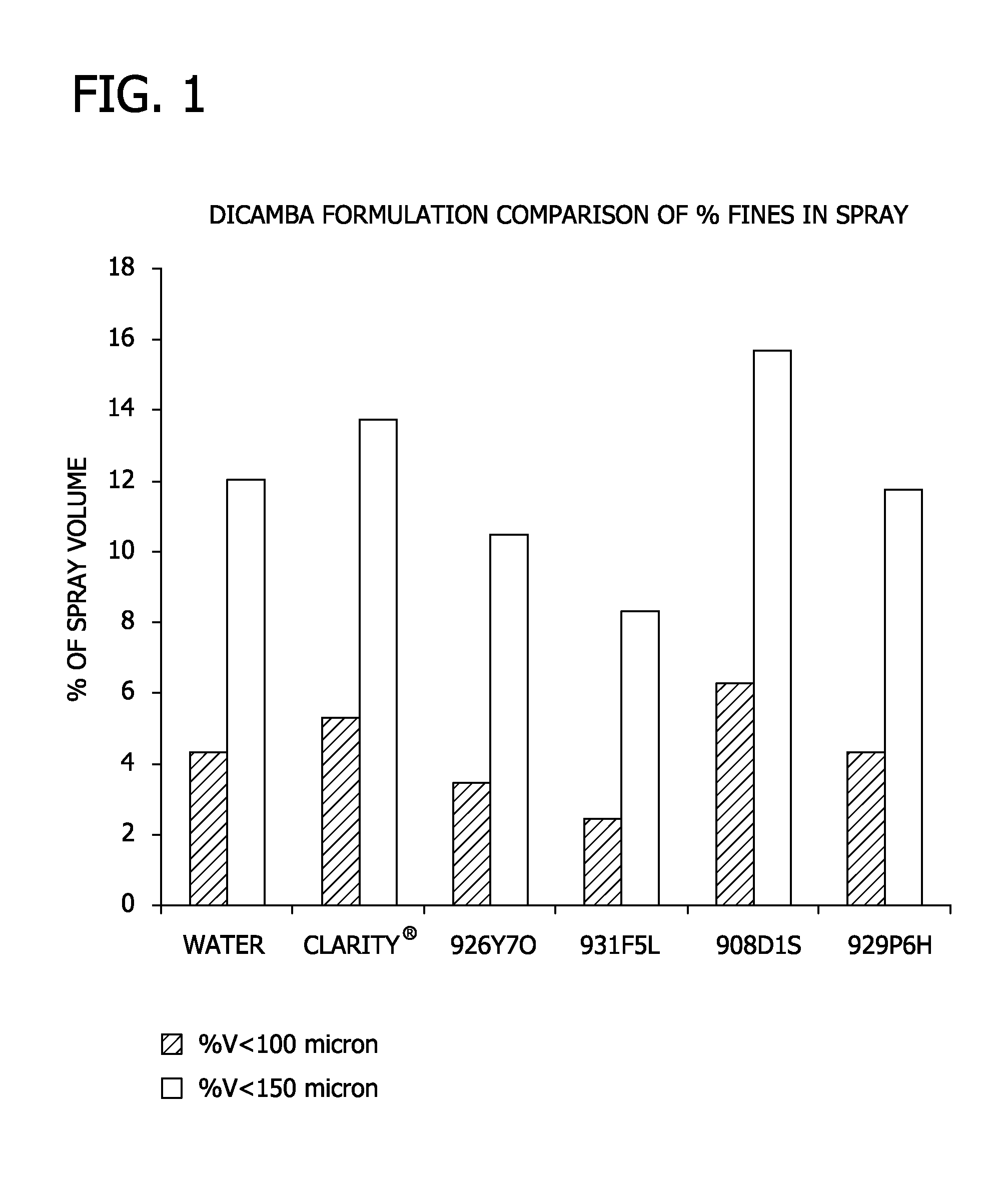
Low volatility auxin herbicide formulations
a technology of auxin herbicide and low volatility, which is applied in the direction of biocides, herbicides and algicides, botany apparatus and processes, etc., can solve the problems of inability to successfully regulate the movement of auxin herbicides from the application site, volatile and drift, contact damage to sensitive plants, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing the volatility of auxin herbicides
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0157]An experiment was performed to determine the efficacy of experimental application mixtures prepared by aqueous dilution of experimental MEA dicamba salt formulations containing a surfactant relative to comparative application mixtures prepared by dilution of the commercial products CLARITY and BANVEL.
[0158]Aqueous formulations comprising MEA dicamba were typically prepared by mixing water and monoethanolamine for 5 min followed by addition of dicamba acid (98.3% purity) in one portion. The resulting suspensions were stirred until all of the solids had dissolved by visual inspection, typically between 60 min and overnight. Relative amounts of dicamba and MEA used to give 61% by wt solutions of dicamba are reported in Table 1a. These and MEA dicamba solutions prepared using this procedure were subsequently used in preparation of MEA dicamba formulations containing polyimine polymers and / or surfactants.
TABLE 1aDicamba WaterMEADicambamol eqwt %(g)(g)(g)MEA:dicamba61108.2881.45310....
example 2
[0186]Aqueous formulations comprising MEA dicamba and various coco and tallow di- and tri-amine ethoxylates were prepared as indicated in Table 2a wherein the dicamba concentration in each formulation was 633 g a.e. / ha (47.9 wt % a.e.) and the concentration of the other components in wt % is indicated in parenthesis.
TABLE 2aFormulation504A3F504B5T504C8N504D3JMEA Dicamba61616161SurfactantSurf9 (10)Surf10Surf11Surf12 (10)(wt %)(10)(10)Formulation504E7C504F2I504G0L504H6TMEA Dicamba61616161Surfactant Surf13Surf14Surf15Surf16 (10)(wt %)(10)(10)(10)Formulation504I8L504J4P504K1B504L9OMEA Dicamba61616161SurfactantSurf17Surf18Surf19Surf20 (10)(wt %)(10)(10)(10)Formulation504M6K504N5U504O7X50P1FMEA Dicamba61616161SurfactantSurf21Surf22Surf23Surf24 (10)(wt %)(10)(10)(10)Formulation504Q3D504R6E504S9M504T7QMEA Dicamba61616161SurfactantSurf25Surf26Surf27Surf28 (10)(wt %)(10)(10)(10)
[0187]The formulations from Table 2a and CLARITY were sprayed over the top of velvetleaf (ABUTH) plants evaluate her...
example 3
[0189]The specific gravity and pH of potassium and MEA dicamba aqueous solutions were evaluated. The results are reported in Table 3a wherein “Dicamba wt %” refers to weight percent acid equivalent dicamba in solution and “SG” refers to specific gravity in grams per mL. The pH of MEA dicamba was measured for two lots of material.
TABLE 3aK DicambaMEA DicambaDicamba wt %SGpHSGpHpHg a.e. / L51.035.41.026.68.3—101.055.41.056.78.4—151.095.41.076.88.5—201.125.91.096.98.55—251.156.31.1278.6—301.186.51.147.18.65291351.226.81.177.38.7391401.2571.27.48.8478451.297.31.237.58.85554501.337.61.257.68.9623551.367.81.287.78.95684601.48.11.317.89741
[0190]The data indicate that solutions of potassium dicamba have a greater specific gravity and lower pH at a given concentration than do solutions of MEA dicamba.
[0191]In a set of experiments, the crystallization behavior of formulations containing MEA dicamba, potassium glyphosate and a surfactant was evaluated. The formulation of the experimental dicamba...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com