Animal feed amendments for lowering ammonia concentrations in animal excrement
a technology of animal excrement and ammonia concentration, which is applied in the field of animal feed and/or water amendments, can solve the problems of aggravated ammonia in cattle excrement, negative impact on animal health and production, and increased susceptibility to bacterial respiratory infection, so as to reduce gaseous ammonia concentration and high usefulness. , the effect of good
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 3
Preparation of Tetrapolymer Partial Salts
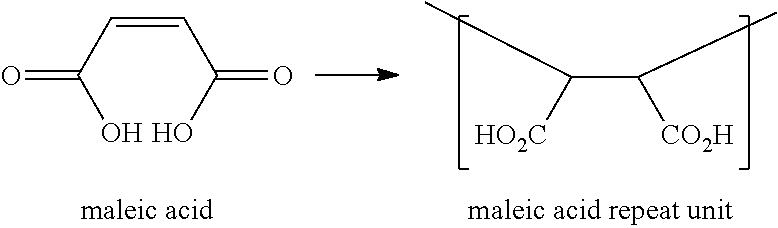
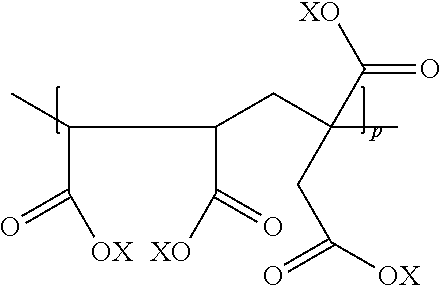
[0075]A tetrapolymer partial sodium salt dispersion containing 40% by weight copolymer solids in water was prepared by the preferred free radical copolymerization synthesis of the invention, using an aqueous monomer reaction mixture having 45 mole percent maleic anhydride, 35 mole percent itaconic acid, 15 mole percent methallylsulfonate sodium salt, and 5 mole percent allylsulfonate. The final tetrapolymer dispersion had a pH of slightly below 1.0 and was a partial sodium salt owing to the sodium cation on the sulfonate monomers. At least about 90% of the monomers were copolymerized in the reaction.
[0076]This sodium partial salt tetrapolymer was used to create a series of 40% solids in water partial salts. In each instance, apart from the sodium present in the tetrapolymer mixture, appropriate bases or base precursors (e.g., carbonates), or mixtures thereof were added to the aqueous tetrapolymer at room temperature to generate the correspond...
example 4
Exemplary Synthesis
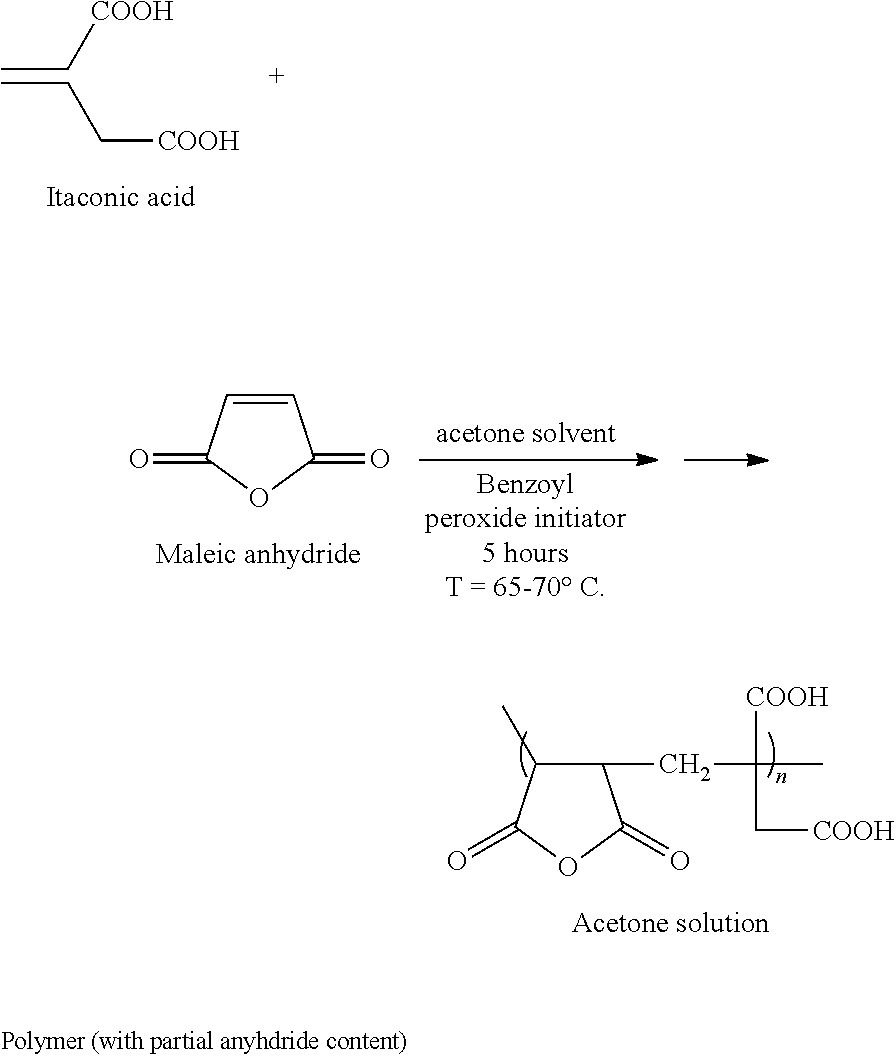
[0088]A terpolymer salt dispersion containing 70% by weight copolymer solids in water was prepared using a cylindrical reactor capable of being heated and cooled, and equipped with an efficient mechanical stirrer, a condenser, a gas outlet open to the atmosphere, respective ports for charging liquids and solids to the reactor, a thermometer, and a peroxide feeding tube.
[0089]Water (300 g) was charged into the reactor with stirring and heating to a target temperature of 95 C. During heating, itaconic acid, sodium methallylsulfonate, and maleic anhydride were added so as to make a 75% w / w solids dispersion with the following monomer mole fractions: maleic anhydride-20%; itaconic acid-60%; methallylsulfonate sodium salt-20%. When the monomers were initially added, they were in suspension in the water. As the temperature rose, the monomers became more fully dissolved before copolymerization was initiated, and the maleic anhydride was hydrolyzed to maleic acid. When th...
example 1
Poultry
[0100]Twenty broiler chickens of common variety were separated into two groups denoted “A” and “B,” with group A being the research group, and B being the control group. The chickens were placed into conventional chicken coops made of wire and wood, with typical litter on the floor trays of the coops. Heat lamps were attached to each coop at identical locations, along with a gravity-fed one-gallon water container and a gravity-fed feeder. Plastic sheeting was placed over the coops in order to trap volatilizing ammonia with open-ventilation at the front and sides of the coops. The birds had access to water and feed during all daylight hours.
[0101]During the test, both the A and B groups were fed Purina Flock Raiser premium quality poultry feed. However, feed for the group A chickens was supplemented with 0.25% (w / w) of the previously described MTM® copolymeric material, and the Group A water was also supplemented with 0.5% (v / v) of the MTM® material.
[0102]During the course of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com