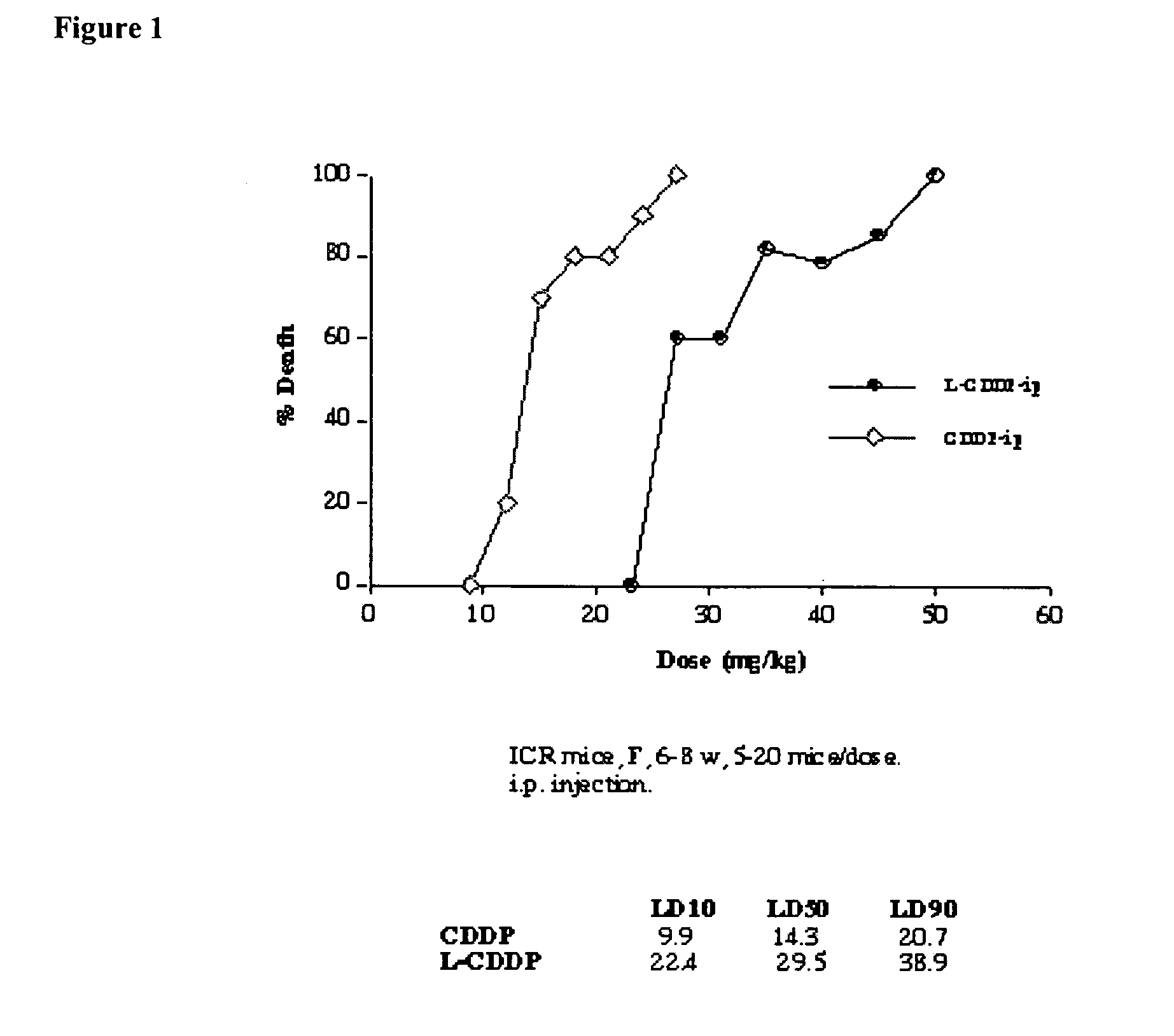
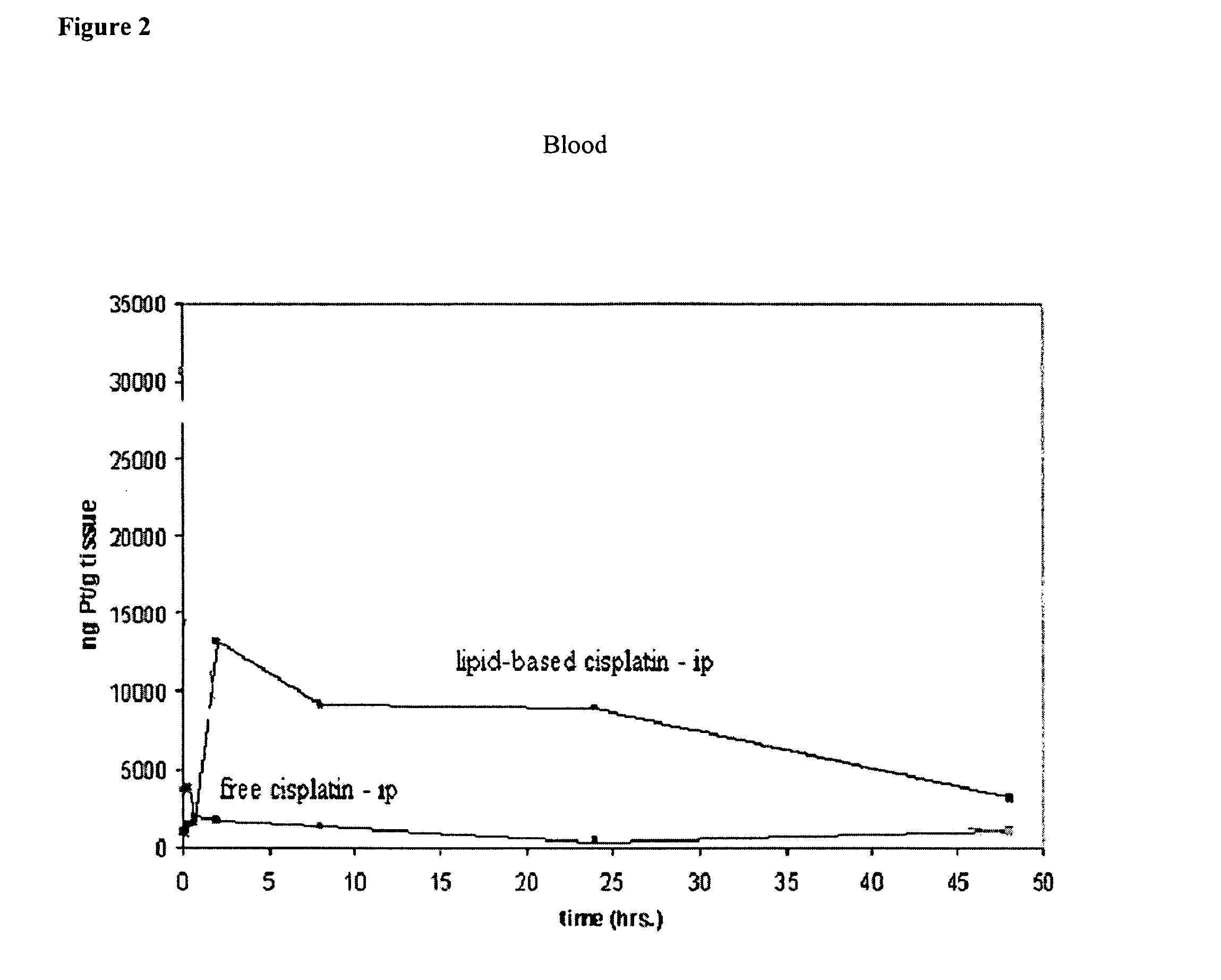
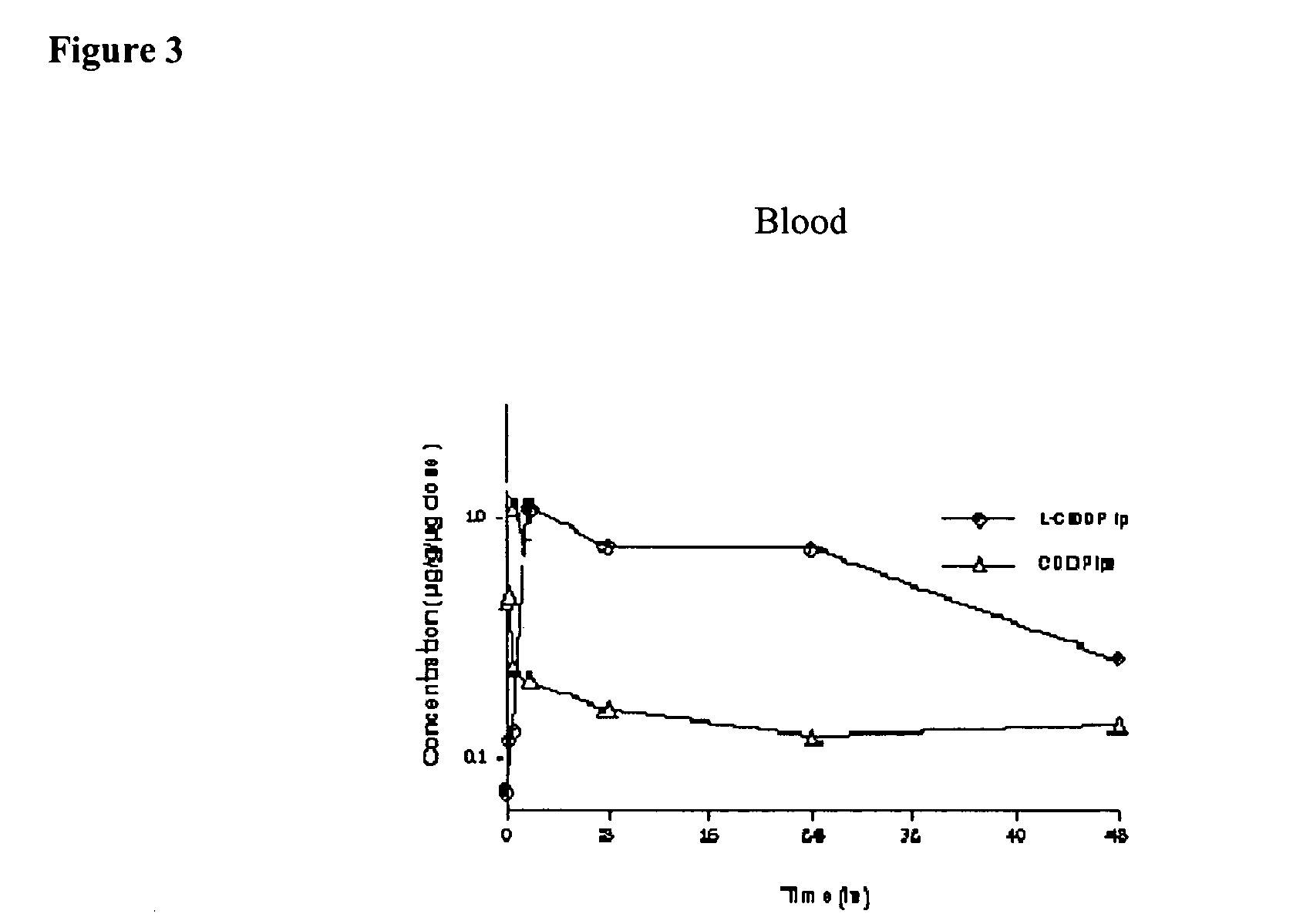
Methods of treating cancer with high potency lipid-based platinum compound formulations administered intraperitoneally
a technology of lipid-based platinum and compound formulations, which is applied in the direction of heavy metal active ingredients, organic active ingredients, drug compositions, etc., can solve the problems of dose-limiting factor, high toxicity of active platinum compounds such as cisplatin, and extreme nephrotoxicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Method of Producing an Aqueous Cisplatin with Higher Potency than its Aqueous Solubility Limit at Room Temperature
[0112]1) At temperatures about 50-60° C., cisplatin in 0.9% sodium chloride solution at a level of 4 mg / ml and an ethanolic solution of about 16 mg / ml DPPC and 8 mg / ml cholesterol at about 55° C. are aseptically prepared.[0113]2) The lipid solution is infused into the cisplatin solution while mixing the cisplatin solution.[0114]3) After infusion, cisplatin / lipid dispersion is cooled down to about 10° C. and then warmed up again to about 50-60° C. for 15 min.[0115]4) Step 3) is repeated 2-3 times.[0116]5) The dispersion is aseptically washed with sterile 0.9% sodium chloride solution to remove residual ethanol and un-associated cisplatin via 500,000 MW cut-off membrane diafiltration unit.
[0117]After washing process, the dispersion provides about 1 mg / ml cisplatin potency and concentrated to 3 mg / ml cisplatin and further concentrated to 5 mg / ml cisplatin by aseptically rem...
example 2
[0118]70 mg DPPC and 28 mg cholesterol was dissolved in 1 mL ethanol and added to 10 mL of 4 mg / mL cisplatin in 0.9% saline solution.
[0119](i) An aliquot (50%) of the sample was treated by 3 cycles of cooling to 4° C. and warming to 50° C. The aliquot, in a test tube, was cooled by refrigeration, and heated in a water bath. The resulting unentrapped cisplatin (free cisplatin) was washed by dialysis.
[0120](ii) The remainder of the sample was not treated by temperature cycles and directly washed by dialysis.
TABLE 1Percentage entrapment of cisplatin with andwithout cooling and warming cycles.Final Concentration of%cisplatin, μg / mLEntrapmentLipid-complexed cisplatin without561.4cooling and warming cycleslipid-complexed cisplatin after3609.0cooling and warming cycles
example 3
[0121]The rigidity of a membrane bilayer in lipid-complexed cisplatin prepared with cool / warm cycling as described in Example 2 was measured by fluorescence anisotropy of diphenylhexatriene (membrane probe) inserted in the hydrophobic core region of the bilayer. [Ref. Jahnig, F., 1979 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76(12): 6361.] The hydration of the bilayers was gauged by the deuterium isotope exchange effect on fluorescence intensity of TMA-DPH (trimethylamine-diphenylhexatriene). [Ref. Ho, C., Slater, S. J., and Stubbs, C. D., 1995 Biochemistry 34: 6188.]
TABLE 2Degree of hydration and rigidity of liposomes, lipid-complexedcisplatin without and with cool / warm cycling.PlaceboLipid-complexedLipid-complexed(Liposomescisplatincisplatinwithoutwithout cooling &with cooling &cisplatin)warming cycleswarming cyclesDegree bilayer0.290.290.36rigidityDegree of bilayer1.131.151.02hydration
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com