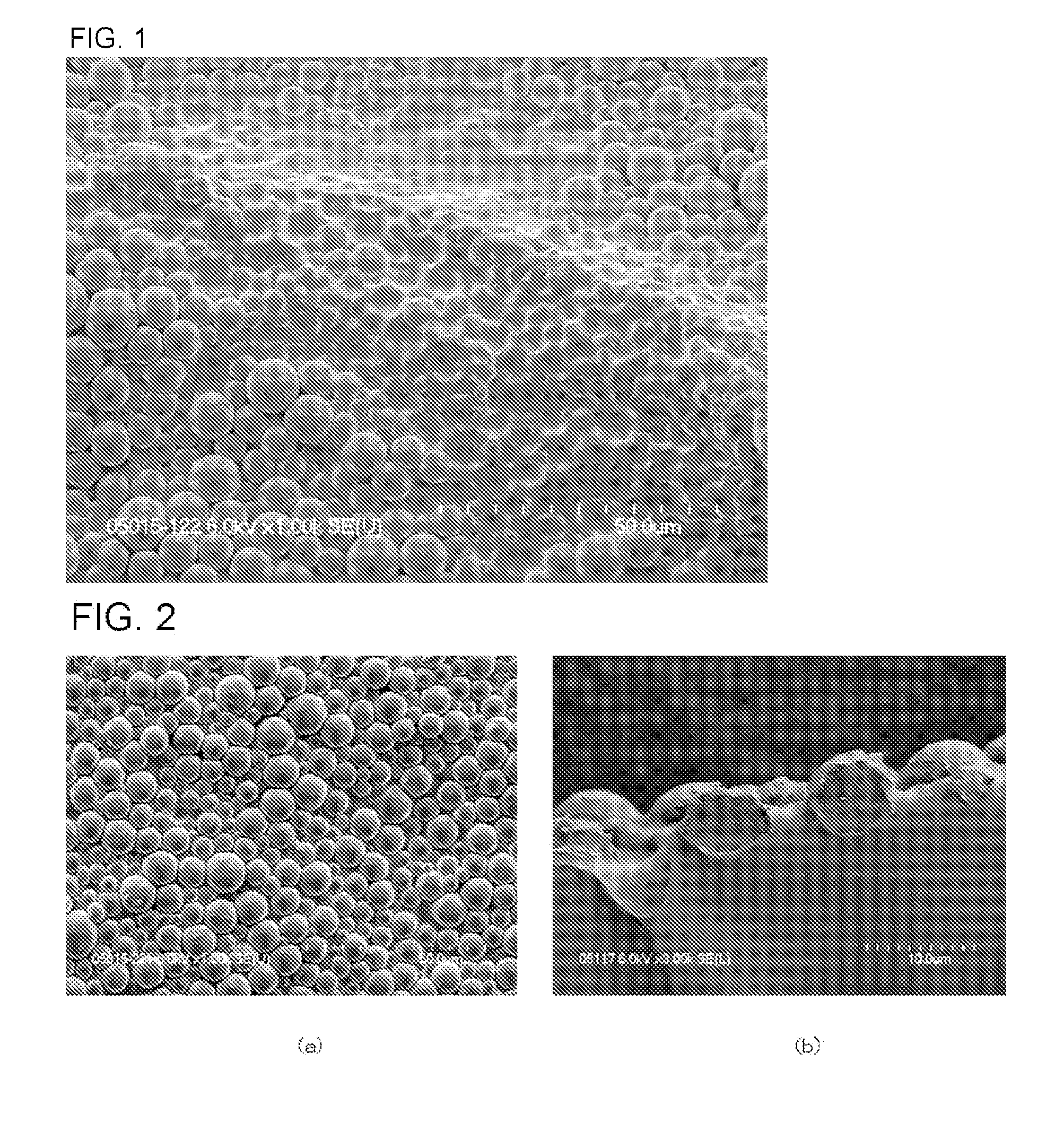
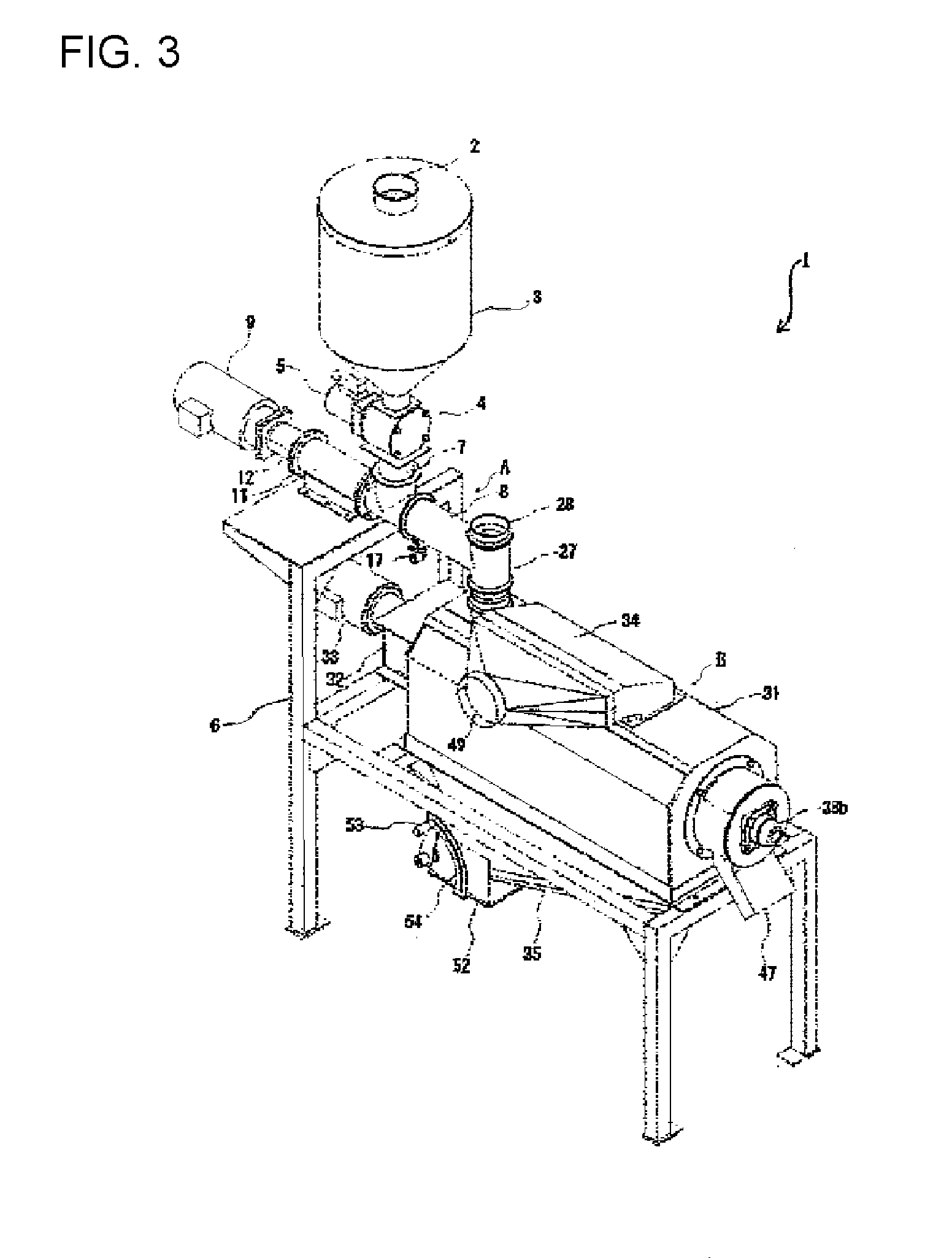
Resin pellet and method for producing the same
a technology of resin pellets and resin powders, applied in the field of resin pellets, can solve the problems of easy dislocation of resin powder layers on copolymerized polyester resins, limited storage of resin pellets, and frequent blockage of resin pellets, so as to achieve effective suppression of blocking, reduce contact area of resin pellets, and reduce the effect of blocking
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0101]An aqueous dispersion (solid content concentration: 40 mass %) was prepared by dispersing microparticles composed of an ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer having the content of vinyl acetate of 19 mass %, MFR of 150 g / 10 min, a Vicat softening point of 42 degrees centigrade, a shore hardness of 86 and the degree of crystallinity of 26. 500 g of the aqueous dispersion was heated to 45 degrees centigrade, and 100 g of pellets (pellet temperature: 15 degrees centigrade) was added thereto, and the aqueous dispersion and pellets were contacted under stirring for 30 seconds. The pellets were composed of an ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer having the content of vinyl acetate of 46 mass %, MFR of 100 g / 10 min, a Vicat softening point of equal to or less than 25 degrees centigrade (ΔT≧17), a shore hardness of 16 (ΔHS: 70) and the degree of crystallinity of 0% (Δa: 26%) as a resin base material. Subsequently, the obtained resin pellets were cooled in cold water of 10 degrees centigrade an...
example 2
[0102]To 10 kg of pellets (pellet temperature: 20 degrees centigrade) was added 300 g (corresponding to 0.03 times relative to total weight of base material) of an aqueous dispersion (solid content concentration: 40 mass %), and the resulting mixture was heated until the pellet temperature became 30, 40 and 50 degrees centigrade respectively. The pellets were composed of an ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer having the content of vinyl acetate of 46 mass %, MFR of 100 g / 10 min, a Vicat softening point of equal to or less than 25 degrees centigrade, a shore hardness of 16 and the degree of crystallinity of 0% as a resin base material, while the aqueous dispersion was prepared by dispersing microparticles composed of an ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer having the content of vinyl acetate of 19 mass %, MFR of 150 g / 10 min, a Vicat softening point of 42 degrees centigrade (ΔT≧17), a shore hardness of 86 (ΔHS: 70) and the degree of crystallinity of 26% (Δa: 26%). The mixture was heated by ...
example 3
[0103]To 100 g of pellets (pellet temperature: 15 degrees centigrade) was added 3 g (corresponding to 0.03 times relative to total weight of base material) of an aqueous dispersion (solid content concentration: 40 mass %), and the resulting mixture was allowed to stand in an oven at a temperature of 45 degrees centigrade and a humidity of 30% for 15, 30, 45, 50 and 60 minutes respectively. The pellets were composed of an ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer having the content of vinyl acetate of 46 mass %, MFR of 100 g / 10 min, a Vicat softening point of equal to or less than 25 degrees centigrade, a shore hardness of 22 and the degree of crystallinity of 0% as a resin base material, while the aqueous dispersion was prepared by dispersing microparticles composed of an ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer having the content of vinyl acetate of 19 mass %, MFR of 150 g / 10 min, a Vicat softening point of 42 degrees centigrade (ΔT≧17), a shore hardness of 86 (ΔHS: 64) and the degree of crystallin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com