Bi-component fiber for the production of spunbonded fabric
a technology of fibers and fibers, applied in the field of bicomponent fibers, can solve the problems of additives that can affect the production process, additives can be associated with high costs, additives can be health or environmental hazards, etc., and achieve the effects of improving the softness and/or surface feel of the spunbond fabric, improving the spinning stability and expandability of the fibers, and improving the solidification of the material
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
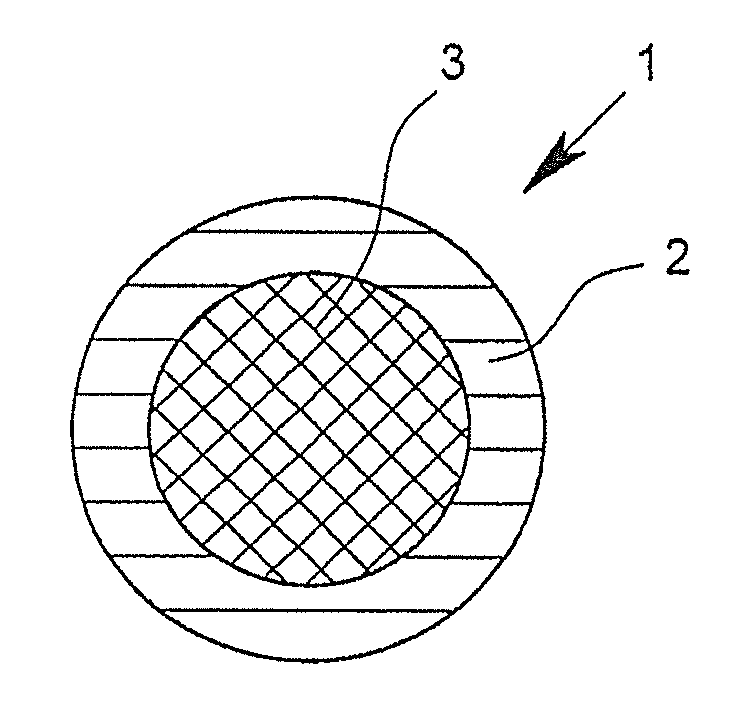
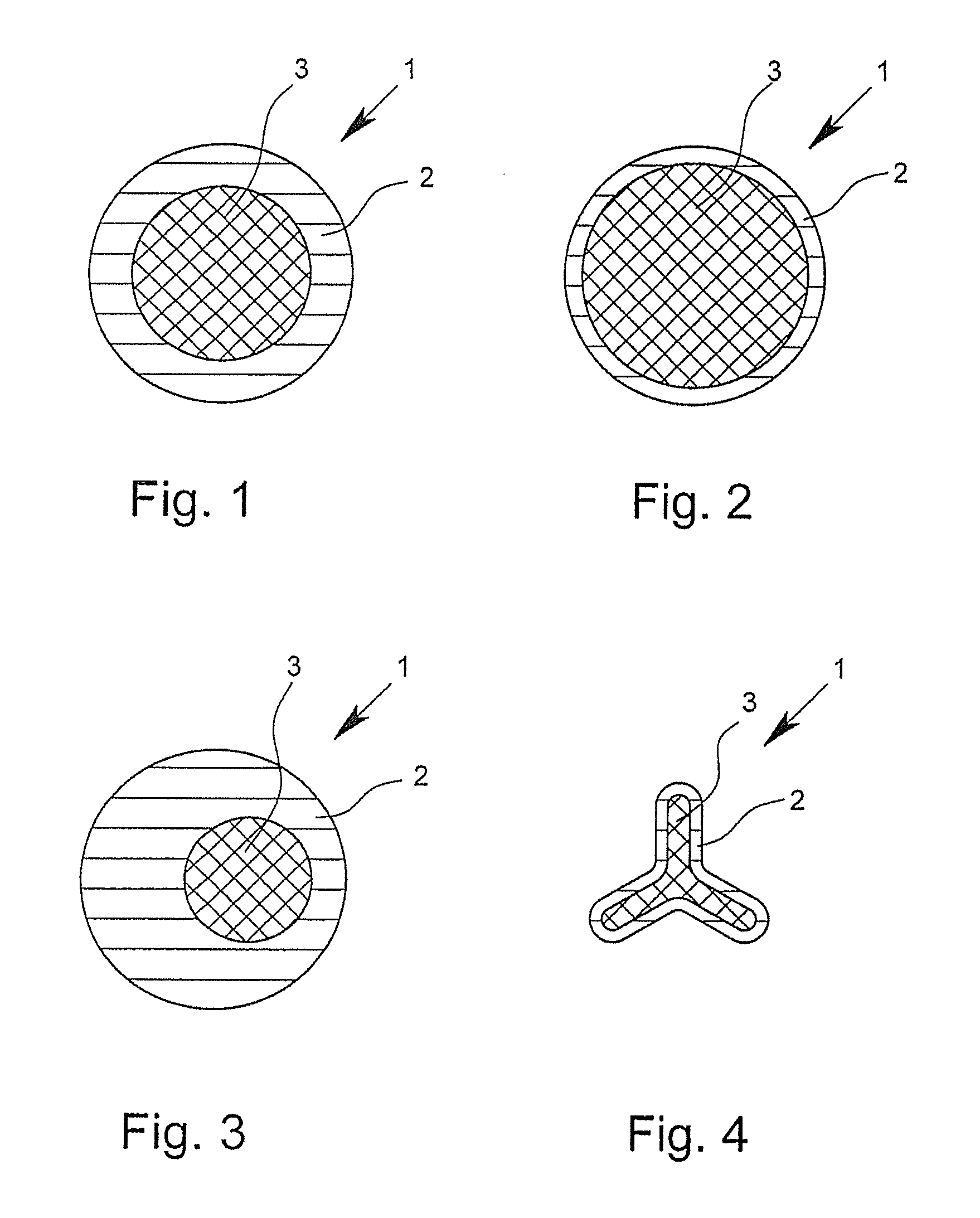
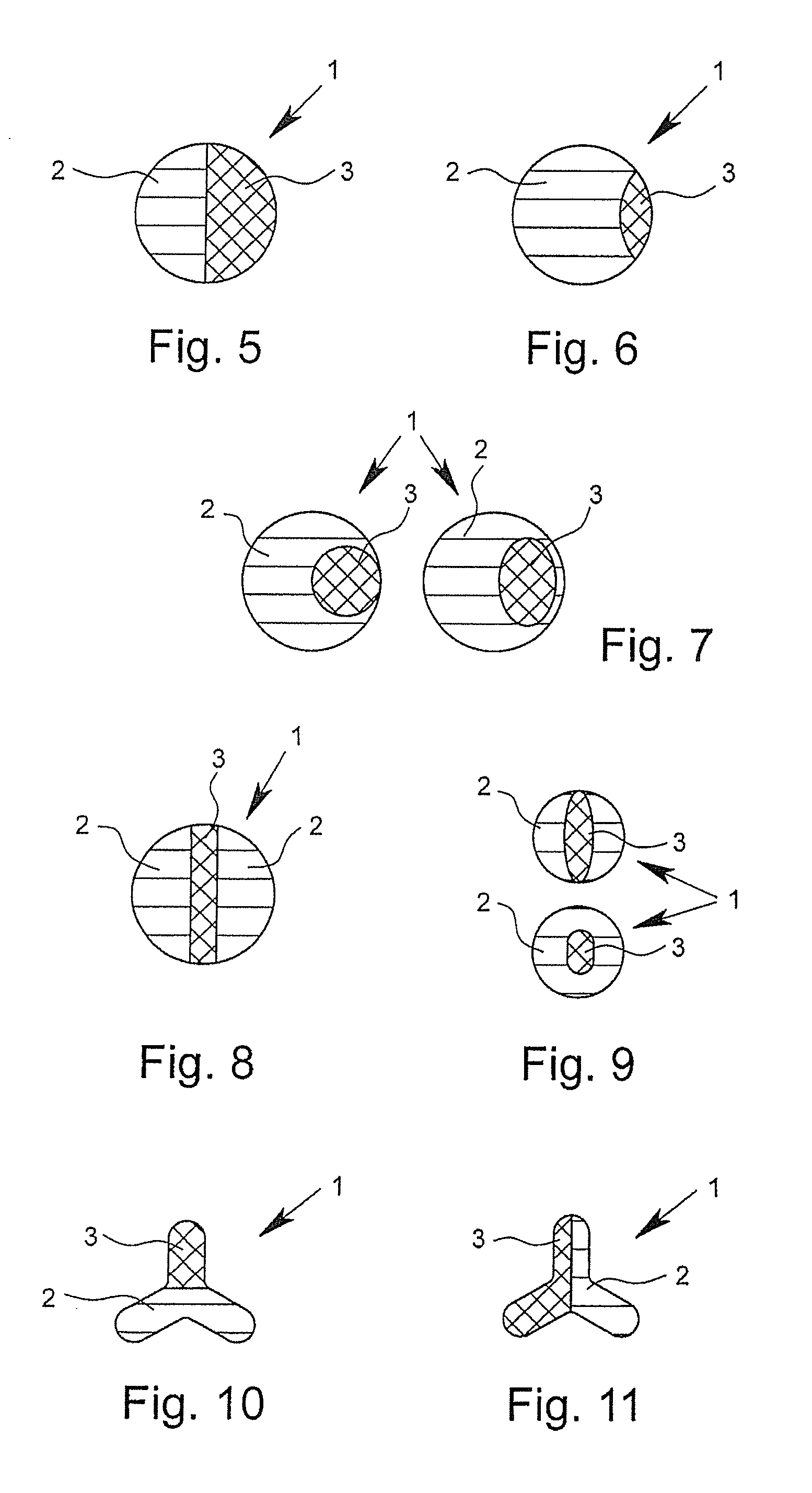
[0093]FIGS. 1 to 16 show cross-sectional views of bi-component fibers 1 according to the invention by way of example. The depicted bi-component fibers 1, in each case, have a first component 2 and a second component 3. In the core-sheath fibers depicted in FIGS. 1 and 4, in this case, the first component 2 surrounds the second component 3 and thus forms the outer surface of the fiber. In this case, the bi-component fibers 1 depicted in FIGS. 1 to 3 have an at least approximately circular or round geometry in cross-section. The bi-component fiber depicted in FIG. 4 shows, however, a trilobal cross-section. Such trilobal cross-sections, like other multilobal cross-sections as well, have the effect that the fiber has a larger outer surface in relation to its mass than is the case with fibers with a circular cross section. In the case of “core-sheath fibers,” in which the proportion of the components forming the sheath is very small, for example approximately 2%, but certainly even in “...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting points | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting points | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting points | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com