System for airborne bacterial sample collection and analysis
a technology for airborne bacteria and sample collection, applied in the field of system for collecting and analyzing airborne bacteria or biological particles, can solve the problems of low diagnostic sensitivities, unpleasant and difficult for both healthcare providers and patients, and particularly difficult procedures in some patient populations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Comparison of Performance with Conventional. Systems—Environmental. Sampling
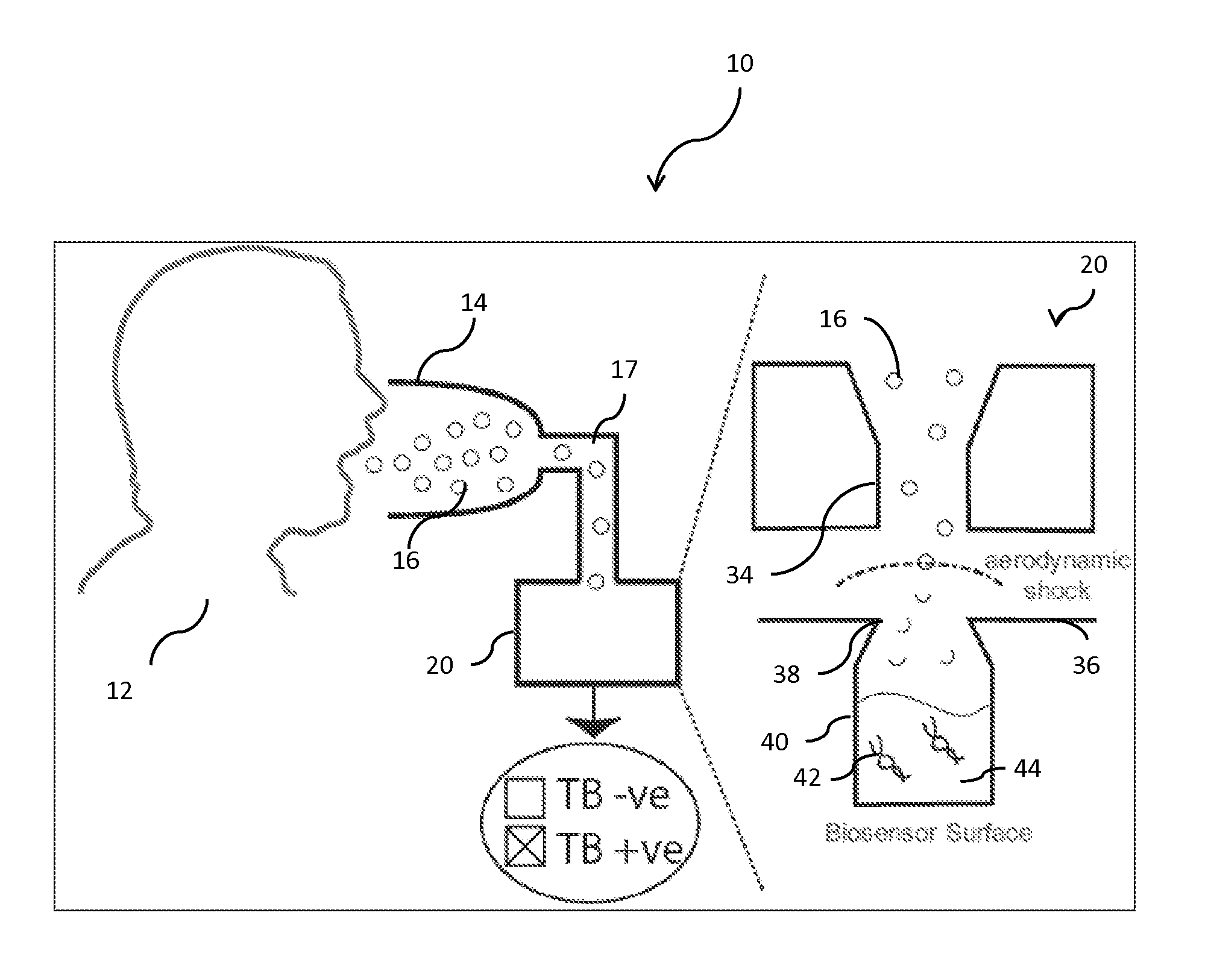
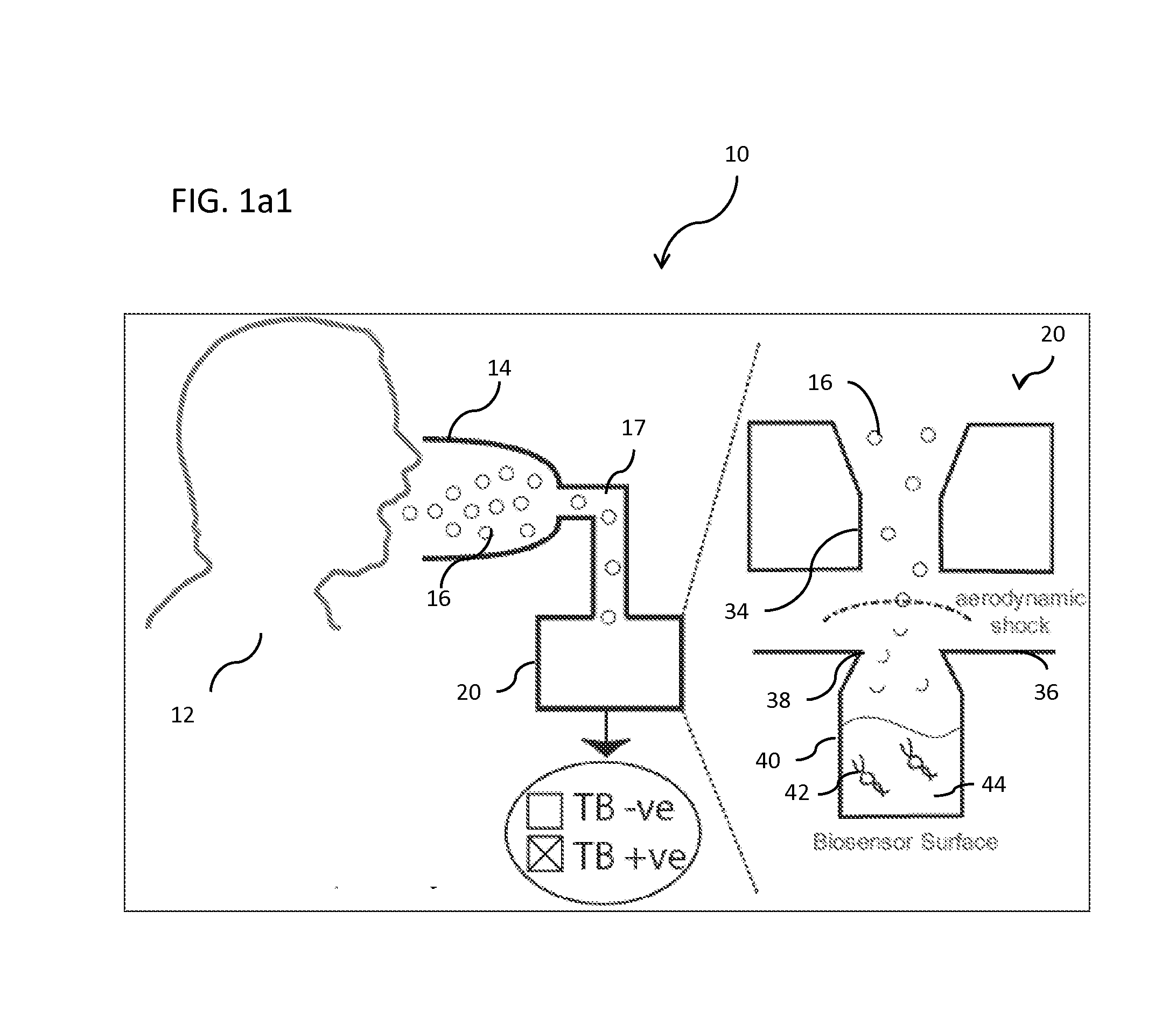
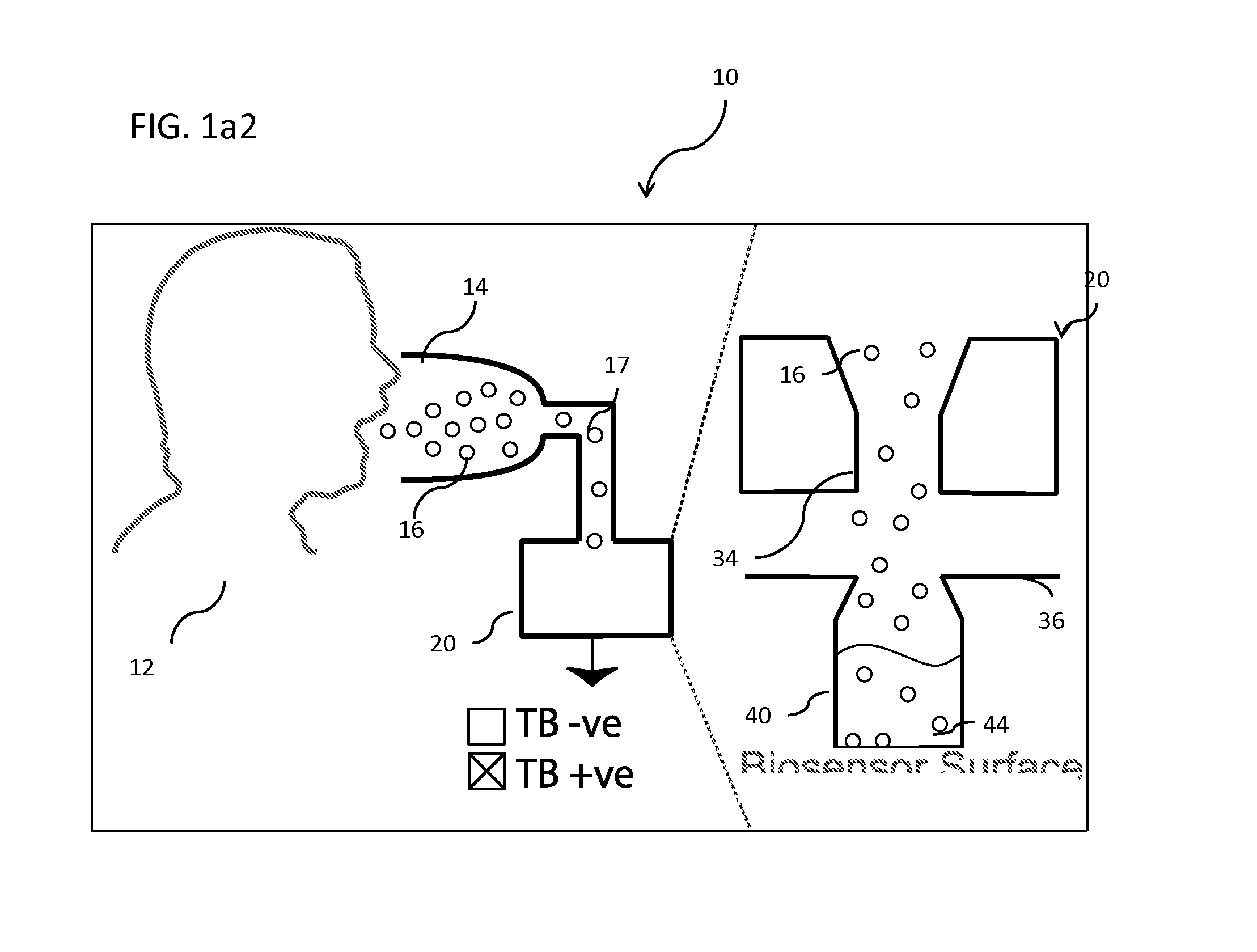
[0076]Turning to a comparison of the operation of the instant invention with that of a conventional aerosol collection and analysis system, it should be understood at the outset that access to the internal components (ICs) of cells, mainly DNA, is necessary for most detection methods. (See, e.g., N. Bao and C. Lu., Principles of Bacterial Detection: Biosensors, Recognition Receptors and Microsystems, pages 817-831. Springer, (2008), the disclosure of which is incorporated herein by reference.) In conventional biosensor systems, as shown in a block-diagram in FIG. 2a, the bacterial aerosol is first collected in a first unit (46), and then lysed (48) in a second unit by either mechanical, heat, chemical, electrical, or laser systems. The lysis products are then purified in subsequent units (not shown) to deliver the target molecules to a suitable sensor. (For FIGS. 2a and 2b it should be noted that the shaded ...
example 2
Study of Cell Break-Up
[0086]Studies have been conducted using the experimental apparatus described in Example 1, above, to show that airborne bacteria passing through an aerodynamic shock breaks-up by experiencing a relative deceleration because of sharp changes in the gas velocity. An aerodynamic shock is created by operating the impactor nozzle at sonic velocity when χ=P1 / P01 is the pressure downstream and P0 is the pressure upstream of the nozzle). Uncontrolled instabilities in the form of waves on the surface of the bacterium perpendicular to the direction of acceleration cause bacterial cells to break-up. The critical acceleration ac is given by:
ac=4π2σρpdp2[EQ.3]
where σ is the surface tension of the bacterium, dp is the diameter of the bacterium, and ρp is the density of the bacterium. (See, e.g., D. D. Joseph, et al. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 25(6-7):1263-1303, (1999); Sislian (2009) & Sislian (2010), the disclosure of each of which are incorporated herein by ...
example 3
Methods of Measuring DNA Collection Efficiency
[0089]The experimental setup provided in Example 1, can also be used to measure the collection efficiency (ηd) of the system. In such an experiment, the bacterial suspension would be aerosolized using a capillary nebulizer (TR-30-A1, Meinhard Glass Products) at a Nitrogen flow-rate of 0.2 mL / min. The suspension concentration and flow-rate will be controlled to produce single bacterial cells in the aerosol.
[0090]E. coli will be used as the test aerosol because (1) it does not require biosafety chambers and (2) is easily cultured and washed. In addition, S. pneumoniae is a vegetative bacterium expected to have an ac similar to E. coli vs. B. atropheus spores and hence a similar value of ƒ. The ds-DNA (double stranded) in our samples will be stained with PicoGreen fluorescent dye (P11495, Life Technologies) using the protocols provided by the manufacturer and in other work. (See, W. Martens-Habbena and H. Sass, cited above.)
[0091]Quantitati...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com