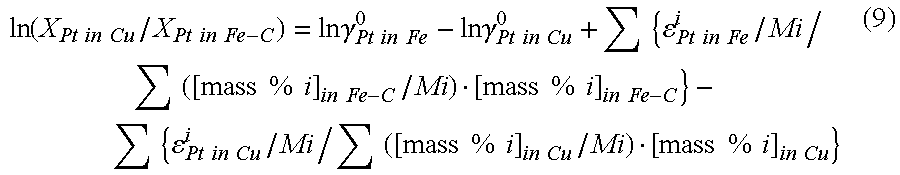Method for efficiently recovering platinum group elements from copper-iron scrap
a platinum group element and scrap technology, applied in the field of efficiently recovering platinum group elements from copper iron scrap, can solve the problems of difficult selection of an efficient process for platinum, large amount of acid, and difficulty in actual practice for recovering platinum from molten iron phase, and achieve efficient recovery of platinum group elements, high distribution ratio, and efficient concentrating of platinum group elements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
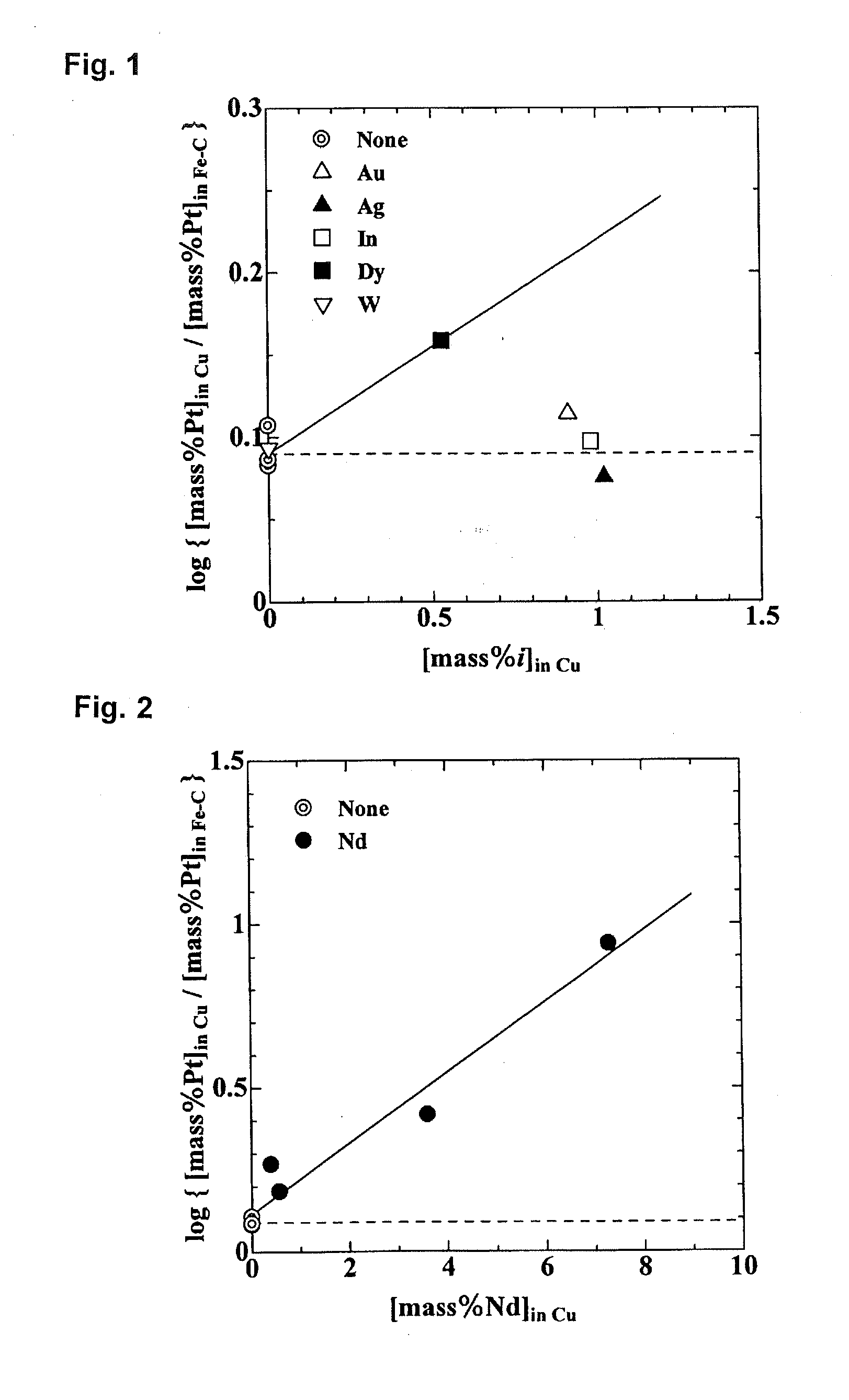
[0084]5 grams of C-saturated Fe, 5 grams of Cu, and 0.05 grams of Pt were placed into a graphite crucible. In each experiment, under conditions in which from 0.7 to 1 gram of Au, Ag, In, Dy, or W was or was not added, the mixture was melted at 1823 K using an electric furnace in an atmosphere containing 100 ml / min of Ar (converted to standard conditions) and held for 2 hours. The sample was then removed from the furnace and cooled by blowing Ar gas.
[0085]Table 3 shows the concentration of added element i in the copper phase [mass % i]in Cu and the concentration of added element i in the iron phase [mass % i]in Fe-C in the sample after cooling, the distribution ratio of i in the copper phase / iron phase [mass % i]in Cu / [mass % i]in Fe-C, and the distribution ratio of Pt [mass % Pt]in Cu / [mass % Pt]in Fe-C. The results of experiments in which no element was added are also shown.
TABLE 3Element i———AuAgInDyW[mass % i]in Cu———0.911.020.980.530.001[mass % i]in Fe—C———0.010.0030.0010.180.92...
example 2
[0088]5 grams of carbon-saturated iron, 5 grams of a combination of a copper-neodymium alloy and copper in predetermined different proportions in order to vary the neodymium concentration in the copper, and 0.05 grams of platinum were placed into a graphite crucible. Using an electric furnace, the mixture was melted at 1823 K in an atmosphere of 100 ml / min of argon gas (converted to standard conditions) and held for 2 hours. The sample was then removed from the furnace and cooled by blowing argon gas.
[0089]Table 4 shows the neodymium concentration in the copper phase [mass % Nd]in Cu and the neodymium concentration in the iron phase [mass % Nd]in Fe-C in the sample after cooling, and the distribution ratio of neodymium [mass % Nd]in Cu / [mass % Nd]in Fe-C. FIG. 2 shows the results of plotting this data with the neodymium concentration in the copper phase on the abscissa and the common logarithm of the distribution ratio of neodymium on the ordinate.
TABLE 4[mass % Nd]in Cu0.40.573.597...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com