Diagnosis of melanoma and solar lentigo by nucleic acid analysis
a nucleic acid analysis and melanoma technology, applied in the field of diagnosis of melanoma and solar lentigo by nucleic acid analysis, to achieve the effect of less trauma
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
RNA Quantitation and Profiling
[0102]The core hypothesis of this study is that epidermal cells overlying in situ or invasive melanoma, including but not limited to the stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, and stratum granulosum, can be recovered by adhesive means and that the quality and quantity of gene expression in the form of RNA contained within this sample is differently expressed than from a nearby epidermal sample, i.e. that the sampled RNA is diagnostic because of the underlying melanoma. It has been previously shown that changes in gene expression of specific genes are detectable in epidermal hyperplasia overlying cutaneous human melanoma samples obtained from surgical specimens of the epidermis (McCarty et al., 2003).
[0103]The present study is divided into two separate phases, a sample collection and characterization phase (phase 1) and an RNA profiling phase (phase 2). In phase 1 the tape stripped specimens and biopsied sample collections were performed by the principal inve...
example 2
Preliminary Power and Sample Size Studies
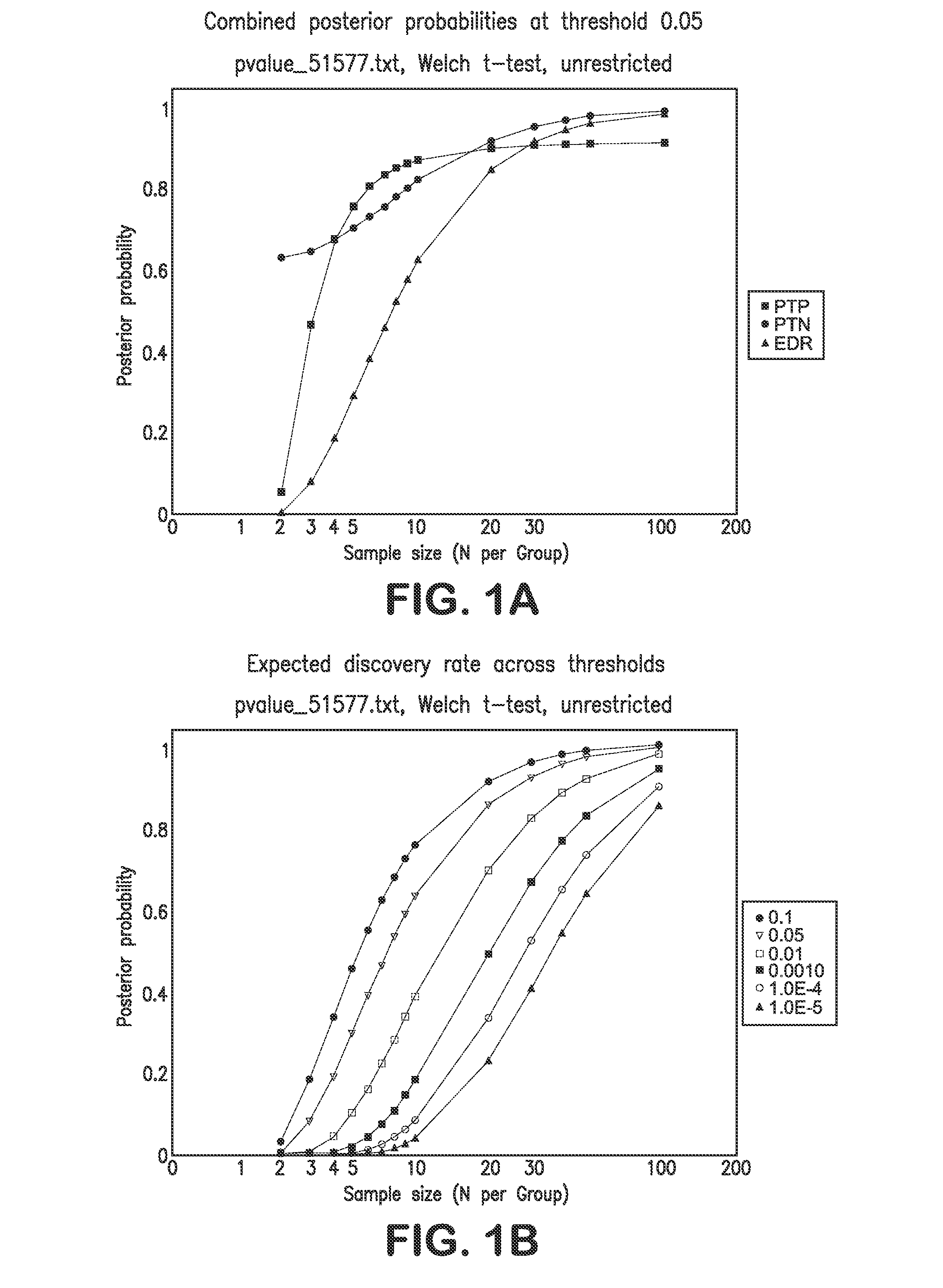
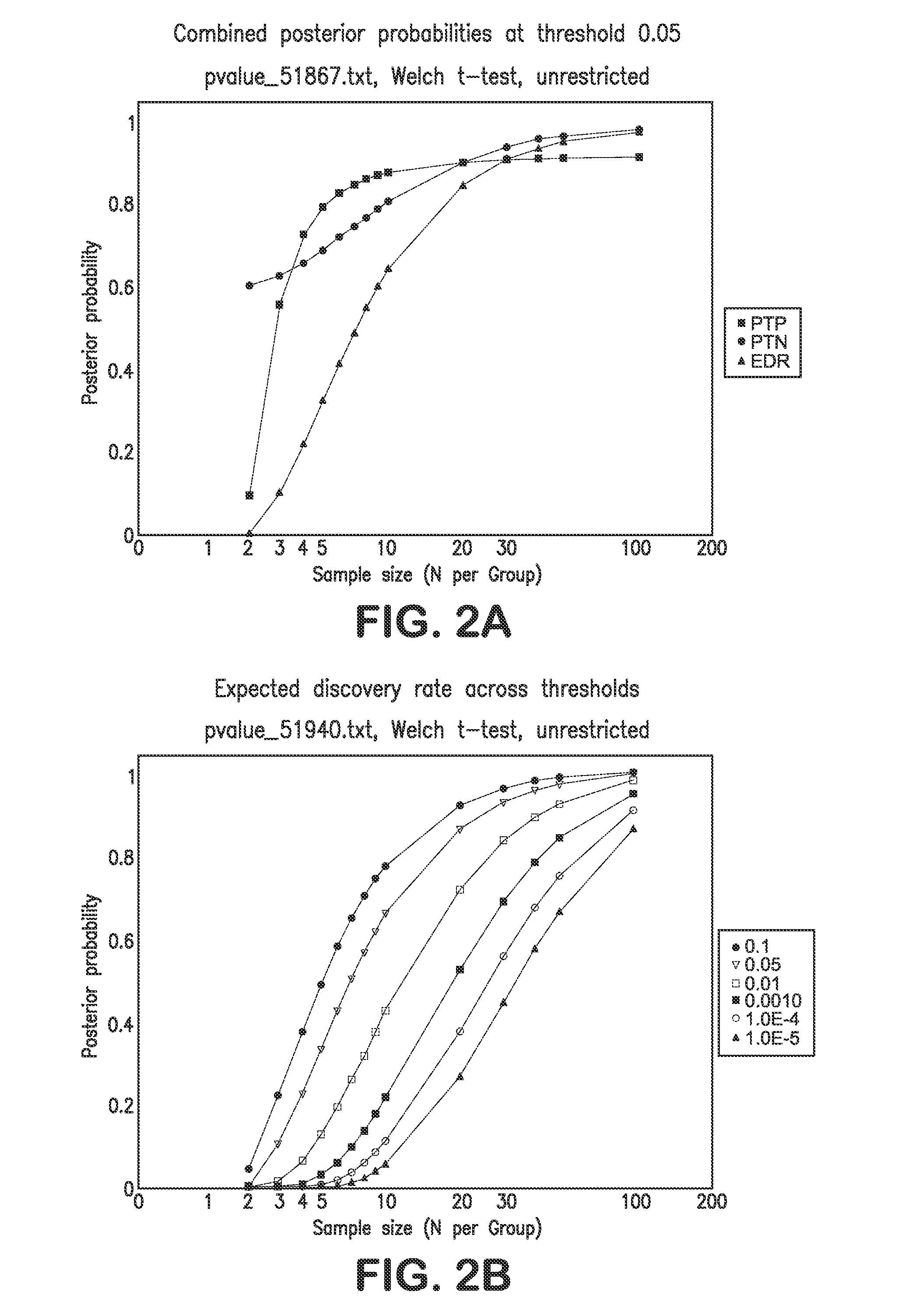
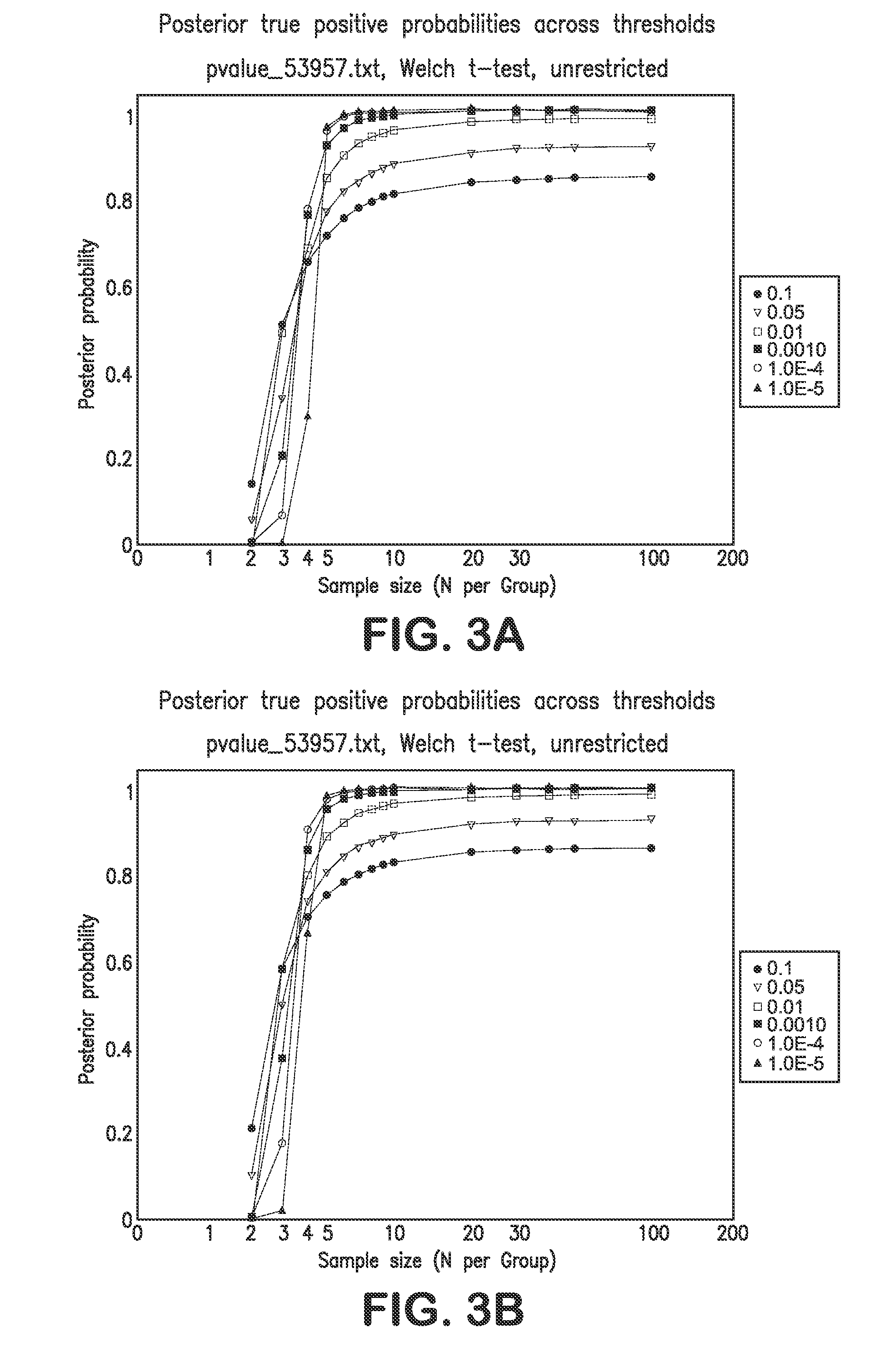
[0134]Nevi vs. Primary Melanoma
[0135]The following sample size and power calculations are based exclusively on the large-scale cDNA study data provided in Haqq et at (2005). That data focused on normal skin (n=3 samples), nevi (n=9), primary melanomas (n=6) and metastatic melanomas (n=19). For purposes of the sample size calculations, the focus was on the comparison of nevi to primary melanomas. Power and sample size assessments were calculated based on the bootstrap strategy outlined by Page et al. Using the raw data available from the Haqq et at (2005) study, gene expression differences—based on all 14,772 probes used in their cDNA assay—between nevi and primary melanomas were computed using simple t-tests for each probe / gene. Note that multiple probes can be used interrogate individual genes. In addition, normal skin, nevi, and primary melanoma gene expression differences were also assessed in a three group analysis of variance (ANOVA), wi...
example 3
Tape Stripping to Recover Nucleic Acids from Normal Skin
[0144]The following procedure was used to recover nucleic acids from normal skin (e.g., the mastoid or upper back areas) of a subject.
[0145]Tapes were handled with gloved hands at all times. Locate a particular site that is relatively blemish-free and healthy, unless otherwise specified by the protocol. Preferred normal skin sites are the mastoid process (the bony process behind the ear at the base of the skull) and the upper back, immediately superior to the scapular spine. Shave the site if necessary to remove non-vellus hairs. Cleanse the site with an alcohol wipe (70% isopropyl alcohol). Let the site air dry completely before application of the tape. It is recommended to wait approximately 2 minutes to ensure the site is completely dry before application of the tape.
[0146]Apply the tape to the skin site. If more than one tape is used, apply tapes in sequential order starting from the left side. Use a surgical skin marker an...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| median survival time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| median survival time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com