Methods and compositions for inducing an immune response using conserved element constructs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Illustration of Enhanced Immune Responses Obtained with CE Construct Prime Followed by CE and Full-Length Polypeptides as Boost
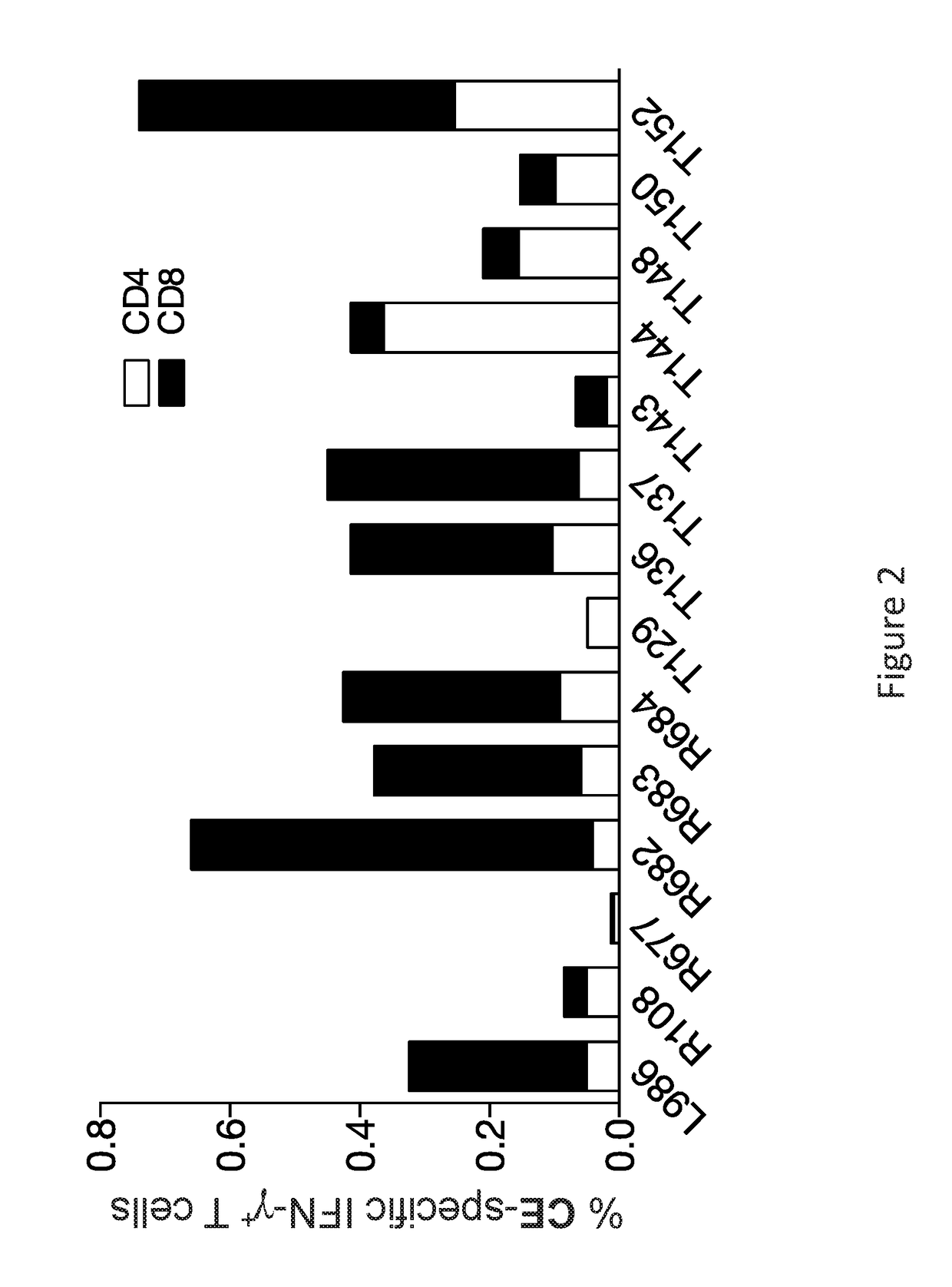
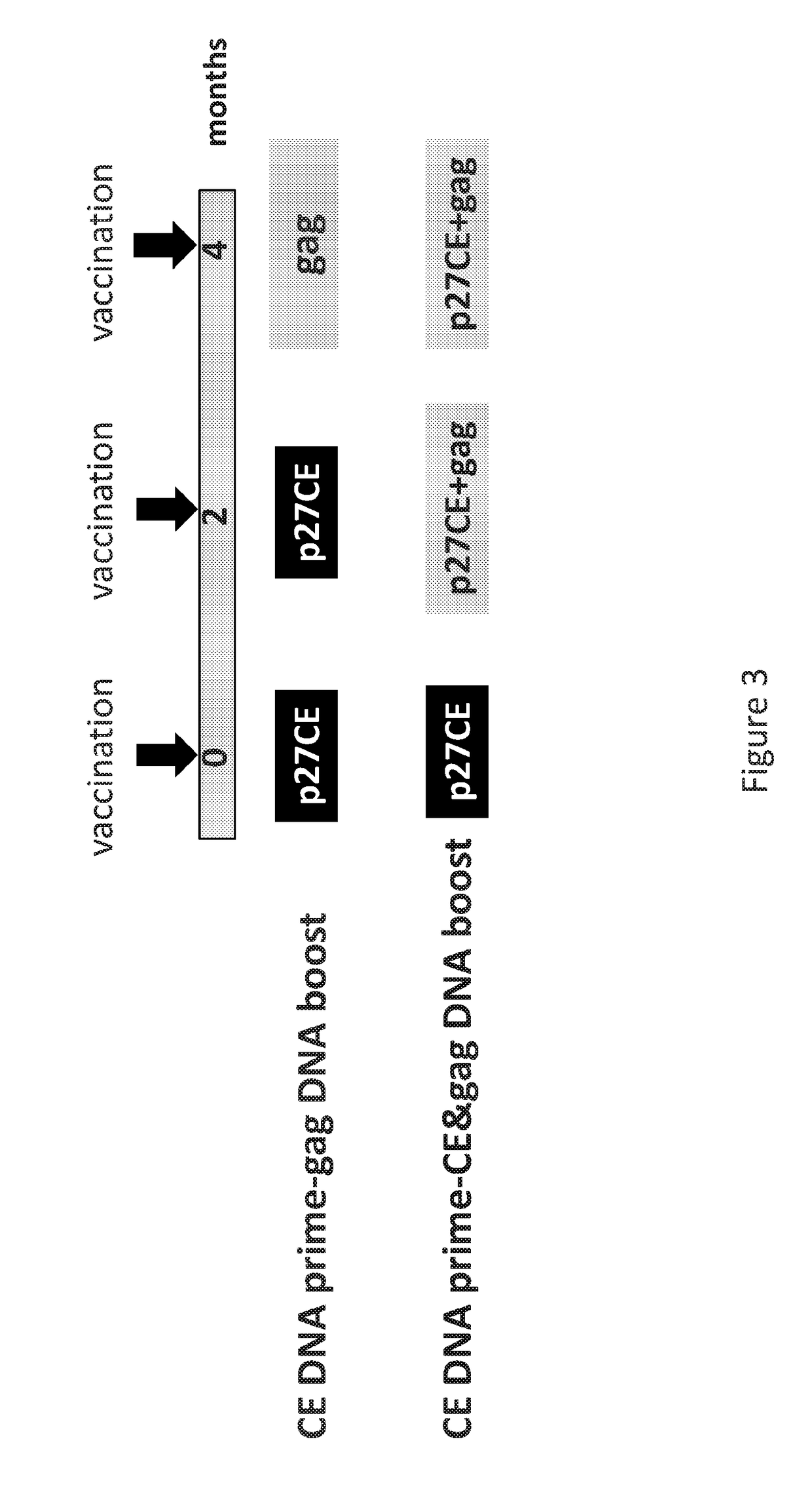
[0257]This example evaluated prime-boost combination vaccines to increase breadth of immunity. In addition to the CE prime-full length molecule boost, it was found that using a boost involving co-delivery of CE and full-length molecule resulted in significantly further improved breadth of the responses. This boost further elicited higher levels of cytotoxic T cells focusing the immune responses to the highly conserved epitopes.
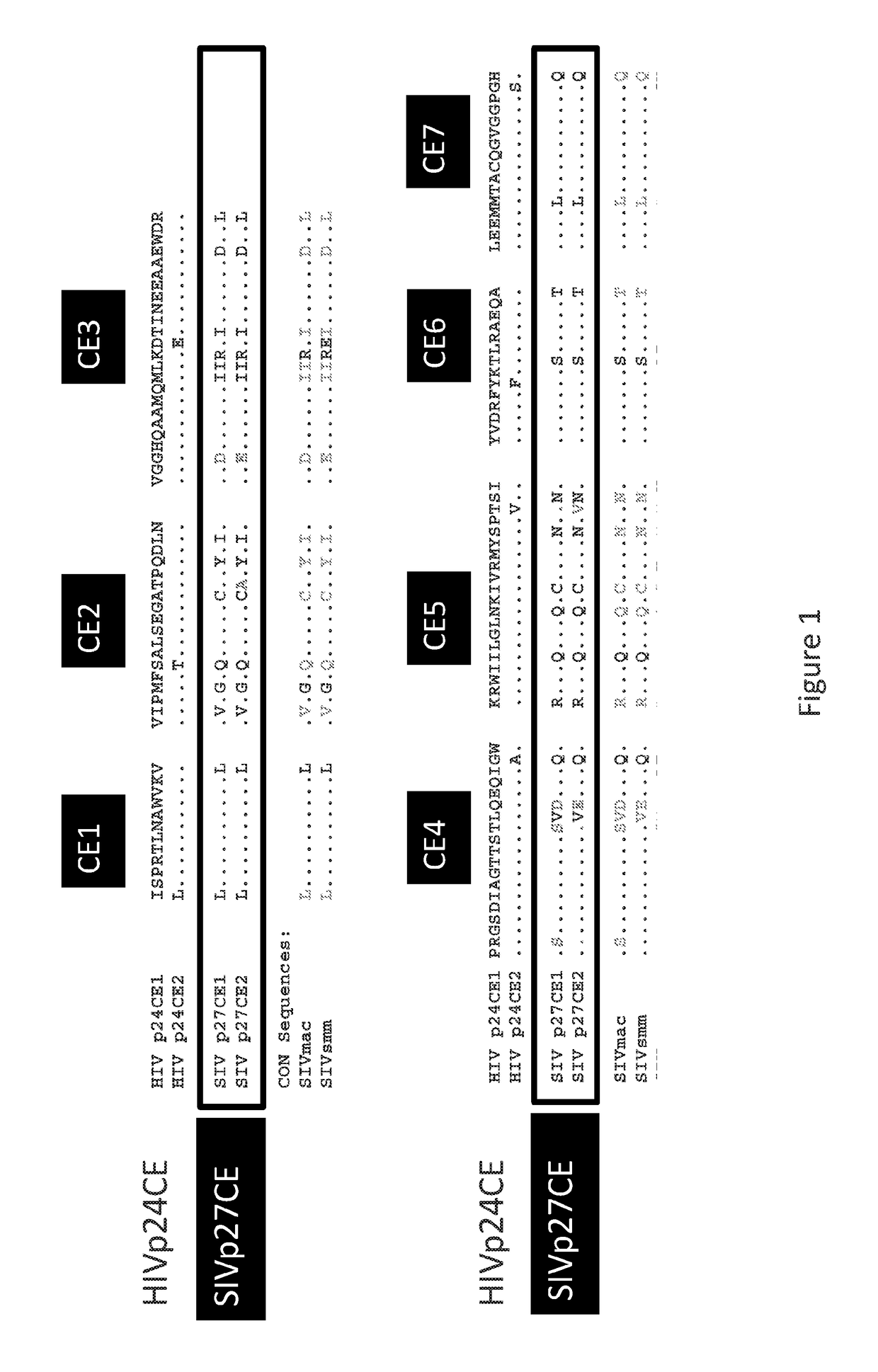
[0258]Method: this study was performed using a simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) derived conserved element pDNA vaccine that was designed from the SIV p27gag capsid protein by analogy to an HIV CE vaccine. The SIV p27gag is the proteolytic processing product derived from the full length SIV p57gag protein. Seven highly conserved elements were identified within the p27gag capsid protein by (i) analogy to HIV CE sequences and (ii) sequ...
example 2
Env DNA Vaccination Induces Cross-Clade Specific Cellular Immune Responses in Mice
Result:
Conserved Element DNA Vaccines
[0270]A set of conserved elements (CE) was identified in the HIV Env protein (FIG. 9). This example describes the identification of 12 conserved elements in HIV Env of 11, 14, 21, 15, 23, 21, 13, 12, 14, 43, 20, and 13 AA in length (FIG. 10). Each CE segment is separated by linkers 3 amino acids in length, composed of alanine and some of which also contain a valine, glutamic acid, lysine, aspartic acid, phenylalanine or glycine, designed to facilitate processing of the protein. Expression-optimized synthetic Env-CE1 and Env-CE2 genes were inserted into an eukaryotic expression vector pCMVkan between the human CMV promoter and bovine growth hormone poly A signal. pCMVkan is optimized for optimal growth in bacteria (kanR) and expression of the insert in mammalian cells.
[0271]Regions for inclusion / exclusion from the vaccine were selected based on whether immune respons...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com