Method for assaying lower respiratory tract infection or inflammation
a technology of infection or inflammation, applied in the field of prognosis or survival prediction and/or diagnosis of infections or inflammatory diseases of the airways and lungs, can solve the problem that none of these biomarkers is completely satisfying, and achieve the effect of high levels of psp/reg
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
PSP / reg is a Suitable Marker to Assess Disease Severity and Stratify Risk in VAP
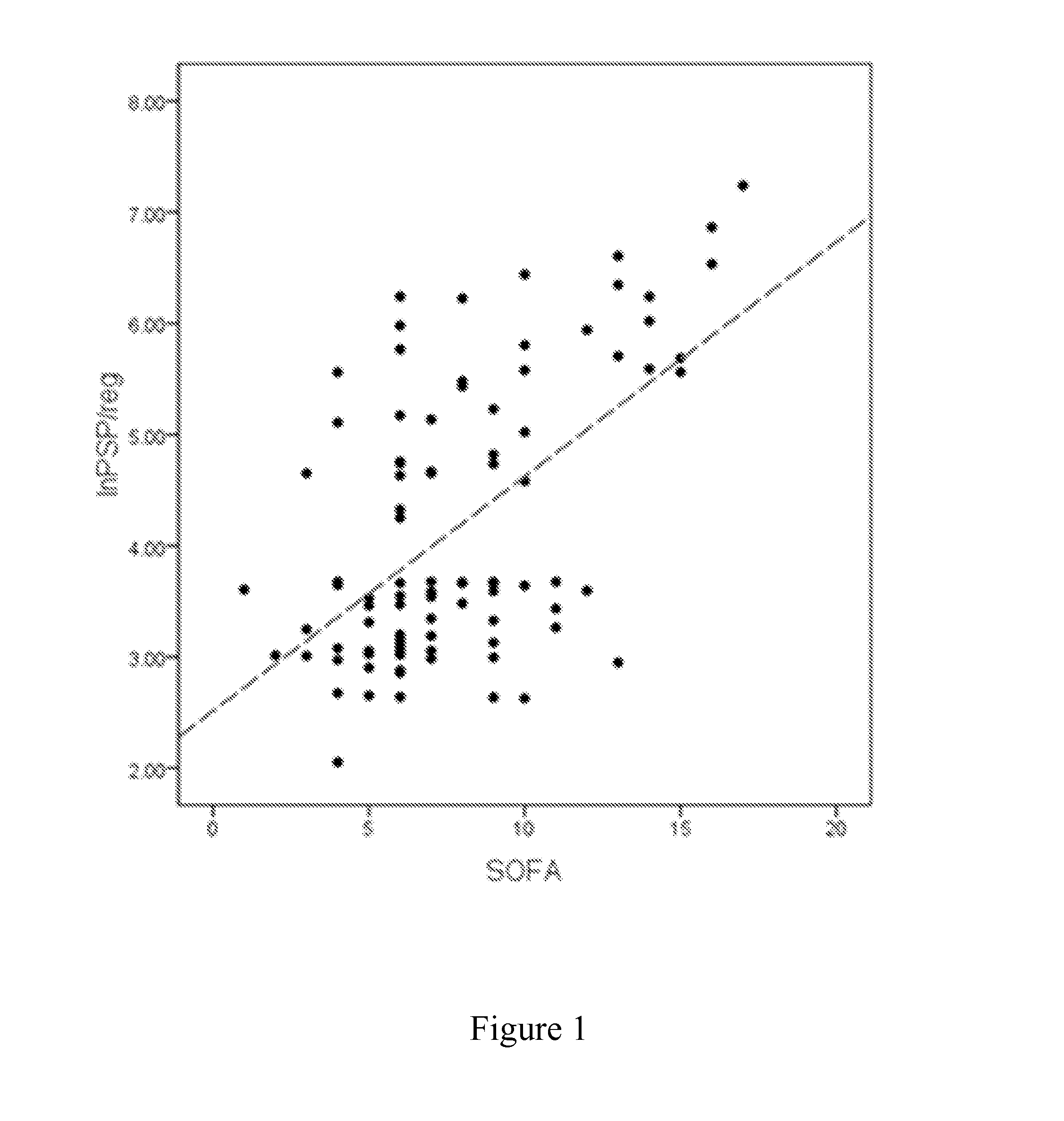
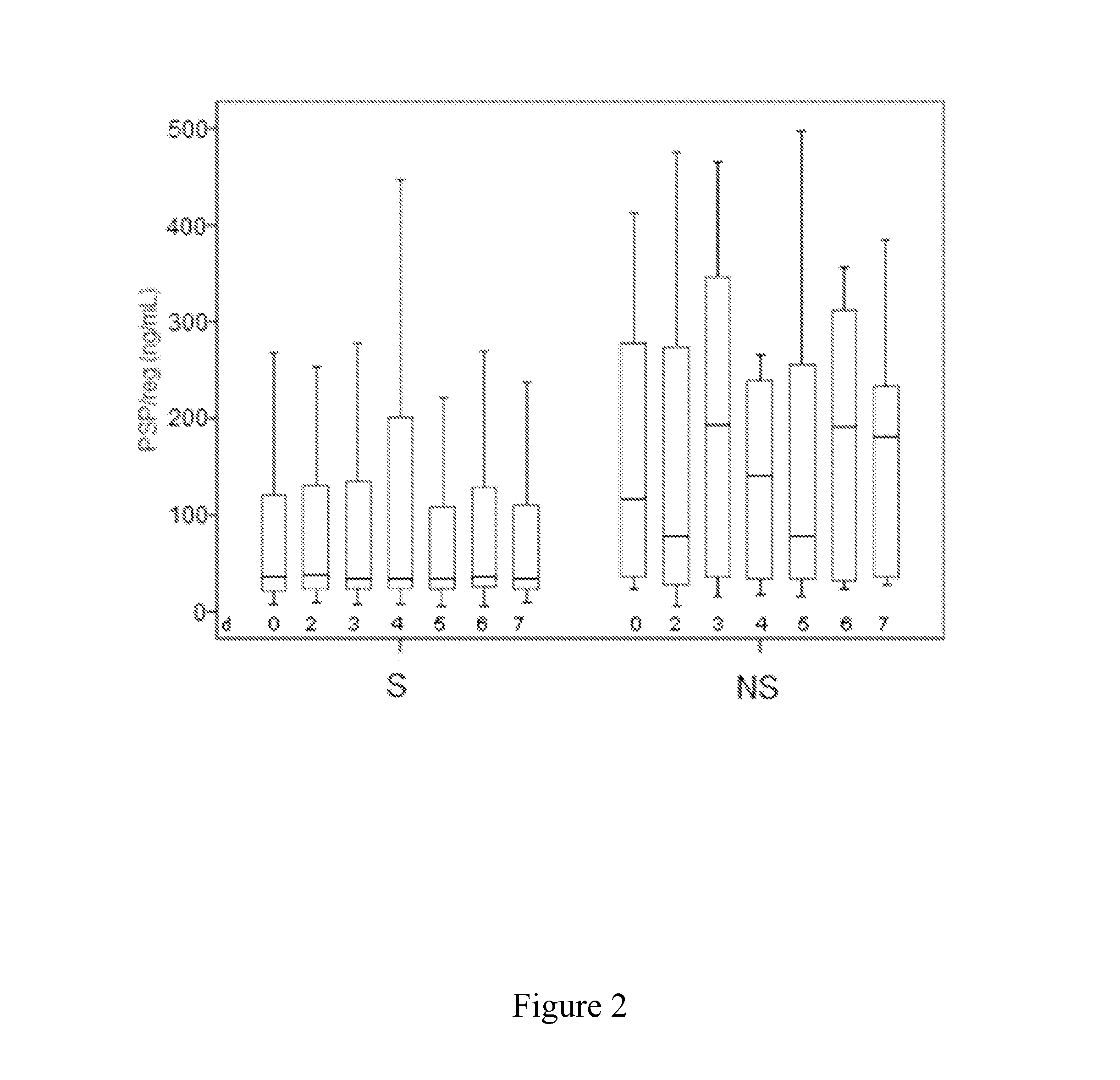
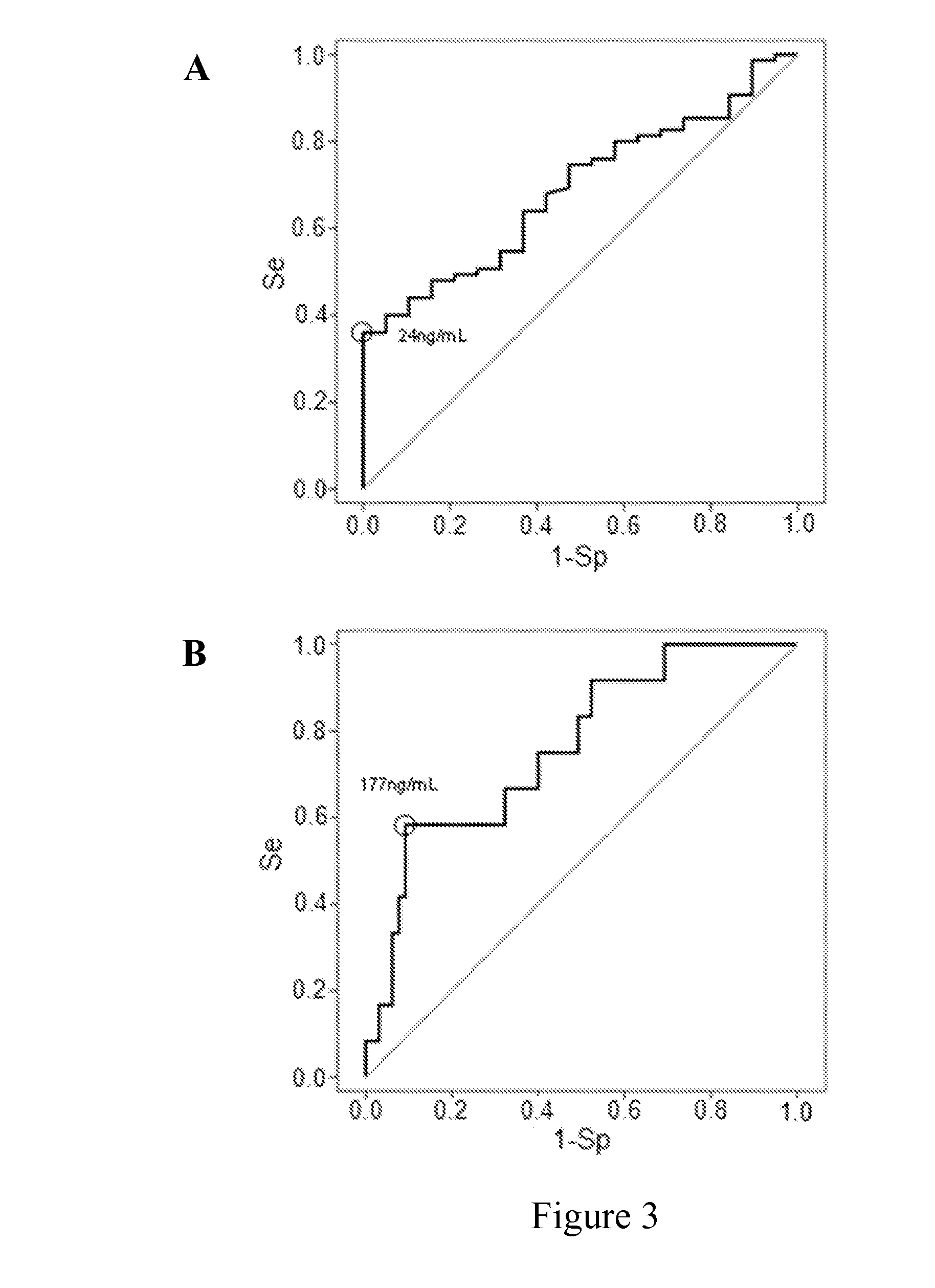
[0055]It has been investigated whether PSP / reg is predictive for survival in ventilator associated pneumonia.
Test Patients
[0056]The study included 101 patients (mean age, 56 years) with clinically diagnosed VAP. Patients deceased within 28 days were classified as non-survivors (NS). PSP / reg levels and sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) scores were obtained on the day of VAP-onset and for 10 consecutive days. Detailed baseline characteristics for survivors and non-survivors are summarized in Table 1. Despite high antibiotic pre-treatment within 14 days prior to study inclusion (75%), respiratory specimens identified a causative organism in 74 patients (76%). The most frequent pathogens were Staphylococcus aureus (30%), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (25%) and Klebsiella species (13%). Appropriate initial antibiotic therapy, defined as a regimen combining an aminoglycoside or a fluoroquinolone plus a betal...
example 2
PSP / reg is Increased in Acute Exacerbations of COPD with Positive Sputum Culture
[0063]It has been investigated whether serum and plasma PSP / reg is increased in acute exacerbations of COPD and whether PSP / reg detects positive sputum in COPD.
Test Patients
[0064]200 patients admitted to hospital for acute exacerbation of COPD were examined and were followed up for 2 years. The short and long term follow-up visits were performed 14-18 days, 6 months and 2 years after hospital admission, and comprised clinical, laboratory and lung function assessments. Clinical outcome data were obtained from medical records from hospital admission and family physicians. Patients were classified as clinical success or clinical failure. Clinical failure was defined by the occurrence of an exacerbation of COPD requiring hospitalisation or death of any cause. For survival analysis all patients were classified as survivors or non-survivors after two year follow-up. All cause mortality was assessed at 6 months...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com