Energy generation from waste heat using the carbon carrier thermodynamic cycle
a technology of thermodynamic cycle and waste heat, applied in the direction of heating fuel, energy-efficient heating/cooling, other heat production devices, etc., can solve the problem of high cost of used h
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
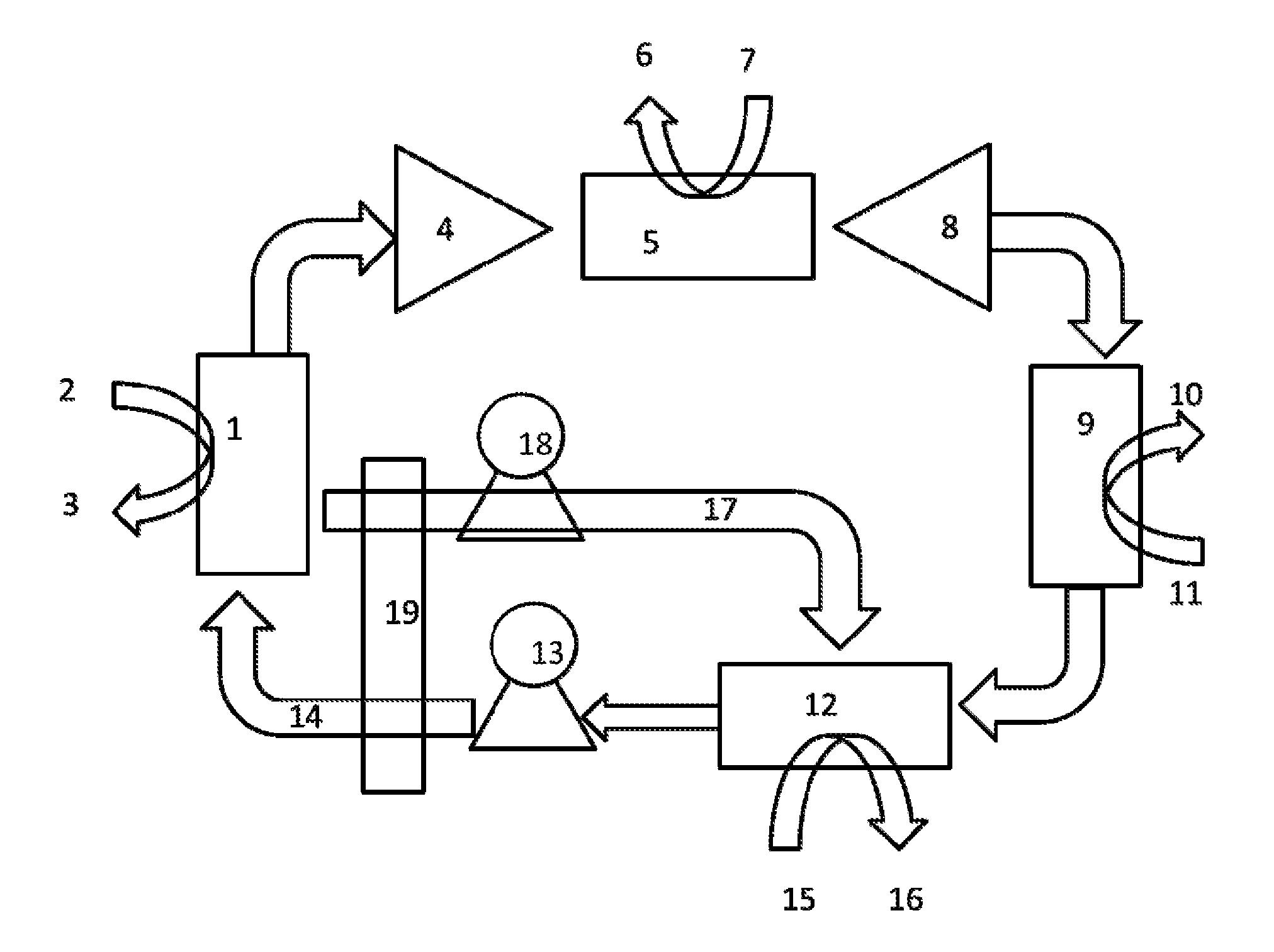
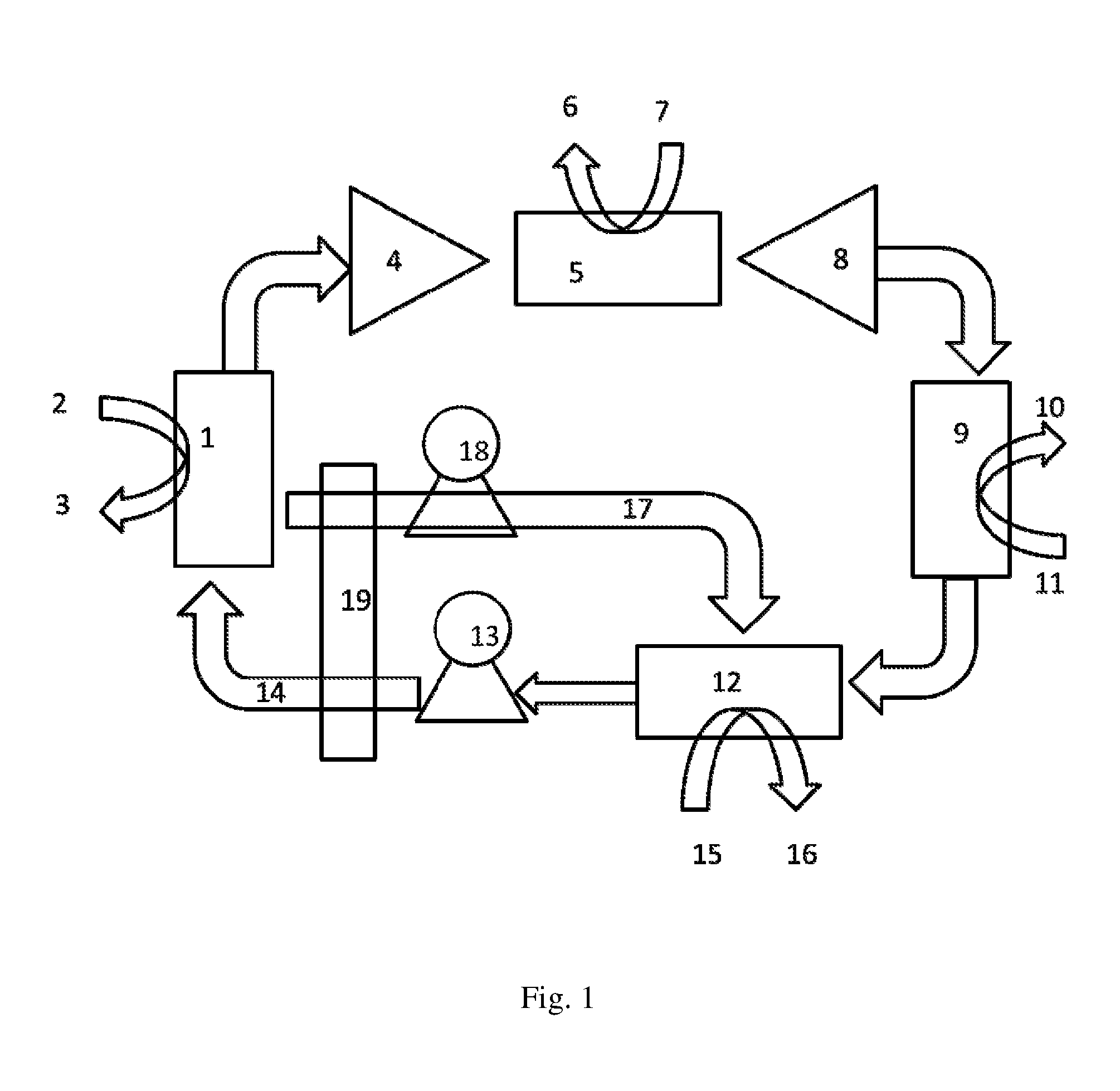
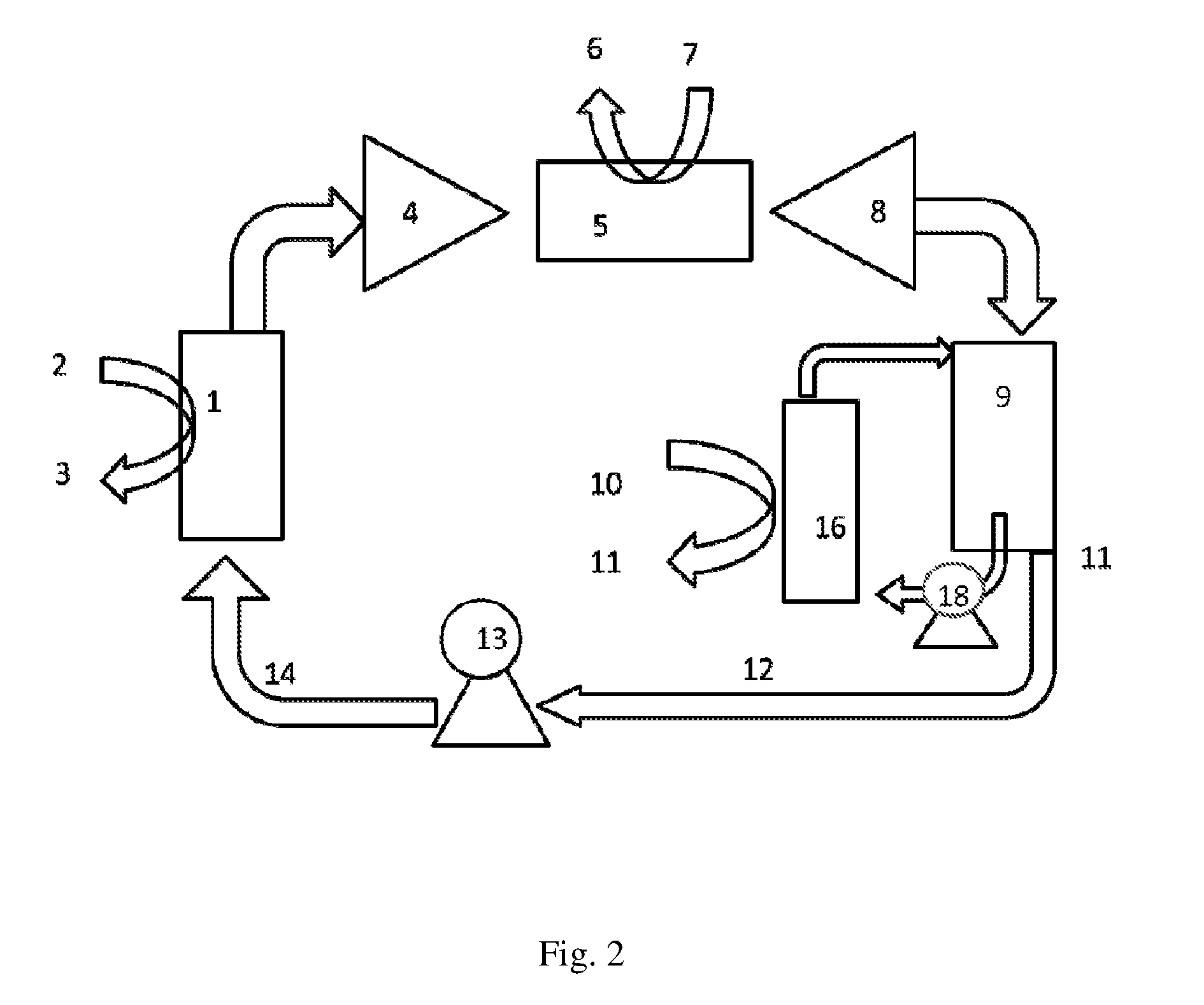
[0026]The heat pump is shown in one embodiment in FIG. 1.
[0027]The heat pump according to the invention operates as follows: heat, e.g. geothermal or waste heat of e.g. 40-70° C., is supplied via heat exchanger (1) (flow in at (2), flow out at (3) to a mixture of CO2 and absorbent (CO2-rich absorbent mix). This mixture, as described in the a.m. disclosures and essentially comprising amines (including ammonia, NH3) and CO2, e.g. in the form of carbonates or carbamates, is pumped using pump (13) into the heat exchanger through pipe (14). In the desorber (1), CO2 gas is desorbed at a pressure dependent on the nature of the absorbent, but typically being 0.3 to 2 bar. CO2 gas is compressed in compressor (4) to a higher pressure, e.g. 5-20 bar, and the CO2 is heated by compression. This heat is extracted in heat exchanger (5), and the heat is transferred to a medium through pipes (6) and (7). The colder gas is expanded through an expansion machine (8) which preferably is mechanically cou...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com