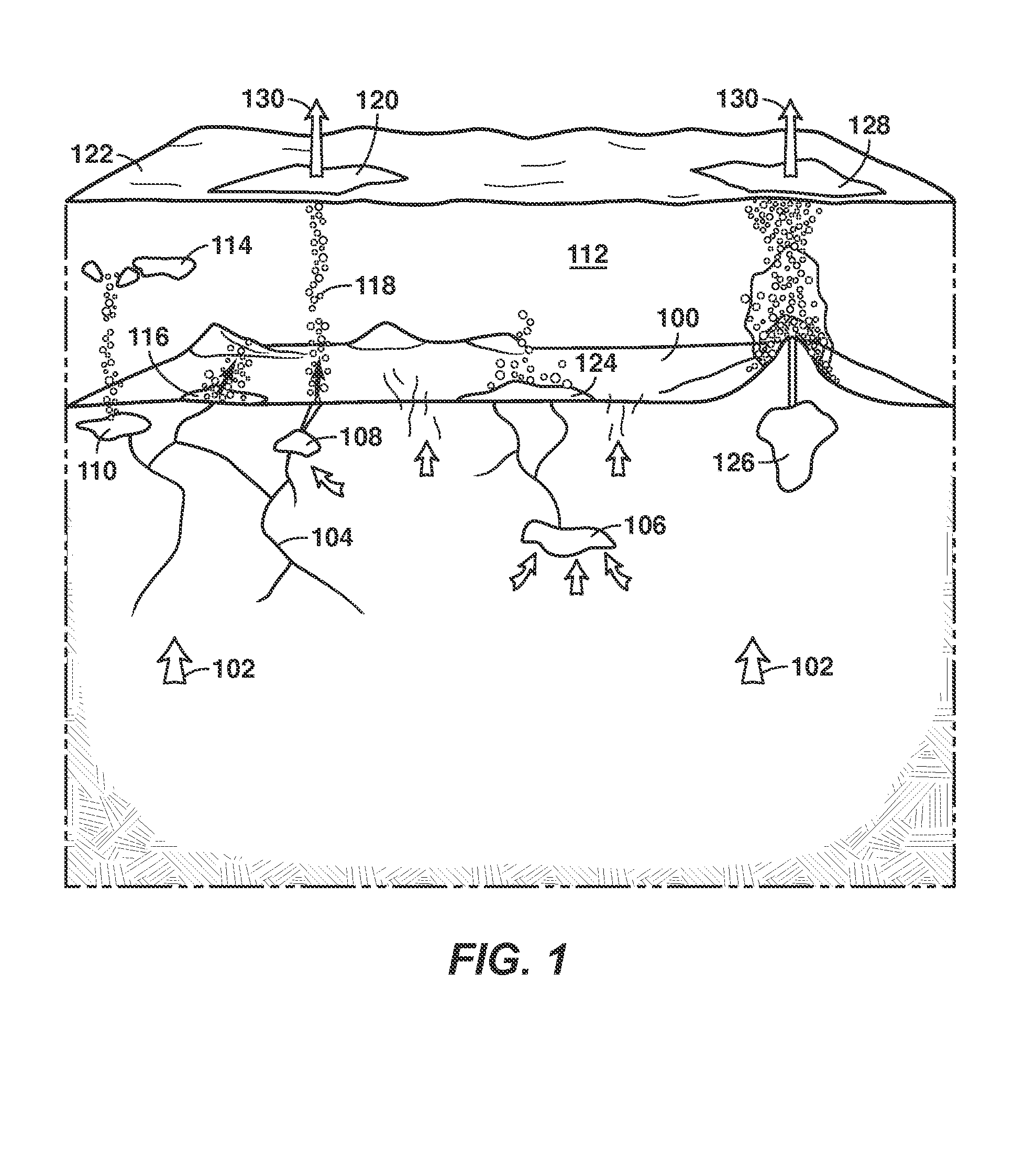
Method of measuring the flux of a soil gas
ActiveUS20120035850A1Easy to practiceEasy to deploySamplingProspecting/detection of underground/near-surface gasesSoil gasGas flux
A method for determining a flux of a gas contained in a medium through a boundary of the medium comprises 1) measuring at least twice with a probe a concentration C of the gas over a time interval Δt and 2) determining the flux of the gas using the following mathematical equation: (I) where F is the gas flux, D is the diffusivity value and ΔC is a variation in the gas concentration during the time interval Δt. The probe is placed proximate the boundary. The probe has a gas inlet, a cavity, a gas concentration sensor and a membrane. Each element is in fluid communication with each other so that the gas flows from the gas inlet through the membrane and contacts the gas concentration sensor.F=(D∂C(z,t)∂z)z=0=DΔCπΔt(I)
Owner:EOSENSE INC
Fugitive emission flux measurement
A method of obtaining a fugitive emission flux measurement of airborne matter is provided. The method involves measuring the airborne matter along one or more than one measurement surface that spans the fugitive emission using two or more than two measurement beam paths where each of the two or more than two measurement beam paths are parallel to each other, or substantially parallel to each other, and determining a mass per unit length measurement for the measurement surface, determining a representative wind velocity at or near the one or more than one measurement surface, and calculating the fugitive emission flux of the airborne matter in mass per unit time using the mass per unit length determination and representative wind velocity.
Owner:GOLDER ASSOCIATES
Fugitive emission flux measurement
A method of obtaining a fugitive emission flux measurement of airborne matter is provided. The method involves measuring the airborne matter along one or more than one measurement surface that spans the fugitive emission using two or more than two measurement beam paths where each of the two or more than two measurement beam paths are parallel to each other, or substantially parallel to each other, and determining a mass per unit length measurement for the measurement surface, determining a representative wind velocity at or near the one or more than one measurement surface, and calculating the fugitive emission flux of the airborne matter in mass per unit time using the mass per unit length determination and representative wind velocity.
Owner:GOLDER ASSOCIATES
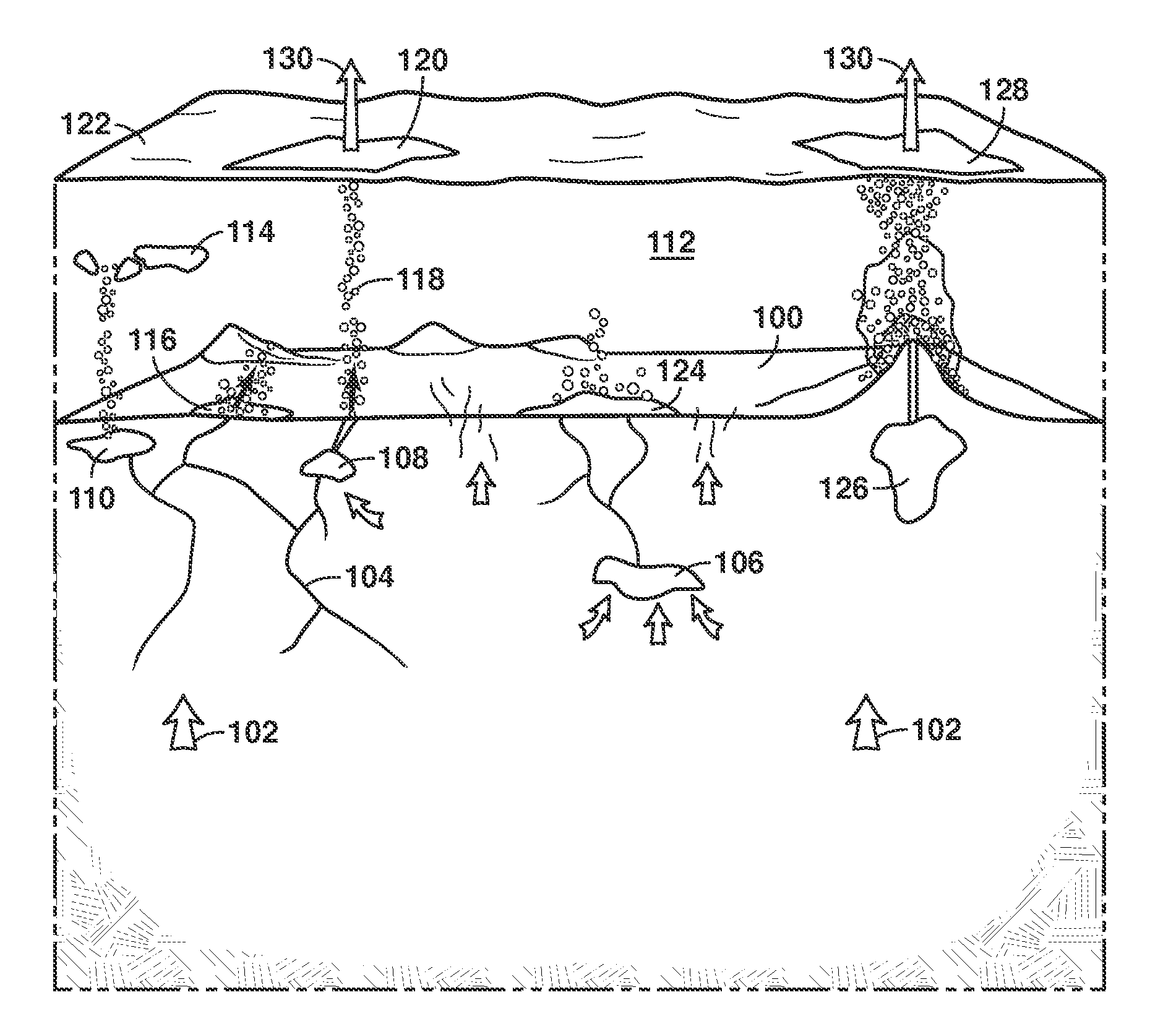
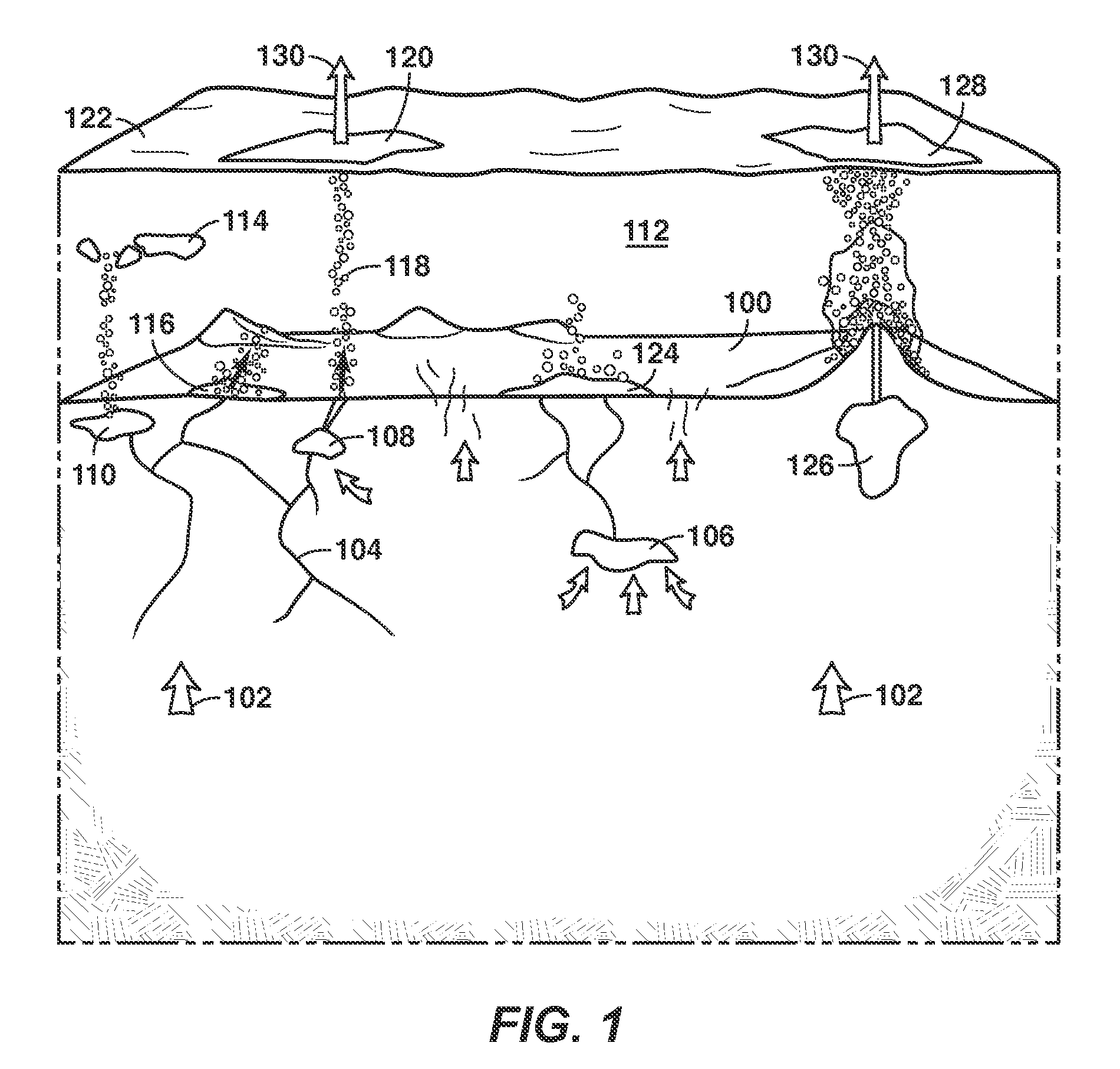
Exploration method and system for detection of hydrocarbons with an underwater vehicle
ActiveUS20140284465A1SamplingMaterial analysis using acoustic emission techniquesUltravioletHydrogen compounds
Owner:KNIGHT BRENT R
Exploration method and system for detection of hydrocarbons with an underwater vehicle
ActiveUS9146225B2SamplingMaterial analysis using acoustic emission techniquesHydrocotyle bowlesioidesUltraviolet
A method for detecting hydrocarbons with an underwater vehicle equipped with one or more measurement components is described. The method includes navigating the UV within the body of water; monitoring the body of water with measurement components associated with the UV to collect measurement data. The collected data from the UV is used to determine whether hydrocarbons are present and at the location.
Owner:KNIGHT BRENT R
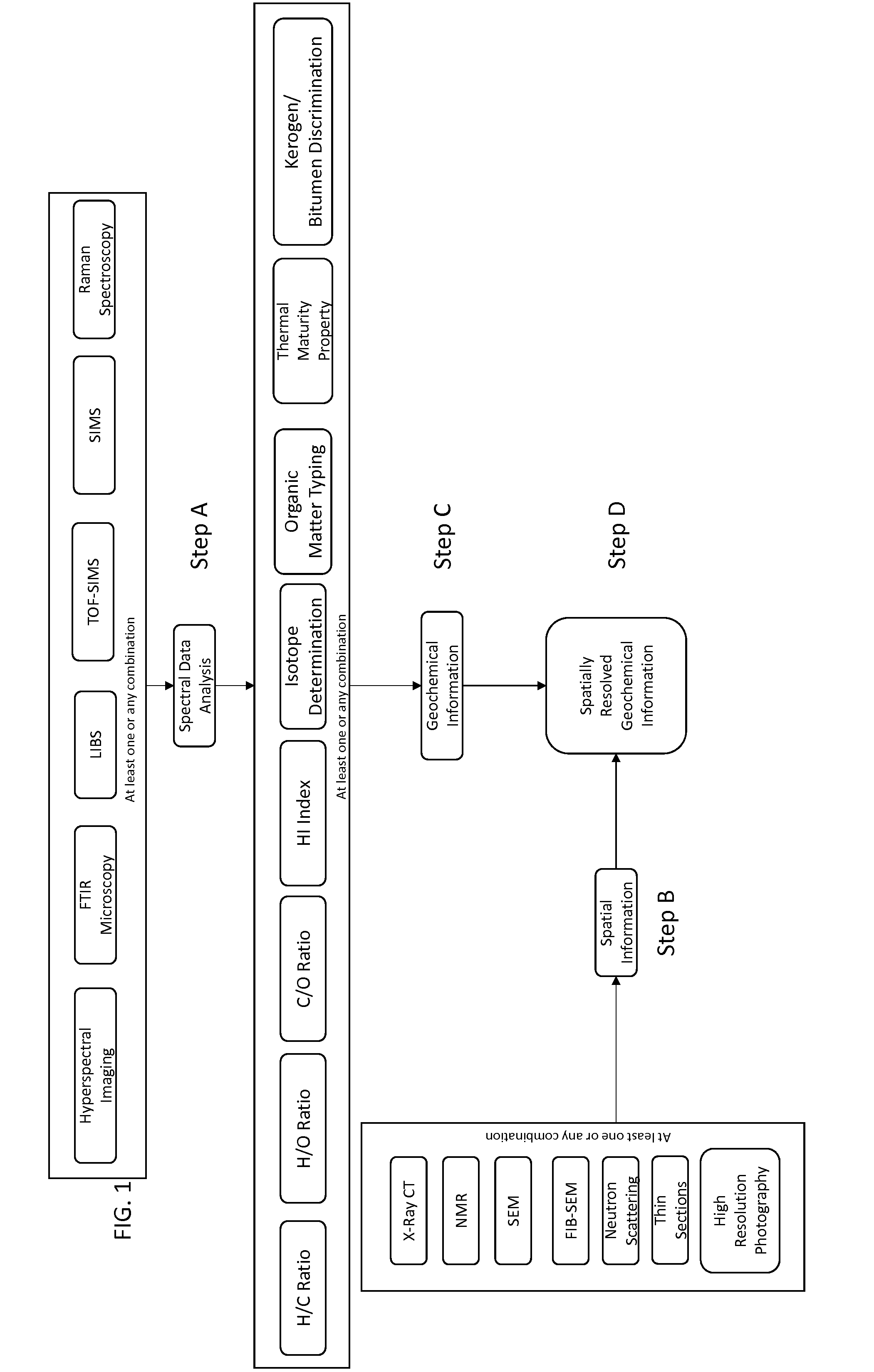
Method And System For Spatially Resolved Geochemical Characterisation
InactiveUS20150323516A1Chemical analysis using combustionMolecular entity identificationSpatially resolvedImage resolution
A method which allows for determining geochemistry with spatial resolution of geological materials or other materials is provided. The method can provide a non-bulk method of characterizing the geochemistry of a sample with spatial resolution. A system for performing the method also is provided.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Portable gas monitor
ActiveUS20120297868A1Easy to identifyEasily obtain informationSurveyConstructionsControl unitElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:ELKINS EARTHWORKS
Seabed shallow-layer gas detection method based on MIP-CPT technology
InactiveCN105353426ALow costReduce operational complexityProspecting/detection of underground/near-surface gasesOcean bottomElectrolysis
The invention relates to a seabed shallow-layer gas detection method based on the MIP-CPT technology. According to the invention, a conventional CPTU probe is additionally provided with an MIP module, thereby enabling organic matters in a ground layer to be continuously decomposed along with the probe and to be diffused through a semi-permeable MIP film during exploration operation when CPTU data is obtained. Then, the organic matters are conveyed to a gas chromatograph on a mother ship, and are detected by a photo ionization detector, a flame ionization detector and a dry-type electrolysis electrical conductivity detector in the gas chromatograph. Testing parameters are obtained through analysis, and the phase state and content condition of organic matters in the ground layer are obtained.
Owner:SECOND INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY MNR
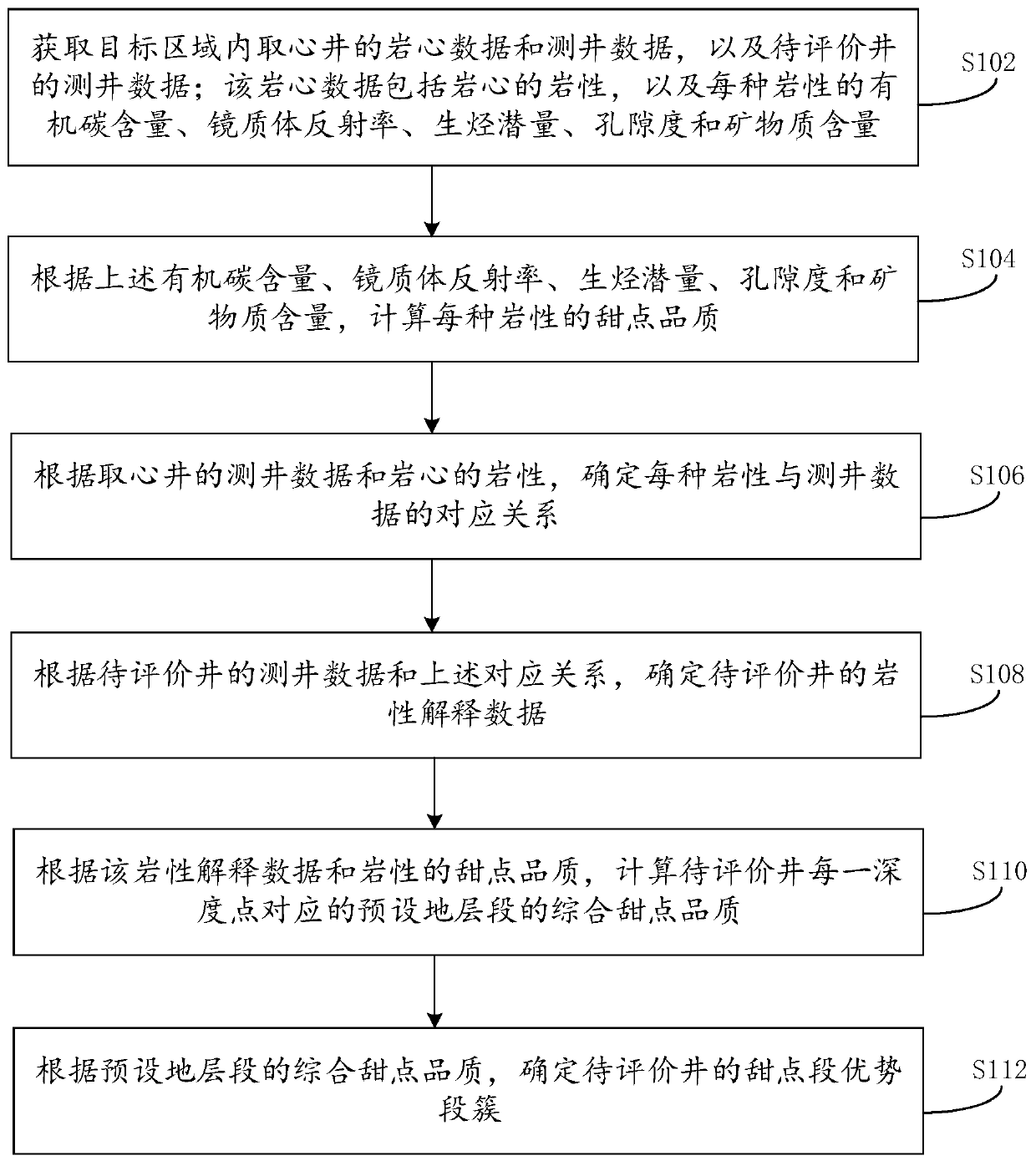
Evaluation method and device for dominant segment cluster of sweet heart segment of fine-grained rock oil and gas reservoir
ActiveCN110412661AConvenient spacingImprove crack initiation efficiencyEarth material testingProspecting/detection of underground/near-surface gasesLithologyRock core
The invention provides an evaluation method and device for a dominant segment cluster of a sweet heart segment of a fine-grained rock oil and gas reservoir. Firstly, core data and logging data of a cored well in a target area and logging data of a to-be-evaluated well are acquired; the sweet heart quality of each kind of lithology is calculated; then, according to the logging data of the cored well and the lithology of a core, a corresponding relationship between each kind of lithology and the logging data is determined; then, according to the logging data of the to-be-evaluated well and the corresponding relationship, lithology interpreting data of the to-be-evaluated well is determined; secondly, according to the lithology interpreting data and the sweet heart quality of the lithology, comprehensive sweet heart quality of a preset stratum segment corresponding to each depth point of the to-be-evaluated well is calculated; according to the comprehensive sweet heart quality of the preset stratum segment, the dominant segment cluster of the sweet heart segment of the to-be-evaluated well is accordingly determined. The method has the advantages that by screening the dominant segmentcluster of the sweet heart segment out from the to-be-evaluated well, the cracking efficiency of perforation clusters can be improved, the fracturing cost is reduced, and the yield of single well is increased.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
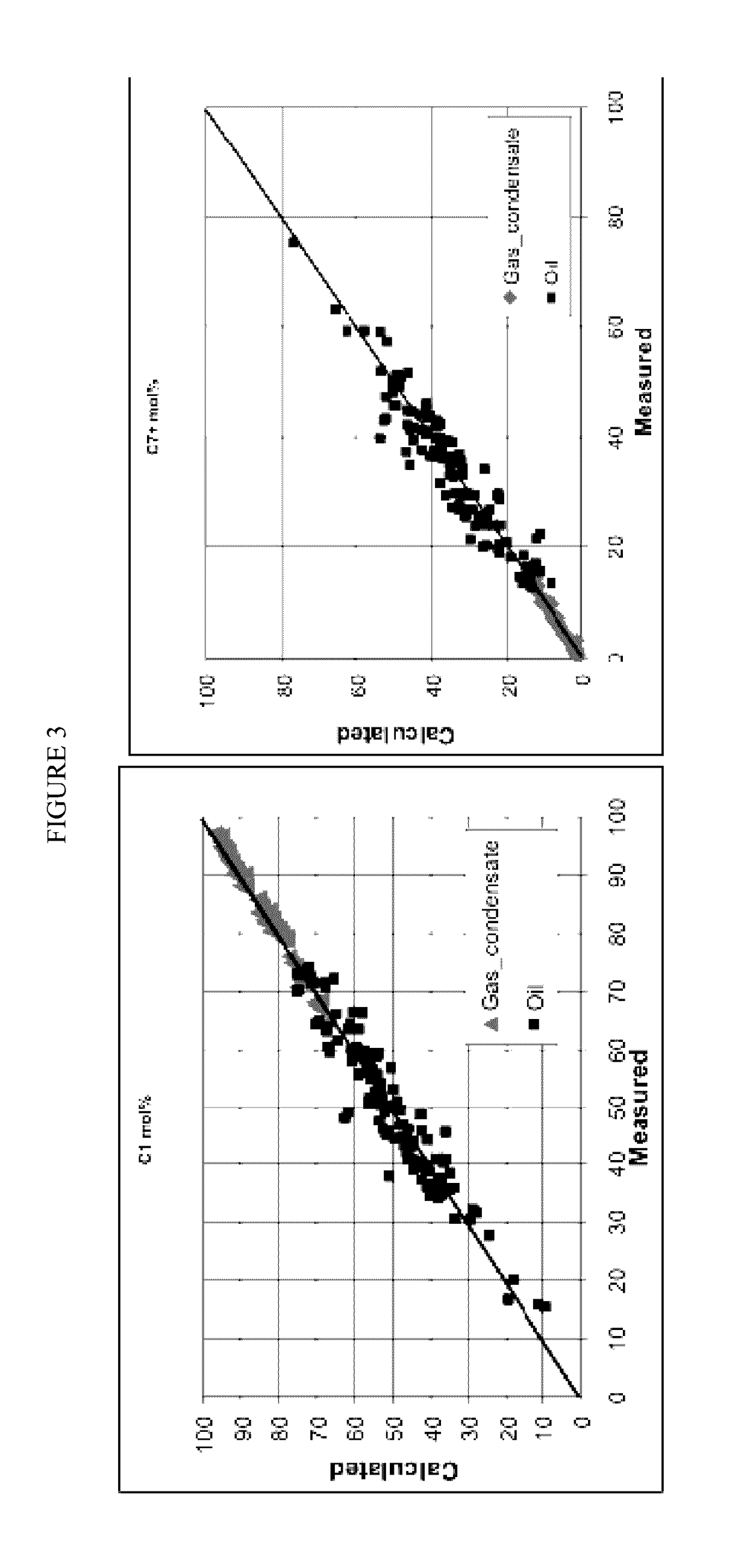
Phase predictions using geochemical data
ActiveUS20170075028A1Simple calculationBig advantageProspecting/detection of underground/near-surface gasesGeomodellingEquation of statePetroleum reservoir
Methods for developing equation-of-states (EOS) composition models for predicting petroleum reservoir fluid behavior and understanding fluid heterogeneity in unconventional shale plays are described. In particular, limited geochemical data from samples taken from the reservoir of interested are utilized to build and tune the EOS model and improve predictions. Real-time applications are also described.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
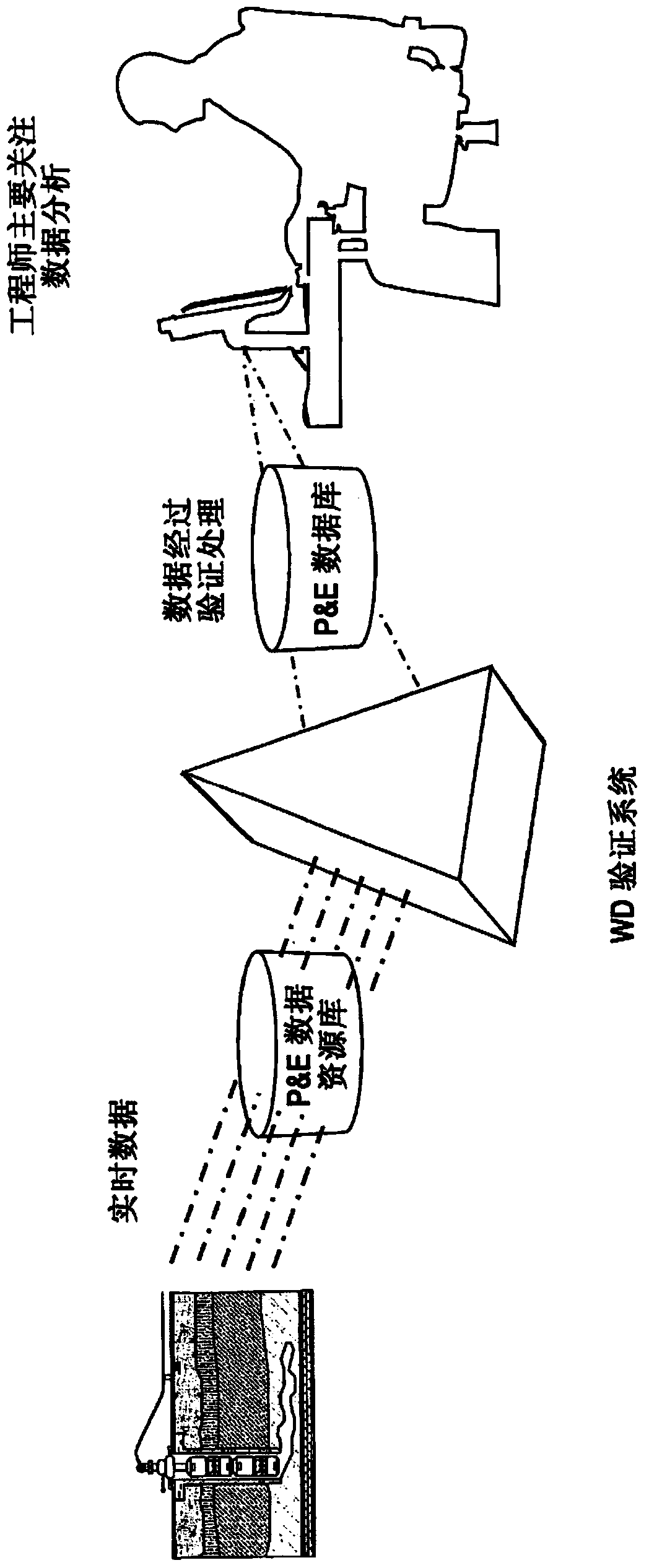
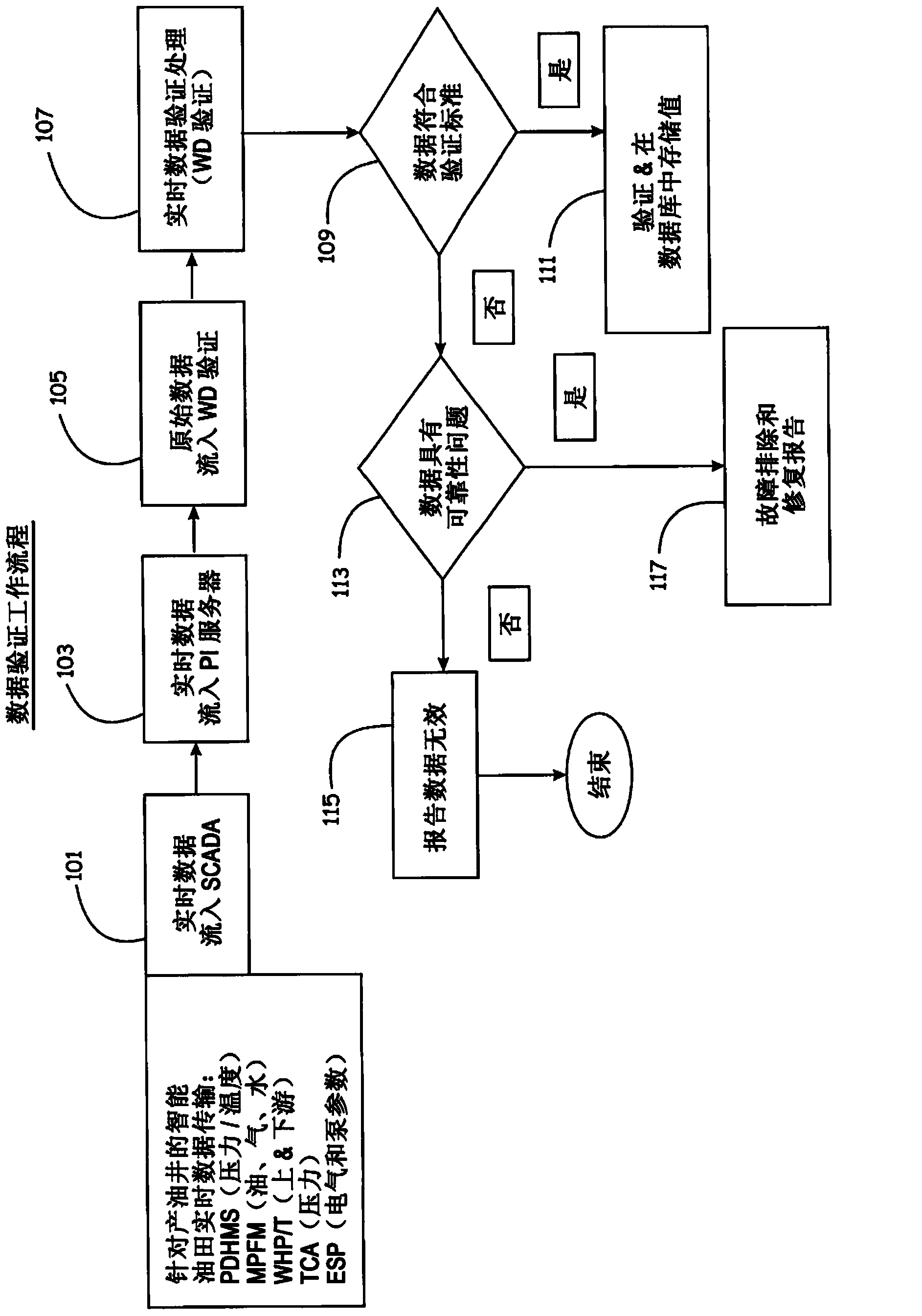
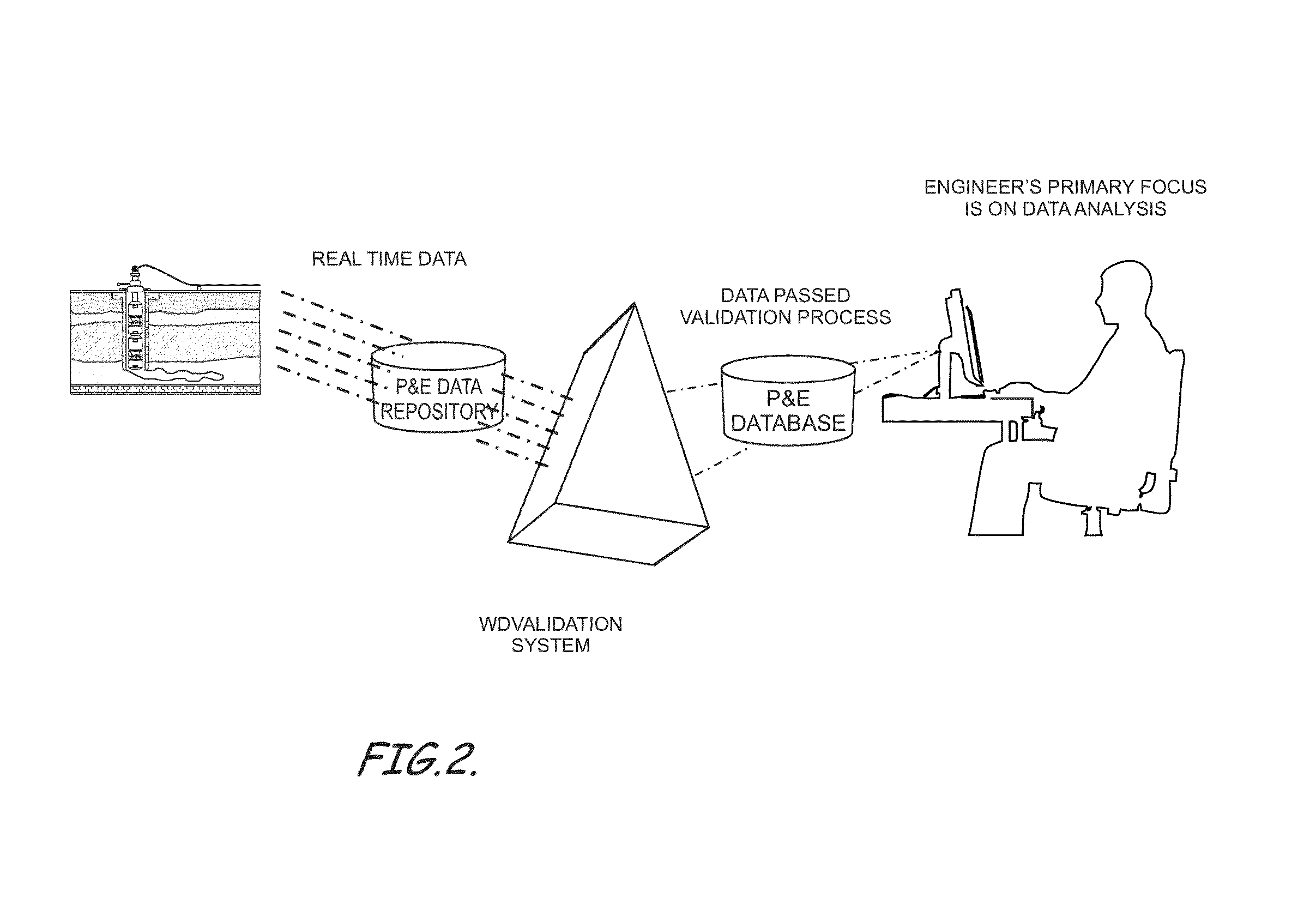
Real-time dynamic data validation apparatus, system, program code, computer readable medium, and methods for intelligent fields
ActiveCN104093931AImprove work efficiencySimple designSurveyFluid removalData validationDynamic field
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Method and apparatus for detection of hydrocarbon deposits
InactiveUS8483965B2Easy to identifyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingProspecting/detection of underground/near-surface gasesData setCo ordinate
A method and apparatus is provided for detecting and categorizing subsurface hydrocarbon reservoirs. Air samples are collected and analyzed by counting hydrocarbon ions, such as methane ions and counting at least one higher order hydrocarbon ions, such as propane, pentane or hexane. The methane ions and at least one higher order hydrocarbon ions are associated with location co-ordinates to form a first raw data set and second raw data set. The first and second raw data sets are analyzed and processed to produce hydrocarbon footprints. The hydrocarbon footprints are superpositioned with other available geological information and subsurface formations of interest are identified.
Owner:SKY HUNTER CORP
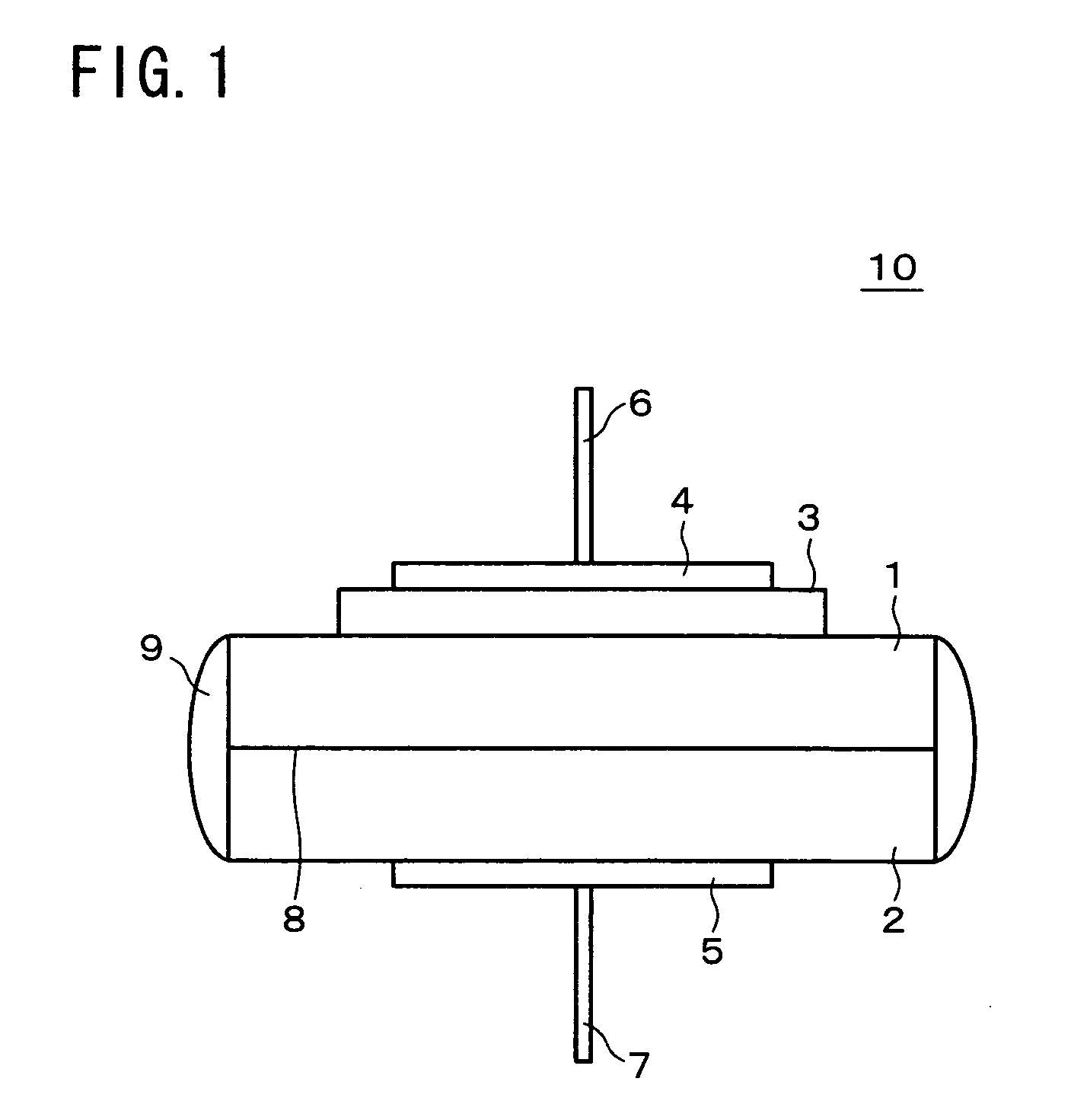
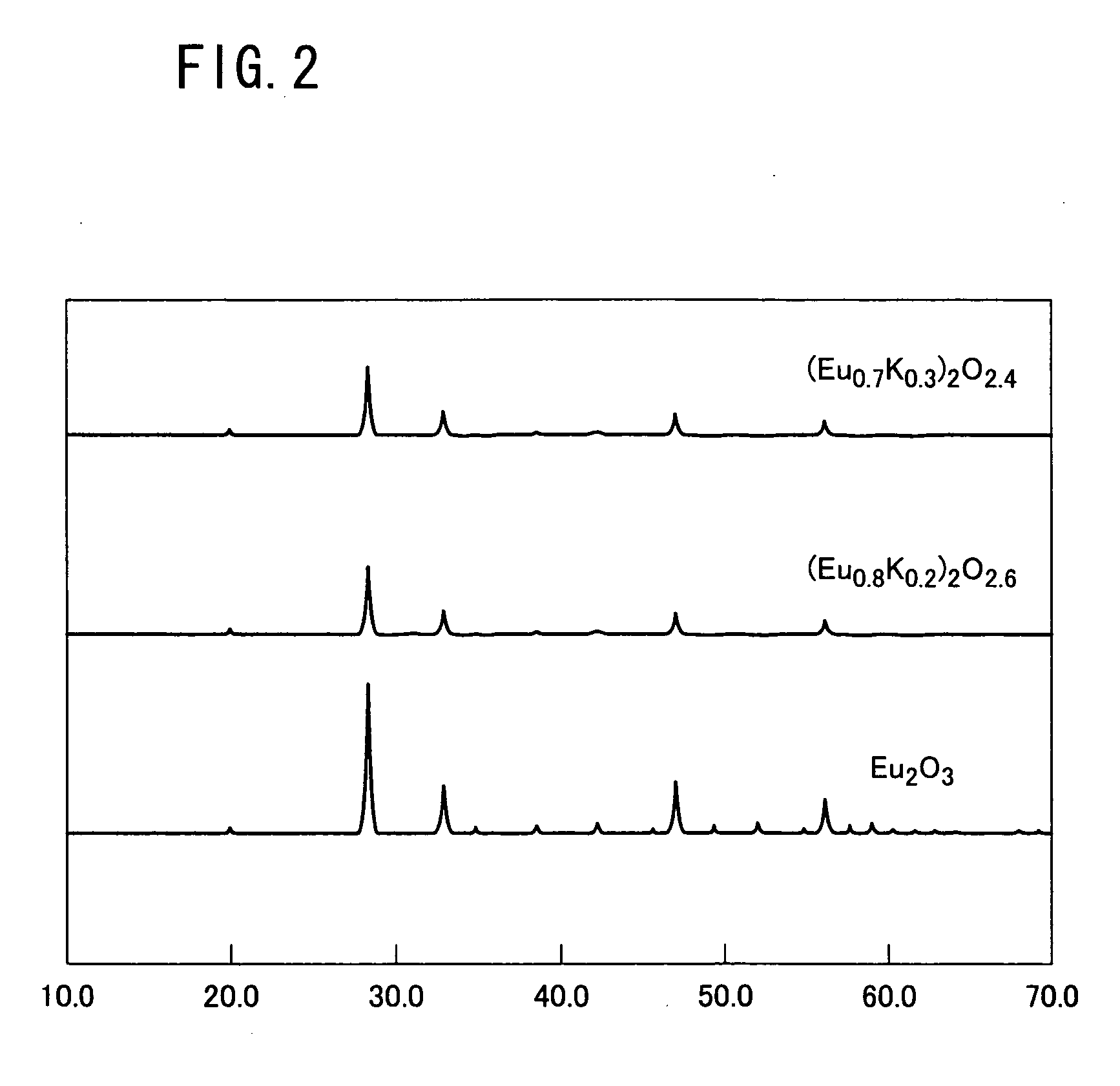
Detecting electrode and nitrogen oxide sensor using the same
InactiveUS20050205423A1Highly practicalSuitable for measuringMachining electrodesWeather/light/corrosion resistanceRare-earth elementWater vapor
The present invention uses a sensor electrode (3) in a nitrogen oxide sensor (10) which includes a nitrate or nitrite of an alkali metal and an oxide of a rare-earth element. The nitrate / nitrite of the alkali metal replaces part of the lattice of the oxide of the rare-earth element, forming a solid solution. The sensor electrode (3) therefore exhibits highly practical features, especially high water-insolubility and capability of nitrogen oxide measurement in a hot and humid atmosphere containing water vapor. Thus, a highly practical nitrogen oxide sensor electrode and nitrogen oxide sensor are provided which are usable in measurement in a hot and humid atmosphere containing water vapor.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for detection of hydrocarbon deposits
InactiveUS20110137568A1Sure easyEasy to identifyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingProspecting/detection of underground/near-surface gasesData setCo ordinate
A method and apparatus is provided for detecting and categorizing subsurface hydrocarbon reservoirs. Air samples are collected and analyzed by counting hydrocarbon ions, such as methane ions and counting at least one higher order hydrocarbon ions, such as propane, pentane or hexane. The methane ions and at least one higher order hydrocarbon ions are associated with location co-ordinates to form a first raw data set and second raw data set. The first and second raw data sets are analyzed and processed to produce hydrocarbon footprints. The hydrocarbon footprints are superpositioned with other available geological information and subsurface formations of interest are identified.
Owner:SKY HUNTER CORP
Method, system and apparatus for use in locating subsurface ore bodies
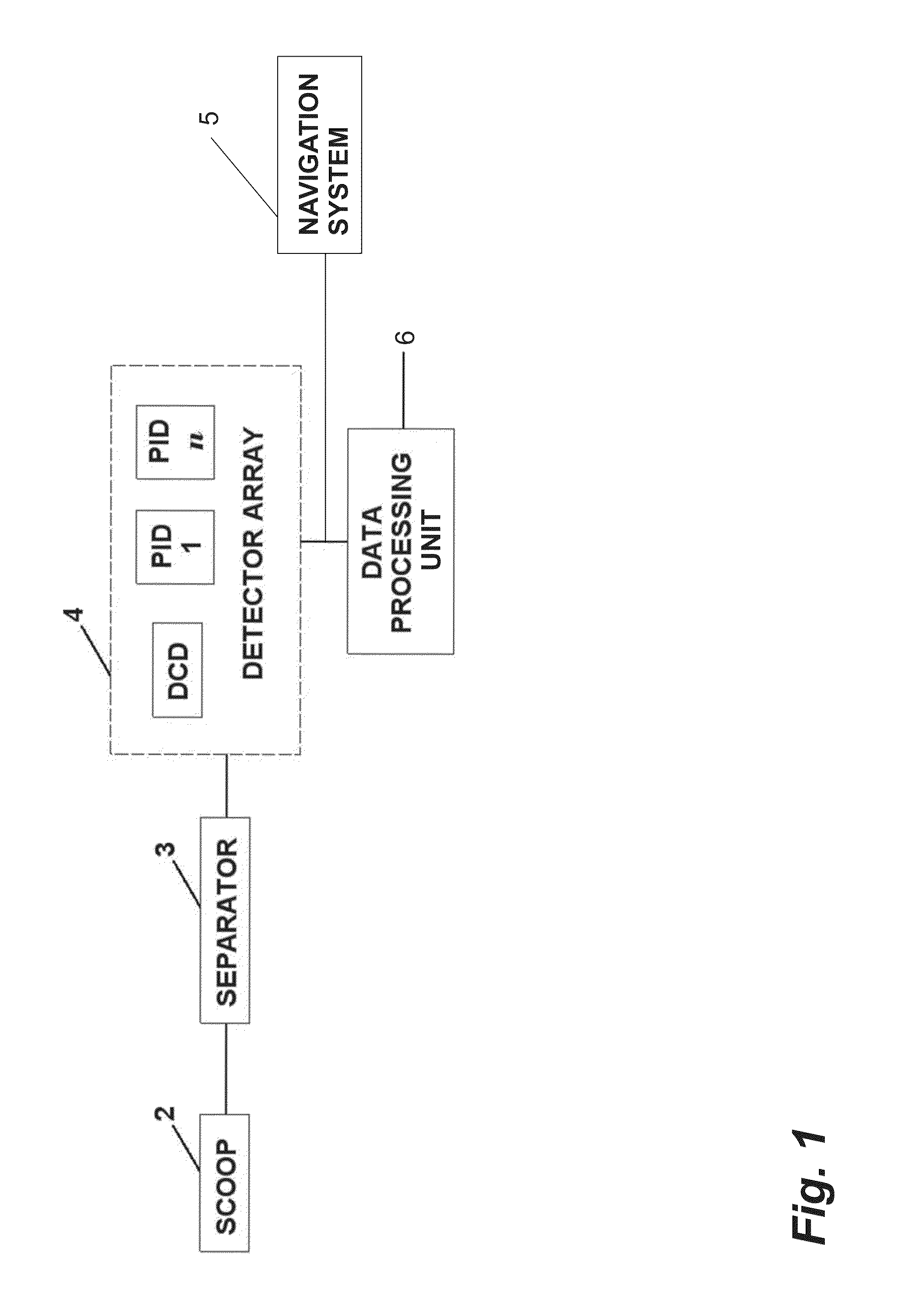
ActiveUS20140047932A1Reduce in quantityFast sampling speedWithdrawing sample devicesProspecting/detection of underground/near-surface gasesMagnetic tapeBarcode
A method and system for locating subsurface ore bodies. Samples of near surface soil are collected over a predetermined geographical area. The samples are analysed to discover any chemical anomalies in the dust particles as a way of identifying possible subcropping mineralization. A tine (22) and collection tube (24) engage into subsurface soil and samples are drawn up the tube into a dust collection module (12). Sub 5 micron particles are captured on an electrostatically charged tape (40). Consecutive samples are indexed on the tape e.g. with a barcode. Collected dust samples are ablated by a laser ablation cell (72) and the ablated sample analysed by a mass spectrometer for presence of ions indicating presence of a resource body, such as a body of ore, minerals or hydrocarbons.
Owner:GLOBAL SCI SERVICES
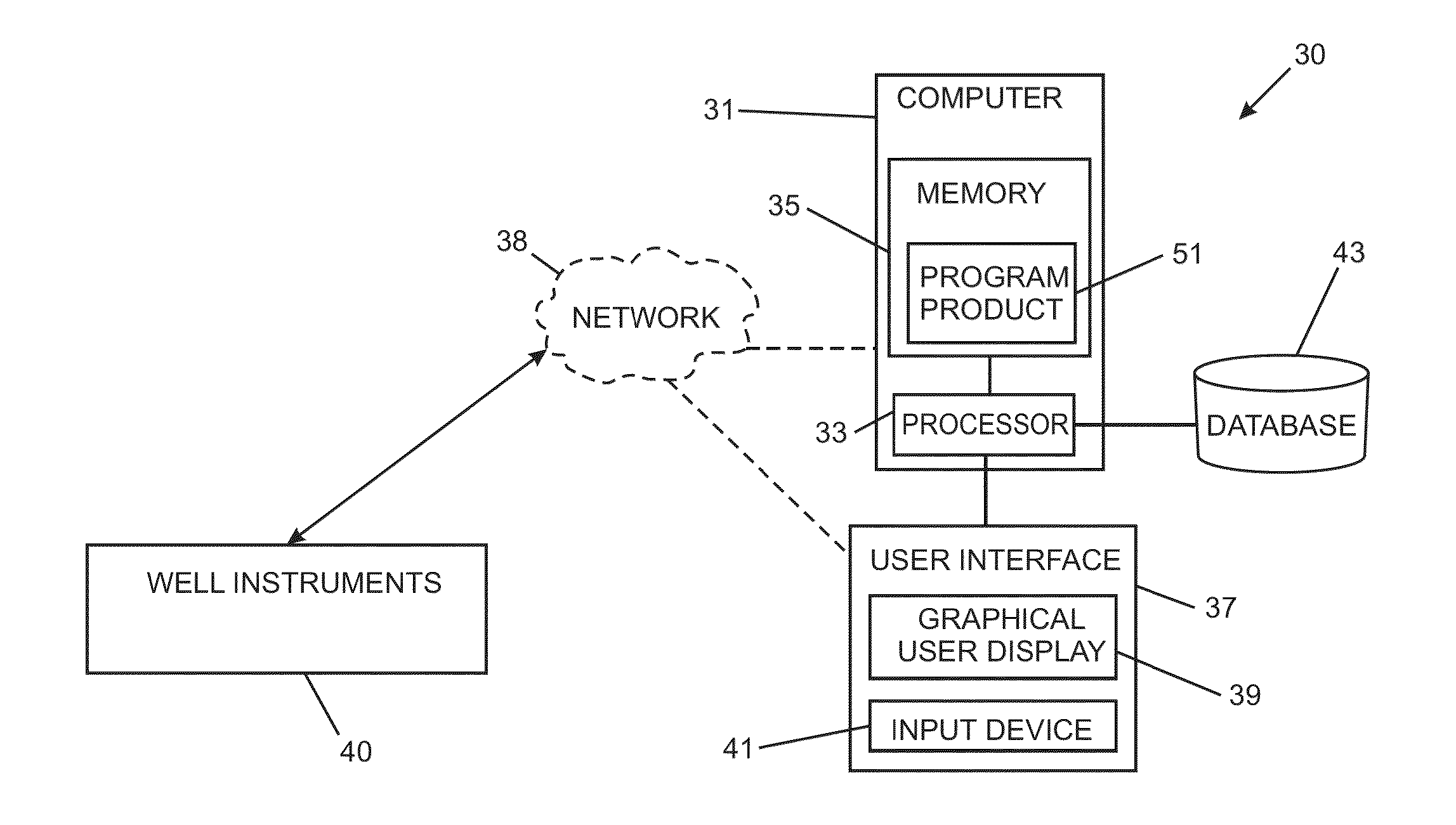
Real-Time Dynamic Data Validation Methods For Intelligent Fields
ActiveUS20130173167A1Detection process can be enhancedEfficient detectionElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyDynamic fieldData validation
Methods for managing an intelligent field, are provided. An exemplary method can include receiving real-time dynamic field data, analyzing validity of the dynamic field data, validating values of the field data, validating a state / condition of a well, and flagging well components, well conditions, and / or well state validation issues.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
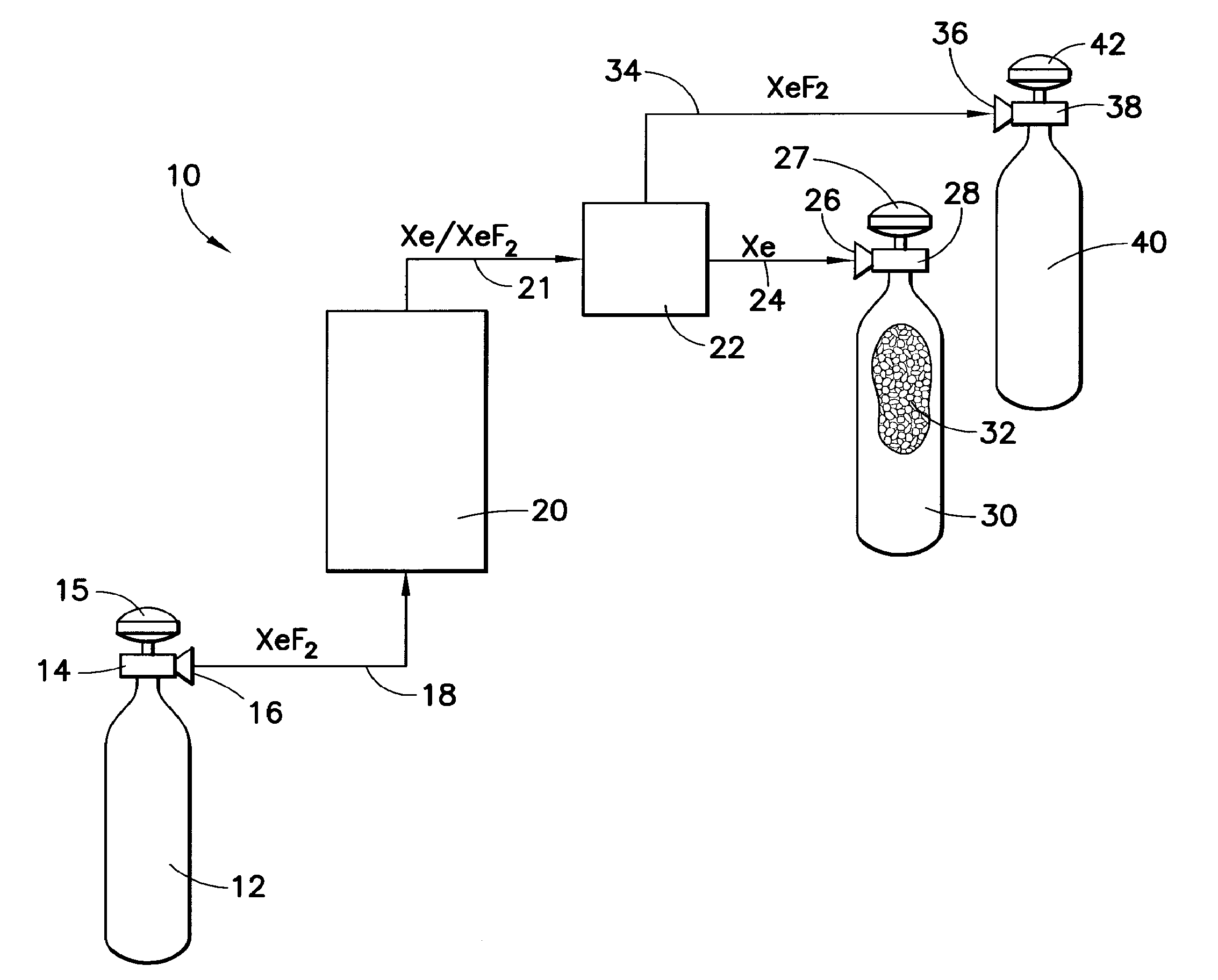
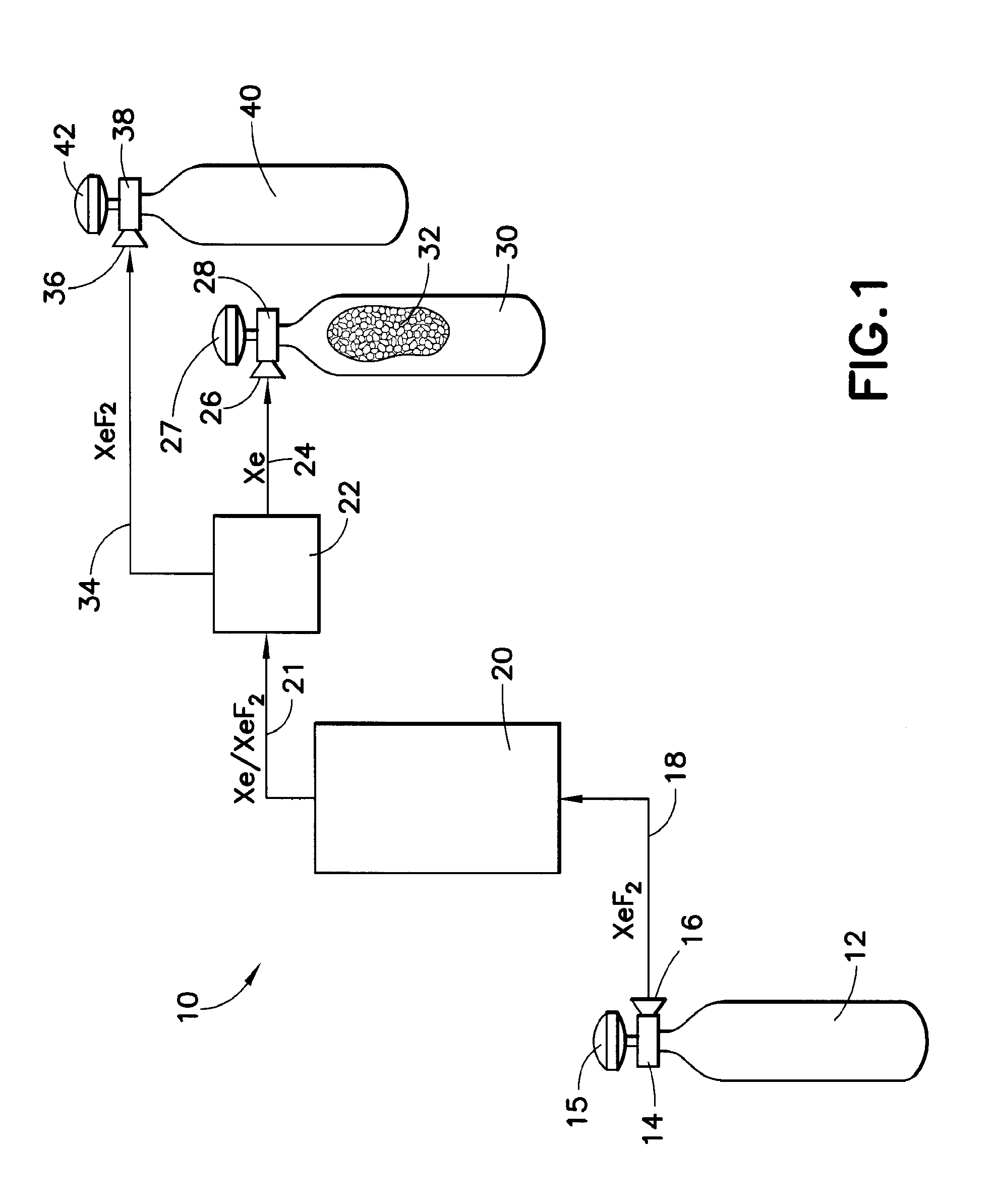
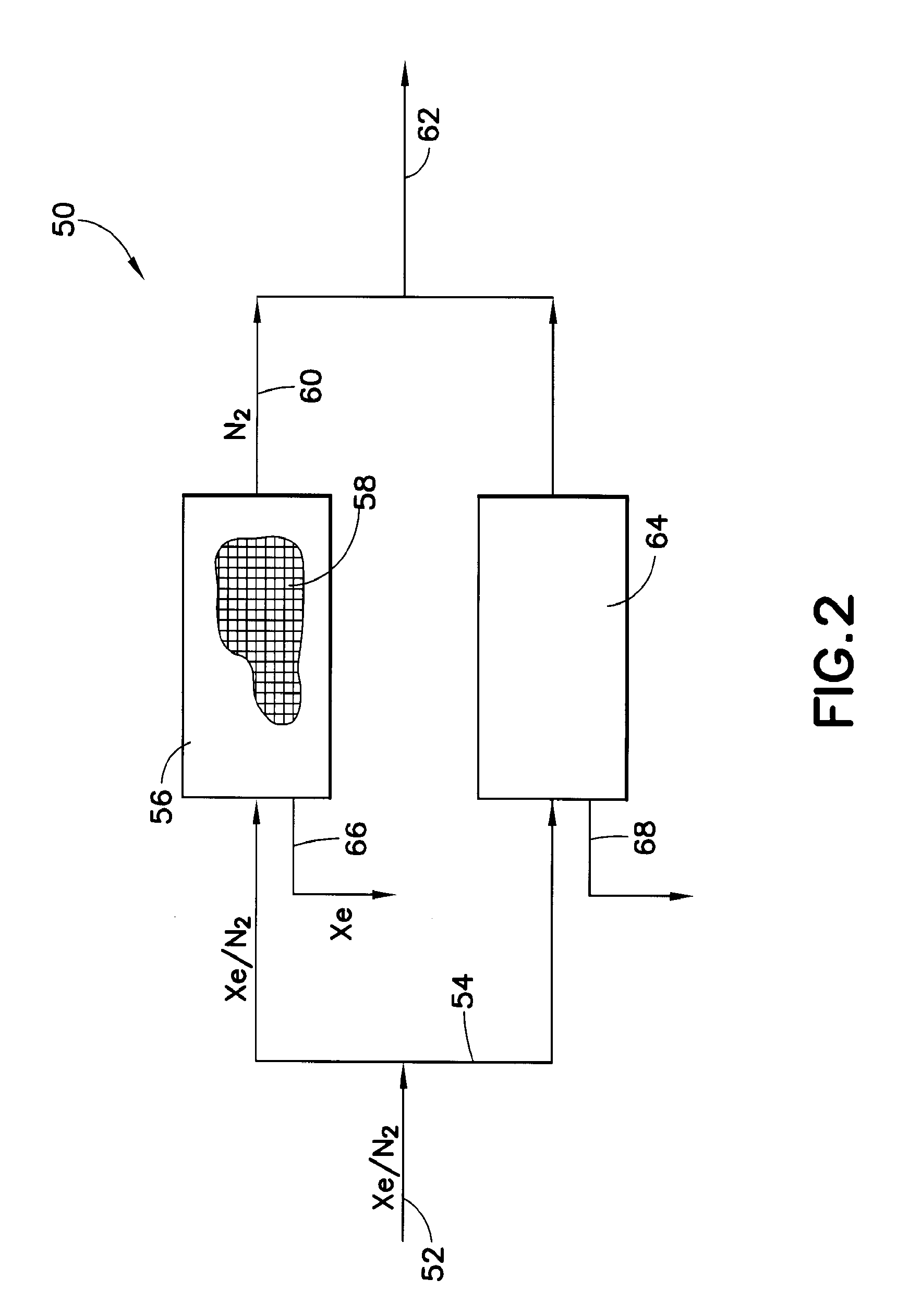
RECOVERY OF Xe AND OTHER HIGH VALUE COMPOUNDS
A system and method for recovering high value gas from a process stream, material or environment containing same, e.g., xenon by contacting gas from the process stream, material or environment with a carbon adsorbent effective to sorptively capture same, free of or with reduced concentration of fluid species present with the high value gas in the high value gas-containing gas in the process stream, material or environment. Other aspects of the disclosure include a radon detection method and product.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
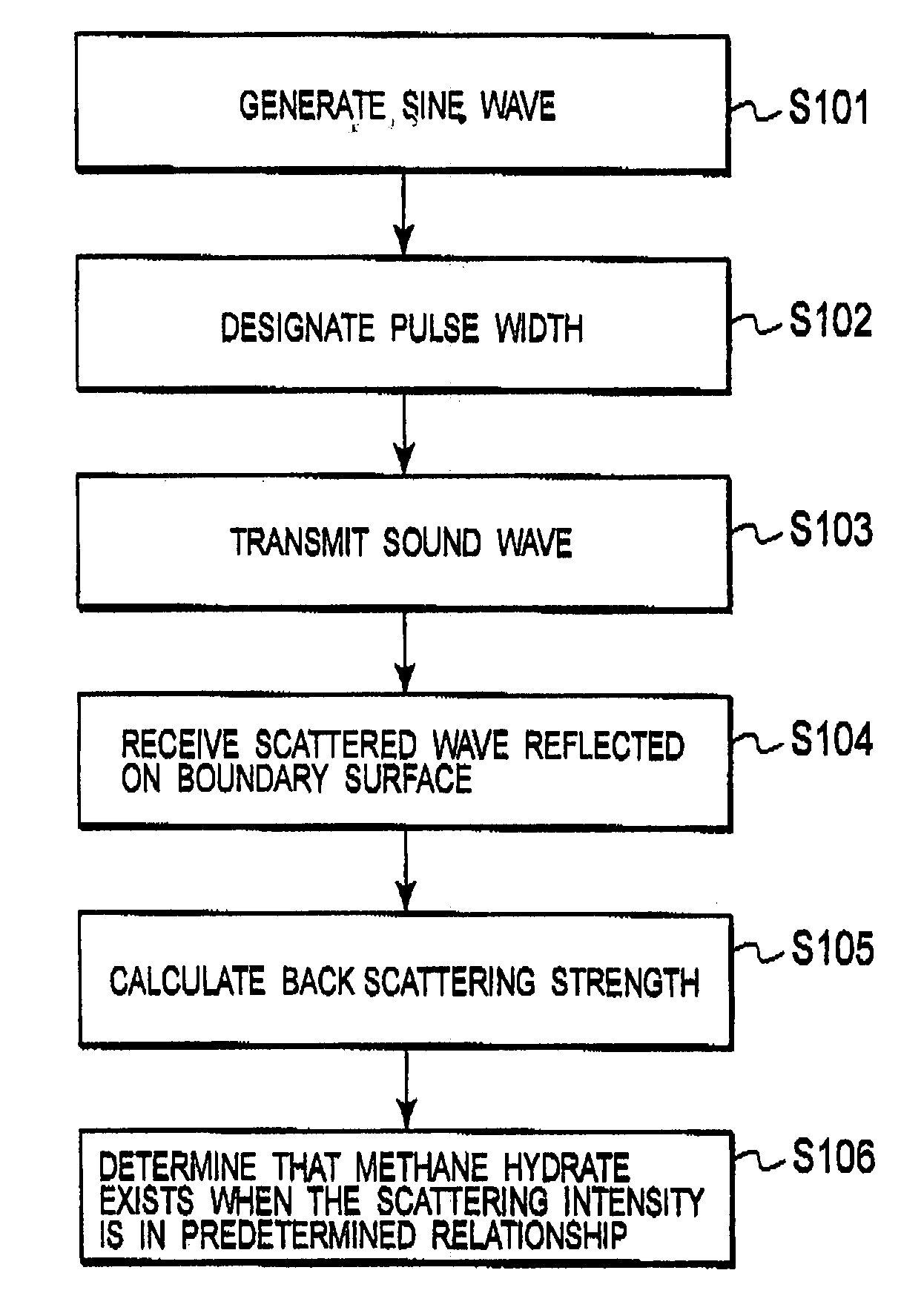
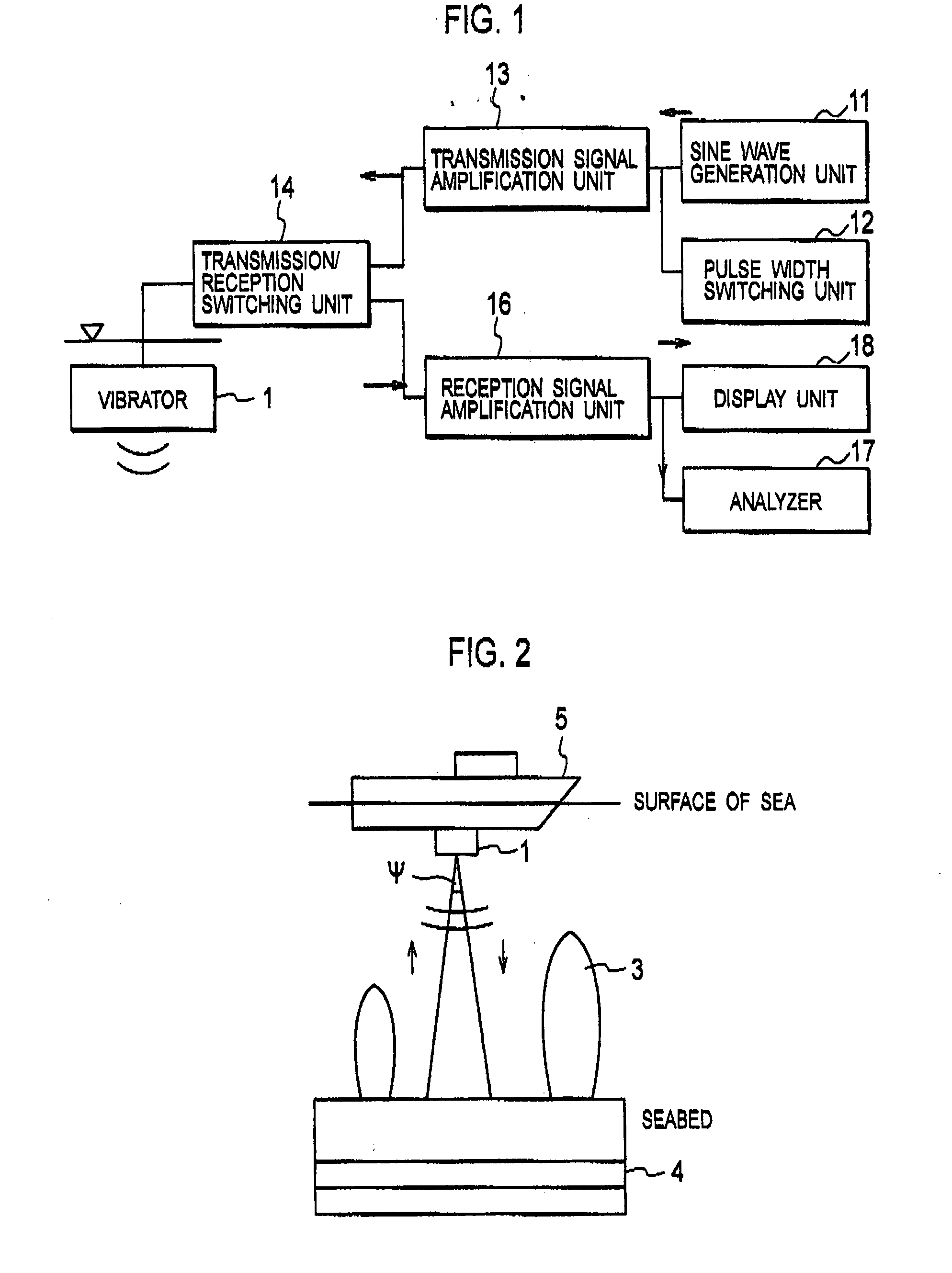
Seabed Resource Exploration System and Seabed Resource Exploration Method
ActiveUS20080112266A1Sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionProspecting/detection of underground/near-surface gasesPhysicsSeawater
A seabed resource exploration system includes: a vibrator 1 for transmitting a sound wave into the sea and receiving a scattered wave in which the sound wave is reflected on a boundary surface between seawater and a mixture of methane gas and methane hydrate, which exists in the seawater; and an analyzer 17 for determining that the methane hydrate exists in a seabed immediately under the mixture when backscattering strength, calculated by the transmitted sound wave and the received scattered wave, is in a predetermined relationship. The predetermined relationship satisfies a relationship that a maximum value of the backscattering strength is −60 to −30 dB and an average value of the backscattering strength is −70 to −50 dB. The backscattering strength is on a grid obtained by cutting the mixture into round slices in the depth direction by a predetermined width, in a range from the seabed to a predetermined height.
Owner:KUBUSHIKI KAISHA AOYAMA
Method for optimizing the working of a deposit of fluid by taking into account a geological and transitory exchange term between matrix blocks and fractures
ActiveUS20140372042A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingFluid removalComputer scienceSediment
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Karst fissure water detection system and method
ActiveCN107289997ASimple structureEfficient detectionProspecting/detection of underground/near-surface gasesIndication/recording movementInjection wellKarst
The present invention discloses a karst fissure water detection system and method. According to the karst fissure water detection system and method, a pumping and injection well is drilled at the center of a region to be detected, geological boreholes are drilled with the pumping and injection well as a center; water is pumped from the pumping and injection well, water pumping time, pumped water quantity as well as the water level changes of the pumping and injection well and the geological boreholes are recorded; salinity sensors and water temperature sensors are distributed, and the salinity sensors and the water temperature sensors are connected into a computer through a data acquisition module so as to acquire the initial salinity and water temperature of karst fissure water; the salinity change of the karst fissure water in each borehole is acquired in real time until values acquired by some salinity sensors obviously changes, and hot water is injected into the pumping and injection well, and the temperature change of the karst fissure water in each borehole is acquired in real time until values acquired by some water temperature sensors obviously changes; and the permeability, flow direction, flow rate and main water channels of the karst fissure water are analyzed.
Owner:JINAN RAILWAY TRANSPORT GRP CO LTD
Well pattern mature region underground river course sand body quick identification method
ActiveCN107728227AEfficient identificationLow efficiencyProspecting/detection of underground/near-surface gasesBody identificationGeomorphology
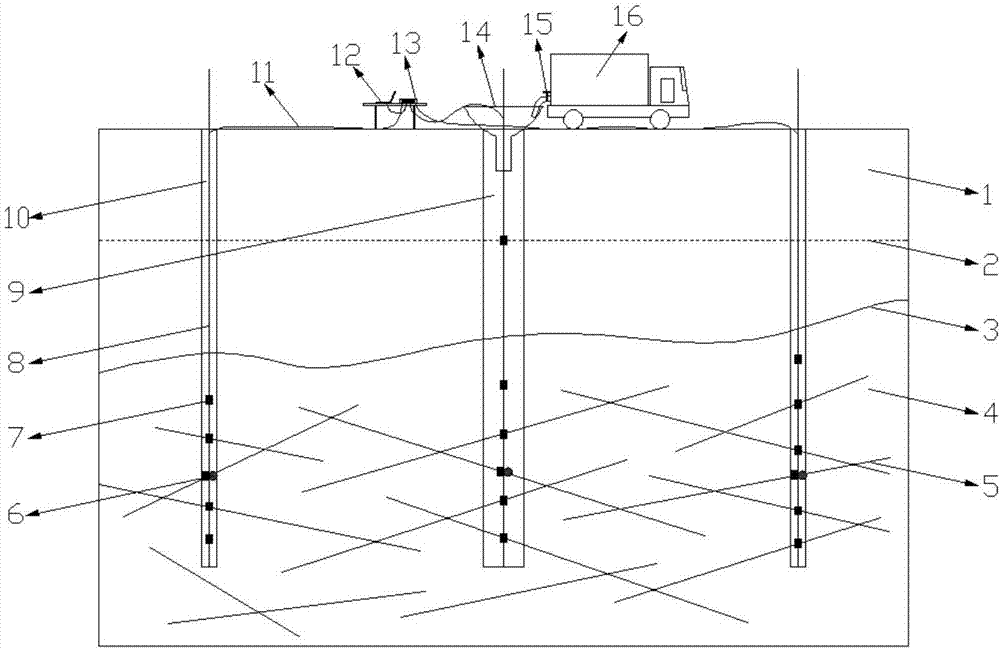
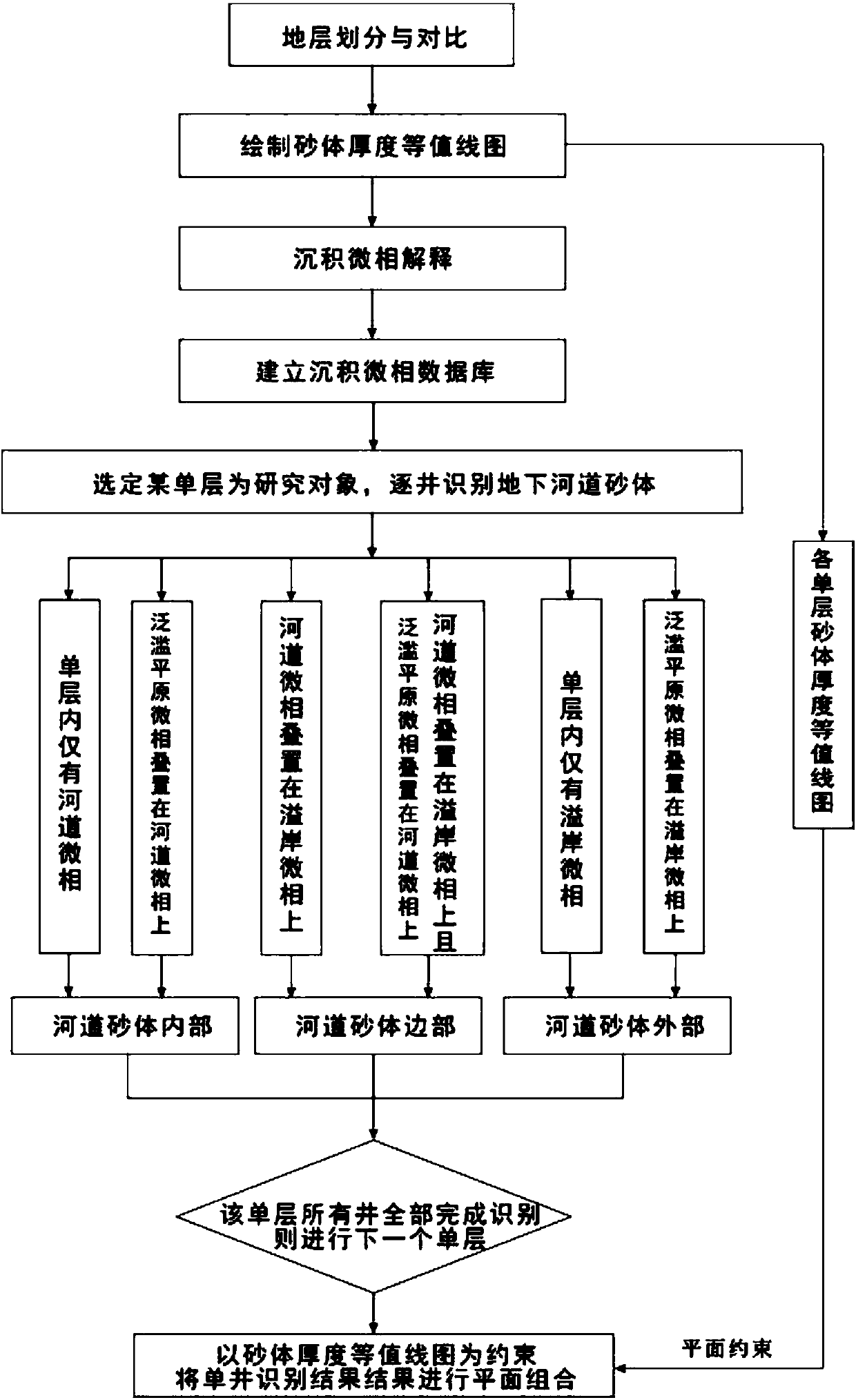
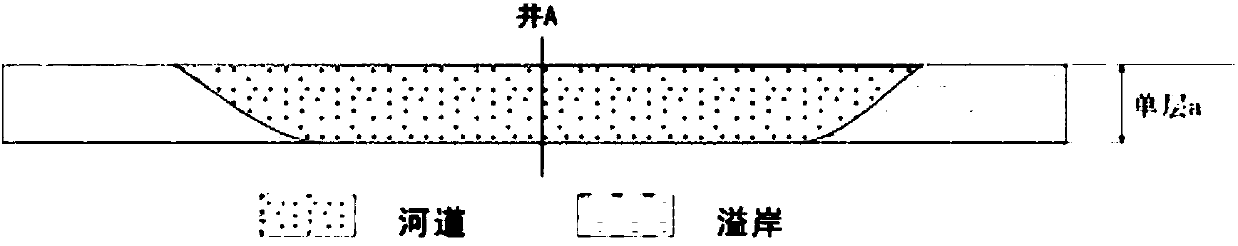
The invention relates to a well pattern mature region underground river course sand body quick identification method. The method includes the following steps that: 1) stratum division and comparison are performed, and an isochronal stratigraphic comparison framework is established; 2) the sand body thicknesses contour line maps of each stratum are drawn; 3) under the constraint of the isochronal stratigraphic comparison framework, sedimentary microfacies interpretation is carried out based on a well logging curve pattern and rock debris data; 4) a sedimentary microfacies database is established with single strata adopted as basic units; 5) with any single stratum adopted as a research object, river course sand body identification is performed on each well on by one; 6) after all the wellsof the single stratum which is adopted as the research object all participate in comparison, river course sand body identification is performed on the next stratum until the river course sand body identification of all the single strata is completed; and 7), the identification results of all the wells of any single stratum are projected onto the sand body thickness contour line map of the single stratum according to the coordinates of the locations of the wells, with the sand body thickness contour line map adopted as a constraint, identified underground river course sand bodies are subjectedto plane combination.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Popular searches
Seismology for water-logging Special data processing applications Acoustic wave reradiation Nuclear radiation detection Material analysis by optical means Electrical measurements Particle suspension analysis Permeability/surface area analysis Gravitational wave measurement Specific gravity measurement
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com