Industrial fabric, method for producing a nonwoven, and use of an industrial fabric
a technology of industrial fabric and nonwoven, which is applied in the field of industrial fabric, can solve the problems of inadequate wetting of the polymer dispersion having the bonding properties, the inability to heat the fibers forming the nonwoven web, and the inability to meet the needs of woven fabrics, etc., and achieves the effects of low tendency to adhere, long service life and small fabric thickness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
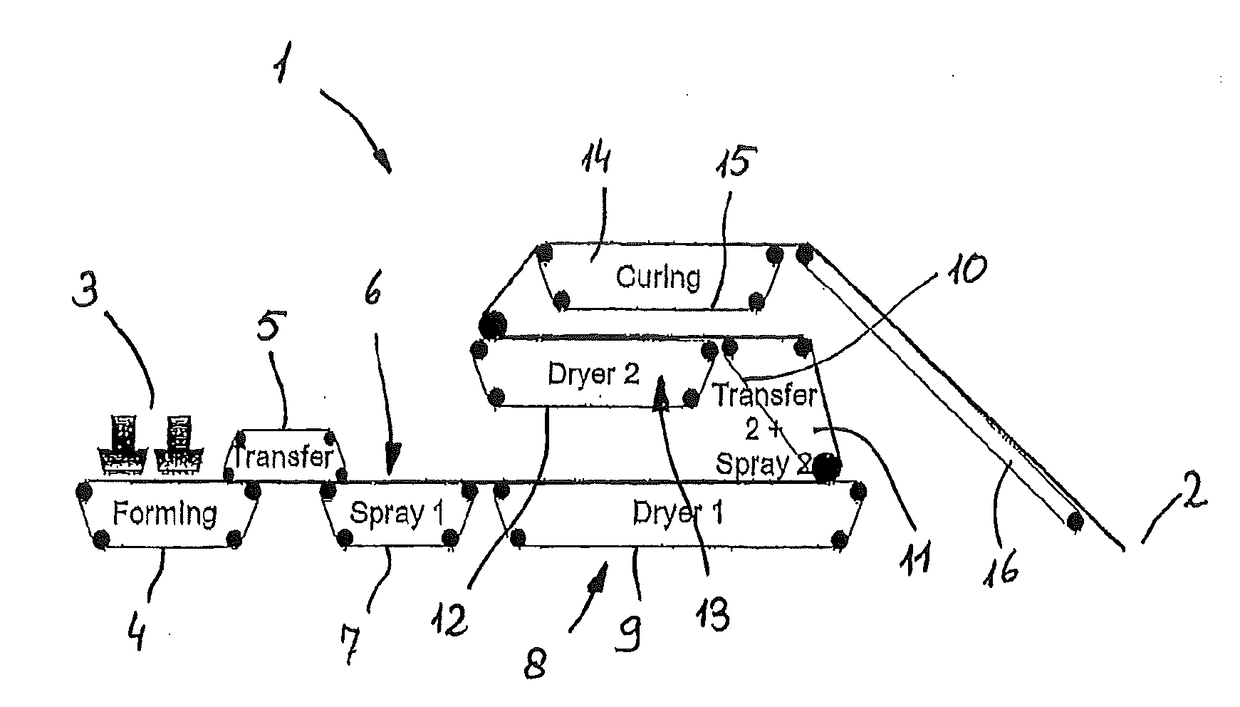
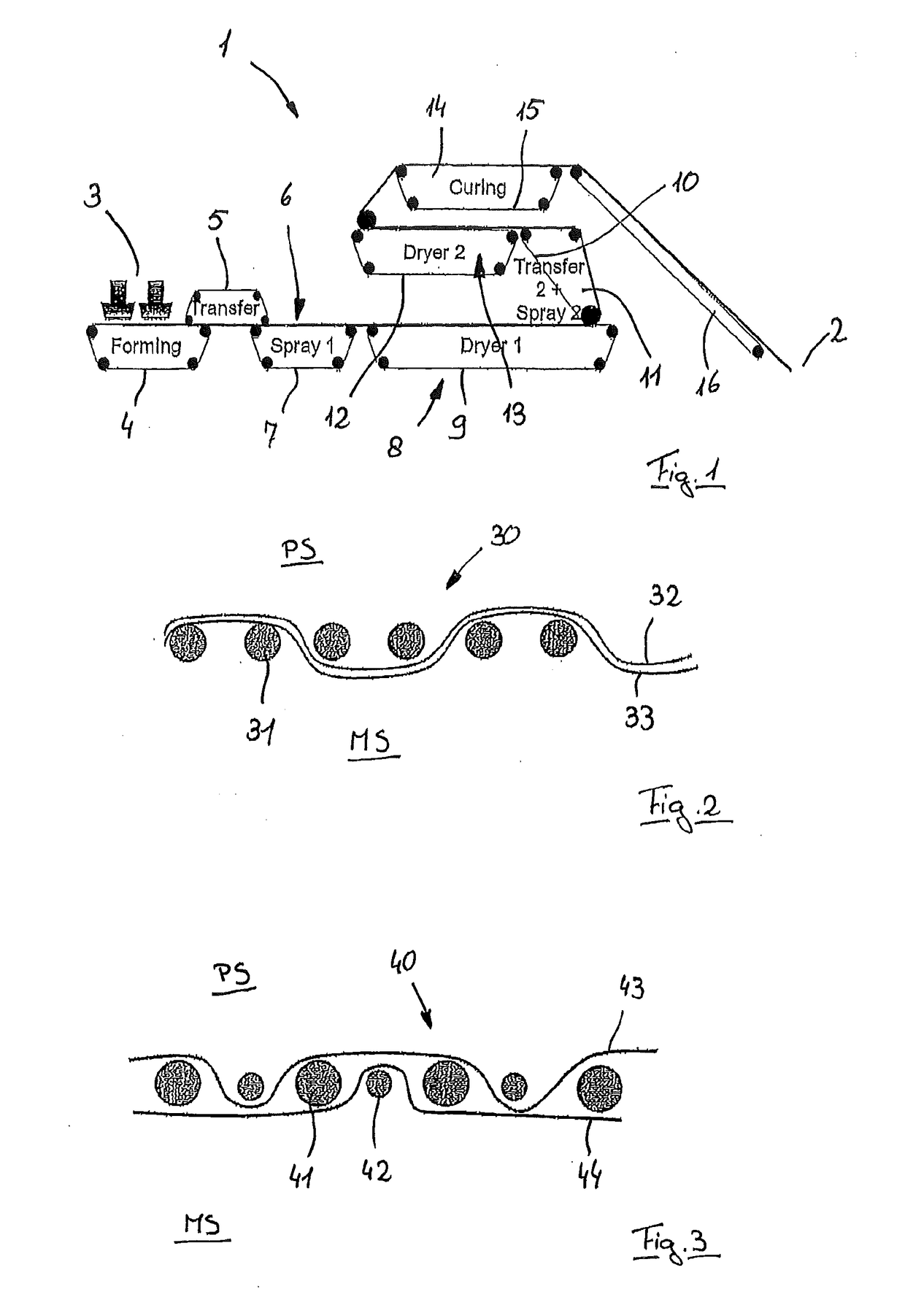
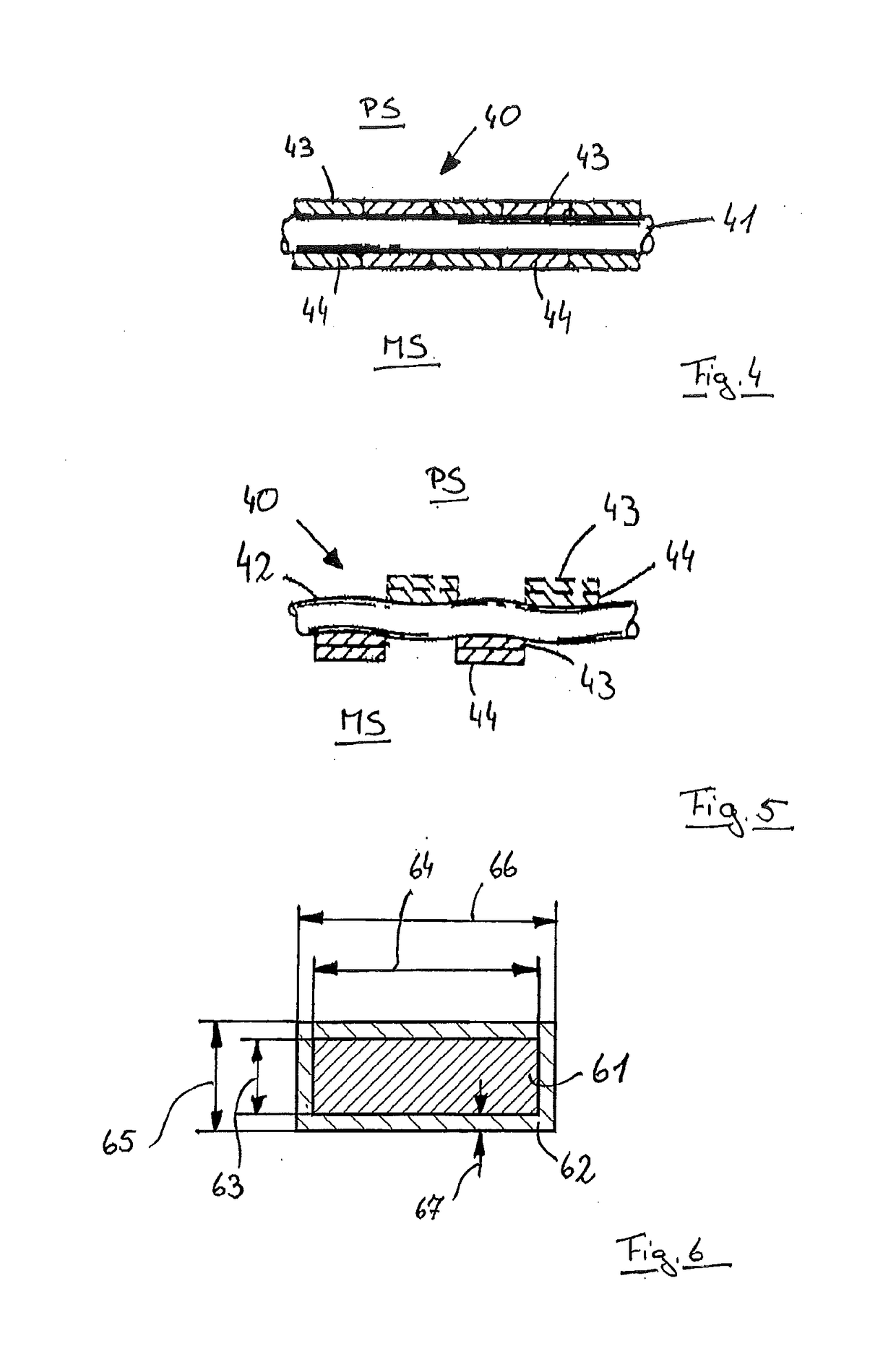
[0043]A system 1 shown in FIG. 1 is used for producing an aerodynamically formed and both thermally and also chemically cured nonwoven that leaves the system 1 at the position 2 as an endless web. The nonwoven is formed from a fiber pulp, mixed with two-component fibers and a very water-absorbent plastic granulate. The two-component fibers have a core made from polypropylene with a higher melting point and a casing made from polyethylene surrounding the core with a lower melting point. The starting materials are fed by means of a feeder 3 to a forming belt 4 where a material layer is formed. With the help of a transfer belt 5, the nonwoven web is transferred to a spraying device 6 where a coating of a polymer dispersion with bonding properties is applied. For passing through the spraying device 6, the nonwoven web is transported by a belt 7.
[0044]Downstream of the spraying device 6, the nonwoven web is fed into a first drying device 8 (furnace) where the web is transported by a conv...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com