Device and method for storing thermal energy
a technology of thermal energy and storage device, which is applied in the direction of storage heaters, domestic heating details, space heating and ventilation details, etc., can solve the problems of difficult management of lack of uniform consumption, difficult situation, and uniform energy demand emanating from climatic apparatuses, and achieve high thermal diffusivity, reduce the division of pcm, and high degree of porosity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
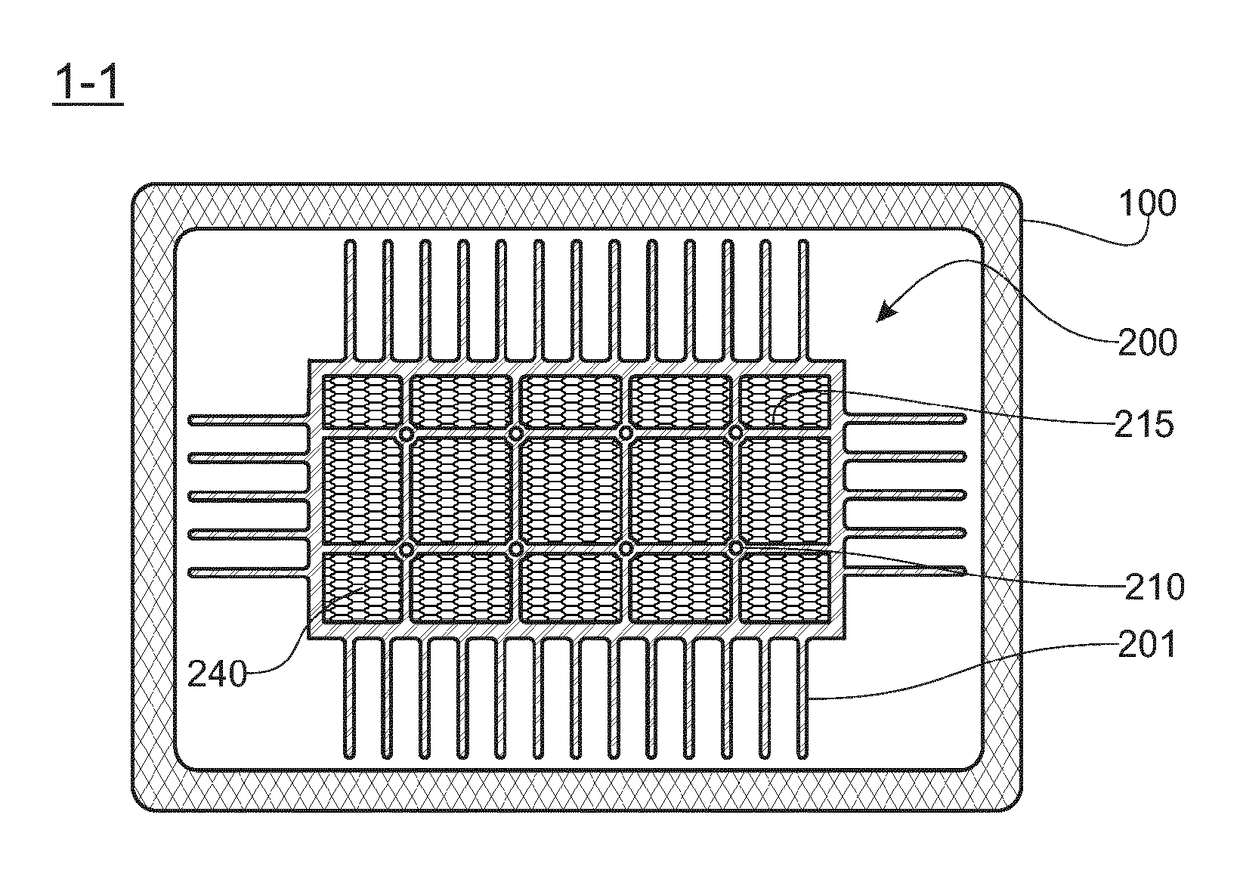
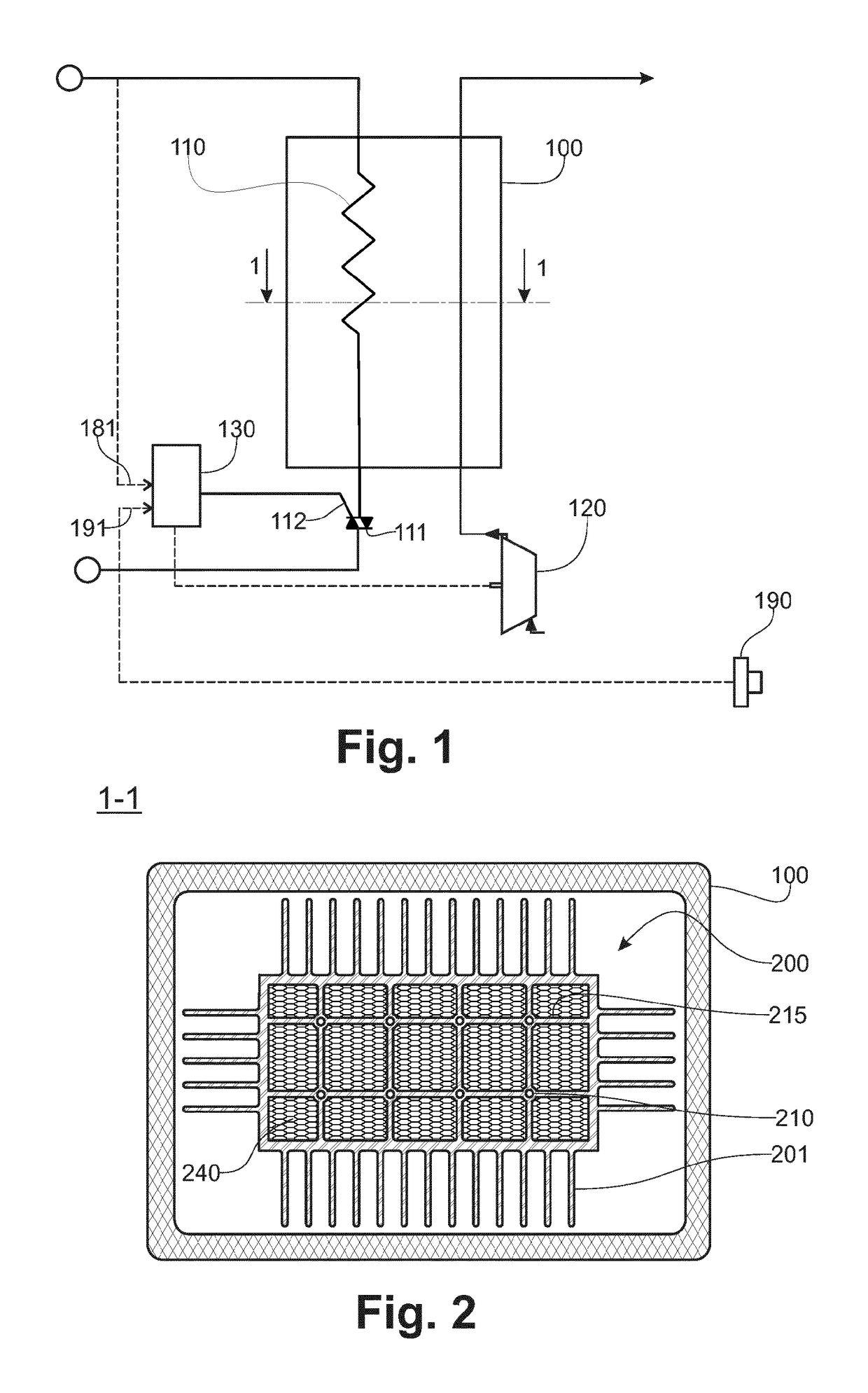
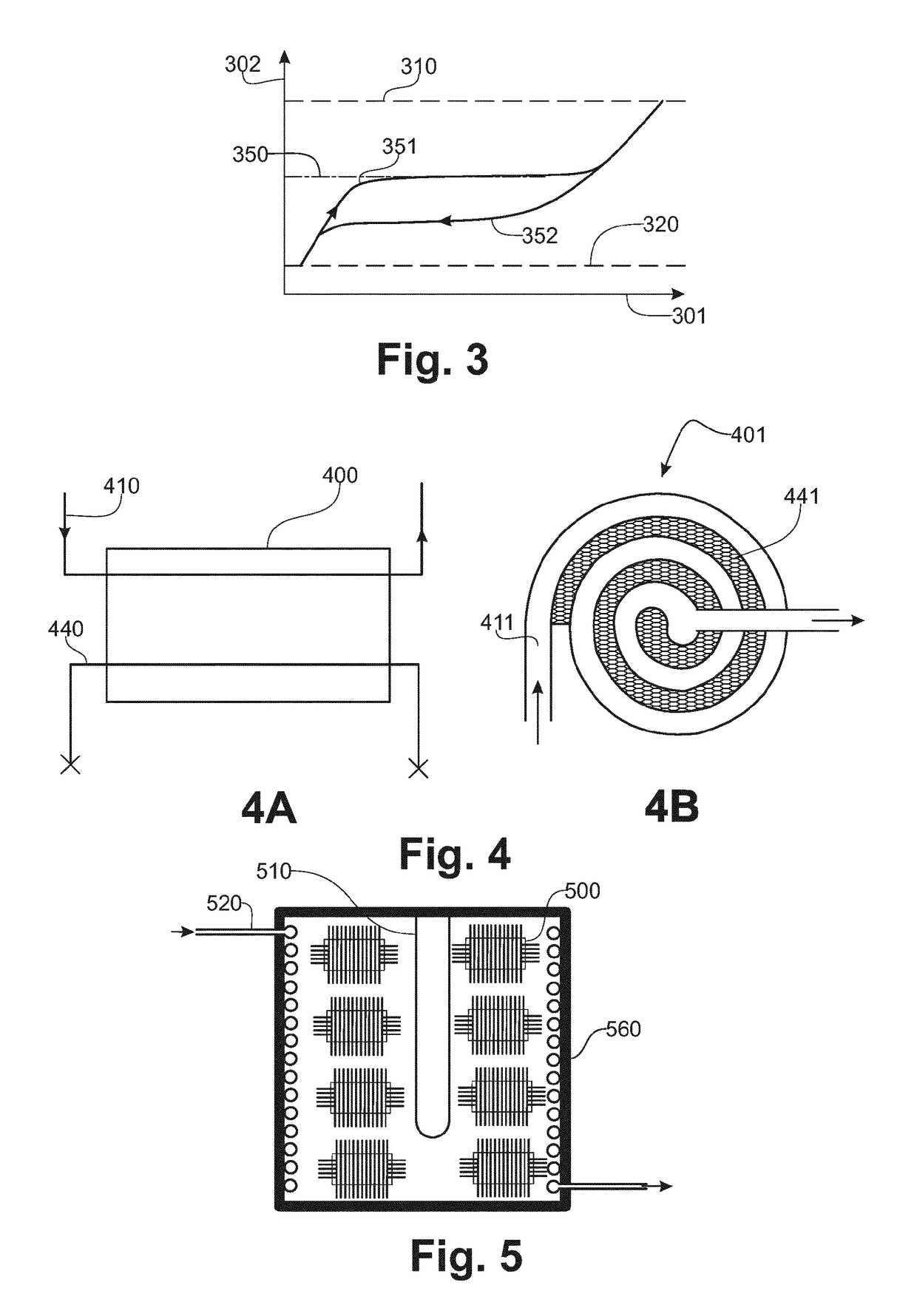
[0062]FIG. 1, according to one schematic implementation and embodiment example of the device that is the subject of the invention, this device comprises a source (110), such as an electric resistance heater, which resistance heater is connected to the electrical network and the operation of which is, for example, controlled by means of a TRIAC (111), the trigger gate (112) of which is controlled by a control device (130). Said control device (130) comprises, according to one exemplary embodiment, computational and memory means, an output interface and an input interface. The trigger gate (112) of the TRIAC (111) is connected to the output interface. According to this exemplary embodiment, the resistance heater (110), when it is supplied with electrical current, heats an energy storage core included in a thermally insulating chamber (100). A turbine (120) makes it possible to blow air into said chamber, so that the air is heated in contact with the energy storage core before being se...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com